-
磺胺类抗生素(sulfonamides, SAs)是一种具有磺胺类基本结构的化学合成的广谱抗生素。磺胺类抗生素的应用前景十分广阔,主要用于动物体和人体中细菌感染疾病的防治[1]。随着我国对于磺胺类抗生素的需求和消费量的日渐增长,导致大量的磺胺类抗生素会排入环境并在环境中聚集和富集,造成了巨大的风险[2]。目前,有关磺胺类抗生素的残留检测研究主要集中在动物源食品[3-4]中,而环境水体中的残留检测却常常被忽略。何秀婷等[5]调查阳江和大亚湾海水养殖区发现,虽然鱼肉组织中仅磺胺二甲基嘧啶含量超标,但肝脏样品中的磺胺类抗生素计算超标率却高达89%。虽然对比世界规定的日允许摄入量(ADI≤50 μg·kg−1)来说,远未达到规定值,但如若长期暴露于低浓度情况下,水生生物极有可能受到危害[6]。由于磺胺类抗生素的耐久性,“二次暴露”的可能性也十分大。水体中残留的磺胺类抗生素通过饮用水[7]或水生动物富集[8]进入人体。细菌与磺胺类抗生素接触后,对磺胺类抗生素的敏感性降低甚至消失,形成耐药菌株。如果人类长期食用带有耐药菌株的肉制品,耐药菌株会继续在人体内积蓄,使得人体健康受到影响[9]。 因此,建立一种快速检测多种磺胺类抗生素的方法刻不容缓。
目前,磺胺类抗生素残留检测技术主要包括免疫分析法、液相色谱法、液质联用法等。免疫分析法一般用于大量样品的常规分析或者样品的定性筛查。相比于其他检测方法,其灵敏度不高,还易出现假阳性。液相色谱法的灵敏度较低,一般仅作为筛选方法。液质联用法灵敏度高、选择性特异性好,对含量较低的目标物也可以进行较好地定性确认,是目前较为先进的药物残留检测方法[10]。刘培勇等[11]建立了一种高效液相色谱-串联质谱用于检测猪肉中常见的11种磺胺类抗生素残留的方法,样品使用Oasis MCX SPE柱进行固相萃取,使用正离子模式测定,11种磺胺类抗生素的检出限为0.1~1.0 μg·L−1,在20~400 μg·L−1内线性良好,回收率为79.3%~105.5%,相对标准偏差为1.3%~11.6%(n=6)。环境水样中磺胺类抗生素的富集提取方法主要包括液液萃取、固相萃取和加速溶剂萃取等。作为最早被应用和普及的样品预处理技术,液液萃取具有操作简单、设备易获取、成本低廉等优点。但传统液液萃取方法存在耗时长、对溶剂要求高、可能造成环境二次污染的缺点。与传统的液液萃取方法相比,固相萃取具有更高的回收率、更少的有机溶剂、更简易的操作、更低廉的价格和更低的环境负荷等优点。其作用机理是利用固体吸附剂使样品中的目标化合物先被富集吸附,再利用特定有机溶剂洗脱或者热解吸附,使目标化合物从吸附剂中脱离出来。液质联用法中的基质效应是制约高通量检测的主要技术瓶颈,固相萃取则成为去除基质效应的研究重点[12-14],并被广泛应用于环境水体中抗生素的富集。WANG等[15]采用三聚氰胺/邻苯二醛共价有机框架作为固相萃取剂,对水样中磺胺类抗生素进行富集,检测到6种抗生素,检出限为0.05~0.36 ng·L−1,回收率为82.5%~104.8%。
为提高检测方法的高效性及检测结果的准确性,本研究在参考美国及欧盟分析测试PPCPs方法和已有检测仪器原理的基础上,采用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱联用检测技术,比对不同固相萃取柱及水样pH值,探讨最佳固相萃取条件,建立8种磺胺类抗生素标准物质的线性方程,讨论检测技术的定量限、检出限、稳定性、精密度及空白基质加标回收率,分析检测技术的时效性、稳定性、灵敏性和数据的准确性,旨在为水环境中磺胺类抗生素残留问题提供简单、快速、高效、灵敏的检测方案,亦为我国检测方法标准体系的建设提供参考。
-
1)实验仪器。1290-AB 5500QTRAP三重四级杆液相色谱质谱联用仪(上海SCIEX分析仪器贸易有限公司);Phenomenex Kinetex F5色谱柱(美国飞诺美公司);EVA30A多功能样品氮吹浓缩仪(北京普立泰科仪器有限公司);RayCure HLB 固相萃取小柱(60 mg, 3 mL, 技迩(大连)科技有限公司);玻璃纤维滤膜(0.45 μm,江苏绿盟科学有限公司);Milli-Q超纯水仪(美国密理博公司);隔膜真空泵(天津市津腾实验设备有限公司)。
2)实验试剂。磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM)、磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)、磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ)、磺胺氯哒嗪(SPSD)、磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP)、磺胺吡啶(SASP)、磺胺喹恶啉(SQ)、磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ)(100 μg·mL−1, 坛墨质检有限公司), 甲醇、乙腈(色谱纯, 美国Tedia公司),甲酸(99%, 美国ACS恩科化学公司),盐酸(优级纯, 国药集团化学试剂有限公司),氨水(分析纯,江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司),乙二胺四乙酸二钠(≥99.0%, 上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司)。8种磺胺抗生素CAS号、分子式、相对分子质量和结构式如表1所示。
-
混合标准储备溶液质量浓度为100 μg·L−1,分别量取8种磺胺类标准品(磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶、磺胺二甲基嘧啶、磺胺甲恶唑、磺胺氯哒嗪、磺胺甲氧哒嗪、磺胺吡啶、磺胺喹恶啉、磺胺甲噻二唑)各1 mL,用乙腈定容至100 mL,于−18 ℃条件下避光保存备用。实验用水为超纯水。
-
水样(取自实验室)使用前,经0.45 µm滤膜过滤,再调节pH至3。每1 L过滤水样中加入500 mg EDTA(以乙二胺四乙酸二钠计)。依次使用 3 mL甲醇和3 mL超纯水对Waters Oasis HLB 固相萃取小柱进行活化。水样过滤后,取50 mL水样并控制水样在6 mL·min−1流速下通过萃取柱,直至液体抽干。富集完成后,用 3 mL超纯水淋洗数次。在真空泵作用下,抽干萃取柱中液体,最后使用1 mL 2%甲酸甲醇溶液洗脱3次,在自然重力作用下收集洗脱液于10 mL管中。在40 ℃条件下,氮吹浓缩吹干,使用超纯水复溶至1 mL,待测。
-
1)色谱条件。选择Phenomenox Kinetex F5色谱柱(2.6 μm,50 mm×3.0 mm),柱温为40 ℃,进样量为100 µL,流速为0.4 mL·min−1;流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液,流动相B为0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液。采用梯度洗脱,其洗脱程序见表2。
2)质谱条件。ESI电喷雾离子源电压为5 500 V;扫描釆用正离子(ESI+)模式;气帘气(CUR)压力为206.84 kPa;雾化气(GS1)压力为344.74 kPa;辅助气(GS20)压力为413.69 kPa;源温度(TEM)为500 ℃;碰撞气(CAD)压力等级为55.16 kPa;监测模式釆用多反应监测(MRM)。
-
采用0.1%甲酸溶液与0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液为流动相,MRM模式下对磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM)、磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)、磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ)、磺胺氯哒嗪(SPDZ)、磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP)、磺胺吡啶(SASP)、磺胺喹恶啉(SQ)与磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ)进行检测。进入一级质谱后,在正离子检测方式下,SDM、SDD、SMZ、SPDZ、SMP、SASP、SQ与SMTZ产生稳定的[M+H]+分子离子峰,即m/z分别为311.1、279.1、254.1、285.1、281、250.1、301.1和271。进行二级质谱扫描,得到8种磺胺类抗生素特征碎片离子m /z,分别为156.1、186.1、156、156、126.1、156.1、156和156.1。8种磺胺类抗生素的质谱监测离子与主要参数值见表3。
-
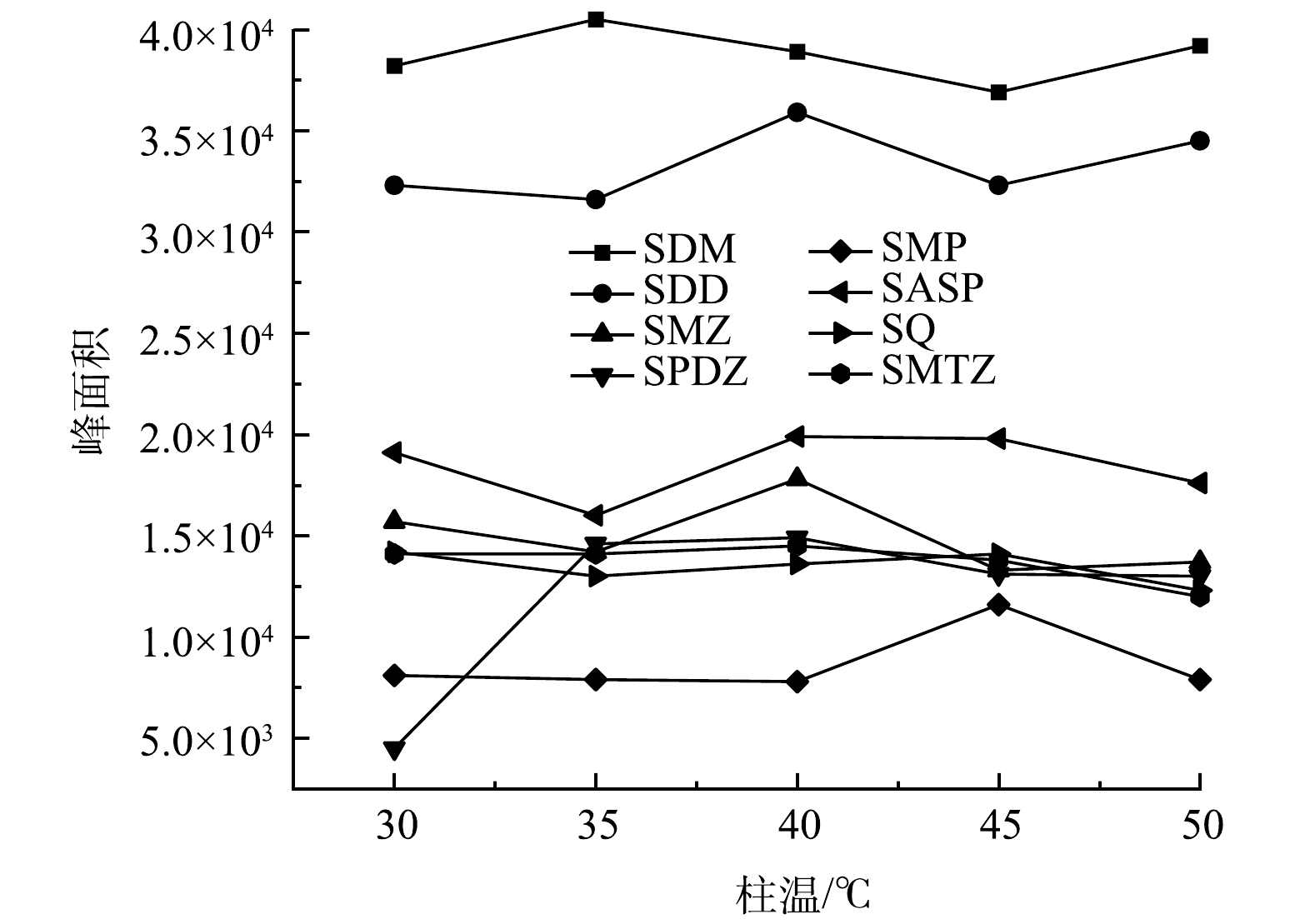
1)柱温优化。柱温对物质保留性质的影响主要是由于温度的不同导致溶质在流动相中的溶解度不同而造成的[16]。在其他色谱条件不变的情况下,考察了柱温(30、35、40、45和50 ℃)对峰面积的影响(图1),并进行了优化。结果显示,当温度从30 ℃升至50 ℃过程中,各目标物色谱峰的保留时间依次减小。磺胺二甲基嘧啶、磺胺甲恶唑、磺胺氯哒嗪、磺胺吡啶和磺胺甲噻二唑在柱温为40 ℃时,各色谱峰的峰面积最大,响应值最高。磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶在柱温为35 ℃时,色谱峰峰面积最大;40 ℃时的色谱峰峰面积次之。磺胺甲氧哒嗪在柱温为45 ℃时,色谱峰峰面积最佳,但温度较高会影响色谱柱寿命。综合考虑,选取色谱柱柱温为40 ℃时的色谱峰峰面积最为合适。因此,本实验的柱温设定为40 ℃。
2)流动相条件优化。由于磺胺类抗生素呈弱碱性,分子形态只在酸性溶液中存在,故加入一定量的甲酸以促进磺胺类抗生素电离,使其更好地离子化,且在电离时更易被检测[17]。目前,磺胺类抗生素检测中最为常用的有机相为甲醇[18]和乙腈[17, 19]。本研究对甲醇和乙腈2种流动相进行了考察,色谱图如图2所示。可以看出,使用甲醇作为有机相时,虽然分离度良好,但由于磺胺类药物在结构中含有氨基,易与色谱填料中的残余硅羟基产生氢键,造成峰形拖尾、展宽以及保留时间漂移等现象,从而增加优化难度。乙腈作为有机相时分离效果更明显,质谱信号响应更强烈。故选择0.1%甲酸水溶液和0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液作为流动相。
-
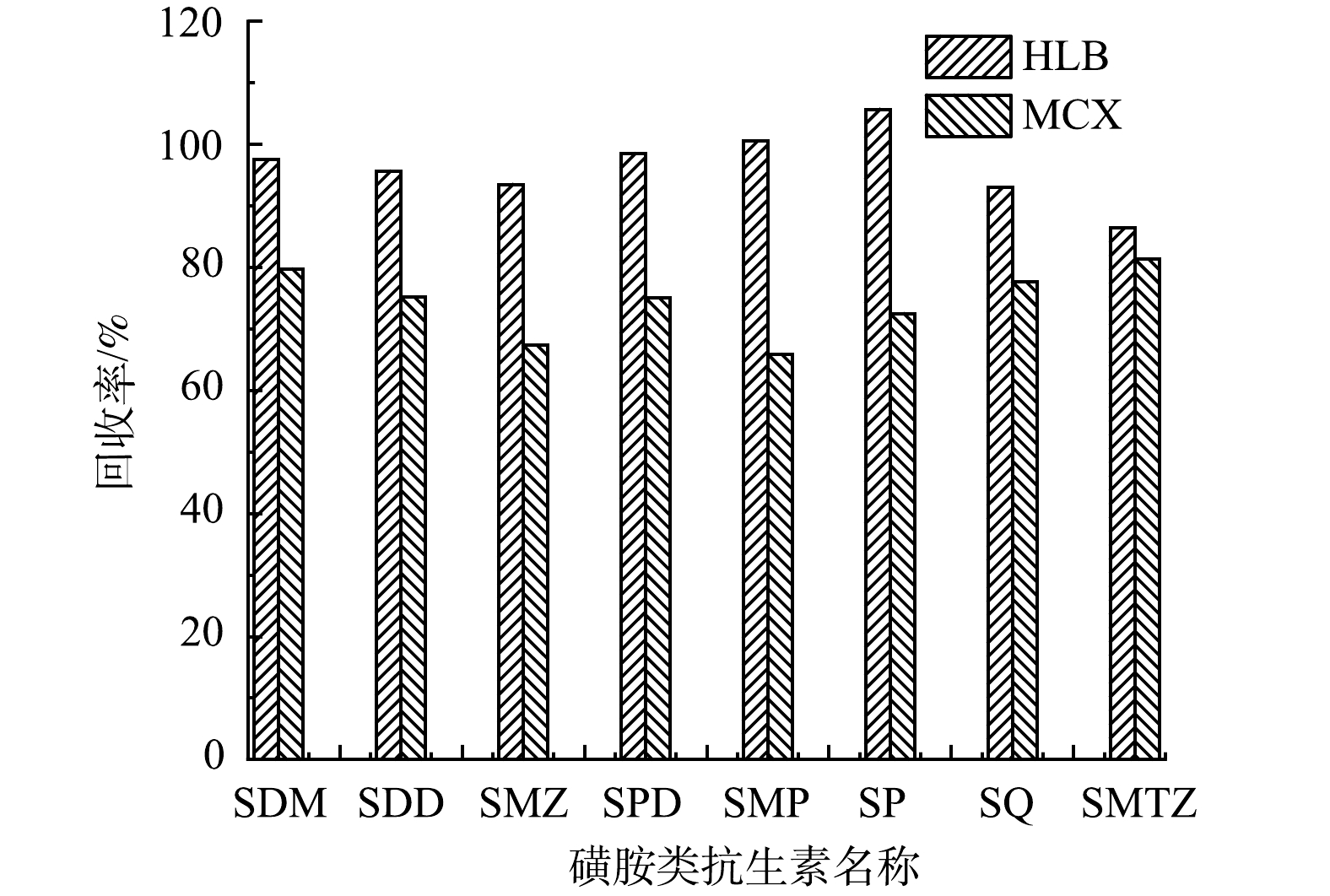
1)固相萃取柱的选择。目前,磺胺类抗生素前处理常见的几种固相萃取柱包括HLB[20]、MCX[11,21]、Silica[22]、C18、ENV+柱等[23]。已有研究[20,24-25]表明,HLB柱在萃取效果方面的综合性能较好。本研究比较了pH=3条件下HLB柱、MCX柱的回收率。依次用3 mL甲醇、3 mL超纯水活化HLB柱、MCX柱。HLB柱实验组用3 mL 2%甲酸甲醇溶液洗脱;MCX柱实验组用3 mL 5%氨水甲醇溶液洗脱。
洗脱后结果如图3所示。可以看出,HLB柱的萃取效果最好,加标回收率为86.45%~105.70%;MCX柱的萃取效果次之,加标回收率为65.86%~81.36%。这可能是因为磺胺类抗生素是极性物质造成的。而HLB柱是由亲脂基团和亲水基团聚合而成的,对于极性化合物的保留有很好的效果[26]。磺酰基团会导致磺胺类抗生素带有弱酸性,选择0.2%甲酸甲醇溶液洗脱,能去除部分碱性和中性干扰物。综合考虑,选择HLB固相萃取柱作为吸附剂。
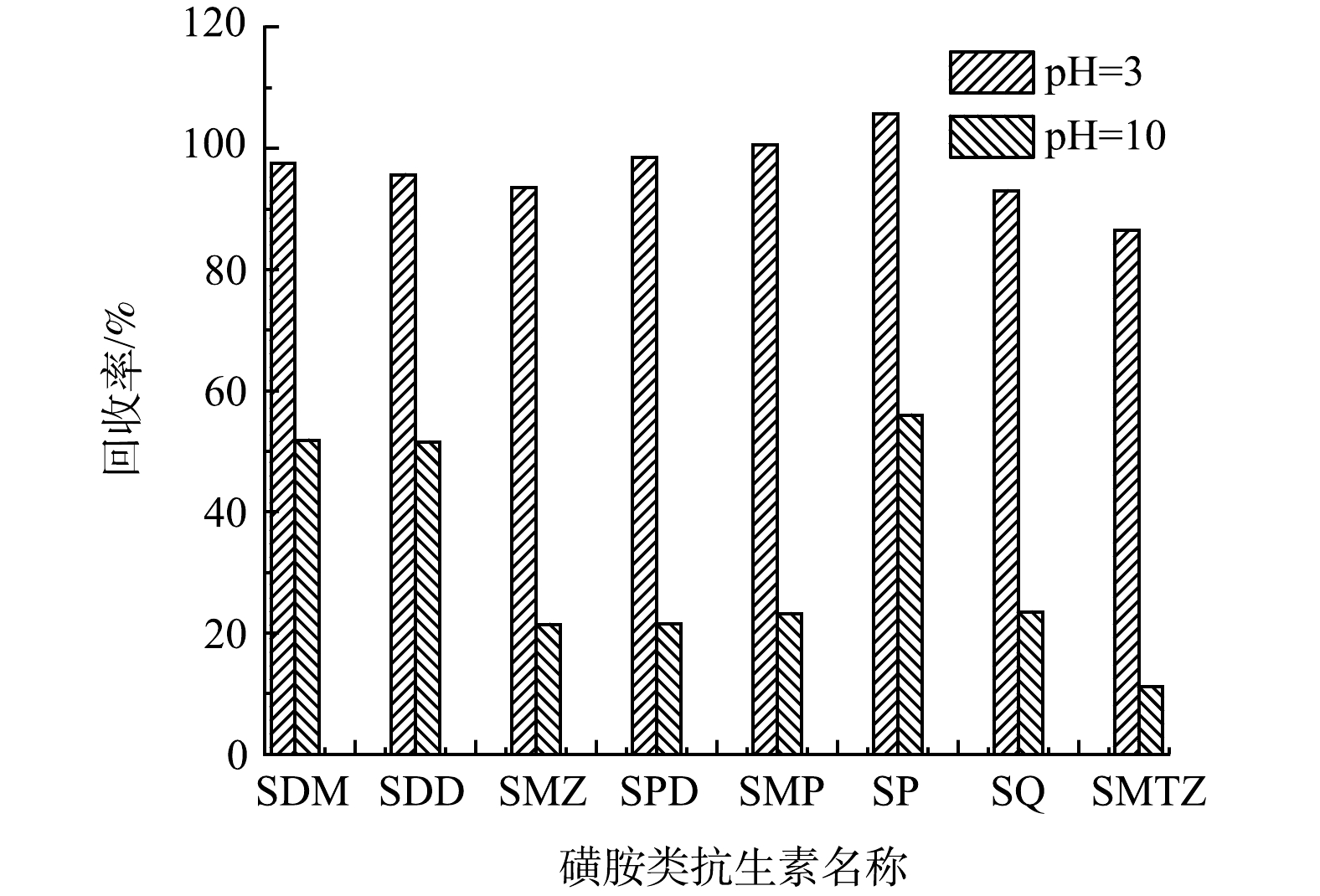
2)水样pH值的优化。已有研究[27]表明,水样pH值对固相萃取回收率存在一定影响。本研究比较了磺胺类抗生素样品在pH值为3和7时的回收效率(图4)。结果表明:pH=3时,磺胺类抗生素回收率保持在80%以上;而pH=10时,回收率不是很理想。这可能是由于磺胺类抗生素(pKa1=1.11~2.75,pKa2=4.18~7.59)是具备弱碱性和酸性的两性电解质而导致的。当pH为2~5时,磺胺类抗生素呈中性状态,在水样中能保持等电状态,从而达到优秀的吸附效率[19]。已有研究[28]在酸性条件下进行固相萃取并取得了满意的结果。因此,本研究选用pH值为3的水样进行固相萃取。
-
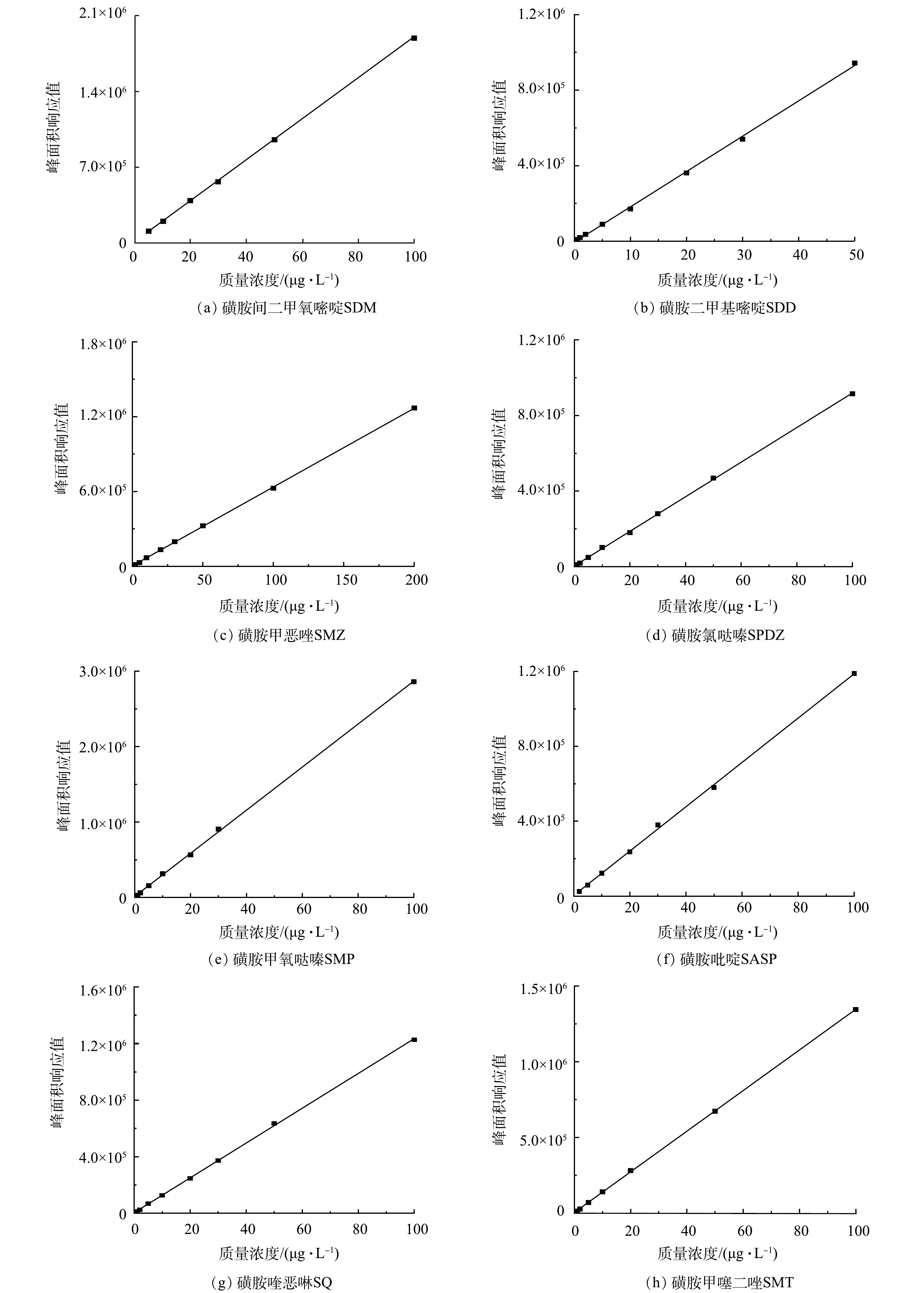
对配制好的0.5、1、2、5、10、20、30、50、100和200 μg·L−1的混合标准溶液进行测定。以峰面积响应值为纵坐标(y),溶液浓度为横坐标(x),绘制相应的标准曲线(其标准曲线见图5)。由表4可以看出,8种磺胺类抗生素计算所得拟合度均在0.999 0以上,说明该方法具有可靠性。
1) 方法定量限及检出限。根据信噪比理论,8种抗生素方法的检出限计算结果(表5)为0.1~0.5 μg·L−1,定量限为0.5~2 μg·L−1。除磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)以外,其余抗生素测定相对标准偏差均在5%以内,磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)在5%左右,说明该方法精密度高。
2) 方法的精密度。准确吸取质量浓度为10 μg·L−1的混标溶液1 mL,重复进样6次,计算8种磺胺类抗生素的峰面积的相对标准偏差(RSD),结果如表6所示。可以看出,除磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)外,其余抗生素测定相对标准偏差均在5%以内,磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD)维持在5%左右,说明该方法精密度高。
3) 方法的稳定性。将10 μg·L−1的混标溶液在环境中密封保存,分别在0、4、8、24和48 h对该溶液进行测定。各化合物峰面积响应值如表7所示。可以看出,48 h之内,溶液中8种抗生素含量的波动在7%以内,说明该方法稳定性较好。
4) 加标回收率。向水样中添加不同浓度的目标抗生素混合标准溶液,进行加标回收实验,测得8种磺胺类抗生素的回收率及RSD,结果如表8所示。为进一步确认方法的可靠性,向水样中分别添加质量浓度为1、5和50 μg·L−1抗生素,每组进行3次重复实验。结果表明,8种磺胺类抗生素的加标回收率分别78.85%~103.10%、76.69%~107.01%和73.55%~107.66%,相对标准偏差均在15%以内。
-
1)采用固相萃取净化法,建立了水环境中8种磺胺类抗生素(磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶、磺胺二甲基嘧啶、磺胺甲恶唑、磺胺氯哒嗪、磺胺甲氧哒嗪、磺胺吡啶、磺胺喹噁啉、磺胺甲噻二唑)的超高效液相色谱-串联质谱检测方法。8种磺胺类抗生素线性关系良好,且拟合度均大于0.999 0。
2)固相萃取-液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱检测方法定量限为0.5~2 μg·L−1 ,检出限为0.1~0.5 μg·L−1。用空白基质做3种不同质量浓度1、5、50 μg·L−1的加标回收,加标回收率分别为78.85%~127.96%、76.69%~114.38%和73.55%~125.92%,相对标准偏差均小于15%。
3)固相萃取-液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱检测方法通过精密度测试,得出各类磺胺类抗生素测定相对标准偏差均在5%左右,同时通过稳定性测试得出溶液中8种抗生素含量的波动在7%以内,说明该方法稳定且可靠。
水环境中磺胺类抗生素固相萃取-液质联用检测方法的建立及效果评估
Establishment of solid phase extraction-liquid mass spectrometry method for detection of sulfa antibiotics in water environment and its effect evaluation
-
摘要: 为快速、同步检测分析磺胺类抗生素,有效削减并控制水体中磺胺类上抗生素含量,基于已有检测仪器和分析测试方法,建立了一种用于同时测定水体中8种磺胺类抗生素(磺胺氯哒嗪、磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶、磺胺二甲基嘧啶、磺胺甲恶唑、磺胺喹恶啉、磺胺甲氧哒嗪、磺胺甲噻二唑、磺胺吡啶)残留的固相萃取-液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱检测方法;在检测过程中,调节水样的pH为3,用HLB固相萃取柱进行净化、富集,在40 ℃条件下用氮吹浓缩吹干,用超纯水复溶至1 mL;以0.1%甲酸水溶液和0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液作为流动相,使用Phenomenex Kinetex F5 色谱柱(50 mm×3.0 mm, 2.6 μm)进行分离,在多反应监测模式(MRM)下对样品进行定量、定性分析。结果表明:8种磺胺类抗生素线性关系良好,且拟合度均大于0.999 0;检出限为0.1~0.5 μg·L−1,定量限为0.5~2.0 μg·L−1;质量浓度为1、5、50 μg·L−1的混标溶液的加标回收率分别为78.85%~127.96%、76.69%~114.38%和73.55%~125.92%, 相对标准偏差均在15%以内。该方法快捷、高效、灵敏,能够满足水中磺胺类抗生素的定性、定量检测,可为我国检测方法标准体系的建设提供参考。Abstract: In order to quickly and synchronously detect and analyze sulphonamides, effectively reduce and control sulphonamides content in water, based on the existing detection instruments and analysis and testing methods, a liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry method was developed to simultaneously detect the residues of 8 antibiotics in water: sulfadiazine, sulfadimethyrimidine, sulfadimethyrimidine, sulfamethoxazole, sulfamequinoline, sulfamethoxyazine, sulfamethothiazole, sulfamepyridine. During the detecting process, the sulfonamides in water samples were enriched with HLB solid phase extraction column at pH=3, then dried by nitrogen blowing at 40 ℃ and re-dissolved to 1mL by ultrapure water, lastly separated by Phenomenex Kinetex F5 column (50 mm×3.0 mm, 2.6 μm) using 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile as mobile phase. The results showed that there was a good linear relationship between the 8 sulfonamides antibiotics and the fitting degree was higher than 0.999. The limits of detection were 0.1~0.5 μg·L−1, and the limits of quantification were 0.5~2.0 μg·L−1. The recoveries of mixed standard solutions with mass concentrations of 1, 5 and 50 μg·L−1 were 78.85%~127.96%, 76.69%~114.38% and 73.55%~125.92%, respectively, and the relative standard deviations (RSD) were not higher than 15%. The method is quick, efficient and sensitive, and can satisfy the qualitative and quantitative detection of sulfa antibiotics in water. It can provide a reference for the construction of standard system of detection methods in China.
-

-
表 1 8种磺胺抗生素的CAS号、分子式、相对分子质量和结构式
Table 1. CAS number, molecular formula, relative molecular weight and structural formula of 8 sulfa antibiotics
化合物 CAS号 分子式 相对分
子质量磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶
(sulfamethazine,SDM)155-91-9 C12H14N4O4S 310.33 磺胺二甲基嘧啶
(sulfamethazine,SDD)57-68-1 C12H14N4O2S 278.33 磺胺甲恶唑
(sulfamethoxazole,SMZ)723-46-6 C10H11N3O3S 253.28 磺胺氯哒嗪
(sulfachloropyridazine,SPDZ)80-32-0 C10H9ClN4O2S 284.72 磺胺甲氧哒嗪
(sulfamethoxypyridazine,SMP)80-35-3 C11H12N4O3S 280.30 磺胺吡啶
(sulfapyridine,SASP)144-83-2 C11H11N3O2S 249.29 磺胺喹恶啉
(sulfaquinoxaline,SQ)59-40-5 C14H12N4O2S 300.34 磺胺甲噻二唑
(sulfamethizole,SMTZ)144-82-1 C9H10N4O2S2 270.33 表 2 梯度洗脱程序
Table 2. Gradient elution procedures
时间/
min流速/
(mL·min−1)流动相A
体积分数/%流动相B
体积分数/%0 0.4 97 3 1 0.4 97 3 1.1 0.4 85 15 9.5 0.4 25 75 9.6 0.4 5 95 11.5 0.4 5 95 11.6 0.4 97 3 13.6 0.4 97 3 表 3 8种磺胺类抗生素的质谱监测离子与主要参数
Table 3. Monitoring ions and main parameters of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics by mass spectrometry
化合物 母离子m/z 定量子离子m/z 碰撞能/eV 定性子离子m/z 碰撞能/eV 去簇电压/V SDM 311.1 156.1 28 218 28 200 SDD 279.1 186.1 23 156 27 175 SMZ 254.1 156 22 108 37 138 SPDZ 285.1 156 23 108.1 33 140 SMP 281 126.1 21 156 20 150 SASP 250.1 156.1 20 108 39 150 SQ 301.1 156 20 108 36 167 SMTZ 271 156.1 19 108 32 110 表 4 8种磺胺类抗生素的回归方程及拟合度
Table 4. Regression equation and correlation coefficient of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics
名称 线性方程 拟合度 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SMD) y = 18 883x + 7 996.2 0.999 9 磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SM2) y = 18 719x – 5 789.2 0.999 1 磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ) y = 6 311.6x + 4 186.6 0.999 9 磺胺氯哒嗪(SPD) y = 9 147.4x + 3 617.4 0.999 7 磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP) y = 28 527x + 13 484 0.999 6 磺胺吡啶(SP) y = 11 841x + 3 076.3 0.999 3 磺胺喹噁啉(SQ) y = 12 326x + 2 834.8 0.999 7 磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ) y = 13 402x + 4 856.1 0.999 9 表 5 8种磺胺类抗生素的定量限、检出限
Table 5. Limits of quantitation and detection of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics
名称 定量限/(μg·L−1) 检出限/(μg·L−1) 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM) 0.5 0.1 磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD) 0.5 0.1 磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ) 2.0 0.5 磺胺氯哒嗪(SPDZ) 1.0 0.1 磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP) 2.0 0.5 磺胺吡啶(SASP) 0.5 0.1 磺胺喹恶啉(SQ) 1.0 0.1 磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ) 1.0 0.1 表 6 8种磺胺类抗生素的精密度
Table 6. Precision of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics
名称 峰面积 相对标准偏差/% 第1次 第2次 第3次 第4次 第5次 第6次 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM) 299 200 284 600 286 400 289 300 292 700 265 300 4.01 磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD) 255 700 275 900 262 300 249 700 255 600 236 700 5.09 磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ) 106 800 108 400 10 6800 10 4000 96 530 108 500 4.31 磺胺氯哒嗪(SPDZ) 78 570 75 830 8 1520 79 370 74 020 79 720 3.52 磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP) 191 800 185 300 193 000 188 800 191 500 191 900 1.5 磺胺吡啶(SASP) 156 700 167 500 160 700 155 200 162 300 159 600 2.73 磺胺喹恶啉(SQ) 104 800 109 200 111 300 101 100 107 200 111 800 3.81 磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ) 194 000 183 400 185 000 198 800 185 300 181 200 3.66 表 7 8种磺胺类抗生素的稳定性测定
Table 7. Stability determination of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics
名称 峰面积 相对标准偏差/% 初始时刻 放置4 h 放置8 h 放置24 h 放置48 h 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM) 450 400 445 600 463 600 451 400 432 600 2.49 磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD) 379 000 352 900 389 700 401 900 346 600 6.34 磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ) 173 900 185 000 170 300 179 600 161 400 5.18 磺胺氯哒嗪(SPDZ) 150 300 145 500 140 000 139 300 134 800 4.23 磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP) 110 800 112 200 121 500 111 800 102 100 6.16 磺胺吡啶(SASP) 248 600 233 800 242 500 237 200 219 600 4.61 磺胺喹恶啉(SQ) 91 680 92 780 97 230 101 200 95 920 3.95 磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ) 345 100 347 200 359 600 340 900 334 700 2.67 表 8 8种磺胺类抗生素的回收率测定
Table 8. Recovery rate of 8 sulfonamides antibiotics
抗生素名称 质量浓度为1 μg·L−1 质量浓度为5 μg·L−1 质量浓度为50 μg·L−1 回收率/% RSD/% 回收率/% RSD/% 回收率/% RSD/% 磺胺间二甲氧嘧啶(SDM) 103.1 14.3 107.01 4.07 93.26 9.43 磺胺二甲基嘧啶(SDD 94.56 7.21 97.49 7.14 102.44 11.8 磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ) 94.98 7.81 89.41 5.19 87.38 10.98 磺胺氯哒嗪(SPDZ 78.85 8.42 85.37 3.89 86.17 7.17 磺胺甲氧哒嗪(SMP) 104.47 2.93 100.56 3.78 107.66 3.95 磺胺吡啶(SASP) 95.77 10.63 94.7 7.01 92.94 5.54 磺胺喹噁啉(SQ) 90.02 7.25 76.69 4.31 84.24 8.47 磺胺甲噻二唑(SMTZ) 83.96 10.17 81.03 10.22 73.55 5.53 -
[1] JIN L, JIANG L, HAN Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of thirteen sulfonamides antibiotics in a drinking water source in East China[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(7): 2515-2521. [2] KOLPIN D W, FURLONG E T, MEYER M T, et al. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U. S. streams, 1999-2000: A national reconnaissance[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 2002, 36(6): 1202-1211. doi: 10.1021/es011055j [3] 杨梅, 孙思, 王安波, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定猪肉中磺胺类药物残留量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2017, 8(9): 3633-3638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.09.060 [4] ZHE M, SHI Z H, LIANG S X, et al. Residues investigation of fluoroquinolones and sulphonamides and their metabolites in bovine milk by quantification and confirmation using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-Tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 174: 597-605. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.067 [5] 何秀婷, 王奇, 聂湘平, 等. 广东典型海水养殖区沉积物及鱼体中磺胺类药物的残留及其对人体的健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(7): 2728-2735. [6] 孔志明. 环境毒理学[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2017. [7] 陈哲, 吴立明, 苏怡. 生活饮用水中磺胺类抗生素污染现状及其控制的研究进展[J]. 上海预防医学, 2018, 30(5): 412-415. [8] 李秀文, 何益得, 张巍, 等. 磺胺类抗生素对水环境的污染及生态毒理效应[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(S1): 62-67. [9] JIAN X, XU Y, WANG H M, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics and aantibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 1379-1385. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.040 [10] 张天, 王仁萍, 王猛, 等. 芬太尼的人体内分析及药动学研究进展[J]. 药学服务与研究, 2017, 17(3): 167-173. [11] 刘培勇, 张惠, 米之金, 等. 两步液液萃取-固相萃取净化结合高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定猪肉中11种磺胺类兽药残留[J]. 色谱, 2019, 37(10): 1098-1104. [12] 陈岑, 颜琳琦, 程巧鸳. QuEChERS-HPLC-MS/MS法测定4种化妆品基质中15种硝基咪唑类非法添加药物的基质效应研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2020, 50(4): 275-281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1803.2020.04.011 [13] 刘红, 杨飘飘, 李丽霞. 通过式高效净化/超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定化妆品中73种糖皮质激素[J]. 分析测试学报, 2020, 39(9): 1112-1119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2020.09.008 [14] 罗辉泰, 黄晓兰, 吴惠勤, 等. QuEChERS-同位素稀释-液相色谱-高分辨飞行时间质谱法高通量筛查化妆品中86种糖皮质激素[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(9): 1381-1388. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170194 [15] WANG X M, XU G J, WANG X L, et al. Melamine/o-phthalaldehyde covalent organic frameworks for solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of sulfonamide antibiotics in environmental samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(12): 1990-1996. [16] 陈辉华. 水产品中四环素类和氟喹诺酮类药物残留的同时检测[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2008. [17] CHEN X H, ZHAO Y G, QIU Q L, et al. A fast and high throughput LC-MS/MS method for the determination of 58 human and veterinary drugs in river water[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 29(9): 4228-4233. [18] MYCHELLE A, BERNARDETE F, ROSANA G, et al. Development and validation of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methods for determination of beta-lactams, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides and tetracyclines in surface and drinking water from Rio De Janeiro, Brazil[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 2018, 29(4): 801-813. [19] 高凯, 孟祥峰, 杨永顺, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时测定黑臭河体中的7种抗生素[J]. 广东化工, 2019, 46(16): 174-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2019.16.076 [20] WU D Q, SUI Q, YU X, et al. Identification of indicator PPCPs in landfill leachates and livestock wastewaters using multi-residue analysis of 70 PPCPs: Analytical method development and application in Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 141653. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141653 [21] 王军淋, 胡争艳, 冯靓, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定消毒产品中的22种抗生素[J]. 卫生研究, 2019, 48(1): 129-135. [22] HONG C, HU J, ASAMI M, et al. Simultaneous analysis of 16 sulfonamide and trimethoprim antibiotics in environmental waters by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2008, 1190(1/2): 390-393. [23] GROS M, RODRÍGUEZ-MOZAZ S, BARCELÓ D. Rapid analysis of multiclass antibiotic residues and some of their metabolites in hospital, urban wastewater and river water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-linear ion rrap tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1292(1): 173-188. [24] 李柳毅, 范辉, 范磊, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定地表水中4种磺胺类抗生素[J]. 化学分析计量, 2017, 26(6): 38-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2017.06.009 [25] CHAI Y F, ZHANG Y X, CHEN M X, et al. Distribution and treatment of antibiotics in typical WWTPs in small towns in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2724-2731. [26] KIM C, RYU H D, CHUNG E G, et al. A review of analytical procedures for the simultaneous determination of medically important veterinary antibiotics in environmental water: Sample preparation, liquid chromatography, and mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 217: 629-645. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.006 [27] 王大鹏, 张娴, 颜昌宙. 高效液相色谱串联质谱法测定污水污泥中4种磺胺类药物及其乙酰化代谢物[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(10): 2143-2151. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017120804 [28] LI T, WANG C, XU Z A, et al. A coupled method of on-line solid phase extraction with the UHPLCMS/MS for detection of sulfonamides antibiotics residues in aquaculture[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254: 126765. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126765 -



 下载:
下载: