-
静电除尘器具有处理风量大、阻力能耗低、耐高温、除尘效率高等诸多优点,被广泛应用于工业尾气颗粒物净化领域[1-2]。电除尘设备除尘性能受到电场结构、电场电压、气流速度等众多因素的影响[3-5]。其中,电场结构直接影响电场分布和流场分布,进而影响除尘效率[6-7],故电场内部电极排列布置对设备除尘性能影响较大。
国内外学者做了大量关于电场结构优化相关的研究工作。依成武等[8]设计了单区双涡旋型极板电除尘器,通过实验证实了电压、收尘面积、流速以及粉尘粒径等对除尘效率的影响,并发现当电极电压约为18 kV、有效收尘面积为2.7 m2时,除尘效率最大。胡建华等[9]发现,改变极板间距会影响荷电颗粒的沉降速度与运动轨迹,电极线间距存在一个最佳值。张立莹等[10]研究得出,增大极板间距会降低电场强度和颗粒的荷电量,最终致使颗粒捕集效率下降。崔晓慧等[11]对新型阳极板进行排布优化研究,证明错位板排布有利于提高对微细粉尘的收集效率。AHMED等[12]研究了线板式电除尘的电场特性,得出减小线间距会增大放电电流值的结论。DONG等[13]研究表明,放电极间距在大于150 mm时,颗粒捕集效率没有明显提升,设定合适的放电极间距对电除尘器的设计至关重要。又有研究人员[14-16]提出,极板极线间距在符合一定比例时具有较好捕集效率,优化极-板间距对提高电除尘效率有重要作用。
本研究拟利用电晕电场模型、k-ε湍流模型、Lawless电荷累积模型来建立新的静电除尘多场模拟模型,并通过改变极板间距和极线间距,分析电场电势、风速、颗粒运动轨迹、除尘效率的变化特征,以揭示极线间距和极板间距对线板式除尘器效率的影响,从而为线板式电除尘内部结构和电极排布的优化和设计提供参考。
-
线板式静电除尘器电场内部由收尘极板和电极线组成,如图1所示。其工作原理是:电极线与收尘极板之间形成高压电场,电极附近产生电晕放电,致使空气发生电离;当含尘气流穿过电晕区时,粉尘颗粒物在库仑力的作用下向收尘极板运动,被收尘极板捕集,实现气固分离、净化空气的目的。
本实验通过调节两收尘极板和电极线的间距监测电场内电势和风速,在收尘极板至第2根与第3根放电极中间 (即ab线) ,和第1根电极至收尘极板 (即cd线) 设置监测位,监测并收集数据。
-
本研究依据带电粒子传输电流的守恒性建立电晕模型,故使用电流连续性方程和Poisson方程来求解带电粒子输运问题[17]。电晕模型的控制方程见式 (1)~(4) 。
式中:J为电流密度,A·m−2;kion为离子迁移率,(m2·V−1·s−1);ρion为离子电荷密度,C·m−3;E为电场强度,V·m−1;Dion是离子扩散系数,m2·s−1;ɛ0为真空介电常数;V为电势,V。
-
湍流模型使用动量守恒的Navier-Stokes方程和质量守恒的连续性方程进行求解,见式 (5)~(7)。
式中:μc为层流黏度系数,kg·m−1·s−1;μT为湍流黏度系数,kg·m−1·s−1;ρ为流体密度,kg·m−3;I为单位矩阵;p为气体静压力,Pa;FEHD为电流体力,N·m−3。
标准k-ε湍流模型由湍动能方程和耗散率方程组成,控制方程见式 (8)~(10) 。
式中:k为湍流动能;ɛ为湍流耗散率;Pk为湍动能每单位耗散净产出;湍流场参数:σk为1;σε为1.3;Cε1为1.44;Cε2为1.92;Cε3为0.09。
-
根据牛顿第二运动定律,对颗粒位置矢量分量的二阶运动方程进行求解,以求得运动颗粒的位置,控制方程见式 (11)~(12) 。
式中:q为颗粒的位置,m;v为颗粒运动的速度,m·s−1;mp为颗粒的质量,kg;Ft为施加在粒子上的合力,N。
使用LAWLESS模型[18]计算颗粒上累积的电荷,计算方程见式 (13)~(14) 。
式中:v=(qpe/2πε0dpkBT),其含义为无量纲的粒子荷电;w=(εp/(εp+2))(Edpe/2kBT),其含义为无量纲的电场强度;qp为颗粒荷电量,C;e为电子的电荷,1.6×10−19C;dp为颗粒直径,m;kB为玻尔兹曼常数,1.3806×10−23 J·K−1;T为热力学温度,K;εp为颗粒介电常数;τ=(ρionkiont/ε0),其含义为无量纲的充电时间;ρion为离子电荷密度,C·m−3;kion为离子迁移率,m2·V−1·s−1;t为实际荷电时间,s。
模型求解共分为两步。第一步是稳态计算,计算电场、电荷传输、湍流场和多物理场耦合。基于稳态计算的结果再进行第二步瞬态计算,计算流体流动颗粒追踪。最终得出颗粒在电场、流场的运动轨迹和除尘效率。
-
为验证数值模拟模型的可靠性和准确性,选取前人的实验数据作为基准,采用COMSOL软件建立模型对静电除尘器性能进行数值模拟,将模拟结果与实验数据进行验证。
-
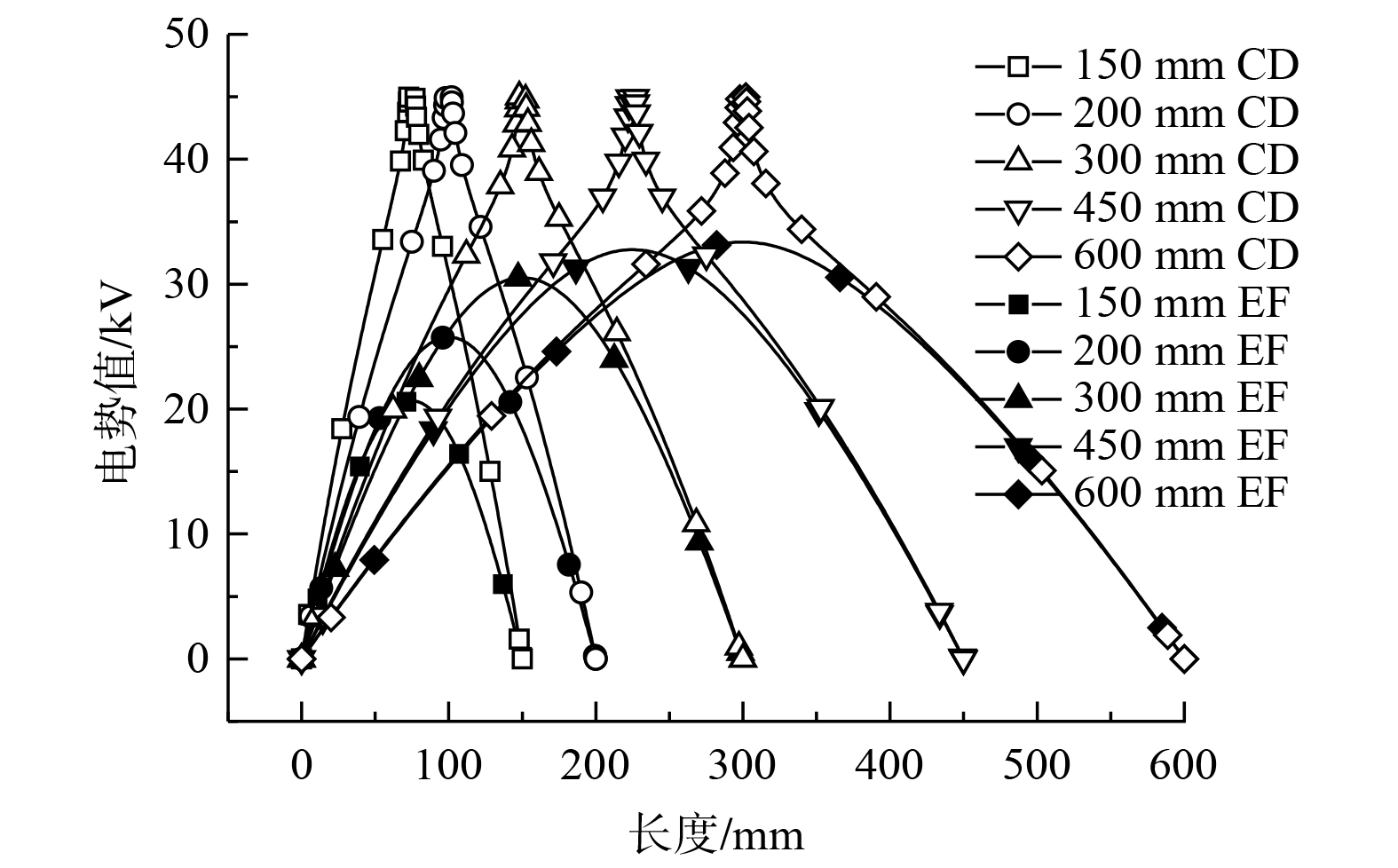
电势验证选用PENNEY[19]的线板式电除尘器实验数据进行验证,通过数值模拟软件建立1∶1的物理模型。在电场电压为28.7 kV、43.5 kV、46.5 kV的3种工况下,模拟收尘极板至第2根与第3根放电极中间 (即图1中ab线位置) 的电势值,并将模拟结果与实验数据进行对比,得出电势验证结果如图2所示,电势模拟结果与实验数据具有良好的拟合度。
-
静电除尘器内部流场实验数据选择KALLIO [20]的线板式电除尘器流场实验的数据,通过模拟计算进行风速验证。验证的实验工况:电场内3根放电极等距布置,电场电压为42 kV,入口风速分别为0.8 m·s−1、1.2 m·s−1、1.8 m·s−1时,模拟第1根电极至收尘极板 (即图1中cd线位置) 的风速值,模拟值与实验数据具有较高的一致性,如图3所示。
-
选择KIHM [21]的实验数据进行除尘效率的验证,实验模型参数:极板长度400 mm,板间距50 mm,8根放电极间距50 mm,入口风速2.0 m·s−1,颗粒粒径为4 μm。模拟不同电压下的除尘效率,模拟结果与实验数据对比如图4所示,当电压7.7 kV时,除尘效率相对误差最大,其值为5%。
综合电势、流场、除尘效率的验证结果,采用本文数学模型经COMSOL软件对静电除尘器性能进行数值模拟具有较高的可靠性,可以用于开展线板结构排布对电除尘性能影响的研究。
-
为研究线板结构排布对电除尘性能的影响趋势,分别设置2个实验组合,通过改变极板间距或极线间距,揭示其对除尘效率的影响规律。组合一几何模型如图5 (a) 所示:固定极线间距为180 mm,选择极板间距分别为150 mm、200 mm、300 mm、450 mm、600 mm下5种工况的模拟结果进行分析。组合二几何模型如图5 (b) 所示:固定极板间距为250 mm,选择极线间距分别为100 mm、150 mm、225 mm、300 mm、450 mm下5种工况的模拟结果进行分析。为了观测电场内部电势、空间电荷密度、风速、压力等参数的数据,设置4条观测线,如图5所示,其中AB线为穿过所有放电极且平行于极板的直线,CD线为穿过放电极且垂直于极板的直线,EF线位于两根放电极中间且垂直于极板的直线,GH线位于放电极与极板中间且平行于极板的直线。
对模型进行控制网格划分,网格总体大小设置细化网格,将电极附近网格进行加密,对边界网格设置了5层边界层和超细化网格,保证模型具有较高的单元网格质量,使模型具有较高的计算精度,几何模型网格划分如图6。
设定模型的参数,如表1所示。计算过程中,忽略温度、大气压力对除尘工况的影响,将入口风速、电场电压设置为定值,假设粉尘形状为球形颗粒物。收尘极板电势值设为零 (接地) ,通过记录总粒子数与出口壁面上的粒子数,得出除尘效率。模型的边界条件如表2所示。
-
1) 不同极板间距电势分布特征。在线板式电场内,放电极线上电势值为最大,收尘极板上电势为零,电势大小以电极线为圆心,向周围呈现发散式降低的分布趋势。如图7所示,随着极板间距变大,电场空间尺寸相应地增加,电势分布发生变化。从电极线至极板方向上电势的变化速率逐渐减小,电极线之间电势梯度随之降低,且电极线对附近电势的影响程度减轻。
在改变极板间距工况中,监测GH线上的电势值的变化。如图8所示,入口与出口处GH线上电势值随着极板间距增大而升高,而电极线位置处的电势峰值呈现下降趋势,且GH线上电势波动幅度随极板间距增大而降低。由于电场中极线与极板之间电势差为恒定值,故随着极板间距的增大,电极线至极板方向上的电势降低速率变缓,GH线上的电势值变化幅度明显降低,电势的变化趋势变缓。
在改变极板间距时,将CD线与EF线上的电势值变化联合考虑。如图9所示,电极线处电势最大值为45 kV,极板上电势值的最小值0 kV,在数值上与图7所呈现的趋势一致。随着极板间距的增大,CD、EF线上的电势值变化趋势逐渐变缓,且EF线上电势值的最大值逐渐升高,即两电极中间位置的电势值逐渐增大。
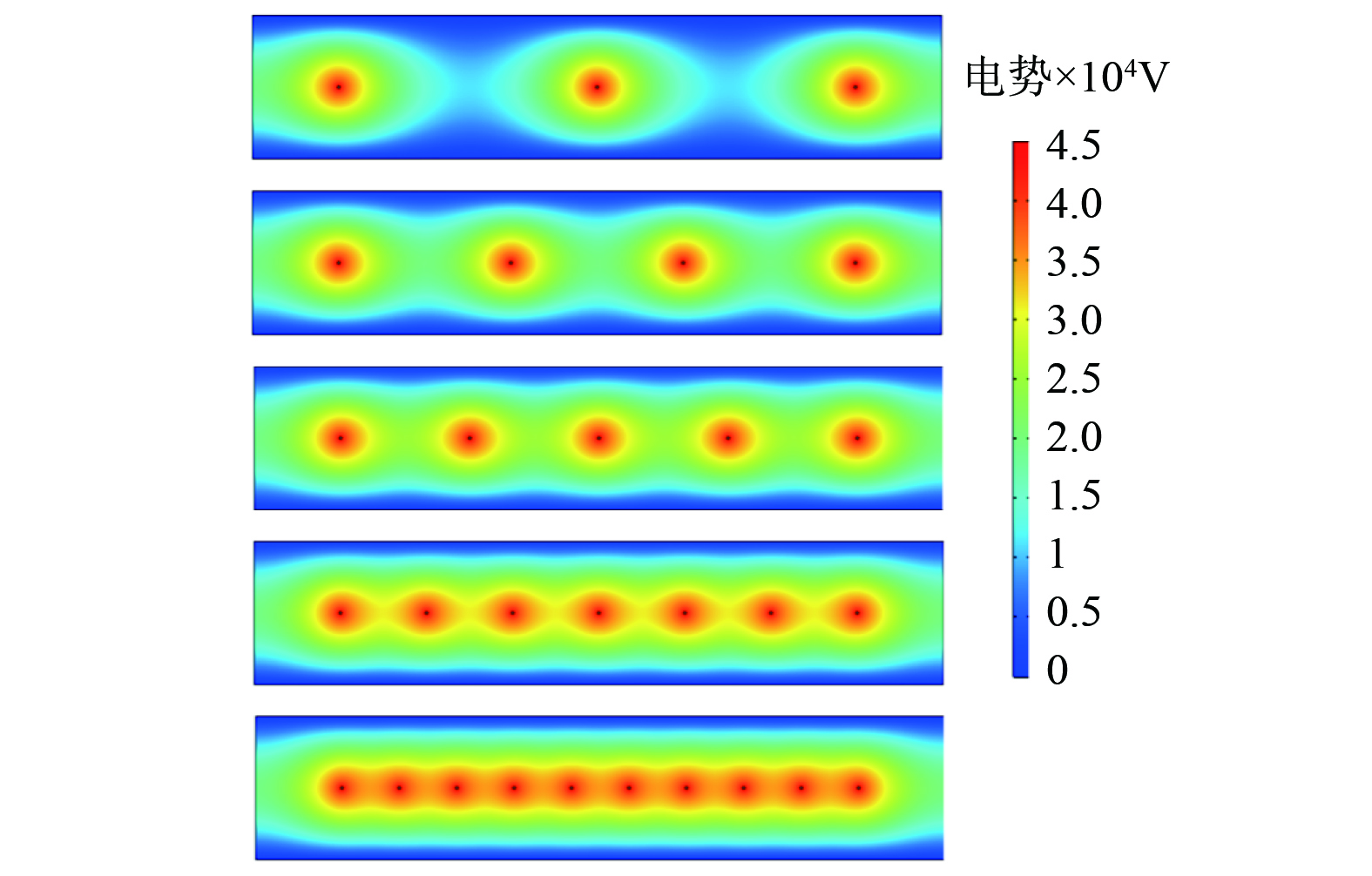
2) 不同极线间距电势分布特征。如图10所示,当极线间距减小时,单个电极产生电势的辐射范围发生了近距离重叠,电极之间的电势由点式分布呈现为条状分布,极线周围电势的影响程度增强,而电极至极板方向上电势分布没有发生明显变化。
通过监测AB线上的电势值变化,分析极线间距变化对电场电势值的影响趋势。如图11所示,随着极线间距减小,入口、出口处AB线上的电势值和电极处电势峰值保持不变,两电极之间的电势值逐渐增大,且电势值变化幅度逐渐降低,而两电极之间电势梯度基本不变。
电极线间距减小时,CD线上的电势值没有明显变化,而EF线上电势最大值逐渐升高,且EF线上数据变化速率也随之增大。如图12所示,CD线上电势变化表明,穿过电极线至极板方向上的电势大小不受极线间距的影响;EF线上电势呈现的趋势说明,两电极间距减小会引发两电极中间位置电势值的降低。
-
1) 极板间距对流场分布的影响。电场入口风速为1.0 m·s−1,当极板间距改变时,电场内部风流流动的雷诺数发生相应的变化。如图13所示,随着极板间距的增加,雷诺数变大,流场内产生的涡流的范围越小,流速分布更加均匀,电极对气流的扰动影响程度降低,流场较为稳定。
通过测量GH线上的风速变化,分析极板间距对风速的影响。如图14所示,极板间距为150 mm工况时,GH线上的风速波动幅度最大,流场风速最高值达1.21 m·s−1,此时GH线距离电极线较近,流动受到电极的影响较大。随着极板间距的增大,GH线上速度值浮动越小,当极板间距为600 mm时,GH线上的风速值波动较小,流场相对稳定。
2) 极线间距对流场分布的影响。如图15所示,当电极线数量较少时,电极彼此之间的影响较小,流场相对较为稳定;随着电极线数量增加,极线间距逐步减小,流场被隔离成两个流动通道,流动紊乱程度明显增大,流场内部速度波动较大,流速形成不均匀分布。
通过改变极线间距时,测量EF线上的风速变化。如图16所示,EF线上风速呈现倒双沟的形状,在两极线中间位置的风速最低;随着极线间距减小,EF线上风速有所增加;当极线间距为450 mm时,电极对EF线速度的影响较小,则风速值变化幅度相对最小,即极线间距越大,风速值改变的幅度越小。
-
粒径2.5 μm颗粒的运动轨迹如图17所示。颗粒在电场力的作用下,在运动过程中会向收尘极板移动,最终被收尘极板捕集,减小极板间距或极线间距,颗粒轨迹偏移的角度越大,颗粒的捕集效率越高,且颗粒在电场停留的时间越短;反之,随着极板间距或极线间距的增大,颗粒向极板偏移的角度越小,部分颗粒穿过出口直接逃逸。由于极线周围的高电势,颗粒在电极附近会有较高的速度值,随着距极线的距离越远,颗粒运动速度越小。所以,适当的控制极板间距或极线间距能够有效的提高除尘效率。
颗粒在模型中的能量密度如图18所示,电极线附近的粒子具有较大的能量密度,这是因为电极放电,空气被电离,粒子在电场内迅速荷电,从而获得电能,荷电后的粒子在电场力作用下运动向收尘极板,此时粒子具有较大的动能和电能。入口、出口处的粒子由于距离电极较远,则呈现出较低的能量密度;随着极板间距增大,电场内颗粒的能量密度逐渐降低;当极线间距减小时,由于电极彼此之间的相互影响,颗粒可以在电场中充分荷电,获得较多的能量,从而具有较高的能量密度。
-
在考虑不同的极板间距和极线间距对电场、流场性能的影响的同时,也探究了极板、极线间距对不同粒径颗粒的除尘效率的影响,选择颗粒的粒径分别为1 μm、2 μm、2.5 μm、3 μm、4 μm、5 μm进行模拟试验。如图19 (a) 所示,在极板间距和极线间距固定的情况下,颗粒粒径越大,捕集效率越高;颗粒粒度越小,捕集难度越高。对同一粒径的颗粒物,减小极板间距或极线间距促使颗粒除尘效率升高,然而,极板间距或极线间距的减小增加钢材使用成本和处理风量的降低,需要综合考虑。在组合一中,当极线间距为180 mm且极板间距为200 mm时,除尘效果最佳,对于粒径为2.5 μm的颗粒除尘效率达到98.6%。如图19 (b) 所示,当极板间距固定为250 mm时,对同一粒径的颗粒物,极线间距越大,颗粒除尘效率越低;当极线间距为225 mm时,对于粒径为3 μm的颗粒除尘效率达到95.2%。
-
1) 线板式电场电势呈现以电极线为圆心,向周围发散式降低的分布特征;随着极板间距变大,从电极线至极板方向电势的变化速率减小,电极线之间电势梯度随之降低;当极线间距减小时,电极之间的电势由点式分布呈现为条状分布,极线周围电势的影响程度增强。
2) 随着极板间距的增加,流场内产生的涡流的范围减小,电极对气流的扰动影响程度降低;当电极线数量增加时,极线间距减小,流场被隔离成类似两流动通道,流动紊乱程度明显增大,流场内部速度波动较大,流速形成不均匀分布。
3) 减小极板间距或极线间距,颗粒轨迹偏移的角度越大,颗粒的捕集效率越高,且颗粒在电场停留的时间越短;随着极板间距或极线间距增大,电场内颗粒的能量密度逐渐降低。
4) 颗粒粒径越大,除尘效率越高;极板间距或者极线间距越大,除尘效率越低。当极板间距为200 mm,且极线间距为180 mm时,对于粒径为2.5 μm的颗粒除尘效率达到98.6%。当极板间距为250 mm,且极线间距为225 mm时,对于粒径为3μm的颗粒除尘效率达到95.2%。
线板排布对静电除尘性能影响的数值模拟
Numerical simulation of the influence of wire and plate arrangement on electrostatic precipitator performance
-
摘要: 为揭示电极排布对线板式电除尘器除尘性能的影响规律,基于电晕电场模型、k-ε湍流模型、Lawless电荷累积模型,建立了电除尘多物理场模拟模型,并通过改变极板间距和极线间距,分析了电场电势、风速、颗粒运动轨迹、除尘效率的变化特征。结果表明:极板间距增大降低了电势变化速率,极线间距减小导致放电极电势分布由点式转为条状,极线周围电势影响程度增强;增加极板间距或极线间距,均能减小流场内涡流范围,提高流速分布的均匀性;极板间距或极线间距减小,颗粒轨迹偏移的角度增大,除尘效率随之升高,且颗粒在电场停留的时间缩短;除尘效率与颗粒粒径呈正相关,除尘效率与极板间距或极线间距呈负相关。模拟得到的优化工况为:当极线间距为180 mm、极板间距为200 mm时,电除尘器对粒径为2.5 μm的颗粒除尘效率为98.6%。本研究通过构建新的模拟模型应用于线板式电除尘器的工况优化中,可为电除尘器结构优化设计和性能提升提供参考。Abstract: In order to obtain the influence law of electrode arrangement on the performance of wire-plate electrostatic precipitator, the multi physical field simulation model was established based on corona electric field model, k-ε Turbulence model and Lawless model. The variation characteristics of electric field potential, wind speed, particle trajectory and dust removal efficiency were analyzed via changing the distance between plates or lines. The results showed that the increase of polar plate spacing reduced the potential change rate, and the decrease of polar line spacing led to the change of electrode potential distribution from point to strip, and the in-fluence degree of potential around electrode was enhanced. Increasing the distance between plates or lines could reduce the eddy current range and improve the uniformity of velocity distribution. With the decrease of polar plate spacing or polar line spacing, the angle of particle trajectory offset increased, and the dust removal efficiency increased. The dust removal efficiency was positively correlated with particle size, and negatively correlated with polar plate spacing or polar line spacing. When the polar line spacing was 180mm and the polar plate spacing was 200mm, the removal efficiency of particles with the size of 2.5μm was 98.6%. The research on the arrangement of wire plate structure can provide theoretical reference for the optimization of wire plate electrostatic precipitator.
-

-
表 1 模型相关参数设置
Table 1. Setting of model related parameters
参数 数值 极板长度 1 200 mm 电极直径 2 mm 电极电压 45 kV 入口风速 1.0 m·s−1 空气温度 293.15 K 空气压力 101.3 kPa 颗粒直径 2.5 μm 颗粒密度 2 200 kg·m−1 表 2 模型边界条件
Table 2. Model boundary conditions
位置 边界条件 壁面条件 入口 速度入口 通过 出口 压力出口 冻结 电极 壁面 反弹 极板 壁面 冻结 -
[1] 刘学军, 胡汉芳, 郦建国, 等. 2020年电除尘行业发展评述和展望[J]. 中国环境产业, 2021, 3: 23-27. [2] 张金龙, 党小庆, 乐文毅, 等. 多孔收尘电极电场中荷电粒子的沉降规律及其除尘性能预测[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(05): 1589-1601. [3] 翁棣, 许冬冬, 张煜耀, 等. 高压静电除尘及伏安特性实验研究[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2019, 36(12): 52-56. [4] 张建平,高鹏飞,徐达成,等. 不同烟气流速下线板式电除尘器中磁场效应验证[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(11): 3121-3127. [5] 东明, 张宇轩, 李素芬, 等. 烟气流速对不同极线结构下静电除尘器内微细颗粒脱除的影响[J]. 热科学与技术, 2018, 17(1): 41-48. [6] 张哲, 李彩亭, 李珊红. 板式电除尘器多物理场耦合数值分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(11): 187-192. [7] 裴艺凯, 杨振民, 黄超, 等. 电除尘器内部流动特性的数值模拟[J]. 应用能源技术, 2019, 263(11): 21-26. [8] 依成武, 刘诗雯, 史雪欣, 等. 单区式双涡旋型极板电除尘器除尘性能实验研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(8): 2651-2658. [9] 胡建华, 李海燕. 电除尘器结构对除尘效率影响的数值分析[J]. 环境保护科学, 2018, 44(01): 83-88. [10] 张立莹, 雷洪, 牛宏, 等. 线板型静电除尘器的电场、流场与颗粒浓度分布的数值模拟[J]. 高电压技术, 2021, 47(11): 4144-4151. [11] 崔晓慧, 侯雪超, 张文婷, 等. 新型错位板对静电除尘器流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(01): 200-207. [12] AHMED K. Computation and measurement of corona current density and V-I characteristics in wires-to-plates electrostatic precipitator[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2016, 81: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2016.02.005 [13] DONG M, ZHOU F, ZHANG Y X, et al. Numerical study on fine-particle charging and transport behaviour in electrostatic precipitators[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.02.038 [14] ARIF S, BRANKEN D J, EVERSON R C, et al. The influence of design parameters on the occurrence of shielding in multi-electrode ESPs and its effect on performance[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2018, 93: 17-30. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2018.03.001 [15] WANG Y F, ZHANG H, GAO W C, et al. Improving the removal of particles via electrostatic precipitator by optimizing the corona wire arrangement[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 388: 201-211. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.04.087 [16] WANG X. Effects of corona wire distribution on characteristics of electrostatic precipitator[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 366: 36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.02.044 [17] 龙正伟, 冯壮波, 姚强. 静电除尘器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(11): 3393-3401. [18] LAWLESS P. A. Particle charging bounds, symmetry relations, and an analytic charging rate model for the continuum regime[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 1996, 27(2): 191-215. doi: 10.1016/0021-8502(95)00541-2 [19] PENNEY G W, MATICK R E. Potentials in D-C corona fields[J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, Part I:Communication and Electronics, 1960, 79(2): 91-99. doi: 10.1109/TCE.1960.6368550 [20] KALLIO G A, STOCK D E. Interaction of electrostatic and fluid dynamic fields in wire-plate precipitators[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 240: 133-166. doi: 10.1017/S0022112092000053 [21] KIHM K D. Effects of nonuniformities on particle transport in electrostatic[D]. Palo Alto : Stanford University, CA(USA), 1987. -




 下载:
下载: