-
活性污泥法是目前我国处理污水最常用的方法。2020年,我国污水处理率达到了97.53%,日处理污水量超过2×108 m3,由此产生的生物污泥已突破6×107 t (以80%含水率计算) [1-2]。污泥的主要组成成分是水和有机物,有着体量大和易腐败发臭的特点。此外,污泥中还含有多种有害物质,如细菌、病毒和寄生虫卵等,若不加以处理和处置可能会危害人群健康。污泥处理和处置费用通常要占污水处理厂总费用的一半以上,主要原因是污泥高含水率导致的巨大体积问题。
在污泥最终处置前,如焚烧或填埋,需要对其进行调理脱水以达到合适的含水率 (通常60%以下) 。以聚合氯化铝 (Polyaluminum Chloride, PAC) 为调理剂的化学调理法是当下广泛使用的调理手段。与其他无机调理剂相比,PAC调理具有污泥产量少、对温度和pH不敏感等优点。针对PAC调理,相关学者进行了广泛研究。ZHAO等[3]研究了不同pH下PAC的水解过程,结果显示,随着pH的增加,单体铝和二聚铝发生聚合反应形成小的聚合铝,然后通过进一步聚合或者自组装形成中间形态的聚合铝或大的聚合铝种。CAO等[4]认为,在PAC调理过程中通过控制铝的形态来改善污泥脱水是一种新的思路。对于高级厌氧消化污泥,高碱度是其显著特征,通常碱度值高达500~8 000 mg·L−1[5]。碱度的变化不仅会影响到污泥的基本特性,也不利于PAC的水解,进而恶化调理污泥的脱水效果[6]。ZHANG等[7]研究发现,PAC水解过程中碱度变化会改变污泥的絮凝行为,在高碱度环境下,PAC水解产物的电中和及络合能力遭到削弱,调理污泥的脱水效果受到影响。在低碱度条件下,污泥颗粒与蛋白质、腐殖酸的结合增强,絮团结构更加致密,可导致污泥饼压缩性下降[8]。
污泥是一种典型的非牛顿流体,其流变学在描述污泥水力特性方面发挥重要作用,几乎影响污泥处理和处置全过程[9]。有研究发现,随着调理剂添加量的不同,污泥除了脱水性能发生改变外,也会对其流变特性产生影响[10]。在实际生产中,通过调整流变参数优化污泥管道输送可以降低运营成本[11]。但是,目前大多数研究集中于不同碱度下PAC调理污泥过程中铝形态的转化,关于流变特性变化的研究鲜有报道。本研究以热水解高级厌氧消化污泥为原料,探究了不同碱度条件下污泥理化性质的变化。并且以PAC为调理剂对不同碱度下的污泥进行调理,通过对其流变特性和脱水性能的考察,探究碱度变化对污泥脱水效果及对调理剂投加量影响,以期从污泥碱度变化的角度为污泥脱水性能的提升与调理剂的优化投加提供参考。
-
实验所用高级厌氧消化污泥取自北京市某污水处理厂厌氧消化罐取样口。该厂运行工艺为典型A2O (厌氧/缺氧/好氧) ,日处理规模为1×106 t,污泥在进行厌氧消化前经过165 ℃高温热水解进行预处理。高级厌氧消化污泥的基本性质:pH为8.14、含水率为93.52%、TS为41.34 g·L−1、VS为14.40%,碱度为8 980.00 mg·L−1、SCOD为50 300.00 mg·L−1、平均粒径为13.72 μm。为减小污泥特性变化对实验造成影响,取回污泥后立即放入4 ℃的冰箱备用。实验所用PAC为商业通用药剂。
-
1) 碱度变化对污泥理化性质影响实验。用质量分数为10%的盐酸将高级厌氧消化污泥的碱度分别调至8 980.00、7 598.00、5 756.00、3 223.00、1 842.00和921.00 mg·L−1,测量污泥在不同碱度条件下的理化指标 (pH、氨氮、总磷、溶解性蛋白和多糖等) 。
2) 碱度调节对聚合氯化铝调理污泥脱水性能和流变特性的影响。分别取不同碱度的污泥200 mL,然后分别按照0、0.01、0.02、0.03、0.04、和0.05 g·g−1 (g·g−1,每克TS的污泥投加对应Al的克数) 的PAC投加量进行调理。将调理污泥样品放置在六联搅拌器上,先以480 r·min−1的转速快速搅拌2 min,再以40 r·min−1的转速缓慢搅拌8 min,搅拌结束后立即进行脱水和流变性能测定。
-
pH采用便携式pH计测定 (Mettler-Toledo 210,瑞士) ;碱度采用酸碱滴定法进行测量;含水率、TS和VS采用重量法测定;污泥上清液中总P和氨氮由水质测定仪和预制试剂测定 (格林凯瑞GL-900,中国) ;溶解性蛋白质和溶解性多糖则分别使用考马斯亮蓝法和苯酚-硫酸法测定。
抽滤泥饼含固率采用重量法测定,将污泥样品放置于砂芯抽滤装置的漏斗中,在6 MPa压力条件下抽滤30 min,得到的滤饼在105 ℃烘箱内干燥24 h,含固率的测定参考文献[11],计算方法见式 (1) 。
式中:TS为泥饼的含固率;
$ {m}_{1} $ 为坩埚的质量,g;$ {m}_{2} $ 为干燥前污泥和坩埚的总质量,g;$ {m}_{3} $ 为干燥后污泥和坩埚的总质量,g。污泥流变学指标采用旋转黏度计测定 (HAAKE Viscotester 550,德国) ,该装置通过热系统控制实验温度为 (20±0.1) ℃。对污泥流变测量前,先在1 000 s−1剪切速率下进行5 min的预剪切,然后以0 s−1的剪切速率保持1 min的平衡[12]。之后,通过设定剪切速率在180 s内从0 s−1增加到1 000 s−1来测量污泥流变曲线。
-
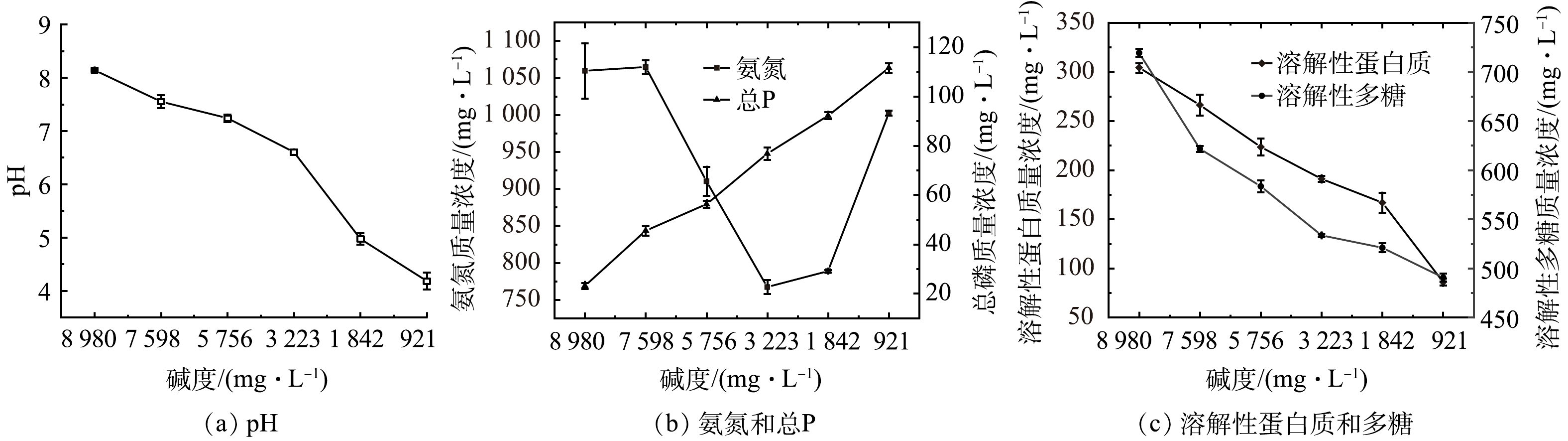
经过碱度调节后,污泥的理化性质变化如图1所示。图1 (a) 为不同碱度条件下的污泥pH变化曲线。随着碱度值的降低,污泥pH也随之降低。这是因为,污泥的碱度值变化由添加的盐酸控制,随着盐酸用量的增加,污泥碱度逐渐降低。图1 (b) 为污泥上清液中氨氮和总磷变化曲线。从图1 (b) 可以看出,在碱度降低过程中,污泥氨氮质量浓度先降低后升高,当污泥碱度被调节为3 223.00 mg·L−1时,氨氮达到最低值767.18 mg·L−1。污泥中氨氮主要来自微生物,适当降低pH可以抑制氨氮的释放[12]。然而,过度酸化的环境下,微生物细胞可能被破坏而释放出大量氨氮。与氨氮不同的是,污泥中总磷质量浓度随着碱度的降低逐渐升高,当碱度为921.00 mg·L−1时,总磷达到最高值111.51 mg·L−1。这可能是部分聚磷微生物随着碱度变化将细胞内的含磷物质溶出,导致总磷质量浓度不断上升。氮和磷是植物生长必须的营养元素,若污泥以土地利用的方式进行后续处置,污泥中的氮和磷要达到相应的标准。《城镇污水处理厂污泥处置 土地改良用泥质》 (GB/T 24600-2009) [13]指出,当污泥用于土地改良时,TN和TP (以P2O5计) 的质量分数要不少于1%。通过调节污泥的碱度值,将N元素和P元素保存在污泥中,有利于污泥的资源化利用。
蛋白质和多糖是污泥中胞外聚合物 (Extracellular Polymeric Substances, EPS) 的主要成分,约占其总量的70%~80%[14]。由图1 (c) 可以看出,随着碱度逐渐降低,污泥溶解性蛋白质和多糖均随之降低。其中,溶解性蛋白质的质量浓度从304.25 mg·L−1降低到86.09 mg·L−1,降幅高达71.70%;溶解性多糖的质量浓度从719.33 mg·L−1降低到490.67 mg·L−1,降幅为31.79%。污泥的碱度值经盐酸调节后逐渐降低,溶液中H+与EPS表面的多种负电荷基团,如-OH和-COOH等发生反应聚沉,致使溶解性蛋白质和多糖质量浓度的减少。蛋白质和多糖这2类物质被认为是影响污泥脱水的重要因素,其质量浓度过高会使污泥的脱水效果变差[15]。
-
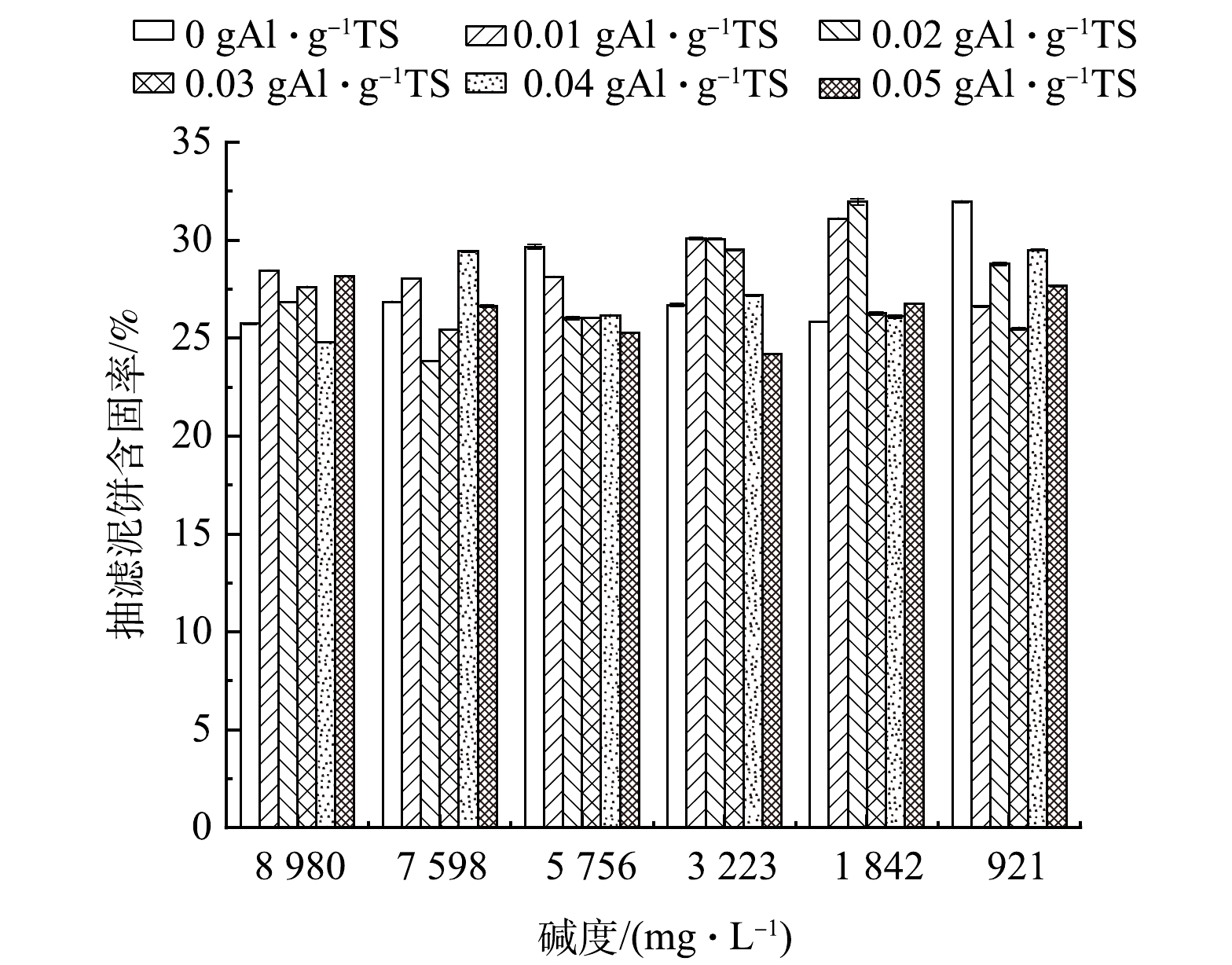
图2为PAC调理的不同碱度污泥抽滤泥饼含固率变化柱状图。从图2可以看出,在碱度为8 980.00 mg·L−1时,未进行碱度调节的热水解高级厌氧消化污泥需要添加更多的PAC调理才能达到较好的脱水效果,当PAC投加量为0.05 g·g−1时,滤饼含固率为28.16%。污泥碱度降低至7 598.00 mg·L−1时,PAC投加量为0.04 g·g−1的滤饼含固率达到最高,为29.44%。相比之下发现,降低碱度后高级厌氧消化污泥在减少调理剂投加量的情况下实现了脱水效果的改善。继续降低污泥的碱度,脱水效果较好的处理组出现在较低的PAC投加量情况下,如碱度值为3 223.00 mg·L−1时加入0.01 g·g−1的PAC,抽滤泥饼含固率达到最高值,为30.09%。在碱度值为1 842.00 mg·L−1时,经过0.02 g·g−1的PAC调理后的污泥泥饼含固率为31.97%,达到整个实验中的最优脱水效果,同时达到这个脱水效果的还有最低碱度条件下 (碱度值为921.00 mg·L−1) 未添加调理剂的处理组。
总的来说,随着污泥碱度值的降低,投加少量PAC便能达到更好的调理脱水效果,过量的调理剂甚至恶化脱水,这是因为多余的正价金属盐离子改变了体系内的Zeta电位。根据DLVO理论,Zeta电位影响污泥颗粒的聚合和沉降水平,多余的正电荷导致污泥体系重新稳定,不利于污泥的聚集和水分脱出[15]。此外,污泥EPS中的蛋白质和多糖严重影响其脱水性能,这主要与大量的结合水有关[16]。在本实验中,随着碱度值降低,溶解性蛋白质和多糖的质量浓度降低 (图1 (c) ) ,结合水被有效释放,脱水效果也因此得到改善,这与何培培等[17]的研究结果一致。污泥中存在的大量EPS也会影响其Zeta电位,PAC能够很好地压缩EPS结构和去除可溶性EPS中蛋白等物质,在合适的碱度条件下,PAC的电中和作用可以实现最佳脱水效果[4,18]。在污泥碱度值较低时,如图2中碱度分别为3 223.00、1 842.00和921.00 mg·L−1,投加较少或不投加调理剂依旧可以达到不错的脱水效果。这表明,通过对污泥进行碱度调节,可以降低调理剂的使用量。这是因为,PAC在高碱度条件下调理污泥时,聚合物Alb被快速水解转为Alc,Alc是一种高聚合态或胶体物质,其电中和特性和吸附效果较差;而在低碱度时,大多数铝以Alb的形态存在,其是铝盐混凝剂中优势铝形态,具有很好的混凝特性[5]。
-
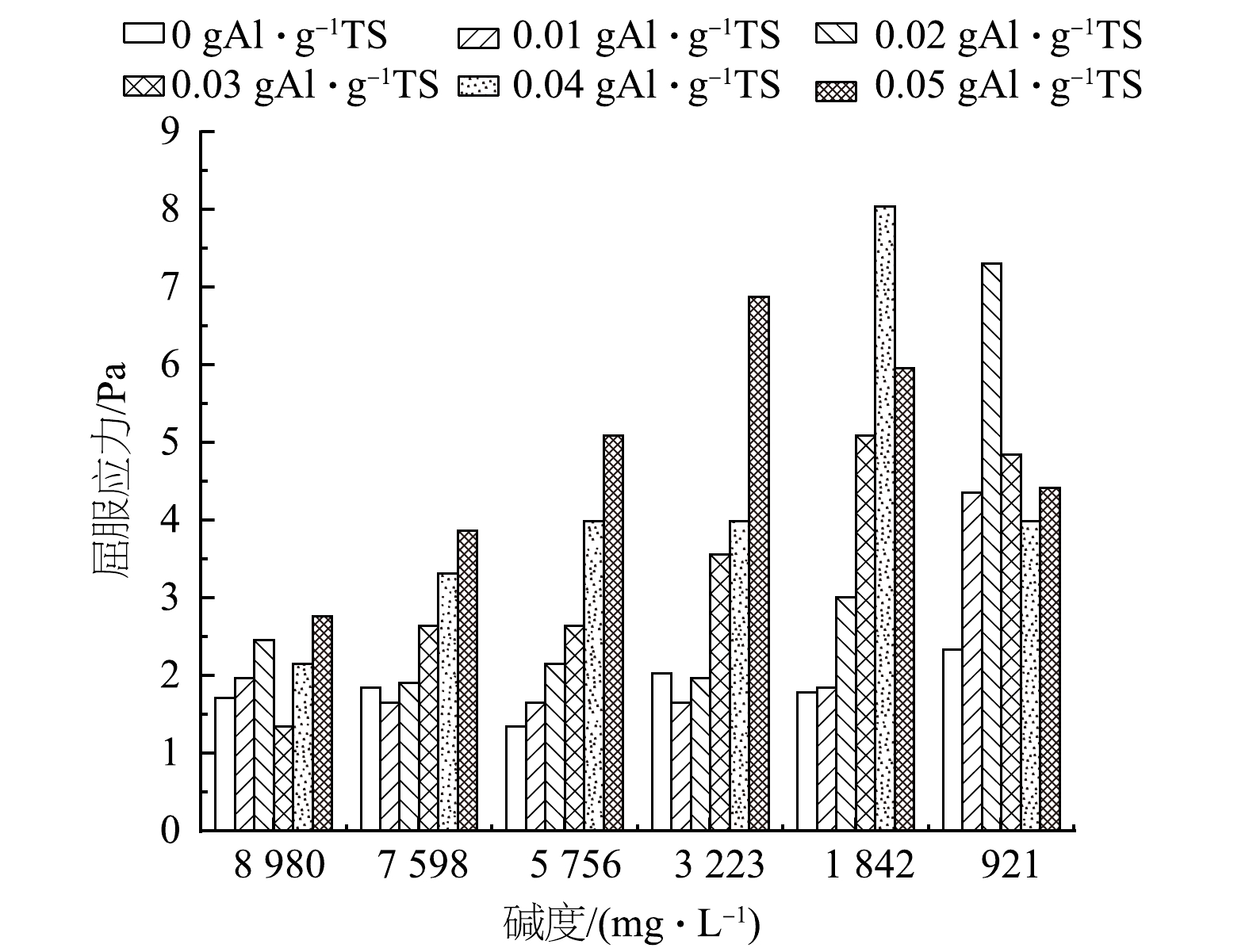
1) 屈服应力。在污泥管道运输过程中,屈服应力是使物料连续流动所需的最小施加应力,对于污泥的搅拌和泵送具有重要影响[19]。较低的屈服应力有利于污泥处理,如脱水过程和污泥储存[11]。图3为不同碱度条件下经PAC调理后高级厌氧消化污泥的屈服应力变化柱状图。整体上看,在相同的碱度下,随着PAC投加量的增加,调理污泥的屈服应力呈现出增加的趋势。当PAC投加量为0、0.01和0.02 g·g−1时,随着碱度值的降低,调理污泥的屈服应力逐渐变大;而PAC投加量为0.03、0.04和0.05 g·g−1时,屈服应力则表现为先增大后减小。污泥的表面电荷受到碱度值的影响,进而改变颗粒间相互作用的方式以及力的大小,从而影响污泥的流动性。本实验中用到的PAC水解作用受碱度影响较大,随着碱度的降低,PAC的水解程度减小,低聚态的Ala和中等聚态的Alb并未形成无定形胶体态的Al(OH)3,形成的絮体粒径较大,故在投加较多的PAC时屈服应力增加,不利于污泥的流动和泵送[6]。低碱度条件下,少量投加PAC可以保障更好的流动性。这是因为,PAC中的中等聚态Alb还未进行下一步水解,其电中和絮凝调理特性还保持在较高水平,污泥更易形成絮体颗粒,有利于流动。此外,在低碱度时,污泥EPS中的蛋白质和多糖质量浓度较低 (图1 (c) ) 。有研究表明,EPS蛋白和多糖对污泥的流变特性有重要影响,降低污泥中的EPS有助于流动性能的提升[20]。
2) 表观黏度。黏度是描述污泥絮凝体与流体内部和外部相互作用力的基本参数,可以通过污泥流动曲线来评价。就活性污泥这一典型的非牛顿流体而言,表观粘度对泵送、流体动力学、传质速率、污泥水分离(沉降和过滤)等都有影响[21]。图4所示为不同碱度下经PAC调理的污泥表观黏度变化曲线,实验中所有组别的调理污泥表观黏度随着剪切速率的增加均表现出降低的趋势。对于相同PAC投加量的处理组,随着碱度值的不断降低,调理污泥的最大初始黏度逐渐增大。未进行碱度调节时,即污泥碱度为8 980.00 mg·L−1,PAC投加量为0.05 g·g−1的调理污泥有着最大初始表观黏度,为0.46 Pa·s;当碱度值不断降低为7 598.00、5 756.00、3 223.00、1 842.00和921.00 mg·L−1时,各组最大初始表观黏度分别为0.61、0.82、1.09、1.33和1.18 Pa·s。通过比较可以发现,在碱度值较高时,即碱度为3 223.00~8 980.00 mg·L−1的处理组,最大初始表观黏度均出现在投加0.05 g·g−1的PAC调理实验组;而在碱度值较时,最高的PAC投加量却未表现出最大的初始表观黏度。这可能是因为,碱度值的降低使得污泥泥质特性发生了改变,在低碱度下污泥EPS结构遭到严重破坏。在一定的PAC投加情况下,碱度越低,EPS类凝胶结构被压缩的程度越高,从而对污泥的表观黏度产生了影响[22]。
随着剪切速率的不断升高,所有调理污泥均表现出明显的剪切稀化现象,各组的极限黏度均趋向于0,且低碱度下更加明显。在高剪切速率下,当表观黏度趋向于稳定时,流体动力相互作用占据主导地位,污泥具有牛顿流体的特征从而更易于流动[23]。值得关注的是,当碱度值为1 842.00 mg·L−1且PAC投加量为0.02 g·g−1和碱度值为921.00 mg·L−1且不投加PAC时,污泥经剪切后极限黏度的值最低,表明这2组调理污泥有着更好的流动性。同时,第2.2小节发现,在碱度值为1 842.00和921.00 mg·L−1时,分别投加0.02 g·g−1的PAC和不投加时,高级厌氧消化污泥抽滤泥饼的含固率达到最高。曹秀芹等[24]和EUGENE等[25]研究表明,污泥的流变规律与脱水性能之间具有一定的相关性,关键流变参数可能被用作控制污泥脱水过程调理剂的最佳用量,指导脱水过程进行。
-
1) 高级厌氧消化污泥经碱度调节后上清液中总P和氨氮质量浓度会发生变化,在对污泥进行相应的处置前可以通过调节碱度控制P和N的比例,将P和N等保存于污泥中增加肥效以提高使用价值。
2) 降低高级厌氧消化污泥的碱度有利于减少PAC的使用量,当污泥碱度值为1842.00 mg·L−1时,经过0.02 g·g−1的PAC调理后污泥抽滤泥饼含固率达到最高值,为31.97%。
3) 污泥的屈服应力随着PAC投加量的增加而变大,过量投加PAC不利于污泥的流动。污泥在碱度值为1 842.00 mg·L−1且PAC投加量为0.02 g·g−1时有着最低的极限黏度值;在高剪切速率下污泥具有牛顿流体特性,更易于流动。
碱度对聚合氯化铝调理污泥脱水和流变的影响
Effect of alkalinity on dewatering and rheology of Polyaluminium Chloride conditioned sludge
-
摘要: 针对厌氧消化污泥的难脱水问题,探究了不同碱度条件下污泥经聚合氯化铝调理后的脱水效果和流变特性变化。以高级厌氧消化污泥为研究对象,调节碱度后考察污泥理化性质的变化。在碱度调节的基础上投加聚合氯化铝进行调理,通过测定抽滤泥饼含固率、屈服应力和表观黏度等指标,研究不同碱度下调理污泥的脱水效果和流动性改善情况。结果表明,污泥碱度调节会对上清液中总磷和氨氮的质量浓度产生影响,可以通过碱度变化控制污泥中的P和N等元素的质量浓度。在低碱度条件下,减少聚合氯化铝的投加量可以获得较好的污泥脱水效果和流动性。当污泥碱度值为1 842.00 mg·L−1时,添加0.02 g·g−1的聚合氯化铝进行调理,抽滤泥饼的含固率达到最高值31.97%;同时,在这个条件下,污泥的极限黏度接近0,达到最低值,污泥的流动性得到了提升。调理污泥在具有最佳流动性能的同时达到最佳脱水效果。本研究结果可从污泥碱度变化的角度为污泥脱水性能的提升与调理剂的优化投加提供参考。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of difficult dehydration of anaerobic digestion sludge, the dewatering effect and rheological properties of sludge were explored, which were conditioned by polyaluminum chloride (PAC) under different alkalinity conditions. Taking advanced anaerobic digested sludge as research object, the changes of the physical and chemical properties of the sludge were investigated after adjusting the alkalinity. On the basis of alkalinity adjustment, PAC was added for conditioning. The dewatering effect and fluidity improvement of conditioned sludge under different alkalinity were researched by measuring the changes of the suction filter cake’s solid content, yield stress as well as apparent viscosity. The results demonstrated that the adjustment of the sludge alkalinity would affect the content of total phosphorus and ammonia nitrogen in the supernatant. Meanwhile, the proportion of P and N elements in the sludge could be controlled by adjusting the alkalinity. Under the condition of low alkalinity, better sludge dewatering effect and fluidity could be brought out by reducing the dosage of PAC. When the alkalinity value of the sludge was 1 842.00 mg·L−1, the conditioned sludge had a 31.97% solid content by adding PAC of 0.02 g·g−1; At the same time, the limiting viscosity of sludge was close to zero in this case, reaching the lowest value, and the fluidity of sludge was improved. Conditioned sludge had the best flow performance as well as the dehydration effect. In conclusion, the results of this study can provide some references for the improvement of sludge dewatering performance and the optimal dosing of conditioner from the perspective of sludge alkalinity adjustment.
-

-
-
[1] DONG Y T, SHEN Y W, GE D D, et al. A sodium dichloroisocyanurate-based conditioning process for the improvement of sludge dewaterability and mechanism studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 284: 112020-112020. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112020 [2] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2020年城市建设统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. [3] ZHAO H, LIU H J, QU J H. Effect of pH on the aluminum salts hydrolysis during coagulation process: Formation and decomposition of polymeric aluminum species[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 330(1): 105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.10.020 [4] CAO B D, ZHANG W J, WANG Q D, et al. Wastewater sludge dewaterability enhancement using hydroxyl aluminum conditioning: Role of aluminum speciation[J]. Water Research, 2016, 105: 615-624. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.016 [5] YANG P, LI D D, ZHANG W J, et al. Flocculation-dewatering behavior of waste activated sludge particles under chemical conditioning with inorganic polymer flocculant: Effects of typical sludge properties[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218: 930-940. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.169 [6] 杨鹏. 基于污泥特性的化学调理技术及其作用机制[D]. 中国地质大学, 2019. [7] ZHANG W J, TANG M Y, LI D D, et al. Effects of alkalinity on interaction between EPS and hydroxy-aluminum with different speciation in wastewater sludge conditioning with aluminum based inorganic polymer flocculant[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 100: 257-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.05.016 [8] QI Y, THAPA K B, HOADLEY A F A. Benefit of lignite as a filter aid for dewatering of digested sewage sludge demonstrated in pilot scale trials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 166(2): 504-510. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.003 [9] 曹秀芹, 柳婷, 江坤, 等. 低温热水解对污泥触变性及脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(4): 977-983. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201811089 [10] CHEN Q, WANG Y L. Influence of single- and dual-flocculant conditioning on the geometric morphology and internal structure of activated sludge[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 270: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.10.002 [11] CAO X Q, PAN Y H, JIANG K, et al. Effect of high-temperature thermal hydrolysis on rheological properties and dewaterability of sludge[J]. ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY, 2021, 42(23): 3707-3715. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1739751 [12] RAJINIKANTH R, DANIEL I. M, GURSHARAN S. A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 143: 632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.030 [13] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局、中国国家标准化管理委员会. 城镇污水处理厂污泥处置 土地改良用泥质标准: GB/T 24600-2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [14] MORE T T, YADAV J S S, YAN S, et al. Extracellular polymeric substances of bacteria and their potential environmental applications[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 144: 1-25. [15] CAO B D, ZHANG T, ZHANG W J, et al. Enhanced technology based for sewage sludge deep dewatering: A critical review[J]. Water Research, 2021, 189: 116650. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116650 [16] ZHANG W J, CAO B D, WANG D S, et al. Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)[J]. Water Research, 2016, 88: 728-739. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.049 [17] 何培培, 余光辉, 邵立明, 等. 污泥中蛋白质和多糖的分布对脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2008(12): 3457-3461. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.028 [18] MURUGESAN K, RAVINDRAN B, SELVAM A, et al. Fate of extracellular polymeric substances of anaerobically digested sewage sludge during pre-dewatering conditioning with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans culture[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 217: 173-178. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.081 [19] ESHTIAGHI N, MARKIS F, YAP S D, et al. Rheological characterisation of municipal sludge: A review[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(15): 5493-5510. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.001 [20] WEI H, GAO B Q, REN J, et al. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review[J]. Water Research, 2018, 143: 608-631. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.029 [21] RATKOVICH N, HORN W, HELMUS F P, et al. Activated sludge rheology: A critical review on data collection and modelling[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(2): 463-482. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.021 [22] BIEN B, BIEN J D. Influence of digested sludge conditioning on the dewatering processes and the quality of sludge liquid[J]. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering S, 2020, 27(1): 151-164. doi: 10.2478/eces-2020-0010 [23] HII K, PARTHASARATHY R, BAROUTIAN S, et al. Rheological measurements as a tool for monitoring the performance of high pressure and high temperature treatment of sewage sludge[J]. Water Research, 2017, 114: 254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.031 [24] 曹秀芹, 王浩冉, 江坤, 等. 污泥厌氧消化过程的流变规律与脱水性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(5): 233-240. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.05.027 [25] EUGENE H, ANTENEH M Y, TUSHAR K S, et al. A comprehensive review on rheological studies of sludge from various sections of municipal wastewater treatment plants for enhancement of process performance[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 257: 19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2018.06.002 -



 下载:
下载: