-
我国正在推行生活垃圾分类制度,建设分类收集、分类处置的生活垃圾处理体系[1-2]。厨余废弃物是生活垃圾的主要组成部分,具有高含水率、高有机质的特点[3-4],含有丰富的有机质、氮、磷、钾等资源,利用高温好氧发酵技术将厨余废弃物进行快速无害化、减量化和资源化利用符合我国国情,是我国厨余废弃物处理和处置的重要研究方向。
厨余废弃物的好氧发酵是通过好氧微生物将厨余废弃物中大分子有机物降解成可被作物利用的小分子和矿化的过程,得到高肥力、高稳定性的腐殖质[5]。在发酵过程中需要通过辅料的添加来调节发酵堆体中含水率和养分等理化指标,为好氧微生物的快速代谢和繁殖提供必要的条件,达到微生物最佳的生长繁殖条件[6-7]。我国是农业大国,农作物秸秆资源丰富,花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯中含有丰富的有机碳和营养元素,粗纤维含量高,在有机废弃物好氧发酵过程中常被当作调理剂使用[8-11]。
经热水解预处理后的厨余废弃物由于表面结构和理化性质的改变,更容易被微生物利用,高温发酵阶段更有利于纤维素、木质素的分解,驱动腐殖化进程[12]。因此本文研究热水解后的厨余废弃物与不同辅料进行高温好氧发酵,利用高通量测序技术对不同辅料发酵过程高温区细菌在门与属分类水平下的优势菌群进行鉴定,并对不同辅料与热水解后厨余废弃物好氧发酵过程菌群结构进行解析,以期为厨余废弃物的无害化处置和资源化利用技术提供理论依据和技术支撑。
-
本研究所用的厨余废弃物采集自烟台市农贸市场,目测主要种类有大葱、南瓜、土豆、地瓜、玉米、胡萝卜、鲜玉米叶等,采集厨余废弃物约1000 kg统一运送至烟台市生活垃圾处理场。
试验所用的辅料分别为粉碎后的花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯,采集自烟台市周边农庄,秸秆采集后利用卧式粉碎机粉碎,粉碎机出料口设置5 cm的筛网,经粉碎后的秸秆直径为1—3 cm,3种粉碎的辅料装袋运送至场内发酵场地,厨余废弃物和3种辅料理化指标见表1。
-
分别用花生壳、玉米秆、玉米芯经过粉碎后的秸秆与热水解后的厨余废弃物进行好氧发酵试验,分别定义为HS处理组、YM处理组、YX处理组,并设置1组不添加辅料的对照组(CK),好氧发酵试验共4组。每组分别取粉碎后的秸秆25 kg、热水解产物48 kg、复合菌种1 kg,经过充分混匀后装入到发酵箱中;发酵箱长宽高均为60 cm,侧面均匀设置4块宽15 cm的木挡板,挡板间距为5 cm,发酵箱有较好的透气性。对照组中没有添加秸秆,直接取热水解产物48 kg、菌种1 kg,混匀后装入发酵箱内,各处理组处置完成后,堆肥箱中分别插入数字显示温度计,记录当时的堆体温度。
-
完成好氧发酵试验的混料和装箱后,记录当时的发酵箱堆体的温度,测温时分别量取堆体上1/3部位、中心和下1/3部位,各测3个点,计算平均温度;首次完成混料装箱后记作第0天,以后每天记录堆体温度的变化,每3 d取样1次检测有机质等理化指标,其余样品保存至-20 ℃冰箱储藏,留作微生物多样性检测使用,整个厨余废弃物好氧发酵试验共持续到第21天;每次取样采用无菌操作将样品放入无菌袋中,同时测量取样部位温度,堆体上1/3处、中心和下1/3处各取等量样品,每点取3个平行样。
-
理化指标检测方法[13-14]:温度用LCD-105型461探针数字温度仪,有机质采用重铬酸钾容量法,pH值采用pH计测定,种子发芽指数(GI)采用油麦菜种子进行测定[15]。
-
DNA提取步骤:添加0.5 g样品、978 µL磷酸钠缓冲溶液和122 µL MT缓冲液到裂解介质管E中;在MP研磨仪中振荡40 s,速度为6 m·s−1;在14000 r·min−1条件下离心10 min后转移上清至1.5 mL离心管中,加入250 µL蛋白沉淀溶液(PPS)混匀;室温14000 r·min−1,离心5 min。转移上清至已加入900 µL结合基质悬浮液的2 mL管中,混匀,上下颠倒3 min;瞬离5 s弃上清液。加入500 µL 5.5 mol·L−1的异硫氰酸胍溶液,混匀后转移到SPIN过滤器中;加入500 µL SEWS-M溶液,14000 r·min−1离心1 min,弃滤液,再重复洗涤1次;弃去收集管中液体,14000 r·min−1离心3 min,去除残留溶液,晾干3 min;加入100 µL 55 ℃预热的低共熔溶剂(DES)洗脱液,静置5 min;室温14000 r·min−1离心2 min,弃SPIN过滤器,得到总DNA。
DNA完整性检测方法为1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,电压5 V·cm−1,时间为20 min;DNA纯度和浓度检测设备为NanoDrop 2000超微量分光光度计。
-
PCR扩增反应体系按以下步骤进行:5×FastPfu缓冲溶液4 µL, 2.5 mmol·L−1 dNTPs 2 µL,正向引物(5 µmol·L−1) 0.8 µL,反向引物(5 µmol·L−1) 0.8 µL, FastPfu聚合酶0.4 µL,牛血清白蛋白0.2 µL,模板DNA 10 ng,补ddH2O至20 µL。
细菌16S rRNA基因在V3-V4区的PCR扩增条件: 95 ℃预变性3 min;然后在95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃复性30 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,循环数30次;最终在72 ℃延伸45 s,10 ℃冷却。
每个样本3个PCR重复,将3个重复的PCR产物混合;使用2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测产物。
PCR产物纯化使用AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit,将PCR产物用QuantusTM Fluorometer进行检测定量,按照每个样本的测序量要求,进行相应比例的混合,使用NEXTFLEX® Rapid DNA-Seq Kit进行建库,利用Illumina公司的MiseqPE 300平台进行测序。
-
用Microsoft Excel 2010和SPSS 26统计分析软件对于试验数据进行整理计算和分析,用OriginPro 8绘图软件绘制点线图等。
-
温度是好氧发酵过程中堆体微生物活性的重要指标,也是评价发酵效果的重要指标[15-16]。不同的发酵温度直接影响不同微生物种群的生长繁殖和微生物酶的活性,进而影响发酵效率和发酵产品的品质[17-18]。
发酵试验开始时记作第0 d,此时室外温度为20.0 ℃,各试验组堆体温度均为26.0 ℃,不同试验组发酵过程温度的变化见图1。温度的动态变化显示,前3天,各处理组温度呈上升趋势,第3天,HS、YM和YX处理组温度分别为65.3 ℃、64.5 ℃和49.7 ℃;第4天开始,各处理组温度开始缓慢下降,第5天,对3个处理组进行翻堆处理。翻堆处理后,HS和YM处理组第6天温度略有波动,但变化不大,此后温度逐渐降低,直至发酵结束的第21天,堆体温度接近室温;YX处理组在第6天温度有较大提升,首次超过60.0 ℃,达到65.2 ℃,第7天持续保持高温状态,此后开始缓慢下降,与HS和YM处理组相比,HX处理组温度下降速率较慢。整个发酵过程中对照组温度略高于室温,堆体温度变化不大。
堆体温度保持在50.0 ℃ 5—7 d,或者55.0 ℃ 3 d,可以杀灭堆体中的虫卵和种子,达到无害化处理要求[19],由此可见,除对照组外,HS、YM和YX组3种辅料处理的厨余废弃物均达到无害化处理要求。与HS和YM处理组相比,YX处理组温度上升较慢,持续时间较长,这可能因为经过粉碎的玉米芯相比于花生壳和玉米秆,比表面积较小,不能被微生物快速附着,内部营养物质持续释放,降解效率相对较低,发酵组温度变化分析表明,3种辅料发酵效果HS优于YM和YX。
-
各处理组在发酵过程中pH随发酵时间变化情况见图2。第0—2天,由于发酵过程中有机酸的产生会降低堆体的pH值[20],导致各处理组pH均出现下降趋势。第3 d,各处理组pH均有较大提升,这是因为蛋白质类有机物在微生物的作用下降解产生氨氮,使pH值快速上升[21-22]。第4天和第5天,YM处理组pH持续降低,可能是因为堆体氨气挥发导致;HS处理组由于孔隙率高,比表面积大,对产生的氨气有较好的吸附性,pH值处于较高水平,除了第6天由于翻堆导致氨的外溢pH突然降低,自第7天至发酵结束,HS处理组pH值一直处于较高水平。发酵结束的第21天,HS组pH最高,为9.64,YX和YM组pH值差别不大,分别为8.03和7.91。
-
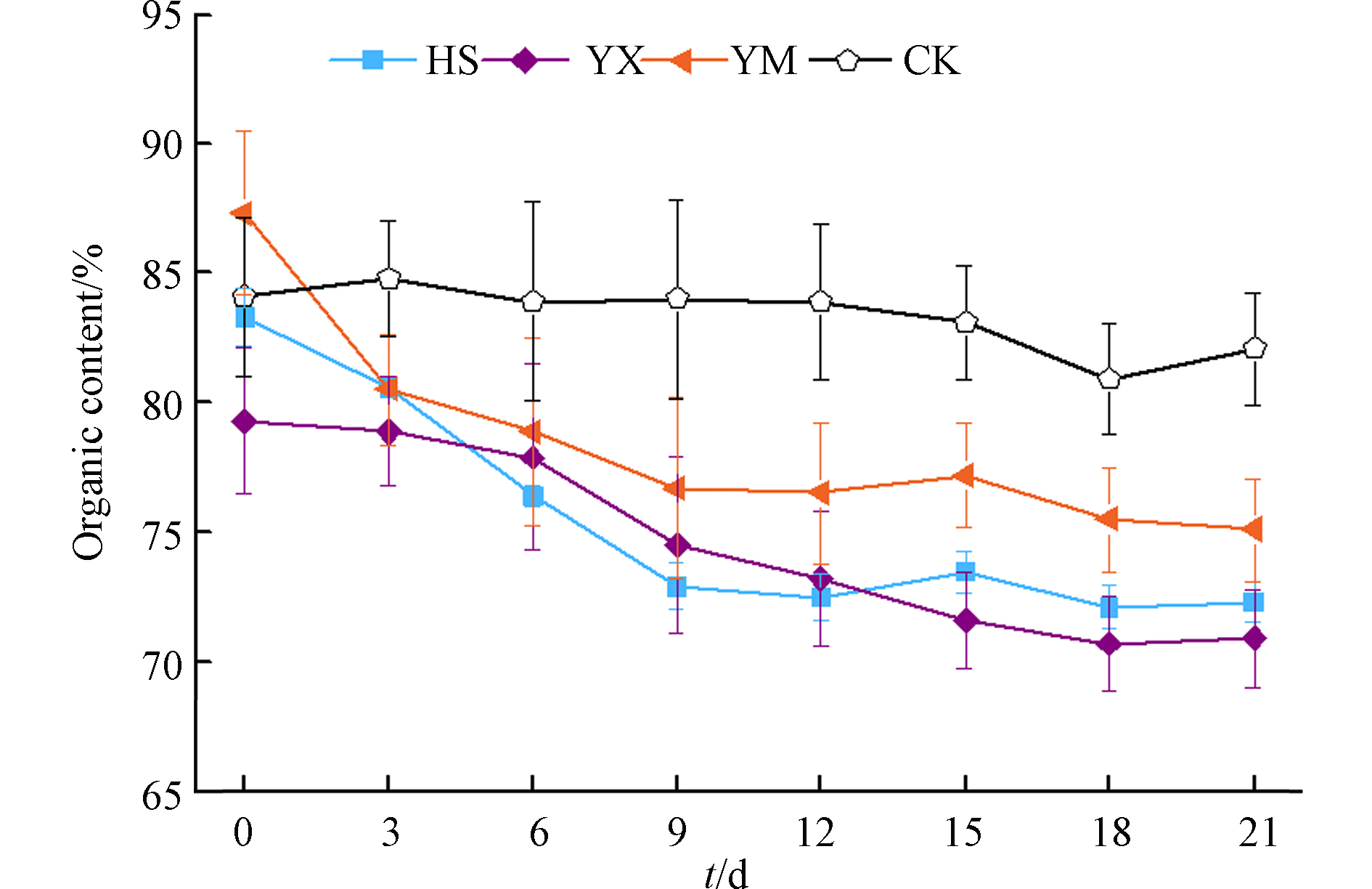
各处理组有机质随时间的变化曲线见图3。第0 d到第6 d,HS、YM处理组有机质含量下降明显,YX组有机质含量逐渐降低但下降的比例要小于HS和YM组,HS、YM和YX组第6天的有机质含量与第0 d相比分别降低了8.3%、9.6%和1.8%;第6天至第9天,HS、YM和YX处理组有机质分别减少了4.6%、2.8%、4.4%;第9天到第21天,HS和YM组有机质含量出现波动,但变化不大,YX组有机质含量呈持续降低趋势;第21天与第0天相比,HS、YM、YX和CK有机质减少比例分别为13.2%、14.0%、10.6%和2.3%。
发酵初期HS和YM处理组可被微生物利用的小分子有机物充足,温度快速上升,有机碳快速消耗导致有机质含量明显降低[23]。YX处理组温度上升相对较慢,有机碳的消耗量也相对较小;第6天至第9天,YX处理组温度一直处于高温区,高温发酵菌群处于活跃期,导致有机质含量快速下降[24]。
-
有研究表明种子发芽指数(GI)可作为发酵是否腐熟的标准,当GI值超过80%可以认为发酵完全腐熟[25-26]。将各处理组第0—21天每3天的发酵产物做种子发芽率检测,计算不同处理组在好氧发酵期间的GI值,见图4。
HS和YM处理组随着发酵时间的持续GI迅速蹿升,第9天分别达到了97.5%和86%,说明HS和YM处理组在第9 d即达到了腐熟标准,此后GI持续增大,HS处理组在第15天后增速减缓,YM处理在第18天后增速减缓,第21 d两组GI分别达到122.6%和119.5%,HS组略优于YM组。YX处理组GI在0—3 d增长明显,第3天后GI增长幅度明显放缓,但仍然呈快速增长趋势,在第18天,YX处理组GI首次超过80%,达到96%,第21天达到105%,完全达到腐熟标准。CK处理组在发酵结束的第21天,GI仅为25.69%,没有达到腐熟要求。
通过对好氧发酵过程中种子GI动态变化的研究,结果表明,HS、YM和YX处理组均达到腐熟标准,GI值的动态变化与好氧发酵过程中温度的变化存在一定的相关性,花生壳组和玉米秆组第2天温度即超过60.0 ℃,首先达到高温区,而玉米芯组首次超过60.0 ℃为第6天,说明好氧发酵过程中快速进入高温期有助于有机物料的快速腐熟。
-
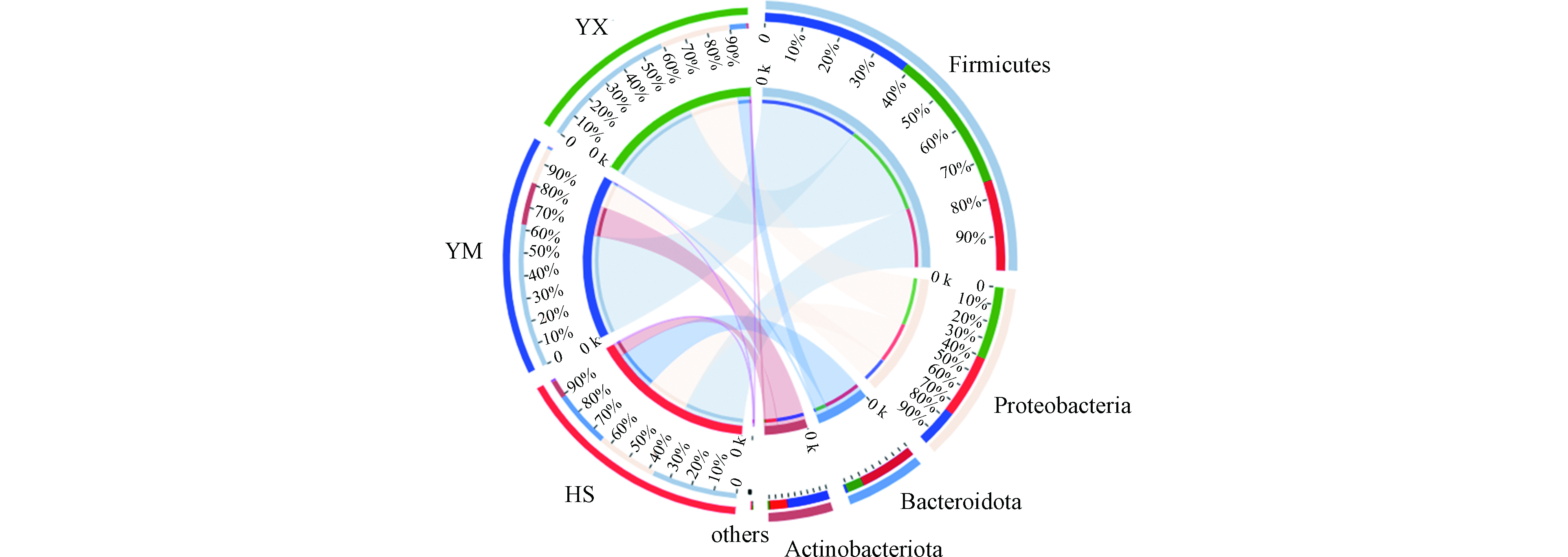
由于升温速率不一致,HS和HM处理组测序样本取自第3天,HX处理组样本取自第6天。高温发酵阶段在门分类水平下对样本进行分类学分析,得到Circos图(见图5)。图5中左半圆表示不同样本相对应的物种组成情况,右半圆表示物种在不同样本中的分布情况。在门水平下,将样品中丰度均小于0.01的菌门归类为其他,单个样品中丰度大于0.01的菌门显示菌门名称,在HS、YM和YX高温组发酵试验中,细菌主要的菌门包括厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)和放线菌门(Actinobacteriota),4种菌门在各处理组中的占比存在差异,其中在HS处理组中的占比分别为:38%、27%、25%、8.1%,YM组占比64%、16%、1.0%、19%,YX组占比60%、31%、7.4%、0.85%。
在门分类水平下,HS、YM和YX发酵组中,好氧发酵优势细菌菌门为厚壁菌门、变形菌门、放线菌门和拟杆菌门,王秀红等[27]利用玉米秸秆与牛粪混合,用少量石膏粉和尿素等进行调配,C/N比30左右,水分65%—70%,进行高温好氧发酵试验,对试验过程的细菌群落多样性进行连续检测,得到在好氧发酵过程中,主要的优势菌门为厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteriota)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota),与本试验研究结果一致;Wei等[28]对玉米秸秆发酵过程微生物群落代谢进行研究,用稻草和尿素调整C/N必为30:1,水分65%左右,发酵样品厚壁菌门、变形菌门、放线菌门和拟杆菌门占比92.2%,虽然随着发酵时间的延长,厚壁菌门丰度相对下降,但仍是发酵过程中的优势菌门。
-
在属水平下对HS、YM和YX组高温区占比位于前50的细菌进行分析,菌群丰度见图6。
HS组高温阶段细菌菌群丰度超过1%的菌属共有15个,其中黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)11.44%,魏斯氏菌属(Weissella)10.2%,鞘氨醇杆菌属(Sphingobacterium)9.47%,芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)8.2%,苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum)4.91%,丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)4.52%,短芽孢杆菌属(Brevibacillus)4.52%,类芽孢杆菌属(Paenibacillus)4.00%,纤维菌属(Cellulosimicrobium)3.81%,norank_f__Bacillaceae 3.54%,unclassified_f__Rhizobiaceae 3.01%,DSSF69 2.86%,沉积物漠河杆菌属(Moheibacter)2.58%,赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属(Lysinibacillus)2.44%,微杆菌属(Microbacterium)1.18%。
YM组高温阶段细菌菌群丰度超过1%的菌属共有12个,其中芽胞杆菌属(Bacillus)18.96%,魏斯氏菌属(Weissella)16.81%,葡萄球菌属(Staphylococcus)16.33%,肠杆菌属(Enterobacter)11.04%,小短杆菌属(Brachybacterium)5.6%,短芽孢杆菌属(Brevibacterium)5.29%,李斯特氏菌属(Listeria)3.34%,微杆菌属(Microbacterium)2.39%,水原拉梅尔芽孢杆菌属(Rummeliibacillus)2.15%,库特氏菌属(Kurthia)1.94%,居白蚁菌属(Isoptericola)1.44%,norank_f__Bacillaceae 1.22%。
YX组高温阶段细菌菌群丰度超过1%的菌属共有12个,其中,不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)22.75%,乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)20.38%,魏斯氏菌属(Weissella)14.37%,库特氏菌属(Kurthia)8.03%,肠球菌属(Enterococcus)5.27%,稳杆菌属(Empedobacter)3.62%,乳球菌属(Lactococcus)3.38%,明串珠菌属(Leuconostoc)2.65%,丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)2.62%,醋杆菌属(Acetobacter)1.72%,Dysgonomonas 1.45%,弗氏弧菌属(Vagococcus)1.01%。
魏斯氏菌属(Weissella)在HS、YM和YX处理组中均大量存在,其主要功能是对发酵过程中产生的糖类化合物快速消耗[29];黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)具有代谢复杂有机化合物的能力[30];鞘氨醇杆菌属(Sphingobacterium)、肠杆菌属(Enterobacter)是对木质素的降解有较高活性的微生物[31-32];芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)和类芽孢杆菌属(Paenibacillus)可以产生纤维素酶,对纤维素和半纤维素的降解有促进作用[33-34];苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum)、丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)对多环芳烃(PAHs)的降解有较好的效果[35-38];短芽孢杆菌属(Brevibacillus)可以分泌功能性的代谢产物将芳香族化合物转化为没有毒性的中间体[39];纤维菌属(Cellulosimicrobium)可以分泌烃类降解酶,对烷烃进行降解,是降解纤维素的优势菌群[40]。
葡萄球菌属(Staphylococcus)、肠球菌属(Enterococcus)具有代谢芳环化合物的能力[41-44];乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)适宜在兼性厌氧的条件下生长繁殖,可将发酵堆体中的糖转化为有机酸[45],由于YX比表面积和孔隙率较小,通透性不足,堆体中的氧气含量不足,所以高温阶段乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)大量存在。
-
(1)花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯作为辅料与热水解后的厨余废弃物高温好氧发酵可以使厨余废弃物有效降解,发酵结束后有机质含量分别降低13.2%、14.0%、10.6%,发酵产物达到腐熟标准;堆体温度变化表明,花生壳处理组对厨余废弃物的降解效果最好,优于玉米秆和玉米芯处理组。
(2)门分类水平下,各处理组高温发酵阶段优势菌群具有相似性,优势菌门为:厚壁菌门、变形菌门、放线菌门和拟杆菌门。
(3)属分类水平下,花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯为辅料的优势细菌菌属存在差异。花生壳处理组优势菌属为:黄杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、鞘氨醇杆菌属、芽孢杆菌属;玉米秆处理组优势菌属为:芽胞杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、葡萄球菌属、肠杆菌属、小短杆菌属和短芽孢杆菌属;玉米芯处理组优势菌属为:不动杆菌属、乳杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、库特氏菌属和肠球菌属。
不同辅料对热水解厨余废弃物好氧发酵过程理化性状和微生物菌群的影响
Effect of different additives on physicochemical properties and microflora during aerobic fermentation of thermal hydrolysis kitchen waste
-
摘要: 本文对经过热水解预处理的厨余废弃物与3种不同辅料进行好氧发酵对比研究,测定热水解后厨余废弃物分别以花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯作为辅料好氧发酵过程中温度、pH、有机质和GI的动态变化,并对3种辅料高温发酵处理阶段样品进行高通量测序,鉴定不同辅料高温区优势菌群。结果表明,花生壳对热水解后厨余废弃物处理效果优于玉米秆和玉米芯。高温发酵阶段样品高通量测序结果显示,门分类水平下花生壳、玉米秆和玉米芯的3种辅料堆体中优势菌群具有相似性,样本丰度大于0.01的细菌菌门共4个,分别为厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)和放线菌门(Actinobacteriota);属分类水平下各组优势细菌菌属存在差异,其中花生壳处理组适宜添加的主要细菌菌属为黄杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、鞘氨醇杆菌属、芽孢杆菌属;玉米秆处理组适宜添加的主要细菌菌属为芽胞杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、葡萄球菌属、肠杆菌属、小短杆菌属和短芽孢杆菌属;玉米芯处理组适宜添加的主要细菌菌属为:不动杆菌属、乳杆菌属、魏斯氏菌属、库特氏菌属和肠球菌属。Abstract: In this paper, a comparative study was conducted on the aerobic fermentation of kitchen waste pretreated by thermal hydrolysis and three different additives, the dynamic changes of temperature , pH, organic matter and GI of kitchen waste after thermal hydrolysis were measured during aerobic fermentation with peanut shell, corn stalk and corn cob as additives, and high-throughput sequencing was performed on the samples of the three additives in the high temperature fermentation stage to identify the dominant bacterial community in the high temperature region of different additives. The results showed that the treatment effect of peanut shell on kitchen waste after thermal hydrolysis was better than that of corn stalk and corn cob. The results of high-throughput sequencing of samples at the high temperature fermentation stage showed that the dominant bacterial communities of peanut shell, corn stalk and corn cob were similar at the gate classification level. There were four bacterial phylas with a sample abundance greater than 0.01 which are Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota and Actinobacteriota. At the level of genus classification, there were differences among the dominant bacterial genera in each groups. The main bacterial genera suitable for peanut shell treatment group were Flavobacterium, Weissella, Sphingobacterium and Bacillus. The suitable bacterial species in corn stalk treatment group were Bacillus, Weissella, Staphylococcus, Enterobacter, Brevibacterium and Brevibacterium. The main bacteria suitable to be added in corn cob treatment group were Acinetobacter, Lactobacillus, Weissella, Kurthia and Enterococcus.
-
Key words:
- additives /
- kitchen waste /
- aerobic fermentation /
- flora structure
-

-
表 1 原料基本理化性质
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of raw material
名称
Name有机质/(g·kg−1)
Organic matter总氮/(g·kg−1)
Total nitrogen总磷/(g·kg−1)
Total phosphorus总钾/(g·kg−1)
Total potassium含水率/%
Water content花生壳 834.23±30.08 3.91±0.14 1.51±0.05 6.52±0.24 9.73±0.35 玉米秆 941.38±33.94 7.43±0.27 1.79±0.06 4.63±0.17 9.37±0.34 玉米芯 705.33±32.32 5.62±0.26 4.93±0.23 7.08±0.32 6.83±0.31 厨余废弃物 846.17±22.39 16.29±0.43 5.42±0.14 13.51±0.35 92.43±2.45 -
[1] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中央财经领导小组第十四次会议召开[EB/OL]. [2022-05-22]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/21/content_5151201.htm. Central People’s Government of the People's Republic of China, The 14th meeting of the central leading group for financial and economic affairs was held [EB/OL]. [2022-05-22]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/21/content_5151201.htm(in Chinese).
[2] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 国务院办公厅转发生活垃圾分类制度实施方案[EB/OL]. [2022-05-22]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2017-03/30/content_5182184.htm. Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, The General office of the state council forwarded the implementation plan of household garbage classification system[EB/OL]. [2022-05-22]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2017-03/30/content_5182184.htm(in Chinese).
[3] 邹联沛, 宋琳, 李小伟, 等. 湿垃圾组分对厌氧消化抑制作用的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(S2): 362-371. ZOU L P, SONG L, LI X W, et al. Research progress of the inhibition of components of food waste on anaerobic digestion[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(Sup 2): 362-371(in Chinese).
[4] 周营, 朱能武, 刘博文, 等. 微生物菌剂复配及强化厨余垃圾好氧堆肥效果分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(1): 294-303. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201703044 ZHOU Y, ZHU N W, LIU B W, et al. Effect analysis of compound microbial agents and enhancement on kitchen waste aerobic composting [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(1): 294-303(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201703044
[5] 李扬, 李彦明. 蔬菜废弃物的堆肥化处理技术研究进展 [J]. 北方园艺, 2015(19): 180-184. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.201519045 LI Y, LI Y M. Research progress on composting technology of vegetable wastes [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2015(19): 180-184(in Chinese). doi: 10.11937/bfyy.201519045
[6] 张邦喜, 罗文海, 杨仁德, 等. 添加菌糠对鸡粪-烟末堆肥腐熟度及污染气体排放的影响 [J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(11): 2578-2586. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.11.2578 ZHANG B X, LUO W H, YANG R D, et al. Effects of spent mushroom substrate on the maturity and gaseous emissions in Co-composting of chicken manure and tobacco wastes [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(11): 2578-2586(in Chinese). doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.11.2578
[7] LIU D D, MA X X, HUANG J L, et al. Study on personalized microbial formulation during high-temperature aerobic fermentation of different types of food wastes [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 814: 152561. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152561 [8] 张国占. 碳源调理剂对牛粪高温好氧堆肥发酵的影响 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(12): 99-106. doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2018.0415 ZHANG G Z. Effect of carbon source conditioner on high temperature aerobic compost fermentation of cow manure [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(12): 99-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2018.0415
[9] 周孝琼, 陈洪博, 韦建云, 等. 发酵花生壳对湖羊生长性能、血液生化及免疫指标的影响 [J]. 中国饲料, 2022(4): 109-112. doi: 10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.20220428 ZHOU X Q, CHEN H B, WEI J Y, et al. Effects of fermented peanut shell on growth performance, blood biochemistry and immune indexes of lake sheep [J]. China Feed, 2022(4): 109-112(in Chinese). doi: 10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.20220428
[10] 李思敏, 赵阳悦, 唐锋兵. 辅料配比对市政污泥堆肥效果的影响 [J]. 当代化工, 2020, 49(4): 564-567,571. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.04.016 LI S M, ZHAO Y Y, TANG F B. Influence of additive ratio on municipal sludge composting effect [J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(4): 564-567,571(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.04.016
[11] 余鑫, 郑云昊, 朱志平, 等. 猪场沼渣与玉米芯混合槽式堆肥氨气排放特征 [J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(3): 138-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.03.002 YU X, ZHENG Y H, ZHU Z P, et al. Characteristics of ammonia emissions from trough composting of swine manure biogas residue and corn cob [J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2020, 41(3): 138-145(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.03.002
[12] 江高飞, 暴彦灼, 杨天杰, 等. 高温秸秆降解菌的筛选及其纤维素酶活性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2465-2472. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0958 JIANG G F, BAO Y Z, YANG T J, et al. Screening of thermophilic cellulolytic bacteria and investigation of cellulase thermostability [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2465-2472(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0958
[13] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[14] 胡诚, 刘东海, 乔艳, 等. 施用生物有机肥对土壤酶活性及作物产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2017, 32(S1): 308-312. HU C, LIU D H, QIAO Y, et al. Effect of biological organic manure on soil enzyme activity and crop yields[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2017, 32(Sup 1): 308-312(in Chinese).
[15] 中华人民共和国农业部. 有机肥料: NY 525—2012[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2012. Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. Organic fertilizer: NY 525—2012[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[16] 徐谞, 王心怡, 王定一, 等. 接种高温芽孢杆菌促进堆肥腐熟研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(5): 1134-1141. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020.05.17 XU X, WANG X Y, WANG D Y, et al. Effects of inoculation of thermophiles Bacillus strains on composting efficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(5): 1134-1141(in Chinese). doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2020.05.17
[17] 杨海君, 许云海, 肖为, 等. 温度和物料配比对城市园林绿化废物与鸡粪水浴法好氧堆肥的影响 [J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(6): 35-43,51. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.06.006 YANG H J, XU Y H, XIAO W, et al. Effects of temperature and substrate composition on aerobic composting of urban landscape waste and chicken manure using water bath method [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 35-43,51(in Chinese). doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.06.006
[18] 马闯, 扈斌, 刘福勇, 等. 有机废弃物好氧堆肥过程中微生物及酶活性变化状况综述 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(9): 159-164,187. MA C, HU B, LIU F Y, et al. Review on changes of microorganisms and enzyme activities during aerobic composting of organic waste [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(9): 159-164,187(in Chinese).
[19] 王代懿, 余洋, 张丰松, 等. 堆肥方式和温度对牛粪堆肥过程中天然类固醇激素降解的影响 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(12): 2104-2108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2017.12.20 WANG D Y, YU Y, ZHANG F S, et al. Effects of composting temperature and manner on degradation of natural hormones during cattle manure composting [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2017, 29(12): 2104-2108(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2017.12.20
[20] 周喜荣, 张丽萍, 蒋鹏, 等. 牛粪与秸秆类废弃物配比好氧发酵新工艺对堆肥效果的影响 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(6): 75-83. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2020.06.11 ZHOU X R, ZHANG L P, JIANG P, et al. Effect of new process of aerobic fermentation of cow manure and straw waste on composting [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(6): 75-83(in Chinese). doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2020.06.11
[21] 刘文杰, 王黎明, 沈玉君, 等. 碳氮比对蔬菜废弃物好氧发酵腐熟度及臭气排放的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(6): 233-239. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202006038 LIU W J, WANG L M, SHEN Y J, et al. Effects of carbon to nitrogen ratio on maturity and odor emission in aerobic fermentation of vegetable waste [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(6): 233-239(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202006038
[22] 周海瑛, 邱慧珍, 杨慧珍, 等. C/N比对好氧堆肥中NH3挥发损失和含氮有机物转化的影响 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(2): 69-77. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2020.02.10 ZHOU H Y, QIU H Z, YANG H Z, et al. Effects of C/N ratio on NH3 volatilization loss and nitrogen-containing organic compounds conversion in aerobic composting [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(2): 69-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2020.02.10
[23] 张玉凤, 田慎重, 边文范, 等. 牛粪和玉米秸秆混合堆肥好氧发酵菌剂筛选 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(3): 172-178. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.18318 ZHANG Y F, TIAN S Z, BIAN W F, et al. Screening of aerobic fermentation microbial agents mixed with cow dung and corn straw [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(3): 172-178(in Chinese). doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.18318
[24] 曹云, 黄红英, 钱玉婷, 等. 超高温预处理装置及其促进鸡粪稻秸好氧堆肥腐熟效果 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(13): 243-250. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.13.032 CAO Y, HUANG H Y, QIAN Y T, et al. Hyperthermophilic pretreatment device and its application on improving decomposition effect for chicken manure and rice straw aerobic composting [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(13): 243-250(in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.13.032
[25] 晏琛, 曹雷鹏, 刘玉环, 等. 利用新型高温好氧堆肥器提高鸡粪谷壳有机肥肥效 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(3): 1103-1111. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202008103 YAN C, CAO L P, LIU Y H, et al. Effect of new high temperature aerobic composting device on maturation of chicken manure and rice chaff [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(3): 1103-1111(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202008103
[26] 王世朋, 帅文亮, 王婷婷, 等. 油菜秸秆比例对好氧堆肥过程及产品特性的影响 [J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 54(6): 1334-1340. WANG S P, SHUAI W L, WANG T T, et al. Effect of rape straw ratio on performance of aerobic composting process and characteristic of final product [J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 54(6): 1334-1340(in Chinese).
[27] 王秀红, 李欣欣, 史向远, 等. 玉米秸秆不同发酵时期理化性状和细菌群落多样性 [J]. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(3): 144-152. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.03.022 WANG X H, LI X X, SHI X Y, et al. Physicochemical properties and bacterial community diversity during different fermentation periods of corn straw [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2018, 33(3): 144-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.03.022
[28] WEI H W, WANG L H, HASSAN M, et al. Succession of the functional microbial communities and the metabolic functions in maize straw composting process [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 256: 333-341. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.050 [29] TEIXEIRA C G, FUSIEGER A, MILIÃO G L, et al. Weissella: An emerging bacterium with promising health benefits [J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2021, 13(4): 915-925. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09751-1 [30] KRAUT-COHEN J, SHAPIRO O H, DROR B, et al. Pectin induced colony expansion of soil-derived Flavobacterium strains [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 651891. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.651891 [31] BESAURY L, FLORET J, RÉMOND C. Sphingobacterium prati sp. nov., isolated from agricultural soil and involved in lignocellulose deconstruction [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2021, 71(8): 004963. [32] ZHANG Q, ZHANG J, ZHAO S, et al. Enhanced biogas production by ligninolytic strain Enterobacter hormaechei KA3 for anaerobic digestion of corn straw [J]. Energies, 2021, 14(11): 2990. doi: 10.3390/en14112990 [33] ZHANG S B, XIA T Y, WANG J L, et al. Role of Bacillus inoculation in rice straw composting and bacterial community stability after inoculation: Unite resistance or individual collapse [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125464. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125464 [34] 陈峥, 刘波, 邓文琼, 等. 14株芽胞杆菌菌株的分子鉴定及其促生机理分析 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(3): 789-799. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.03.026 CHEN Z, LIU B, DENG W Q, et al. Molecular identification and growth promoting mechanisms of 14 Bacillus strains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(3): 789-799(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.03.026
[35] HU M Y, LI X G, LI Z J, et al. Ochrobactrum teleogrylli sp. nov., a pesticide-degrading bacterium isolated from the insect Teleogryllus occipitalis living in deserted cropland [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2020, 70(4): 2217-2225. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.003964 [36] 赫法贵, 任政华, 弭晓菊, 等. 睾丸酮丛毛单胞菌降解石油污染物的研究进展 [J]. 生命科学, 2013, 25(1): 106-112. doi: 10.13376/j.cbls/2013.01.016 HE F G, REN Z H, MI X J, et al. Advances in degradation of petroleum pollutants by Comamonas testosteroni [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2013, 25(1): 106-112(in Chinese). doi: 10.13376/j.cbls/2013.01.016
[37] 王乔, 郑瑞, 孙学婷, 等. 睾丸酮丛毛单胞菌对羊草根际土壤PAHs降解及细菌群落结构的影响 [J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(12): 2657-2673. WANG Q, ZHENG R, SUN X T, et al. Effects of Comamonas testosteroni on PAHs degradation and bacterial community structure in Leymus chinensis rhizosphere soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(12): 2657-2673(in Chinese).
[38] 张立志, 余思彤, 袁欣, 等. 丛毛单胞菌对邻甲酚及对甲酚的降解特性 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(7): 820-825,832. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.07.004 ZHANG L Z, YU S T, YUAN X, et al. Degradation characteristics of o-cresol and p-cresol by Comamonas sp [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(7): 820-825,832(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.07.004
[39] LI C, ZHANG X, LU Y, et al. Cometabolic degradation of p-chloroaniline by the genus Brevibacillus bacteria with extra carbon sources [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 121198. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121198 [40] BERTEL-SEVILLA A, CERVANTES-CEBALLOS L, TIRADO-BALLESTAS I, et al. Biodegradation of biodiesel-oil by Cellulosimicrobium sp. isolated from Colombian Caribbean soils [J]. Environmental Technology, 2020, 41(18): 2337-2349. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1564798 [41] SHAHI A, CHELLAM P V, SINGH R S, et al. Biodegradation of reactive red 120 in microbial fuel cell by Staphylococcus equoruma RAP2: Statistical modelling and process optimization [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 40: 101913. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101913 [42] SUMAN S, TANUJA. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial strain Enterobacter cloacae (accession No. KX438060.1) capable of degrading DDTs under aerobic conditions and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soil[J]. Microbiology Insights, 2021, 14: 11786361211024289. [43] FARSI R M, ALHARBI N M, BASINGAB F S, et al. Biodegradation of picric acid (2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol, TNP) by free and immobilized marine Enterococcus thailandicus isolated from the red sea, Saudi Arabia [J]. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 2021, 47(3): 307-312. doi: 10.1016/j.ejar.2021.05.002 [44] 余琴, 马现永, 邓盾, 等. 海氏肠球菌IDO5对猪粪废水中吲哚降解条件优化及降解途径分析 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(12): 113-123. doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-0071 YU Q, MA X Y, DENG D, et al. Optimization of indole-degrading conditions in pig manure waste water by enteroccus hirae IDO5 and analysis of its corresponding degradation pathway [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(12): 113-123(in Chinese). doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-0071
[45] KOO J R, MIN PARK H, KYUNG KIM S, et al. Lactic acid fermentation from coffee ground waste hydrolysate by Lactobacillus rhamnosus [J]. Journal of Renewable Materials, 2019, 7(4): 365-372. doi: 10.32604/jrm.2019.04170 -




 下载:
下载: