-
河口既是陆地与海洋的连接通道,也是海岸带的重要组成部分,沉积环境与生态系统受到海洋和陆地的共同作用,构成海洋与陆地相互影响的敏感区域。河口区域的沉积物是流域各种化学元素迁移转化的积蓄库和归宿地。河口区域的沉积物不仅记录了受人类活动影响以前各化学元素环境背景值,同时还记录了人类活动影响后的污染物的供给、迁移和沉淀历史。因此成为研究流域人类活动强度和海洋环境变化的重要载体[1]。沉积物中的N与P作为生源要素,不仅直接影响着海洋的初级生产力,而且N、P与C的关系密切,直接记录了古环境的演变历程。一般来说, 沉积记录中N、P与C初级生产力异常大幅增加的历史时期与水体富营养化时期存在较好的对应关系。流域的人类活动会引起径流中营养盐数量的变化,这种变化会带来河口及邻近海湾的营养盐浓度水平及自然结构的改变,进而造成河口区域一系列的生态环境问题。因此,河口及邻近海湾对流域人类排放的N、P的响应及其机制,成为国内外研究和迫切需要解决的科学热点[2-4]。
总有机碳(TOC)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)的变化常被用来解译河口沉积物形成时的古环境演变,而碳氮比(C/N)、碳磷比(C/P)、氮磷比(N/P)可以被用来探索沉积物中不同来源有机质的贡献[5-6]。
在长江口、珠江口、渤海等海域生源要素的研究起步较早,N、P与C带来水体富营养化的研究已相对较为系统[7-10],在北黄海和鸭绿江口,水体富营养化的研究工作尚显薄弱。但限于鸭绿江口特殊的政治地缘环境,野外调查限制很多,河口水体富营养化的系统性研究欠缺,制约了鸭绿江口及其邻近的北黄海海域富营养化形成机制及生态响应的深入探索,还涉及到海洋国土安全或海洋权益区分等一系列敏感问题。
虽然已有研究呈现了鸭绿江口西汊道沉积物中生源要素的沉积特征[11],但因其反映的是近百年来已经脱离径流影响的鸭绿江西汊道沉积环境的变化,生源要素主要来源于附近海岸及相邻海水养殖区域。目前鸭绿江口的主水道已由西汊道转移至东汊道,对东汊道生源要素沉积记录的研究才能全面反映鸭绿江流域的营养盐物源状况及其指示的生态环境变化过程。本文通过分析鸭绿江东汊道A4柱的沉积记录,利用TOC、TN和TP等沉积指标来追溯鸭绿江口及邻近海域环境变化的历史,为鸭绿江口乃至北黄海海域的生态环境保护和可持续发展提供科学依据。
-
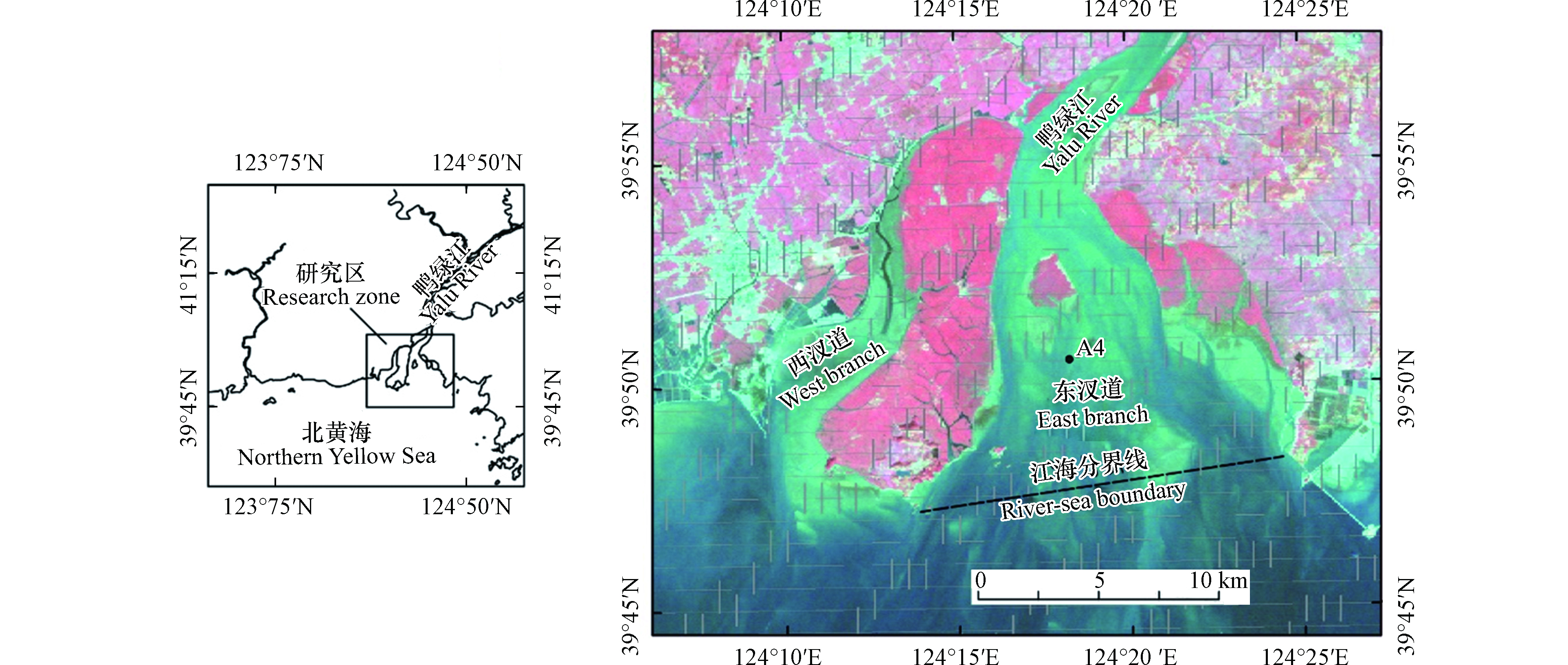
2018年8月在鸭绿江主汊道的江心滩,于水深约1 m时利用重力采样器采集了一根146 cm长的柱状样,编号为A4,位置见图1。样品的野外采集、包装运输和送检测定的全过程严格执行《海洋调查规范》[12]和《海洋化学调查技术规程》[13]相关要求。柱状样分样间距为2 cm,分样样品用自封袋包装,送入冰箱冷藏保存。整个柱状样呈现青灰色黏土质粉砂,肉眼未见明显差异。
-
210Pb和137Cs测试均在中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所湖泊与环境国家重点实验室进行,利用高纯锗井型探测器(Ortec HPGe GWL)γ谱仪进行测定。标准样品由中国原子能研究院和英国利物浦大学提供,226Ra标准样品由中国原子能研究院提供[5]。
对于210Pb数据,通过测定沉积物中的226Ra来确定本底210Pb值,并将其扣除,从而获得过剩的210Pb比活度值[14]。计算沉积速率过剩210Pb比活度采用CIC(Constant Initial Concentration)模式。之所以采用CIC模式,是考虑到210Pb主要来源于流域的表土侵蚀,210Pb在水中滞留时间较短,其含量受控于物源,即210Pb增加是沉积物增加所致[15-16]。
式(1)中,A为剖面中质量深度H处的过剩210Pb比活度(Bq·kg−1);A0为剖面中质量深度为沉积物—水界面上的初始比活度 (Bq·kg−1);λ为衰变系数,取值为0.03114 a−1;t代表沉积物年龄(a)。
对于137Cs数据,用1963年的主计年时标来计算沉积速率;其余各层的标年根据137Cs计算出的沉积速率用线性内插(或外延)法计算获得[17]。尽管137Cs沉积蓄积峰可能存在向上或向下的扩散运移,但不会改变137Cs蓄积峰在沉积剖面中的赋存位置,不影响137Cs蓄积峰的断代标志意义[18]。
式(2)中,r为沉积速率(cm·a−1);H为137Cs蓄积峰的深度(cm);n为取样年份。
-
采用重铬酸钾氧化—还原容量测定总有机碳:通过加热,使加入标准重铬酸钾的浓硫酸中的样品中的有机碳氧化为二氧化碳,再用硫酸亚铁标准溶液回滴过量的重铬酸钾。计算消耗的重铬酸钾量,推算出样品中有机碳的含量[11]。采用凯氏滴定法测定总氮:在催化剂的作用下,加入浓硫酸转化样品中的有机物,使含氮有机物转化为硫酸铵;加入强碱蒸馏使氨逸出;再用硼酸吸收后,用酸滴定测出氮的含量[11]。采用分光光度法测定总磷:用催化剂和浓硫酸处理样品,再用X荧光光谱仪测试[11]。样品测试相对偏差均<2%,回收率>98%。
埋藏通量的计算:样品的平均干密度乘以沉积速率再乘以生源要素的百分含量得出该时段内陆源物质的埋藏通量[2]。
式中,BFTP (μmol·a−1·cm−2) 是沉积物的埋藏通量;Ci (μmol·g−1) 是沉积物中不同形态生源要素的浓度;S (cm·a−1)为沉积速率;ρd为沉积物样品的干密度。
-
黏土含量采用BT-9300HT激光粒度仪进行测试,测量范围为0.1—2000 μm,重复测量误差小于3%。分析前,样品中加入10—20 mL浓度为0.05 mol·L−1的[NaPO3]6作为分散剂,沉积物粒度参数根据Folk和Ward算法公式得出[19]。
含水率的测定采用《海洋监测规范》中的重量法[20]。
-
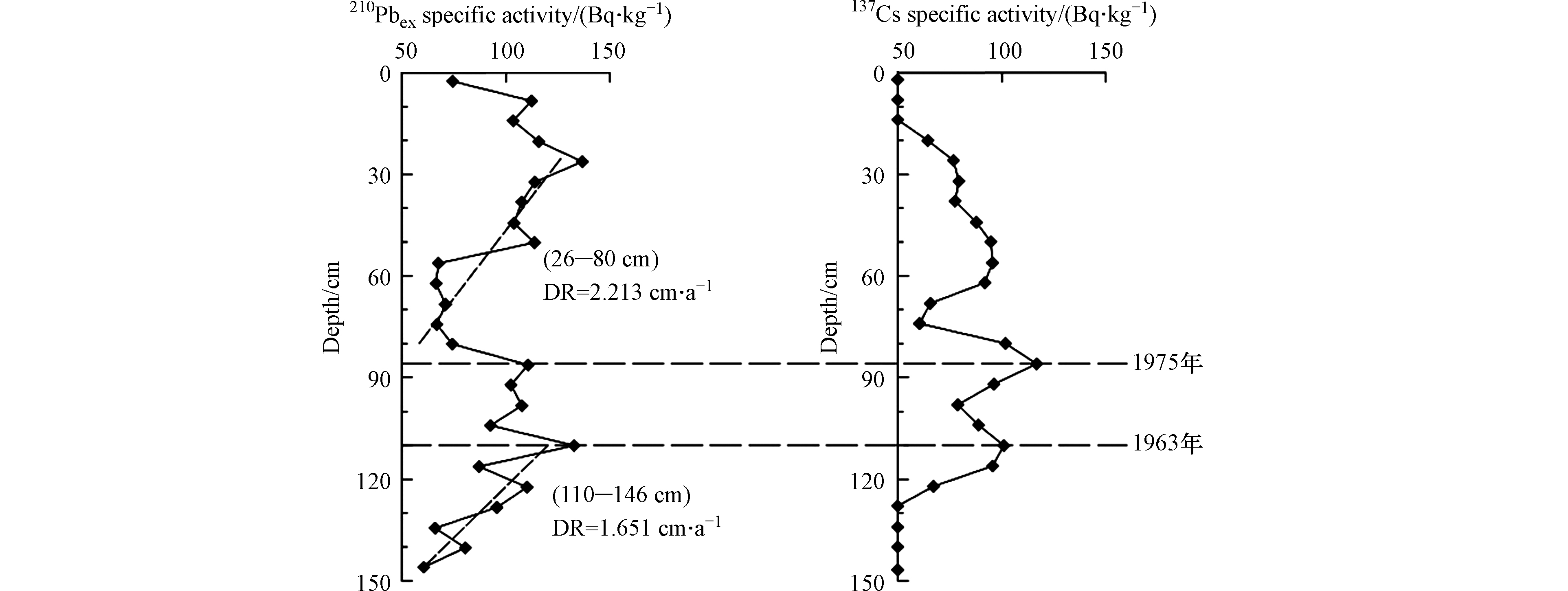
210Pbex的比活度理想状态下是随深度呈指数衰减的趋势,但是,鸭绿江A4柱状样并未呈现出理想状态,其衰变曲线形态呈现1个表层干扰段和2个衰减段(见图2),这种210Pb曲线类型多出现在河口地区,当沉积速率变化较快或沉积环境发生较大改变时,210Pb垂直分布模式常呈现多段式[20-21]。在这种情况下,可按指数函数分别拟合来计算年龄[16]。A4柱状样26—80 cm和110—146 cm按指数函数拟合的沉积速率分别为2.21 cm·a−1和1.65 cm·a−1。
当210Pb垂直分布模式呈现多段式时,需要137Cs方法加以佐证,得到精确沉积速率[21-22]。当潮流作用或人为扰动影响不大时,137Cs在柱状样中含量偏低,其沉积速率计算与210Pb方法相比不占优势[23];但当潮流作用或人为扰动的影响偏大时,尽管137Cs的含量偏低,因其抗干扰能力强,137Cs沉积速率的计算比210Pb更可靠。137Cs为人工放射性同位素[18],来自于大气核实验或来自于核事故,输入函数简单清楚。A4柱状样137Cs曲线出现3个蓄积峰(图2),1963年以前的核试验无论是大气沉降还是受其影响的各类沉积物都留下了可识别的沉积记录。用A4首个蓄积峰代表1963年,由此得出137Cs的沉积速率为2.08 cm·a−1,与210Pb拟合的平均沉积速率较为吻合。A4柱状样84 cm处的137Cs蓄积峰用沉积速率推算是1975年。1975年前后,中国进行了22次核试验,鸭绿江口保留有这一事件的沉积记录[24]。
-
含水率、黏土含量与TOC、TN、TP的相关关系见表1。结果表明,含水率对TOC、TN、TP沉积几乎没有影响;黏土含量对TOC、TN沉积的影响也非常小,只与TP的相关系数达到了0.43;粒度效应总体不明显。究其原因是主汊道A4柱状样自下而上粒径组分及中值粒径变化幅度不大,沉积物粒度松散,均为粉砂质黏土,在很大程度上排除了沉积物中TOC、TN和TP含量变化的粒度效应。因此河口沉积物中TOC、TN和TP含量的总体变化更多地反映出其沉积环境的变化。
TN与TP之间的相关系数偏高,达到了0.43,表明鸭绿江口主汊道沉积物受到了相同的生物地球化学过程调控,或TN和TP可能有部分相同的物质来源。
-
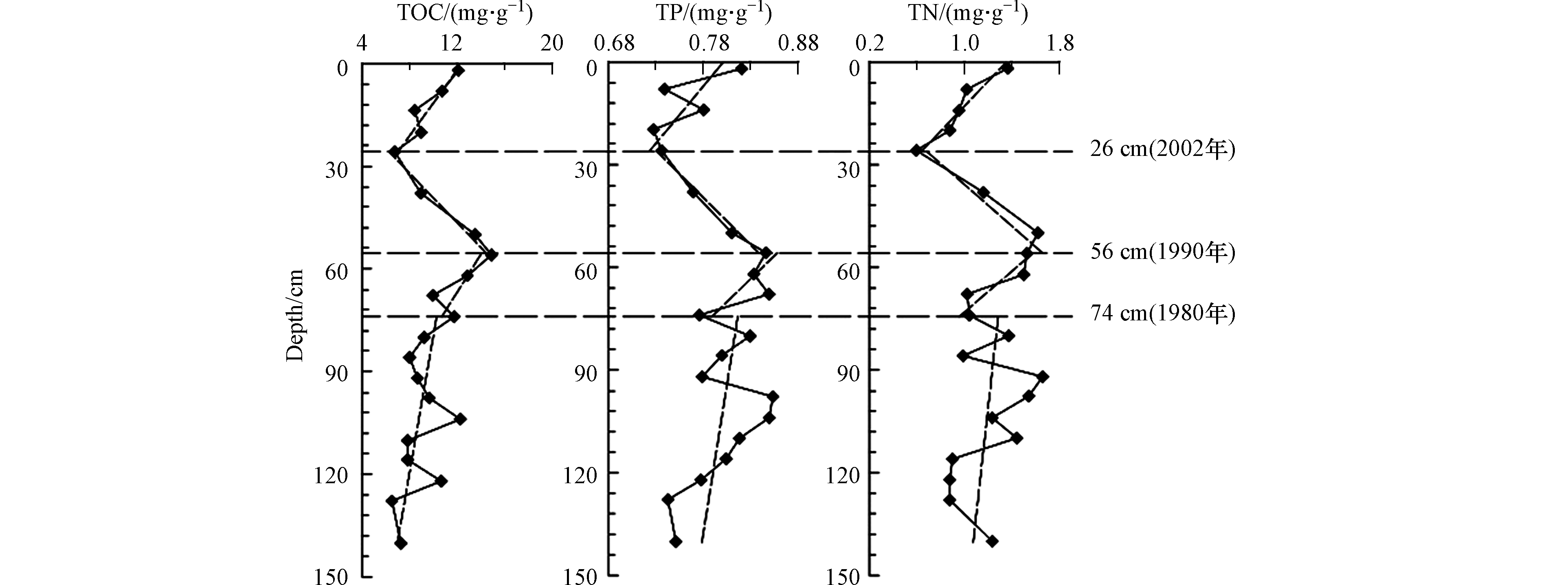
鸭绿江主汊道柱状沉积物中TOC、TN、TP含量特征值见表2。结果显示,TOC的含量在6.56—14.82之间,平均含量为9.87 mg·g−1;TN的含量在0.59—1.65 mg·g−1之间,平均含量为1.18 mg·g−1;TP的含量在0.73—0.85 mg·g−1之间,平均含量为0.79 mg·g−1。
河口水体的富营养化程度主要受到流域营养盐的输送量的变化的影响,而水体富营养化程度的提升必然导致河口水体初级生产力的增加,也必然能够在河口沉积物中留下相应的沉积记录[1]。TOC的含量介于0.656%—1.482%之间(均值为0.987%),满足海洋沉积物一类标准2%[25]。但是,TP的含量介于0.073%—0.085%之间(均值为0.079%);TN的含量范围介于0.059%—0.165%之间(均值为0.118%),高于引起最低级别生态风险效应的下限0.055%和0.06%[26],这意味着TP、TN已经成为鸭绿江口沉积物的污染物,需要引起警觉。生源要素含量的垂直分布曲线见图3。
主汊道柱状样TOC、TN、TP的垂向曲线自下而上都可以大致分为4段:146—74 cm是波动很大,但各要素含量总体上升趋势缓慢,说明尽管人类活动的影响已经存在,但人类作用的影响还相对微弱;74—56 cm波动减小,但各要素含量上升趋势明显加快,短期就达到极大值,说明人类活动的影响急剧增加;56—26 cm各要素含量波动很小,但各要素含量下降趋势明显,从最大值直抵最小值或接近最小值,表明上世纪90年代以来,严格的环境保护和生态建设政策发挥作用;26—0 cm波动不大,但各要素的含量又开始缓慢回升,这一现象不是人类活动造成的,而是生源要素矿化作用的自然过程。
TOC、TN、TP的垂向曲线自下而上的这种变化是对鸭绿江口不同时段环境变化的响应。74 cm以下的TOC、TN、TP的含量波动较大,主要原因是当时鸭绿江干流的太平湾水库尚未建成,河流的年际径流变差系数较大造成的;74 cm以上的TOC、TN、TP的含量都波动较小,主要原因是太平湾水库的修建改变了河流的年际径流变差系数。
TOC、TN、TP的次高值均出现在表层,揭示流域新输入河口的、还没来得及矿化的陆源有机质增量的贡献主要集中在表层。这里也是动植物遗体与代谢产物分解、生物泵向下传递、物理化学凝聚等生物化学作用的起点[27]。起分解作用的微生物大多生存在沉积物表层,随水深增加,氧气逐渐缺乏,微生物分解有机物的作用将迅速减弱[28],大致在26 cm位置,由于沉积作用和微生物数量的减少等原因,使这种生物化学作用影响降到最低。生源要素这种矿化作用自然过程在其它河口湾区普遍出现[3]。
-
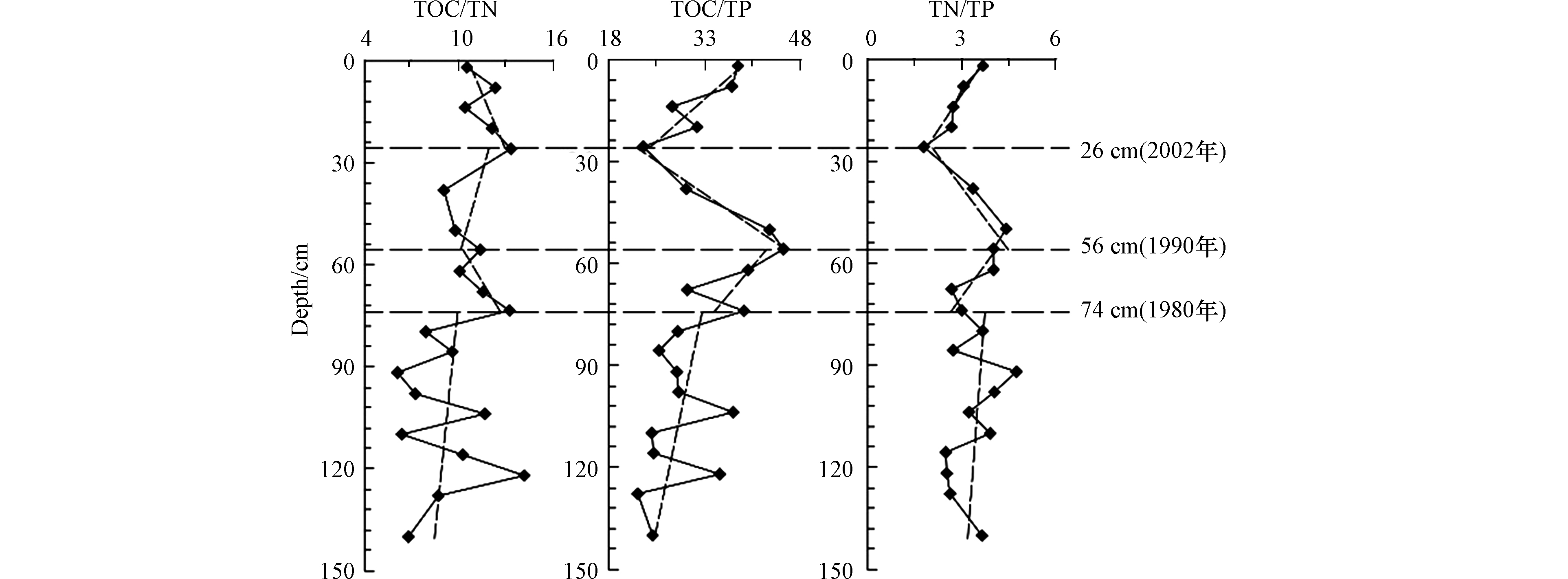
沉积物中TOC、TN、TP的比值在早期成岩过程中具有重要的指示意义。如果是非陆源物质为主的沉积物,则TOC、TN、TP的比值在沉积初期时保持106∶16∶1的比值,称之为Redfield比[3]。在受陆源输入物质影响强烈的区域,TOC、TN、TP的比值往往会偏离Redfield比值,成为指示河口区域有机质来源变化的重要指标。TOC/TN、TN/TP、TOC/TP的垂直分布曲线见图4。
-
TOC/TN的取值范围为6.13—14.13,平均值为10.13。TOC/TN是用于沉积物中有机质来源甄别的常用指标。水生藻类一般富含蛋白质但缺乏纤维素,相比陆地维管束植物富含纤维素但缺乏蛋白质,因此海洋植物有机质TOC/TN普遍偏低[29],新鲜藻类有机质的TOC/TN在3—8,而陆地植物有机质的TOC/TN水平较高,通常为14—23,如果沉积物中有机质TOC/TN在5—20,常被认为受到两种物源的影响[29]。鸭绿江主汊道柱状样的TOC/TN的平均值为10.13,说明这里的沉积物中有机质总体是双源的。
TOC/TN在146—74 cm范围内波动增大,可能也是前述的河流年际径流变差系数较大造成的;74 cm以上受太平湾水库修建的影响而波动变小。
TOC/TN比值的垂向分布自下而上分3段:146—74 cm是缓慢降低,74—26 cm是先降后升,26—0 cm又是逐渐降低。沉积物TOC/TN的垂向分布,是对不同沉积时期有机质输入的响应,可以推断出沉积物中有机质的海、陆来源变化。74 cm以下TOC/TN比值在缓慢上升,表明有机质来源开始发生改变,陆源的贡献逐渐增加,海源的贡献增加减少;74—26 cm TOC/TN比值是先降后升,说明陆源的贡献有一段时间的减少,但并没有改变沉积物陆源的贡献越来越大的总体趋势。24—0 cm在垂向上陆源有机碳比例逐渐降低,海源有机碳比例逐步升高,这不一定是海源和陆源有机质输入发生了逆转,更有可能与近表层的生源要素的矿化作用有关。
-
TOC/TP的取值范围为22.75—45.20,平均值为31.92;其垂向变化趋势是146—74 cm缓慢上升,74—56 cm是急速上升,56—26 cm是急速下降,26—0 cm是迅速回升。
TOC/TP垂向74 cm以下的波动剧烈也是前述的河流的年际径流变差系数较大造成的,74 cm以上在太平湾水库修建以后的这一时间段就和缓许多。
沉积物TOC/TP对早期成岩过程具有重要指示意义。相关分析表明,TOC与TP的线性相关性差(R=0.15,P<0.05),这说明TP的变化与TOC的变化关系不大。146—74 cm的TOC/TP比值缓慢上升,可能与P的含量逐渐减少有关,因为P除有机磷形态外,还存在无机磷,时间越早以磷酸钙的形式固定下来的P就越多。74—56 cm的TOC/TP比值急速上升,可能主要与流域陆源输入的TOC明显增加有关,是河口沉积环境对营养盐结构变化的一种响应(没有证据表明这段时间内P的输入减少,相反因为人类活动的影响还有可能增加,但TOC的增加速度更快)。56—26 cm的TOC/TP比值急速下降,说明鸭绿江口的营养盐结构再一次发生了改变,极有可能也是国家环境保护与生态环境政策发挥了作用,使得TOC含量的急速下降。26—0 cm间TOC/TP比值的变化并不代表沉积环境营养盐结构的改变,也是近表层生物化学作用的结果。近表层的生物死亡后,P快速分解释放,表层沉积物中P含量相对降低,使得表层TOC/TP处在较高的水平,随后TOC/TP比值逐渐降低。
-
TN/TP是水中N、P与沉积物中溶出、释放两种动态过程的综合反映。TN/TP常被用来判定是受N限制还是P限制,若比值小于16,为P限制[29]。鸭绿江口沉积物中的TN/TP比值在1.77—4.70之间变化,均小于16,远低于Redfield比,说明柱状样总体上受P限制。
与前两种比值相比,TN/TP波动不是很剧烈,与TOC/TP具有类似的垂向变化趋势:146—74 cm 是缓慢上升,74—56 cm是急剧上升,56—26 cm是迅速下降,26—0 cm是缓慢升高。
相关分析表明,TN与TP有一定的相关性(R=0.43,P<0.05),表明TN与TP可能同步变化。146—74 cm的TN与TP都在增加,但十分和缓;74—56 cm的TN与TP增加很快,是陆源输入迅速增加的结果,和改革开放后迅速发展的经济活动有关;56—26 cm的TN与TP的下降同样是政策调整带来的河口营养盐结构改变;同样,26—0 cm TN/TP比值的变化与近表层的生物化学过程有关。
-
河口沉积物的埋藏通量主要受沉积物孔隙度、微生物活性、生物扰动、底层水含氧量、沉积速率等众多因素的制约[3],在一定程度上反映人类活动所带来的沉积环境的变化。
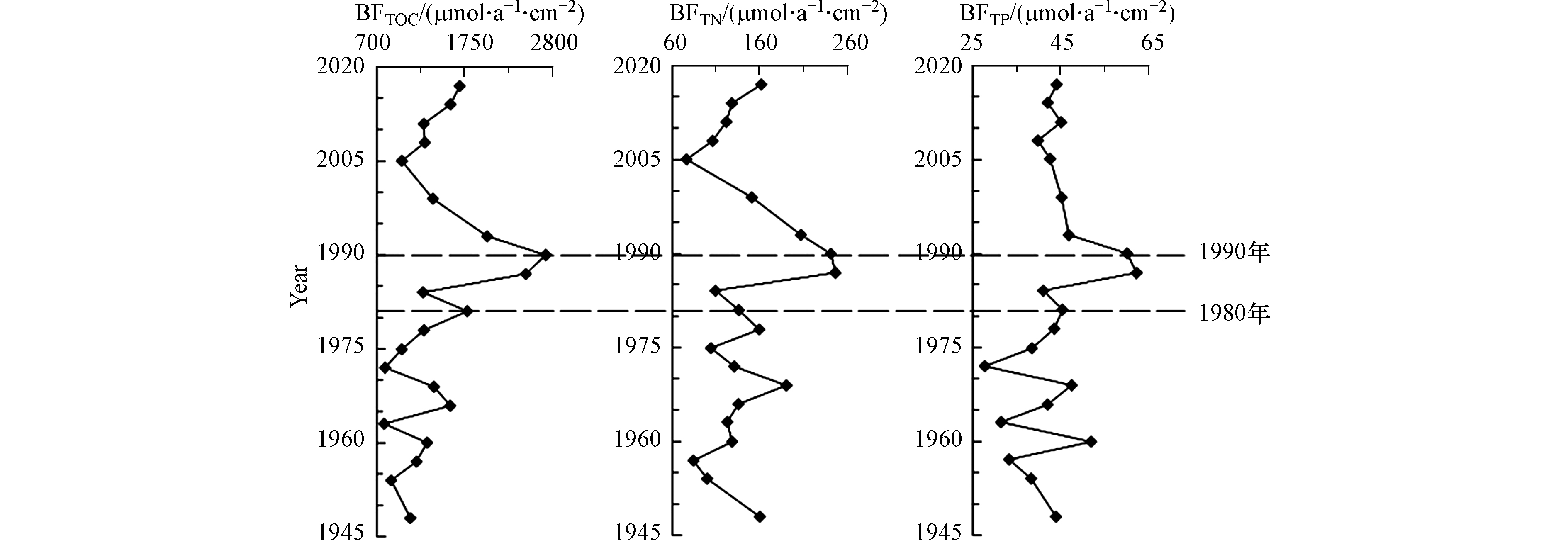
鸭绿江主汊道不同沉积年代的生源要素埋藏通量结果见图5。TOC的埋藏通量为2717.63—783.58 μmol·a−1·cm−2,平均值为1413.30 μmol·a−1·cm−2。TN的埋藏通量为245.86—75.69 μmol·a−1·cm−2,平均值为142.20 μmol·a−1·cm−2。TP的埋藏通量为62.24—27.73 μmol·a−1·cm−2,平均值为43.5 μmol·a−1·cm−2。各生源要素埋藏通量在1980年前(74 cm)尽管波动很大,但沉积通量相对较低,1980年后波动变小,但沉积通量开始明显增加,1990年(56 cm)前后达到极值,TOC和TN的沉积通量1990年后开始下降;TP值1993年后基本没有变化,TOC、TN在2005年降低到极值或次极值后又逐渐回升。
生源要素的埋藏通量反映不同时期河口沉积环境演变的趋势或人类活动的影响程度[1]。依据沉积物生源要素埋藏通量的垂向分布可将鸭绿江口环境演变大致分为3个阶段:
上世纪80年代前,TOC、TN、TP 的埋藏通量受河流的年际径流变差系数高的影响,波动加大,但保持在相对较低水平。当时我国还未进入改革开放的快速发展时期,虽然人类活动对河口影响已经初步显现,但河口水体中初级生产力相对偏低,生源要素的埋藏通量也较低,有机质输入以自然源为主。
上世纪80年代开始,伴随着改革开放和经济的高速增长,流域不断增加的生活污水和工业废水等有机类污染物与农业面源污染物大量进入河口。与此同时河口水产养殖和港口码头等涉海工程的建设,改变了岸线形态、破坏了鸭绿江口湿地和水文沉积环境,也改变了河口区域的营养盐结构。因为向海洋输入了大量的营养元素,为浮游植物的生长提供了必要的物质基础,进而使得更多的生源要素得以保留在沉积物中,致使各生源要素的埋藏通量猛增。上世纪80年代的10年间,各生源要素的埋藏通量先后达到了极值。
上世纪90年代后,伴随着高强度治理环境问题的国家政策的实施,工业和生活污染源达标排放和总量控制等措施被严格执行,鸭绿江口生态环境得到了极大的改善。生源要素的埋藏通量先后开始下降,TP降低最快,1993年就稳定了下来;TOC、TN也迅速降低。需要特别指出的是,图5显示埋藏通量2005年以后,TOC、TN又逐渐增加(TP 基本不变),并不代表人类活动的影响,这是前述的表层生物化学作用和早期成岩作用的效应。
-
(1)鸭绿江主汊道沉积物TOC的含量符合国家海洋沉积物一类标准要求,但TP和TP略高于可引起最低级别生态风险效应的下限。
(2)146—74 cm各生源要素波动较大,是河流的年际径流变差系数较高的结果,受到人类活动的影响相对较小。
(3)鸭绿江口沉积物中的有机质总体上都是双源,前期波动大,以海源为主,陆源输入影响较小,后期受太平湾水库的调节波动变小,但陆源的输入影响反而增加。
(4)鸭绿江口环境演变大致分为3个阶段:20世纪80年代以前是以自然源输入为主的时期;20世纪80年代间,人类活动使河口沉积环境营养盐结构发生了较大的改变;20世纪90年代后,国家环境保护措施起到了极大的作用,使鸭绿江口的营养盐结构逐渐趋于自然状态。
(5)26—0 cm生源要素及埋藏通量的变化,并不代表人类活动的影响,主要是表层生物化学作用和早期成岩作用的效应。
鸭绿江口生源要素的垂直分布及对环境变化的响应
Vertical distribution of the biogenic elements and their response to the environmental change in the Yalu River estuary
-
摘要: 限于鸭绿江口特殊的地缘环境,对该区域生源要素的历史演变进程不明确。在对鸭绿江主汊道A4柱状样210Pb和137CS测年的基础上,分析了总有机碳(TOC)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)等生源要素的垂向分布、特征值及埋藏通量,揭示了鸭绿江口历史时期的环境变化。结果表明,鸭绿江主汊道沉积物中TOC、TN、TP含量的变化范围分别为6.56—14.82 mg·g−1、0.59—1.65 mg·g−1、0.73—0.85 mg·g−1。除受到生物化学或早期成岩作用影响的26 cm外,生源要素垂向上都呈现先升后降的趋势,在56 cm左右达到了极值。TOC/TN显示沉积物中有机质是双源,自下而上陆源增加、海源减少。TN与TP在56 cm达到极值,都是河口沉积环境对流域营养盐输入变化的响应。根据生源要素沉积通量判断,鸭绿江河口环境演变大致分为3个阶段:上世纪80年代以前,以自然源输入为主;上世纪80年代至90年代初,人类活动带来了河口营养盐结构的变化;上世纪90年代以后,鸭绿江口的生态环境得到了很大改善。Abstract: The historical evolution process of biogenic elements in the Yalu River estuary has been unclear owing to the constraint imposed by the special geographical environment. Age determination was conducted based on 210Pb and 137Cs concentrations in the main branch of Yalu River; the vertical distribution of TOC, TN, and TP, characteristic value, and burial flux were analyzed to understand the environmental evolution of the Yalu River estuary. The range of content of TOC, TN, and TP in the sediments was 6.56—14.82 mg·g−1, 0.59—1.65 mg·g−1, and 0.73—0.85 mg·g−1, respectively, in the main branch. Except for effects of biochemical or early diagenesis at 26 cm, the vertical change in biogenic elements increased initially and then decreased, reaching an extreme value at approximately 56 cm. TOC/TN values revealed that the organic matters in the sediments had dual sources. The land sources increased and sea sources decreased with increase depth. The extreme values of TN and TP at 56 cm was caused due to the response of the estuarine depositional environment to changes in the nutrient salt input into the basin. The environmental evolution of the Yalu River estuary was divided into three stages: natural source input before the 1980s, structural changes in the nutrient input caused by human activities from the 1980s to the early 1990s, and great improvement in the ecological environment after the 1990s.
-
Key words:
- Yalu River estuary /
- biogenic elements /
- environmental change
-

-
表 1 鸭绿江口柱状样生源要素与含水率和黏土含量相关系数
Table 1. Correlation of TOC, TN, TP, water content and clay content
相关系数
CorrelationTOC含量
TOC contentTN含量
TN contentTP含量
TP content含水率
Water content黏土含量
Clay contentTOC含量 1 0.23 0.15 0.042 0.17 TN含量 1 0.43 0.0029 0.0093 TP含量 1 0.00004 0.43 含水率 1 0.51 黏土含量 1 表 2 生源要素特征值
Table 2. Characteristic values of the biogenic elements in the core of A4
特征值
Characteristic valuesTOC /(mg·g−1) TN /(mg·g−1) TP /( mg·g−1) 最小值 6.56 0.59 0.73 最大值 14.82 1.65 0.85 平均值 9.87 1.18 0.79 -
[1] 夏鹏, 孟宪伟, 李珍, 等. 广西海岸带近百年来人类活动影响下环境演变的沉积记录 [J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(2): 325-332. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2012.02.006 XIA P, MENG X W, LI Z, et al. Sedimentary records of environmental evolution during the recent 100 years in the coastal zone of Guangxi Province [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(2): 325-332(in Chinese). doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2012.02.006
[2] 杨茜, 孙耀. 东、黄海生源要素的埋藏通量及其时空分布特征 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(5): 680-685. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2015.05.007 YANG Q, SUN Y. The spatial and temporal distribution of the biogenic elements sedimentation flux in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(5): 680-685(in Chinese). doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2015.05.007
[3] 何桐, 杨文丰, 谢健, 等. 大亚湾柱状沉积物中C、N、P的分布特征及其环境意义 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(4): 524-529. HE T, YANG W F, XIE J, et al. Distribution characteristics and environmental significance of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in core sediments of Daya Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(4): 524-529(in Chinese).
[4] 杨庶, 杨茜, 曲克明, 等. 南黄海近海富营养化长期演变的沉积记录 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(1): 22-28. YANG S, YANG Q, QU K M, et al. Sedimental records of eutrophication in coastal waters of the southern Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(1): 22-28(in Chinese).
[5] 麻福伟, 李茂田, 刘演, 等. 埃及Burullus潟湖沉积生源要素变化: 百年来人类活动影响 [J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(6): 1249-1257. MA F W, LI M T, LIU Y, et al. Changes of nutrient salts deposited in the Burullus lagoon, Egypt: Effects of human activity over the past century [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(6): 1249-1257(in Chinese).
[6] 宋金明, 王启栋, 张润, 等. 70年来中国化学海洋学研究的主要进展 [J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10): 65-80. SONG J M, WANG Q D, ZHANG R, et al. Main progress on chemical oceanography in China over the past 70 years [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(10): 65-80(in Chinese).
[7] HUANG X P, HUANG L M, YUE W Z. The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River Estuary, South China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 47(1/2/3/4/5/6): 30-36. [8] ZHANG J, LIU S M, REN J L, et al. Nutrient gradients from the eutrophic Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary to the oligotrophic Kuroshio waters and re-evaluation of budgets for the East China Sea Shelf [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2007, 74(4): 449-478. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.04.019 [9] YU Y, SONG J M, LI X G, et al. Geochemical records of decadal variations in terrestrial input and recent anthropogenic eutrophication in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(8): 1556-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.05.002 [10] STROKAL M, KROEZE C, LI L L, et al. Increasing dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus export by the Pearl River (Zhujiang): A modeling approach at the sub-basin scale to assess effective nutrient management [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2015, 125(2): 221-242. doi: 10.1007/s10533-015-0124-1 [11] 李富祥, 李雪铭, 高建华, 等. 基于垂向沉积的近百年来鸭绿江河口环境演变分析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2012, 34(10): 1-5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.10.001 LI F X, LI X M, GAO J H, et al. Analysis of environmental evolution during last hundred years according to vertical sediment in the Yalu River Estuary [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2012, 34(10): 1-5, 10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.10.001
[12] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检疫总局. 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查: GB/T 12763.8—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 8: Marine geology and geophysics survey: GB/T 12763.8—2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese).
[13] 国家海洋局908专项办公室. 海洋化学调查技术规程[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2006. Special Project Office 908, State Oceanic Administration of China. Oceanic chemistry survey technical regulations [M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2006(in Chinese).
[14] 范德江, 杨作升, 郭志刚. 中国陆架210Pb测年应用现状与思考 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(3): 297-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011 FAN D J, YANG Z S, GUO Z G. Review of 210Pb dating in the continental shelf of China [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2000, 15(3): 297-302(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011
[15] 姚书春, 薛滨. 东太湖钻孔揭示的重金属污染历史 [J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(1): 158-165. YAO S C, XUE B. Heavy metal pollution history inferred from east Taihu Lake cores sediment [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(1): 158-165(in Chinese).
[16] 李亚南, 高抒. 长江水下三角洲沉积物柱状样重金属垂向分布特征 [J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(2): 154-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.02.005 LI Y N, GAO S. Heavy metal characteristics in the sediment cores from the Changjiang subaqueous delta [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(2): 154-161(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.02.005
[17] 甘华阳, 梁开, 林进清, 等. 北部湾北部滨海湿地沉积物中砷与镉和汞元素的分布与累积 [J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3): 15-28. GAN H Y, LIANG K, LIN J Q, et al. Distribution and accumulation of arsenic, cadmium and mercury in coastal wetland sediment of northern Beibu Gulf [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(3): 15-28(in Chinese).
[18] 张信宝, 龙翼, 文安邦, 等. 中国湖泊沉积物137Cs和210Pbex断代的一些问题 [J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(3): 430-440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.03.09 ZHANG X B, LONG Y, WEN A B, et al. Discussion on applying 137Cs and 210Pbex for lake sediment dating in China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(3): 430-440(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.03.09
[19] 刘月, 程岩, 李红军, 等. 鸭绿江口与邻近西海岸沉积记录的耦合 [J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(1): 76-88. LIU Y, CHENG Y, LI H J, et al. The coupling of the sedimentary records in the Yalu River Estuary and the adjacent western coasts [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(1): 76-88(in Chinese).
[20] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋监测规范 第5部分: 沉积物分析: GB 17378.5—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. The specification for marine monitoring—Part 5: Sediment analysis: GB 17378.5—2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese).
[21] 孙丽, 介冬梅, 濮励杰. 210Pb、137Cs计年法在现代海岸带沉积速率研究中的应用述评 [J]. 地理科学进展, 2007, 26(2): 67-76. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2007.02.008 SUN L, JIE D M, PU L J. An overview on the application of 210Pb and 137Cs dating in the research of recent sediment accumulation rate of coastal zone [J]. Progress in Geography, 2007, 26(2): 67-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2007.02.008
[22] 曾理, 吴丰昌, 万国江, 等. 中国地区湖泊沉积物中137Cs分布特征和环境意义 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.01.001 ZENG L, WU F C, WAN G J, et al. The distribution characteristic and environmental significance of Cesium-137 deposit profile in Chinese lacustrine sediment [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2009, 21(1): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.01.001
[23] 王慧娟, 何正中, 胡金君, 等. 广西北部湾沉积速率研究 [J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 42(6): 2120-2126. WANG H J, HE Z Z, HU J J, et al. Sedimentation rates in Guangxi Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 42(6): 2120-2126(in Chinese).
[24] CHENG Z X, JALON-RÓJAS I, WANG X H, et al. Impacts of land reclamation on sediment transport and sedimentary environment in a macro-tidal estuary [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 242: 106861. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106861 [25] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 海洋沉积物质量: GB 18668—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Marine sediment quality: GB 18668—2002[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2004(in Chinese).
[26] LEIVUORI M, NIEMISTÖ L. Sedimentation of trace metals in the Gulf of Bothnia [J]. Chemosphere, 1995, 31(8): 3839-3856. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(95)00257-9 [27] 袁华茂, 吕晓霞, 李学刚, 等. 自然粒度下渤海沉积物中有机碳的地球化学特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2003, 22(2): 115-120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.02.003 YUAN H M, LU X X, LI X G, et al. Geochemical characteristics of organic carbon in Bohai Sea sediments with natural grain size [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2003, 22(2): 115-120(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.02.003
[28] 刘霞, 徐青, 史淼森, 等. 沱江流域沉积物中氮赋存状态及其垂向分布特征 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3): 320-326. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801250012 LIU X, XU Q, SHI M S, et al. Nitrogen species and vertical distribution characteristics in the sediment of the Tuo River [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3): 320-326(in Chinese). doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801250012
[29] 曲宝晓, 宋金明, 袁华茂. 近百年来大亚湾沉积物有机质的沉积记录及对人为活动的响应 [J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(10): 119-130. QU B X, SONG J M, YUAN H M. Sediment records and responses for anthropogenic activities of organic matter in the Daya Bay during recent one hundred years [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 40(10): 119-130(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: