-
石油烃(petroleum hydrocarbons)包括汽油、煤油、柴油、润滑油、沥青等,是一类由烷烃、环烷烃、芳香烃、烯烃等烃类物质,含O、S、N化合物等非烃组分组成的一类高毒性及难降解有机污染物[1]。在勘探、开采、运输、贮存、加工和使用过程中易造成石油烃类物质的非正常泄漏[2-4],并进入土壤介质。石油烃对土壤的危害主要表现在两个方面:1)石油烃会改变土壤成分、结构,使其通透性发生改变;2)石油烃易对人体产生较强烈的致突变、致癌和致畸效应,在动植物体内产生生物富集作用。因此,保障土壤环境安全,开展石油烃污染土壤修复工作意义重大。
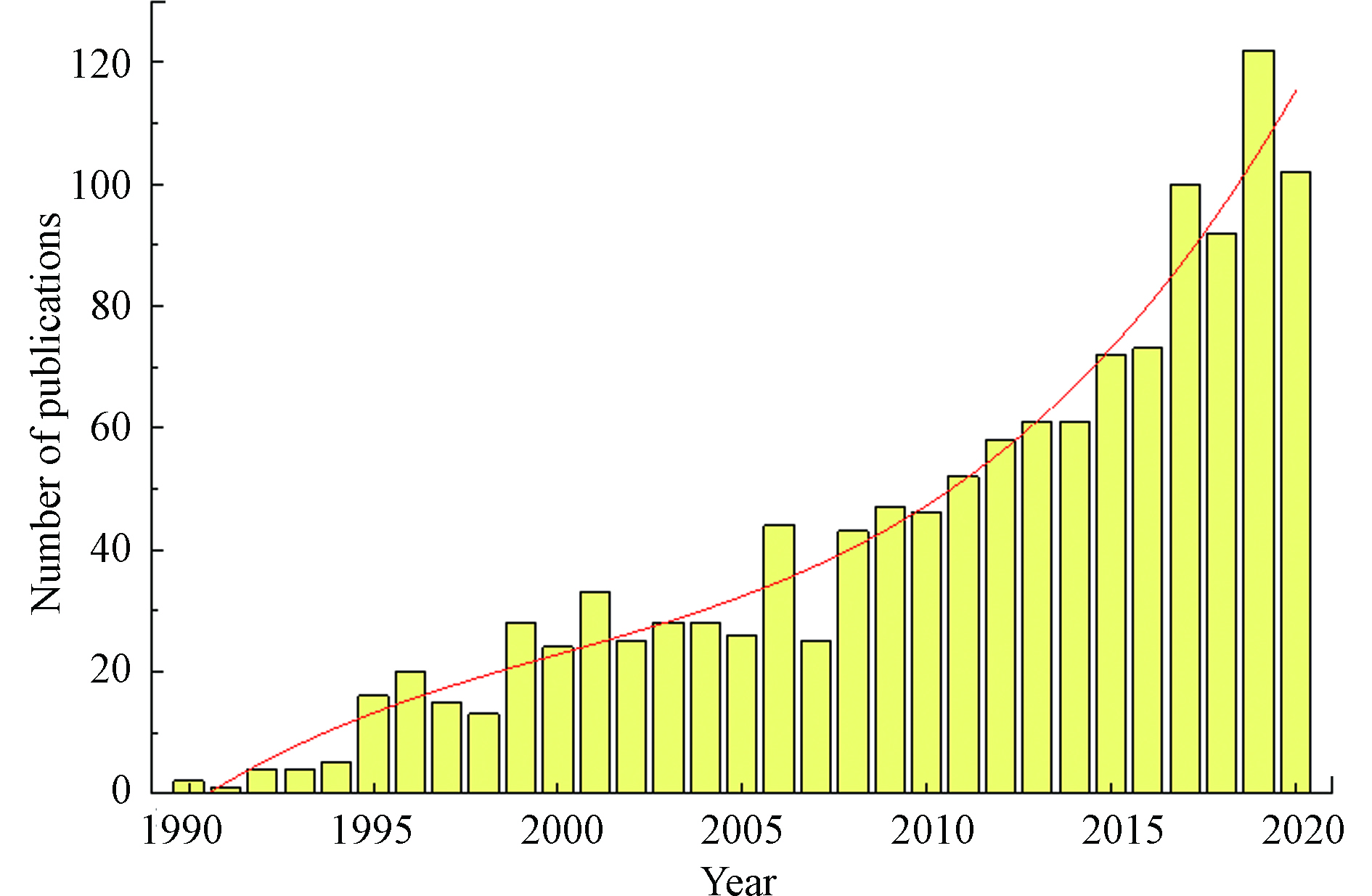
目前,石油烃污染土壤修复主要采用的技术有:化学修复技术、物理修复技术和生物修复技术。相比于物理修复技术对机械设备和人力要求高,生物修复技术修复周期长等技术短板问题,化学修复技术因具有成本低、修复周期短、效能高及适用性强等优势,常被用于石油烃污染土壤修复[5-6]。其中,经化学氧化处理后的石油烃污染土壤,后续还有利于有机衔接生物或者物理修复技术强化修复效果[7]。为掌握化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤发展动态与趋势,采用Web of ScienceTM,以石油烃、土壤和化学氧化为主题词检索,发现以化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤的研究报道的发文量呈上升趋势,统计1990年至2020年年底共有1270篇,如图1所示。由此反映出,基于化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤的研究受到研究者亲睐。
通过国内外文献的归纳整理,本文系统综述了现有的氧化技术主要类型;汇总了基于化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤的强化措施、关键影响因素及其在修复石油烃污染土壤方面的应用效果;对比分析了不同类型氧化技术应用于石油烃污染土壤修复的优缺点;并对今后化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤的发展方向与挑战提出了展望。
-
传统的芬顿是以Fe2+作为双氧水(hydrogen peroxide,H2O2)的激化剂,使体系中产生强氧化性的自由基,无差别地攻击体系中的有机污染物,从而实现有机污染物的矿化[8]。在芬顿基础上发展的类芬顿技术,主要是采用零价铁、铁氧化物及铁矿物等作为活化剂活化双氧水,实现污染物的高效降解[9-10]。基于H2O2的高级氧化技术去除土壤中石油烃的研究分析可知,不同铁基材料活化H2O2修复石油烃污染土壤的效果存在差异。现阶段,按照活化剂类型区分,主要为铁盐、铁矿物和零价铁三大类,其余归结为其他含铁物质一类。
-
基于铁盐(二价铁/三价铁)活化H2O2是最为常见的一种活化手段,在活化剂作用下H2O2高效分解生成强氧化性的羟基自由基(·OH),其主要反应过程如公式(1—5)所示[10-12]:
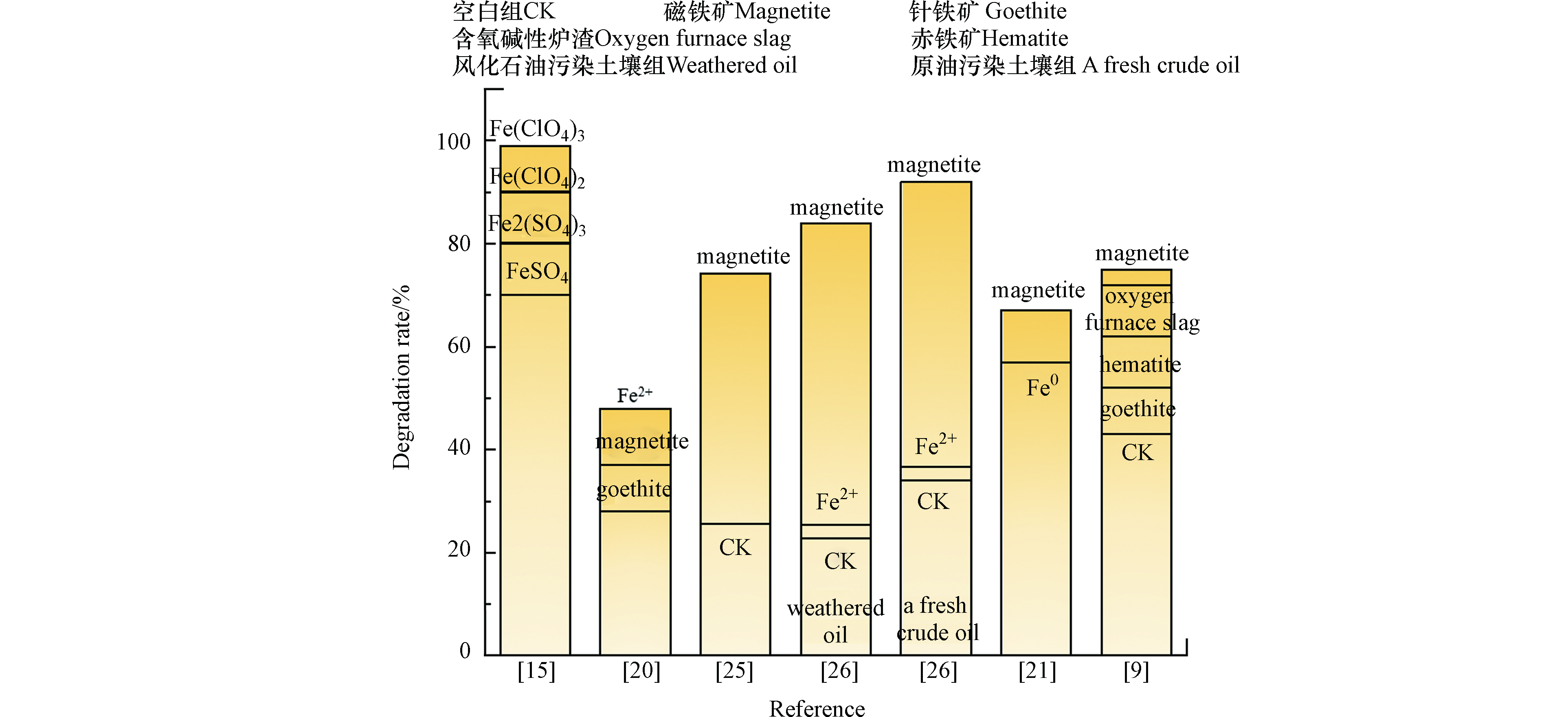
例如,LU等[13]采用间歇实验确定了H2O2和Fe3+的最佳摩尔比为300:1,反应结束时,可萃取的石油烃物质总量从32400 mg·kg−1降至21800 mg·kg−1,土壤中石油烃的去除率为32.7%。陈彩成等[14]分别采用FeSO4和Fe2(SO4)3活化H2O2修复石油烃浓度为2146.1 mg·kg−1的滩涂土壤,实验发现Fe2+和Fe3+活化H2O2体系对石油烃的去除效果分别为57.4%和48.9%。WATTS等[15]对比了不同类型的铁盐(Fe(ClO4)3、Fe(NO3)3、Fe2(SO4)3、Fe(ClO4)2、FeSO4和Fe(Ⅲ)-NTA络合物)活化H2O2去除土壤中柴油,发现采用Fe(ClO4)3和Fe(NO3)3活化H2O2时柴油的去除率达到99.0%,远高于其他铁盐Fe2(SO4)3、Fe(ClO4)2、FeSO4作用下70.0%—80.0%的去除率。从上面分析可知,Fe2+和Fe3+活化H2O2的效果不一,这可能是由于石油烃的初始浓度及土壤本身理化性质差异导致的。由于在中性条件下铁盐活化过程中存在活性差、易产生铁泥以及H2O2利用率低等缺陷,研究者们开始探寻更低廉高效的H2O2活化剂[16]。
-
土壤中本身含有针铁矿、赤铁矿和磁铁矿等铁矿物,其在土壤中的含量约为0.5%—5.0% [17]。因而,来源广泛、性能稳定的铁矿物活化H2O2应用于石油烃污染土壤修复具有良好的应用前景。
铁矿物活化H2O2过程中铁矿物表面会与H2O2形成络合物,该过程伴随着络合物内部的电子转移,并产生了≡Fe2+和HO2·。自由基反应活性很高,导致络合物不断快速分解,进一步与H2O2反应产生强氧化性的·OH[18]。铁矿物活化H2O2过程能有效降低H2O2分解速率、提高其稳定性,具有优良的传质潜力和处理效果,所以利用铁矿物作为活化剂修复石油烃污染土壤是不错的选择[19]。
SUNG等[20]研究发现在中性条件下,可溶性铁盐Fe2+和铁矿物活化H2O2,反应72 h后,铁矿物(投加量为5.0%)降解同等质量的石油烃污染土壤所需H2O2的量约为Fe2+体系的一半。这项实验结果表明应用铁矿物作为活化剂时,在达到同等降解效果的前提下能有效提高H2O2利用率。但是,铁矿物所需的反应时间远大于Fe2+。另一项实验研究表明[9],不同铁矿物活化H2O2(H2O2投加量为15.0%)去除石油烃效能存在差异。其中,磁铁矿/H2O2体系对石油烃去除率可达到79.0%,而赤铁矿/H2O2和针铁矿/H2O2体系中石油烃的去除率分别为62.0%和52.0%。由于磁铁矿中Fe(II)含量远高于针铁矿和赤铁矿,其活化H2O2的能力优于针铁矿和赤铁矿。另外,已有研究表明磁铁矿活化H2O2需要更长的反应时间,导致其能在长时间内持续产生·OH。因此,相比于其他铁矿物,磁铁矿活化H2O2更有优势[21]。当H2O2应用于实际污染场地修复时,其成本是主要考虑的因素。另外,相对于铁盐活化双氧水,铁矿物不要求苛刻的pH值,且反应过程中铁泥产生量少[22]。因此,铁矿物活化的H2O2体系在应用于石油烃污染土壤修复时比可溶性铁盐体系更具优势。
-
零价铁(Zero-valent iron, ZVI)也能用以活化H2O2,ZVI参与活化的机理与铁矿物和铁盐活化反应相似。ZVI和H2O2发生的反应如(6—7)式所示[17]:
Jamialahmadi等[21]研究了中性条件下,H2O2浓度、ZVI及磁铁矿对石油烃去除效率的影响。实验结果显示,在活化剂投加量为4.3%,H2O2浓度为2.17 mol·L−1的最佳条件下,基于磁铁矿和ZVI类芬顿体系对石油烃的去除率分别为57.0%和67.0%。从方程式(6)可以看出,ZVI活化H2O2效能高于磁铁矿的原因可能是由于ZVI持续释放Fe2+的能力优于磁铁矿。Ouriache等[23]用ZVI活化H2O2去除土壤中的老化石油,反应48 h后,石油烃的降解率达到72.2%。零价铁与铁矿物一样,其活化H2O2应用于石油烃污染土壤修复时,也能有效克服可溶性铁盐活化H2O2存在的缺陷。
-
铁基材料已被证实能有效地活化H2O2,并用于石油烃污染土壤修复。但是,为了进一步降低成本,采用含铁氧化物的固体废物是常见的手段。废含氧碱性炉渣中铁氧化物含量高,因而,以炉渣作为活化剂活化H2O2用以处理石油烃污染土壤具有理论可行性。例如,Tsai等[19]研究表明,在石油烃污染土壤(初始浓度为10000 mg·kg−1)中加入15.0%的H2O2和100 g·kg−1的含氧碱性炉渣(含有5.0%—20.0% FeO和1.0%—8.0% Fe2O3),反应40 h后,土壤中石油烃的去除率大于76.0%。同时,该研究还证实采用炉渣作为活化剂活化H2O2的石油烃去除效果优于采用等量的赤铁矿和针铁矿。另外,为了进一步强化铁基材料活化H2O2效果,有研究者采用载铁沸石(投加量为20.0%)活化H2O2修复石油烃污染土壤,反应结束后,初始浓度为6798.5 mg·kg−1的轻度污染土壤石油烃去除率可达70.1%[24]。
不同铁基活化剂活化H2O2对土壤中石油烃去除效果的影响汇总如图2和表1所示。在同一研究中,铁基材料活化H2O2降解石油烃的效果高于无活化剂的空白组,与无活化剂的空白组相比,添加了不同的活化剂的实验体系对石油烃的去除效果提高了1.11—3.70倍。不同的铁基材料活化H2O2修复石油烃污染土壤效能存在差异性,若使用铁矿物作为活化剂,赤铁矿和针铁矿的效果不如磁铁矿,使用铁盐作为活化剂时还需考虑阴离子对其的影响。此外,与铁盐相比,采用零价铁、铁矿物等材料活化H2O2时,具有pH适用范围宽及铁泥产生量少等优势。
-
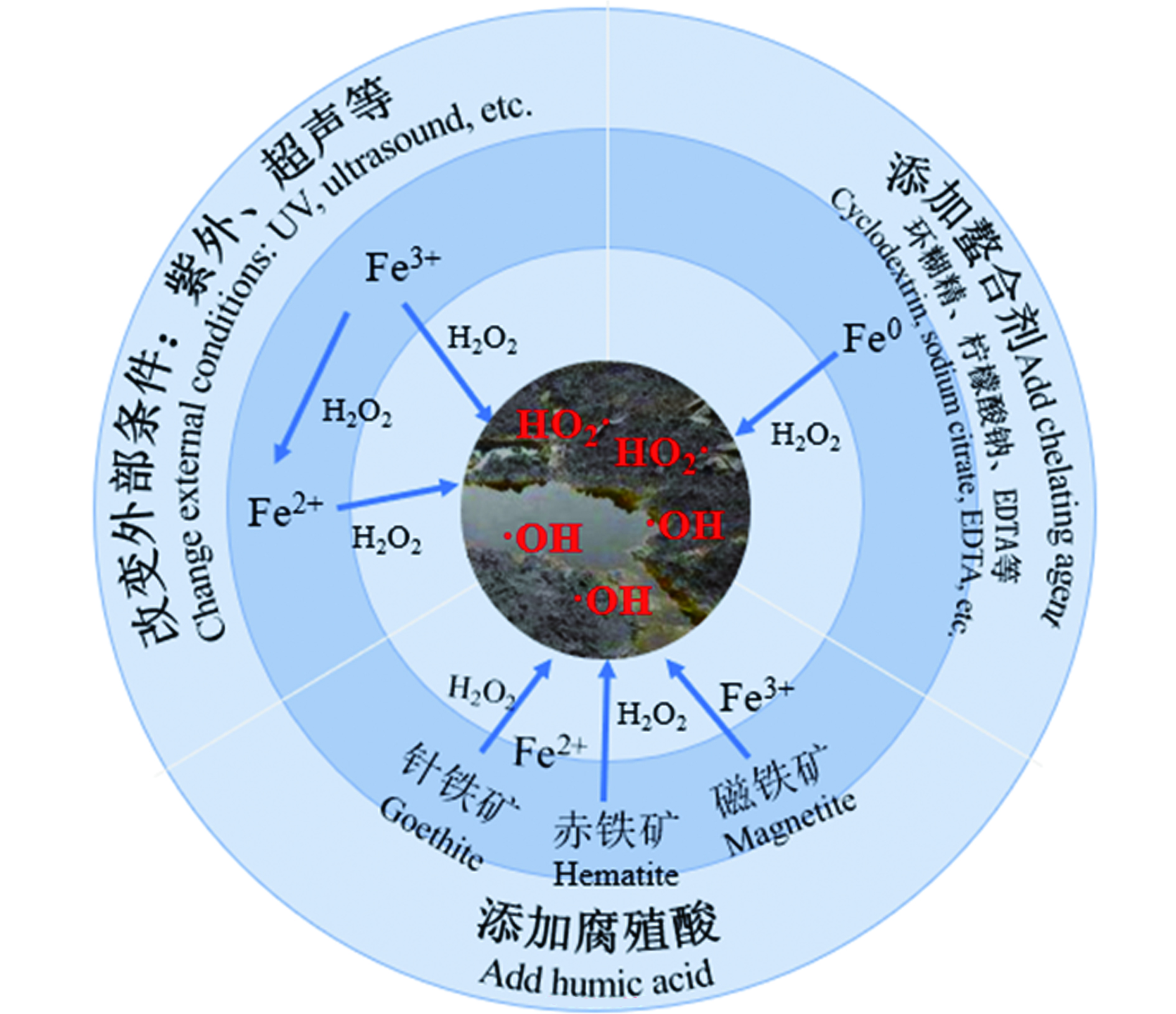
为进一步强化活化剂活化H2O2修复石油烃污染土壤效能,通过改变反应条件或添加辅助剂等措施,将有利于·OH的产生,提高石油烃污染土壤修复效率,节省反应时间和降低应用成本。目前,常用的措施主要为(具体如图3所示):1)引入超声或者紫外辅助;2)添加螯合剂;3)添加腐殖酸。
-
通过引入其他方法辅助芬顿/类芬顿修复石油烃污染土壤,是提高修复效能的有效措施。现阶段,主要有超声和紫外光辅助。超声辅助可以提高土壤中石油烃的解吸速率和降解速率,利用超声空化形成微小气泡的原理,产生高温、高压的冲击波和微射流使污染物从土壤中解吸出来,同时超声波使水分子分解成·OH等具有强氧化性的自由基[27-28]。例如,Sivagami等[29]采用超声辅助芬顿用于处理含油污泥中的石油烃,结果表明,当pH为3.0,超声功率为100 W,超声波振幅为40.0%—50.0%条件下,超声10 min可去除84.3%的石油烃,是单独芬顿的2倍。可见,超声辅助可有效促进芬顿/类芬顿修复石油烃污染土壤效能。采用紫外辅助芬顿/类芬顿是提高石油烃污染土壤修复效能的另一重要手段。例如,GHARAEE等[30]发现紫外辅助纳米ZVI活化H2O2,可使土壤中石油烃去除率高达91.0%,约是纳米ZVI活化H2O2体系的1.08倍。
采用超声和紫外协同辅助芬顿/类芬顿也受到了研究者青睐。例如,艾勇军等[31]在处理老化石油烃污染土壤时采用超声波和紫外线−芬顿反应联用的方法,其中超声波、紫外线辐射与芬顿试剂共同作用时,石油烃的最大去除率达到71.6%,分别是超声波-芬顿体系和紫外−芬顿体系的1.82倍和1.70倍。同样地,GHARAEE等[30]通过紫外光强化纳米ZVI活化H2O2与超声波联用技术对石油烃污染土壤进行修复,在最佳工艺条件下,紫外超声波联用-芬顿体系下的石油烃去除率为99.0%,分别约是芬顿、紫外-芬顿、超声波-芬顿体系的1.18倍、1.09倍和1.11倍。因此,利用超声及紫外辅助是提高芬顿/类芬顿修复石油烃污染土壤效果的有力手段。但是,上述辅助措施应用于实际石油烃修复工程仍然存在鸿沟。
-
螯合剂在芬顿/类芬顿反应中具有以下优势:1)螯合剂的存在可以限制过渡金属的沉淀,促进过渡金属从固体表面溶解,并加速活性氧化物种的产生;2)螯合剂的存在促进了·OH等活性物种在活化剂固体表面形成,从而提高了反应的降解速率。因此,在芬顿/类芬顿反应过程中,添加螯合剂是常见的强化措施。常用的螯合剂有乙二胺四乙酸(简称EDTA)、柠檬酸及其钙、钾、钠盐和草酸及其钙、钾、钠盐等[3235]。例如,Ouriache等[23]采用EDTA和ZVI的类芬顿工艺去除土壤中的老化石油,在最佳工艺条件下(H2O2、ZVI和EDTA摩尔比为15:4:4),处理48 h后,石油烃的降解率达到72.2%,约是ZVI类芬顿体系的2倍。Lu等[36]研究发现采用EDTA螯合Fe3+的类芬顿可使土壤中石油烃含量从14800 mg·kg−1减少至2300 mg·kg−1,去除率为84.5%。李方敏等[37]对比了四种不同的螯合剂β-环糊精、草酸钠、EDTA二钠和柠檬酸三钠处理室内模拟石油烃污染土壤,反应结束后发现β-环糊精体系石油烃去除效果最好,去除率为41.5%,是空白对照组的3.05倍[38-39]。因此,螯合剂是提升芬顿/类芬顿修复石油烃污染土壤效果的良方。但是,在实际应用中应充分考虑螯合剂本身对土壤环境的危害,结合实际情况优选环境友好的螯合剂。
-
腐殖酸是一类广泛存在于土壤中的大分子有机物质,其与活化剂中的金属离子结合可以提高·OH的形成速率、加快活化剂的氧化还原循环过程,从而加速反应的氧化进程[40]。因此,腐殖酸的存在能有效强化芬顿/类芬顿反应过程。Xu等[41]研究了用腐殖酸和溶解性Fe2+溶液进行预浸渍后再添加H2O2修复原油污染土壤。实验结果表明,加入了腐殖酸后H2O2分解速率较慢,并且能产生较多稳态·OH。控制该体系的最佳反应条件(25 mmol·L−1 Fe2+溶液、0.7 mg·mL−1腐殖酸和700 mmol·L−1 H2O2)下能有效去除65.7%链长为C21—C30的石油烃。另一项研究[42]也表明在氧化长链原油时,腐殖酸这类土壤有机质与铁的结合能产生较多的·OH。值得注意的是,腐殖酸一般在pH为5—7范围内对芬顿/类芬顿反应具有较好的促进效果[43]。
-
已有研究表明[23-24]过量的H2O2会抑制芬顿/类芬顿反应,导致石油烃污染土壤修复效能低,其主要原因在于加入过量的H2O2会消耗或清除·OH,并形成反应性较低的HO2·(原理如反应式8−9所示[12])。反应过程中,将等量的H2O2分批投加可有效解决这个问题。分批投加等量的H2O2有利于产生适量的·OH,提高其与污染物接触率,并有效解决了H2O2反应迅速的问题。基于H2O2的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤时,分批投加还可以减少土壤有机物质的氧化,这将利于石油烃去除率的提高。
徐金兰等[44-46]研究发现,将H2O2分次投加,比提高H2O2浓度或者增大Fe2+浓度效果更佳,将等量的H2O2分3次投加,土壤有机质氧化率与单次投加相比降低了25.0%,而石油烃的氧化率提高至50.0%。再如,辛磊等[47]同样发现,将H2O2分批投加对石油烃的氧化效果有所提高,H2O2投加次数的增加可有效提高H2O2稳定性,同时也能降低土壤有机质氧化率。因此,通过改变H2O2的投加方式是提高石油烃污染修复效能的有力途径。
-
无螯合剂的芬顿/类芬顿反应受pH影响较大,一般控制该反应pH为3以防止体系中的铁离子形成沉淀。但WATTS等[48]研究发现,在类芬顿反应体系中,pH中性条件下可能产生更多·OH。同时有研究表明,加入螯合剂后形成的螯合铁氧化体系将芬顿/类芬顿反应的理想pH范围扩展到6.0—8.5 [49]。因此,在自然土壤pH值条件下即可应用H2O2降解土壤中的石油烃。在无螯合剂的芬顿/类芬顿反应体系需严格控制反应pH为酸性,但是土壤酸化势必会改变土壤中其他物质的活性,尤其是重金属类物质。因此,添加螯合剂拓宽芬顿/类芬顿体系pH适用范围是解决上述问题的有效途径。
-
芬顿/类芬顿体系的反应温度在一定范围内升高有利于促进H2O2分解产生·OH,同时也提高了分子的运动速率,加快了H2O2氧化速率,进而提高了石油烃的去除率。有研究控制类芬顿反应温度为10—40 ℃,结果显示在20 ℃体系下H2O2的氧化降解效果最好,石油烃去除率为70.1%,大约分别是10 ℃和40 ℃的1.4倍和7.57倍[24]。但是,反应温度过高会使H2O2分解产生H2O和O2,极大地影响氧化剂的氧化活性。因此,反应温度为20—25 ℃是芬顿/类芬顿反应比较适宜的反应温度。
-
随着反应体系H2O2浓度升高,产生·OH的量随之增多,当H2O2浓度过高时,过量的H2O2消耗体系的·OH,且H2O2会与土壤有机质发生反应,影响催化氧化效率,导致石油烃降解率降低。蔡嘉希等[24]控制不同H2O2投加量处理轻度、中度和重度石油烃污染的土壤时,发现当H2O2投加量为0.75 mL·g−1时,轻度污染土壤去除率最高为70.1%,而针对中度和重度污染土壤,H2O2投加量为0.6 mL·g−1时,石油烃去除率分别为65.3%和52.3%。因此,依据实际污染物浓度的差异,合理的投加H2O2是保障修复效果的关键。
-
H2O2与活化剂的投加比例在石油烃降解过程中起着重要作用。在一定范围内,石油烃的降解率随活化剂与H2O2比例的增大而增大[39]。活化剂浓度高,对H2O2活化效果好,一定时间内产生较多的·OH攻击附着在土壤颗粒表面的石油烃,在该过程中生成的·OH对石油烃的降解速率高于生成其他氧化基团的速率[50]。活化剂浓度低,活化H2O2产生的·OH量少,限制石油烃氧化降解过程[51]。已有实验表明[37-39,51-52],当控制H2O2与活化剂Fe2+摩尔比约为100:1时,能取得较理想的石油烃去除效果。
基于H2O2的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤主要影响因素及其影响的关键原因,归结如表2所示。
-
H2O2是无选择性氧化的氧化剂(E0=1.8 V),在铁基材料活化剂的作用下可分解生成具有强氧化能力的·OH(E0=2.8 V),能有效去除石油烃,且反应后便于促进石油烃降解菌等微生物的生长[10, 53]。基于H2O2高级氧化技术中,无论是芬顿,还是类芬顿处理石油烃污染土壤的副反应剧烈,存在·OH寿命短且反应过程产生的热效应和白烟易造成二次环境风险和安全问题的劣势。另外,芬顿反应修复石油烃污染土壤,需要苛刻的pH条件(pH=3),产生大量的铁泥,过低的pH条件极易活化土壤中的重金属,二次污染风险问题不容忽视。同时,芬顿反应过程中产生的铁泥容易水解沉淀,生成胶体或者沉淀物包覆在土壤颗粒表面,影响修复效率。除此之外,芬顿试剂进入土壤后,H2O2快速分解使土壤有机质含量显著下降[54]。在芬顿基础上发展的类芬顿技术,不仅有较广泛的pH使用范围和丰富的催化剂种类,同时还减少了铁泥的产生量,有效地克服芬顿反应的缺点。因此,类芬顿比芬顿更适合用于石油烃污染土壤修复。最后,基于H2O2的高级氧化技术修复石油烃实际污染场地时,应考虑药剂投加量、修复成本和中间产物对环境生态的影响等因素,加强对于实际污土壤修复应用的理论和实践研究。
-
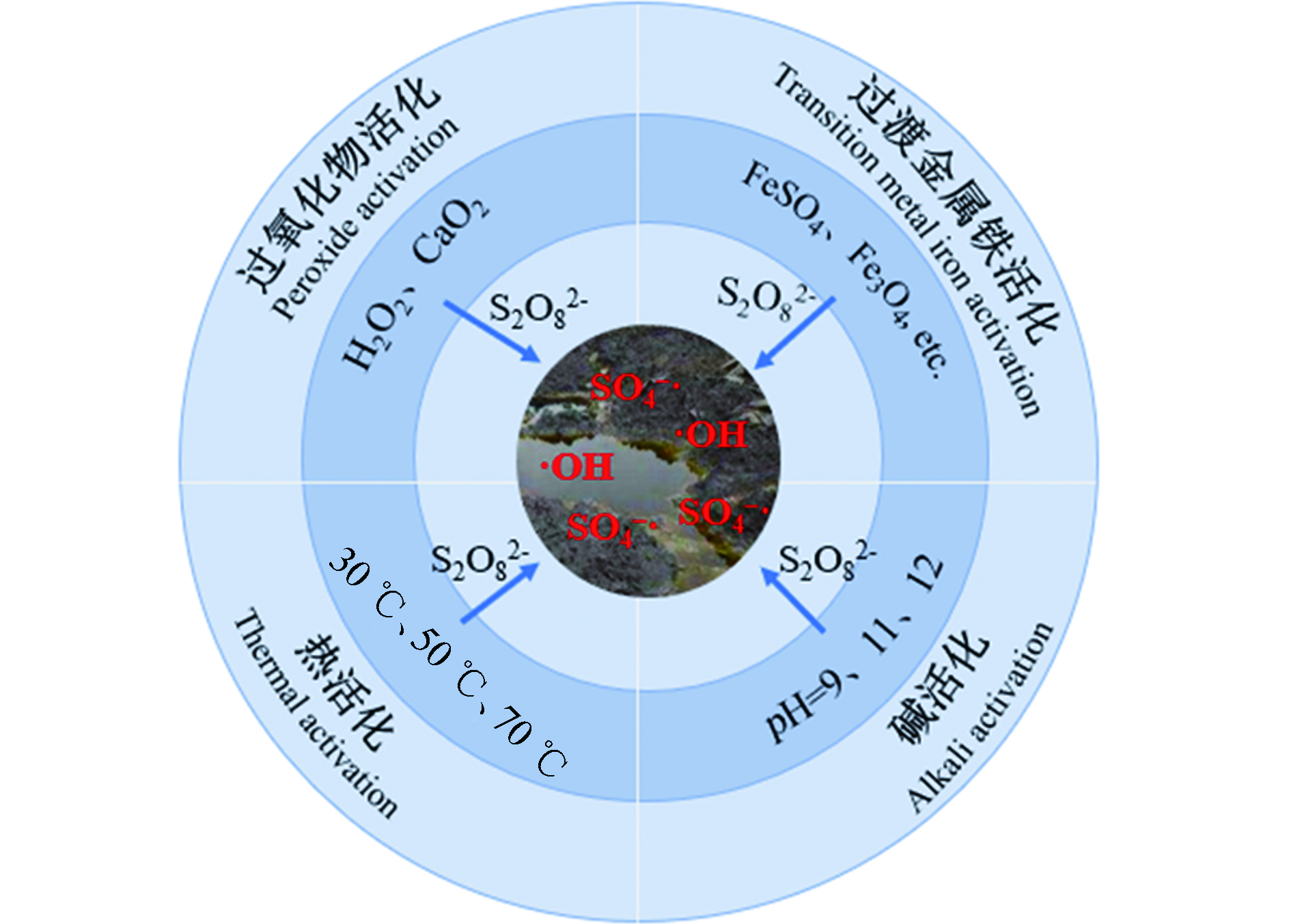
过硫酸盐(Persulfate, PS)在一定条件下可以产生氧化性自由基,攻击土壤中的有机污染物,实现有机污染物的有效降解。PS主要有钠盐、钾盐和铵盐,但钾盐溶解度小,铵盐易挥发。因此,常选择过硫酸钠等盐作为氧化剂。PS在不同活化手段的激活下可产生具有强氧化性的硫酸根自由基(SO4−·)(E0=2.6 V)和羟基自由基(·OH)(E0=2.8 V),可去除土壤中的大部分石油烃[55]。基于PS的高级氧化技术去除土壤中石油烃的研究分析可知,为促进PS分解,使体系中产生更多的SO4−·等活性物种,实现石油烃的高效降解,常引入过渡金属、碱及热活化等多重手段。常用的PS活化手段归结如图4所示。
-
铜、镍等过渡金属也能作为活化PS的活化剂,但是其产生的毒性会给土壤带来二次环境风险,因而常选用具有易传质、低毒性等特性的铁作为活化剂[56]。活化过程将电子转移至S2O82−中实现—O—O—键的断裂而使其激活,产生SO4−·。以Fe2+与PS为例,其反应过程如公式(10−13)[57]:
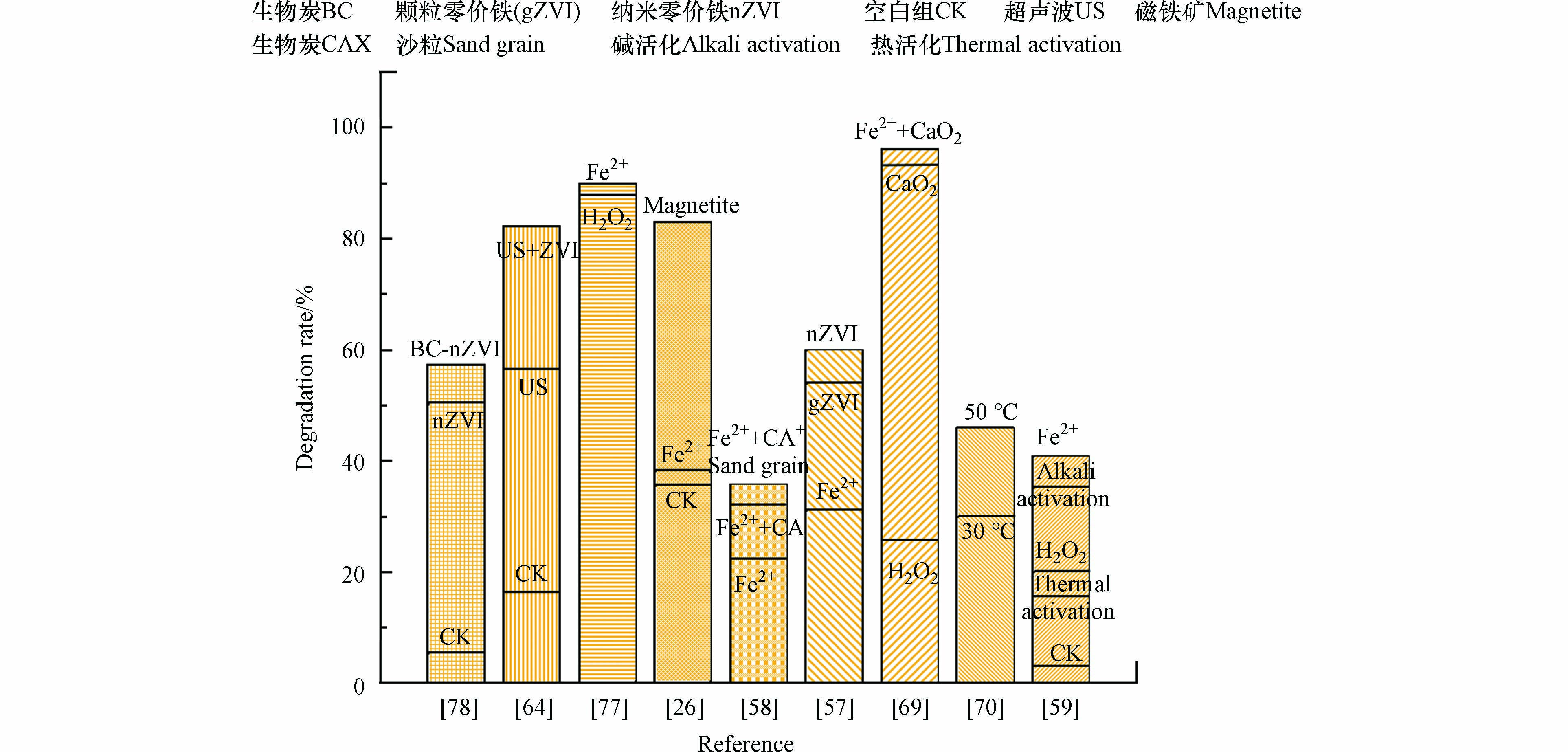
Fe2+是活化PS常用的过渡金属离子活化剂。例如,曾琪静等[58]用FeSO4活化PS处理实际石油烃污染土壤,发现Fe2+活化PS效果较Fe3O4好,对石油烃的去除率为18.8%,是Fe3O4活化体系去除率的3.46倍。同样地,吴昊等[59]研究也发现Fe2+能有效活化PS,反应24 h后,石油烃浓度为14432.5 mg·kg−1的高浓度污染场地的降解率达到40.8%。虽然Fe2+可以活化PS加强氧化效果,但Fe2+也是SO4−·的清除剂,应控制Fe2+和S2O82−的投加比以最大程度降低不利影响,Fe2+和SO4−·之间的清除反应过程如公式(13)[60-61]。Fe3+作为可溶性铁盐同样也能活化PS。在其他有机物和电场的条件下,Fe3+可先还原成Fe2+后,再进一步活化PS降解土壤中的石油烃。例如,KAKOSOVÁ等[62]采用FeCl3活化PS降解石油烃污染土壤,结果表明,石油烃降解效率最高可达78.0%。由于Fe3+自发地还原成Fe2+的过程较难实现,有关Fe3+活化过硫酸盐修复石油烃污染土壤的研究较少。
铁矿物如磁铁矿、针铁矿和赤铁矿等对PS能起到一定的活化作用。与前述铁矿物活化H2O2研究结果一致,磁铁矿表现出较优异的活化效果。SATAPANAJARU等[63]研究加入质量比为5:1的PS和铁氧化物(磁铁矿、磁赤铁矿、赤铁矿和针铁矿)用以修复石油烃浓度为 4200 mg·kg−1的污染土壤,结果显示对石油烃的去除效果大小顺序为磁铁矿>磁赤铁矿>赤铁矿>针铁矿。
零价铁参与活化PS的过程本质上仍是腐蚀过程产生的Fe2+活化PS。由于ZVI能不断与足量的S2O82−反应生成Fe2+,因而,活化后PS对石油烃的降解效果好。ZVI和S2O82−反应过程参考公式(14)。例如,PARDO等[57]对比了Fe2+、颗粒零价铁(gZVI)和纳米零价铁(nZVI)等3种材料活化PS去除土壤中柴油,结果表明,在添加等量活化剂的条件下,对石油烃的去除率大小顺序为nZVI> gZVI> Fe2+。同样地,LI等[64]的研究表明,投加ZVI后土壤中的石油烃降解率大幅提高至82.2%。BAJAGAIN等[65]采用nZVI有效激活PS以修复被柴油污染的老化土壤,实验结果显示,反应2 h后柴油降解率达到61.2%。以铁相关的过渡金属活化PS修复石油烃污染土壤的研究表明,不同铁基材料活化效果大小顺序为ZVI> Fe2+ > Fe3+。土壤天然含有的铁氧化物中,磁铁矿活化PS效果最佳。
-
H2O2和CaO2等过氧化物可有效促进PS形成SO4−·和·OH,常用于活化PS。H2O2分解产生的热量可促进PS释放SO4−·和·OH,同时,这些自由基又激发H2O2分解,形成自由基的互为激发链反应,提高污染物的降解效率[66]。CaO2在反应体系中缓慢释放H2O2直接氧化污染物或者在其他金属离子的活化下产生·OH以强化污染物的降解[67-68],该过程如公式(15)所示[69]。
吴昊等[69]采用H2O2、CaO2活化PS修复石油烃污染土壤的实验发现,活化剂和氧化剂摩尔投加比为1:1时,CaO2/PS体系降解率高达93.2%,而H2O2/PS体系降解率仅为25.6%。而导致去除效果产生差异的原因主要在于:1)CaO2活化PS使带有强氧化性的SO4−·缓慢释放;2)部分CaO2直接参与石油烃的降解过程。CaO2克服了H2O2反应迅速的缺点,是活化过硫酸盐性能优异的活化剂之一。
-
在适宜的温度下,PS可被激活产生大量强氧化性自由基,攻击土壤中的有机污染物。例如,周颖等[70]研究了不同温度下PS降解石油烃的效果,结果显示,反应5 d后50 ℃体系对石油烃去除率为45.5%,而30 ℃体系仅为30.0%左右。同样地,李永涛等[71]研究表明,热活化PS氧化降解柴油为自发、吸热、熵增的过程,实验温度为70 ℃时柴油降解率可达77.9%,比30 ℃体系提高了约10倍。随着反应体系温度升高,PS裂解产生SO4−·的速率不断增大,若不控制反应温度和时间,反应生成的SO4−·之间、无机离子与SO4−·之间则会发生猝灭反应,降低PS的利用效率[72]。热活化PS技术具有快速、高效可控等优势,再结合反应温度和时间以达到最佳氧化降解条件,新型加热技术的发展将进一步推动该活化技术的应用[73]。
-
在碱性条件下,PS可被活化并产生·OH、SO4−·等自由基。有研究表明[74]在酸性和中性条件下产生的是SO4−·,而在碱性条件下主要产生具有更强氧化性的·OH,因而在碱性条件下石油烃的去除率更高[75]。碱活化反应过程如下公式(16−18)[76]:
研究表明随着反应体系碱性的增强,石油烃的降解率会逐渐提高。例如,研究者采用NaOH调节反应体系至pH=12时发现,石油烃去除率最高为45.5%,分别为pH=9和pH=11的2.17倍和1.3倍[59]。虽然碱活化能有效地激活PS,但是,碱性环境对土壤带来的其他负面效应值得关注。
不同活化手段活化PS对土壤中石油烃去除效果的影响汇总如图5和表3所示。在同一实验体系下,不同的活化手段辅助PS去除土壤中石油烃的效果不一。根据文献归纳发现,ZVI和Fe2+活化后的PS能极大提高石油烃的去除率,与无活化剂的空白组相比,去除率提高了约9.36−13.6倍。在此基础上添加沙粒、螯合剂和利用超声波等手段能有效辅助活化剂提高PS对土壤石油烃的降解。
-
PS的投加量直接影响石油烃的降解效果。PS投加量少,石油烃降解不充分,投加量多将导致氧化剂与土壤有机物发生反应造成浪费,也可能使土壤酸化带来环境二次风险问题[80]。由于过量的PS会抑制SO4−·的产生或者使SO4−·发生猝灭而影响石油烃的去除效果,如公式(11)所示。因而,石油烃降解率只在一定范围内随PS投加量增加而升高。例如,吴非等[81]在无活化剂的条件下,仅使用5.0%和10.0%的PS处理柴油浓度为10000 mg·kg−1的污染土壤,反应90 d后柴油去除率为37.0%和58.0%。由此可知,提高PS的投加量,也未导致石油烃的去除率得以大幅度提升。因此,PS的投加量,应视石油烃污染浓度、土壤本身理化特性、修复效果及成本而定。
-
过氧化物、碱、过渡金属等能有效活化PS产生强氧化性自由基降解土壤中的石油烃。在一定范围内,降解效果随活化剂与PS比例的增大而提高,由于活化剂浓度处在较高水平,能快速分解PS产生大量的自由基去除污染物。当投加比超过一定限度后,会产生负面效应。例如,过量的nZVI和Fe2+本身消耗PS,被氧化为Fe3+,消耗了大量SO4−·,抑制了SO4−·对石油烃的降解。过氧化物活化PS过程中,活化剂占比提高至一定量时,由于高浓度的过氧化物产生·OH会消耗一定量的SO4−·而使石油烃降解率上升平缓。NaOH作为碱性活化剂活化PS时需严格控制用量,注意修复后土壤pH过高带来的环境二次风险问题。
-
PS投加后的反应初始阶段,石油烃的降解率随反应时间延长而增大,当到达反应平衡点后,石油烃去除率不再改变。吴昊等[59, 69, 76]的研究表明,用Fe2+活化PS降解土壤中的石油烃的反应可分为2个阶段:1)快速反应阶段(0−5 min):石油烃去除率迅速上升伴随着PS浓度的快速下降;2)慢速反应阶段(5 min后):反应速度明显变缓直至PS消耗殆尽。归纳各项研究发现,采用PS氧化石油烃的过程相对H2O2较慢,适当延长反应时间不仅可进一步提升石油烃去除效率,还能减少PS的用量,节约成本。
-
反应体系初始pH影响活化剂对PS的活化效果,间接影响了石油烃的降解效果。在偏酸性的条件下,过渡金属不易发生沉淀,酸性环境亦促进了土壤金属氧化物溶解,能较好激活PS氧化降解石油烃[82-83]。同时应该注意到:1)酸性条件下,PS产生的自由基会发生猝灭反应,会消耗PS造成药剂浪费,但酸性条件下又能在一定程度上抑制过硫酸根的水解;2)碱性条件下,土壤中的金属元素可能会生成胶状物,影响了PS与土壤中的石油烃分子接触。例如,吴昊等[59]采用Fe2+活化PS修复石油烃污染土壤,发现土壤pH值在5.44−7.68之间,石油烃的去除率均为40.0%左右,说明pH对该实验的降解效果影响可忽略。同样地,研究者采用热活化PS修复柴油污染土壤的实验中发现,土壤初始pH=3−11下对石油烃的降解效果分布在60.0%−80.0%,其中,pH=11时降解率最高达到77.9%[71]。结合上述分析可知,采取不同的活化手段,初始pH对石油烃降解效果影响较小,为了防止对土壤理化性质造成影响,故而实验一般选择在pH中性条件下进行。
-
PS投加方式分为一次投加和序批式投加两种,不同的投加方式产生SO4−·的量不同。研究发现与芬顿/类芬顿反应不同,PS一次投加的效果比多次投加效果好[59]。其原因在于在高浓度污染土壤中序批投加导致反应初期氧化剂的浓度不足,SO4−·产生量受到抑制,氧化反应推动力受到影响。因此在高浓度石油烃污染土壤中,一次投加高浓度的氧化剂较分批添加效果好。
通过上述分析,汇总了基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术的主要因素及其影响原因,结果如表4所示。
-
基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤应用方法,其优点主要如下:1) PS可在土壤环境中稳定存在较长时间,稳定性远远优于H2O2,有利于自由基在传质过程与土壤中的石油烃充分接触;2) PS的自然氧化需求量低,不易氧化土壤有机质;3)PS降解反应受反应体系pH影响小[84]。因此,相对于其他氧化技术来说,基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术操作更便利。尽管如此,基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术仍存在以下不足:1)PS氧化石油烃污染土壤过程中可能会产生高浓度的SO42−残留在土壤介质中,反应产生的H+和SO42−也可能导致受试土壤酸化和盐碱化,对土壤微生物群落多样性造成破坏[85];2)相比于H2O2,PS修复石油烃污染土壤所需时间较长,修复效率在一定程度上受到限制;3)单一的PS技术氧化石油烃可能难以达到较理想的修复效果,用不同的活化方式协同处理或与其他技术联用可以弥补这项不足;4)由于土壤环境的异质性,PS在实际场地修复中难以充分有效地与土壤中的石油烃接触以达到降解修复的目的,因而该技术不适合用于修复污染面积大的土壤[86]。
-
除了上述双氧水和过硫酸盐两种主要氧化剂外,也有直接利用其他氧化性物质的氧化特性直接氧化修复石油烃污染土壤的研究。目前,常见的氧化物质主要为:臭氧、高锰酸盐、次氯酸钠和过氧化钙等。
-
臭氧(O3)是一种亲电性和活性较强的物质,是自然界中重要的氧化剂。臭氧在水溶液和土壤表面通过反应发生分解,目前普遍认为臭氧是攻击烷烃的C-H键从而达到降解污染物的目的[87-89]。研究表明臭氧可以用于降解土壤中的农药、石油烃、多氯联苯和多环芳烃等有机污染物[90-93]。臭氧与土壤中石油烃发生反应有两种方式:1)有机污染物直接被O3氧化分解;2)O3分解产生·OH,通过·OH氧化有机污染物[94]。臭氧能够无选择性地氧化污染土壤中C12—C24的石油烃。
YU等[90]以50 mL·min−1的流速注入浓度为119 mg·L−1的臭氧,用于修复柴油污染土壤,结果显示,在干燥土壤中的柴油去除率达到94.9%,而在含水率5.0%和10.0%的土壤中去除率分别为55.5%和33.8%。含水率提升,柴油去除率降低的原因在于,臭氧与土壤颗粒上的污染物发生反应的活性位点数量随着土壤水分的减少而增多。臭氧的氧化效果同时受反应pH影响,当pH从2增加到8时,柴油降解率逐渐提高。研究表明pH>6时,O3分解产生的·OH促进了石油烃氧化[95]。但当pH过高(pH>12)时,自由基的清除作用会减少反应体系中的反应物,使石油烃的去除率下降[96-97]。臭氧作为修复受污染土壤的处理技术之一,土壤理化性质,如含水率、结构、pH均影响臭氧的氧化效果。在实际污染场地的应用中,需要现场制备O3再通入土壤中,使得O3的利用率低,迫使修复成本增加。因此,在实际石油烃污染土壤修复应用中该技术受到一定的限制。
-
高锰酸盐是一种氧化性比H2O2和PS低的氧化剂,主要以固体粉末存在,起氧化作用的物质主要是MnO4−(E0=1.7 V)。高锰酸盐是通过提供氧原子与有机物发生氧化反应,从而断开有机物上的氢键,实现有机物去除[7]。常见的高锰酸盐有NaMnO4和KMnO4,鉴于NaMnO4成本较高,一般采用固体KMnO4并配成溶液后注入受石油烃污染的土壤中,反应过程中会形成不溶性副产物MnO2固体[98]。高锰酸盐在去除土壤中的石油烃时受pH影响较小,且土壤中的碳酸根、碳酸氢根等不会影响MnO4−的氧化作用[99]。但是,使用高锰酸盐氧化处理后土壤pH值可能会降低,影响其中的重金属离子的迁移性能,同时土壤中的铝、钴、锌、镍等离子可能会被MnO2固体所吸附[100]。
研究者发现,在3D沙箱实验中注入50 g·L−1的KMnO4溶液,可使石油烃浓度从1.05×106 mg·kg−1降低至6200−10600 mg·kg−1,KMnO4对柴油污染土壤的修复范围在实验15 d后达到了99.9%[101]。韩国某柴油污染场地石油烃初始浓度为3300 mg·kg−1,采用0.1 mol·L−1的KMnO4溶液处理1 h后发现石油烃去除率达到67.5%[102]。KMnO4对柴油、汽油和苯系物等污染物的处理效果比挥发性和半挥发性污染物质差,且当土壤中含有较多铁离子、锰离子和有机质时,KMnO4的投加量需要大大增加[103-104]。高成本的高锰酸钾不适合大范围污染场地的使用,并且高锰酸钾的色度会影响地下水质,这些劣势均使高锰酸盐的应用受到制约。
-
次氯酸钠(NaClO)与土壤中石油烃的反应取决于土壤pH和NaClO浓度等。实验体系pH为中性至碱性条件下,NaClO的最终的氧化产物为NaCl,而在酸性条件下反应终产物为有机氯化物[105]。PICARD等[106]采用3%的NaClO溶液氧化石油烃污染土壤,反应结束后,石油烃浓度从5473 mg·kg−1的土壤降低至700 mg·kg−1。另外,其他研究者发现带有疏水位点的腐殖酸能促进NaClO氧化石油烃污染物[107] ,并且在控制总投加量不变的情况下,分批次投加NaClO可使氧化反应效果更好[108]。最后,采用NaClO会改变土壤微生物的生存环境和干扰土壤微生物群落结构,不利于后续有机结合微生物修复[109]。
-
过氧化钙(CaO2)被称为固体H2O2,具有强氧化性和缓释性的优点而被应用于化学氧化修复[110]。CaO2与水接触产生的H2O2可间接氧化土壤中的石油烃,CaO2产生·OH自由基的反应过程如公式(19−21)[69, 111]:
例如,NDJOU等[110]采用CaO2修复石油烃污染土壤(初始浓度为10604 mg·kg−1)发现,石油烃的最高去除率可达96.0%。李振宇等[111]发现在同等条件下,当氧化剂的浓度为166.67 mmol·L−1,氧化剂/Fe3+/柠檬酸的摩尔比为6:1:1时,反应24 h后,CaO2体系的柴油降解率达到44.1%,而H2O2体系仅有17.7%。由此可知,采用CaO2修复柴油污染浓度为13200 mg·kg−1的土壤的效果优于H2O2体系。此外,后续的毒理实验表明CaO2比H2O2体系对植物生长的毒性效应更小。尽管如此,CaO2用以土壤修复时,存在投加量大及成本高的问题。因此,CaO2多应用于水体污染修复。
在一定条件下,臭氧、高锰酸钾、次氯酸钠和过氧化钙作为氧化剂修复石油烃污染土壤时能实现石油烃的有效去除。但是,这些氧化剂的可操作性、成本和二次污染等问题极大限制了其规模化应用。已有报道采用其他氧化剂氧化修复石油烃污染土壤汇总如表5所示。
-
本文综述了基于双氧水和过硫酸盐及其他氧化剂氧化修复石油烃污染土壤的研究进展,发现基于双氧水和过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术是现阶段常用的氧化技术。通过归纳基于双氧水的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤发现,以零价铁和铁矿物等构建的类芬顿体系比芬顿体系更有利于石油烃污染土壤修复;通过添加螯合剂及改变双氧水的投加方式作为强化措施优于超声及紫外辅助;反应过程中的pH、温度、双氧水的投加量及其与活化剂的比例等参数均能影响石油烃污染土壤修复效果。通过分析基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术的研究进展发现,为强化过硫酸盐修复石油烃污染土壤效能,过渡金属、碱、热活化及过氧化物是常用的活化手段;反应过程中的pH、过硫酸盐的投加量及其与活化剂的比例等参数均是影响基于过硫酸盐高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤的关键参数。最后,本文概述了其他氧化剂氧化修复石油烃污染土壤的研究情况,旨在为后续研究者提供借鉴与参考。
尽管,化学氧化法能高效地修复石油烃污染土壤,但是,仍然存在一些关键问题未得到满意的答复。未来基于化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤应重点关注以下几个方面:
1)研发流动性强及活性高的活化剂,提高双氧水和过硫酸盐等氧化剂的有效利用率,减少氧化剂的无效损失;开发新的强化措施,强化双氧水和过硫酸盐等氧化剂氧化修复石油烃污染土壤效能;
2)探究反应过程中石油烃的去除作用机制,减少反应过程中与土壤有机质的无效反应,提高选择性氧化石油烃的能力和氧化效率;探究氧化剂在修复过程中对微生物群落的影响机制,开展反应后土壤安全性评价,构建石油烃降解中间产物及终产物的监测和风险防控技术体系;
3)探究化学氧化与物理修复或者生物修复有机衔接的联合修复技术,将化学氧化作为预处理阶段促进后续技术对石油烃的降解过程。在此基础上探索修复石油烃污染土壤的最佳修复方案,发展绿色、经济的化学氧化修复技术。
基于化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤研究进展
Research progress on remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil using chemical oxidation
-
摘要: 石油作为现代工业的血液,被广泛应用于各行各业。但是,其带来的环境污染问题不容忽视,尤其是泄漏等生产事故诱发的土壤污染。化学氧化法因具有修复效能高、成本低及操作便利等优势,常用于石油烃污染土壤修复。本文重点综述了基于过氧化氢和过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤过程中常用的活化剂、强化措施、关键影响因素及其效能;汇总了其他氧化剂在修复石油烃污染土壤方面的效果;分析了不同高级氧化技术应用于石油烃污染土壤修复的优缺点;展望了化学氧化法修复石油烃污染土壤未来的发展方向与挑战。Abstract: Petroleum is considered to be the blood of the modern industry, which has been widely used in a wide range of industries. However, the environmental pollution caused by petroleum, especially the soil pollution induced by petroleum leakage accidents could not be ignored. The chemical oxidation method is a suitable and widespread remediation approach to petroleum-contaminated soil since it has the advantages of high remediation efficiency, low cost, and easy operation. This paper mainly provided an up-to-date overview of two common advanced oxidation techniques, hydrogen peroxide and persulfate separately. This part focused on the activators, intensification measures, key influencing factors, and their effectiveness. Besides, the effects of other oxidants on the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil were summarized. Meanwhile, the advantages and disadvantages of various advanced oxidation techniques for the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil were also highlighted. Finally, the future development directions and challenges of the chemical oxidation method of remediation for petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil were also proposed.
-
Key words:
- petroleum hydrocarbon /
- chemical oxidation /
- soil remediation /
- hydrogen peroxide /
- persulfate
-

-
表 1 不同铁基材料活化H2O2修复石油烃污染土壤汇总表
Table 1. Summary of different iron-based activators activate H2O2 for remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
污染物浓度/
(mg·kg −1)
Concentration土壤类型
Soil
type活化剂类型
Activator
type活化剂
Activators反应条件 Reaction conditions 降解率/%
Degradation
rate文献来源References 活化剂与H2O2
摩尔投加比
Molar dosing
ratio of activator
to H2O2反应时间/h
Reaction
time反应体系
pH反应温度/℃
Reaction
temperature32400 砂质壤土 铁盐 硫酸铁 1:300 24 pH=7 25 32.7 [13] 1000 粉质壤土 铁盐 高氯酸铁(Ⅲ) 1:60 1 pH=7 — 99.0 [15] 1000 粉质壤土 铁盐 硫酸铁(Ⅲ) 1:60 1 pH=7 — 80.0 [15] 1000 硅砂 铁盐 硫酸亚铁 1:380 72 pH=7 20±2 50.0 [20] 1000 硅砂 铁矿物 磁铁矿 质量占比5.0% 192 pH=7 20±2 49.0 [20] 1000 硅砂 铁矿物 针铁矿 质量占比5.0% 192 pH=7 20±2 60.0 [20] 32000 砂质土 铁矿物 磁铁矿 1:17.5 6 pH=3 25 74.2 [25] 4000 砂质土 铁矿物 磁铁矿 1:10 168 pH=7—8 20—25 84.0 [26] 5000 砂质壤土 铁矿物 磁铁矿 质量占比4.3% 24 pH=6.7—7.4 25—27 57.0 [21] 10000 砂质土和
硅砂铁矿物 含氧碱性
炉渣质量占比15.0% 40 pH=12.1 23.5—30.8 96.0 [9] 30510 砂质土 零价铁 零价铁 1:3.75 48 pH=7 环境温度 39.3 [23] 5000 砂质壤土 零价铁 零价铁 质量占比4.3% 24 pH=6.7—7.4 25—27 67.0 [21] 6798.5 黏质土 其他 载铁沸石 质量占比30.0% 25 pH=6 20 70.1 [24] 表 2 基于H2O2的高级氧化技术修复石油烃污染土壤的主要影响因素
Table 2. The main influencing factors of advanced oxidation technology based on H2O2 for remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
影响因素
Influencing factors影响方面
Influence双氧水投加方式 一次性加入过量H2O2可能会消耗或清除·OH并产生反应性低的HO2·,适量增加投加次数可有效提高H2O2稳定性 pH pH高会导致铁元素形成胶体或沉淀,也会消耗·OH;pH低抑制H2O2分解 反应温度 影响反应体系分子热运动,影响 ·OH与污染物的碰撞和反应 双氧水投加量 H2O2浓度高消耗体系·OH或是与土壤有机质发生反应;H2O2浓度低产生的·OH量不足 双氧水与活化剂之比 影响活化剂活化H2O2分解产生·OH 表 3 不同活化手段活化PS修复石油烃污染土壤汇总表
Table 3. Summary of different activation methods for PS remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
污染物浓度/(mg·kg−1)
Concentration土壤类型
Soil type活化措施
Activation measures活化剂
Activators反应条件 Reaction conditions 降解率/%
Degradation rate文献来源
References活化剂与PS
摩尔投加比
Molar dosing
ratio of
Activator
to PS反应时间/d
Reaction
time反应体系pH
pH of
reaction
system反应温度/℃
Reaction
temperature7650 — 过渡金属
活化Fe2+ 5.25:1 — — 20 91.9 [77] 62200 砂质土 过渡金属
活化Fe3+ 质量比17:60 2 pH=7.76 20 78.0±3 [62] 4000 砂质土 过渡金属
活化磁铁矿 1:1 7 pH=7—8 20—25 73 [26] 62940-84960 — 过渡金属
活化Fe2+ 1:1 2 pH=4 20 18.8 [58] 62940-84960 — 过渡金属
活化Cu2+ 1:1 2 pH=4 20 6.6 [58] 62940-84960 — 过渡金属
活化Fe3O4 1:1 2 pH=4 20 5.5 [58] 1000 砂质黏土 过渡金属
活化颗粒零价铁 1:10 4 pH=7 20 54.0 [57] 1000 砂质黏土 过渡金属
活化纳米零价铁 1:10 4 pH=7 20 60.0 [57] 1000 砂质黏土 过渡金属
活化Fe2+ 1:10 4 pH=7 20 31.0 [57] 13259 壤土 过渡金属
活化零价铁 1:1 60 pH=7 25 57.4−62.6 [78] 19850 — 过渡金属
活化Fe 5:1 3 pH=5 22±1 82.2 [64] 5000 砂质土 过渡金属
活化Fe2+ 1:10 40 — 25 55.0 [61] 15000 砂质壤土 过氧化物
活化CaO2 1:2 7 pH=7 20 82.1 [69] 7650 — 过氧化物
活化H2O2 2.14:1 — — 20 92.4 [77] 58837 — 热活化 — — 5 pH=7 50 45.5 [70] 14432.5 砂质壤土 碱活化 NaOH — 1 pH=12 20 35.0 [59] 4930±50 砂质壤土 碱活化 NaOH 4:1 56 pH>12 20 98.0 [79] 表 4 基于PS氧化修复石油烃污染土壤的主要影响因素
Table 4. The main influencing factors of PS oxidation degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
影响因素
Influence factors影响方面
InfluencePS投加量 投加量少产生的氧化性物质少;投加量太多导致氧化剂与土壤中的有机物质或其他还原性物质发生反应造成浪费,甚至造成二次污染问题 活化剂与PS投加量比 在一定范围内,活化剂与PS投加比越高,对石油烃的降解效果越好;投加比过高会导致活化剂消耗SO4-· 反应时间 控制反应时间保证反应进行完全 pH值 pH主要影响起活化作用的重金属的活化效果,间接影响石油烃降解率 PS投加方式 一次投加能保证氧化剂浓度处在较高水平 表 5 其他氧化剂氧化修复石油烃污染土壤汇总表
Table 5. Summary of other oxidants for oxidative remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil
氧化技术
Oxidation technology污染物浓度/
(mg·kg−1)
Concentration土壤类型
Soil type反应条件 Reaction conditions 降解率/%
Degradation rate文献来源
References氧化剂投加量
Oxidant
dosage反应时间/h
Reaction
time反应体系pH
pH of reaction
system反应温度/℃
Reaction
temperature臭氧氧化 10314 砂质土 臭氧浓度
119 ± 6 mg·L−1 、
流速50 mL·min−114 pH<2 22±2 94.0 [90] 高锰酸钾氧化 5542 壤质砂土 5.0% 744 pH=7.8 24 72.0 [112] 高锰酸盐氧化 1.05×106 砂质土 50 g·L−1 360 — — 99.0 [100] 次氯酸钠氧化 5473 砂质土 3.0% NaClO、0.12 g NaClO·g−1 土 2 pH=7 — 85.0 [104] 过氧化钙氧化 10604 砂质土 2.5% 60 pH=8 — 95.6 [110] 过氧化钙氧化 13200 壤土 0.83 mmol CaO2 ·g−1土 24 — 25 44.1 [111] -
[1] 生态环境部. 水质 石油类和动植物油类的测定 红外分光光度法: HJ 637—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2018. Water quality—Determination of petroleum, animal fats and vegetable oils—Infrared spectrophotometry: HJ 637—2018[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2018(in Chinese).
[2] 刘文霞, 孟祥远, 冯建灿, 等. 中原油田耕地污染分析 [J]. 农业环境保护, 2002, 21(1): 56-59. LIU W X, MENG X Y, FENG J C, et al. Pollution of farmland soil by petroleum industry in the central Plains oil field [J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 2002, 21(1): 56-59(in Chinese).
[3] 昆仑. 输油管道爆炸的惨痛教训 [J]. 城市与减灾, 2010(5): 46-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2010.05.014 KUN L. Painful lessen on explosion accident of oil pipeline [J]. City and Disaster Reduction, 2010(5): 46-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2010.05.014
[4] SAMMARCO P W, KOLIAN S R, WARBY R A F, et al. Distribution and concentrations of petroleum hydrocarbons associated with the BP/Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill, Gulf of Mexico [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 73(1): 129-143. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.029 [5] 王威, 苏小四, 张玉玲, 等. 石油类污染场地的自然衰减作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(S1): 310-314, 327. WANG W, SU X S, ZHANG Y L, et al. Natural attenuation of A petroleum contaminated site[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(Sup 1): 310-314, 327(in Chinese).
[6] 张峰, 薛晓虎. 石油污染土壤的生物通风修复 [J]. 能源环境保护, 2008, 22(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2008.03.001 ZHANG F, XUE X H. Bioventing remediation of soil polluted by oil [J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2008, 22(3): 1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8759.2008.03.001
[7] 罗玉虎, 卢楠. 高级氧化技术在石油污染土壤修复中的应用 [J]. 乡村科技, 2019(10): 107-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7909.2019.10.061 LUO Y H, LU N. Application of advanced oxidation technology in remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil [J]. Rural Science and Technology, 2019(10): 107-109(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7909.2019.10.061
[8] 陈胜兵, 何少华, 娄金生, 等. Fenton试剂的氧化作用机理及其应用 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2004, 27(3): 105-107,120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.03.045 CHEN S B, HE S H, LOU J S, et al. Oxidation mechanism and application of Fenton reagent [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 27(3): 105-107,120(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.03.045
[9] TSAI T T, KAO C M. Treatment of petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated soils using hydrogen peroxide oxidation catalyzed by waste basic oxygen furnace slag [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 170(1): 466-472. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.073 [10] 崔英杰, 杨世迎, 王萍, 等. Fenton原位化学氧化法修复有机污染土壤和地下水研究[J]. 化学进展, 2008, 20(S2): 1196-1201. CUI Y J, YANG S Y, WANG P, et al. Organically polluted soil and groundwater remediation by in situ Fenton oxidation[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2008, 20(Sup 2): 1196-1201(in Chinese).
[11] LIN S S, GUROL M D. Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on iron oxide: kinetics, mechanism, and implications [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1998, 32(10): 1417-1423. [12] 潘玥. 类芬顿技术处理多环芳烃污染土壤及过氧化钙体系的反应机理研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019.PAN Y. Fenton-like reaction for remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil and mechanism of calcium peroxide based Fenton-like reactions[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019(in Chinese). [13] LU M, ZHANG Z Z, QIAO W, et al. Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil after composting by sequential treatment with Fenton-like oxidation and biodegradation [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2106-2113. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.002 [14] 陈彩成, 李青青, 王旌, 等. 滩涂石油污染高级氧化修复技术 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(5): 2700-2706. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509240 CHEN C C, LI Q Q, WANG J, et al. Advanced oxidation technology for remediation of petroleum-contaminated tidal flat [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(5): 2700-2706(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509240
[15] WATTS R J, DILLY S E. Evaluation of iron catalysts for the Fenton-like remediation of diesel-contaminated soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1996, 51(1/2/3): 209-224. [16] YANG X J, XU X M, XU J, et al. Iron oxychloride (FeOCl): An efficient Fenton-like catalyst for producing hydroxyl radicals in degradation of organic contaminants [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(43): 16058-16061. doi: 10.1021/ja409130c [17] WATTS R J, KONG S, DIPPRE M, et al. Oxidation of sorbed hexachlorobenzene in soils using catalyzed hydrogen peroxide [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1994, 39(1): 33-47. doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(94)00055-7 [18] FRITZ H, JOSEPH W. The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron salts [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A - Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1934, 147(861): 332-351. [19] WATTS R J, TEEL A L. Chemistry of modified fenton's reagent (catalyzed H2O2 propagations–CHP) for in situ soil and groundwater remediation [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 612-622. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2005)131:4(612) [20] KONG S H, WATTS R J, CHOI J H. Treatment of petroleum-contaminated soils using iron mineral catalyzed hydrogen peroxide [J]. Chemosphere, 1998, 37(8): 1473-1482. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00137-4 [21] JAMIALAHMADI N, GITIPOUR S, JAMIALAHMADI O, et al. Remediation of a diesel-contaminated soil using a Fenton-like advanced oxidation process: Optimization by response surface methodology [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2015, 24(6): 609-623. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2015.996633 [22] LIM H, LEE J, JIN S, et al. Highly active heterogeneous Fenton catalyst using iron oxide nanoparticles immobilized in alumina coated mesoporous silica [J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2006(4): 463-465. doi: 10.1039/B513517F [23] OURIACHE H, ARRAR J, NAMANE A, et al. Treatment of petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil by Fenton like oxidation [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 232: 377-386. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.060 [24] 蔡嘉希, 雷雨坤, 章诗辞, 等. 载铁沸石非均相芬顿修复石油污染土壤试验研究 [J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2018, 40(7): 78-83. CAI J X, LEI Y K, ZHANG S C, et al. Oxidation of petroleum contaminated soil by supported iron zeolite heterogeneous Fenton [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2018, 40(7): 78-83(in Chinese).
[25] MIRZAEE E, GITIPOUR S, MOUSAVI M, et al. Optimization of total petroleum hydrocarbons removal from Mahshahr contaminated soil using magnetite nanoparticle catalyzed Fenton-like oxidation [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(4): 1-13. [26] USMAN M, FAURE P, HANNA K, et al. Application of magnetite catalyzed chemical oxidation (Fenton-like and persulfate) for the remediation of oil hydrocarbon contamination [J]. Fuel, 2012, 96: 270-276. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.01.017 [27] FLORES R, BLASS G, DOMÍNGUEZ V. Soil remediation by an advanced oxidative method assisted with ultrasonic energy [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 140(1/2): 399-402. [28] SAWARKAR A N, PANDIT A B, SAMANT S D, et al. Use of ultrasound in petroleum residue upgradation [J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 87(3): 329-342. doi: 10.1002/cjce.20169 [29] SIVAGAMI K, ANAND D, DIVYAPRIYA G, et al. Treatment of petroleum oil spill sludge using the combined ultrasound and Fenton oxidation process [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 51: 340-349. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.09.007 [30] GHARAEE A, KHOSRAVI-NIKOU M R, ANVARIPOUR B. Hydrocarbon contaminated soil remediation: A comparison between Fenton, sono-Fenton, photo-Fenton and sono-photo-Fenton processes [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2019, 79: 181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2019.06.033 [31] 艾军勇, 张道勇, 牟书勇, 等. 超声波/紫外线-Fenton反应联用去除克拉玛依土壤中石油类污染物 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(3): 983-988. AI J Y, ZHANG D Y, MU S Y, et al. Removal of petroleum from soil in Qaramay using ultrasound/ultraviolet-Fenton reaction [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(3): 983-988(in Chinese).
[32] KEENAN C R, SEDLAK D L. Ligand-enhanced reactive oxidant generation by nanoparticulate zero-valent iron and oxygen [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(18): 6936-6941. [33] WANG N, ZHU L H, LEI M, et al. Ligand-induced drastic enhancement of catalytic activity of nano-BiFeO3 for oxidative degradation of bisphenol A [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(10): 1193-1202. doi: 10.1021/cs2002862 [34] XUE X F, HANNA K, DESPAS C, et al. Effect of chelating agent on the oxidation rate of PCP in the magnetite/H2O2 system at neutral pH [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2009, 311(1/2): 29-35. [35] SUN S P, ZENG X, LI C, et al. Enhanced heterogeneous and homogeneous Fenton-like degradation of carbamazepine by nano-Fe3O4/H2O2 with nitrilotriacetic acid [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 244: 44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.039 [36] LU M, ZHANG Z Z, QIAO W, et al. Removal of residual contaminants in petroleum-contaminated soil by Fenton-like oxidation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 179(1/2/3): 604-611. [37] 李方敏, 柳红霞, 梅平, 等. 络合剂改进Fenton反应去除土壤中石油污染物的效果 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(1): 88-94. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.01.011 LI F M, LIU H X, MEI P, et al. Enhanced removal of soil petroleum pollutants by modified Fenton reaction with chelating agents [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(1): 88-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.01.011
[38] 徐金兰, 宋少花, 黄廷林, 等. 柠檬酸改性Fenton氧化石油污染土壤的影响因素研究 [J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 47(4): 605-608,616. XU J L, SONG S H, HUANG T L, et al. Study on influence factors of citric acid modified Fenton oxidation of petroleum-contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 47(4): 605-608,616(in Chinese).
[39] 杨玲引, 宜慧, 常波, 等. 柠檬酸改性Fenton氧化技术对陕北石油污染土壤的修复影响研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(6): 1118-1121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.06.022 YANG L Y, YI H, CHANG B, et al. Research on remediation of oil contaminated soil in northern Shaanxi by citric acid modified Fenton technology [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(6): 1118-1121(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.06.022
[40] CHRISTOFORIDIS K C, LOULOUDI M, DELIGIANNAKIS Y. Effect of humic acid on chemical oxidation of organic pollutants by iron(II) and H2O2: A dual mechanism [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(4): 2991-2996. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.005 [41] XU J L, LI X M, HUANG T L. Abatement of sorbed crude oil by heterogeneous Fenton process using A contaminated soil pre-impregnated with dissolved Fe(II) and humic acid [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2017, 26(2): 195-209. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2017.1269721 [42] XU J L, ZHAO M H, WANG R, et al. Efficiently dedicated oxidation of long-chain crude oil in the soil by inactive SOM-Fe [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 121913. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.121913 [43] FAN C, TSUI L, LIAO M C. Parathion degradation and its intermediate formation by Fenton process in neutral environment [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(2): 229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.016 [44] 徐金兰, 雷绒娟, 邓海鑫, 等. Fenton改性对土壤有机物氧化及修复石油污染土壤的影响 [J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2014, 30(6): 1113-1118. XU J L, LEI R J, DENG H X, et al. Effects of Fenton modifications on oxidation of soil organic matter and remediation of petroleum contaminated soil [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2014, 30(6): 1113-1118(in Chinese).
[45] 徐金兰, 刘博雅. 盐酸羟胺促进分级Fenton氧化土壤长链原油的试验研究 [J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(3): 539-544. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.03.017 XU J L, LIU B Y. Experimental study of hydroxylamine hydrochloride on improving Fenton oxidation of long chain crude oil in soil [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(3): 539-544(in Chinese). doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.03.017
[46] 徐金兰, 郭阳, 刘博雅. H2O2分次投加对Fenton氧化修复石油污染土壤及后续生物降解的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1266-1273. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082005 XU J L, GUO Y, LIU B Y. Impact of stepwise addition of H2O2 on Fenton oxidation and subsequent biodegradation of oil-contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1266-1273(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082005
[47] 辛磊. 逐级Fenton化学氧化重度石油污染土壤的实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2012. XIN L.Graded modified Fenton oxidation of highly oil contaminated soil[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [48] WATTS R J, UDELL M D, KONG S, et al. Fenton-like soil remediation catalyzed by naturally occurring iron minerals [J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 1999, 16(1): 93-103. doi: 10.1089/ees.1999.16.93 [49] WATTS R J, BOTTENBERG B C, HESS T F, et al. Role of reductants in the enhanced desorption and transformation of chloroaliphatic compounds by modified fenton's reactions [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(19): 3432-3437. [50] 张秋子, 韦云霄, 姜永海, 等. 催化过氧化氢对石油烃污染土壤的氧化能力 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2017, 7(1): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.01.010 ZHANG Q Z, WEI Y X, JIANG Y H, et al. Oxidizing capacity of catalyzed hydrogen peroxide to petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2017, 7(1): 65-70(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2017.01.010
[51] 宜慧, 常波, 杨玲引, 等. 改性Fenton氧化法修复石油污染土壤影响因素分析 [J]. 科技通报, 2018, 34(9): 249-253,258. doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2018.09.051 YI H, CHANG B, YANG L Y, et al. Study on influence factors of petroleum contaminated soil remediated by modified Fenton technology [J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2018, 34(9): 249-253,258(in Chinese). doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2018.09.051
[52] 张碧波, 陈剑, 冉启洋, 等. 柠檬酸改性芬顿对土壤中石油烃的去除效果 [J]. 湖南农业科学, 2019(12): 38-41. ZHANG B B, CHEN J, RAN Q Y, et al. Practical application of citric acid modified Fenton to remove petroleum hydrocarbons from soil [J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2019(12): 38-41(in Chinese).
[53] 孙燕英. 土壤中石油类污染物的化学氧化净化法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.SUN Y Y. Study on degradation of petroleum contaminants in soil by chemicai oxidation technology[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2007(in Chinese). [54] 周洋, 邓亚梅, 朱凤晓, 等. 过氧化氢及类芬顿试剂对土壤碳、氮和微生物的影响 [J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(5): 969-977. ZHOU Y, DENG Y M, ZHU F X, et al. Effect of hydrogen peroxide and Fenton-like reagent on soil carban, nitrogen and microorganism [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(5): 969-977(in Chinese).
[55] LIAO X Y, ZHAO D, YAN X L, et al. Identification of persulfate oxidation products of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon during remediation of contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 276: 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.018 [56] ANIPSITAKIS G P, DIONYSIOU D D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(13): 3705-3712. [57] PARDO F, ROSAS J M, SANTOS A, et al. Remediation of a biodiesel blend-contaminated soil with activated persulfate by different sources of iron [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(2): 1-12. [58] 曾琪静, 丁丽, 文方, 等. 优化过硫酸盐体系处理石油类污染土壤 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(2): 170-174. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902032 ZENG Q J, DING L, WEN F, et al. Treatment of petroleum-contaminated soil by optimized persulfate system [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(2): 170-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201902032
[59] 吴昊, 孙丽娜, 李玉双, 等. 活化过硫酸钠去除长期污染土壤中的TPH [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 5231-5237. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201504043 WU H, SUN L N, LI Y S, et al. Application of persulfate to remediatiate long-term TPH contaminated soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(9): 5231-5237(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201504043
[60] KILLIAN P F, BRUELL C J, LIANG C J, et al. Iron (II) activated persulfate oxidation of MGP contaminated soil [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2007, 16(6): 523-537. doi: 10.1080/15320380701623206 [61] YEN C H, CHEN K F, KAO C M, et al. Application of persulfate to remediate petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil: Feasibility and comparison with common oxidants [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2/3): 2097-2102. [62] KAKOSOVÁ E, HRABÁK P, ČERNÍK M, et al. Effect of various chemical oxidation agents on soil microbial communities [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 314: 257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.065 [63] SATAPANAJARU T, CHOKEJAROENRAT C, SAKULTHAEW C, et al. Remediation and restoration of petroleum hydrocarbon containing alcohol-contaminated soil by persulfate oxidation activated with soil minerals [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2017, 228(9): 1-15. [64] LI Y T, LI D, LAI L J, et al. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil by using activated persulfate with ultrasound and ultrasound/Fe [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 238: 124657. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124657 [65] BAJAGAIN R, JEONG S W. Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil via advanced oxidation process using peroxymonosulfate activated by nanoscale zero-valent iron [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 128627. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128627 [66] CRIMI M L, TAYLOR J. Experimental evaluation of catalyzed hydrogen peroxide and sodium persulfate for destruction of BTEX contaminants [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2007, 16(1): 29-45. doi: 10.1080/15320380601077792 [67] CHEVALIER L, MCCANN C D. Feasibility of calcium peroxide as an oxygen releasing compound in treatment walls [J]. International Journal of Environment and Waste Management, 2008, 2(3): 245. doi: 10.1504/IJEWM.2008.018246 [68] NORTHUP A, CASSIDY D. Calcium peroxide (CaO2) for use in modified Fenton chemistry [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(3): 1164-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.096 [69] 吴昊, 孙丽娜, 王辉, 等. CaO2/Fe2+活化过硫酸钠对石油类污染土壤的修复效果 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(4): 623-628. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015110101 WU H, SUN L N, WANG H, et al. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils by CaO2/Fe2+ activatal persulfate [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(4): 623-628(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015110101
[70] 周颖, 谢海燕, 赵晨曦, 等. 活化过硫酸盐处置石油污染土壤技术研究 [J]. 新疆环境保护, 2016, 38(2): 12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2301.2016.02.003 ZHOU Y, XIE H Y, ZHAO C X, et al. Study on the technology of petroleum contaminated soil treatment with activated sulfate [J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 2016, 38(2): 12-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2301.2016.02.003
[71] 李永涛, 罗进, 岳东. 热活化过硫酸盐氧化修复柴油污染土壤 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(10): 1143-1146. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.10.021 LI Y T, LUO J, YUE D. Thermo activated persulfate oxidation for remediation of diesel oil contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39(10): 1143-1146(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.10.021
[72] ZHAO D, LIAO X Y, YAN X L, et al. Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 254/255: 228-235. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.056 [73] XIE X F, ZHANG Y Q, HUANG W L, et al. Degradation kinetics and mechanism of aniline by heat-assisted persulfate oxidation [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(5): 821-826. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60844-9 [74] 冯凯. 活化过硫酸钠高级氧化环境修复技术综述 [J]. 环境科技, 2017, 30(5): 75-78. FENG K. A review on activated sodium persulfate oxidation technology [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 30(5): 75-78(in Chinese).
[75] FURMAN O S, TEEL A L, WATTS R J. Mechanism of base activation of persulfate [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(16): 6423-6428. [76] 吴昊, 孙丽娜, 王辉, 等. 活化过硫酸钠原位修复石油类污染土壤研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(11): 2085-2095. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.11.2015052601 WU H, SUN L N, WANG H, et al. Persulfate In-situ remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(11): 2085-2095(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.11.2015052601
[77] 邓强. 过硫酸盐高级氧化技术修复土壤原油污染研究 [J]. 河北地质大学学报, 2020, 43(3): 51-56. DENG Q. Study on repairing soil crude oil pollution by persulfate advanced oxidation technology [J]. Journal of Hebei GEO University, 2020, 43(3): 51-56(in Chinese).
[78] ZHANG B W, GUO Y, HUO J Y, et al. Combining chemical oxidation and bioremediation for petroleum polluted soil remediation by BC-nZVI activated persulfate [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 123055. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123055 [79] LOMINCHAR M A, SANTOS A, de MIGUEL E, et al. Remediation of aged diesel contaminated soil by alkaline activated persulfate [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622/623: 41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.263 [80] JONSSON S, PERSSON Y, FRANKKI S, et al. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in contaminated soils by Fenton's reagent: A multivariate evaluation of the importance of soil characteristics and PAH properties [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 149(1): 86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.057 [81] 吴非, 陈谷汎, 林伟翰, 等. 包覆型纳米零价铁活化过硫酸处理柴油污染土壤 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(7): 2589-2595. WU F, CHEN G F, LIN W H, et al. Remediation of diesel-contaminated soil using coated nano zero valent iron/sodium peroxydisulfate system [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(7): 2589-2595(in Chinese).
[82] WU H, SUN L N, WANG H, et al. Persulfate oxidation for the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils [J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2016, 25(2): 851-857. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/60857 [83] DO S H, KWON Y J, KONG S H. Effect of metal oxides on the reactivity of persulfate/Fe(Ⅱ) in the remediation of diesel-contaminated soil and sand [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182(1/2/3): 933-936. [84] HUANG K C, COUTTENYE R A, HOAG G E. Kinetics of heat-assisted persulfate oxidation of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) [J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 49(4): 413-420. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00330-2 [85] LIANG C J, CHIEN Y C, LIN Y L. Impacts of ISCO persulfate, peroxide and permanganate oxidants on soils: Soil oxidant demand and soil properties [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2012, 21(6): 701-719. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2012.691129 [86] 李丽, 张兴, 王亚军, 等. 过硫酸钠对黄土高原石油类污染土壤的处理 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(12): 159-165. LI L, ZHANG X, WANG Y J, et al. Treatment of petroleum hydrocarbons in loess by sodium persulfate [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(12): 159-165(in Chinese).
[87] JANS U, HOIGNÉ J. Atmospheric water: Transformation of ozone into OH-radicals by sensitized photoreactions or black carbon [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2000, 34(7): 1069-1085. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00361-1 [88] VOLOSHIN A I, SHARIPOV G L, KAZKOV V P, et al. Generation of singlet oxygen from the adsorption and decomposition of ozone on silica gel [J]. Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science, 1986, 35(11): 2397-2399. doi: 10.1007/BF00953370 [89] GORDON G, BUBNIS B. Ozone and chlorine dioxide: Similar chemistry and measurement issues [J]. Ozone:Science & Engineering, 1999, 21(5): 447-464. [90] YU D Y, KANG N, BAE W, et al. Characteristics in oxidative degradation by ozone for saturated hydrocarbons in soil contaminated with diesel fuel [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(5): 799-807. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.053 [91] KIM J, CHOI H. Modeling in situ ozonation for the remediation of nonvolatile PAH-contaminated unsaturated soils [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2002, 55(3/4): 261-285. [92] RIVAS J, GIMENO O, de la CALLE R G, et al. Ozone treatment of PAH contaminated soils: Operating variables effect [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 169(1/2/3): 509-515. [93] PIERPOINT A C, HAPEMAN C J, TORRENTS A. Ozone treatment of soil contaminated with aniline and trifluralin [J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 50(8): 1025-1034. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00635-5 [94] CHENG M, ZENG G M, HUANG D L, et al. Hydroxyl radicals based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for remediation of soils contaminated with organic compounds: A review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 582-598. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.001 [95] LUSTER-TEASLEY S, UBAKA-BLACKMOORE N, MASTEN S J. Evaluation of soil pH and moisture content on in situ ozonation of Pyrene in soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 701-706. [96] LEE B T, KIM K W. Ozonation of diesel fuel in unsaturated porous media [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(8): 1165-1170. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00011-2 [97] YAN Y E, SCHWARTZ F W. Oxidative degradation and kinetics of chlorinated ethylenes by potassium permanganate [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 1999, 37(3/4): 343-365. [98] 纪录, 张晖. 原位化学氧化法在土壤和地下水修复中的研究进展 [J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2003(6): 37-42. JI L, ZHANG H. The progress in soil and groundwater remediation by in situ chemical oxidation [J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2003(6): 37-42(in Chinese).
[99] SIEGRIST R L, CRIMI M, SIMPKIN T J. In Situ Chemical Oxidation for Groundwater Remediation[M]. New York, NY: Springer New York, 2011. [100] OLA S A, FADUGBA O G, OJURI O O. Comparison of effectiveness of two remediating agents on hydrocarbon contaminated soil/groundwater in the laboratory [J]. Environment and Natural Resources Research, 2014, 5(1): 5539. [101] YOO J C, LEE C, LEE J S, et al. Simultaneous application of chemical oxidation and extraction processes is effective at remediating soil Co-contaminated with petroleum and heavy metals [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 186: 314-319. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.016 [102] GATES D D, SIEGRIST R L, CLINE S R. Chemical oxidation of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in soil[J]. Office of entific & Technical Information Technical Reports, 1995. [103] NADUPALLI S, KOORBANALLY N, JONNALAGADDA S B. Kinetics and mechanism of the oxidation of amaranth with hypochlorite [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2011, 115(27): 7948-7954. doi: 10.1021/jp202812f [104] PICARD F, CHAOUKI J. Sodium hypochlorite oxidation of petroleum aliphatic contaminants in calcareous soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 145: 200-206. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.040 [105] GEORGI A, REICHL A, TROMMLER U, et al. Influence of sorption to dissolved humic substances on transformation reactions of hydrophobic organic compounds in water. I. chlorination of PAHs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(20): 7003-7009. [106] PICARD F, CHAOUKI J. NaClO/NaOH soil oxidation for the remediation of two real heavy-metal and petroleum contaminated soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5(3): 2691-2698. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.005 [107] 黄凤莲, 邹璇, 陈灿, 等. 亚铁活化次氯酸钠降解土壤中阿特拉津 [J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(2): 160-165,172. HUANG F L, ZOU X, CHEN C, et al. Degradation of atrazine by ferrous activated sodium hypochlorite [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(2): 160-165,172(in Chinese).
[108] LU S G, ZHANG X, XUE Y F. Application of calcium peroxide in water and soil treatment: A review [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 337: 163-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.064 [109] WATTS R J, FOGET M K, KONG S H, et al. Hydrogen peroxide decomposition in model subsurface systems [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, 69(2): 229-243. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00114-4 [110] NDJOU’OU A C, CASSIDY D. Surfactant production accompanying the modified Fenton oxidation of hydrocarbons in soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(9): 1610-1615. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.036 [111] 李振宇, 刘亚男, 王铮, 等. CaO2及H2O2类Fenton降解土壤石油烃污染 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 780-788. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201909063 LI Z Y, LIU Y N, WANG Z, et al. Degradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons pollution in soil by CaO2/H2O2-Fenton-like system [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(3): 780-788(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201909063
[112] BAJAGAIN R, GAUTAM P, JEONG S W. Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in unsaturated soil and effects on subsequent biodegradation by potassium permanganate [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(6): 1705-1714. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00346-y -



 下载:
下载: