-
塑料是一种高分子有机聚合物,被广泛应用于建筑建造,汽车制造,电子和农业生产等领域。2018年塑料的全球年产量已达3.6亿吨,并仍将持续增长[1]。除去工业活动直接产生的微米级塑料,塑料制品也会在环境中发生物理、化学和生物作用,碎化降解为尺寸小于5 mm的微塑料颗粒或碎片[2-4]。英国普利茅斯大学的汤普森等在2004年首次将直径小于5 mm的塑料纤维、颗粒或薄膜定义为“微塑料”[5]。相比大塑料,微塑料体积小、在环境中分布广泛,更容易被生物摄入。研究发现,微塑料在鱼类、贝类等水生生物体内普遍存在,并会发生食物链迁移现象[6-7],从而对生物体的健康和生态系统构成潜在威胁。
文献计量分析是一种基于数学统计的文献和信息挖掘方法,可以通过文献关键词的聚类关系来反映研究趋势和热点,已成为各个科学领域进行全球分析的重要工具[8-10]。微塑料作为一种新兴的环境污染物,全球都对微塑料研究给予了越来越多的关注。目前,已有许多微塑料及其相关领域的文献,但未见对全球微塑料研究文献进行统计分析并总结的相关综述,在分析当前研究热点和未来趋势方面尚显不足。
本文通过创建国际微塑料研究关键词聚类共现网络图和关键词突现图来探索全球微塑料研究的发展状况,创建国内微塑料研究关键词共现图来揭示我国微塑料研究的热点及趋势并对当前微塑料研究的热点和挑战进行了系统地总结。此外,还评估了未来微塑料研究的重点和前景,为研究人员提供了参考和思路。
-
本研究外文数据来源于Web of Science核心合集,以“microplastic*”OR “micro-plastic” OR “micro-plastics” OR “micro-sized plastic” OR “micro-sized plastics”为搜索主题词,由于“微塑料”一词是普利茅斯大学在2004年定义的,是开始进行微塑料研究的一个里程碑,因此选择2004年作为本研究的起始年份。2020年数据还在更新,为包含所有的出版年,检索时间跨度设为2004—2019年,文献类型选择数量较多的综述(9.49%)和研究论文(82.77%),剔除微塑性变形、金属材料的微塑性和微塑形应变等与材料力学和物理学相关的文献,最终获得2560篇有效文献作为分析数据。
中文数据来源于中国知网(CNKI),以“微塑料”为主题进行检索,时间跨度为2004—2019年,剔除其中外文期刊、会议报告等无效论文,共检索到226篇有效文献作为分析数据。
社交网络分析(SNA)是文献计量学中共现分析的主要方法,该方法可以反映微塑料研究的热点和趋势,具有多维信息显示的功能。VOSviewer和CiteSpace是对研究热点和主题等文献信息进行数据挖掘和可视化分析常用的软件。本研究主要利用文献计量分析软件VOSviewer和CiteSpace对微塑料领域的文献进行聚类共现分析。具体步骤如下:对WoS核心库中检索到的2560条数据,通过选择记录内容为“全记录与引用的参考文献”,文件格式为“制表符分隔(Win)”将数据导出,并用VOSviewer进行关键词共现分析;对于CNKI库中检索出的226条文献,先利用EndNote将数据转化为“.ris”格式,再导入至VOSviewer中,进而得到高频关键词关联关系的共现网络可视图。国际微塑料研究关键词演变网络图是将2506条数据以Refworks格式导入至CiteSpace中而得到,通过识别具有高集中度的关键字和检测关键词的变化情况,分析微塑料的研究趋势变化。
-
关键词共现分析是科学计量学中一种常见的研究方法。通过关键词共现分析可以描述微塑料研究领域的结构组成并揭示该领域的研究热点,研究热点包含当前研究热点和研究趋势中不断出现的新热点,在VOSviewer中,使用共现分析生成国际与微塑料研究相关文章的关键词共现网络图。“突现词”是指一段时间内经常被引用的词,利用CiteSpace进行关键词突现分析可以探索国际微塑料的研究动态,有效揭示该领域的研究前沿。
-
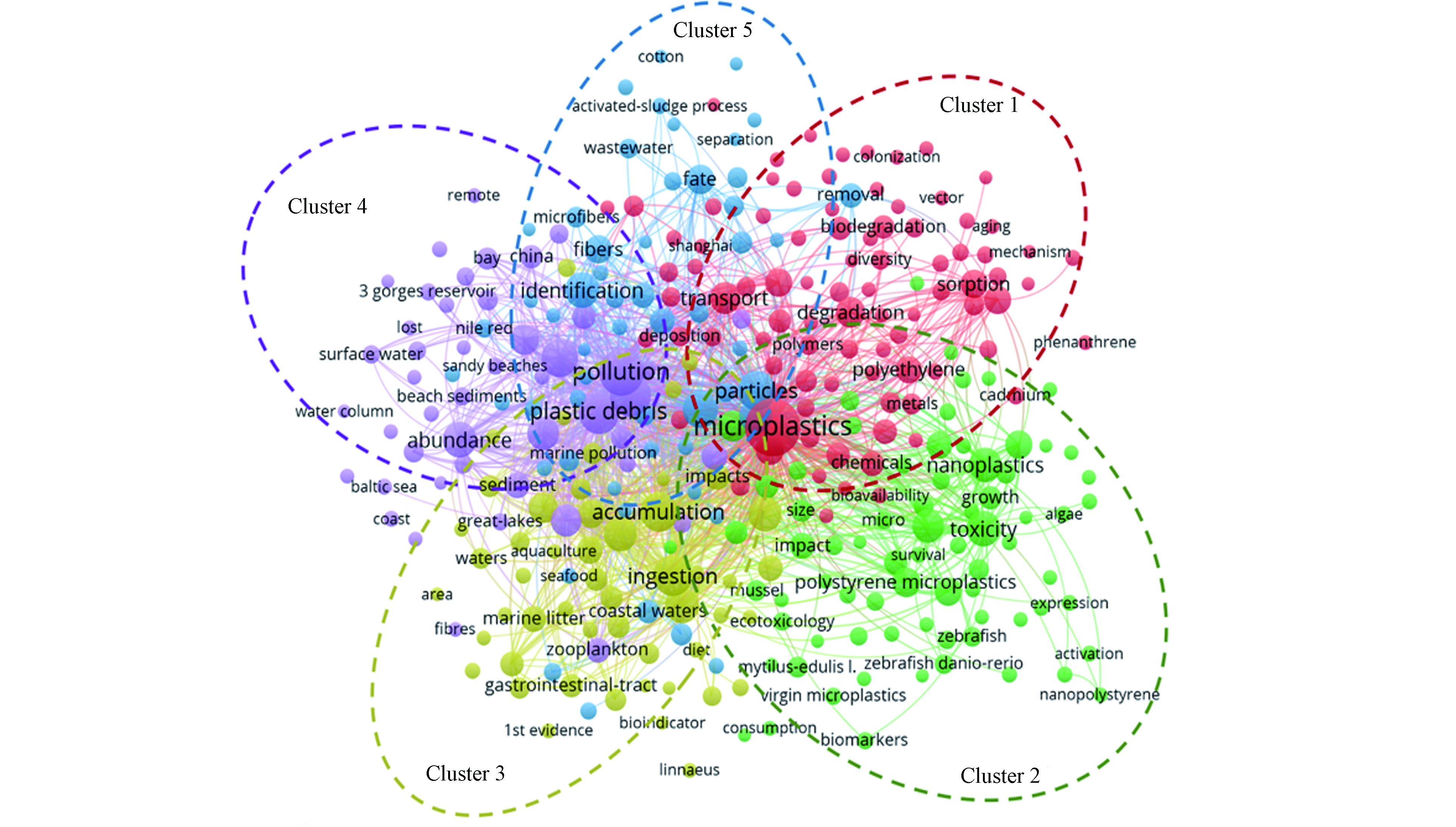
国际微塑料研究关键词共现图如图1所示。图1中的节点代表关键词,相同颜色的节点表示同一聚类,同一聚类中的关键字都具有相似的研究主题。根据图中形成的5个聚类可以将国际微塑料研究热点与主题概括为“微塑料的生物毒性作用”、“微塑料在海洋环境中的分布与丰度”、“微塑料的迁移与鉴定方法”、“微塑料的吸附作用”和“微塑料的归趋和降解”的5个方面。对2020年已有文献进行关键词共现分析,形成的5个聚类与图1相比,未有明显差异(图S1),故该研究热点和趋势具有一定的延续性。其中,聚类1“微塑料的生物毒性作用”和聚类4“微塑料的吸附作用”主要从微塑料的吸附特性入手,研究微塑料单一毒性及其与有毒物质(重金属和有机污染物)的复合毒性效应对生物体的影响。聚类2“微塑料在海洋环境中的分布与丰度”揭示了微塑料在全球各海域中的分布,从而明确海洋中微塑料的污染现状和成因。聚类3“微塑料的迁移与鉴定方法”和聚类5“微塑料的归趋和降解”则对微塑料在环境中的迁移路径、环境归趋进行了分析,并对其监测手段(定性定量分析技术)和降解方式进行了总结,有利于形成较为完整的研究体系。
(1)聚类1:微塑料的生物毒性作用。该主题涵盖图中所有紫色的关键词,包括ingestion、toxicity、exposure、fish、nanoplastics等75个关键词。微塑料不易降解,大多数微塑料会在环境中累积数百年或更长时间,微塑料一旦摄入,会对动植物产生多种生物毒性效应. 对植物来说,微塑料会阻碍浮游植物的光合作用,当聚氯乙烯微塑料颗粒和聚丙烯微塑料颗粒浓度为250 mg·L−1时,相对于对照组,蛋白核小球藻的叶绿素a含量最大降低55.23%[11];对动物来说,微塑料颗粒在摄入后会长期停留在体内,进入胃肠道周边其他组织,甚至是循环系统,引起肠道损伤和扰乱生物体内能量流动,并导致生物体存活率降低、生长繁殖能力降低及免疫和遗传毒性的产生。Browne等[12]研究发现,微塑料通过肠道进入贻贝的循环系统,在经微塑料暴露3 h后,贻贝的血细胞吞噬功能、血淋巴氧化程度和摄食能力均下降;在暴露48 d之后,在其血淋巴的组织中仍检测到了微塑料的存在。此外,微塑料颗粒被生物摄入后还会通过食物链传递,不仅对浮游植物、浮游动物、鱼类等不同营养级生物产生一系列的毒性效应,最终还可能对人类健康产生直接或间接影响,严重影响生态环境系统的可持续发展[13]。例如,聚苯乙烯(PS)被大型溞摄食后能够通过食物链转移到鲤鱼体内并富集,影响了鲤鱼的脂质代谢和行为活动[14],人类食用了这些受污染的鱼肉,可能会威胁到人类健康。
塑料中的添加剂在环境中的释放是造成微塑料生物毒性的原因。最常见的塑化剂邻苯二甲酸二酯,释放到环境后便成为环境雌激素中的酞酸酯类,当摄入并累积到一定的数量后,就会以假激素的形式向身体传递虚拟的化学讯号,从而干扰生物体的内分泌功能,甚至影响其生殖和发育。除了单一生物毒性外,微塑料颗粒与吸附的其他污染物还会对生物体产生复合毒性效应。但是,复合毒性效应是否促进了污染物在生物体内富集及加剧其毒性效应是一个极其复杂的问题,目前还未得到充分的解释。一些研究认为微塑料会对其他污染物产生吸附富集作用,吸附的污染物在生物体内释放会对生物体造成更为严重的危害,如天然有机质和微塑料的联合作用可促进铜在斑马鱼中的积累,进而加剧铜对肝脏和肠胃的毒性[15]。但是也有一些实验研究表明,微塑料会吸附生物体中的污染物导致游离有机污染物的浓度显著降低,从而降低了生物毒性。Zocchi等[16]测试了草甘膦化学制剂与聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)对大型溞的联合毒性影响,发现在单一化学制剂的条件下,对大型溞有致死效应,然而在复合体系中,微塑料降低了化学制剂的毒性,且致死效果不明显。微塑料毒性研究结果产生差异的原因可能为:(1)微塑料的复合生物毒性与污染物和微塑料的种类、污染物在生物体内的停留时间以及不同微塑料的吸附/解吸能力都有关系,不同的实验条件可能造成了毒性评估结果的差异。(2)目前的毒性研究是在实验室条件下进行,与实际环境相比,微塑料的浓度高且实验中选择的生物体和微塑料较为单一,这可能会夸大微塑料的生物毒性。(3)检测手段不能定性和定量分析添加剂或污染物在生物体内的释放,从而使不同毒性实验的结果难以对比。
(2)聚类2:微塑料在海洋环境中的分布与丰度,该主题涵盖图中所有黄色的关键词,包括marine debris、abundance、marine litter等75个关键词。微塑料在全球大部分海洋(太平洋、印度洋、大西洋和北冰洋)、河流湖泊、沉积物中均有分布。近年来,关于微塑料在环境中分布与丰度的研究主要集中在海洋环境。表1中总结了全球各海域中微塑料的分布情况。
不同海岸带地区的微塑料粒径和丰度不同,且变化范围较大。其中,微塑料在大西洋分布广泛,沿北/南纬度梯度收集到的样本中微塑料的丰度为0—8.5 颗·m−3[17];在印度洋收集的样本中微塑料的种类主要为PET、聚丙烯(PP)和发泡PS,丰度达(35.8±42.5)颗·m−2[20];北冰洋海域和南极洲的罗斯海海水中也发现了微塑料碎片,证明微塑料已经侵入了极地地区[21, 23]。微塑料在水环境的分布和丰度受风,潮汐和洋流等环境因素的影响:风的混合作用会改变微塑料的垂直分布;洋流的作用使微塑料在部分区域聚集,形成一个微塑料的“汇”;潮汐可以将微塑料冲刷到海岸,使暴露于海流和潮汐流的地区具有更高的微塑性丰度。除了环境因素,人类活动和城市化也会影响微塑料的分布和丰度。在沙特阿拉伯红海的海滩沉积物中微塑料的丰度达到160 颗·m−2,其分布主要受人类活动的影响[24];在中国渤海旅游区的海滩沉积物中发现以聚乙烯醋酸乙烯酯(PEVA),轻密度聚乙烯(LDPE)和PS为主的微塑料,其来源于游客丢弃的塑料产品和衣服中释放的纤维[25]。当前微塑料的分布调查存在研究数据的缺乏和采样方法和定量单位差异的问题,各国的研究结果难以进行直接比较。因此,应该在考虑微塑料种类、体积、颜色和形态多样性的前提下,建立全球统一的海洋微塑料研究监测和分析鉴定方法来确定全球河流和河口微塑料的污染情况。
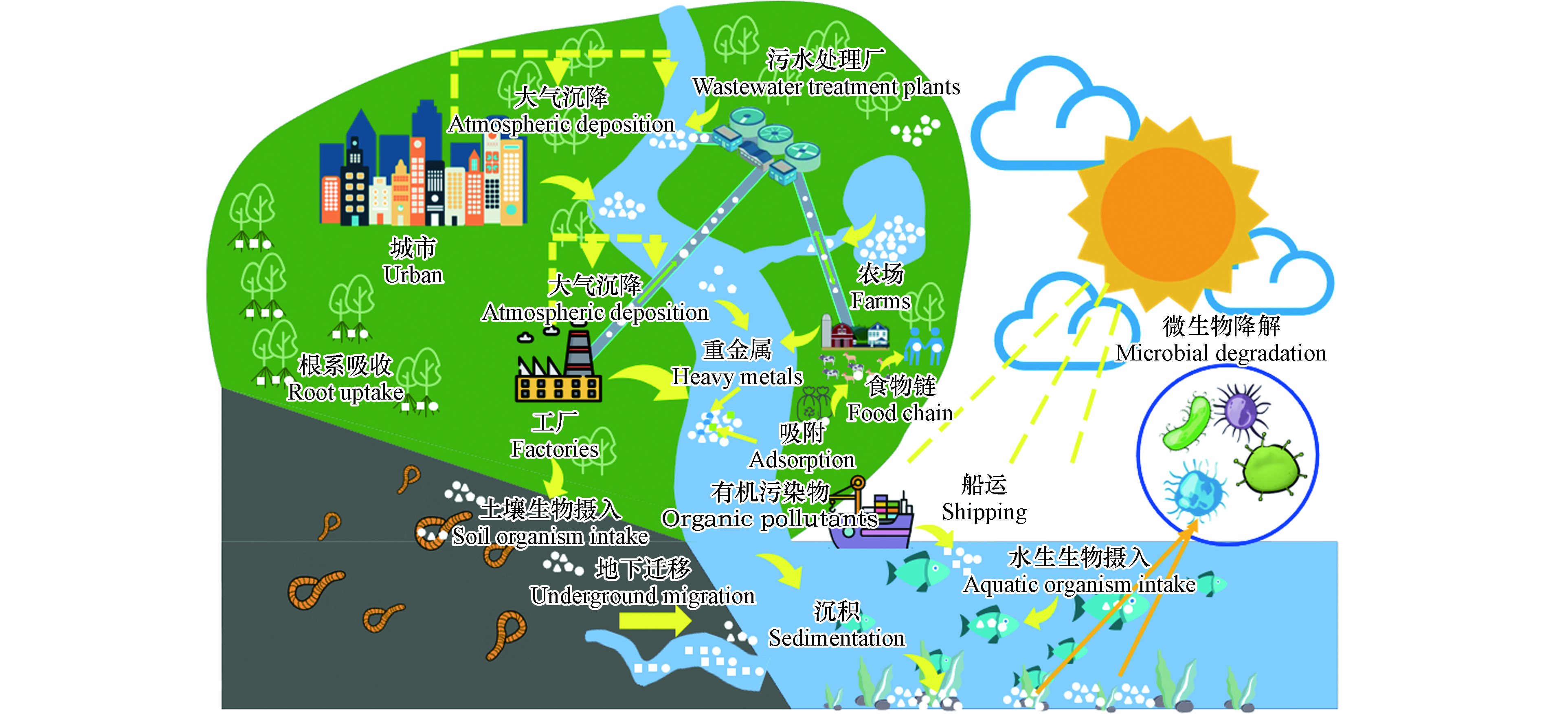
(3)聚类3:微塑料的迁移与鉴定方法。该主题涵盖图中所有红色的关键词,包括sediment、identification、transport、spectroscopy等59个关键词。微塑料可以在不同的环境介质(大气、水和陆地)中发生迁移,迁移过程见图2。陆地环境中的微塑料易在地表径流和风力等作用下迁移扩散至水环境,且部分微塑料会在重力或土壤动物的作用下迁移到深层土壤,甚至进入地下水系统;海洋或河流中的微塑料会在涨潮或发生洪水时向陆地迁移,水体表面的微塑料能够在紫外辐射的作用下发生分解,密度较小的微塑料会通过河流迁移至海洋环境中,密度较大的微塑料会沉降在底部的沉积物中;大气中的微塑料可通过雨水或沉降作用进入到水体和陆地环境中。此外,微塑料也可以通过食物链,由低营养级生物向高营养级生物迁移。Lwanga等[27]研究了微塑料在土-蚯蚓-鸡食物链中的迁移,微塑料的浓度在鸡粪中达到了最大值。同时,人类排泄物中同样检测到了微塑料的存在,表明环境中的微塑料会通过食物链的传递转移给人类。微塑料的迁移过程受微塑料本身性质、水文等因素的影响:环境中的微塑料具有较大的比表面积,导致其易吸附有毒污染物、海藻和微生物等,进而影响其迁移过程;水动力条件会影响微塑料碎片在水体中的垂直迁移,使其在沉积物表面发生不均匀分布,如法国布列斯特湾表层水体和沉积物中微塑料的含量分别为(0.24±0.35)颗·m−3和(0.97±2.08)颗·kg−1干重[28];除此之外,气候也同样会对微塑料的迁移产生影响,O'connor等[29]在沙土柱中微塑料渗透迁移模拟实验中发现,微塑料的迁移深度随干-湿循环次数的增加而显著增加,而表面微塑料浓度对迁移深度影响较小。
为了更好地进行微塑料相关研究,统一、准确的分析方法必不可少。定性分析主要分析微塑料的物理形态和化学组分,而定量分析则是分析微塑料的数量,多用丰度和浓度来表示。目前,微塑料的定性定量分析的方法有目视鉴别法、光谱分析法和热分析法等。目视鉴别法快速、方便,但目视鉴别法不能用于识别粒径<500 µm的颗粒[30]。此外,目视鉴别法非常耗时,即使是经验丰富的人也无法明确地区分所有潜在的微粒;光谱分析法主要分为傅里叶变换红外光谱法与拉曼光谱法,红外光谱法是较为普遍的鉴定微塑料化学组成的方法,具有快速、操作简单、鉴定准确等优点[31]。该方法通过对待测颗粒进行图谱分析,获得聚合物的成分信息,并与标准谱库对比,从而识别出微塑料颗粒。但其易受被测微塑料老化程度、不均性等因素的干扰。拉曼光谱法是将塑料的特征拉曼光谱与光谱库比较来识别微塑料的组成,检测限可以达到500 nm[32],但是拉曼光谱不能测量在激光中产生荧光效应的样品,在测量之前需提纯样品以防止荧光效应。将显微镜与拉曼光谱结合,可以获得表面官能团和微观形貌信息,已成功用于鉴定不同环境样品中的微塑料颗粒;热分析法是通过待测样品加热后的分解产物来鉴别微塑料成分,具有样品用量小,无需前处理等优点,但会对样品造成破坏。示差扫描量热法、热重分析法和裂解气相色谱-质谱法是三种最常见的热分析方法,通常与其他分析方法联用来提高目标组分的检出灵敏度。微塑料鉴别分析是一项较为复杂的工作,在实际应用中,应该充分考虑微塑料的组分特征,建立适用于不同介质的联合分析方法,为实现微塑料的定性定量分析提供技术保证。
(4)聚类4:微塑料的吸附作用。该主题涵盖图中所有绿色的关键词,包括sorption、bioaccumulation、persistent organic pollutants等50个关键词。微塑料具有颗粒小、比表面积大等特点,使其对持久性有机污染物、重金属和抗生素等有较强的吸附富集能力,从而成为污染物的载体[33-34],它们随颗粒一起进入生物体,并可以通过吸附解吸作用改变共存有机污染物的浓度、环境行为和生态风险[35]。有机物的性质、微塑料的性质(类型、粒径大小和风化程度)以及环境因素都会影响微塑料对有机污染物的吸附[36],如聚乙烯(PE)和聚氯乙烯(PVC)对全氟辛烷磺酰胺(PFOSA)的分配系数比PS高,导致PE和PVC对PFOSA的吸附能力比PS强[37];在0.125—5.000 mm范围内,PP的粒径越小,其吸附的3,6-二溴咔唑和1,3,6,8-四溴咔唑越多[38];海滩中风化的PS颗粒具有更大的比表面积和氧化程度,其对四环素的吸附能力是未风化PS的2倍[39]。徐鹏程等[40]研究了在人工紫外光照射下老化的微塑料对2,2',4,4'-四溴联苯醚(BDE-47)的吸附行为。结果表明,老化后PS的表面产生了 —OH、 C—O和 C—OH等含氧官能团,颗粒表面的极性增加,其对弱极性有机物BDE-47的吸附能力降低。此外,与有机污染物相似,微塑料对金属的吸附也受微塑料老化程度的影响。由于老化PVC的表面积和极性更高,其对Cu的吸附量比未老化的PS对Cu的吸附量多[41]。环境pH值、离子强度和环境中共存的有机污染物都会影响微塑料的吸附能力。pH值会改变微塑料和有机污染物在溶液中的存在形式,进而通过静电作用影响微塑料的吸附能力。以PS颗粒吸附环丙沙星为例,当pH值较高时,环丙沙星表现为负电性,与带负电的PS颗粒间的静电排斥力增大,导致PS颗粒吸附能力相应降低[42];在水环境中存在的离子和多种污染物可能会与有机污染物竞争微塑料表面的吸附位点,从而影响吸附过程。Llorca等[43]发现,与淡水相比,海水中存在的无机盐离子和天然有机物会显著降低高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)对全氟烷基物质的吸附量。
实际环境中污染物与微塑料的种类繁多,吸附体系复杂,有必要建立对不同条件下微塑料的吸附行为进行定量分析的快速预测模型。
(5)聚类5:微塑料的归趋和降解行为研究。该主题涵盖图中所有绿色的关键词,包括life、model、behavior等47个关键词。环境中的塑料不仅容易受到颗粒摩擦、风化、海浪和紫外光等作用发生物理降解,也可以在微生物的作用下发生生物降解[44]。蔡立奇[45]研究发现,紫外光照射时间和塑料颗粒所处的环境体系的差异是影响塑料颗粒降解程度(化学风化程度)的重要因素。如大气、纯水和模拟海水环境中的PE、PP和PS在3个月的紫外光照射之后发生了不同程度的降解行为,且降解程度随紫外光照射时长的增加而增加。此外,一些PE、PS和聚氟乙烯的塑料可以在细菌、真菌等微生物的作用下发生不同程度的生物降解[46]。Auta等[47]发现从环境中分离的红球菌和芽孢杆菌可以使PP的重量分别减轻6.4%和4.0%。同时,PP表面形成了各种不规则的孔。除纯细菌之外,细菌群落也被广泛用于微塑料降解的研究中,蚯蚓肠道细菌可以介导低密度聚乙烯的降解,从而降低塑料的尺寸[48]。真菌也有粘附和利用微塑料的潜力。Russell等[49]鉴定出丝氨酸水解酶是造成聚氨酯降解的原因,表明真菌分泌的酶可以促进微塑料的生物降解。此外,真菌还可以将微塑料作为碳源,无需任何预处理和助氧化剂。Sangeetha-Devi等[50]发现分离出的VRKPT1和VRKPT2真菌菌株可以在以HDPE作为唯一碳源的液体合成培养基中生长,经过30 d的培养后,HDPE表面上形成了生物膜,且HDPE的重量减少,表面也变得粗糙。
微塑料的生物膜介导降解比纯细菌和真菌的降解更复杂,其可以通过多种方式破坏微塑料的结构,包括掩盖表面特性,降解添加剂,分泌微塑料修饰/降解酶以及释放代谢副产物[51]。目前,生物膜对微塑料的降解研究多集中于塑料重量和表面形貌的变化,还未有微塑料降解产物检测分析相关的研究。
-
国际微塑料研究突现关键词分析结果如表2所示。突现词表主要展示了突现词的时间跨度及突现率,图中的红线表示该关键词被引用最多的时间段。选取具有代表性的突现词进行演进趋势分析,可以将2004—2019年全球的微塑料研究前沿的演进趋势分为“稳态型研究前沿”、“渐进型研究前沿”和“最新研究前沿”。
(1) 稳态型研究前沿
“海洋塑料碎片”(marine plastic debris),“有机污染物”(organic pollutant)和多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon)等关键词的时间跨度在4年及以上,表明这些研究方向曾长期受到研究者的广泛关注,并已经进行了较为深入的研究,属于稳态型研究前沿。突现词“海洋塑料碎片”表明全球对于不同环境介质中微塑料的研究是从海洋环境切入和展开的。与“海洋塑料污染”相关的文献最早可以追溯到1972年,Carpenter等[52]在《Science》上发表了题为“Plastics on the sargasso sea surface”的文章,首先关注到了海洋环境中塑料的污染问题。2015年,微塑料污染被联合国列为海洋生物的“温柔杀手”,并成为与全球气候变化、臭氧耗竭和海洋酸化并列的全球重大环境问题。从此,水体环境中微塑料的污染越来越受到全球性的关注。目前,学者已经开展了大量关于微塑料在水生环境中尤其是海洋环境中的环境行为和生态毒性研究。其中,环境中的微塑料与其他污染物之间的相互作用也是生态毒性研究中一个重要的课题。大量研究证明由于其较高的比表面积和疏水性,微塑料可作为环境中重金属、多氯联苯、多环芳烃(菲、芘、荧蒽)和抗生素等有毒有害物质的载体。但是微塑料对于其他污染物迁移行为影响机制尚不清晰,微塑料与重金属和有机污染物复合体系毒性效应的理论研究也仍需加强。
(2) 渐进型研究前沿
渐进型研究前沿是指发展趋势逐渐增强的高突现性关键词。此类突现词有“量化”(quantification),“大湖”(great lake)和“生物体”(organism)。表明,研究逐渐向微塑料在淡水环境(大湖)中的污染及其对生物体(海鸟,贻贝)的影响转移。人们最早发现微塑料污染是在海洋环境中,海洋中微塑料污染的关注远远早于淡水。然而,河流是海洋中微塑料的重要来源,该阶段,学者开始呼吁关注淡水中的微塑料污染,淡水环境中微塑料污染走进了人们的视线。2015年,Zhang等[53]报道了三峡水库地表水中微塑料的丰度和类型,这是我国第一篇与淡水环境微塑料污染相关的文献。此后,我国对淡水中微塑料污染的调查研究陆续展开,监测范围扩大至黄河及其入海口、太湖流域、洞庭湖和鄱阳湖等;国外则主要集中在一些大型的湖泊与河流,例如,劳伦斯五大湖、多瑙河、北美的苏必略湖、休伦湖等,然而可能受到微塑料污染较为严重的恒河、湄公河,以及较为重要的河流,如刚果河、尼罗河等数据匮乏,总体而言,淡水系统相关的研究仍存在缺口,应该得到更多的科学关注。
从微塑料的分析方法来看,全球对海水、湖泊、沉积物和生物体中微塑料的鉴定和定量分析方法进行了探讨,如何建立微塑料在不同环境介质中的定量分析技术和统一的定量单位成为本阶段的研究趋势。
(3) 最新研究前沿
最新研究前沿是指近3年(2017—2019)出现在文献中的高突现性关键词,主要有“地中海”(mediterranean sea),“空间分布”(spatial distribution),人类健康(human health)和“底栖鱼类”(demersal fish)。表明近3年的热点话题是微塑料在封闭或者半封闭的海域(主要是地中海)中的空间分布及微塑料对底栖鱼类和人类健康的影响。世界自然基金会2018年发布报告,认定地中海微塑料污染达到创纪录水平,成为世界上受微塑料污染最严重的地区之一,地中海地区微塑料的空间分布统计研究受到越来越多的关注。造成这一现象主要是因为地中海沿岸国家众多及其特殊的地理结构,使得地中海内的微塑料污染不易扩散至广阔的海域,从而造成内部的积累。地中海沿岸国家(意大利、希腊、法国、埃及等)对于该海域沉积物中微塑料污染的研究结果较为一致,丰度为 105—422 颗·kg−1,该范围比较能反映地中海沿岸沉积物中微塑料污染的情况。目前缺乏地中海中主要河流和过渡区的数据,未来研究应补全这些区域监测数据的空白,注重微塑料来源和循环动力学的调查,全面理解地中海微塑料的源头并提出相关管理措施。
随着微塑料研究的逐渐深入,全球对微塑料的研究对象也从典型的海洋生物扩大至淡水底栖生物,甚至是人类。微塑料容易在海底沉积物中聚集,因此会极大地影响滤食性的底栖生物。对底栖生物体内微塑料污染现状进行调查可以揭示海洋沉积物中微塑料的分布规律;研究微塑料对底栖生物的生态毒性效应也为积累更多毒理学基础数据和评价海洋微塑料的生态风险提供了重要参考。Wang等[54]发现微塑料不仅会损害海水青鳉肠道、鳃、性腺等组织的结构特征与氧化应激防御系统,还会干扰鱼类的生殖与子代的发育,首次证实了微塑料具有生殖内分泌干扰效应。由于作物、食物和空气中存在的微塑料可能进入人体并产生毒性效应,近年来人们对食品安全和人类健康的关注持续上升。尺寸在亚微米级甚至是微米级的塑料颗粒可以穿透小麦和生菜根系进入植物体,并在蒸腾拉力的作用下通过导管系统随水流和营养流进入作物的可食用部位[55],进而通过食物链对动物和人类造成威胁。每人每年通过食盐、饮用水和呼吸进入人体的微塑料分别为(0—7.3)×104个、(0—4.7)×103个和(0—3.0)×107个,且吸入的微塑料的量远高于通过其他接触途径的摄入量,长期吸入可能增加罹患癌症的风险[56]。Catarino等[57]在2018年发表的研究中通过比较食物准备过程中从空气中飘落到食物上的塑料纤维的含量和通过食用贻贝摄入的微塑料的含量,发现与食用贻贝相比,在空气中传播的塑料纤维对人体产生的危害更大。现有研究已在人体粪便中检测到了微塑料的存在,每10 g人类粪便中,平均有20个微塑料颗粒。其中,PP和PET含量最高[58]。虽然已经证明微塑料颗粒在人体中存在,但有关人体呼吸摄入、人体暴露水平、慢性毒性效应浓度以及微塑料潜在毒理学机制的研究仍存在欠缺,所以还无法精确评估微塑料对人体的危害。因此,有必要建立统一的实验数据分析方法来判断人类消化系统中残留的塑料颗粒的数量,并弄清其在人体中的转移途径,以期为人类风险评估提供生物学依据。
通过以上分析可以发现,全球已经对水环境中微塑料的来源、分布、积累和生态毒性进行了广泛研究,而对陆地、土壤和大气环境中的微塑料的相关研究还不够成熟,对人类健康的危害未能精确评估;另一方面,已有多项研究表明海洋和淡水环境中微塑料污染严重,最新研究甚至在两极地区发现了微塑料的存在,当前亟需采取相应的措施来控制全球微塑料的污染。
-
国内微塑料研究关键词共现图如图3所示。图中节点的大小代表着关键词出现的频次,节点的颜色代表了关键词出现的不同时段,颜色在紫色区域的节点表示在2017年之前提出的关键词,节点的颜色越黄,则关键词越新。图中大多数关键词在最近2年出现,反映出微塑料在国内是一个较新的研究领域。“海洋微塑料”、“海洋污染”和“海洋生物”出现频次最高,表明我国微塑料研究围绕海洋环境展开。国内对于微塑料的初期研究主要为微塑料的来源和对海洋生物的生态毒性,共现较强的关键词为“洗护用品”、“摄食”、“复合污染”、“毒理学效应”等。
2018—2019年,随着微塑料研究的不断深入,除“海洋环境”、“丰度”和“沉积物”等关键词之外,还出现了诸如“人类健康”和“食品安全”之类的关键词,说明该阶段国内关于微塑料研究热点集中在水环境(海洋和污水处理厂)和沉积物中微塑料的污染情况、微塑料对污染物的吸附动力学研究以及微塑料带来的食品安全和人类健康风险问题上。国内关于海洋中微塑料污染的研究较为广泛,主要集中在黄渤海海域、珠江流域以及南海海域,而关于城市污水处理厂中微塑料的研究较少,主要包括微塑料在污水处理厂中的物理性质(颗粒类型和大小)及其在污水、污泥中的赋存归趋。到目前为止,在污水处理厂检测出的微塑料类型达30多种,其中常见的包括聚酯、PE和PET等。污水处理工艺可以实现微塑料较高的去除率,去除的微塑料中超过90%会被截留或转移到污泥中,并随着污泥农业利用进入土壤生态系统,对生态系统和食品安全带来威胁。厦门市筼筜污水处理厂一级处理和二级处理对微塑料的去除率分别为35.99%和80.97%,由于污水处理厂处理水量较高,约为26万m3·d−1,每天向厦门西海域中排放的微塑料总量仍然相当高,预计为9.72×104个[59]。通过对我国28个污水处理厂污泥中微塑料的调研,发现其平均含量较高,可达22.7×103 个·kg−1(干污泥)[60],预计每年由于污泥不当处置或农业利用而引入土壤生态系统的微塑料总量可达15万亿—51万亿个[61]。
2019—2020年共现较强的关键词主要为“检测方法”、“空间分布”、“控制对策”、“土壤生态系统”和“鄱阳湖”等,这表明当前我国微塑料热门的研究主题可以概括为微塑料在环境(土壤和淡水)中的分布特征、鉴定和量化技术及其防控措施。微塑料的鉴定和量化流程包括在不同环境介质(水体、土壤沉积物和大气等)中的样品采集、分离提取和定性定量分析,样品采集方法分为直接挑选法、大样本法和生物取样法;常用的分离提取方法主要有视觉分选法、过滤筛分法和密度分离法,生物样品中的微塑料常采用消解法来进行预处理;定性定量分析除了沿用国际上常用分析方法之外(图1中聚类3分析),中国研究者也探究了多种技术联用的新方法,例如傅里叶红外光谱和热重分析联用,这有利于推动定量分析方法的优化。针对日益严重的微塑料污染问题,我国提出了一系列防控策略。如中国在2019年10月提出,到2020年12月31日禁止生产,到2022年12月31日禁止销售含塑料微珠日化品的政策;在2020年1月发布2020年底全国餐饮行业禁止使用不可降解的一次性塑料吸管的规定。“禁塑令”、“水十条”和“生活垃圾分类制度”等政策也在削减塑料污染方面发挥了重要作用。除此之外,中国还十分重视国际合作,积极与东盟、加拿大等国家开展海洋塑料垃圾污染防治合作。
总体来看,不同时间段出现的国内微塑料研究关键词与表2国际微塑料研究突现关键词有较多的重叠,表明中国紧跟国际微塑料的研究热点和趋势,成为该领域重要的研究力量。
-
使用VOSviewer和Citespace对微塑料研究进行了多角度的分析。主要研究结论如下:
(1)对国际微塑料研究关键词共现图进行分析,发现国际微塑料研究的研究热点主要由5个领域组成:“微塑料的生物毒性作用”,“微塑料在水环境中的分布与丰度”,“微塑料的迁移和分析方法”,“微塑料的吸附作用”和“微塑料的归趋和降解行为研究”。五个聚类之间互有重叠,各个研究热点之间存在交叉研究。
(2)国际微塑料研究前沿的演进趋势分为“稳态型研究前沿”“渐进型研究前沿”和“最新研究前沿”。对外文文献的突现关键词进行分析,发现自2017年至今,“地中海”,“空间分布”已逐渐成为新的突现词,微塑料在封闭或者半封闭的海域(主要是地中海)中的空间分布及其在底栖鱼类和人类中的污染现状调查和生态毒性分析成为研究趋势。当前亟需进行陆地、土壤和大气环境中微塑料的相关研究和采取相应的措施来控制全球微塑料的污染。
(3)中国紧跟国际微塑料的研究热点和趋势,2019年共现较强的关键词主要为“检测方法”、“空间分布”、“控制对策”、“土壤生态系统”和“鄱阳湖”等,微塑料在环境(土壤和淡水)中的分布特征、鉴定和量化技术及其防控措施成为当前我国的研究热点,研究趋势从初期的微塑料的来源和对海洋生物的生态毒性逐步向微塑料在不同环境介质中的污染情况、对食品安全和人类健康的威胁以及相关防控政策的实施上转移。
结合微塑料的文献计量结果以及当前我国的研究现状,对未来开展微塑料研究提出以下展望:
(1)完善微塑料毒性的测定方法:现有的微塑料毒性效应的研究大多在实验室中模拟,暴露实验中采用的暴露浓度通常高于实际环境浓度,暴露时长较短,且毒性终点指标不够全面。未来应开展微塑料低剂量长期暴露的相关实验,加强微塑料结合其他痕量污染物复合毒性测定方法和机制的研究,并制定标准毒性测试指标。
(2)建立微塑料检测的标准体系:微塑料的研究存在采样方法和丰度单位不同(颗·m−2、颗·m−3、g·m−2、g·m−3)等问题,数据之间难以比较。因此需统一不同单位间的换算关系并建立全球不同介质中微塑料污染量化分析的标准方法。例如,在采集沉积物样品时,由于不同密度的沉积物重量不同,建议使用颗·m−2、颗·m−3作为单位。
(3)制定微塑料污染控制对策:微塑料在环境中的数量不断增加,未来应健全微塑料污染控制方面的法律法规,尽快开展限制微塑料产品的生产使用的立法调查工作,并研发相应的替代产品来减少塑料的使用。
全球微塑料研究现状及热点可视化剖析
Visual analysis of global microplastics research status and hotspots
-
摘要: 为探究微塑料的研究现状、热点及研究趋势,本文以Web of Science核心数据库和中国知网数据库作为数据源,使用VOSviewer和CiteSpace软件对2004—2019年的微塑料领域研究文献进行关键词聚类和突现分析。结果表明,微塑料的国际研究热点主要集中在“微塑料的生物毒性作用”、“微塑料在水环境中的分布与丰度”、“微塑料的迁移和鉴定方法”、“微塑料的吸附作用”和“微塑料的归趋和降解行为”等5个方面。2017年后外文文献的主要突现关键词为“地中海”、“空间分布”等,表明当前微塑料的国际研究趋势是探究微塑料在封闭或者半封闭的海域(主要是地中海)中的空间分布及其在底栖生物中的污染现状和生态毒性效应。2019年中文文献共现较强的关键词主要为“检测方法”、“空间分布”、“控制对策”、“土壤生态系统”和“鄱阳湖”等,表明当前我国微塑料的研究热点可以概括为微塑料在环境(土壤和淡水)中的分布特征、鉴定和量化技术及其防控措施。未来的研究还需要完善微塑料毒性的测定方法,建立微塑料检测的标准体系并制定微塑料污染控制对策。Abstract: In order to explore the research status, hotspots and research trends of microplastics, this paper used the Web of Science core database and CNKI database as the data source, the VOSviewer and the CiteSpace as analysis tools to perform keyword cluster and bursts analysis on research literature in the field of microplastics from 2004 to 2019. Results showed that the international research hotspots of microplastics were mainly focused on “biological toxicity of microplastics”, “distribution and abundance of microplastics in aquatic environment”, “migration and identification methods of microplastics”, “adsorption of microplastics” and “the fate and degradation behavior of microplastics”. Bursts keywords of foreign literature after 2017 mainly include “mediterranean sea” and “spatial distribution”, which indicated that the research trend of microplastics was to explore the spatial distribution of microplastics in enclosed or semi-enclosed seas (mainly the Mediterranean Sea) and their pollution status and ecotoxicological effects in demersal organisms. The keywords with strong co-occurrence of Chinese literature in 2019 are mainly “detection methods”, “spatial distribution”, “control strategy”, “soil ecosystem” and “Poyang Lake”, which showed that the current research hotspots of microplastics in China can be summarized as the distribution characteristics of microplastics in the environment (soil and fresh water), identification and quantification techniques, and its prevention and control measures. Future research also needs to improve the methods for determining the toxicity of microplastics, establish a standard system for microplastics testing, and formulate microplastics pollution control countermeasures.
-
Key words:
- microplastics /
- ecological toxicity /
- occurrence /
- bibliometrics /
- research hotspots
-

-
表 1 各海域中微塑料的分布情况
Table 1. Distribution of microplastics in various sea areas
地点
Location采样介质
Sampling medium聚合物类型
Polymer types粒径范围
Particle size range丰度
Abundance参考文献
Reference大西洋 海水 94%纤维 0.25—5 mm 0—8.5颗·m−3 [17] 东北大西洋 海水 95.9%纤维 0.2—5 mm 0—22.5颗·m−3 [18] 北大西洋亚热带环流系 海水 48%PET、 PP 10—1000 µm 13—501颗·m−3 [19] 印度洋 海水 PET、 PP、发泡PS (35.8±42.5)颗·m−2 [20] 北冰洋 海水 95%纤维 0.25—5 mm 0—11.5颗·m−3 [21] 东北太平洋 海水 75%纤维 64.8 µm—5 mm 279 ± 178颗·m−3 [22] 南极洲罗斯海 海水 PP, PE 0.0032—1.18 颗·m−3 [23] 阿拉伯红海 海滩沉积物 PE 160颗·m−2 [24] 渤海 海滩沉积物 PEVA、LDPE、 PS (102.9±39.9)—(163.3±37.7)颗·kg−1 [25] 欧洲13国海岸 海滩沉积物 PET、PP、PE < 1 mm (72±24)—(1512±187)颗·kg−1 [26] PET:聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯;PP:聚丙烯;PS:聚苯乙烯;PE:聚乙烯;PEVA:聚乙烯醋酸乙烯酯;LDPE:轻密度聚乙烯. 表 2 2004—2019年国际微塑料研究突现关键词
Table 2. The keywords with the strongest citation bursts of international microplastic research between 2004 and 2019
关键词
Keywords年份
Year强度
Strength起始
Begin结束
End2004—2019 marine plastic debris 2006 8.8069 2011 2014 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ transport 2006 5.1280 2011 2013 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ organic pollutant 2006 7.8122 2011 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ accumulation 2006 4.4659 2012 2013 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ toxic chemical 2006 6.5740 2013 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon 2006 6.9843 2013 2017 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▂▂ polychlorinated biphenyl 2006 3.9219 2013 2015 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ plastic ingestion 2006 3.3611 2013 2015 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ pellet 2006 7.9862 2013 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ seabird 2006 3.9341 2014 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂ pacific ocean 2006 7.3839 2014 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂ mytilus edulis 2006 15.1625 2014 2017 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂ organism 2006 8.8645 2014 2016 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂ estuary 2006 5.4438 2015 2017 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂ contaminant 2006 6.7441 2015 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▃ quantification 2006 9.3881 2016 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ great lake 2006 9.1132 2016 2017 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂ spatial distribution 2006 9.4358 2017 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ mediterranean sea 2006 7.6536 2017 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ coastal water 2006 6.4330 2017 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ demersal fish 2006 11.7249 2017 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ human health 2006 7.2478 2018 2019 ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃ -
[1] PLASTICSEUROPE. Plastics – the facts 2018: An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data[EB/OL]. [2019-01-15].www. plasticseurope. org. 2018. [2] ANDRADY A L. Microplastics in the marine environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596-1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [3] ARTHUR C, BAKER J E, BAMFORD H A. Proceedings of the international research workshop on the occurrence, effects, and fate of microplastic marine debris[R]. University of Washington Tacoma, WA, USA, 2009: 1-49. [4] MOORE C J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat [J]. Environmental Research, 2008, 108(2): 131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2008.07.025 [5] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic?[J] Science, 2004, 304(5672): 838. [6] CAUWENBERGHE L V, JANSSEN C R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 193: 65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.010 [7] ROCHMAN C M, HOH E, KUROBE T, et al. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress [J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 3263. doi: 10.1038/srep03263 [8] NEDERHOF A J. Bibliometric monitoring of research performance in the social sciences and the humanities: A review [J]. Scientometrics, 2006, 66(1): 81-100. doi: 10.1007/s11192-006-0007-2 [9] HOLDEN G, ROSENBERG G, BARKER K. Tracing thought through time and space: A selective review of bibliometrics in social work [J]. Social Work in Health Care, 2005, 41(3-4): 1-34. doi: 10.1300/J010v41n03_01 [10] GAEDE J, ROWLANDS I H. Visualizing social acceptance research: A bibliometric review of the social acceptance literature for energy technology and fuels [J]. Energy Research & Social Science, 2018, 40: 142-158. [11] WU Y, GUO P, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of microplastics exposure on the photosynthesis system of freshwater algae [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 374: 219-227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.039 [12] BROWNE M A, DISSANAYAKE A, GALLOWAY T S, et al. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L. ) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(13): 5026-5031. [13] 张瑾, 李丹. 环境中微/纳米塑料的污染现状、分析方法、毒性评价及健康效应研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 28-40. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062003 ZHANG J, LI D. Review on the occurrence, analysis methods, toxicity and health effects of micro-and nano-plastics in the environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 28-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062003
[14] MATTSSON K, EKVALL M T, HANSSON L A, et al. Altered behavior, physiology, and metabolism in fish exposed to polystyrene nanoparticles [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(1): 553-561. [15] QIAO R, LU K, DENG Y, et al. Combined effects of polystyrene microplastics and natural organic matter on the accumulation and toxicity of copper in zebrafish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 682: 128-137. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.163 [16] ZOCCHI M, SOMMARUGA R. Microplastics modify the toxicity of glyphosate on Daphnia magna [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 697: 134194. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134194 [17] KANHAI L D K, OFFICER R, LYASHEVSKA O, et al. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition along a latitudinal gradient in the Atlantic Ocean [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 115(1-2): 307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.025 [18] LUSHER A L, BURKE A, O’CONNOR I, et al. Microplastic pollution in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: Validated and opportunistic sampling [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 88: 325-333. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.08.023 [19] ENDERS K, LENZ R, STEDMON C A, et al. Abundance, size and polymer composition of marine MPs≥10 µm in the Atlantic Ocean and their modelled vertical distribution [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 100(1): 70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.027 [20] IMHOF H K, SIGL R, BRAUER E, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of macro-, meso-and microplastic abundance on a remote coral island of the Maldives, Indian Ocean [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 116(1-2): 340-347. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.010 [21] LUSHER A L, TIRELLI V, O’CONNOR I, et al. Microplastics in Arctic polar waters: The first reported values of particles in surface and sub-surface samples [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 14947. doi: 10.1038/srep14947 [22] DESFORGES J P W, GALBRAITH M, DANGERFIELD N, et al. Widespread distribution of microplastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 79(1-2): 94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.12.035 [23] CINCINELLI A, SCOPETANI C, CHELAZZI D, et al. Microplastic in the surface waters of the Ross Sea (Antarctica): Occurrence, distribution and characterization by FTIR [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 391-400. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.024 [24] RUIZ-COMPEAN P, ELLIS J, CURDIA J, et al. Baseline evaluation of sediment contamination in the shallow coastal areas of Saudi Arabian Red Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 123(1-2): 205-218. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.059 [25] YU X, PENG J, WANG J, et al. Occurrence of microplastics in the beach sand of the Chinese inner sea: The Bohai Sea [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 722-730. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.080 [26] FROUKJE A E L, BEHRENS P, VIJVER M G, et al. A large-scale investigation of microplastic contamination: Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in European beach sediment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 123(1-2): 219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.057 [27] LWANGA E H, VEGA J M, QUEJ V K, et al. Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 14071. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14588-2 [28] FRERE L, PAUL-PONT I, RINNERT E, et al. Influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors on the composition, concentration and spatial distribution of microplastics: A case study of the Bay of Brest (Brittany, France) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225: 211-222. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.023 [29] O'CONNOR D, PAN S Z, SHEN Z T, et al. Microplastics undergo accelerated vertical migration in sand soil due to small size and wet-dry cycles [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 249: 527-534. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.092 [30] 郝双玲, 刘海成, 薛婷婷, 等. 水环境中微塑料的样品采集与分析进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2020, 83(5): 427-433. HAO S L, LIU H C, XUE T T, et al. Progress in sample collection and analysis of microplastics in the water [J]. Chemistry, 2020, 83(5): 427-433(in Chinese).
[31] LÖDER M G, GERDTS G. Methodology used for the detection and identification of microplastics—A critical appraisal[M]. Marine anthropogenic litter. Springer. 2015: 201-227. [32] FISCHER D, KAEPPLER A, EICHHORN K J. Identification of microplastics in the marine environment by Raman microspectroscopy and imaging [J]. American Laborotory, 2015, 47(3): 32-34. [33] 杨婧婧, 徐笠, 陆安祥, 等. 环境中微(纳米)塑料的来源及毒理学研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 383-396. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002 YANG J J, XU L, LU A X, et al. Research progress on the sources and toxicology of micro (nano) plastics in environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 383-396(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017071002
[34] 刘鹏, 王焓钰, 吴小伟, 等. 粒径对聚苯乙烯微塑料吸附环丙沙星的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(11): 3153-3160. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082802 LIU P, WANG H Y, WU X W, et al. Effects of particle size on the adsorption of ciprofloxacin on polystyrene microplastics [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(11): 3153-3160(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082802
[35] WRIGHT S L, THOMPSON R C, GALLOWAY T S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 178(1): 483-492. [36] WANG F, ZHANG M, SHA W, et al. Sorption behavior and mechanisms of organic contaminants to nano and microplastics [J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(8): 1827. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081827 [37] WANG F, SHIN K M, LI X Y. The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonatequba (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide (FOSA) on microplastics [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 841-847. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.047 [38] ZHANG X J, ZHENG M G, YIN X C, et al. Sorption of 3, 6-dibromocarbazole and 1, 3, 6, 8-tetrabromocarbazole by microplastics [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 138: 458-463. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.055 [39] ZHANG H B, WANG J Q, ZHOU B Y, et al. Enhanced adsorption of oxytetracycline to weathered microplastic polystyrene: Kinetics, isotherms and influencing factors [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 1550-1557. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.122 [40] 徐鹏程, 郭健, 马东, 等. 新制和老化微塑料对多溴联苯醚的吸附 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1329-1337. XU P C, GUO J, MA D, et al. Sorption of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by virgin and aged microplastics [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1329-1337(in Chinese).
[41] BRENNECKE D, DUARTE B, PAIVA F, et al. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 178: 189-195. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.003 [42] LIU G, ZHU Z, YANG Y, et al. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100 [43] LLORCA M, SCHIRINZI G, MARTINEZ M, et al. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances on microplastics under environmental conditions [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235: 680-691. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.075 [44] ANDRADY A L. The plastic in microplastics: A review [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 119(1): 12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.082 [45] 蔡立奇. 微塑料在不同环境中的污染特征及其降解行为研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2019. 30-63. CAI L Q. Study on the characteristics of microplastics in different environments and their degradation behaviors[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2019. 30-63 (in Chinese).
[46] YOSHIDA S, HIRAGA K, TAKEHANA T, et al. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly (ethylene terephthalate) [J]. Science, 2016, 351(6278): 1196-1199. doi: 10.1126/science.aad6359 [47] AUTA H S, EMENIKE C U, JAYANTHI B, et al. Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2018, 127: 15-21. [48] LWANGA E H, THAPA B, YANG X, et al. Decay of low-density polyethylene by bacteria extracted from earthworm's guts: A potential for soil restoration [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 624: 753-757. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.144 [49] RUSSELL J R, HUANG J, ANAND P, et al. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by endophytic fungi [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(17): 6076-6084. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00521-11 [50] SANGEETHA-DEVI R, RAJESH-KANNAN V, NIVAS D, et al. Biodegradation of HDPE by Aspergillus spp. from marine ecosystem of Gulf of Mannar, India [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 96(1-2): 32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.05.050 [51] MIAO L, WANG P, HOU J, et al. Distinct community structure and microbial functions of biofilms colonizing microplastics [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 650: 2395-2402. [52] CARPENTER E J, SMITH K. Plastics on the sargasso sea surface [J]. Science, 1972, 175(4027): 1240-1241. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4027.1240 [53] ZHANG K, GONG W, LV J Z, et al. Accumulation of floating microplastics behind the Three Gorges Dam [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 204: 117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.04.023 [54] WANG J, LI Y, LU L, et al. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 113024. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113024 [55] LI L Z, LUO Y M, LI R J, et al. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode [J]. Nature Sustainability, 2020, 3(11): 929-937. doi: 10.1038/s41893-020-0567-9 [56] ZHANG Q, XU E G, LI J, et al. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: Direct human exposure [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(7): 3740-3751. [57] CATARINO A I, MACCHIA V, SANDERSON W G, et al. Low levels of microplastics (MP) in wild mussels indicate that MP ingestion by humans is minimal compared to exposure via household fibres fallout during a meal [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 675-684. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.069 [58] SCHWABL P, KPPEL S, KNIGSHOFER P, et al. Detection of various microplastics in human stool: A prospective case series [J]. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2019, 171(7): 453-457. doi: 10.7326/M19-0618 [59] 汪文玲, 龙邹霞, 余兴光, 等. 厦门市筼筜污水处理厂中微塑料的特征研究 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(2): 205-210. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20190207 WANG W L, LONG Z X, YU X G, et al. Microplastics characteristic in Yundang Wastewater Treatment Plant of Xiamen [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(2): 205-210(in Chinese). doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20190207
[60] LI X, CHEN L, MEI Q, et al. Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater treatment plants in China[J]. Water Research, 2018, 52(19): 75-85. [61] 李小伟, 纪艳艳, 梅庆庆, 等. 污水处理厂污水和污泥中微塑料的研究展望 [J]. 净水技术, 2019, 38(7): 13-22. LI X W, JI Y Y, MEI Q Q, et al. Review of microplastics in wastewater and sludge of wastewater treatment plant [J]. Water Purification Technology, 2019, 38(7): 13-22(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: