-
近年来,臭氧(O3)逐渐成为各省市的首要污染物[1-2]。近地面的臭氧主要是由大气环境中的挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)与其它化合物(如NOx)在阳光照射下发生光化学反应生成的[3]。因此,VOCs的捕集与治理是控制臭氧工作的难点和关键[4]。VOCs种类繁多,来源复杂[5-7]。其中,溶剂产品使用源在我国VOCs排放中占有较大比重(>20%),而苯系物又占总其排放量比重的30.1%[8]。苯系物不仅会对生态环境造成严重污染[9],同时也会对人体免疫系统造成伤害等。
很多吸附剂在处理低浓度VOCs上取得了有效突破,展现出较大的应用前景[10-14]。廖苑如[9]发现改性SBA-15对甲苯的饱和吸附容量较大,且脱附再生性能优异。黄海凤等[14]发现MCM-41分子筛对低浓度VOCs吸附效果良好。MFI型ZSM-5分子筛具有特殊的高硅三维交叉直通道,丰富可调的表面性质,是理想的催化剂载体[10];同时其孔径尺寸与苯的分子动力学直径相当,可作为苯吸附材料。
虽然许多学者在MFI型分子筛吸附苯方面进行过研究[15-19],但其苯吸附容量有限;且近些年对ZSM-5的改性也多集中于金属负载或是针对工业应用的催化改质[20-26]。而非金属元素负载在保证低成本的前提下能有效提高分子筛的吸附容量[10]。本研究以尿素为氮源制备改性ZSM-5分子筛,通过一系列表征手段考察其微观结构,以稳定的苯分子为探针物,阐明氮改性提高苯吸附性能的机理,为开发高性能、低成本的苯吸附材料提供一定的思路。
-
将尿素(AR,成都科龙化工试剂厂)与ZSM-5分子筛(北京北科新材料有限公司,相对结晶度95%,孔径5Å)按照一定质量比混合均匀,而后置于马弗炉(SXL-1008,上海精宏实验设备有限公司)中以2 ℃·min−1升温速率至550 ℃并煅烧6 h,冷却后取出,所得样品即为改性ZSM-5分子筛,记作αN-ZSM-5,其中α为尿素与ZSM-5分子筛的质量比。
-
实验中采用日本Rigaku公司的D/MAX 2550型粉末X射线衍射仪(XRD)考察样品的晶型晶貌,Cu Kα射线波长λ=0.15418 nm,管电压50 kV,管电流200 mA,扫描速度为10(°)·min−1,扫描范围5°—50°。比表面积和孔结构采用ASAP2020型物理吸附仪(美国Micromeritics公司)测得。在液氮温度(77 K)下进行N2吸附和脱附测试,使用多点BET方法计算样品的比表面积,基于N2脱附曲线使用BJH方法计算样品的孔体积和孔径分布。采用元素分析仪(Flash EA1112, ThermoFinnigan,美国)测定样品中的N元素含量。用SDT-Q600同步热分析仪(美国TA公司)测试样品的热稳定性。
取3—5 mg样品置于坩埚中,在100 mL·min−1的N2氛围中以10 ℃·min−1的升温速率将温度从室温升至800 ℃考察样品在升温过程中的质量变化。采用傅立叶变换红外光谱仪(IR Affinity-1,日本岛津)分析判断样品的表面官能团。将样品充分研磨压制成均匀圆片,扫描范围为400—4000 cm−1,分辨率4 cm−1,扫描次数32次。
-
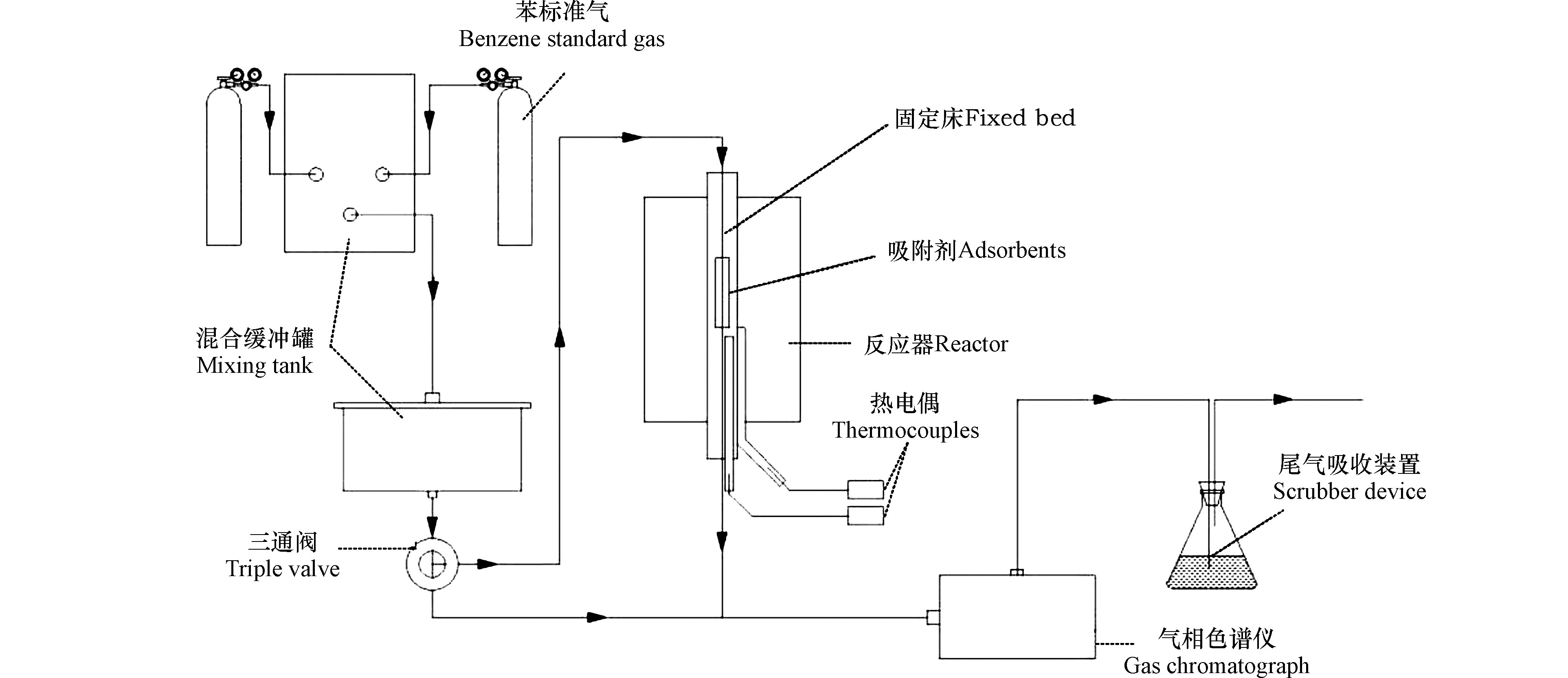
实验中在固定床中测试苯在吸附剂上的穿透曲线,实验装置流程如图1。首先将粉末样品压片筛分制成40—60目的颗粒,称取0.1 g颗粒分子筛装填入填料柱内。将样品在氮气氛围和100 ℃的条件下吹扫1 h,待温度稳定在30 ℃通入100 mL·min−1、0.35 mg·L−1的苯/氮气标准气体,同时采用气相色谱仪(SC-2000G,重庆川仪分析仪器有限公司,FID,KB-wax毛细管柱)每间隔3 min记录反应器出口苯的浓度。当反应器出口处的苯浓度达到入口水平时,认为吸附达到动态平衡。
采用Origin绘制穿透曲线,对穿透曲线进行拟合分析,并按照公式(1)计算样品的吸附容量。
式中,Q-吸附容量,mg·g−1;q-气体质量流量,mg·min−1;m-吸附剂质量,g;C0-吸附质入口浓度,mg·m−3;Ct-t时刻吸附质出口浓度,mg·m−3;t-时间,min。
利用Origin软件中的Logistic函数对穿透曲线进行拟合,得到以时间t为自变量,出口浓度Ct为因变量的带有参数扩散速率p的函数,固定床任意时刻的出气口浓度可由公式(2)算出。
式中,Ct为任意t时刻(min)固定床出口苯浓度;A1-固定床初始出口浓度,mg·m−3;A2-吸附饱和固定床出口浓度,mg·m−3;t-时间,min;t0-穿透时间,min;p-扩散速率常数,min−1。
-
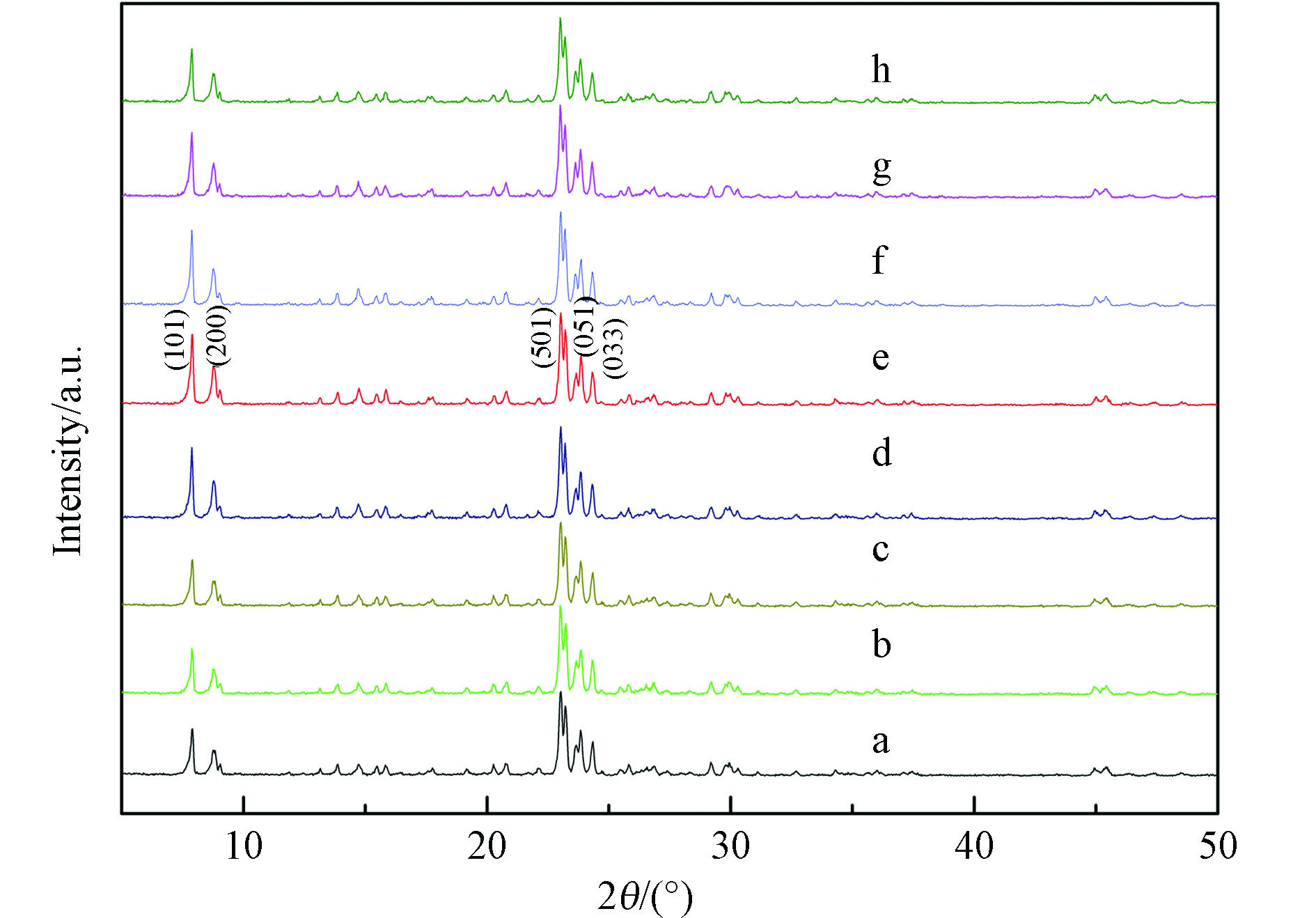
实验中采用XRD考察样品的晶体形态,结果如图2所示。测试样品在2θ=7.9°、8.8°、23.1°、23.8°均出现了较强的衍射峰,分别对应了MFI型分子筛(101)、(200)、(501)、(051)晶面。24.3°处的特征峰对应单斜和对称的平面[27]。与尿素混合煅烧后分子筛的特征衍射峰没有消失,也无新峰出现,说明改性并没有破坏载体晶体结构。但引入氮元素的量不同,衍射峰相对强度有所差异。在(101)和(200)晶面上,随着尿素含量的增加,特征峰变强;但当尿素含量继续增加时,特征峰强又有所削弱,可能是出现孔道内分子团聚现象[28]。
-
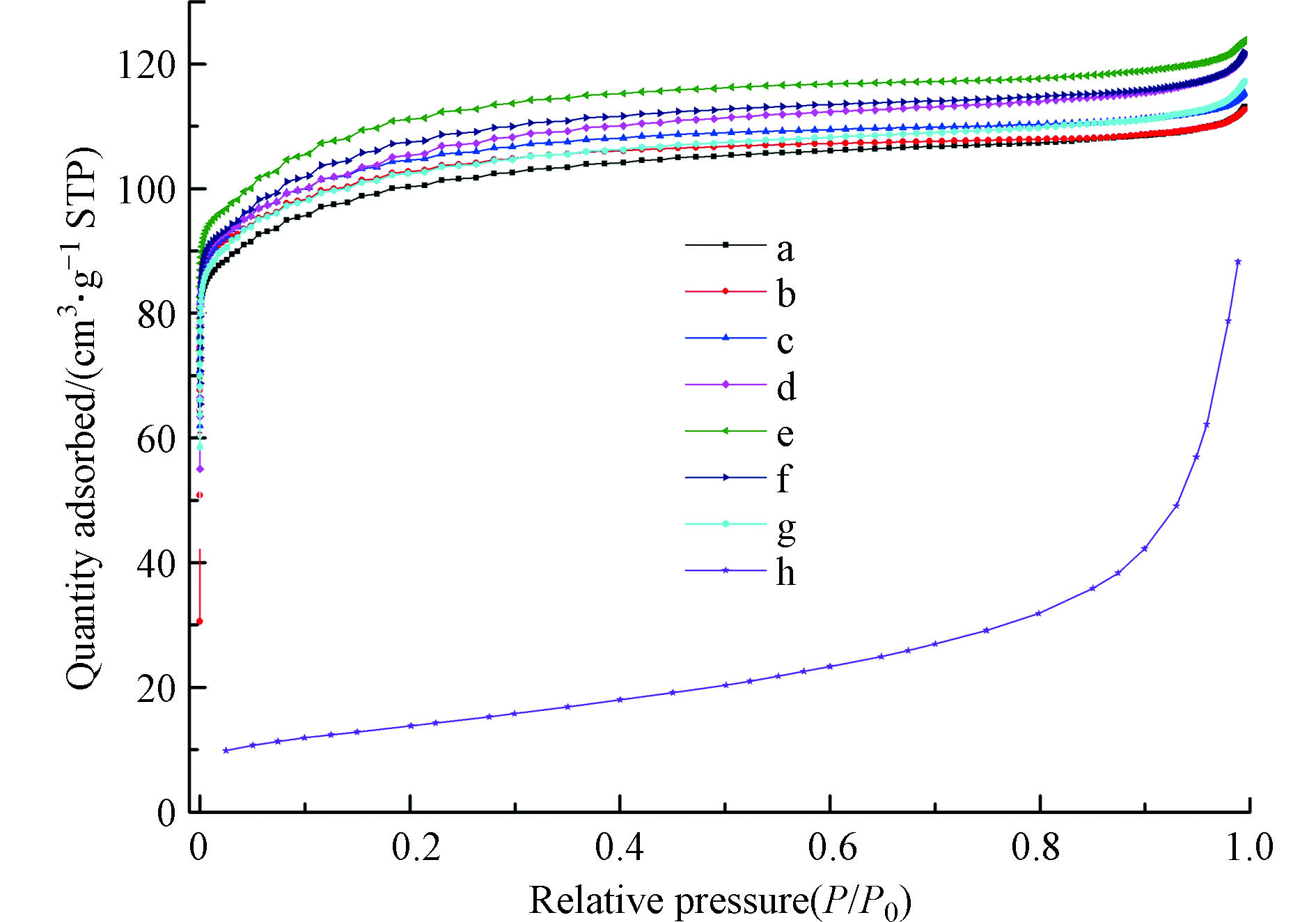
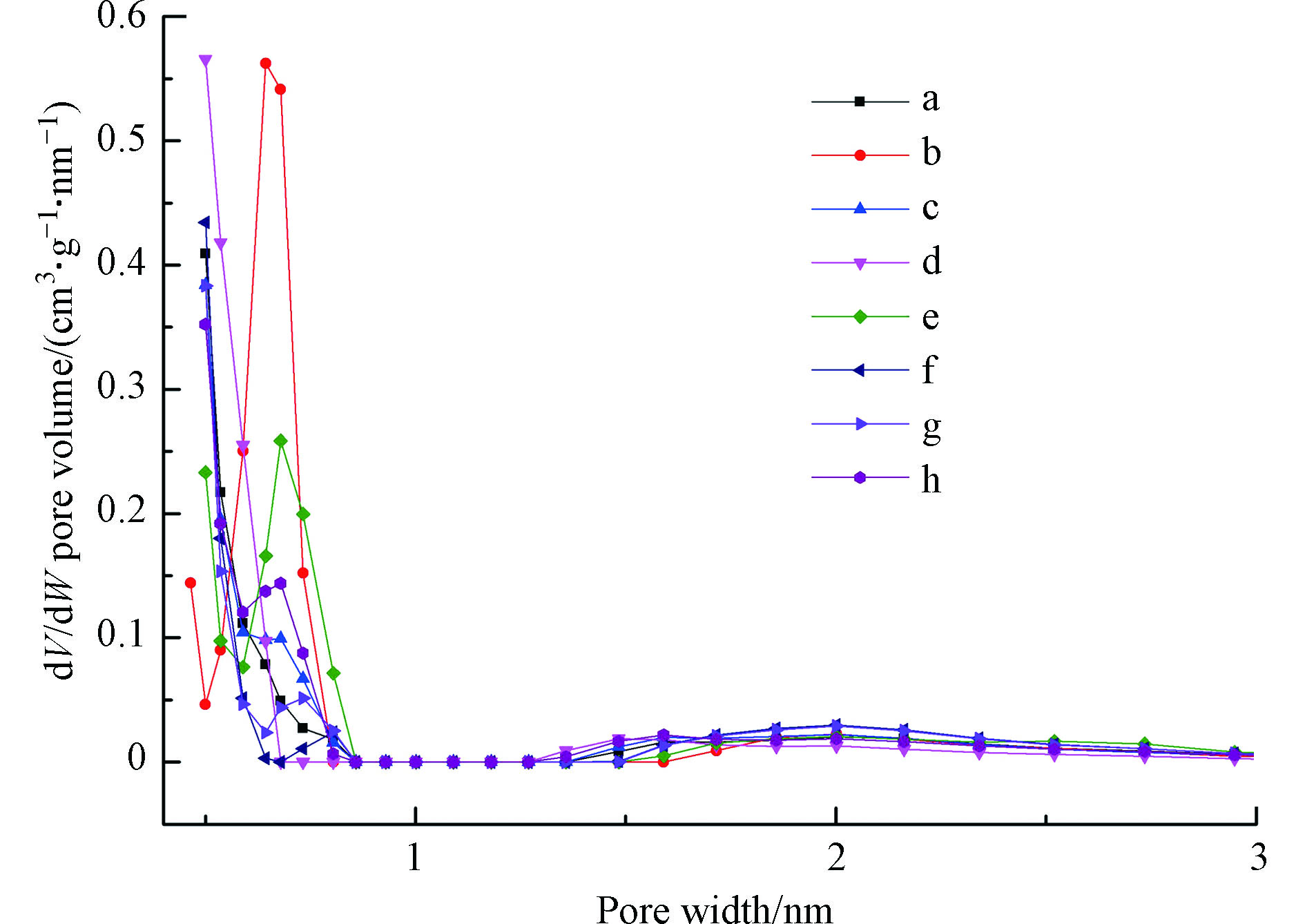
实验中采用N2-吸附/脱附手段考察样品的织构性能(图3、4),计算所得的织构参数见表1。各样品的等温吸附曲线按照IUPAC分类为I型。在低相对压力下为微孔充填,氮气吸附容量随相对分压急剧增加;当微孔被氮气充满,氮气吸附量随相对分压增加缓慢。样品的孔径分布结果表明改性分子筛呈现出典型的微孔结构。
随着尿素引入量增多,进入分子筛孔道内的氮含量越多[29-30](表1)。当尿素与ZSM-5分子筛质量比为1∶1时样品的氮含量达到最大(0.23%),而后又有所减小。改性样品的氮吸附曲线类型没有发生改变,其孔容和孔径亦变化不大,这就说明尿素的加入并未改变分子筛的孔道特征,微观结构没有被破坏,与XRD结果一致。ZSM-5分子筛的孔道结构尺寸约为0.55 nm,这与苯的分子动力学直径相匹配,有利于苯分子在改性分子筛中的吸附。氮元素引入后,N-ZSM-5的比表面积发生改变,呈现先增大再减小的趋势,在2N-ZSM-5达到最大418.43 m2·g−1。当尿素含量继续增加时,分子筛结晶度下降,比表面积下降。
-
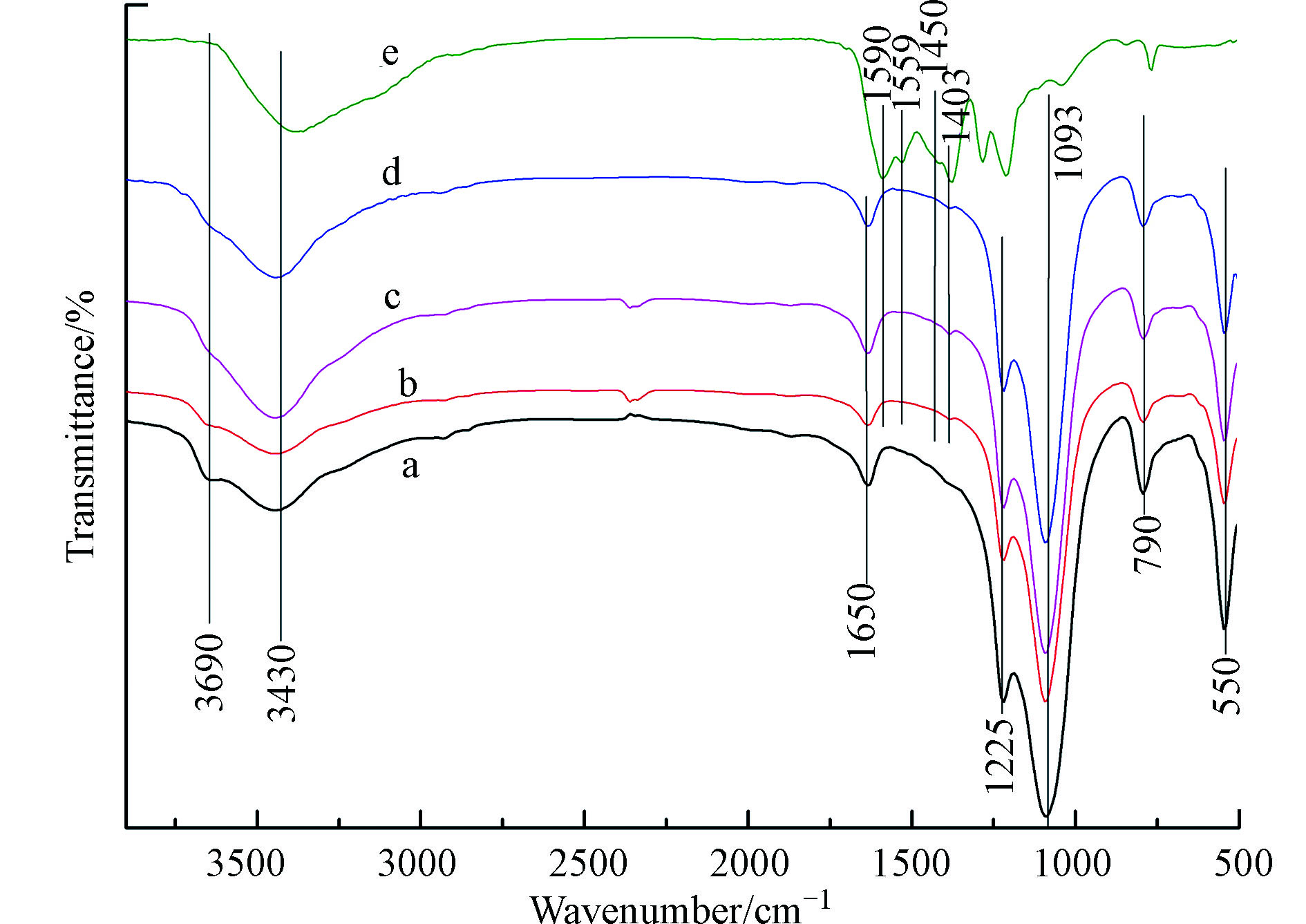
实验中采用傅里叶红外考察氮的引入对吸附剂表面化学性质的影响,结果如图5所示。550、790、1093、1225 cm−1处的吸收峰为ZSM-5分子筛的特征振动峰。1225 cm−1和1093 cm−1分别归属为Si—O—Si和Si—O—Al的反对称伸缩振动,790 cm−1为Si(Al)—O键的振动吸收峰,550 cm−1附近处的吸收峰归因为MFI拓扑结构分子筛的双五元环特征振动[31]。此外,图中3690、3430和1650 cm−1可分别归属为晶体邻近硅羟基、表面吸附水O—H键和表面羟基的振动吸收峰。氮引入后,这些ZSM-5分子筛的特征吸收峰没有发生改变,这说明载体材料的骨架结构未发生改变。但氮引入了新的吸收峰。1450/1403 cm−1处的吸收峰可归属于C—N的伸缩振动[32],1590/1559 cm−1附近的振动峰归属于C=N的伸缩振动[33]。随着氮含量的增加,这些振动峰的相对峰强增加;同时分子筛表面O—H键振动吸收峰峰强变弱。由此可以推测,尿素在煅烧过程或与分子筛表面的硅羟基相结合,致使分子筛的硅羟基和硅窝等缺陷位发生了变化[28]。
-
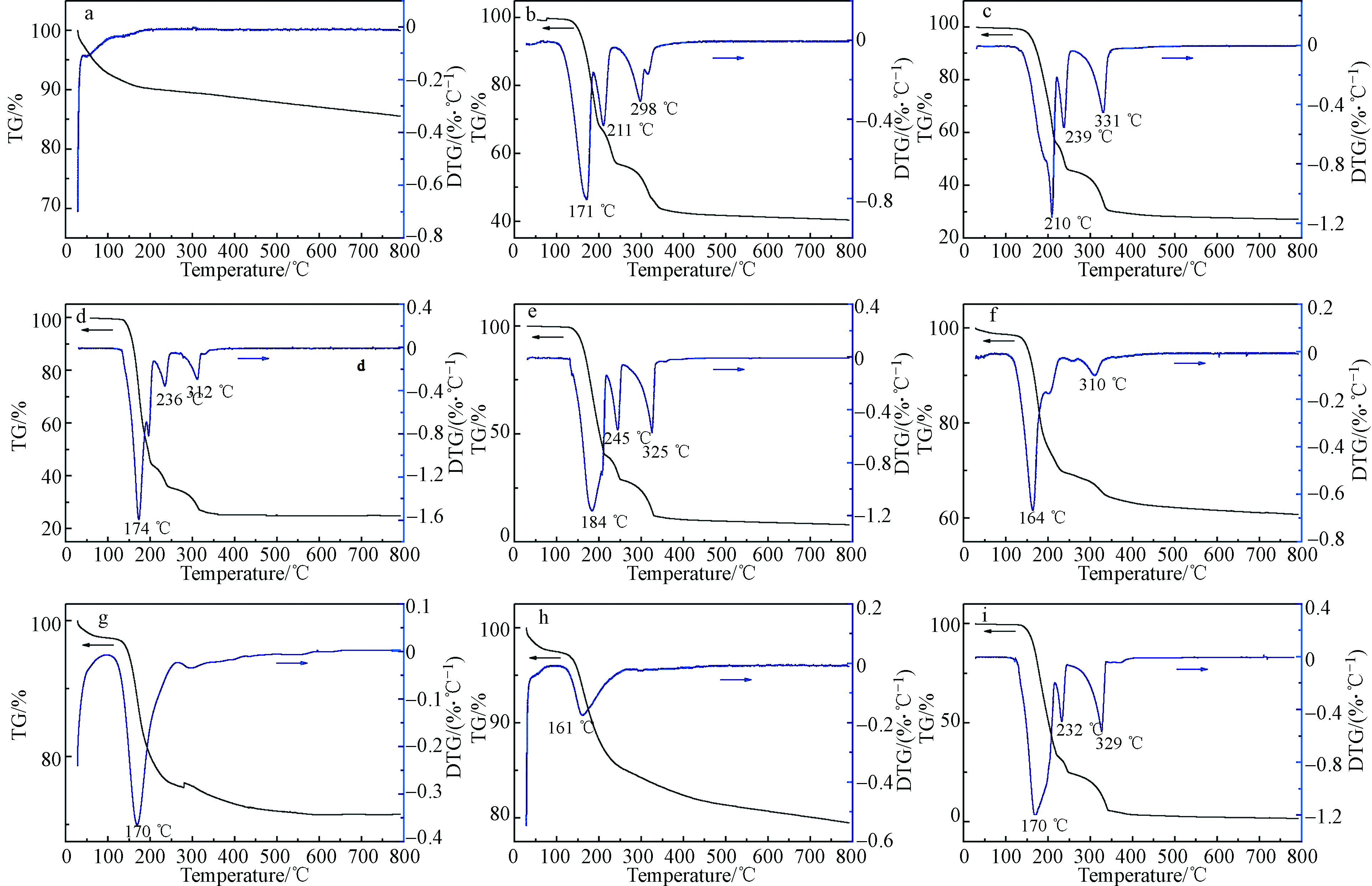
在30 ℃至800 ℃的温度范围内考察ZSM-5分子筛及其改性样品的热分解过程,结果见图6。尿素的分解过程存在3个明显的阶段(图6i):170 ℃时尿素分解并产生缩二脲,232 ℃处的质量失重由分解产生NH3与HNCO(异氰酸)引起,329 ℃处的质量损失由HNO胺热分解生成三聚氰酸和三聚氰酸一酰所致[33]。430 ℃时尿素完全分解,这与文献报道一致[34-35]。与ZSM-5分子筛按照一定比例混合后,样品均呈现3个明显的失重阶段,但尿素的失重速率峰温发生了改变。尿素/分子筛质量比较低时,尿素在分子筛表面分散,受分子筛表面硅羟基的作用分解温度提高,并在1N-ZSM-5样品上达到最大[33]。随着尿素/分子筛质量比的增加,样品的热分解行为越接近尿素,这进一步印证了红外结果。
-
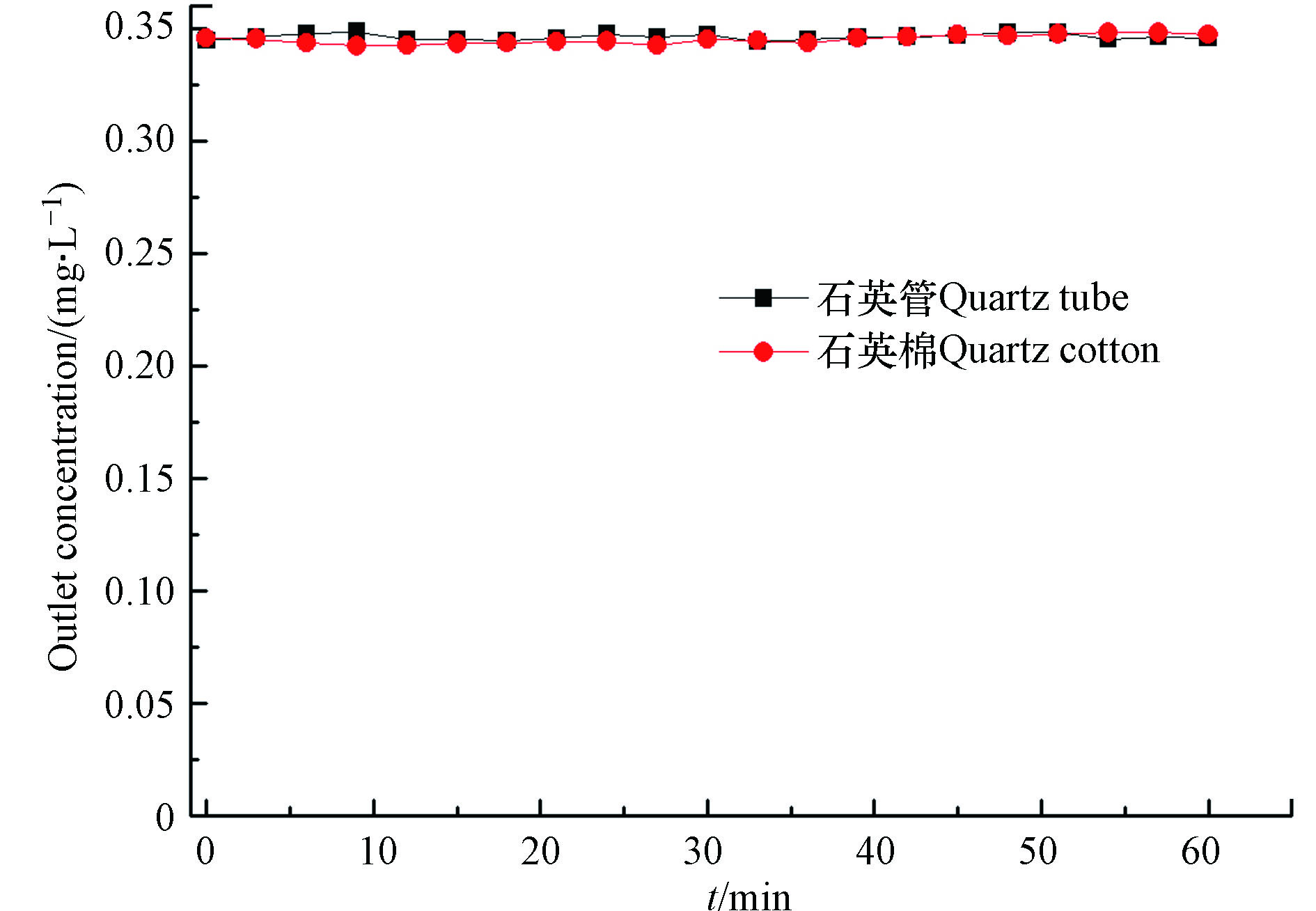
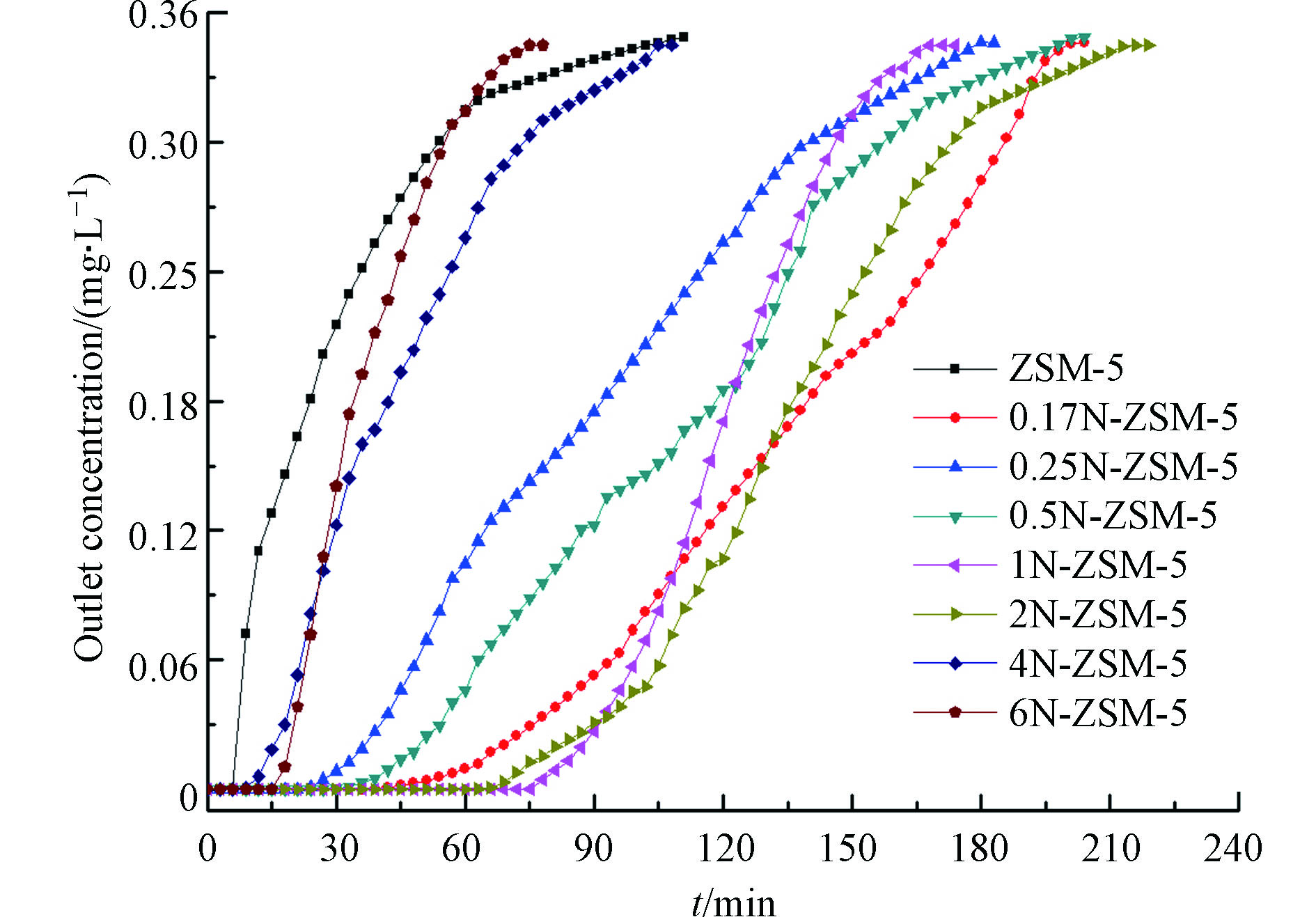
样品的吸附性能测试在装有吸附剂的石英管中进行。为了排除石英管以及石英棉对本实验结果的影响,在相同的实验条件下,分别将未装填任何物质的石英管和装填了石英棉的进行吸附苯的空白对照实验,结果表明(图7),其对于苯并没有吸附性能。实验中通过固定床吸附实验得出样品对苯的吸附穿透曲线(如图8),并由Logistic函数对穿透曲线进行拟合计算样品的吸附容量(表2)。拟合曲线的相关性R2均接近1,表明相关性较好,经验公式可靠,该模型能较好模拟系列改性分子筛对苯的吸附行为.
载体材料ZSM-5本身具备一定的吸附能力,但混合尿素煅烧改性后其对苯的吸附容量显著提高,2N-ZSM-5的苯附容量最大,可达47.56 mg·g−1。其次是N含量最多的1N-ZSM-5(42.27 mg·g−1),它们对苯的吸附容量是纯ZSM-5分子筛(9.70 mg·g−1)的5倍左右。苯分子与吸附剂之间存在范德华力,且分子大小与改性样品的孔道尺寸相当,苯可通过物理吸附作用富集在改性ZSM-5上[35-36],吸附剂的比表面积越大,苯吸附容量越高。值得注意的是,0.17N-ZSM-5样品的苯吸附容量较高,与2N-ZSM-5相比N%相差不大,但0.17N-ZSM-5的比表面积却远小于2N-ZSM-5。由此,分子筛混合尿素煅烧引入的含氮官能团使改性ZSM-5分子筛体现出对苯较强的亲和力。氮引入后增强了吸附剂的表面碱性,增强了吸附剂的得电子能力,而苯分子倾向于给出电子,由此改善了吸附剂与苯的相互作用。改性分子筛对苯的吸附由孔道的物理吸附和分子间相互作用共同决定。一定尿素/分子筛混合质量比下,引入的含氮基团可提高分子筛的苯吸附容量;但混合比过高时,尿素的热分解过程发生改变,引入的氮含量降低,苯吸附容量又减少。
混合尿素煅烧后,改性样品的扩散速率常数p均有所增大,且随着氮含量的增加而增大。当尿素/分子筛质量比为1∶1时,p值最大。p值越大,吸附剂的扩散阻力越低,其吸附性能越好[8],这也进一步说明了含氮官能团与苯的分子间相互作用。
与文献报道的其它改性材料相比(表3),本文的氮改性ZSM-5分子筛在苯的吸附处理上展现出明显优势,为特定工业源的尾气组分的吸/脱附实际应用提供了一定理论依据。
-
实验中采用一步煅烧法制备了一系列氮改性的ZSM-5分子筛,并考察了其对苯的吸附性能。表征结果发现,改性ZSM-5分子筛保持了微孔结构,但其表面化学性质发生了变化。尿素在煅烧过程中与ZSM-5的表面羟基相结合,致使分子筛硅羟基和硅窝等缺陷位发生改变,也影响了尿素的热分解过程,并最终在分子筛上引入了含氮官能团。该含氮官能团增强了吸附剂的表面碱性,提高了材料对苯分子的亲和力,降低了苯在材料孔道中的扩散阻力,由此苯在改性分子筛上的吸附容量和吸附速率均得到显著提升。
氮改性ZSM-5分子筛的苯吸附性能
Study on benzene adsorption properties on nitrogen modified ZSM-5 zeolites
-
摘要: 为解决固体吸附剂ZSM-5型分子筛对VOCs(挥发性有机物)吸附容量较低的难题,本文以ZSM-5型分子筛作为载体材料,尿素作为氮源,采用一步煅烧法制备得到氮改性ZSM-5分子筛。利用X射线衍射分析仪(XRD)、傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR)、比表面与孔隙分析仪(BET-BJH)等对氮改性ZSM-5分子筛进行了表征,并采用固定床探究了氮改性ZSM-5分子筛对苯的吸附机制。结果表明,改性后分子筛的骨架结构未被破坏,氮通过尿素与分子筛上羟基间的相互作用成功引入到ZSM-5型分子筛上,所制备得到的氮改性ZSM-5分子筛具有典型的微孔结构。ZSM-5分子筛中引入的含氮官能团,不仅能作为新的吸附活性位点,还能提高苯在吸附剂孔道中的扩散速率。研究结果能为开发高性能低成本的VOCs吸附材料提供一定思路。Abstract: In this paper, modified ZSM-5 based adsorbents were prepared to enhance its VOCs (volatile organic compounds) adsorption capacity. Different N contents from urea were introduced into ZSM-5 zeolites through one-step solid-state method. The microstructures and surface physic-chemical properties of adsorbents were characterized by various techniques like X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller-Barret-Joyner-Halender Measurement (BET-BJH) and so on. The adsorption performance of benzene was also investigated using fixed bed. The experimental results showed that the typical microporousstructure of ZSM-5 was maintained. Nitrogen contained groups were successfully introducedintoZSM-5 zeolites based on the interaction between urea and the surface hydroxyl groups of ZSM-5. The nitrogen contained groups not only showed strong inter-molecular interaction with benzene, but also modified its diffusion rate in the pores of zeolites. This work provided a novel idea for the development VOCs adsorbents with high performance and low cost.
-
Key words:
- ZSM-5 zeolites /
- urea /
- modification /
- benzene adsorption
-

-
表 1 改性ZSM-5分子筛吸附剂的织构性能和元素含量
Table 1. BET characterizations and element content analysis formodified ZSM-5 adsorbents
样品名
SamplesBET比表面积/(m2 ·g−1)
BET surface
area单点吸附孔容/(cm3 ·g−1)
Single point adsorption
pore volume平均吸附孔/nm
Average particle
sizeN/% C/% ZSM-5 380.54 0.17 1.84 − − 0.17N-ZSM-5 392.11 0.17 1.78 0.15 0.15 0.25N-ZSM-5 398.41 0.18 1.79 0.12 0.14 1N-ZSM-5 399.32 0.19 1.88 0.23 0.21 2N-ZSM-5 418.43 0.19 1.83 0.09 0.18 4N-ZSM-5 404.20 0.19 1.87 0.04 0.01 6N-ZSM-5 392.53 0.18 1.85 0.04 0.03 urea 50.27 0.13 2.04 4.08 2.87 表 2 改性ZSM-5分子筛的吸附容量及拟合曲线参数值
Table 2. Adsorption properties and logistic fitting curve parameters for modified zeolite adsorbents
样品名
SamplesA1/(mg·m−3) A2/(mg·m−3) t0/min p/min−1 R2 吸附容量/(mg·g−1)
Adsorption capacityZSM-5 −3.05 110.45 24.01 1.54 0.99 9.70 0.17N-ZSM-5 −1.23 193.69 198.80 2.91 0.99 40.51 0.25N-ZSM-5 −2.09 129.78 105.56 2.26 0.99 31.99 0.5N-ZSM-5 −0.86 135.59 132.93 2.74 0.99 38.69 1N-ZSM-5 −0.26 106.10 122.38 8.15 0.99 42.26 2N-ZSM-5 0.06 106.21 137.67 6.05 0.99 47.56 4N-ZSM-5 −2.08 112.93 43.97 2.20 0.99 14.73 6N-ZSM-5 −1.96 105.55 35.23 3.43 0.99 11.92 表 3 不同改性ZSM-5对VOCs吸附性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of VOCs adsorption capacity among different zeolites
-
[1] ZHANG J, LIU L, WANG Y Y, et al. Chemical composition, source, and process of urban aerosols during winter haze formation in Northeast China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231(1): 357-366. [2] 生态环境部发布2018年5月、1—5月重点区域和74个城市空气质量状况[J]. 节能与环保, 2018(7): 14. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment issued the air quality status of key regions and 74 cities in May, January to May, 2018[J]. Energy conservation and environmental protection, 2018(7): 14 (in Chinese).
[3] LIANG X M, CHEN X F, ZHANG J N, et al. Reactivity-based industrial volatile organic compounds emission inventory and its implications for ozone control strategies in China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2017, 162: 115-126. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.04.036 [4] GUO S, HU M, ZAMORA M L, et al. Elucidating severe urban haze formation in China [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(49): 17373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419604111 [5] 张嘉妮, 陈小方, 梁小明, 等. "十三五"挥发性有机物总量控制情景分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018(8): 3544-3551. ZHANG J N, CHEN X F, LIANG X M, et al. Scenario analyses of the volatile organic compound emission allowance and allocation in the 13th five-year period [J]. Environment Science, 2018(8): 3544-3551(in Chinese).
[6] 莫梓伟, 邵敏, 陆思华. 中国挥发性有机物(VOCs)排放源成分谱研究进展 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(9): 2179-2189. MO Z W, SHAO M, LU S H. Review on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) source profiles measured in China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(9): 2179-2189(in Chinese).
[7] 丁锋, 李丛妮. VOCs油气回收工艺探讨与分析 [J]. 天然气与石油, 2016, 34(4): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2016.04.006 DING F, LI C N. Discussion and analysis of the recovery process of VOCs in oil and gas [J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2016, 34(4): 28-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2016.04.006
[8] 龚芳. 我国人为源VOCs排放清单及行业排放特征分析[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2013. GONG F. Anthropogenic volatile organic compounds emission inventory and characteristics[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2013 (in Chinese).
[9] 廖苑如. 多级孔分子筛的制备及其对甲苯吸—脱附性能的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. LIAO WR. Synthesisofhierarchicalzeolitesandtheirperformancesoftolueneadsorptionanddesorption[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[10] 黄海凤, 戎文娟, 顾勇义, 等. ZSM-5沸石分子筛吸附-脱附VOCs的性能研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(12): 3144-3151. HUANG H F, RONG W J, GU Y Y, et al. Adsorption and desorption of VOCs on the ZSM-5 zeolite [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(12): 3144-3151(in Chinese).
[11] ZAITAN H, MANERO M H, VALDÉS H. Application of high silica zeolite ZSM-5 in a hybrid treatment process based on sequential adsorption and ozonation for VOCs elimination [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 41(3): 59-68. [12] PASTI L, RODEGHERO E, SARTI E, et al. Competitive adsorption of VOCs from binary aqueous mixtures on zeolite ZSM-5 [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(59): 54544-54552. doi: 10.1039/C6RA08872D [13] JIANG L, NIE G, ZHU R, et al. Efficient degradation of chlorobenzene in a non-thermal plasma catalytic reactor supported on CeO2/HZSM-5 catalysts [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 55(5): 266-273. [14] 黄海凤, 褚翔, 卢晗锋, 等. 两种介孔分子筛动态吸附VOCs的研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(4): 442-447. HUANG H F, CHU X, LU H F, et al. Dynamic adsorption of volatile organic compounds on two kinds of mesoporous molecular sieves [J]. China Environment Science, 2010, 30(4): 442-447(in Chinese).
[15] HANSEN N, KRISHNA R, VAN BATEN J, et al. Analysis of diffusion limitation in the alkylation of Benzene over H-ZSM-5 by combining quantum chemical calculations, molecular simulations, and a continuum approach [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(1): 235-246. doi: 10.1021/jp8073046 [16] YU W B, DENG L L, YUAN P, et al. Facile preparation of hierarchically porous diatomite/MFI-type zeolite composites and their performance of benzene adsorption: the effects of NaOH etching pretreatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 450-458. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.065 [17] REITMEIER S, GOBIN O, JENTYS A, et al. Enhancement of sorption processes in the zeolite H-ZSM5 by postsyntheticsurface modification [J]. AngewandteChemie(International Edition in English), 2009, 121(3): 541-546. [18] MEUNIER F C, VERBOEKEND D, GILSON J P, et al. Influence of crystal size and probe molecule on diffusion in hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites prepared by desilication [J]. Microporous& MesoporousMaterials, 2012, 148(1): 115-121. [19] 陆璐. ZSM-5分子筛催化苯、甲醇烷基化反应的研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2012. LU L. Study on properties of ZSM-5 catalysis in Benzene alkylation with methanol[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2012 (in Chinese).
[20] WANG H L, MA Z G, YANG J J. Direct amination of Benzene with NH3 and H2O2over hierarchical Fe, Cu/ZSM-5 prepared by post-synthesis treatment of nanocrystallite B-ZSM-5 [J]. Catalysis Letters, 2020, 150(5): 1454-1461. doi: 10.1007/s10562-019-03026-9 [21] YANG Z, CAO JP, REN X Y, et al. Preparation of hierarchical HZSM-5 based sulfated zirconium solid acid catalyst for catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis vapors from lignitepyrolysis [J]. Fuel, 2019, 237(FEB. 1): 1079-1085. [22] LI X, ALWAKWAK A A, REZAEI F, et al. Synthesis of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Y-doped 3D-printed ZSM-5 monoliths and their catalytic performance for n-hexane cracking [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(6): 2740-2748. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b00412 [23] DING J J, RUI Z B, LYU P T, et al. Enhanced formaldehyde oxidation performance over Pt/ZSM-5 through a facile nickel cation modification [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 457(1): 670-675. [24] ZHOU W, LIU J X, LIN L, et al. Enhanced dehydrogenative aromatization of propane by incorporating Fe and Pt into the Zn/HZSM-5 catalyst [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(48): 16246-16256. [25] ZHANG L, PENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Adsorptive and catalytic properties in the removal of volatile organic compounds over zeolite-based materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(6): 800-809. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61073-7 [26] FENG A, YU Y, YU Y, et al. Recent progress in the removal of volatile organic compounds by zeolite and its supported catalysts [J]. ActaChimicaSinica-Chinese Edition, 2018, 76(10): 757-773. [27] 徐晨晨. MFI型分子筛膜的制备方法及其透醇性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. XU C C. Studies on preparation and pervaporation property of MFI-type zeolite membranes[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[28] 缪平. 晶体生长抑制剂含量对ZSM-5分子筛晶化合成及催化MTP反应性能的影响 [J]. 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2018, 240(3): 10-18. MIAO P. Effect of the content of crystal growth inhibitor on the synthesis of ZSM-5 molecular sieve and its performance in MTP reaction [J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2018, 240(3): 10-18(in Chinese).
[29] 杭祖圣, 谈玲华, 黄玉安, 等. 非等温热重法研究g-C3N4热分解动力学 [J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(2): 329-333. HANG Z S, TAN L H, HUANG Y, et al. Non-isothermal kinetics studies on therthermal decomposition of g-C3N4by TG method [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(2): 329-333(in Chinese).
[30] CHEN J P, ISA K. The decomposition of urea and urea derivatives by simultaneous TG/(DTA)/MS [J]. Journal of the Mass Spectrometry Society of Japan, 1998, 46(4): 299-303. doi: 10.5702/massspec.46.299 [31] 王达锐. ZSM-5分子筛孔道和结构多级化的方法及其催化性能研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2016. WANG D R. New methods for preparing hierarchical porous and structured catalysts and their application[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[32] 刘宗梅, 赵朝成, 王帅军, 等. 钾离子掺杂g-C3N4催化剂的制备及其性能研究 [J]. 现代化工, 2017, 37(7): 96-104. LIU Z M, ZHAO CC, WANG S J, et al. Preparation and performance of g-C3N4 catalyst doped by potassium ion [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2017, 37(7): 96-104(in Chinese).
[33] 王涛, 司玉君. 层状石墨相g-C3N4氮化碳的建议制备和表征 [J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(19): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.19.009 WANG T, SI Y J. Preparation and characterization of graphitic carbon nitride g-C3N4 [J]. Materials Review, 2012, 26(19): 36-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.19.009
[34] SHCHERBAN N D, FILONENKO S M, YAREMOV P S, et al. Synthesis and physical-chemical properties of N-containing nanoporous carbons [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2014, 49(12): 4354-4362. doi: 10.1007/s10853-014-8133-3 [35] 喻小伟, 李宇春, 蒋娅, 等. 尿素热解研究及其在脱硝中的应用 [J]. 热力发电, 2012, 41(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2012.01.001 YU X W, LI Y C, JIANG Y, et al. Study on pyrolysis of urea and its application in denitrification [J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2012, 41(1): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3364.2012.01.001
[36] 顾勇义. ZSM-5沸石分子筛吸附—脱附VOCs性能的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2012. GU Y Y. Research on the adsorption-desorption performance of VOCs on ZSM-5 Zeolite[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2012 (in Chinese).
[37] WANG S, BAI P, WEI Y Z, et al. 3D-printed core-shell structured MFI-Type zeolite monoliths for volatile organic compound capture under humid conditions [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11: 38955-38963. [38] AZIZ A, SAJJAD M, KIM M, et al. An efficient Co-ZSM-5 catalyst for the abatement of volatile organics in air: effect of the synthesis protocol [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 15(4): 707-718. -



 下载:
下载: