-
《全球及中国污泥处理处置行业发展研究报告》指出,2018年,中国污泥总产量为 5.67×107 t,随着城市化进程的加快,预计到2020年,中国污泥总产量将达到6.18×107 t。产生的大量污泥给污泥的处理工作带来了很大的压力,而且传统的焚烧和填埋等处理方式越来越不能满足处置理念的升级和环境相关管理政策的规定[1]。目前,污泥减量化和资源化是污泥处理处置领域的研究热点之一,通过污泥破解的预处理方式能够实现污泥的资源化和减量化的目标[2]。污泥破解的过程是将污泥絮体内部及表面的胞外聚合物(EPS)破坏,使得细胞壁破裂,胞内有机物溶出的过程[3]。热碱破解法是最常用的方法之一,但该法用碱量大,需要大量能量输入(一般大于100 ℃)[4-6],因此,在污泥资源化大规模处理中,其大量使用受到了限制。
近年来,为了增强污泥破解效果,国内外学者对常用的热碱破解法进行了各种尝试性优化和改进。DEMIR[7]采用The Box-Behnken实验对热碱法破解污泥的参数做了优化,在90 ℃,0.2 mol·L−1 NaOH和25 min破解条件下,污泥最佳破解率为77.83%。DENG等[8]采用响应面优化法对热碱法破解污泥的工艺做了参数优化,在90 ℃、104 min、pH=12的最优条件下,污泥的破解率可达46.45%,破解后甲烷产率比原污泥提高了79%。徐慧敏等[9]将超声和热碱技术联合,找到了最佳的破解工艺组合:温度为73.06 ℃、加碱量为0.085 g(以1 g湿污泥计),超声能量为9 551 kJ·kg−1。徐慧敏等[10]进一步采用超声联合热碱法破解不同含固率的污泥,对有机质释放情况进行了研究,提出污泥含固率为10%时,溶解性蛋白质和多糖浓度的释放最多。
除对热碱法进行中低温下的参数优化和物理方面的改进外,进一步尝试化学等其他改进方向的探索是有必要的。乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)是一种较强的螯合剂,能够改变微生物的细胞结构,促进细胞胞外物质与污泥细胞的分离,故经常被用到污泥EPS的溶解提取中[11-12]。ZOU等[13]在研究废活性污泥在厌氧发酵过程中发现,通过添加EDTA可以增强细胞内磷的释放,经研究表明,这是因为EDTA对细胞膜的损伤所致。NGUYEN等[14]在污泥厌氧发酵中使用EDTA后显著减少了污泥量。肖倩等[15]利用EDTA法对硝化污泥胞外紧密型EPS进行了提取,发现EDTA对紧密型EPS具有一定溶解作用。以上这些研究结果表明EDTA对EPS具有一定的溶解破坏作用,可以造成细胞膜的损伤。本研究尝试将EDTA和热碱法进行耦合,在中低温度条件下,考察EDTA对热碱破解污泥效果的影响,为强化污泥热碱破解提供方法参考。
全文HTML
-
实验所需污泥取自大连春柳河污水处理厂脱水污泥。污泥含水率为84.58%,挥发性固体含量(VS)为71.06%。脱水污泥保存于4 ℃冰箱中备用。
-
批式正交实验和最佳条件下的破解实验均配制4 L污泥反应液,搅拌2 min,过10目的筛网除去毛发、沙粒等大粒径物质后,用1 mol·L−1 NaOH和1 mol·L−1 HCl溶液调节pH,加入EDTA,搅拌2 min,然后放入控制恒定搅拌速度的集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器中,设置反应温度后,进行反应。
1) 正交实验。实验选取对污泥破解效果影响较显著的5个因素:pH、温度、固液比、反应时间、EDTA投量。依据单因素的实验结果,pH水平定为11.5、12、12.5、13,温度水平定为75、80、85、90 ℃,固液比(湿污泥与水的质量比)水平定为1∶8.5、1∶10、1∶11.5、1∶13,反应时间水平定为2.5、3、3.5、4 h,EDTA投量水平定为每10 g湿污泥投加0.08、0.11、0.14、0.17 g。选用5因素4水平正交表L16(45)进行实验设计,设置每个实验组后,同时设置在4 L纯水中只添加EDTA的空白组。
2) 热碱-EDTA耦合法破解效果实验。采用最佳破解条件,配制4 L污泥反应液,调节pH,添加EDTA,放入水浴反应器中,设置反应温度后,进行反应。同时设置未添加EDTA的对照组、只添加EDTA的对照组(在常温下反应)和在4 L纯水中只添加了EDTA的空白组。
-
经过破解的污泥样品每隔30 min进行取样,以10 000 r·min−1离心20 min后,取上清液过0.45 μm滤膜,测定SCOD、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、多糖和蛋白质的质量浓度,测定后弃掉上清液,对剩余的污泥残渣采用重量法测定总固体(TS)和VS。其中,SCOD采用重铬酸钾法[16]测定,TN和TP采用过硫酸钾消解法[16]测定,多糖采用苯酚-硫酸法[17]测定,蛋白质采用考马斯亮蓝法[17]测定。污泥粒径采用激光粒度仪(Malvern Mastersizer 2000,英国Malvern公司)分析。溶解性有机物质(DOM)用凝胶渗透色谱仪(GPC)(VE 2001 GPC-TDA 302,美国Viscotek公司)分析。污泥的微结构采用钨灯丝扫描电镜(QUANTA 450,美国FEI公司)分析。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
选用L16(45)正交实验表设计5因素4水平正交实验,以SCOD溶出量为评价污泥破解效果的指标。正交实验的设计及实验结果如表1所示。由于EDTA可能会对SCOD有所贡献,计算时应减去同条件下的空白值。
热碱-EDTA耦合法破解污泥的正交实验极差分析表明,破解效果影响因素的主次顺序为固液比>pH>EDTA投加量>温度>反应时间。确定最佳条件:固液比为1∶8.5、pH为12.5、EDTA投加量为0.017(以1 g湿污泥计)、反应温度为85 ℃、反应时间为3 h。实验编号为11的最佳组合中,破解后SCOD可达到14 400.0 mg·L−1。
-
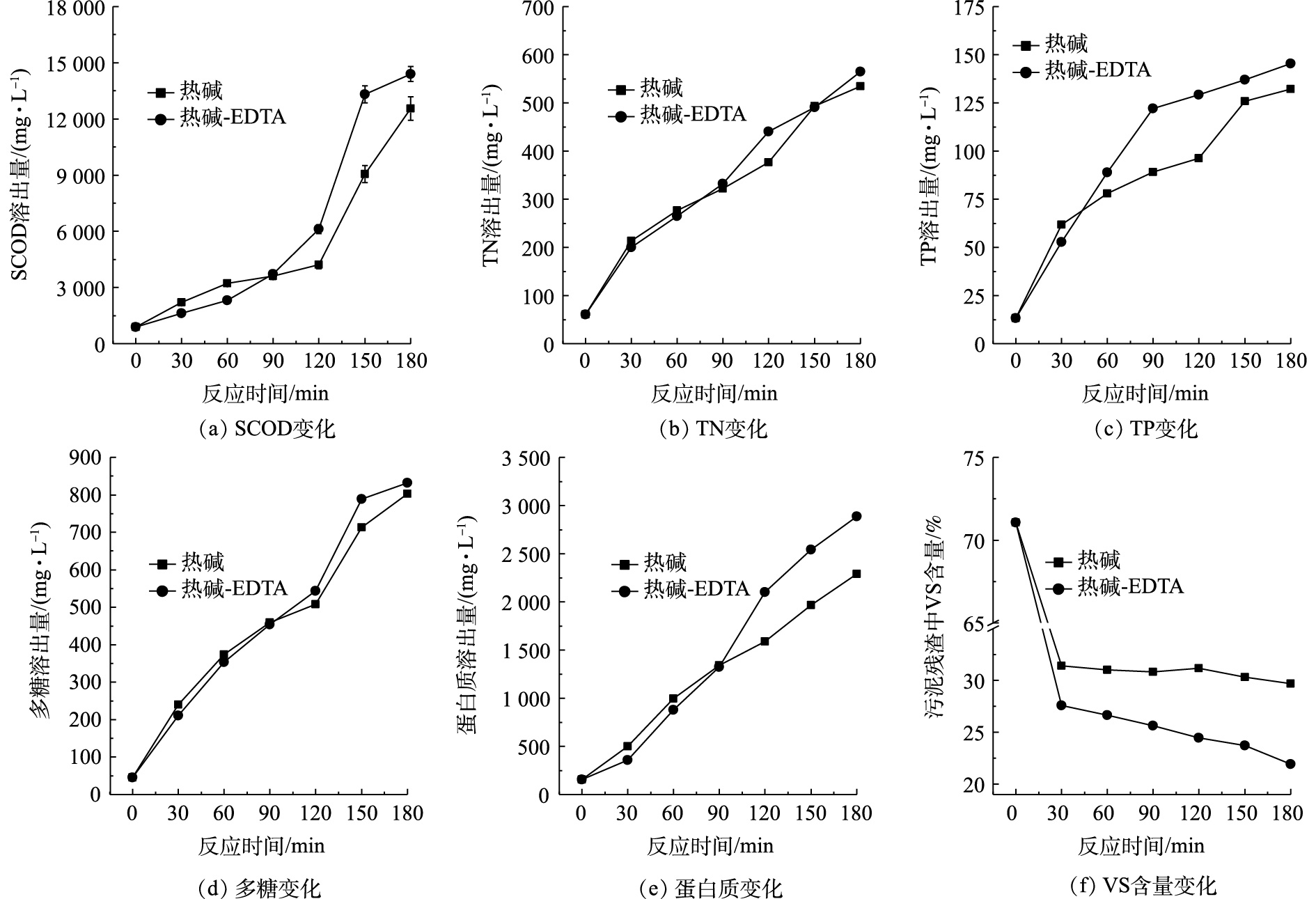
在正交实验所得的最佳破解条件下,热碱法、热碱-EDTA耦合法和单独EDTA法的3组破解实验同时进行检测分析,以全面考察EDTA的加入对热碱破解污泥效果的影响,测定了SCOD、TN、TP、多糖、蛋白质、VS共6项指标随时间变化的关系,结果如图1所示。EDTA会对上清液中SCOD和TN做出一定贡献,SCOD和TN计算时扣除相应空白值。
图1(a)为SCOD浓度在破解过程中的变化。在热碱法和热碱-EDTA耦合法2组实验中,SCOD由875.5 mg·L−1分别增至12 550.0 mg·L−1和14 400.0 mg·L−1,污泥破解结束,耦合法组的溶出量比热碱法组的高14.7%。单一EDTA对照组(在常温下反应)的SCOD在875.5 mg·L−1基础上增加幅度很小。在反应90 min之前,耦合法组SCOD的溶出量小于热碱法组;120 min之后,2组SCOD溶出量均显著增加,但相比耦合法组增加更为明显;150 min之后耦合法组增加幅度减缓。这表示在120 min之后,2组实验中发生了大量污泥细胞破裂,胞内有机物的溶出致使SCOD迅速增高,耦合法实验组中SCOD值响应更迅速。以上实验结果说明,EDTA可以缩短中低温条件下热碱破解的时间,进而提高有机物的溶出率。
图1(b)和图1(c)分别为TN和TP溶出量随时间的变化。热碱法组和耦合法组TN分别由初始的60.56 mg·L−1增至污泥破解结束时的534.23 mg·L−1和564.34 mg·L−1,耦合法组TN溶出量比热碱法组高5.6%,2组的TN变化基本均在同步增加。耦合法和热碱法组的TP分别由初始的13.34 mg·L−1增至污泥破解结束的132.23 mg·L−1和145.28 mg·L−1,耦合法组TP溶出量比热碱法组高9.9%。90 min之前,耦合法组TP增加大于热碱法组,90 min之后,TP增加速度减缓,而热碱法组在30 ~120 min的增加速度相对缓和。这说明EDTA的加入促使TP溶出效果更加明显,这和ZOU等[13]的研究结论相一致。
图1(d)和图1(e)分别为多糖和蛋白质溶出量的变化。热碱法组和耦合法组多糖分别由初始的45.34 mg·L−1增至污泥破解结束的803.23 mg·L−1和832.35 mg·L−1,耦合法组多糖溶出量比热碱法组高3.6%,2组中的多糖变化趋势和TN变化趋势相似,基本均在同步增加。热碱法组和耦合法组中的蛋白质分别由初始的156.37 mg·L−1增至污泥破解结束的2 291.20 mg·L−1和2 884.46 mg·L−1,耦合法组蛋白质溶出量比热碱法组高25.9%。蛋白质的变化趋势和SCOD变化趋势相似,90 min之前,耦合法组蛋白质溶出量小于热碱法组,90 min之后,耦合法组蛋白质浓度的增长速度加快,超过了热碱法组。这说明EDTA加入有助于污泥破解,进而提高了有机物的溶出量,蛋白质贡献更占优势。
图1(f)为污泥残渣中VS含量在破解过程中的变化。热碱法组和耦合法组由初始51.06%分别下降至29.68%和21.93%,处理效果好于LI等[18]用超声处理方式的效果(24.70%)。在反应初期,VS含量显著下降,这是由于污泥大絮体在搅拌的物理作用下被打散的缘故,一部分有机物迅速转移到液相中[19]。
-
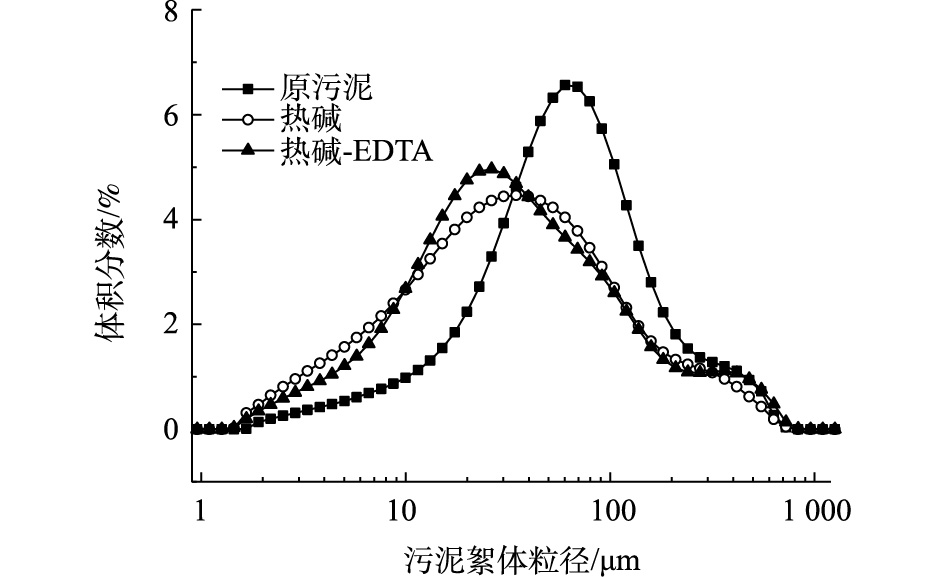
污泥破解后,污泥絮体及污泥微生物细胞结构被破坏,絮体粒径也相应减小[20],图2为不同破解方法下污泥粒径分布情况。破解后,污泥粒径的峰型均变矮,分布变宽,但由于EDTA的作用,热碱-EDTA耦合法对应的峰型稍陡,这说明破解后EDTA有使粒径分布变窄的效果。污泥粒径的峰值响应分别为:原始污泥135.995 μm、热碱破解后30.177 μm、热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后29.350 μm。其中,热碱-EDTA耦合法对应的值小于热碱法。这表明在本研究条件下,热碱-EDTA耦合法的破解效果显著好于热碱破解法。
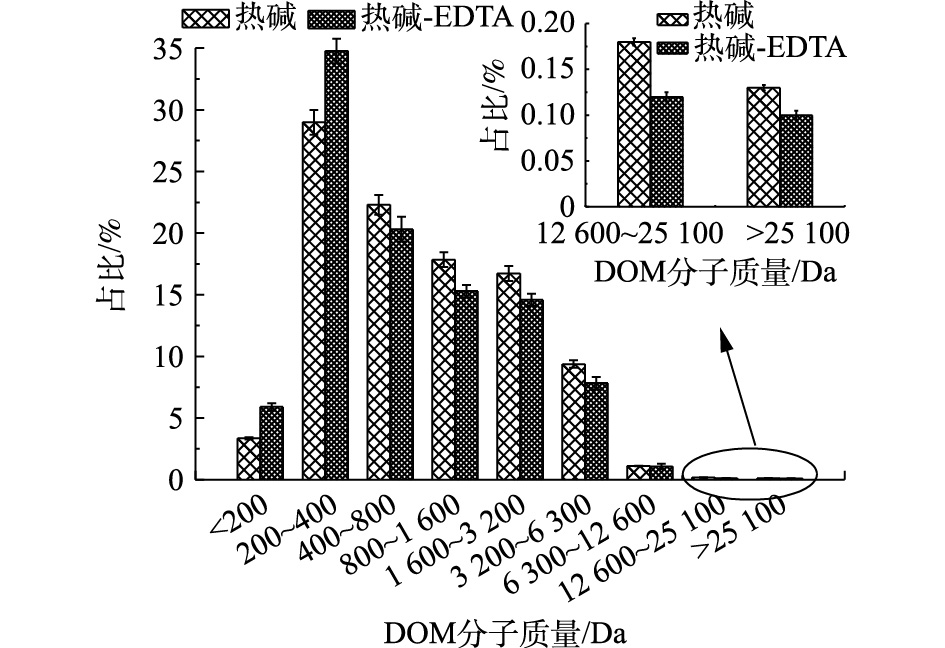
破解后,对破解液中的DOM分子质量分布情况进行了考察,以评估破解后溶出有机物的水解情况。采用条分法对GPC谱图进行分级处理,并对每级进行积分运算,得到DOM的离散型分子质量分布如图3所示。由图3可见,破解后,分子质量在<200 Da和200~400 Da两分级处,热碱-EDTA耦合法所占比例大于热碱法,当DOM分子质量在400 Da以上时,热碱-EDTA耦合法的DOM分子质量相应分布比例均小于热碱破解法。其中,当DOM分子质量<400 Da时,热碱-EDTA耦合法分子质量占比为40.68%,大于热碱破解的32.34%。这说明热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后,DOM的分子质量分布偏小,DOM更容易发生水解。
-
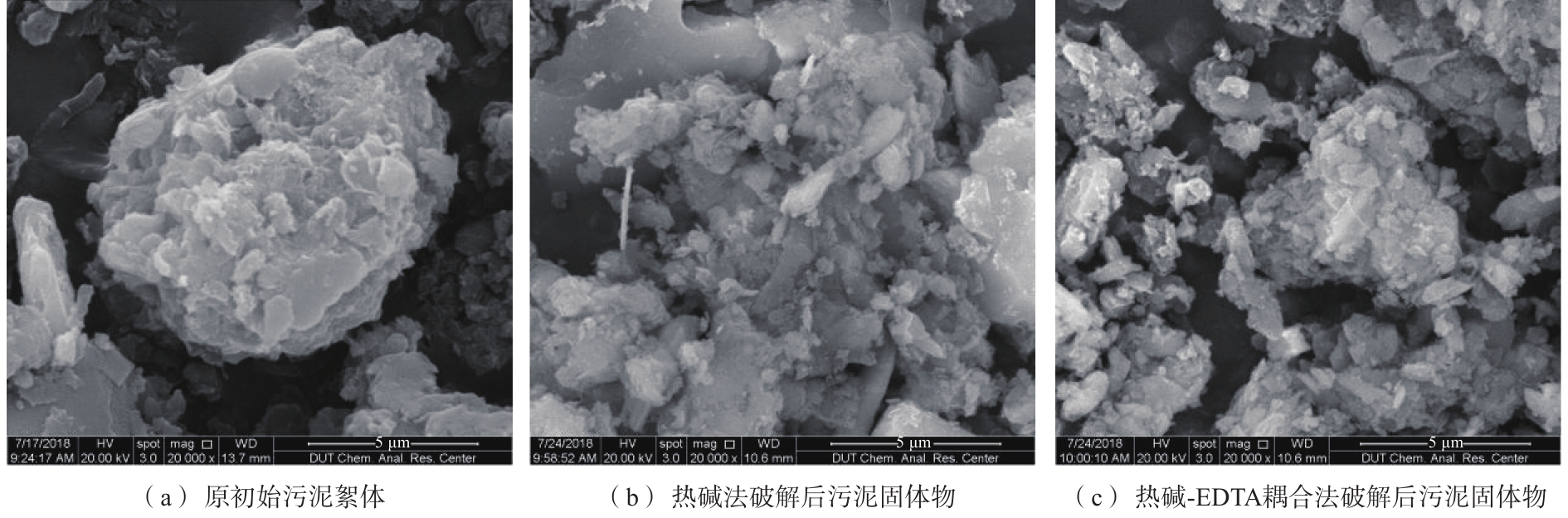
原污泥和破解污泥的扫描电镜照片如图4所示。由图4(a)可以看出,未经破解的原污泥表面紧密严实,完整性较好,呈现大块状。由图4(b)可以看出,经过热碱破解后的污泥残渣成小块黏结在一起,分散性较差。由图4(c)可以看出,经热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后,污泥在形态上变化明显,污泥残渣为比较松散的小块状,这说明热碱-EDTA耦合法对污泥的破解效果更为显著,与污泥的SCOD、蛋白质质量浓度、粒径变化规律及DOM分子质量分布结果一致。
2.1. 最佳破解条件的选取及各影响因素显著性分析
2.2. 热碱-EDTA耦合法处理效果分析
2.3. 污泥破解后粒径变化和溶解性有机物分子质量分析
2.4. 污泥破解后的微观变化
-
1)热碱-EDTA耦合法破解污泥的最优条件:固液比为1:8.5、pH为12.5、EDTA投加量为0.017(1 g湿污泥计)、反应温度为85 ℃、反应时间为3 h。在最优破解条件下,综合性指标SCOD的检测结果表明,投加EDTA可以缩短中低温条件下热碱破解的时间,提高有机物溶出率。
2) SCOD、TN、TP、多糖和蛋白质溶出量及破解结束污泥残渣中VS含量测定结果表明,热碱-EDTA耦合法强化了污泥破解效果。DOM分子质量分布结果证明,热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后,破解液中小于400 Da的小分子物质占比(40.68%)大于热碱法破解中对应的占比(32.34%),这说明热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后DOM更容易水解。
3)污泥絮体粒径测定和絮体形貌SEM观察结果表明,热碱-EDTA耦合法破解后,污泥固体分散性优于热碱破解,粒径分布峰值响应小于热碱破解。热碱-EDTA耦合法对污泥的破解效果优于热碱法,从而对污泥破解起到了强化作用。



 下载:
下载: