-
氨氮一般指水中以游离氨(
$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{3}} $ )和铵离子($ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ )形式存在的氮,是一种水体污染物,主要来源于城市地区人类活动和农业、工业生产过程[1]。氨在水中不完全硝化会产生亚硝酸盐,若被饮用会和蛋白质结合形成致癌的亚硝胺,严重影响人体健康[2-3]。高浓度的氨氮也会使水体富营养化,导致水华和赤潮等现象,直接影响水体生态环境[4]。废水脱氨主要方法有生物法、化学沉淀法、吹脱法、吸附法[5]。但是生物法流程长,反应器大,占地多,常需要额外投加碳源,能耗大,成本高;化学沉淀法成本高,再生难,有二次污染;吹脱法能耗大,有二次污染,出水氨氮浓度仍然偏高。吸附法具有除污效率高、操作便捷、适用范围广、吸附剂可重复使用等优点,在氨氮废水处理中逐渐得到了广泛关注。ALSHAMERI等[6]对比了高岭石、埃洛石、蒙脱石、海泡石等六种天然粘土矿物对
$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 的吸附性能,发现天然粘土矿物是经济、安全且有效的$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 吸附剂,具有良好的发展前景。尽管吸附法具有较高的氨氮去除效率,同时也为废水中氮回收提供了可能,但颗粒吸附材料在废水处理后的低碳回收问题尚未得到有效解决。目前,大部分吸附材料多以微纳米颗粒的形式存在,直接与废水混合能够充分利用其吸附性能,但也存在微纳米材料使用中流失和回收困难等问题。通过微滤或超滤膜辅助回收,将会增加额外能耗和成本,影响其进一步的推广应用。也有研究将吸附材料制备成毫米级微球,通过柱吸附实现污染物去除,但大颗粒吸附材料吸附容量低于微纳米颗粒[7]。因此,如何既能保证吸附容量,又能实现微尺度吸附材料的低碳回收,已经成为吸附法应用中的新困难。动态膜技术具有成本低、操作压力小、清洗简单、微颗粒分离效果好等优点,为微尺度颗粒材料回收提供了绿色低碳新方法[8]。但目前多数研究围绕在动态膜系统过滤特性和应用效能,沸石吸附脱氨效能和优化改性,鲜有对动态膜成膜材料吸附性能的拓展和深度耦合探索,及对动态膜系统和成膜材料作用的独立解析,考虑到沸石吸附脱氨和动态膜分离的优点和不足,本研究尝试构建吸附与动态膜耦合系统,同步实现废水中氨氮去除和颗粒吸附材料回收,从而为吸附法进一步走向工程应用提供新方案。
本研究围绕吸附脱氨和动态膜回收2个方面,通过静态吸附实验,系统探究沸石吸附脱氨效能和投加量、初始氨氮浓度对脱氨效能的影响,揭示沸石吸附氨氮的动力学特性,阐明吸附-动态膜系统的脱氨效果和成膜特征,为沸石吸附脱氨和沸石颗粒回收的进一步应用提供参考。
-
主要使用的实验材料包括:74~150 μm沸石,硅藻土,0.45 μm微孔滤膜,38 μm尼龙网,压力计等。实验所需试剂主要有氯化铵、酒石酸钾钠、纳氏试剂,均为分析纯。
在容量瓶中按照标准配置1 000 mg·L−1的氨氮储备溶液,配置完成后将溶液移入细口试剂瓶待用;使用时,按需求量取一定体积的氨氮储备溶液,按比例稀释为10 mg·L−1氨氮模拟废水。氨氮测定方法参考《纳氏试剂分光光度法》HJ 535-2009。
-
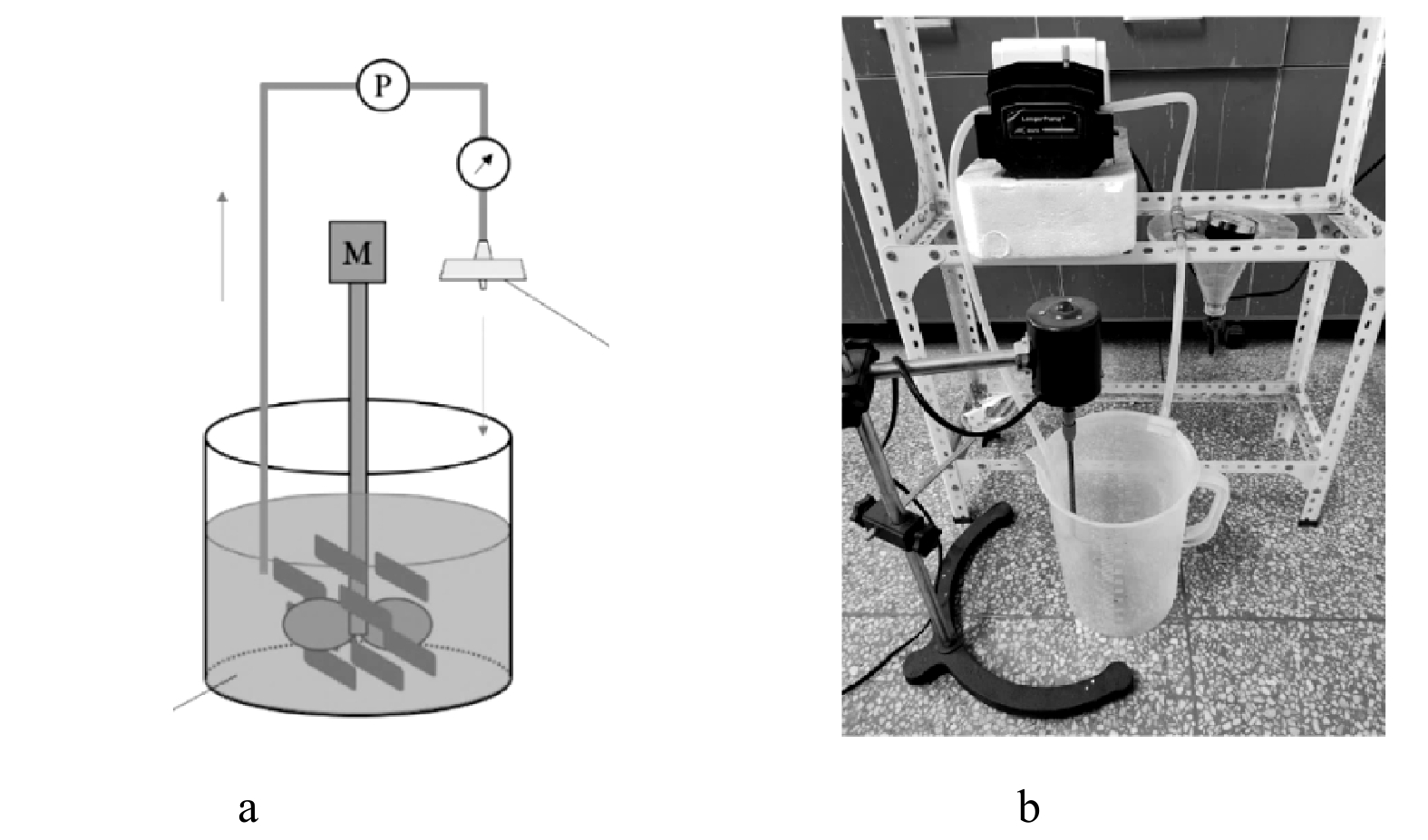
为了保证同步进行氨氮去除和吸附材料的回收,使用自制循环吸附-动态膜系统进行成膜研究。循环吸附-动态膜系统和实验装置见图1,该装置由反应池、蠕动泵、自制膜组件、压力计、电动搅拌器组成。实验过程中,反应池中加入2 L的模拟废水及吸附剂,搅拌加速混合,通过蠕动泵将混合液送入自制膜组件,在膜组件中截留吸附剂并形成动态膜,膜分离后的混合液回流至反应池中。
-
称取0.4 g沸石移至150 mL锥形瓶中,取1 mL氨储备溶液于100 mL容量瓶中定容,配制模拟氨氮污水,初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,再分别转入锥形瓶;将锥形瓶同时放入恒温摇床中振荡(25 ℃,180 r min−1),反应进行至5、10、30 min和1、3、6、12、24 h时取出并取样7 mL左右于10 mL离心管中待滤;经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后测量滤液中氨氮浓度,进行准一级与准二级动力学拟合。
-
分别称取0.4 g沸石移至锥形瓶中,分别取1、2、4、6、8、10 mL氨储备溶液于100 mL容量瓶中定容,配制10、20、40、60、80、100 mg·L−1的模拟氨氮废水,按顺序移入锥形瓶中;将锥形瓶同时放入恒温摇床中振荡(25 ℃,180 r min−1),反应进行至5、10、30 min和1、3、6、12、24 h时取出并取样7 mL;经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后测氨氮浓度,计算去除率与吸附量,进行Langmuir与Freundlich拟合。
-
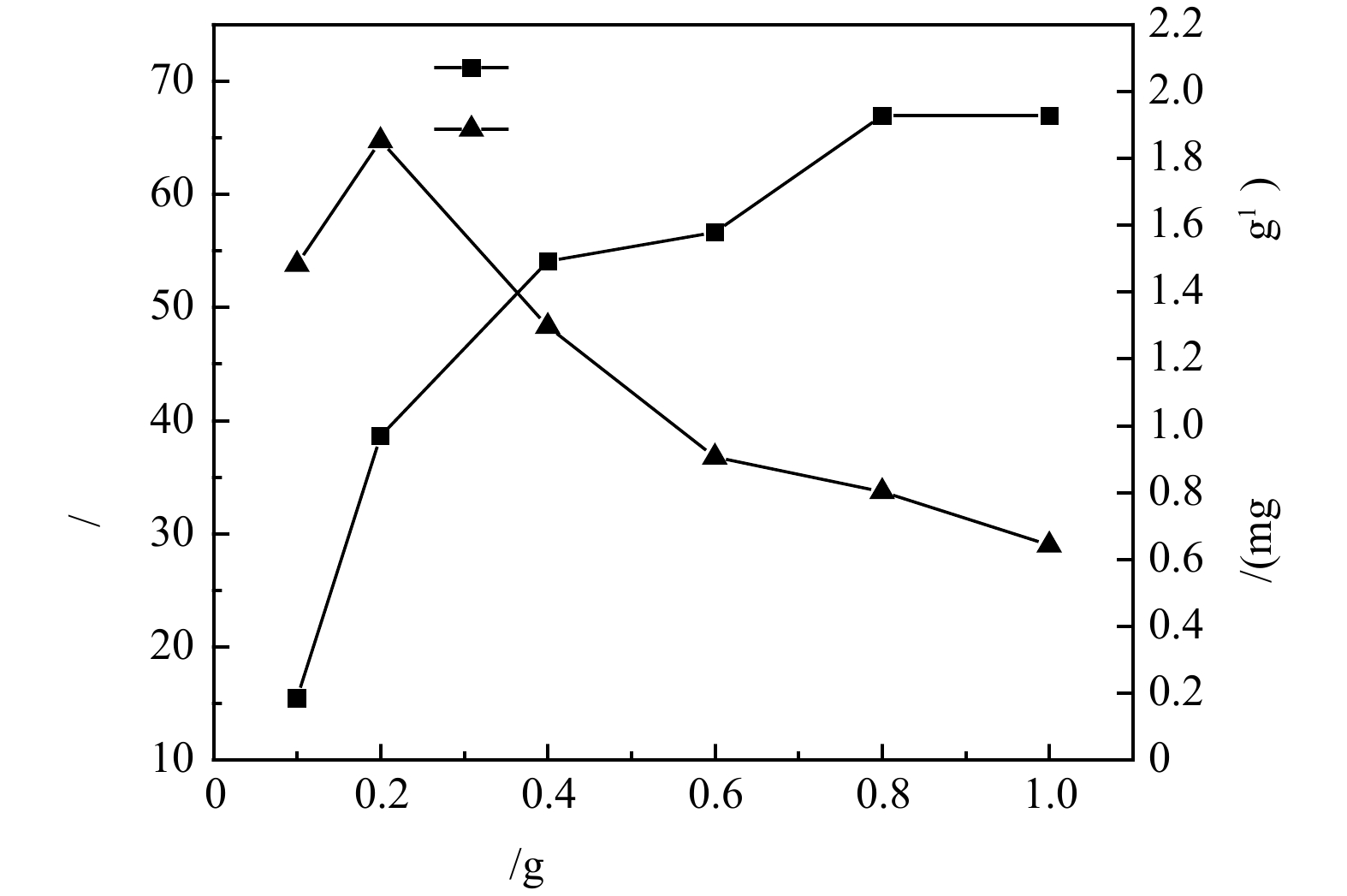
1)沸石投加量对氨氮去除的影响。沸石投加量对氨氮的去除率及吸附量的影响结果如图2所示。可见,在100 mL体系中、25 ℃、180 r min−1恒温振荡箱和初始氨氮质量浓度10 mg·L−1反应条件下,沸石对模拟废水中氨氮的去除率随其投加量的增加逐渐增加,在投加量为10 g·L−1时氨氮去除率可到达67%左右,而当沸石投加量从1 g·L−1增加到10 g·L−1时,吸附量由1.48 mg·g−1降至0.64 mg·g−1。这是因为随着沸石投加量的增加,沸石可以提供更多的吸附位点和更大的比表面积,因此,氨氮的去除率随之增加,但吸附剂投加量的增加也会造成部分吸附位点被覆盖,吸附位点之间产生竞争,故单位质量的沸石的吸附效率随着吸附剂投加量的增大而逐渐降低。在低氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1下开展的投加量优化实验中,沸石对氨氮去除效果较好。这是因为沸石是一种骨架状铝硅酸盐,具有离子交换的特性,对于
$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 有特别选择性[9],沸石去除氨氮的机理包括2个方面:物理吸附[10]归因于沸石具有大量的空隙通道和较大的比表面积,可以在各位点上吸附$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ ;离子交换[11]归因于在吸附材料各位点上的碱土金属离子,或是碱金属,很容易被$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 取代,从而实现氨氮的置换。当沸石投加量为4 g·L−1时,沸石对氨氮去除率和吸附量分别可达54%和1.3 mg·g−1,处于相对较优的水平。综合考虑投加量对氨氮去除率和吸附容量的影响,选用4 g·L−1沸石进行氨氮浓度影响实验。2)初始氨氮浓度对沸石脱氨效果的影响。沸石对氨氮的去除率及吸附量随初始氨氮浓度变化规律如图3 所示。可见,沸石对氨氮的去除率随氨氮初始浓度的增加而下降,而吸附量却随之增加,当沸石投加量为4 g·L−1,初始氨氮质量浓度为100 mg·L−1时,沸石对氨氮吸附量可提升到3.89 mg·g−1,但氨氮去除率也降至17%。随着氨氮浓度的增加,体系中的
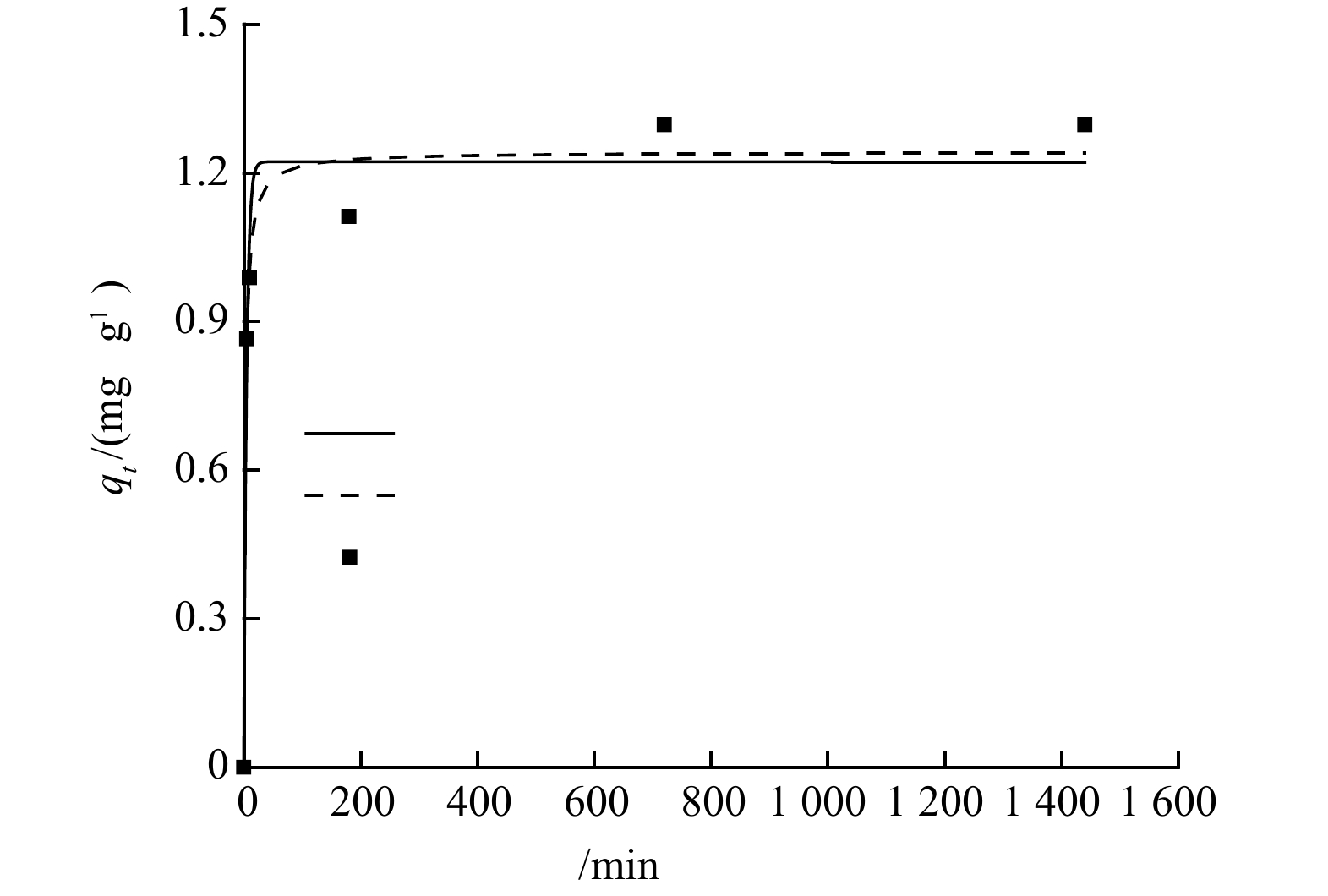
$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 数量增加,沸石与$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 接触更加充分,沸石表面的吸附位点利用率更高,所以沸石对氨氮的吸附量逐渐上升。但随着沸石表面吸附位点的逐渐饱和以及可交换离子的逐步消耗,沸石对氨氮的吸附增量相对较为平缓,且其增速显然低于氨氮浓度的增速,故在高浓度氨氮条件下沸石对氨氮的去除率相对较低。3)沸石对氨氮的吸附动力学研究。采用准一级和准二级动力学模型,对沸石投加量为4 g·L−1,初始氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1的24 h吸附动力学实验数据进行拟合分析。由图4可以看出,在吸附开始的1 h内,沸石对氨氮吸附速率较快,1 h后吸附量缓慢上升,12 h吸附趋于平衡,平衡吸附量在1.3 mg·g−1左右。在吸附初期,沸石颗粒上吸附位点较多,氨氮浓度高,吸附较快,而随着吸附进行,氨氮浓度降低,吸附位点被占用,吸附速率下降。此外,沸石的表面物理吸附及
$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 与表面阳离子的交换速率较快,而$ {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}} $ 进入沸石孔隙内,与内部阳离子进行交换的速率较慢。因此,沸石吸附过程总体呈现先快速吸附后缓慢平衡的特征[12]。对于沸石的吸附动力学过程,以$ \text{q}\text{t} $ 对$ \text{t} $ 通过准一级和准二级方程进行非线性拟合分析,其拟合结果见表1。由表1可见,沸石的吸附动力学实验数据与准一级和准二级动力学方程的拟合程度均较好。通过准二级反应动力学拟合得到的理论平衡吸附量值为1.24 mg·g−1,更接近实验得到的吸附量,因此,准二级动力学模型能更好地描述本实验所采用的沸石对氨氮的吸附过程。4)沸石对氨氮的吸附等温线。在25 ℃的条件下,测定4 g·L−1沸石在不同初始氨氮浓度下的平衡吸附量,进行吸附等温研究,结果见图5。吸附等温模型是用于描述在特定实验温度下,吸附剂与吸附质之间的相互作用[13]。本研究使用Langmuir和Freundlich模型(表2) 对数据进行分析,以准确地研究氨氮在沸石上的吸附机理。首先分别以
$\text{1/}{{q}_\text{e}}$ 对$\text{1/}{{C}_\text{e}}$ 、$\text{lg}{{q}_\text{e}}$ 对$\text{lg}{{C}_\text{e}}$ 作图,进行线性拟合,通过计算拟合方程的斜率和截距得到相关参数,拟合曲线见图5(a)和图5(b),拟合参数及相关系数见表2。由表2可知,2种吸附等温线模型对实验数据的拟合系数均在0.95以上,均能较好的解释沸石对氨氮的吸附。但Langmuir吸附等温模型对沸石的吸附过程拟合度更好,其拟合系数为0.995,拟合得到的最大理论吸附量为4.12 mg·g−1,与实际的3.89 mg·g−1较为接近,证实了实验中沸石对氨氮的吸附过程,属单分子层吸附,即化学吸附过程,和上述反应动力学的结论一致。Freundlich模型中的n是经验常数,通常${n}\text{ \gt 1}$ ,一般认为$ \text{0.1 \lt 1/}{n}\text{ \lt 0.5} $ 时容易吸附,$ \text{1/}{n} $ =1时为线性吸附,$ \text{1/}{n}\text{ \gt 2} $ 时则难以吸附[14]。实验拟合得到的$ \text{1/}{n} $ 为0.40,表明该沸石对氨氮的吸附较为容易。 -
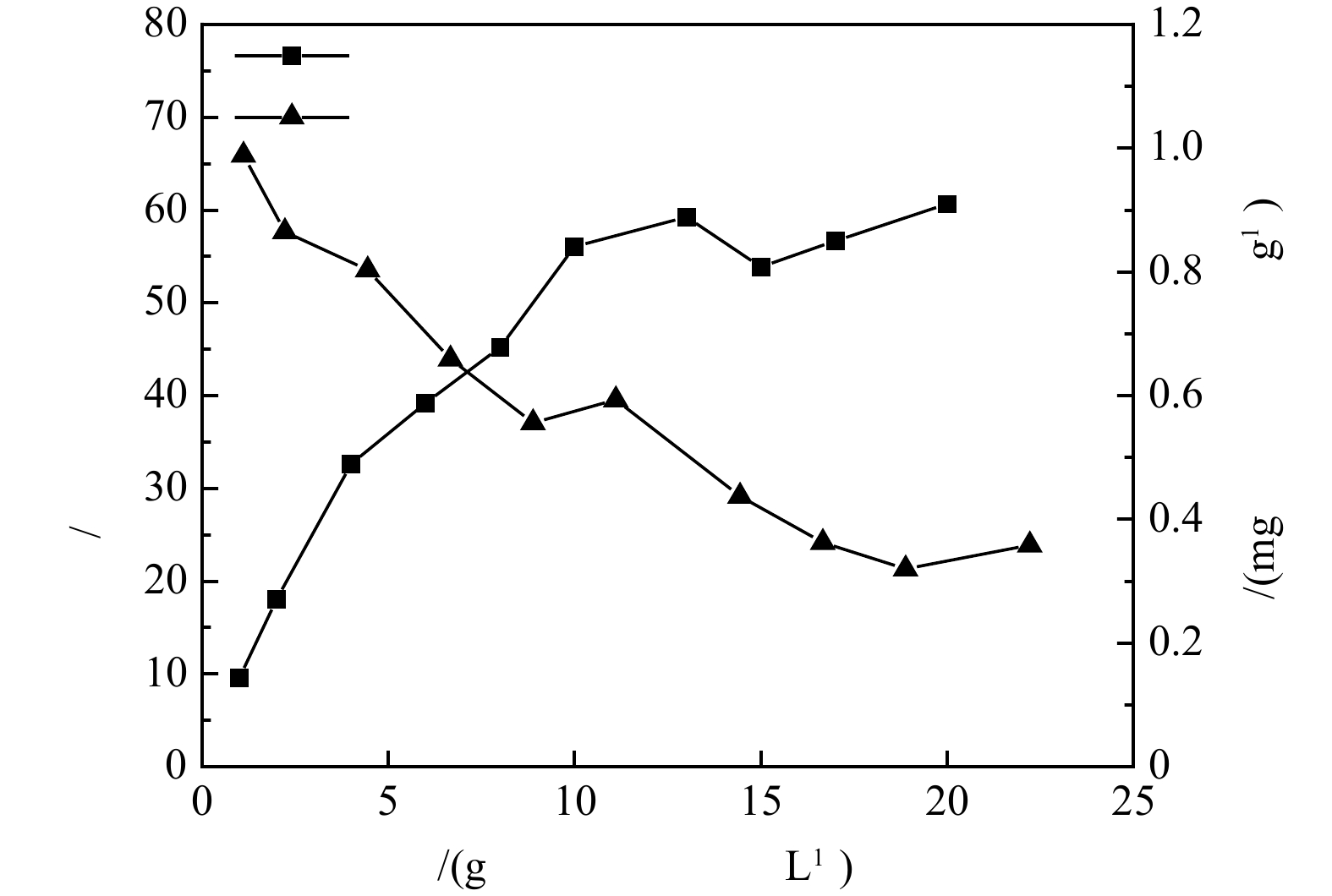
1) 沸石动态膜系统脱氨效果。在初始氨氮质量浓度10 mg·L−1,2 L体系,电动搅拌器室温搅拌1 h条件下,吸附动态膜系统中沸石对氨氮的去除率及吸附量随沸石投加量的变化规律见图6。由图6可以看出,与在100 mL体系中、25 ℃、180 r min−1恒温振荡箱和初始氨氮质量浓度10 mg·L−1反应条件(图2)相比,该条件下沸石对氨氮的去除率与吸附量稍有降低,基本能够充分发挥沸石的吸附脱氨效能,不会造成沸石动态膜系统内沸石吸附位点的浪费。当沸石投加量达到10 g·L−1以后,对氨氮去除率的提升非常有限,基本在55%~60%,吸附量随沸石投加量的增加逐渐下降。为了保证吸附效果,循环吸附-动态膜系统中沸石的投加量以10 g·L−1为宜,此时的去除率与吸附量分别为56%和0.59 mg·g−1。本系统中,沸石吸附容量与NaCl改性沸石[15]吸附容量(0.56 mg·g−1,初始氨氮质量浓度20 mg·L−1,投加量30 g·L−1,室温30 ℃)较为接近,但氨氮去除率明显低于改性4A沸石分子筛(91%)[14] 和NaCl改性沸石(83%)[15],氨氮去除率的差距可能是由于沸石投加量增大和初始浓度差异引起的,后续沸石动态膜系统可根据实际脱氨需要进行沸石改性优化。
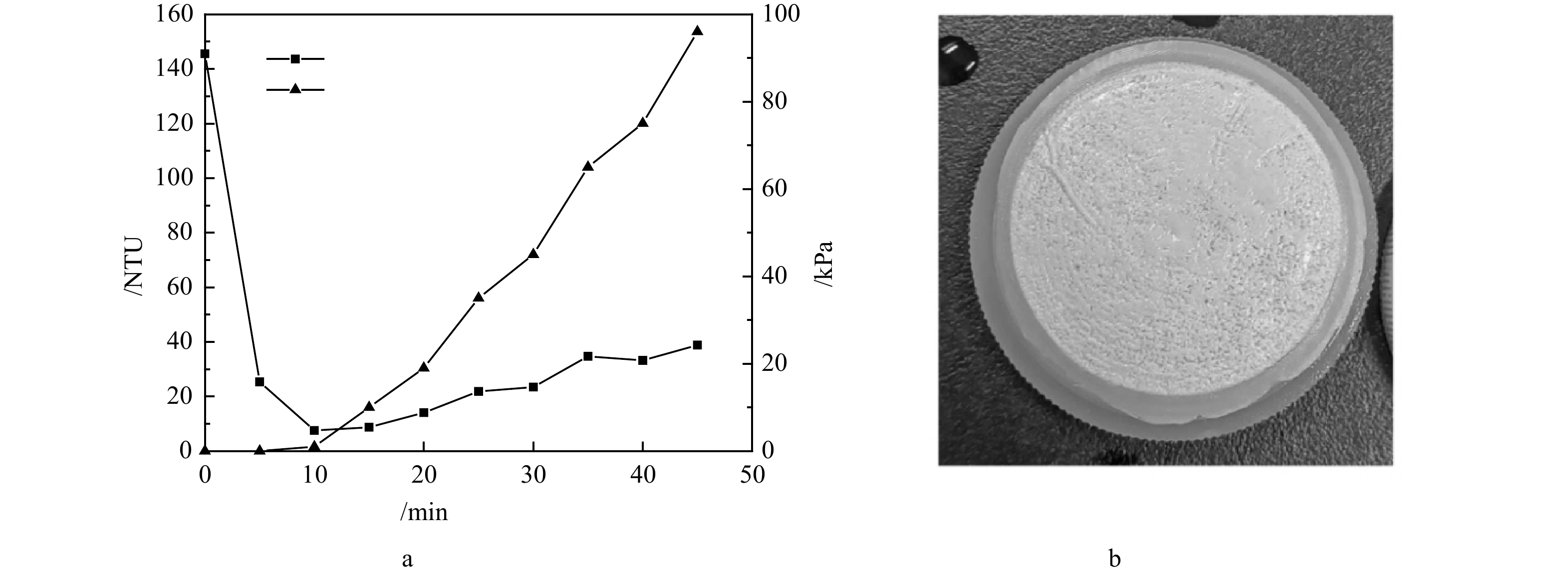
2)沸石动态膜系统的成膜特征。结果表明,在沸石粉投加量为1 g·L−1,蠕动泵流量为40 mL·min−1和38 μm支撑膜的条件下,沸石动态膜的形成效果最佳,其浊度与跨膜压的变化规律如图7(a)所示。从图7(a)中可知,动态膜出水浊度在 5 min即从最初的145.5 NTU降低到25.3 NTU,10 min时降至7.52 NTU,此时跨膜压开始上升,出水浊度也开始缓慢波动上升。动态膜整体形成过程维持了约45 min,而跨膜压在40 min内上升至约95 kPa。在38 μm支撑膜截留作用下,沸石动态膜系统出水浊度逐渐下降,随着动态膜层不断密实,沸石动态膜对小粒径沸石截留效果也在逐渐提升,但实验观察到出水浊度经过下降阶段后,随压力的上升呈现出不断缓慢上升趋势。推测可能是在动态膜形成过程中,进水的冲击及沸石颗粒性质造成动态膜滤饼层并不稳定,在跨膜压作用下小颗粒沸石穿透膜层导致浊度升高。实验中发现在此条件下沸石形成的动态膜层较薄,不太均匀(图7(b)),说明沸石动态膜的稳定性有待进一步提升。若以浊度值去除率近似估算沸石回收率,沸石动态膜系统对沸石颗粒的回收率最高可达到94.8%。
3)复合硅藻土沸石动态膜系统成膜特征和脱氨效果。为了有效提升沸石动态膜稳定性,同时保证动态膜对氨氮的去除效果,后续实验选用硅藻土作为辅助成膜材料,以1:1质量比与沸石进行复配。为了避免动态膜形成过快增加动态膜形成过程的监测困难,先投加10 g·L−1沸石与10 g·L−1硅藻土于2 L 10 mg·L−1氨氮废水中,搅拌1 h以充分混合,然后取200 mL混合液稀释10倍后开始构建复合硅藻土沸石动态膜,在动态膜形成过程中出水浊度与跨膜压随时间的变化情况如图8(a)所示。沸石与硅藻土按质量比1:1复配形成动态膜时,出水浊度下降很快,5 min即由81.6 NTU下降至1.23 NTU,10 min后一直稳定在1 NTU以下,表明动态膜已稳定形成,且连续运行55 min直至跨膜压上升至82 kPa。硅藻土的加入使出水浊度的稳定性得到明显改善,相比于沸石动态膜,沸石与硅藻土混合复配吸附动态膜形成快速且稳定,实验结束后发现复合硅藻土沸石动态膜更加致密而均匀(图8(b)),可以有效截留微尺度沸石。从跨膜压的变化规律来看,沸石与硅藻土复配也一定程度上延长了装置的运行时间。因此,沸石与硅藻土复配形成的动态膜可以有效回收微尺度沸石。若以浊度值去除率近似估算硅藻土和沸石的回收率,复合硅藻土沸石动态膜系统回收率可达到98.77%,高于动态膜对微尺度改性活性炭的回收率(63%~87%)[16]。
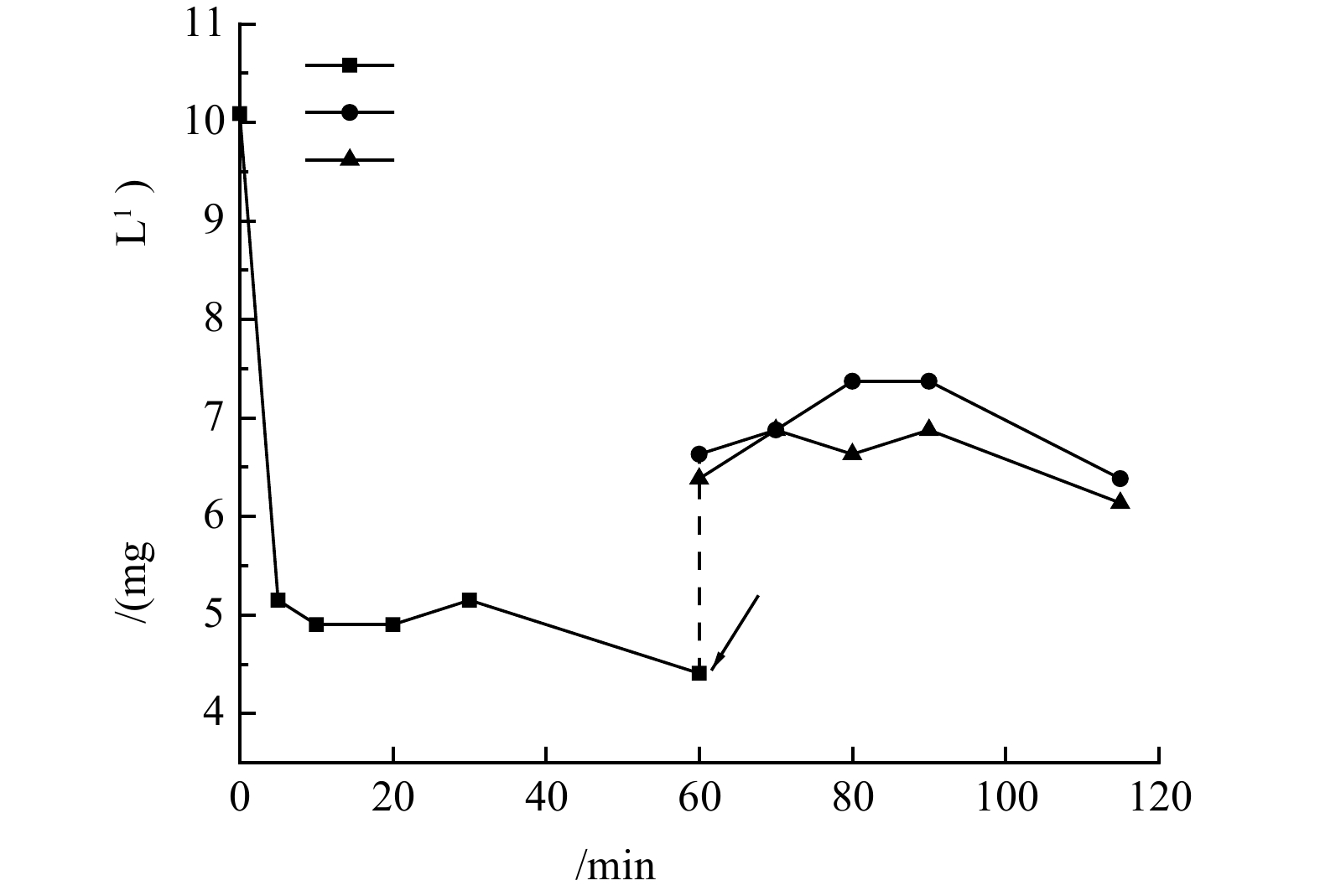
沸石与硅藻土混合复配成膜过程中氨氮浓度的变化规律如图9所示。由图9可知,在反应开始时,在初始氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1时,经过60 min后剩余氨氮质量浓度为4.4 mg·L−1,去除率可达56%,与单独投加沸石时对氨氮的去除效果相近。硅藻土本身对氨氮的吸附效果不佳,该吸附过程主要还是以沸石吸附为主。60 min稀释后开始形成动态膜时,系统内与出水的氨氮质量浓度(折算为稀释前)在6.5 mg·L−1左右,比稀释前略有提升,可能是因为稀释过程导致了氨氮吸附平衡的移动,沸石吸附的氨氮部分转移到了稀释后溶液中。由复合硅藻土沸石动态膜出水浊度的变化规律可知,系统运行5 min即可形成稳定的动态膜,随着动态膜的持续形成和过滤,动态膜出水氨氮浓度略低于反应系统内氨氮浓度。这可能是因为在动态膜成膜前系统混合搅拌过程中,沸石对氨氮的吸附已基本趋于平衡,而氨氮废水经过动态膜时与沸石接触时间较短,无法进行充分接触,因此,复合硅藻土沸石动态膜层对氨氮的去除效果有限。复合硅藻土-沸石-动态膜系统实现了废水中氨氮的吸附去除,同时回收了微颗粒沸石,可为吸附材料的再生和回收利用提供参考。
整体来看,沸石静态吸附与沸石动态膜系统在氨氮去除性能上的表现相差不大,但沸石动态膜系统的优势在于可以对沸石吸附颗粒进行有效回收。尽管单纯沸石构建动态膜系统出现了出水浊度波动上升和沸石颗粒穿透,但通过复合硅藻土沸石动态膜系统能够保证了沸石颗粒的有效回收,从而提升了动态膜系统稳定性,也同步实现了废水中氨氮的去除。
-
1)在沸石静态吸附研究中,在初始氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1,沸石投加量为4 g·L−1时,沸石对氨氮去除率和吸附量分别可达54%和1.3 mg·g−1;当初始氨氮质量浓度增至100 mg·L−1时,沸石对氨氮吸附量可提升至3.89 mg·g−1,但氨氮去除率也降至17%。
2)沸石脱氨过程更符合准二级动力学过程;Langmuir吸附等温模型对沸石吸附脱氨拟合效果更优,理论最大平衡吸附量为4.12 mg·g−1。
3)在10 g·L−1沸石投加量下,沸石动态膜系统对氨氮的去除率为56%,出水浊度可降至7.52 NTU,沸石动态膜的稳定性有待进一步提升。
4)沸石与硅藻土按照1:1的质量比复配,10 min即可快速构建复合硅藻土沸石动态膜,出水浊度稳定在1 NTU以下,氨氮去除率可达到56%,在脱氨的同时能够实现沸石的有效回收,并显著提升了复合硅藻土沸石动态膜系统的稳定性。沸石吸附是复合沸石动态膜系统脱氨的主要作用机制。
复合沸石动态膜系统的脱氨效能及其对沸石的同步回收
Simultaneous ammonia removal and zeolite recovery by a composite zeolite dynamic membrane system
-
摘要: 为同步实现吸附脱氨和微尺寸沸石回收,将沸石与动态膜技术耦合联用,构建了一种复合沸石-动态膜系统,并考察其脱氨和沸石回收效果。在初始氨氮质量浓度为10 mg·L−1条件下,投加10 g·L−1沸石可有效实现氨氮的去除,去除率为67%。吸附动力学和等温模型分析结果表明,该过程符合准二级动力学模型,Langmuir吸附等温模型拟合得到的最大氨氮吸附量为4.12 mg·g −1。按照1:1的质量比投加沸石与硅藻土,在投加量均为1 g·L−1,流量为40 mL·min−1,支撑膜孔径38 μm下可快速形成动态膜,出水浊度稳定在1 NTU以下,氨氮去除率可达到56%,在脱氨的同时能够实现沸石的有效回收。该研究结果可为复合沸石动态膜系统同步吸附脱氨和吸附材料回收提供参考。Abstract: To achieve simultaneous ammonia adsorption and microscale zeolite recovery, zeolite was coupled with dynamic membrane technology to establish a composite zeolite-dynamic membrane system, and its ammonia removal rate and zeolite recovery efficiency were evaluated. At initial ammonia concentration of 10 mg·L−1, 67% ammonia could be removed effectively with 10 g·L−1 zeolite dosing. The adsorption kinetics and isothermal model indicated that the adsorption fitted well with the pseudo-second-order model, and the theoretical maximum adsorption capacity was 4.12 mg·g−1 predicted by Langmuir model. Zeolite and diatomite were mixed in the zeolite-dynamic membrane system at a mass ratio of 1:1, and the composite zeolite dynamic membrane could rapidly form under the conditions of 1 g·L−1 dosage, 40 mL·min−1 flow rate and 38 μm supporting membrane. After the formation of DM layer, the effluent turbidity remained stably below 1 NTU, and ammonia removal rate was 56%. Ammonia removal and zeolite recovery were achieved at the same time, which laid the foundation for simultaneous ammonia adsorption and adsorbents recovery for the composite zeolite dynamic membrane system in future.
-
Key words:
- ammonia /
- adsorption /
- dynamic membrane /
- zeolite /
- recovery
-

-
表 1 准一级与准二级动力学方程拟合参数及相关系数
Table 1. Fitting parameters and correlation coefficients of pseudo-first order kinetics and pseudo second order kinetics
qe,exp /(mg·g−1) 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 qe,celc/(mg·g−1) k1/min−1 R2 qe,celc/(mg·g−1) k2/(g·(mg·min)−1) R2 1.30 1.22 0.21 0.969 1.24 0.34 0.982 表 2 Langmuir与Freundlich吸附等温模型拟合参数及相关系数
Table 2. Fitting parameters and correlation coefficients of adsorption isotherm models of Langmuir and Freundlich
温度/ ℃ Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) b/(L·mg−1) R2 Kf/(mg(1−1/n) g−1 L1/n) 1/n R2 25 4.12 0.33 0.995 0.69 0.40 0.960 -
[1] FU Q, ZHENG B H, ZHAO X R, et al. Ammonia pollution characteristics of centralized drinking water sources in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(10): 1739-1743. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61011-5 [2] KARRI R R, SAHU J N, CHIMMIRI V. Critical review of abatement of ammonia from wastewater[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 261: 21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.120 [3] DING T T, DU S L, HUANG Z Y, et al. Water quality criteria and ecological risk assessment for ammonia in the Shaying River Basin, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 215: 112141. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112141 [4] FAN J W, WU H X, LIU R Y, et al. Non-thermal plasma combined with zeolites to remove ammonia nitrogen from wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123627. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123627 [5] 王皓辉, 郝林林, 李桂菊. 吸附-超滤组合工艺对低浓度氨氮废水的处理研究[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2020, 35(6): 37-43. doi: 10.13364/j.issn.1672-6510.20190229 [6] ALSHAMERI A, HE H P, ZHU J X, et al. Adsorption of ammonium by different natural clay minerals: Characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2018, 159: 83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.007 [7] 马文艳, 裴鹏刚, 高歌, 等. 微纳米粒径生物炭的结构特征及其对Cd2+吸附机制[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3682-3691. [8] LI L C, XU G R, YU H R, et al. Dynamic membrane for micro-particle removal in wastewater treatment: Performance and influencing factors[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 627: 332-340. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.239 [9] DU Q, LIU S J, CAO Z H, et al. Ammonia removal from aqueous solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2005, 44(3): 229-234. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2004.04.011 [10] WANG X L, QIAO B, LI S M, et al. Using natural Chinese zeolite to remove ammonium from rainfall runoff following urea fertilization of a paddy rice field[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(6): 5342-5351. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5743-5 [11] ADAM M R, OTHMAN M H D, ABU SAMAH R, et al. Current trends and future prospects of ammonia removal in wastewater: A comprehensive review on adsorptive membrane development[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 213: 114-132. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.12.030 [12] 王浩, 陈吕军, 温东辉. 天然沸石对溶液中氨氮吸附特性的研究[J]. 生态环境, 2006, 15(2): 219-223 [13] DAWOUD B. Water vapor adsorption kinetics on small and full scale zeolite coated adsorbers; A comparison[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 50(2): 1645-1651. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.07.013 [14] 郜玉楠, 周历涛, 王信之, 等. 改性4A沸石分子筛去除低温水中氨氮机理研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(7): 1-5 [15] 刘丽芳, 林子厚, 杨克敏, 等. 改性沸石滤料吸附氨氮性能研究[J]. 给水排水, 2022, 58(S1): 679-686 [16] LI L C, ZHU Z H, SHI J X, et al. Simultaneous phosphorus removal and adsorbents recovery with Ca-PAC assisted adsorption dynamic membrane system: Removal performance and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 384: 135591. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135591 -



 下载:
下载: