-
我国畜禽粪便污染物总量已达近40×108 t,有效处理量不足50%,其中猪粪占总量比最大,为36.71%[1-4]。清粪工作是解决规模化猪场环境污染的重要内容。在清粪工艺中,干清粪工艺具有机械化程度高、粪中营养成分损失小、耗水量少、可减少污水中大部分污染物(以COD与BOD类指标表征)等优势[5-6]。从清洁生产角度考虑,干清粪工艺是规模化猪场清理猪粪时的首选[7]。干清粪工艺得到的猪粪固含量高、水分含量少,后续输送特别是管道抽吸过程中难度较大。这是由于猪粪含固率变化导致其黏性变化,从而影响了管内流动阻力。因此,对流动黏性阻力这一物理特性进行专门研究是很有必要的,其对运输、搅拌、混合等传质传热过程[8-10]同样有重要影响,属于基础性工艺设计因素。
国内外许多学者对畜禽粪污或类似物料的流变特性和输送性能已有过研究。石惠娴等[10]验证了猪粪为非牛顿流体中的假塑性流体,可使用幂律模型描述切应力与剪切速率之间的关系。LANDRY等[11]拟合了猪粪稠度系数与含固率的函数关系,建立特定剪切速率条件下表观黏度与含固率的函数表达式。刘刈等[12]考察了包括猪粪在内的6种畜禽养殖场废弃物悬浮分散系的流变特性,研究了物料浓度、温度和发酵时间等因素对粪污黏度的影响,以及猪粪表观黏度随温度的变化趋势,分析了颗粒溶解到液相使其浓度增大并产生表观黏度增大的现象。王少勇等[13]测试不同工况下膏体管道输送的黏度-剪切速率流动曲线,采用Herschel-Bulkey模型进行回归分析,获得了管道输送膏体的流变参数。刘晓辉等[14]对具有非牛顿流体特性的膏体尾矿进行管道输送关键工艺参数研究,实现了对膏体在管内流动时流动阻力的精确测算。
然而,对畜禽粪污在管道抽吸过程的非牛顿流体流动阻力特性的研究还较少,还需考虑各种浓度、抽吸压力、抽吸管径及自然放置时间等关键影响因素,并进行系统地理论分析,以便为相关的环保工艺与设备研发提供设计参数。本研究以实验为基础,分析在猪粪管道抽吸过程中影响抽吸流量的主要因素,以及猪粪在管道内流动时非牛顿流体阻力特性的影响机理,以期为畜禽粪污环保处理等相关领域提供参考。
全文HTML
-
新鲜猪粪,不同的猪粪含固率由未稀释新鲜干猪粪添加适当自来水调配获取。
-
实验装置示意图见图1。黏度相关特性的测量仪器为LVDV-II+Pro旋转型黏度计(美国Brookfield公司)。
-
本实验模拟实际管道抽吸粪污的过程,在真空容器间连接不同管径的塑料波纹软管,改变可能影响抽吸流量及流动阻力特性的操作参数,如猪粪含固率、抽吸真空度、抽吸管径和自然放置时间(自然放置的实验环境为室内常温(20 ℃左右))等。
-
根据能量守恒伯努利方程,建立各压头之间的平衡关系式[15](式(1)和式(2))。
式中:P为抽吸真空度,kPa;ρ为猪粪密度,kg·m−3;g为重力加速度,取9.81 m·s−2;L为抽吸管道总长度,取1.5 m;D为抽吸管道内径,m;
$\Delta Z$ 为储粪桶液面到真空容器抽吸口的竖向高度,m;$u$ 为管道内流体平均流速,m·s−1;${h_f}$ 为管内流动阻力,m2·s−2;$f$ 为实验范宁(Fanning)摩擦因子。由于储粪桶截面积较管道截面积大很多,其液位变化可以忽略。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验装置
1.3. 实验方法
1.4. 分析方法
-
图2用Q、x、D和P分别表示抽吸流量、猪粪含固率、抽吸管径和抽吸真空度。图2(a)为抽吸管径为0.03 m时、不同抽吸真空度下,猪粪含固率对抽吸流量的影响。图2(a)内容显示,随着猪粪含固率增加,抽吸流量逐渐减少。且在高抽吸真空度条件下,由于负压压头动力大,其对应的抽吸流量也大。用小抽吸管径(0.015 m,图2(b))同样表现出类似的猪粪含固率和抽吸真空度之间的影响特点。图2(a)和图2(b)不同处在于:较大管径条件下,猪粪含固率低于10%时,含固率对抽吸流量的影响并不明显;含固率超过10%后,抽吸流量值才快速下降,整体上抽吸流量与猪粪含固率更符合二次曲线关系;而较小管径条件下,猪粪含固率对抽吸流量的影响显现线性关系(二次项系数接近0),特别是在低抽吸真空度条件下,线性关系更加显著。
抽吸流量随猪粪含固率增大而减少,说明猪粪固形物增大了管道阻力,这是由猪粪的流体本征特性决定的。从图3可知,随着猪粪含固率增加,流变指数不断下降,从含固率为2%时流变指数接近1,逐渐降至含固率为20%时接近0.3。n为流变指数,是代表流体流动规律的重要指标[16-17],其值在0<n<1时,代表猪粪的流动规律符合假塑性非牛顿流体流动规律,且n值越小代表非牛顿流体特性越强,对应于管道抽吸猪粪过程中管内黏性摩擦力及流动阻力表现越大,带来了表观上抽吸流量减少的效果。
-
猪粪含固率为2%时,此时流变指数为0.952 3,最接近牛顿流体。图4(a)为不同抽吸管径对抽吸流量的影响,可以看出抽吸流量随抽吸管径增大是快速增加的[18],即大管径有更小的相对抽吸阻力,且不同抽吸真空度条件下抽吸流量与抽吸管径之间均呈约1.3次方的幂指数学关系。对于牛顿流体,流体黏度是不受流动速度梯度(剪切速率)影响的,即管径变化带来的管道速度梯度不会对黏性产生影响,抽吸流量表现出了只随抽吸管径变化的特点,抽吸流量和抽吸管径之间存在了一定的幂指数学关系。对于猪粪含固率为20%(图4(b)),此时流变指数为0.300 4,非牛顿流体特性最强)时,抽吸流量随抽吸管径增大同样是快速增加的,但由于非牛顿流体的黏性受流体速度梯度(剪切速率)影响较大,抽吸管径变成了同时影响流体黏性特征的重要间接因素[18],抽吸流量和抽吸管径之间的幂指关系因此变得非常复杂且不再有统一指数数值。
-
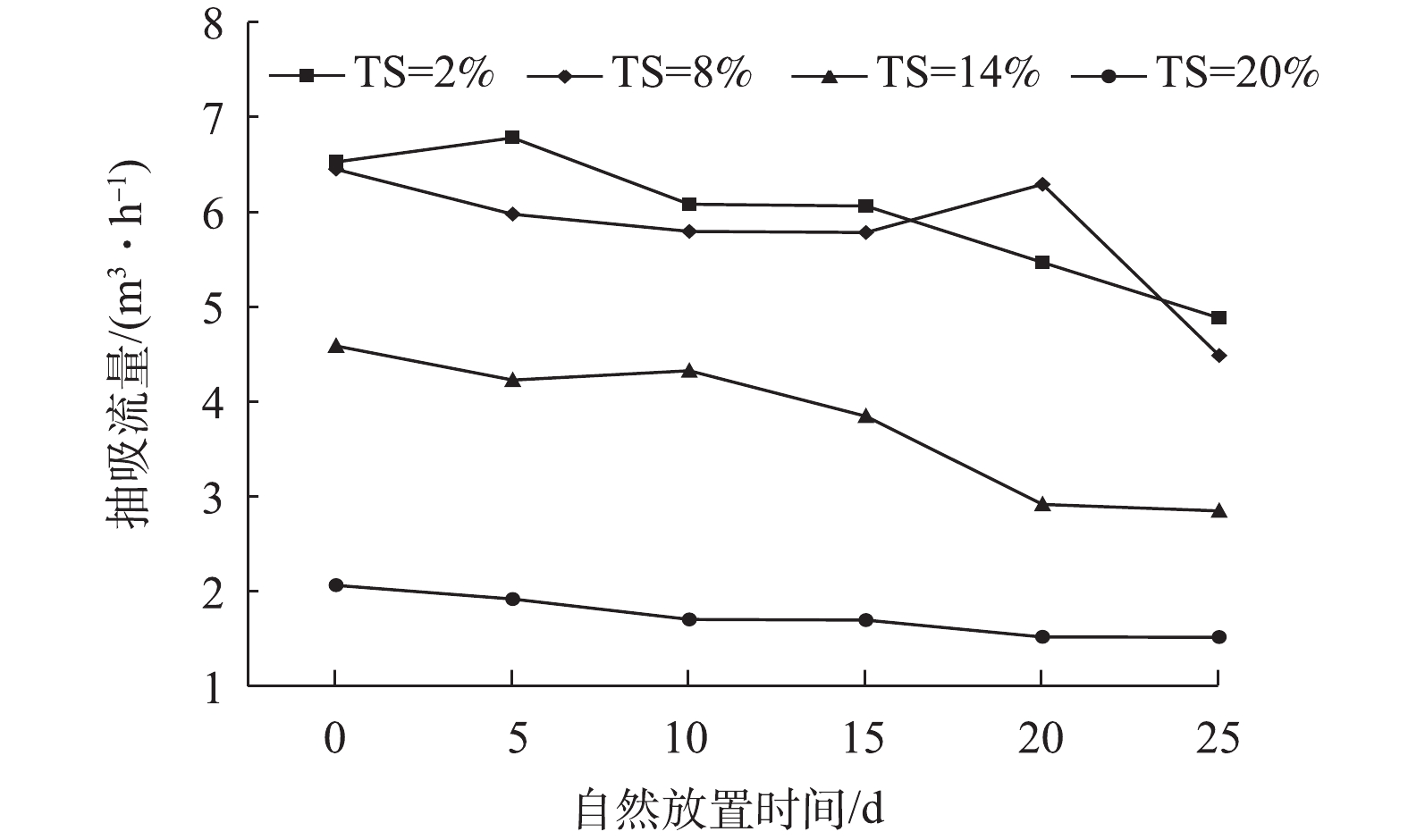
由于在实际情况下,畜禽粪污通常不能被及时清运,所以应重点研究猪粪自然放置时间对抽吸流量的影响。当抽吸管径为0.03 m,抽吸真空度为−50 kPa时,图5表明在不同含固率条件下,抽吸流量随自然放置时间延长均有少量下降,说明自然放置时间会对管道阻力产生增大效应,而且这种增大效应并没有受到猪粪含固率的影响。图6分析了猪粪低含固率为4%和高含固率为16%时,在抽吸实验前(未自然放置)和抽吸实验后(自然放置末期)流变指数的变化,发现流变指数均有所下降。猪粪含固率为4%时其流变指数从0.916 6降至0.832 0,猪粪含固率为16%时其流变指数从0.451 1降至0.408 0,说明当猪粪的非牛顿流体特性增强时,间接增大了猪粪在管内流动时的流动阻力。
猪粪在管道内流动时,流动阻力的影响因素涉及猪粪在自然放置过程中(本实验在室内环境温度20 ℃左右条件下进行)可能发生的复杂物理变化和生化过程,其包括猪粪中的颗粒性物质发生部分降解、固相颗粒尺寸与分布变化[12]、部分大分子向小分子转变、流体内微气泡产生及与颗粒夹杂等。最终在微观上,增强了猪粪中各种微颗粒之间相互作用力,故宏观上表现出了黏性阻力增大的现象。根据图7显示的本研究工况下的平均情况,在管道抽吸不同含固率猪粪过程中,流量的平均降低率随自然放置时间不断增加。自然放置时间从5 d增加到25 d后,其抽吸流量的平均降低率从4.6%增加到26.2%;且15 d内,降低率不显著(8.3%以内);而15 d后明显扩大,25 d后达到26.2%。结果说明,在自然放置过程中,随着时间的推进,猪粪对管道的阻力逐渐增大。
-
范宁摩擦因子用于计算管道对流体流动时摩擦阻力的大小[19-21]。范宁摩擦因子数值越大表示管道阻力越强。由图8(a)可知,在抽吸管径为0.02 m,抽吸真空度为−70 kPa的条件下,实验测定的范宁摩擦因子随猪粪含固率增大而增大,与抽吸流量随猪粪含固率变化呈相反的对应关系。从曲线变化趋势来看,特别在高含固率(>16%)下,实验范宁摩擦因子的增大明显,说明从流动阻力特性角度来说,不宜在高含固率条件下进行粪污抽吸。虽然抽吸流量随抽吸管径增大而迅速增加(见图4),但当含固率为12%,抽吸真空度为−70 kPa时,实验范宁摩擦因子亦随抽吸管径增大而增大(图8(b))。这是由于抽吸管道内壁面积(与流体接触的摩擦面)是随抽吸管径增大而增加的[22]。
雷诺数同样是表征流体流动特性的重要物理量。雷诺数较小说明黏性阻力对流场的影响大于惯性力[21, 23]。从抽吸实验结果来看,由于猪粪黏性阻力较大,实验计算得到的非牛顿流体雷诺数均较小,与实验范宁摩擦因子之间表现出明显的层流特征[15]关系(见图8(c))。图8(c)显示部分代表性实验数据点,最大实验范宁摩擦因子达到3.020 0,而最小实验范宁摩擦因子为0.006 6,最大实验雷诺数达到2 435,而最小实验雷诺数仅有10左右,显示出管道抽吸猪粪过程中阻力特征变化范围较大。另外,由于存在层流关系,由图8(a)和图8(b)可以看出,实验雷诺数与猪粪含固率及抽吸管径的对应关系,同实验范宁摩擦因子的情况相反。
2.1. 不同含固率对抽吸流量的影响
2.2. 不同抽吸管径对抽吸流量的影响
2.3. 不同自然放置时间对抽吸流量的影响
2.4. 不同含固率和抽吸管径对范宁摩擦因子和雷诺数影响
-
1)随着猪粪含固率从2%增加到20%,其流变指数从0.952 3降至0.300 4,导致管道阻力上升,抽吸流量减少,整体上抽吸流量与含固率符合二次曲线关系;抽吸流量随抽吸管径呈幂指增长关系,当猪粪的非牛顿流体特性增强时,管径间接成为影响管道内非牛顿流体黏性阻力的重要因素。
2)在自然放置过程中,不同含固率下猪粪的抽吸流量随自然放置时间的延长有所下降,同时流变指数亦有所下降;抽吸流量的平均降低率随自然放置时间不断增加。15 d内降幅较小,15 d后降幅明显扩大,最大达到了26.2%(25 d),越到后期其影响越明显。
3)本研究条件下的范宁摩擦因子为0.006 6~3.020 0,非牛顿流体雷诺数为10~2 435,二者符合管道层流流动特征关系。实验范宁摩擦因子随含固率增大而增大,特别在高含固率(>16%)下增速最为显著。从非牛顿流体流动阻力特性角度来说,不宜在高含固率条件下进行粪污抽吸。




 下载:
下载: