-
我国是有机磷农药生产大国[1-3],产量约占我国农药总产量的50%—60%[4]。有机磷农药的生产一般需要几步到十几步反应,通常为过量反应[5],产品收率较低,其他原料、中间体及副产物都以“三废”形式排出[6-7],再加上农药生产需要的多种原辅料和溶剂在生产过程中难免存在跑冒滴漏的现象[8-9],这就导致农药场地污染物质存在组成复杂,识别困难的问题。另外,农药场地污染物质具有易挥发、嗅阈值低的特点[10],尤其一些退役农药场地在修复过程中,原本藏匿在土壤中具有刺激性气味的VOCs被释放出来,导致修复现场异味强烈,投诉事件频发。异味污染已成为场地修复过程中最普遍且最棘手的环境问题。
异味是一种感官污染,直接影响人民的生活质量与社会的和谐稳定[11-13]。目前国内外与农药场地相关的研究主要围绕场地健康风险评价以及修复技术研发等方面[14-16],有关异味污染的研究还比较匮乏,农药场地异味污染来源以及致臭因子尚不明晰,修复以及治理工作缺少针对性的理论指导与必要的技术支撑。本研究以有机磷农药场地为研究对象,开展场地环境空气污染调查,感官评估异味污染情况,重点分析场地挥发性异味有机物的污染分布特征、识别关键致臭物质,为该类型污染场地的有效修复治理及合理开发利用奠定基础。
-
调查对象为某有机磷农药厂退役场地,企业主要产品为甲拌磷、辛硫磷、特丁硫磷等四十余种产品。目前处于土壤修复中期,修复项目总占地面积46万m2,其中涉及恶臭污染地块面积约30万m2。场地主要分为3个区域:生产区(包括农药生产合成车间、磷合成车间及中间体生产车间等)、辅助区(包括包装区、原料储存区及公共维修部等)及公共区(包括办公楼、生活楼及餐厅等)。基于空气质量模型CALPUFF和三轴搅拌桩点位(停工状态)实测最大数据进行模拟,预测在最不利气象条件下最大影响距离为2.5 km,其中涉及一个居民区敏感点。
-
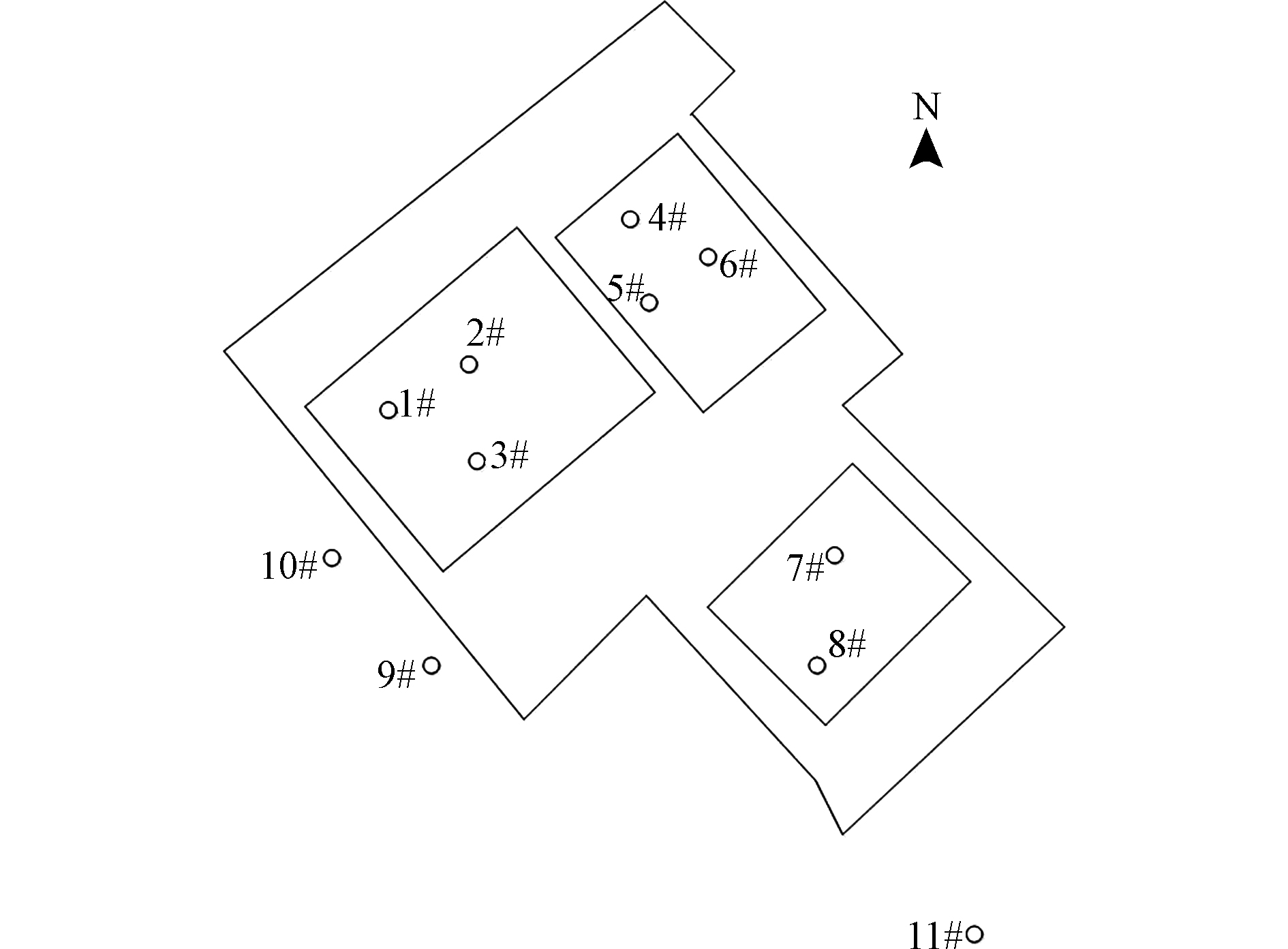
布点方法采用分区布点和专业判断法相结合的方法,布点网格原则上采用20 m×20 m ,其他区域(如办公区、生活区和厂界处等)可适当减少采样点的密度,布点网格采用 40 m×40 m,并调查现场的专业判断,即人为感知(肉眼可见、或嗅觉可识别等)、现场快速检测(如现场PID/FID、XRF 检测)等手段,对采样布点进行科学的调整,点位布设如图1所示。
1—3#所处区域为生产区,4—6#为辅助功能区,7—8#为公共区。根据当天气象条件,于西南厂界处设置两个点位9—10#。除此之外,为判断该厂对敏感点的影响,在敏感点(居民区)设置1个点位11#。应用手持式采样泵及tedlar采样袋在各点位进行采样,采样高度距离地面约1.5 m,采样完毕后,避光运回实验室,24 h内测定。
-
评价异味污染的两个重要的感官指标分别为臭气强度与臭气浓度[17-19]。臭气强度的判定采用六级强度度量法(见表1)[20],臭气浓度的测定采用GB/T 14675-1993《空气质量恶臭的测定 三点比较式臭袋法》[21]。
-
为实现挥发性异味有机物的全面检测识别,本研究应用了多种检测方法,其中包括实验室自主研发的高分辨全扫描以及针对有机酸、有机胺等典型异味物质的检测方法,如表2所示。高分辨气质具有超低灵敏度(检出限fg级)和二级质谱功能,可在复杂污染背景下准确识别低含量异味物质,精确分析致臭物质分子结构,能够分辨非常见的、常规仪器难识别的异味物质,可精准捕捉复杂基质背景下农药场地致臭物质,为寻找场地异味污染成因提供全面准确的物质基础。
-
异味污染往往是多种气态物质的混合物,一般采用各组分气味活度值(Odor Activity Value, OAV)的大小来判断不同组分对异味污染的贡献率[22],进而分析混合体系中的关键致臭物质。气味活度值为某物质的化学浓度与该物质嗅阈值的比值,计算公式如下:
式中,OAVi-第i种异味物质的气味活度值,无量纲;Ci-第i种异味物质的物质浓度,可通过气相色谱等分析仪器进行测试;OTi-第i种异味物质的嗅阈值,本研究主要引用日本环境中心发布的嗅阈值数据[23]。针对未涵盖的物质,由国家环境保护恶臭污染控制重点实验室自行测试 [24],为尽量减少由数据来源不同导致的误差,测试由具有嗅辨员资质的专业人员,采用与日本环境中心相同的测试方法(三点比较式臭袋法)完成。
-
该场地散发着强烈的刺激性气味,表3为各点位臭气强度与臭气浓度测试结果。由表可知生产区气味浓度最强,其中3#点位臭气强度高达4.5级,臭气浓度为3050;其他两个点位臭气强度为4级,臭气浓度分别为1424与1891。辅助区臭气强度略有降低,约为3—4级,臭气浓度为422—1358。公共区异味污染情况最轻,臭气强度约为2级,臭气浓度41—58。厂界处臭气强度为3级,臭气浓度在309—647之间,根据我国GB14554-93 《恶臭污染物排放标准》中规定,二类区厂界臭气浓度值应小于20[25],显然该场地厂界处臭气浓度超过标准要求。敏感点处臭气强度约为2级,臭气浓度为32,具有轻微的汽车尾气味。
-
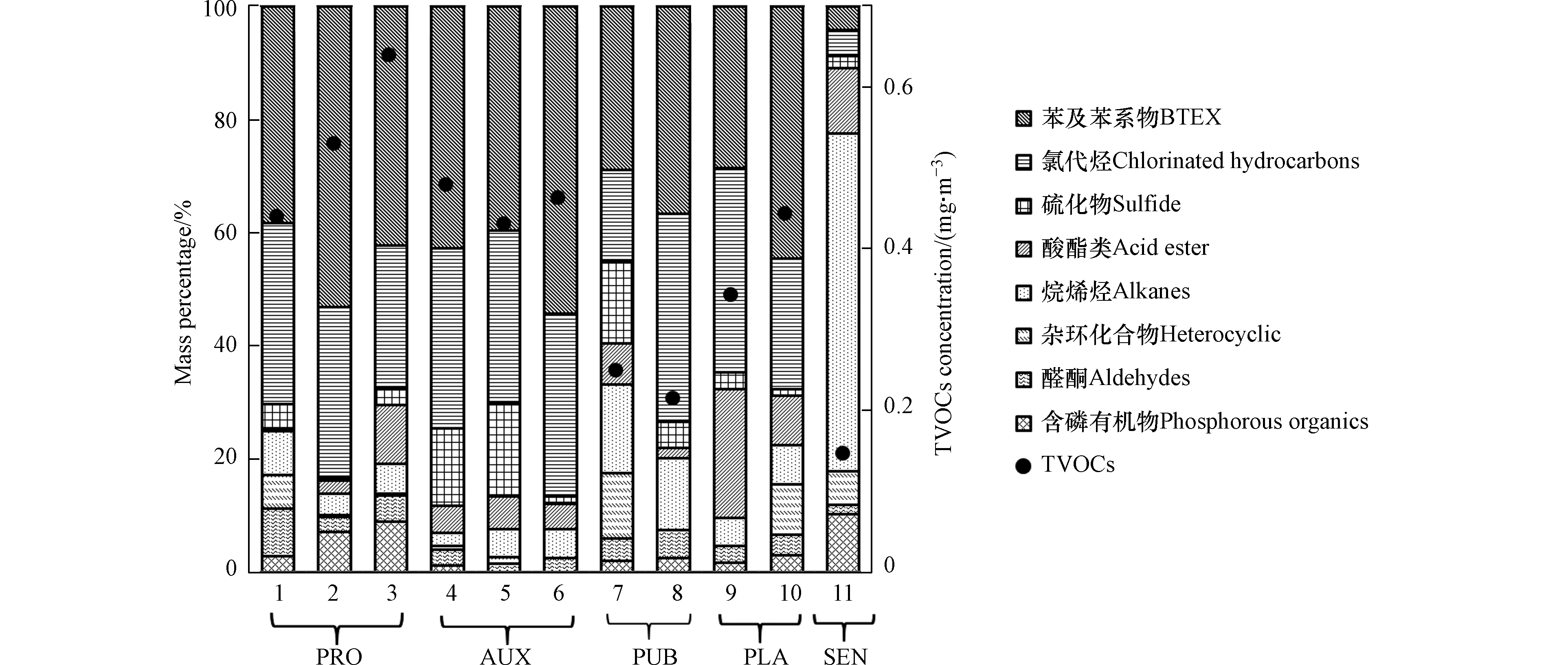
图2是不同点位异味TVOCs浓度水平与其组成特征。由图2可知,场地环境空气中异味VOCs组成及浓度水平与原厂区的生产活动及车间位置分布极为相关。关于异味TVOCs浓度水平,生产区以及辅助区物质含量最高,其中生产区在0.4385—0.6397 mg·m-3之间,辅助区在0.3418—0.4783 mg·m-3之间;处于生产区下风向的厂界处,物质含量为0.3522—0.4409 mg·m-3,仅次于生产与辅助区;公共区为0.2112—0.2477 mg·m-3,约为生产区TVOCs浓度水平的33%—50%;敏感点物质含量最低,约为0.0747 mg·m-3,仅为生产区TVOCs浓度的12%—17%。由此可见,生产区与辅助区环境空气的异味VOCs污染情况最为严重。这是由于生产区主要集中各种新产品试验中试车间以及原药生产车间等,辅助区主要集中原料储罐、成品库以及包装车间等,农药的生产、储存、包装以及运输过程均在以上两个区域进行,或多或少会存在挥发与泄露的问题,进而导致生产区与辅助区的异味VOCs含量高、污染严重。
关于污染物物质组成,生产区、辅助区、厂界处以及办公区以氯代烃以及苯及苯系物为主,占比可达到65%—80%。这说明该场地空气中主要VOCs污染物为氯代烃以及苯及苯系物,这主要与该厂生产历史直接相关,原厂生产过程中使用的原辅材料主要是苯、甲苯、二甲苯、氯仿、四氯化碳等氯代烃以及苯及苯系物。与之比较,含磷有机物占比较低,各点位检出量均不到总物质含量的10%。查找资料分析相关原因,是由于大部分含磷的有机物,其化学性质不稳定,一部分在环境中发生光解、水解等反应,还有一部分形成磷酸盐聚集在土壤中[26],因此环境空气中残留的较少。敏感点的物质组成与其他四个区域有较大的不同,主要以烷烯烃与醛酮类为主,占比约为70%,结合该点所处环境推测可能是与小区中往来机动车的尾气以及小区底商餐饮油烟有关。卤代烃以及苯及苯系物含量极少,占比不到10%,基本未受到该场地的影响。
-
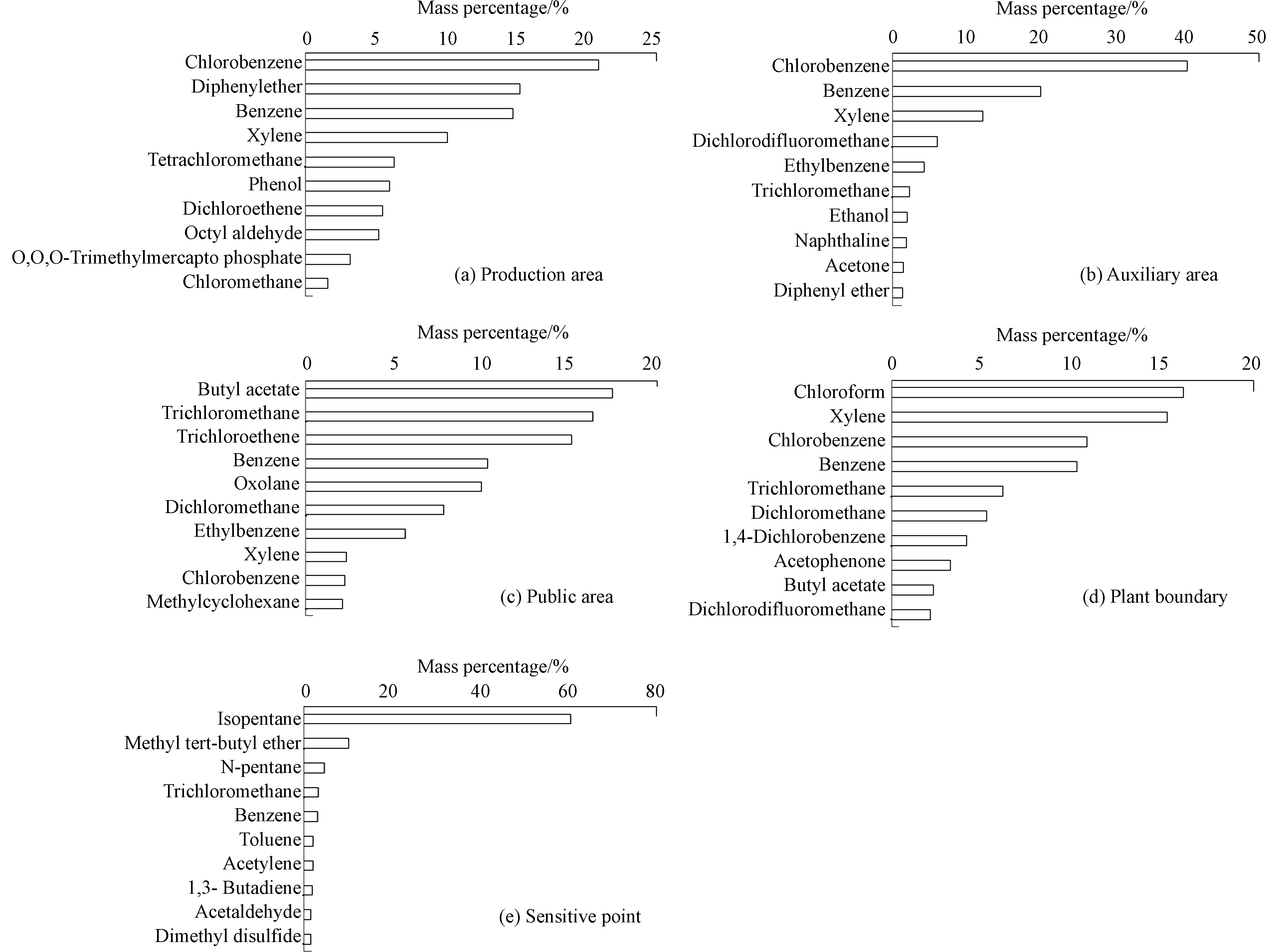
图3为不同区域物质含量排名前10的主要异味VOCs。
生产区共检出物质67种,其中含量最高的为氯苯,占比为20.85%,其次是二苯醚、苯、二甲苯等苯系物,占比分别为15.24%、14.75%以及10.12%。此外,四氯化碳、苯酚、二氯乙烯等也是生产区VOCs的主要污染物。与生产区相比,辅助区检出物质略少,共计55种,其中最主要的组分为氯苯,占比达到40.21%,约为其在生产区比例中的2倍。苯(20.21%)与二甲苯(12.34%)的占比也略高于生产区,而二苯醚的比例(1.4%)要远低于生产区。除此之外,二氟二氯甲烷、乙苯、三氯甲烷等也是排名前10的物质。公共区共检出45种物质,主要污染物与生产区和辅助区差异较大,一些占比很高的物质并没有在生产区与辅助区检测出来,比如乙酸丁酯(17.45%)以及三氯甲烷(16.32%);另外还有一些物质虽然也在生产区与辅助区有检出,但占比差异较大,比如三氯乙烯以及四氢呋喃,在公共区占比分别为15.12%以及10.01%,在生产区以及辅助区检出量不足1%。厂界处共检出49种物质,受风向条件的影响,物质种类与生产区具有明显的一致性,占比排名前10的物质中,苯酚(16.12%)、二甲苯(15.23%)、氯苯(10.77%)、苯(10.23%)、三氯甲烷(6.15%)以及二氯乙烯(5.25%)6种物质也是生产区的主要污染物。敏感点共检出物质30种,除了苯与甲苯以外,其他主要异味VOCs均与场地不同,异戊烷占绝对的主导地位,占比高达60.42%,其次为甲基叔丁基醚,占比约为10.11%,其余物质占比均不超过5%。相关研究表明,异戊烷是汽油挥发的典型示踪物质[27],甲基叔丁基醚是是提高汽油辛烷值的一种汽油添加剂[28],因此敏感区VOCs污染主要来源是汽车尾气,受该场地的影响不大。
-
由于农药场地异味VOCs种类繁多,不可能针对每一种物质制定相应的治理方案,因此筛选出异味贡献率最大的关键致臭物质作为优先控制对象,能够在有限的人力、物力和财力下获得更为显著的治理效果。
理论上讲,对于单一物质,其气味活度值等同于异味浓度,是指该物质被清洁空气稀释至异味消失时的稀释倍数。对于混合气体,当气味活度值大于1时,认为该组分会引起人的嗅觉感知[29],且气味活度值越大,其异味贡献率也越大,对人体的嗅觉刺激也越大。表4为不同区域异味活度值大于1的物质。其中,生产区辛醛与乙醛的气味活度值最大,远超排名第三的壬醛,除此之外,异戊二烯、庚醛与苯酚也产生了一定的气味影响,只不过影响较小。辅助区乙醛的气味活度值最大,乙醇次之,庚醛、丙醛以及己醛等较小。厂界处辛醛的气味活度值最大,苯酚、乙酸丁酯以及壬醛等较小。由此可知,生产区、辅助区以及厂界处的异味来源主要是醛类物质,醛类物质为化工行业常见的中间体,是日本和韩国现行标准《恶臭防止法》主要的一类受控物质。公共区乙酸仲丁酯的气味活度值最大,该物质是一种环保型溶剂,一般用作有机磷酸酯类和拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂的溶剂[30]。敏感点处甲硫醚的异味活度值最大,甲硫醚是典型的异味污染物质,也是我国GB14554-93 《恶臭污染物排放标准》中8种受控物质之一。
通过比较气味活度系数的大小,确定该有机磷农药厂生产区的关键致臭物质为辛醛与乙醛,辅助区为乙醛与乙醇,公共区为乙酸仲丁酯,厂界处为辛醛,敏感点位甲硫醚。这与主要异味VOCs污染物筛选结果并不一致,说明物质浓度高的组分,未必是关键致臭物质。这也是为什么一些场地在修复过程中,仅对含量较高的异味组分进行治理,但是依然不能获得良好效果的主要原因。想要有效去除场地异味问题,不仅要考虑物质含量,还要充分考虑人对该物质气味刺激的敏感程度,即嗅阈值的大小。
-
(1)从感官影响与TVOCs浓度水平两方面对场地异味污染情况进行评估,结果具有一致性:生产区与辅助区臭气强度与臭气浓度最高,TVOCs浓度水平最高,异味污染情况最严重;公共区与敏感点臭气强度与臭气浓度最低,TVOCs浓度水平最低,异味污染情况最轻;厂界处异味污染情况受风向条件的影响,臭气强度、臭气浓度最高、TVOCs浓度水平仅次于生产区与辅助区,且臭气浓度超过国家规定限值。
(2)生产区、辅助区、厂界处以及办公区VOCs以氯代烃以及苯及苯系物为主,如:氯苯、苯、二苯醚以及四氯化碳等,与原厂生产过程中使用的原辅材料有关。敏感点的VOCs组成与其他四个区域有较大的不同,主要以烷烯烃与醛酮类为主,异戊烷、甲基叔丁基醚、正戊烷以及三氯甲烷等物质在该区域中的含量占比较高,敏感点未受到该场地的污染影响,主要异味污染来源为汽车尾气。
(3)不同区域的关键致臭物质不同,生产区、辅助区以及厂界处的异味来源主要是醛类物质,其中生产区关键致臭物质为辛醛与乙醛,辅助区为乙醛与乙醇,公共区为乙酸仲丁酯,厂界处为辛醛,敏感点为甲硫醚。关键致臭物质并不是含量最高的物质,还需综合考虑嗅阈值这一感官因素。
某有机磷农药场地异味VOCs污染特征与关键致臭物质识别
Odour VOCs pollution characteristics and identification of key odorant in an organophosphorus pesticide site
-
摘要: 为了解有机磷农药场地修复过程中异味污染特征及产生原因,对某有机磷农药场地开展系统的场地调查。感官评估不同功能区异味污染情况,分析各区域异味VOCs组分差别,识别主要异味VOCs物质,确定各区域的关键致臭物质。结果表明,该有机磷农药场地生产区与辅助区异味污染最严重,臭气浓度、臭气强度以及TVOCs浓度水平均高于其他区域,公共区与敏感点异味污染最轻。场地主要异味VOCs组分为氯代烃以及苯及苯系物,其中氯苯、苯、二苯醚以及四氯化碳等占比较高。敏感点主要异味VOCs组分为烷烯烃与醛酮类,其中异戊烷、甲基叔丁基醚、正戊烷以及三氯甲烷等物质占比较高。各区域关键致臭物质不同,生产区关键致臭物质为辛醛与乙醛,辅助区为乙醛与乙醇,公共区为乙酸仲丁酯,厂界处为辛醛,敏感点为甲硫醚。Abstract: In order to understand the characteristics and causes of odor pollution during pesticide site remediation, a systematic site survey was carried out on an organophosphorus pesticide site. This investigation includes odor sensory evaluation in different functional areas, analysis of the differences of odorous VOCs components in each area, identification of the main odorous VOCs substances, and determining the key odorants of each area. Results showed that odor pollution of the production area and auxiliary area were the most serious. And the odor concentration, odor intensity and TVOCs concentration level were higher than other areas. The public area and sensitive point had the least odor pollution. The main odor VOCs components of the site were chlorinated hydrocarbons and benzene and benzene series, of which chlorobenzene, benzene, diphenyl ether and carbon tetrachloride were higher in content. The main components of odor VOCs at sensitive points were alkanes and aldehydes, of which isopentane, methyl tert-butyl ether, n-pentane and chloroform had a higher content. The key odorants of each area were different. The key odorants of the production area were octyl aldehyde and acetaldehyde, the auxiliary area were acetaldehyde and ethanol, the public area was sec-butyl acetate, the plant boundary was octyl aldehyde, and the sensitive point was dimethyl sulfide.
-

-
表 1 六级强度度量法
Table 1. The 6 point odor intensity scale
级别
Level嗅觉感受
Olfactory sensation0 无臭 1 刚刚好能感知到臭气(检知阈值) 2 微弱的臭气,但是能确定是什么样的臭气(确认阈值) 3 能够明显的感知到臭气 4 比较强烈的臭气 5 非常强烈,具有刺激性的臭气 表 2 环境空气样品检测方法
Table 2. The detection method of environmental air sample
类别
Category检测项目
Detection item检测方法
Detection method检测依据
Detection reference使用仪器
Instrument空气 物质筛查 高分辨全扫描 自主研发 ThermoFisher QEGC
气相色谱高分辨质谱联用仪热脱附-气相色谱质谱法 HJ 734-2014 Agilent7890A/5975C
气相色谱质谱联用仪挥发性有机污染物 罐采样-气相色谱质谱法 HJ 759-2015 Agilent7890A/5975C
气相色谱质谱联用仪硫化物 气袋采样-气相色谱质谱法 HJ 1078-2019 Agilent7890A/5975C
气相色谱质谱联用仪醛酮 高效液相色谱法 HJ 683-2014 Waters
高效液相色谱仪有机酸 固相微萃取-气相色谱法 自主研发 Agilent7890A
气相色谱仪有机胺 固相微萃取-气相色谱法 自主研发 Agilent7890A
气相色谱仪氨 气相色谱-NCD法 自主研发 Agilent7890B
气相色谱仪萜烯、醇类、酯类 罐采样-气相色谱质谱法 自主研发 Agilent7890A/5975C
气相色谱质谱联用仪表 3 各点位臭气强度与臭气浓度
Table 3. The odor intensity and odor concentration of each point
点位
Point所在区域
Region臭气强度
Odor intensity臭气浓度
Odor concentration1# 生产区 4 1424 2# 4 1891 3# 4.5 3050 4# 辅助区 4 1385 5# 4 1020 6# 3 422 7# 公共区 2 58 8# 2 41 9# 厂界处 3 309 10# 3 647 11# 敏感点 2 32 表 4 各区域关键致臭物质及其异味活度系数
Table 4. The key odorants and its OAV of each area
区域 Region 关键致臭物质(异味活度系数) Key odorant(OAV) 生产区 辛醛(654)、乙醛(125)、壬醛(32)、异戊二烯(2)、庚醛(2)、苯酚(2) 辅助区 乙醛(387)、乙醇(85)、庚醛(21)、丙醛(18)、己醛(15)、戊醛(8)、四氯乙烯(2) 公共区 乙酸仲丁酯(24)、异戊醇(8) 厂界处 辛醛(211)、苯酚(12)乙酸丁酯(8)、壬醛(3)、丙醛(1) 敏感点 甲硫醚(20)、乙硫醚(12)、二甲二硫醚(5)、乙醛(2) -
[1] 丁浩东, 万红友, 秦攀, 等. 环境中有机磷农药污染状况、来源及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 463-479. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405 DING H D, WAN H Y, QIN P, et al. Occurrence, sources and risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticides in the environment, China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 463-479(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405
[2] 阚可聪, 谷孝鸿, 李红敏, 等. 固城湖及出入湖河道表层水体、沉积物和鱼体中有机氯农药分布及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1346-1356. KAN K C, GU X H, LI H M, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of OCPs in surface water, sediments, and fish from lake Gucheng and inflow and outflow rivers [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1346-1356(in Chinese).
[3] 门晓晔. 有机磷农药污染土壤风险评估及热脱附修复研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2016. MEN X Y. Risk assessment and thermal desorption of organophosphorus pesticide contaminated soils[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2016(in Chinese).
[4] 陈锐. 基于建设用地土壤调查分析历史农用地农药潜在污染特征 [J]. 环保科技, 2020, 26(6): 57-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0254.2020.06.012 CHEN R. Contamination characteristics of pesticides in agricultural land transferred to development land [J]. Environmental Protection and Technology, 2020, 26(6): 57-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0254.2020.06.012
[5] 朱国繁, 应蓉蓉, 叶茂, 等. 我国农药生产场地污染土壤修复技术研究进展 [J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(2): 462-473. ZHU G F, YING R R, YE M, et al. Research progress on remediation technology of contaminated soil in pesticide production sites in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(2): 462-473(in Chinese).
[6] YANG K X, WANG C, XUE S, et al. The identification, health risks and olfactory effects assessment of VOCs released from the wastewater storage tank in a pesticide plant [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 184: 109665. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109665 [7] 李开环, 聂志强, 迭庆杞, 等. 废弃农药厂拆除过程对周边土壤DDTs污染影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(2): 658-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.02.030 LI K H, NIE Z Q, DIE Q Q, et al. The effect of a pesticide plant demolition on the concentration of DDTs in its surrounding soils [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(2): 658-664(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.02.030
[8] 张春玲, 杨晓文, 谷中鸣, 等. 农药生产企业废弃场地浅层土壤污染情况调查 [J]. 农药, 2014, 53(6): 460-462. ZHANG C L, YANG X W, GU Z M, et al. Investigation of shallow soil pollution in waste pesticide production enterprises [J]. Agrochemicals, 2014, 53(6): 460-462(in Chinese).
[9] 常春英, 肖荣波, 章生健, 等. 城市工业企业搬迁遗留污染场地再开发环境管理问题与思考 [J]. 生态经济, 2016, 32(8): 191-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2016.08.039 CHANG C Y, XIAO R B, ZHANG S J, et al. The problems and thoughts on environmental management in redevelopment of contaminated sites of relocated industrial enterprises in urban centers [J]. Ecological Economy, 2016, 32(8): 191-195(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2016.08.039
[10] CHEN J, YANG J T, PAN H, et al. Abatement of malodorants from pesticide factory in dielectric barrier discharges [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1/2/3): 908-913. [11] 杨伟华, 肖咸德, 王亘, 等. 香精香料企业挥发性恶臭有机物排放特征分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1071-1077. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020010705 YANG W H, XIAO X D, WANG G, et al. Emission characteristics of volatile odorous organic compounds in fragrance and flavor industry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1071-1077(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020010705
[12] 邹克华, 翟增秀, 李伟芳, 等. 典型生物发酵企业挥发性有机物及恶臭污染物排放特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3574-3580. ZOU K H, ZHAI Z X, LI W F, et al. Emission characteristics of volatile organic compounds and odorous pollutants in typical bio-fermentation industries [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(12): 3574-3580(in Chinese).
[13] 李佳音, 邹克华, 李伟芳, 等. 养猪场恶臭污染的预测模型及感官评估研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(1): 88-93. LI J Y, ZOU K H, LI W F, et al. Prediction model and sensory evaluation of odor pollution in pig farms [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(1): 88-93(in Chinese).
[14] BHANDARI G, ATREYA K, SCHEEPERS P T J, et al. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 253: 126594. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126594 [15] 叶凯, 孙玉川, 贾亚男, 等. 岩溶地下水水体中有机氯农药和多氯联苯的残留特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457. YE K, SUN Y C, JIA Y N, et al. Residual characteristics and health assessment analysis of OCPs and PCBs in Karst groundwater [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5448-5457(in Chinese).
[16] 李倩, 杨璐, 姜越, 等. 农药生产场地污染土壤的化学氧化修复技术研究进展 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(1): 19-29. LI Q, YANG L, JIANG Y, et al. Chemical oxidation techniques for soil remediation of contamination at pesticide-production sites [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(1): 19-29(in Chinese).
[17] BIAN Y G, GONG H N, SUFFET I H M. The use of the odor profile method with an “odor patrol” panel to evaluate an odor impacted site near a landfill [J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(4): 472. doi: 10.3390/atmos12040472 [18] 张欢, 邹克华, 李伟芳, 等. 恶臭污染评估指标体系研究 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(2): 344-347. ZHANG H, ZOU K H, LI W F, et al. Renovated evaluation index system available for the odor pollution assessment [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(2): 344-347(in Chinese).
[19] LIDÉN E, NORDIN S, HÖGMAN L, et al. Assessment of odor annoyance and its relationship to stimulus concentration and odor intensity [J]. Chemical Senses, 1998, 23(1): 113-117. doi: 10.1093/chemse/23.1.113 [20] PARK S. Odor characteristics and concentration of malodorous chemical compounds emitted from a combined sewer system in Korea [J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(6): 667. doi: 10.3390/atmos11060667 [21] 国家技术监督局. 中华人民共和国推荐性国家标准: 空气质量 恶臭的测定 三点比较式臭袋法 GB/T 14675—1993[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. National Standard (Recommended) of the People's Republic of China: Air quality-Determination of odor-Triangle odor bag method. GB/T 14675—1993[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1993(in Chinese).
[22] WU C D, LIU J M. Assessment of odour activity value coefficient and odour contribution bassed on binary interaction effects in a waste disposal plant[C]. 1st Austrian-Chinese Workshop on Environmental Odour. Tianjin, China, 2015. [23] YOSHIHARU I. Odor olfactory measurement[M]. Tokyo: Japan Association on Odor Environment, 2004: 20-31. [24] 王亘, 翟增秀, 耿静, 等. 40种典型恶臭物质嗅阈值测定 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(6): 348-351. WANG G, ZHAI Z X, GENG J, et al. Testing and determination of the olfactory thresholds of the 40 kinds of typical malodorous substances [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(6): 348-351(in Chinese).
[25] 国家环境保护局, 国家技术监督局. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 恶臭污染物排放标准 GB 14554—1993[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1994. State Bureau of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China, State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. National Standard (Mandatory) of the People's Republic of China: Emission STANDARDs for odor pollutants. GB 14554—1993[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1994(in Chinese).
[26] 贺小敏, 施敏芳, 李爱民, 等. 废弃农药厂土壤和地下水中有机磷农药的健康风险评价 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2014, 30(2): 76-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.02.015 HE X M, SHI M F, LI A M, et al. Health risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticides contaminated soil and groundwater in an abandoned factory site [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2014, 30(2): 76-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.02.015
[27] 沈龙娇, 梁胜文, 吴玉婷, 等. 武汉市居民区大气VOCs的污染特征和来源解析 [J]. 南京信息工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 10(5): 527-535. SHEN L J, LIANG S W, WU Y T, et al. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of VOCs in ambient air of a residential area in Wuhan [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 10(5): 527-535(in Chinese).
[28] CONTI C, GUARINO M, BACENETTI J. Measurements techniques and models to assess odor annoyance: A review [J]. Environment International, 2020, 134: 105261. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105261 [29] LI W F, YANG W H, LI J Y. Characterization and prediction of odours from municipal sewage treatment plant [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2018, 2017(3): 762-769. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.233 [30] XU H J, WANG X G, ZOU Y M, et al. Exergy, economic and environmental assessment of sec-butyl acetate hydrolysis to sec-butyl alcohol using a combined reaction and extractive distillation system [J]. Fuel, 2021, 286: 119372. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119372 -



 下载:
下载: