-
地下水是地球宝贵的资源,是重要的生态环境因子和不可忽视的致灾因子[1-2]。地下水水文地球化学特征的变化往往会影响生态环境及人类社会的发展。因此,研究地下水的水文地球化学特征及其演化机理,对地下水资源的开发利用和保护具有重要作用。刘江涛等对沁河冲洪积扇地下水水化学特征进行研究,发现其主要离子的形成受到碳酸盐矿物的溶解、离子交换和蒸发等的共同影响[3]。魏兴等研究了喀什三角洲地区的地下水水化学特征,结果表明浅层地下水主要受蒸发作用的影响,而承压水受到反向阳离子交换和蒸发浓缩作用的共同影响[4]。Chen等研究了吐鲁番盆地地下水水文地球化学特征,结果表明水文地球化学特征受到碳酸钙沉淀、蒸发浓缩、离子交换以及蒸发岩盐的溶解作用的影响,同时,灌溉影响下的碳酸盐岩的溶解对研究区地下水的盐渍化起着重要作用[5]。
滹沱河流域是石家庄的重要水源地,约80%的生活用水及工农业用水均来自于地下水[6]。同时,滹沱河流域又是南水北调工程河北段的重要承接区之一,因此,其地下水水质的好坏直接影响该地区居民的饮水安全。近年来,随着社会经济的快速发展和城市化进程的日益加快,人类活动对研究区地下水影响程度逐年加强,已经对该地区地下水水质造成影响。先前研究主要关注该地区水质污染状况及评价[7-10]、地球化学模拟[11-12]等方面。
本文针对滹沱河流域浅层地下水水化学演化机理开展研究,结合历史水化学资料,运用piper三线图、Gibbs图和离子比例系数法等水化学方法,对该区域水化学类型及其形成演化机制进行分析讨论,有助于了解该区域地下水的形成过程,同时对该区域地下水环境的评价及合理开发利用提供科学依据。
-
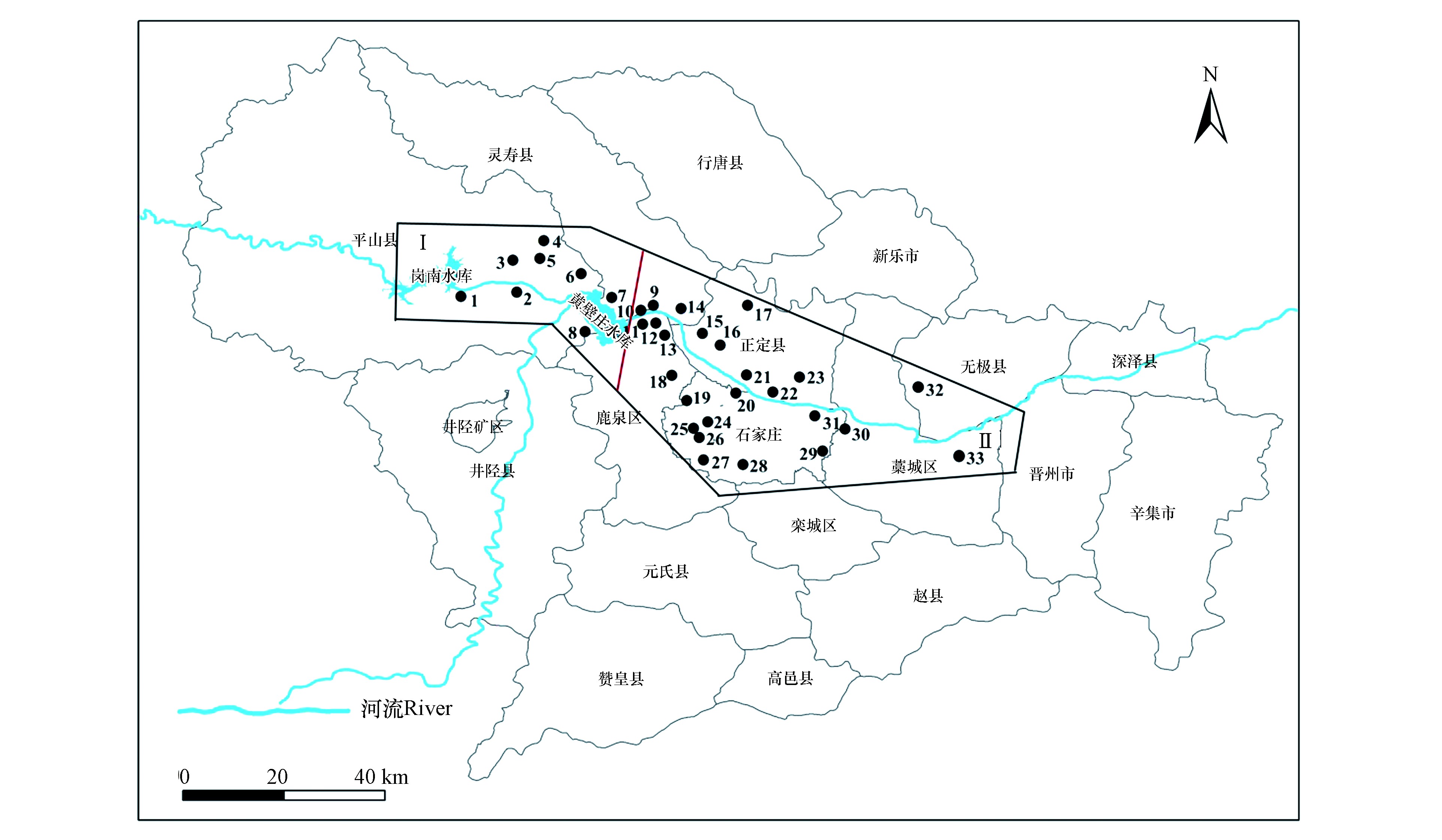
滹沱河流域位于华北平原,属海河流域子牙河水系。研究区地处滹沱河冲洪积扇的中上部,选取岗南水库至藁城段为研究对象,全长约70 km,流域面积约为2442 km2(图1)。整体地势西高东低,地貌形态主要为山前冲洪积作用形成的冲洪积扇群以及由河湖沉积而成的倾斜平原。气候属于温带半干旱半湿润的大陆季风气候,多年平均降雨量为450—700 mm,降雨时空分布不均,其中70%—80%的降水主要集中于6—9月,年平均气温约为13 ℃。
研究区属华北断拗带,区内地质构造以断裂为主。本区第四系沉积物岩性以亚黏土、亚砂土、含砂亚黏土以及卵砾石和砂层为主。研究区内含水层属河北平原第四系巨厚多层型含水层系统,为山前倾斜平原水文地质区,富水性较好。研究区含水层构成及其空间分布具有明显的分带性,水平方向上,自西向东含水层单层厚度由厚变薄,层数由少变多,岩性颗粒由粗变细,富水性由强变弱。地下水主要赋存于第四系松散孔隙含水层,其整体流向为自西北向东南流动。研究区内浅层地下水主要受大气降水、侧向径流、地表水入渗以及农田灌溉水等的补给。本研究根据地形地貌、水文地质条件等将其分为两个水文地质单元:岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间滹沱河河谷平原裂隙孔隙水单元(Ⅰ)、滹沱河冲洪积扇浅层孔隙水单元(Ⅱ)。第Ⅰ水文地质单元,位于山区与平原区的过渡地带,地下水位埋深较浅,一般为2—21 m左右,具有较好的导水性和富水性,以大气降水补给为主;第Ⅱ水文地质单元,沿地下水流向,含水层岩性颗粒由粗变细,层次增多,地下水位埋深逐渐变深,深度多在12—50 m左右。
-
本次研究分别于2018年的枯水期(1月)和丰水期(9月)各采集地下水样品33组(1—8组位于Ⅰ单元,9—33组位于Ⅱ单元),均采自民井或农业灌溉井,采样点分布见图1。
采样前将采样瓶用去离子水洗净,取样时用待取水样润洗3次,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤后于600 mL聚乙烯瓶中保存。其中,用于阳离子测试分析的水样需用1:1硝酸酸化至pH<2。样品采集完成后用封口膜密封冷藏保存。
测试指标包括现场测试指标:pH,使用哈希便携式多参数水质分析仪(HQ40D)测定;室内分析指标包括:K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO
$_4^{2 - } $ 、HCO$_3^ - $ 、NO$_3^ - $ 、总硬度(TH)、溶解性总固体(TDS),参照国家饮用天然矿泉水检测方法标准(GB/T 8538—2008)测定。水样分析由中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所地下水科学与工程实验室完成。 -
为了解研究区地下水水质整体状况,对各采样点水化学参数进行数据统计整理,各化学参数统计见表1。
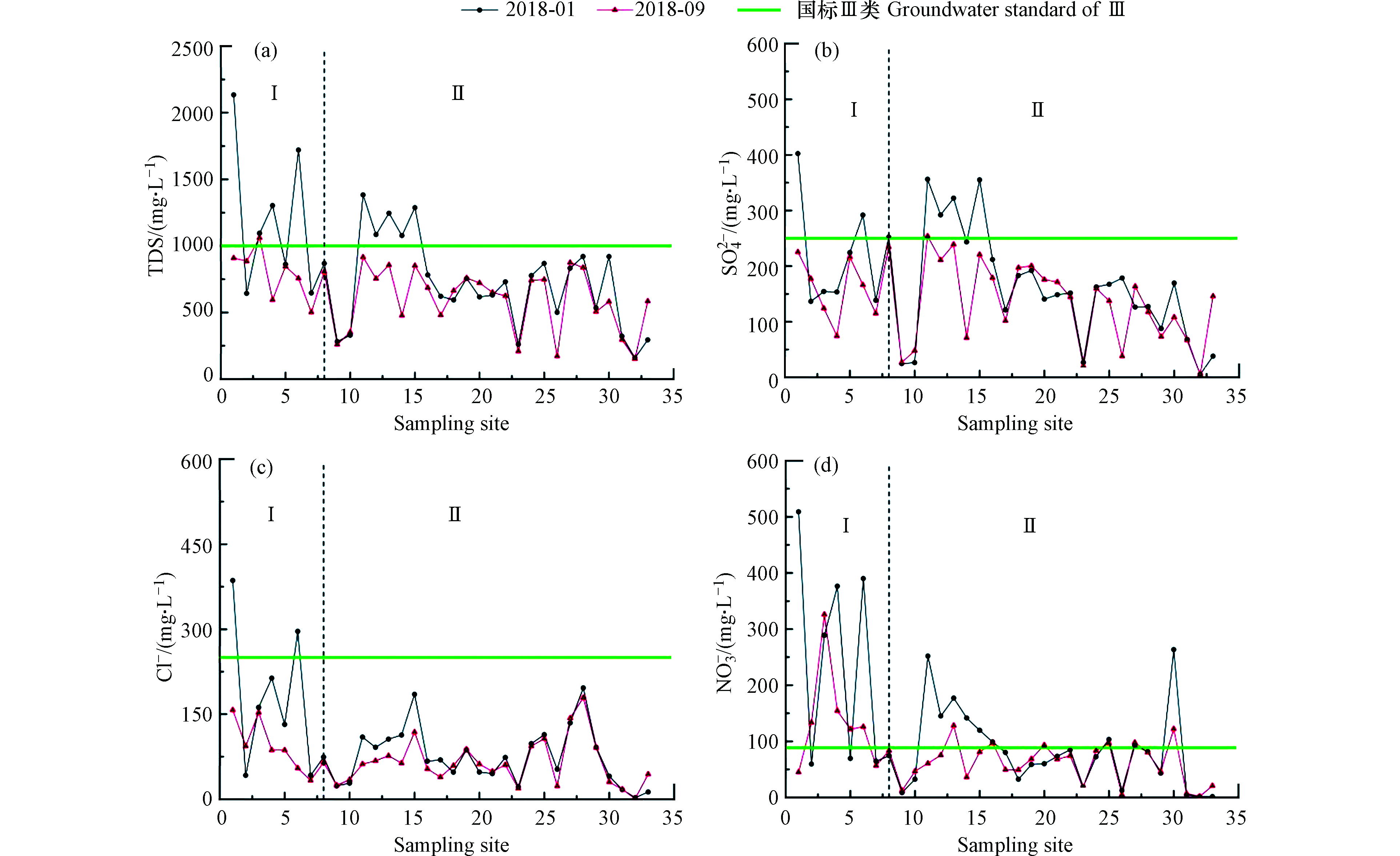
研究区地下水pH值范围6.71—7.94,平均值7.29,呈弱碱性。TDS的浓度范围为158.7—2134.0 mg·L−1,其均值和超标率在枯水期为815.6 mg·L−1和27.3%,丰水期为657.3 mg·L−1和3.0%。枯水期在第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元,TDS均值和超标率分别为1158.8 mg·L−1、50.0%和712.2 mg·L−1、20.0%;丰水期均值和超标率分别为795.1 mg·L−1、12.5%和609.4 mg·L−1、0%。SO
$_4^{2 - } $ 的浓度范围为5.4—402.2 mg·L−1, 均值和超标率在枯水期为172.8 mg·L−1和21.2%,丰水期为143.8 mg·L−1和3.0%。在第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元,SO$_4^{2 - } $ 在枯水期的均值和超标率分别为219.1 mg·L−1、37.5%和157.0 mg·L−1、20.0%;丰水期其均值为166.6 mg·L−1和135.9 mg·L−1,均未出现超标。Cl−仅在枯水期存在超标,超标率为3.0%。在第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元,枯水期Cl−均值和超标率分别为168.5 mg·L−1、25.0%和75.0 mg·L−1、0%;丰水期均值为91.3 mg·L−1和67.9 mg·L−1,且均为超标。值得注意的是TH和NO$_3^ - $ ,其超标率高达69.7%和36.4%,二者的浓度范围分别是77.1—1345.0 mg·L−1和1.6—509.0 mg·L−1,均值和超标率在枯水期为580.2 mg·L−1和75.8%,115.6 mg·L−1和39.4%,丰水期为499.2 mg·L−1和63.6%,82.0 mg·L−1和33.3%;枯水期,TH和NO$_3^ - $ 在第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元均值为780.8、229.1 mg·L−1和520.2、82.4 mg·L−1,超标率高达100.0%、50.0%和64.0%、36.0%;丰水期均值分别为590.9、130.9 mg·L−1和467.3、65.0 mg·L−1,超标率为87.5%、62.5%和60.9%、26.1%,是该地区地下水中主要的污染因子。总体上,地下水水化学指标在枯水期的浓度要高于丰水期,这可能与丰水期降雨稀释作用有关。选择Cl−、NO
$ _3^ - $ 、TDS和SO$_4^{2 - } $ 作为代表性指标分析了该地区地下水水化学指标的时空变化特点。由图2所示,其中,不同水文地质单元间差异较为明显,岗黄水库间沟谷地带(Ⅰ)地下水样品离子浓度较冲洪积扇地带(Ⅱ)波动大,整体呈现由西北向东南递减趋势,表明其可能与地下水水位埋深、包气带岩性和人类活动强度有关。由沟谷地区到冲洪积扇地带,地下水水位埋深增大,包气带颗粒变细,透水性变差,造成污染物不易进入地下水,从而使得离子浓度相对较低。时间上,水化学组分呈现明显的季节性变化,枯水期离子浓度整体高于丰水期,这可能由于丰水期降水较多,降雨入渗补给地下水,通过稀释作用,使得地下水中离子浓度降低。同时,第Ⅰ水文地质单元较第Ⅱ水文地质单元季节性变化更加显著,这是由于在岗黄水库间沟谷地带(Ⅰ)地下水埋深较浅,包气带厚度较小,岩性颗粒较粗,更易受外界条件变化的影响,因此季节性变化更为明显。 -
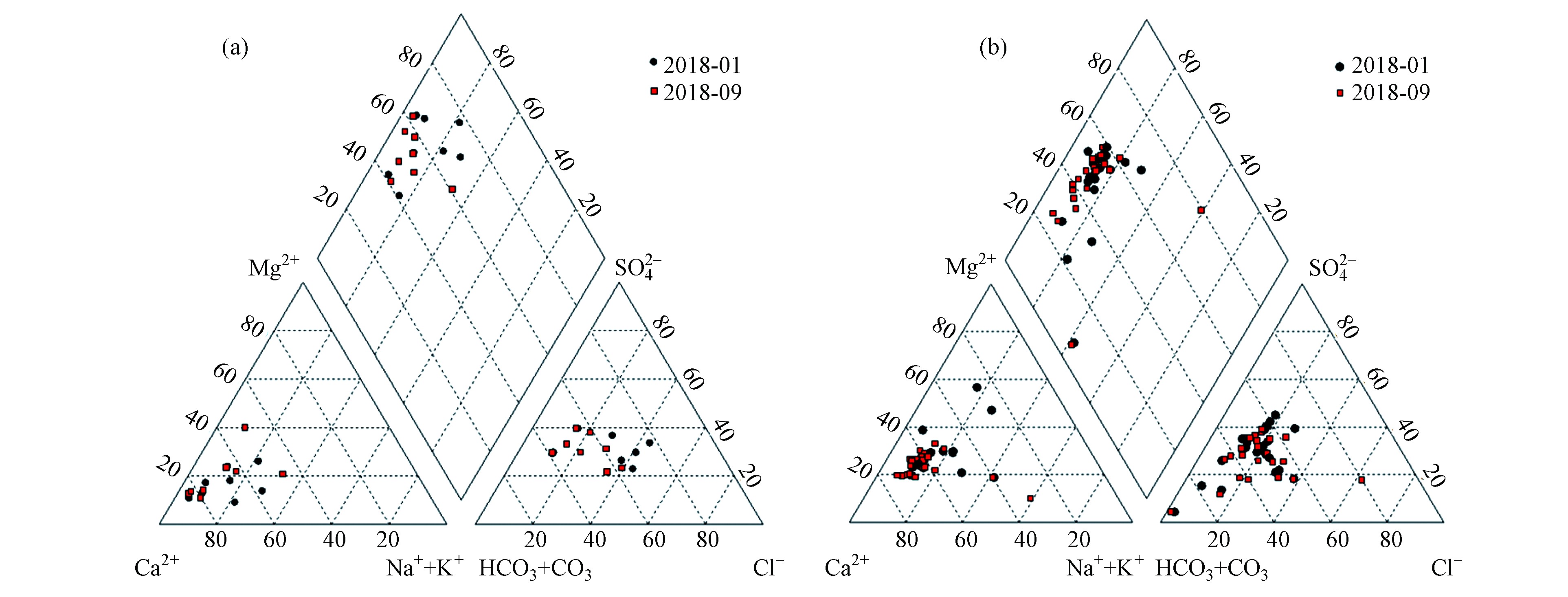
利用Piper三线图对研究区地下水水化学类型、主要离子组成及其演化特征进行分析。如图3所示,按照舒卡列夫分类法对研究区地下水水化学类型进行分类,岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间沟谷地带(Ⅰ)地下水水化学类型主要为HCO3·SO4-Ca型水和Cl·HCO3-Ca型水为主,约占62.5%。滹沱河冲洪积扇地带(Ⅱ)地下水水化学类型以HCO3·SO4-Ca(Ca·Mg)型为主,约占61.7%,硫酸型水比重较大。此外,研究区地下水水化学类型还出现了Cl型水,所占比例约为23%。沿滹沱河水流方向,由岗黄水库间沟谷地带(Ⅰ)至滹沱河冲洪积扇地带(Ⅱ),阴离子整体呈现SO
$_4^{2 - } $ 和Cl−比重逐渐降低,而HCO$_3^ - $ 比重逐渐增加趋势,阳离子整体呈现Ca2+比重递减,而Mg2+和Na+比重递增趋势。这可能与两个分区的地下水位埋深和含水层岩性存在差异有关。在第Ⅰ水文地质单元,地下水水位埋深较浅,且地层岩性较粗,污染物更易进入地下水,且该区内村落未建设污水处理设施,生活污水直接排放进入滹沱河,进而引起地下水SO$_4^{2 - } $ 和Cl−浓度升高[13]。此外,该区域内煤系地层发达,存在多个煤矿和洗煤厂,煤矿排水和洗煤废水均会引起该地区地下水SO$_4^{2 - } $ 浓度升高。然而,在第Ⅱ水文地质单元,地下水埋深加大,含水层岩性颗粒由粗变细,地下水受人类活动影响有所减弱,加之黄壁庄水库大坝拦截,致使上游排放的生活和工业废水未能流入该水文地质单元。因此,沿着地下水流方向,在第Ⅱ水文地质单元表现出SO$_4^{2 - } $ 和Cl−比重逐渐降低,HCO$_3^ - $ 比重逐渐增加。然而,地下水中Ca2+比重递减, Mg2+和Na+比重增加,可能是由于发生阳离子交换作用和碳酸钙沉淀等作用[14-15]。结合历史数据,在20世纪50年代以前,石家庄市地下水开采量较小,受人类活动影响较小,地下水水质较好,其水化学类型主要为HCO3-Ca(Mg)型[16]。1980年以后,石家庄步入城市化大发展时期,随人类活动和自然条件演化的影响,地下水环境变化加剧,且水化学类型演变呈复杂化趋势。此次调查发现,滹沱河流域内硫酸型水比重较高,甚至出现氯型水和钠型水,说明该地区地下水已经受到人类活动的强烈影响。
-
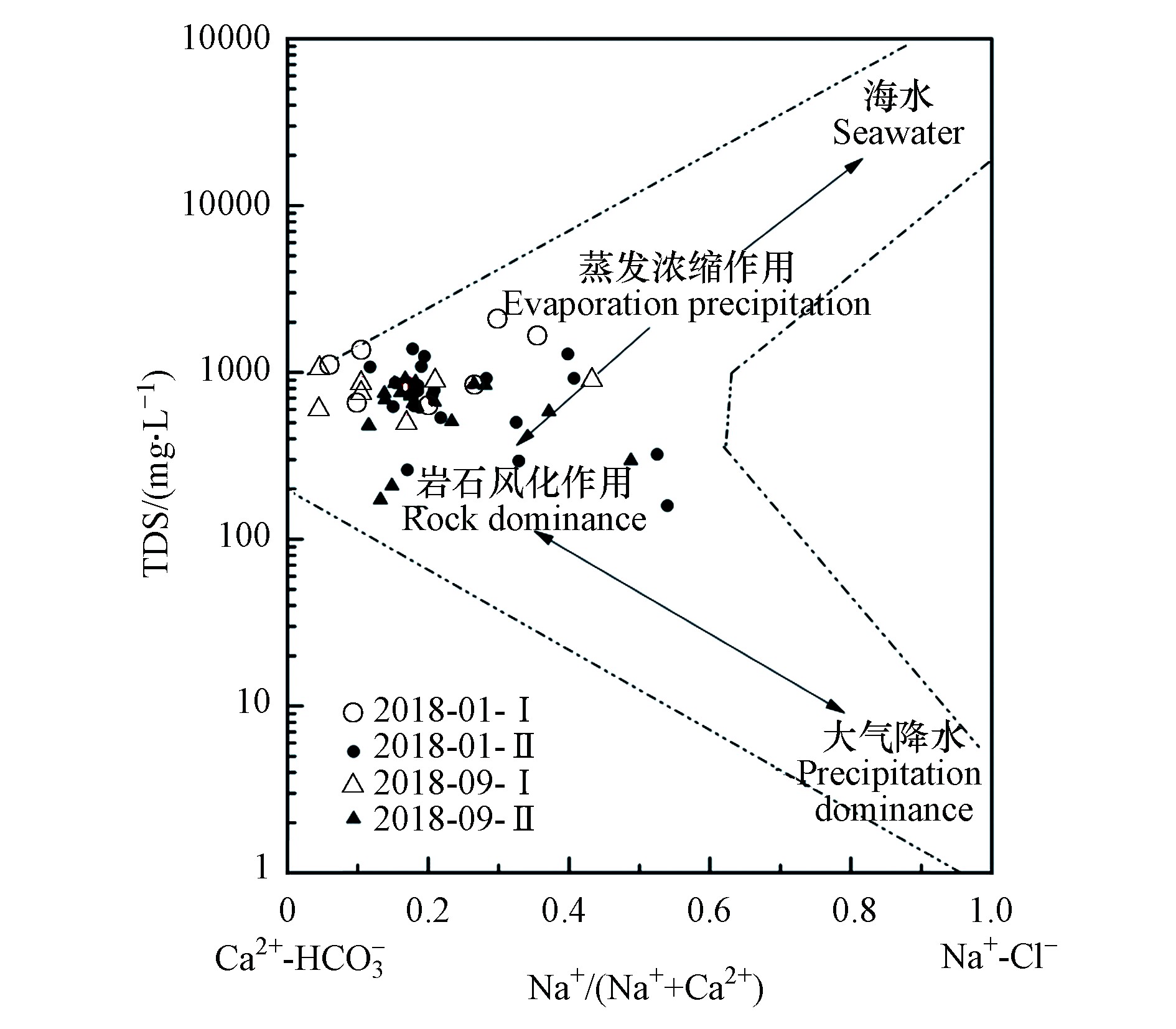
Gibbs图可宏观地反映地下水化学组分的主要控制因素[17]。基于野外采样结果,对研究区地下水环境特征进行分析,如图4所示。研究区TDS主要分布于1000 mg·L−1以内,以Ⅰ—Ⅲ类水为主,阳离子主要以Ca2+为主,阴离子主要以HCO
$_3^ - $ 为主。第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元大部分样品点均位于岩石风化作用区,少部分样品点位于岩石风化与蒸发浓缩作用的过渡地区,且两个水文地质单元间无明显差异,因此,滹沱河流域地下水水化学形成主要受岩土风化-溶滤作用为主,此外,蒸发浓缩作用对其也有一定的影响。 -
为进一步分析滹沱河流域地下水水化学演化过程,应用离子比例系数法对其水文地球化学过程及其成因变化规律进行了分析[18-19]。
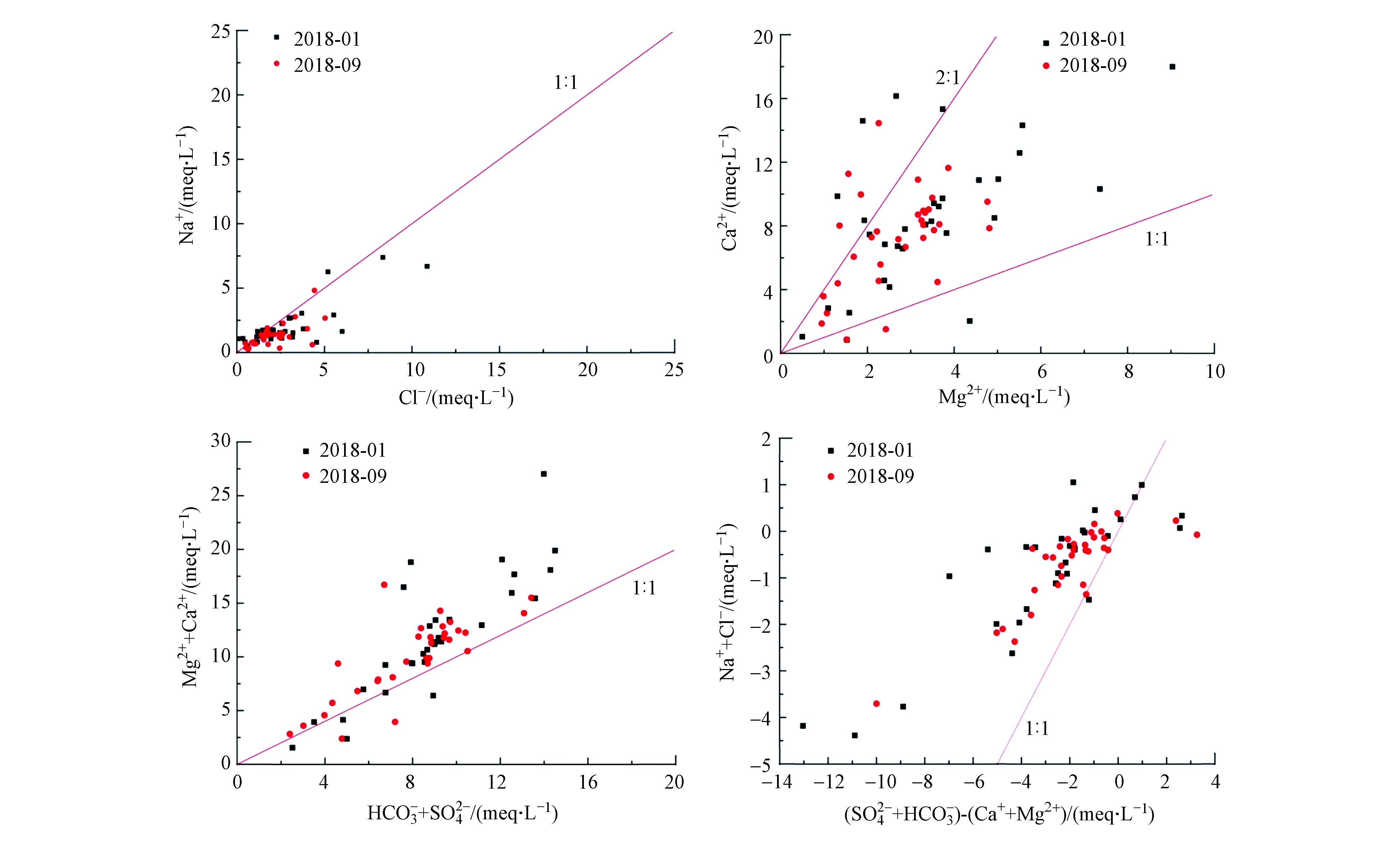
C(Na+)/C(Cl−) (meq·L−1)的比值表征Na+富集程度,海水中二者之比约为0.86,大气降水中二者比值与海水相似[20]。如图5所示,样品点主要集中于图中左下角,表明浓度相对较低。且地下水中Na+和Cl−的比值在1左右,表明其主要来源于岩盐溶解和大气降水。偏离1:1的样品点主要集中在线的下方,表明Cl−可能受到人为污染的影响[21]。
利用Ca2+和Mg2+的毫克当量浓度之比可反映方解石和白云石的溶解情况,若比值接近1,这说明白云石是主要的碳酸盐溶解矿物,若比值增大,可能存在方解石的溶解,比值大于2时,则说明硅酸盐矿物溶解存在[22]。如图5所示,地下水样品点主要集中在1:1—2:1线之间,表明地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于白云石和方解石等碳酸盐矿物的溶解,仅有少部分硅酸盐矿物溶解的存在。
用C(Ca2++Mg2+)/C(HCO
$ _3^ - $ +SO$_4^{2 - } $ )毫克当量浓度之比可表征地下水系统中碳酸盐矿物和硫酸盐矿物的溶解情况。前人研究表明,二者比值若大于1,则主要为碳酸盐的溶解,若比值小于1,则主要为硅酸盐溶解,若近似为1,则既有碳酸盐溶解又有硅酸盐溶解[14, 23]。如图5所示,样品点比值在1:1线上略有偏移,表明SO$_4^{2 - } $ 和Ca2+、Mg2+离子来源略有差异,硫酸根可能来源于硫酸参与碳酸盐岩的溶解以及石膏的溶解等。样品点大部分在1:1线上方,表明研究区地下水中Ca2+、Mg2+离子主要来源于碳酸盐矿物的溶解,硅酸盐矿物溶解较少。水体中C(Ca2++Mg2+-HCO
$_3^ - $ -SO$ _4^{2 - }$ )与C(Na+-Cl−)毫克当量浓度关系表征样品受离子交换作用影响的程度[15]。研究区地下水样品点(图5)二者呈现正相关关系,表明该地区存在离子交换作用,地下水中的Na+将土壤中的Ca2+、Mg2+置换出来,使得地下水中Ca2+、Mg2+浓度升高,进而使得地下水硬度升高。 -
(1)滹沱河冲洪积扇地区浅层地下水中主要的污染因子是TH和NO
$_3^ - $ ,其超标率高达69.7%和36.4%,此外,Cl−、TDS和SO$ _4^{2 - }$ 也有不同程度的超标现象,表明该地区地下水已经受到人类活动的显著影响。同时,第Ⅰ水文地质单元较第Ⅱ水文地质单元,离子浓度和超标率均较高,且季节性变化更为显著。(2)水化学指标的空间变化主要受到人类活动、地下水埋深和地层岩性的控制,其浓度表现为由岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间沟谷地带向冲洪积扇中部递减的趋势;水化学指标的时间变化主要受到季风气候(降雨)的影响,其浓度表现为枯水期要高于丰水期。
(3)研究区内,岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间沟谷地带(Ⅰ)地下水水化学类型主要为HCO3·SO4-Ca型水和HCO3·Cl-Ca型水为主,滹沱河冲洪积扇(Ⅱ)地下水水化学类型以HCO3·SO4-Ca(Mg)型为主。沿地下水流向,地下水TDS有减小趋势,阴离子整体呈现SO
$_4^{2 - } $ 和Cl−比重逐渐降低,而HCO$ _3^ - $ 比重逐渐增加的趋势,阳离子整体呈现Ca2+比重递减,而Mg2+和Na+比重递增趋势。(4)滹沱河流域地下水水化学形成在第Ⅰ、Ⅱ水文地质单元均主要受岩土风化-溶滤作用控制,同时也受到蒸发浓缩作用的影响。Na+和Cl−的主要来源为岩盐溶解和大气降水,此外 Cl−可能受到人为污染的影响。地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于白云石和方解石等碳酸盐矿物的溶解,同时受离子交换作用的影响。SO
$_4^{2 - } $ 的非海相输入占主导,可能来源于硫酸参与碳酸盐岩的溶解以及石膏的溶解等。
滹沱河流域地下水水化学特征演化及成因分析
Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and origin analysis in Hutuo River Basin
-
摘要: 为研究滹沱河流域地下水的水化学特征及其演化规律,2018年1月(枯水期)和9月(丰水期)分别采集该地区地下水样品33组,运用Piper三线图、Gibbs图以及离子比例系数法,全面分析了研究区地下水的时空动态变化、水化学特征及其演化过程。结果表明,研究区地下水主要的污染因子是TH和NO3-,其超标率高达69.7%和36.4%,水化学指标的空间变化主要受到人类活动、地下水埋深和地层岩性的控制,其浓度表现为岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间沟谷地带大于冲洪积扇地区;水化学指标的时间变化主要受到季风气候(降雨)的影响,水化学参数的浓度表现为枯水期要高于丰水期。岗南水库-黄壁庄水库间沟谷地带水化学类型以HCO3·SO4-Ca型水和HCO3·Cl-Ca型水为主,滹沱河冲洪积扇地下水水化学类型以HCO3·SO4-Ca(Mg)型为主。该地区地下水水化学形成主要以岩土风化-溶滤作用为主,同时受蒸发浓缩作用的影响。地下水中的化学组分主要来源于岩盐溶解和大气降水,同时,离子交换作用也有一定的贡献。Abstract: To investigate the hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in Hutuo River Basin, 33 groups of groundwater samples were collected in January (low flow period) and September (high flow period) in 2018. The spatio-temporal dynamic changes, hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of groundwater in the study area were comprehensively analyzed by using Piper trilinear diagram, Gibbs diagram and ion proportion coefficient method. The results show that the main pollution factors of groundwater are TH and NO
$_3^ - $ , and the over standard rates are as high as 69.7% and 36.4%, respectively. The spatial variation of hydrochemical indexes is prinarily controlled by the human activities, the depth of groundwater and the stratum lithology. The main ion concentration in the valley zone between Gangnan and Huangbizhuang Reservoir is higher than that of the alluvial-proluvial fan area. The temporal variation of hydrochemical indexes is mainly affected by monsoon climate (precipitation), characterized by a higher concentration in the dry season. The hydrochemical types of the valley area between Gangnan and Huangbizhuang Reservoir are mainly HCO3·SO4-Ca and HCO3·Cl-Ca type water, while the hydrochemical type of groundwater in the Hutuo River alluvial-proluvial fan is dominated by HCO3·SO4-Ca(Mg) type. The hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in this area is principally controlled by rock weathering-dissolution, and it is also affected by evaporation-concentration process. The chemical components of groundwater mainly originated from the dissolution of halite and atmospheric precipitation, which is also influenced by the ion exchange process.-
Key words:
- Hutuo River Basin /
- hydrochemical characteristic /
- groundwater /
- evolution law
-

-
图 5 滹沱河流域地下水Na+和Cl−(a)和研究区地下水Ca2+和Mg2+(b)、 (Ca2++Mg2+)与(HCO
$_3^ - $ +SO$_4^{2 - } $ )(c)、 (Ca2++Mg2+-HCO$_3^ - $ -SO$_4^{2 - } $ )与(Na+-Cl−)(d)关系图Figure 5. Relationship between Na+ and Cl− (a) of groundwater in Hutuo River Basin and Ca2+/Mg2+ (b) ,(Ca2++Mg2+)/(HCO
$_3^ - $ +SO$_4^{2 - } $ ) (c),(Ca2++Mg2+-HCO$_3^ - $ -SO$_4^{2 - } $ )/(Na+-Cl−)(d)of groundwater in the study area表 1 研究区样品水质指标统计表
Table 1. Statistics of hydrochemical parameters of the study area
参数
Parameters范围/ (mg·L−1) Range 均值/ (mg·L−1) Mean 超标率/%
Over standard rate国标Ⅲ类*
Standard2018.1 2018.9 2018.1 2018.9 pH 7.10—7.94 6.71—7.41 7.43 7.14 0 6.50—8.50 K+ 0.3—24.3 0.6—8.0 3.1 2.1 — — Na+ 9.1—169.7 5.7—110.8 45.5 30.6 0 200 Ca2+ 20.9—359.8 37.4—288.9 168.8 147.8 — — Mg2+ 6.0—108.4 11.4—57.7 38.5 31.6 — — Cl− 2.5—385.9 17.3—179.0 96.5 73.9 3.0 250 SO $_4^ {2-} $ 5.4—402.2 20.3—253.9 172.8 143.8 12.1 250 HCO $_3^ - $ 147.0—462.1 98.1—475.6 310.0 290.4 — — NO $_3^ - $ 1.6—509.0 5.0—326.2 115.6 82.0 36.4 88.6 TH 77.1—1345.0 140.2—833.3 580.2 499.2 69.7 450 TDS 158.7—2134.0 171.8—1061.2 815.6 657.3 15.2 1000 *为地下水质量标准(GB/T 14848-2017)中三类水标准. -
[1] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 第六版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011. ZHANG R Q, LIANG X, JIN M G, et al. Fundamentals of hydrogeology[M]. 6th Edition. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011(in Chinese).
[2] MA B, JIN M G, LIANG X, et al. Groundwater mixing and mineralization processes in a mountain–oasis–desert basin, northwest China: Hydrogeochemistry and environmental tracer indicators [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(D22): 233-250. [3] 刘江涛, 蔡五田, 曹月婷, 等. 沁河冲洪积扇地下水水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(12): 142-153. LIU J T, CAI W T, CAO Y T, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and the origin in alluvial-proluvial fan of Qinhe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(12): 142-153(in Chinese).
[4] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051. WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar Delta area in Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051(in Chinese).
[5] CHEN L, WANG G C, HU F S, et al. Groundwater hydrochemistry and isotope geochemistry in the Turpan Basin, northwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2014, 6(4): 378-388. doi: 10.1007/s40333-013-0249-9 [6] 李亚松, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等. 滹沱河冲积平原浅层地下水有机污染研究 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2012, 26(8): 52-56. LI Y S, ZHANG Z J, FEI Y H, et al. Preliminary study on organic pollution of shallow groundwater in the alluvial plain of Hutuo River [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2012, 26(8): 52-56(in Chinese).
[7] 李亚松, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等. 地下水质量综合评价方法优选与分析——以滹沱河冲洪积扇为例 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(1): 6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.01.002 LI Y S, ZHANG Z J, FEI Y H, et al. Optimal selection and analysis of groundwater quality evaluation methods: A case study in the Hutuo River alluvial pluvial fan [J]. Hydrogeology& Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(1): 6-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.01.002
[8] 昌盛, 耿梦娇, 刘琰, 等. 滹沱河冲洪积扇地下水中多环芳烃的污染特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(7): 2058-2066. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.07.022 CHANG S, GENG M J, LIU Y, et al. Pollution characteristic of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the groundwater of Hutuo River Pluvial Fan [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(7): 2058-2066(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.07.022
[9] 李亚松, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等. 河北省滹沱河冲积平原地下水质量及污染特征研究 [J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(2): 169-176. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.02.07 LI Y S, ZHANG Z J, FEI Y H, et al. Groundwater quality and contamination characteristics in the Hutuo River Plain area, Hebei Province [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(2): 169-176(in Chinese). doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.02.07
[10] LI Y S, ZHANG Z J, FEI Y H, et al. Investigation of quality and pollution characteristics of groundwater in the Hutuo River Alluvial Plain, North China Plain [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(7): 581. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5366-2 [11] 张翠云, 刘文生. 河北平源浅层地下水地球化学演化模拟 [J]. 地学前缘, 1996, 3(1/2): 245-248. ZHANG C Y, LIU W S. Geochemical evolution simulation of shallow groundwater in Hebei Plain [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996, 3(1/2): 245-248(in Chinese).
[12] ZHANG X W, HE J T, HE B N, et al. Assessment, formation mechanism, and different source contributions of dissolved salt pollution in the shallow groundwater of Hutuo River alluvial-pluvial fan in the North China Plain [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(35): 35742-35756. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06502-2 [13] ZHANG Q Q, WANG H W, WANG Y C, et al. Groundwater quality assessment and pollution source apportionment in an intensely exploited region of northern China [J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(20): 16639-16650. [14] 孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 等. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化 [J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141. SUN H Y, MAO Q G, WEI X F, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation evolutionary mechanism of the groundwater system in the Hami basin [J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141(in Chinese).
[15] JIA H, QIAN H, ZHENG L, et al. Alterations to groundwater chemistry due to modern water transfer for irrigation over decades [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 717: 137170. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137170 [16] 曾渊深. 石家庄供水水文地质勘测报告[R]. 河北省地质局水文地质工程地质大队, 1959. ZENG S Y. The report of hydrogeological investigation for water supply in Shijiazhuang[R]. Hydrogeology and engineering geology team of Hebei geological bureau, 1959(in Chinese).
[17] MARANDI A, SHAND P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 29: 209-212. [18] XING L N, GUO H M, ZHAN Y H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70-71: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.017 [19] 陈晨, 高宗军, 李伟, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504 CHEN C, GAO Z J, LI W, et al. Characteristics and possible factors of hydrochemistry in the groundwater in Tailai basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504
[20] 张涛, 蔡五田, 李颖智, 等. 尼洋河流域水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545. ZHANG T, CAI W T, LI Y Z, et al. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the water of the Niyang River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545(in Chinese).
[21] 覃彤, 汤庆佳, 张强, 等. 桂西大型岩溶地下河系统离子来源及碳稳定同位素信息——以坡心地下河流域为例 [J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2): 302-315. QIN T, TANG Q J, ZHANG Q, et al. Chemical ions source analysis and stable isotope implications of different water bodies in large karst underground river system: A case study of Poxin groundwater basin in Guangxi [J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 302-315(in Chinese).
[22] MAYO A L, LOUCKS M D. Solute and isotopic geochemistry and ground water flow in the central Wasatch Range, Utah [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1995, 172(1-4): 31-59. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-E [23] ABDELKADER R, LARBI D, RIHAB H, et al. Geochemical characterization of groundwater from shallow aquifer surrounding Fetzara Lake N. E. Algeria [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2012, 5(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12517-010-0202-6 -




 下载:
下载: