全文HTML
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验药品
1.2 聚合铝及四氧化三铁的制备
1.3 混凝实验方法
1.4 分析方法
2 结果与讨论
2.1 絮凝剂的形态
Table 1 Species distribution, pH and Zeta potential of synthesis flocculants
药剂 | Ala/% | Alb/% | Alc/% | Alt/(mol·L−1) | pH | Zeta/mV | Si/Al |
AC | 95.85 | 3.42 | 0.73 | 0.20 | 3.20 | 8.8 | 0 |
MA | 20.70 | 72.50 | 6.80 | 0.10 | 4.07 | 7.67 | 0 |
MAS1 | 17.80 | 54.00 | 28.20 | 0.11 | 3.94 | 3.41 | 0.05 |
MAS2 | 19.50 | 43.20 | 37.30 | 0.11 | 3.93 | 2.33 | 0.10 |
MAS3 | 26.30 | 9.90 | 63.80 | 0.11 | 3.67 | 16.9 | 0.25 |
2.2 加四氧化三铁前后混凝性能比较
2.2.1 除浊性能比较
Fig. 1 Coagulation characters of flocculants without magnetite
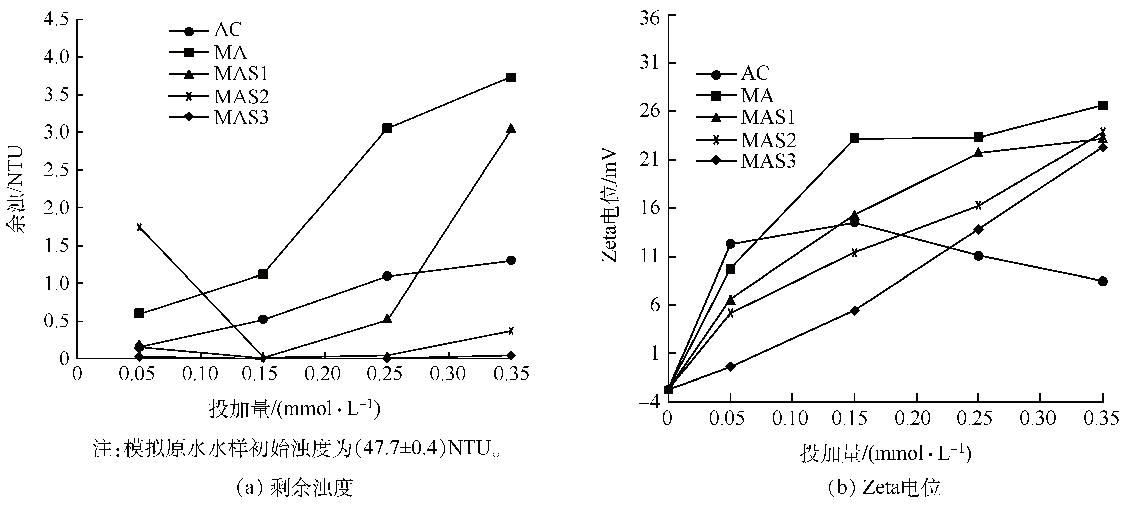
Fig. 2 Flocs size of coagulation of flocculants without magnetite
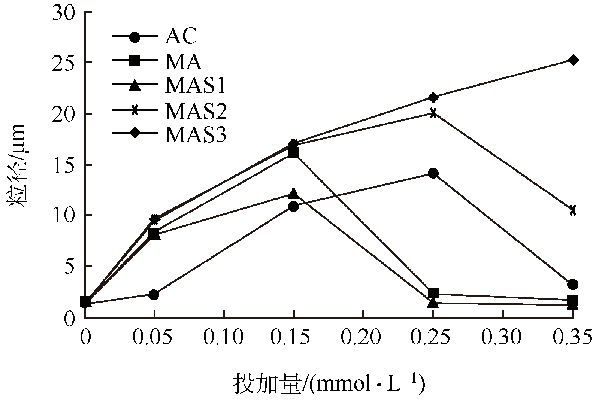
Fig. 3 Coagulation characters of MAS flocculants with magnetite
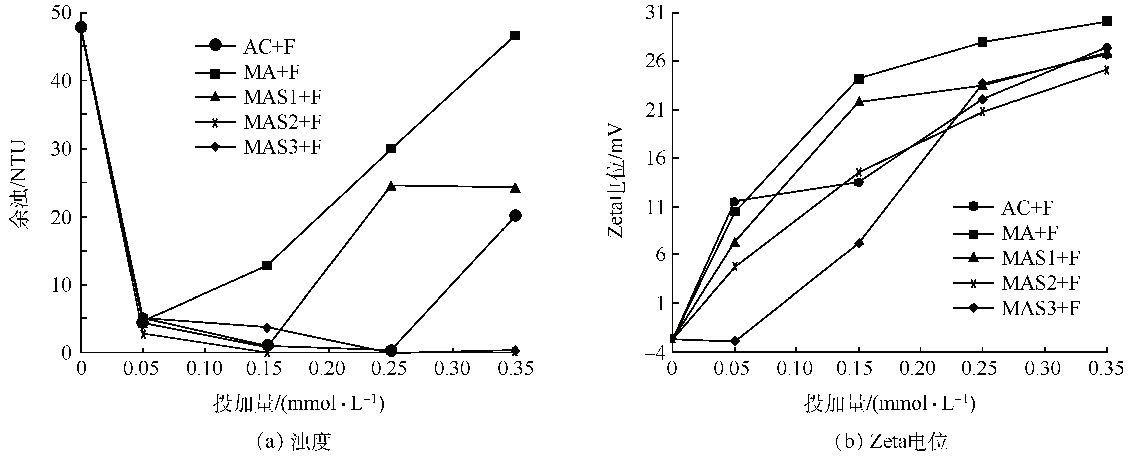
2.2.2 除锌性能比较
Fig. 4 Comparison of zinc removal for MAS coagulation with and without magnetite addition
Fig. 4 Comparison of zinc removal for MAS coagulation with and without magnetite addition
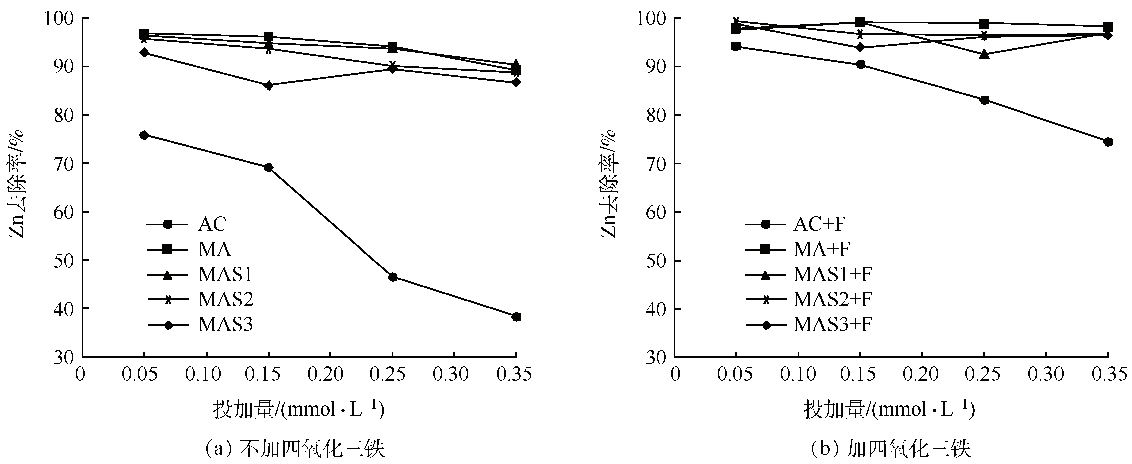
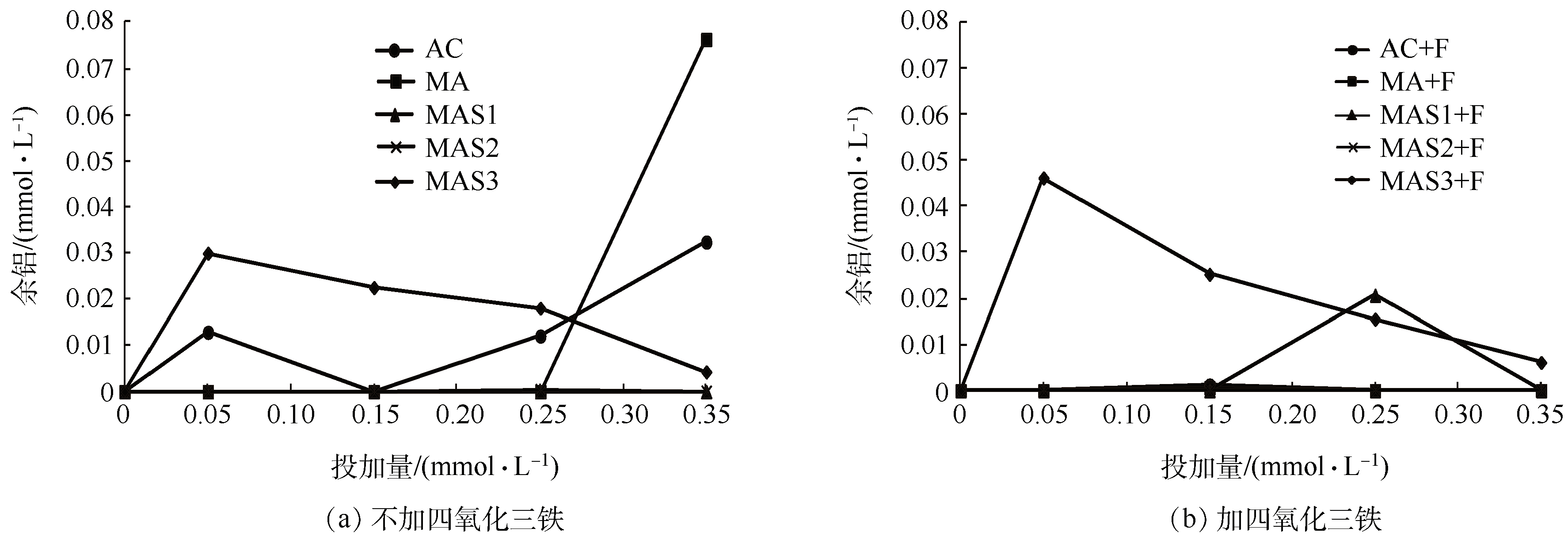
2.2.3 余铝比较
Fig. 5 Comparison of residual aluminum for MAS coagulation with and without magnetite addition
Fig. 5 Comparison of residual aluminum for MAS coagulation with and without magnetite addition
2.3 高岭土的作用
Fig. 6 Effects of kaolin on zinc removal by MAS + F coagulation with Fe/Al ratio of 53, 18 and 7
Fig. 6 Effects of kaolin on zinc removal by MAS + F coagulation with Fe/Al ratio of 53, 18 and 7

Table 2 Residual turbidity of kaolin suspension treated by FMAS with different Fe/Al ratios
Fe/Al | 余浊/NTU | |||
FMAS3 | FMAS2 | FMAS1 | FMA | |
53 | 5.13 | 2.73 | 4.34 | 4.63 |
18 | 3.71 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 12.76 |
10 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 24.55 | 29.95 |
7 | 0.4 | 0.23 | 24.25 | 46.65 |





 百度学术
百度学术


 下载:
下载:
