-
铜矿冶炼渣(以下简称铜渣)是火法炼铜的副产物,我国90%以上的铜是通过火法冶炼生产的[1]. 据估计,每生产1 t铜,就会产生大约2.2 t的铜渣,每年世界铜生产产生的铜渣约为2460万t[2]. 长期堆放的铜渣在风化和淋洗作用下易释放出Cu、Fe、Ni、Zn、Pb、As、Co[3-4]等金属离子. 释放出的金属离子首先进入土壤、农作物、地表水和地下水,然后通过食物链富集于人体内,对人类安全造成严重威胁. 张云等[5]对云南省某典型铜尾矿库的研究结果表明,尾矿区及周边区域受Cu污染最严重,其平均CF(各类重金属污染指数)值达到高度污染水平,Cd达到中度及以上污染水平. 张卫等[6]对HTM铜矿尾矿库污染特征的研究结果表明,尾矿库表层尾矿在闭库20年间持续释放的Cd为516.38 kg,Zn为42.24 t. 黄长干等[7]对江西德兴铜矿采矿区、尾矿堆积区、生活区以及下游河流大圬河、乐安河的水域、土壤铜污染状况进行调查,结果表明矿区铜污染极为严重,土壤中铜含量平均高达186 mg·kg−1,大圬河河水铜含量在15—30 mg·L−1之间,底泥的铜含量在500—9000 mg·kg−1之间,乐安河的底泥铜含量达500 mg·kg−1. 由此可见,铜矿冶炼渣对环境危害极大.
铜矿选冶渣(The reselected copper smelting slag,RCSS)是铜渣再次选别产生的尾渣,其可回收利用价值低,具有独特的的环境危害性. 目前,国内外对铜渣的研究较多,主要集中在有价金属回收、资源化利用和材料制备上[8-12],而对铜矿选冶渣的研究鲜有报道. 为此,本文以四川某铜矿选冶渣为研究对象,采用硫酸硝酸法、改进的BCR、风险评估编码(risk assessment coding,RAC)和次生相与原生相比值(phase and primary comparison,RSP)等方法评价铜矿选冶渣的综合理化特性及环境污染特性,为铜矿选冶渣科学处理处置提供基础数据.
-
四川某铜矿选冶渣场为山谷型渣场,属弱酸雨分布区,堆存库容为262.332万m3,堆存铜矿选冶渣9.82万m3,渣场周围多村庄和河流. 其现场情况如图1所示.
-
2020年3月现场采样,按照多点采样、混合均匀的原则,样品采集根据渣场实际地形地貌条件,采取棋盘式布点法,设置25个采样点,每个点取0—20 cm表层样2.0 kg,将其均匀混合为1个样,用聚乙烯样品袋密封保存. 采集的样品作风干和均质化处理后,装袋并置于阴凉处. 处理后的样品外观如图2所示.
-
采用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF,Axios,PANalytical)、X射线衍射仪(XRD,Ultima Ⅳ,日本理学)、矿物解离分析仪(MLA,FEI650,捷克)、激光粒度分析仪(LPSA,LS13320,美国贝克曼库尔特)、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,Thermo Scientific K-Alpha+,美国Thermo fisher)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Ultra 55,德国蔡司)、傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR,Spectrum One,美国PE)和同步热分析仪-傅里叶变换红外气相色谱质谱联用仪(STA-FTIR-GCMS,STA449F5、Tensor Ⅱ、7890B/5977A,耐驰、布鲁克、安捷伦)等设备分析铜矿选冶渣元素组成、物相组成及其相对含量、重金属元素(如Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb)的赋存状态、粒度分布、形貌特征、表面元素化学组成和原子价态、分子键结构和热稳定性等.
采用TCLP法[13]和硫酸硝酸法[14]测试铜矿选冶渣浸出毒性;对铜矿选冶渣进行消解[15],采用原子吸收光谱仪(AAS,AA7003,北京三雄)测定铜矿选冶渣Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb和Cr的含量;通过改进后的BCR法[16-17]确定铜矿选冶渣Cr、Fe、Cu、Zn和Pb的形态分布.
-
运用风险评估编码(RAC)法和次生相与原生相比值(RSP)法评价铜矿选冶渣潜在的环境污染风险.
-
RAC法通常采用废渣中重金属的可交换态(BCR分级下为可交换态)——即弱酸可提取态,Tessier分级下为可交换态与碳酸盐结合态之和)在总量中的占比对潜在环境风险进行分级,以此评估废渣的潜在环境风险[18].RAC法数学表达式为:
-
次生相即除残渣态以外的形态,原生相即残渣态[18].RSP法数学表达式为:
式中,RSP为污染程度;Msec 为次生相中的重金属含量;Mprim为原生相中的重金属含量. RAC法和RSP法评价标准见表1[19].
-
铜矿选冶渣XRF分析结果如表2所示. 由表2可知,该铜矿选冶渣主要包括Fe、Si和Cu等元素,其中Fe2O3含量为65.94%、SiO2含量为19.16%、CuO含量为0.4%、ZnO含量为4.36%、As2O3含量为0.2%、Cr2O3含量为0.04%、PbO含量为0.89%,故选冶渣中Cr、Fe、Cu、Zn和Pb等重金属元素的潜在环境风险较大.
该铜矿尾矿及其冶炼渣和选冶渣主要元素含量对比见表3. 该矿山企业原矿主要为硫化铜矿,经过浮选获得以黄铜矿为主的铜精矿,尾矿主要为石英、长石、云母和黏土矿物等硅酸盐矿物,铜含量较低[20],仅为0.04%,铅、铬、锌等重金属含量也非常低. 铜冶炼渣中铜的含量较高,含量为1.80%,锌、铅和铬的含量分别为2.36%、0.48%和0.044%,直接堆放至渣场环境风险较大. 采用浮选回收铜冶炼渣中有价元素铜以后,铜含量大大降低,仅为0.18%,锌、铅和铬等重金属含量略上升,因此亟需对铜选冶渣的综合理化特性及环境污染特性进行评估,确保其堆放安全.
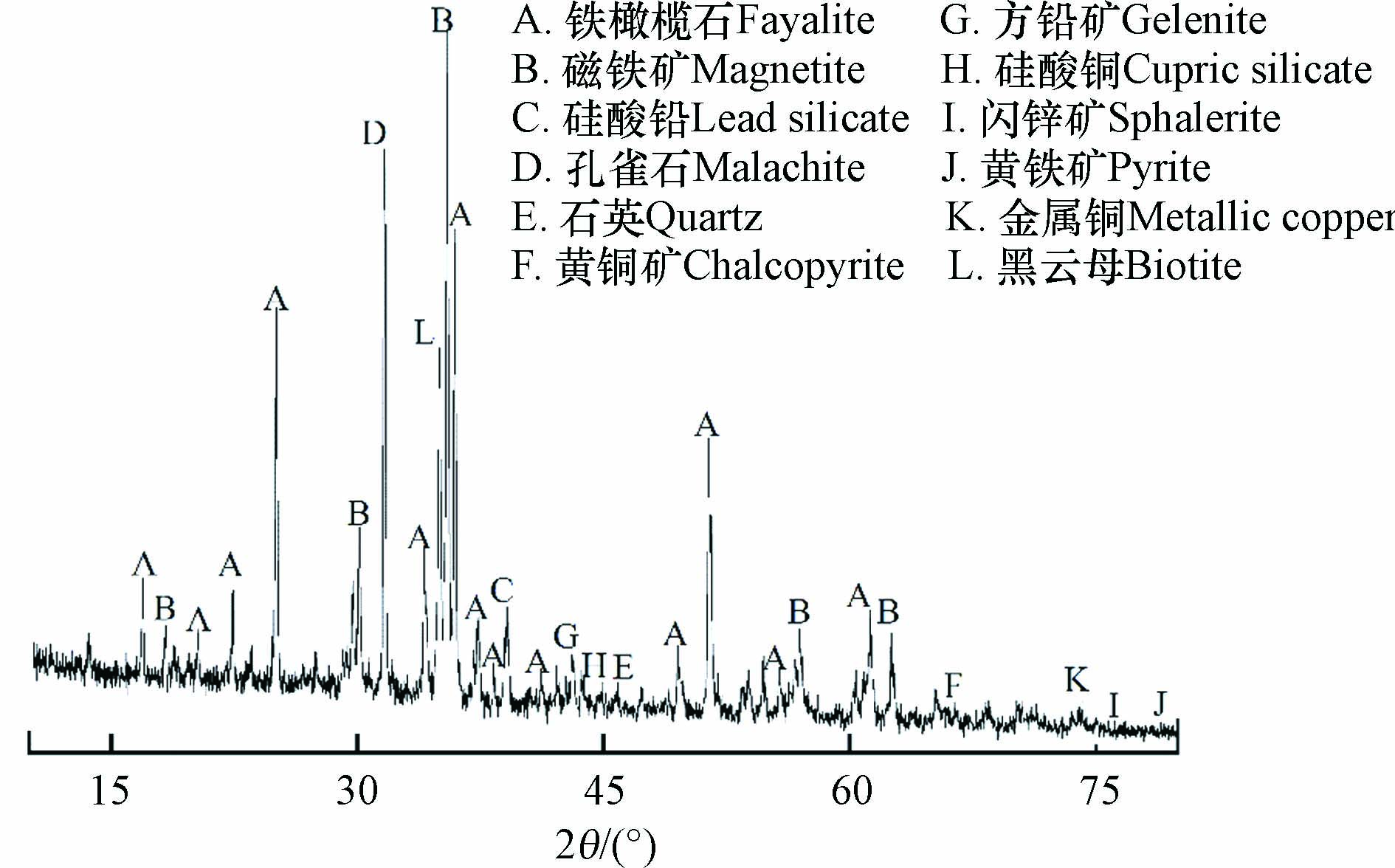
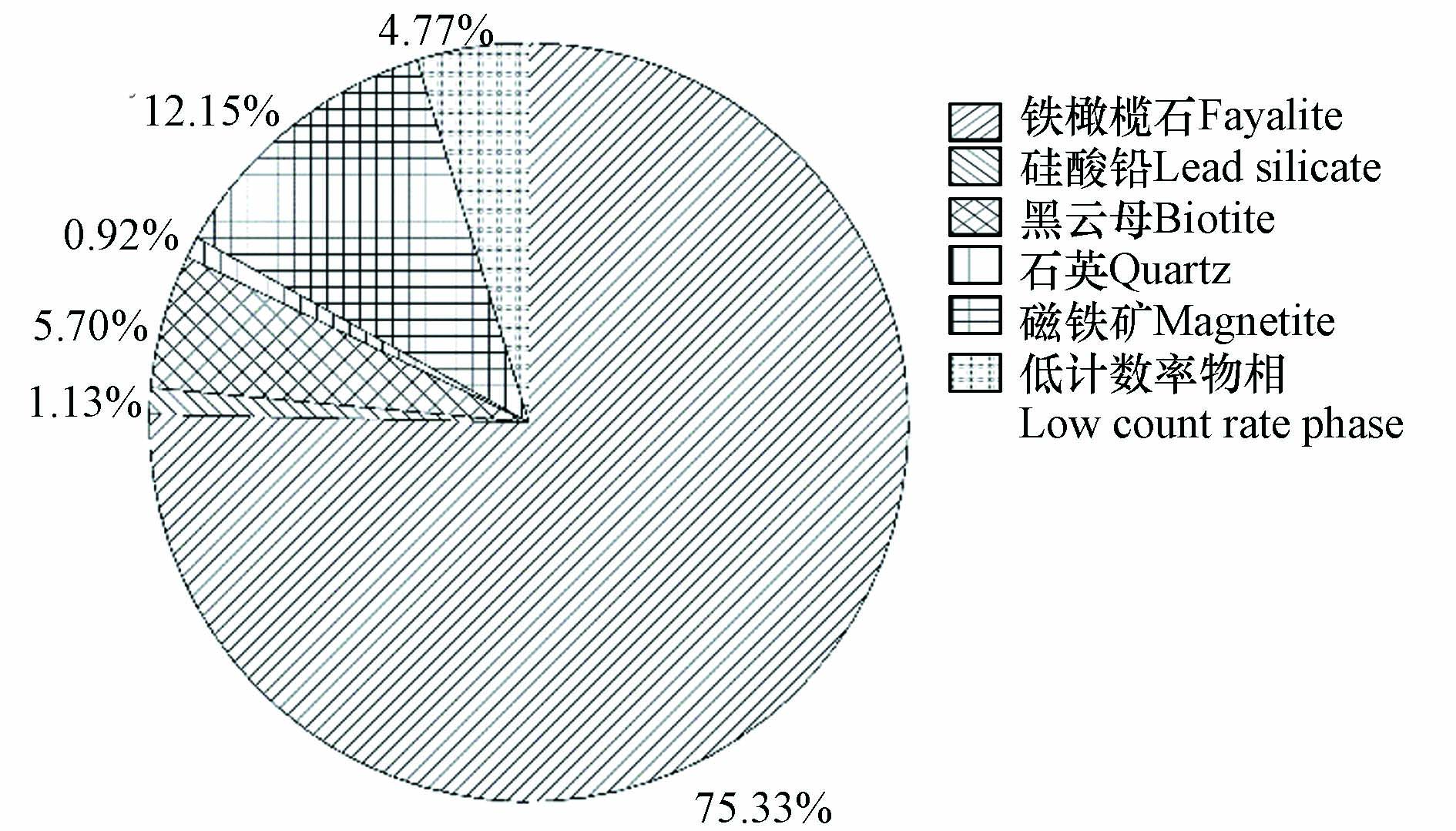
铜矿选冶渣XRD图谱及各物相质量分数分布如图3和图4所示. 由图3和图4知,该铜矿选冶渣包括铁橄榄石、磁铁矿、石英、硅酸铅、硅酸铜、硫化铅、孔雀石、金属铜、黄铜矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿及黑云母等物相,其中,铁橄榄石质量分数最高,达75.33%,磁铁矿次之,达12.15%.
铜矿选冶渣中Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb的赋存状态如表4所示. 由表4知,铜矿选冶渣中Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb赋存的主要矿物分别是铁橄榄石、黄铜矿、硅酸锌、硅酸铅. 在酸性环境下,磁铁矿、黄铁矿、黄铜矿和闪锌矿易溶解并释放Fe2+、Fe3+、Cu2+和Zn2+[21-22]. MLA分析结果与XRD分析结果基本一致.
-
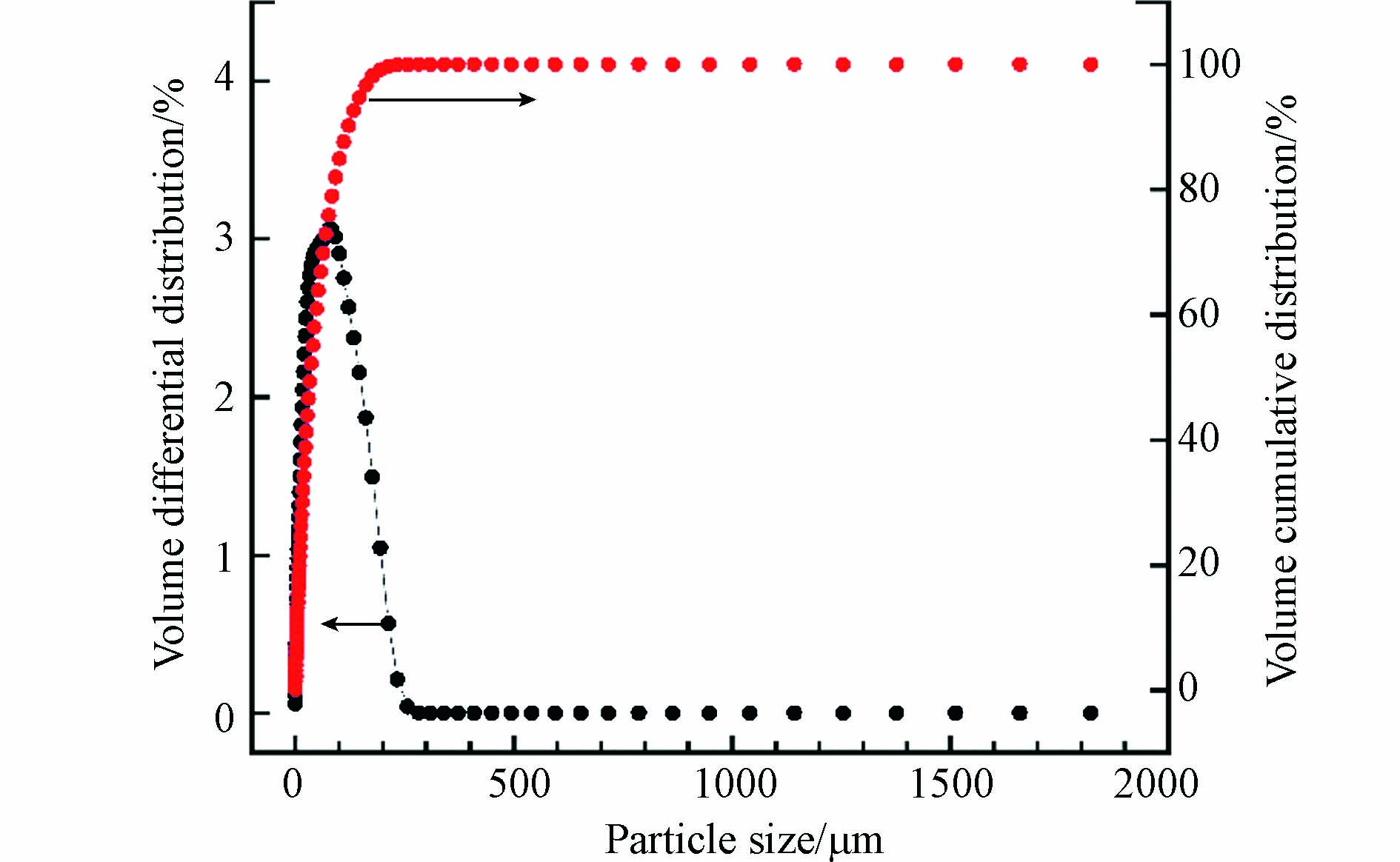
铜矿选冶渣粒度分布测定结果如图5所示. 由图5知,该铜矿选冶渣粒径主要分布在0—200 μm的范围内,其体积平均粒径为54.18 μm,粒径小于3.958、37.02、132.7 μm的颗粒分别占10%、50%、90%. 表明铜矿选冶渣粒度细,比表面积大,易与外界环境中的氧气、水充分接触并发生生物化学反应. 在强氧化性离子(如Fe3+)和降雨作用下,黄铁矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿等硫化物矿物之间的原电池反应更加剧烈,渣场周边重金属污染加剧[23].
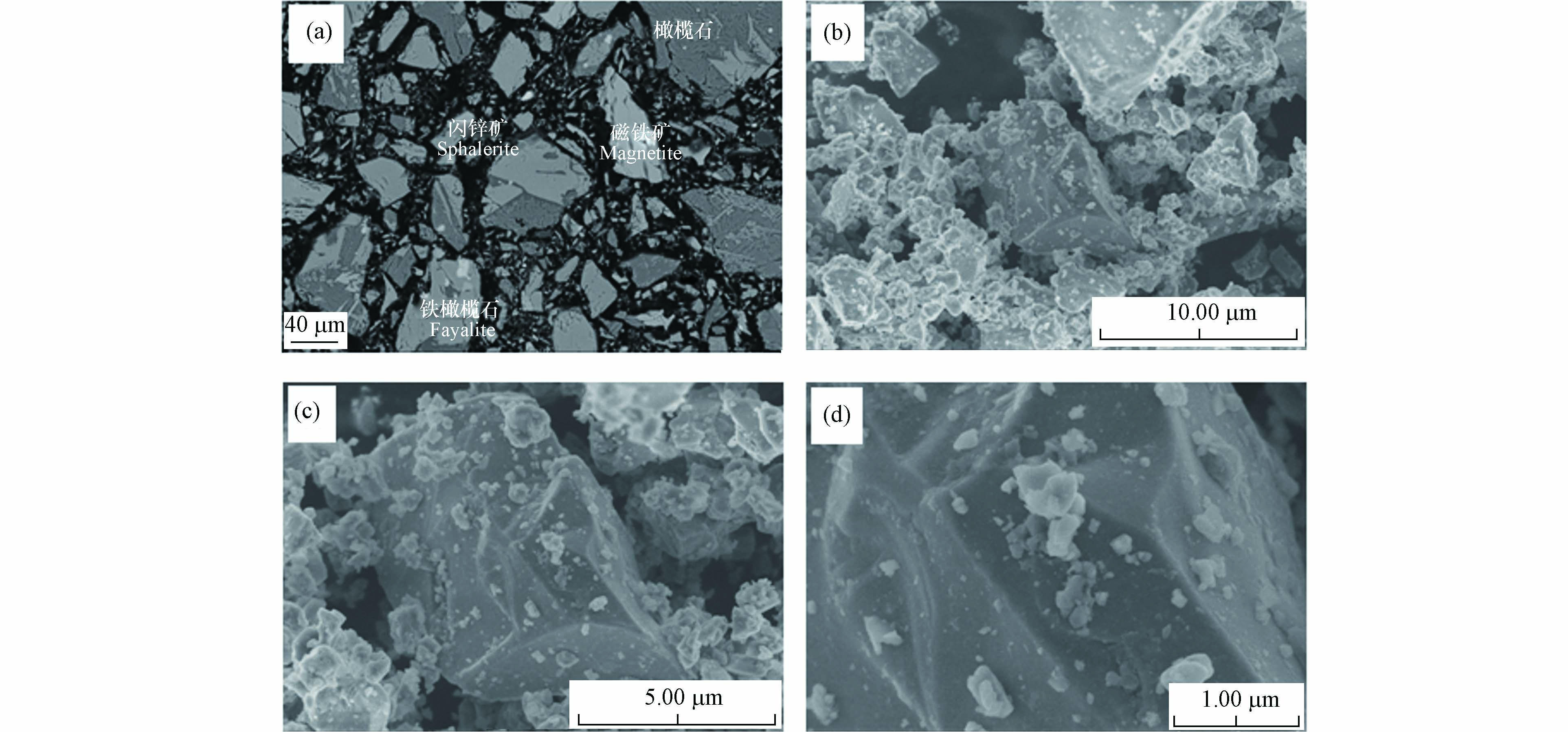
铜矿选冶渣背散射及扫描电镜结果如图6所示. 由图6(a)及上述XRD、MLA分析结果可知,该选冶渣含有铁橄榄石、磁铁矿和闪锌矿等物相. 由图6(b)—(d)可知,细小颗粒吸附在呈不规则块状的大颗粒上,该铜矿选冶渣以团聚状的形式存在.
在风化和淋洗作用下,铜矿选冶渣中吸附在大颗粒上的小颗粒易迁移到周围环境,大颗粒更大的暴露面积和小颗粒吸附的有害重金属离子导致周围环境重金属污染加剧.
-
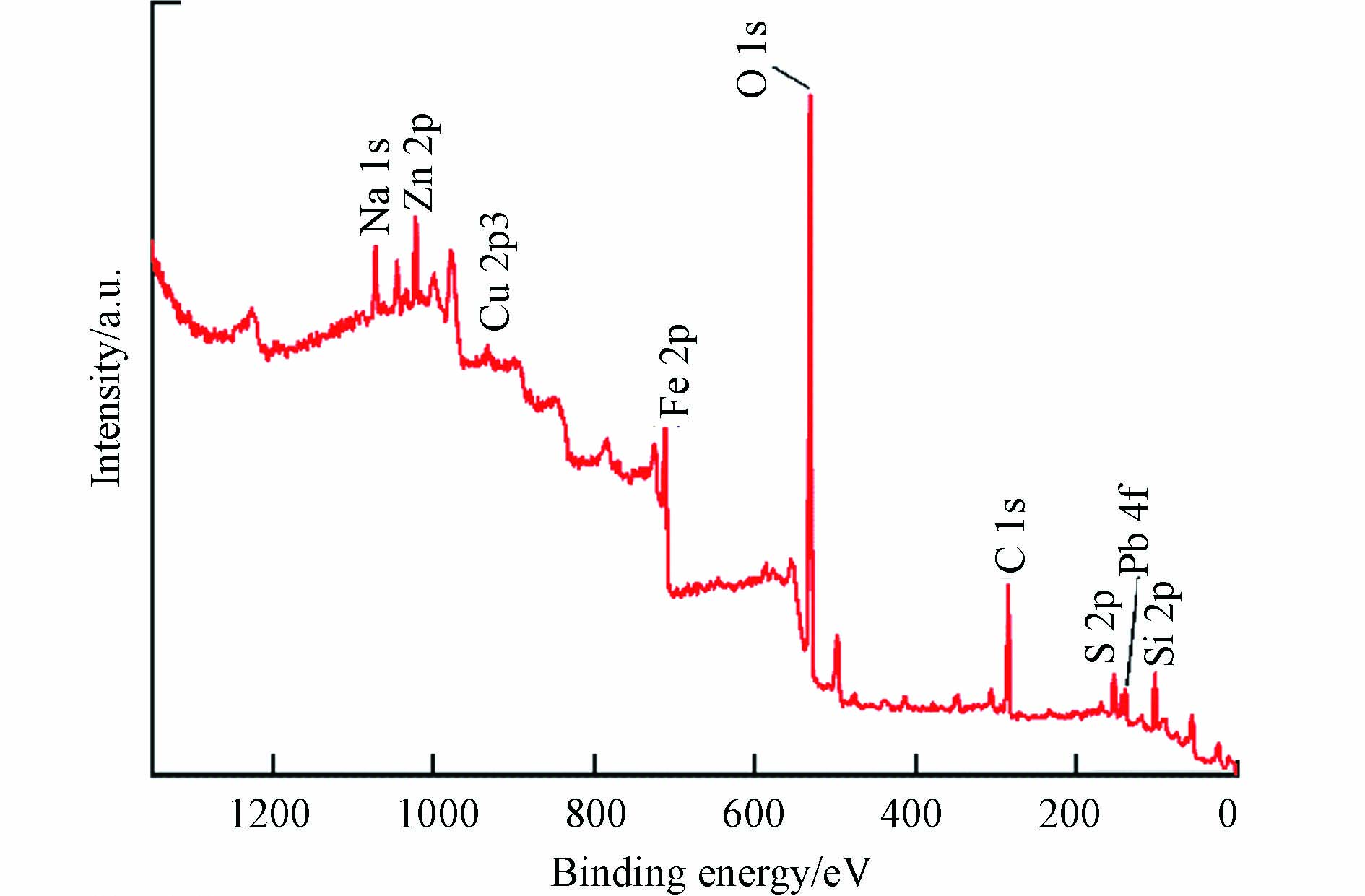
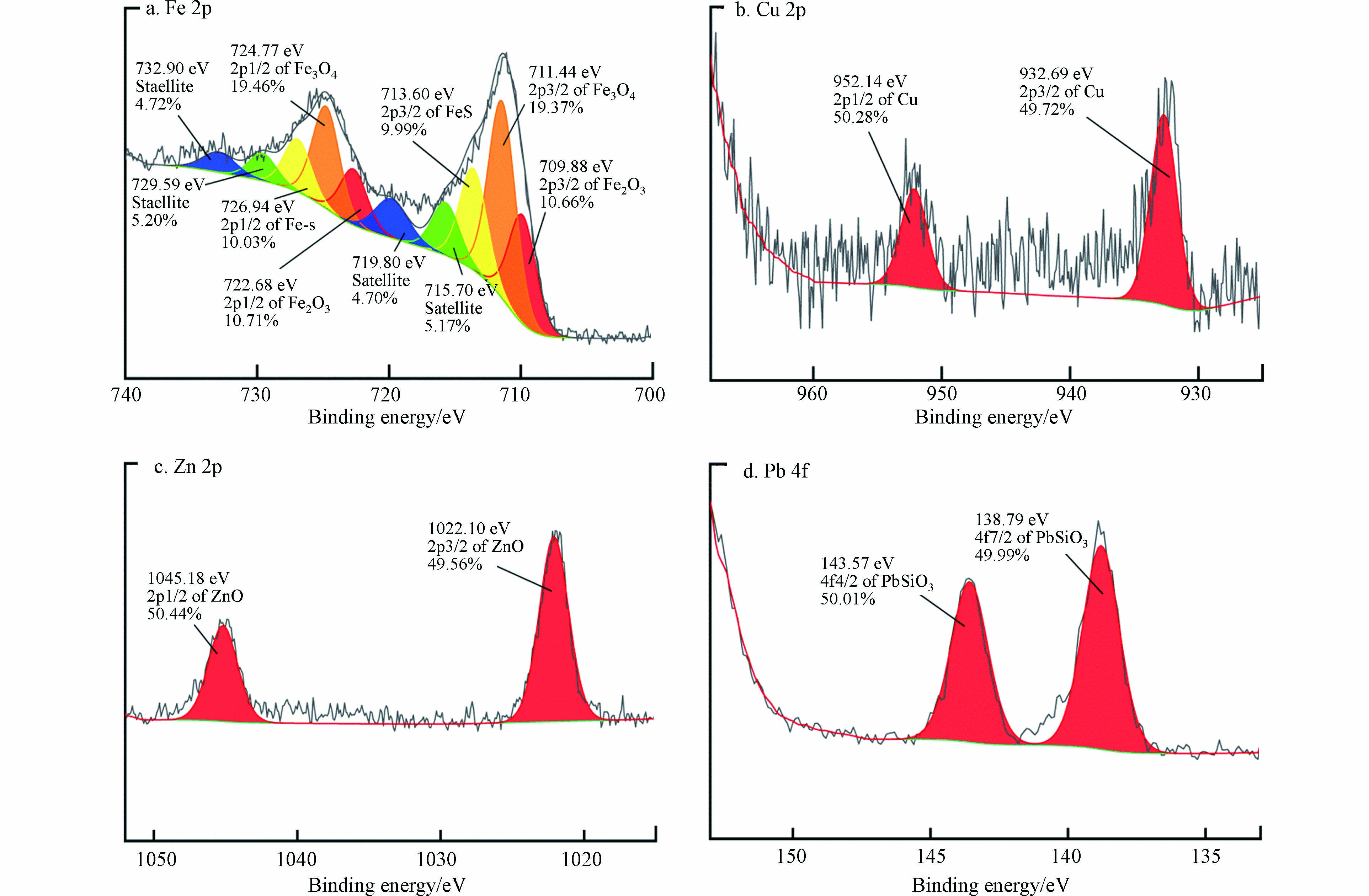
铜矿选冶渣X射线光电子全谱如图7所示. 由图7可知,该铜矿选冶渣表面存在Na、Zn、Cu、Fe、O、C、S、Pb、Si等元素. 对铜矿选冶渣进行窄区扫描,并通过Avantage软件对原始谱线进行拟合. 图8所示为该铜矿选冶渣的Fe2p、Cu2p、Zn2p和Pb4f分谱. 由图8(a)可知,Fe2p3/2主峰对应的结合能分别为709.88 eV、711.44 eV和713.60 eV,依次与文献中Fe2O3[24]、Fe3O4[25]、FeS[26]的Fe2p3/2峰位值接近,判断铜矿选冶渣表面的Fe以+3价和+2价共存;由图8(b)可知,Cu2p3/2主峰对应的结合能为 932.69 eV,与文献中Cu峰位值932.70 eV[27]十分接近,判断铜矿选冶渣表面的Cu以零价存在;由图8(c)可知,Zn2p3/2主峰对应的结合能为1022.10 eV,与文献中ZnO峰位值[28]一致,判断铜矿选冶渣表面的Zn以+2价存在;由图8(d)可知,Pb4f7/2主峰对应的结合能为138.79 eV,与文献中PbSiO3峰位值138.65 eV[29]较为接近,判断铜矿选冶渣表面的Pb以+2价存在.
根据铜矿选冶渣表面元素价态,推断其可能发生如下化学反应:
零价Cu转变为迁移性更强的Cu2+,Fe2+与Fe3+相互转化,促进了铜矿选冶渣中Cu2+、Fe2+和Fe3+的溶出,导致周边土壤污染加剧.
-
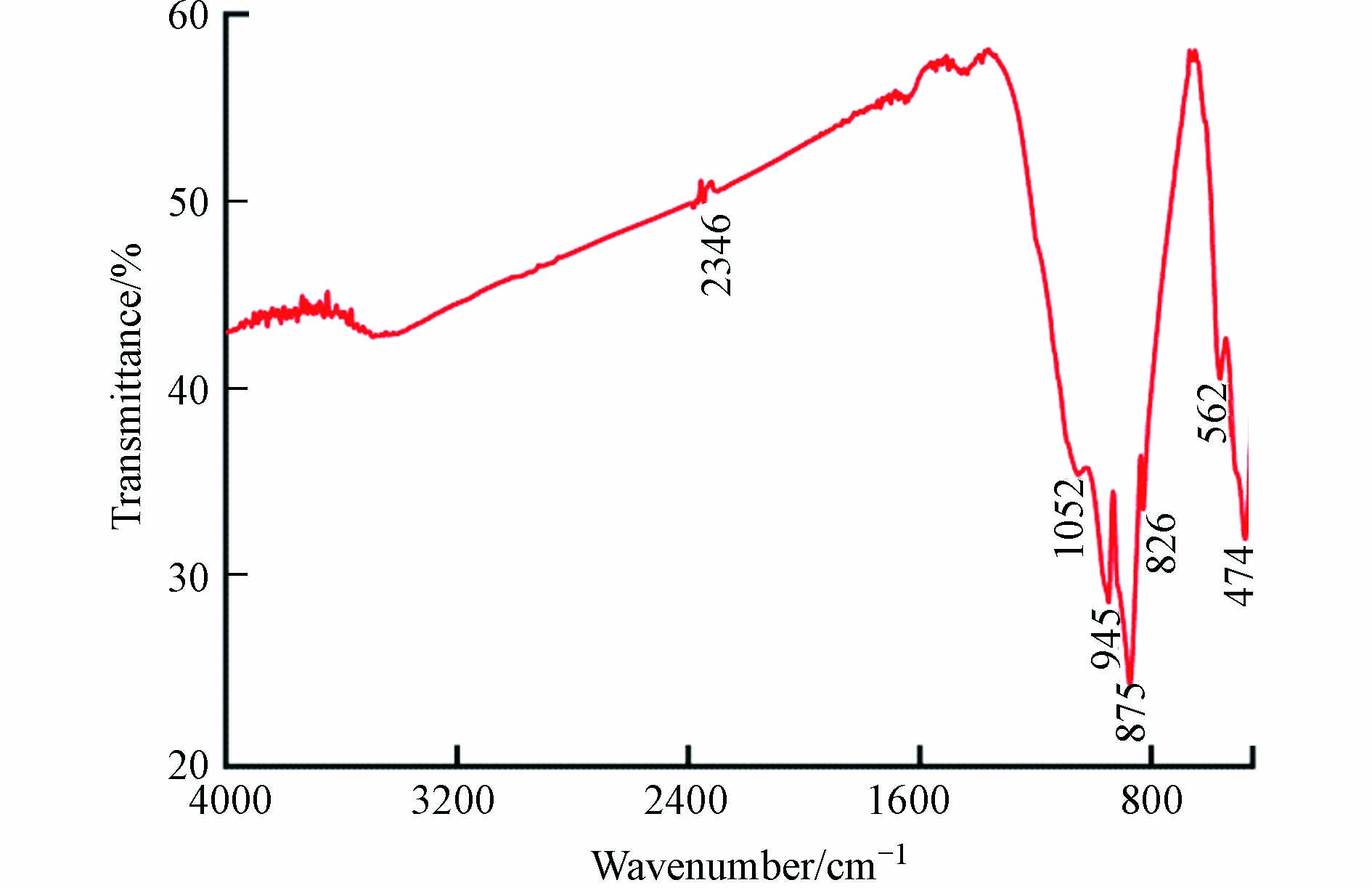
铜矿选冶渣红外光谱如图9所示. 由图9可知,在2346 cm−1处的吸收带为石英包裹体中二氧化碳的振动峰[30-31],与渣中含有一定质量分数的石英相吻合. 在1052 cm−1、945 cm−1、875 cm−1处的吸收带为Si—O键振动峰[32-33],与渣中含有石英、硅酸铅、硅酸铜、铁橄榄石、黑云母等矿物的结果一致. 在826 cm−1左右处的吸收带是孔雀石的特征峰[34],与渣中含有孔雀石相吻合. 在562 cm−1左右处的吸收带为Zn—O键伸缩峰[32],与渣中含有氧化锌固溶体的结果一致. 在474 cm−1左右处的吸收带为黄铜矿的特征峰[35-36],与渣中含有黄铜矿相对应. 由于渣中方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等金属硫化物矿物的含量低,且金属硫化物矿物的特征峰主要在500—50 cm−1范围内[37],因此,红外光谱图中未出现铅、锌和铁等硫化物的特征峰.
含硫矿物如黄铜矿在空气、水及微生物的作用下,发生风化、氧化、水解、溶浸等一系列物化及生化反应生成含酸废水,导致Fe2+、Fe3+、Cu2+和Zn2+等金属离子溶出,从而污染周边土壤[38].
-
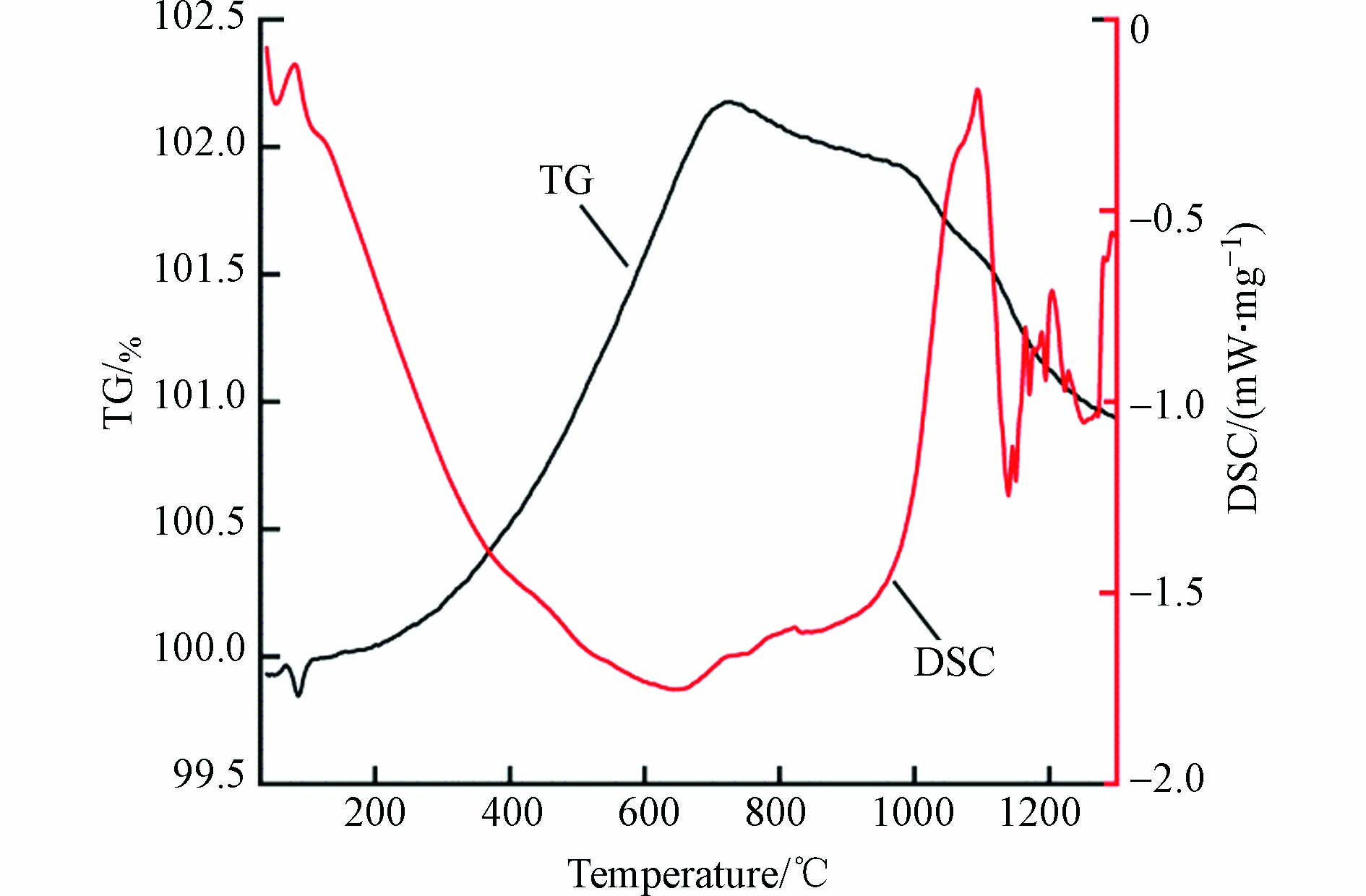
铜矿选冶渣TG-DSC曲线如图10所示. 由TG曲线知,在40—720 ℃范围内,铜矿选冶渣质量整体呈增加趋势,渣中铁橄榄石和磁铁矿被氧化为赤铁矿,黄铁矿等硫化矿物受热氧化分解,生成的气态硫或二氧化硫逸出,孔雀石和单质铜分别发生反应产生二氧化碳和氧化铜[39-41];在720—1300 ℃范围内,铜矿选冶渣质量随温度升高而减少,其原因可能是石英、黑云母等矿物的存在使赤铁矿更早的分解[39,42].
由铜矿选冶渣DSC曲线知,在100—1100 ℃范围内,曲线整体为一个较宽的放热峰,这是因为在空气气氛下,铜矿选冶渣中大量的Fe2+被氧化成赤铁矿,产生了明显的放热效应[39]. 总体而言,铜矿选冶渣热稳定性好,受外界环境温度变化的影响小.
-
按照《固体废物 腐蚀性测定 玻璃电极法》(GB/T 15555.12-1995)[43]对铜矿选冶渣腐蚀性进行了测定,铜矿选冶渣浸出液pH值为6.37,呈弱酸性. 其TCLP法浸出浓度与美国环保署(USEPA)判定阈值及《固体废物 浸出毒性浸出方法 硫酸硝酸法》(HJ/T 299-2007)[44]浸出浓度与《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》(GB 5085.3-2007)[45]判定阈值的比较如表5所示.
由表5知,浸出方法不同,其浸出毒性结果有较大差异.TCLP法测得的Cr、Cu、Zn、Pb的浸出浓度均高于硫酸硝酸法.TCLP法测得的Pb浸出浓度超过USEPA规定的危废标准限值(超标约6倍);硫酸硝酸法测得的Cr、Cu、Zn、Pb的浸出浓度均未超过《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》规定的危废标准限值,铜矿选冶渣为一类一般工业固体废物.,该铜矿选冶渣硫酸硝酸法浸出试验浸出液中 Cr、Cu、Zn、Pb 的浓度分别为 0.122、 5.606、19.951、0.302 mg·L−1,超过《地下水质量标准》(GB/T 14848-2017) [46] 中Ⅳ类水指标限值和《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002) [47] 中Ⅴ类水指标限值. 该铜矿选冶渣场地处中亚热带西部半湿润气 候区,第四系松散岩类孔隙水、基岩裂隙水发育,渣场属高山深谷地区,地形坡降大,选冶渣溶出重金 属易随地表水和地下水迁移,对周边环境构成威胁.
-
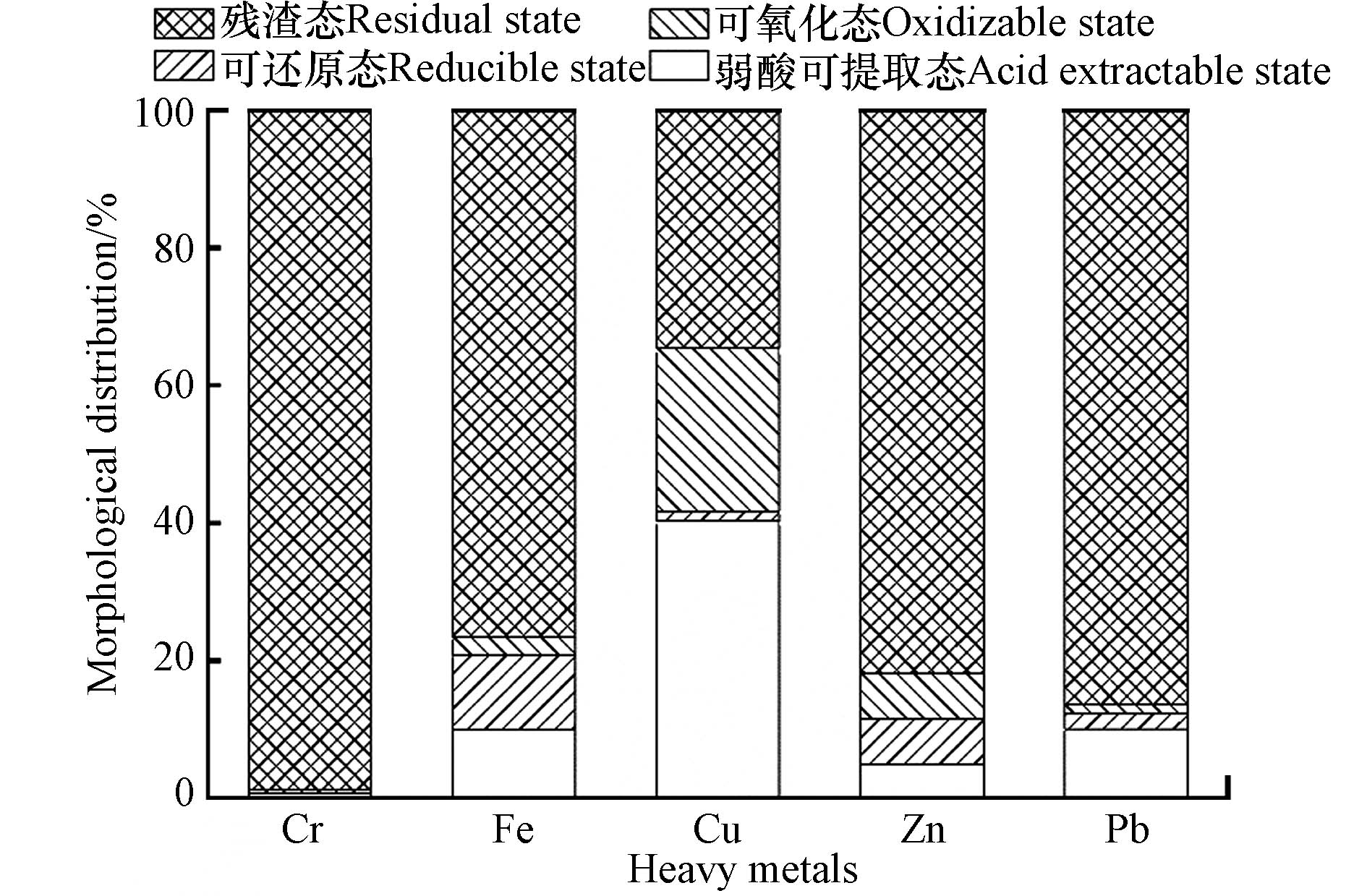
重金属的形态直接决定着重金属在环境中的迁移性和生物有效性. 一般认为,重金属的弱酸可提取态是最容易迁移释放到环境中且最易被生物吸收利用的形态,可还原态、可氧化态及残渣态是比较稳定的形态,其可迁移性依次降低[48].
铜矿选冶渣重金属形态分布如图11所示. 由图11知,残渣态是该铜矿选冶渣重金属主要的存在形态,该铜矿选冶渣Cr、Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb弱酸可提取态的占比分别为0.78%、9.99%、40.3%、4.97%、10.07%,对应的含量分别为3.98、43956、717.34、1275.80、546.80 mg·kg−1.
-
RAC法和RSP法评价结果见表6. 由表6知,RAC法和RSP法评价结果有较大差异.RAC评价结果表明,铜矿选冶渣中Cu和Pb分别属高风险和中风险等级,污染风险高,Fe和Zn属低风险等级,对周围环境影响较小;RSP法评价结果表明,铜矿选冶渣中Cu可能造成土壤轻度污染,Cr、Fe、Zn和Pb无污染风险. 综上所述,Cu是铜矿选冶渣的主要防治对象,Fe、Zn、Pb是铜矿选冶渣的次要防治对象.
-
(1)铜矿选冶渣多呈团聚状,主要含铁橄榄石、磁铁矿、黑云母、硅酸铅、石英等物相,体积平均粒径为54.18 μm,粒度细.
(2)铜矿选冶渣中Cr、Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb的含量分别为510、440000、1780、25670、5430 mg·kg−1;铜矿选冶渣中磁铁矿、黄铁矿、黄铜矿和闪锌矿易释放金属离子.
(3)铜矿选冶渣中含有Si—O键和Zn—O键;铜矿选冶渣表面的Fe以+2和+3价共存,Cu以0价形式存在,Zn和Pb以+2价形式存在;TG-DSC曲线表明,Fe2+和赤铁矿之间的相互转化是铜矿选冶渣增重和失重的主要原因.
(4)采用TCLP法和硫酸硝酸法测得的该铜矿选冶渣Cr、Cu、Zn、Pb的浸出浓度差异较大,且TCLP法测得的铜矿选冶渣Pb浓度超过USEPA规定的危废限值(超标约6倍);该铜矿选冶渣Cr、Fe、Cu、Zn和Pb弱酸可提取态占比分别为0.78%、9.99%、40.3%、4.97%和10.07%,对应的含量分别为3.98、43956、717.34、1275.80、546.80 mg·kg−1.
(5)RAC评价结果表明,铜矿选冶渣中Cu和Pb分别属高风险和中风险等级,污染风险高;RSP法评价结果表明,铜矿选冶渣中Cu可能造成周围土壤轻度污染.
四川某铜矿选冶渣综合理化特性及环境污染特性评价
Comprehensive physicochemical properties and environmental pollution characteristics evaluation of the reselected copper smelting slag
-
摘要: 针对铜矿选冶渣组成复杂、环境特性不清和治理修复难度大等问题,采用矿物解离分析仪(MLA)、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)和同步热分析仪-傅里叶变换红外气相色谱质谱联用仪(STA-FTIR-GCMS)等分析测试仪器研究铜矿选冶渣的综合理化特性;运用毒性浸出程序(TCLP)、改进的三步提取(BCR)、风险评估编码(RAC)和次生相与原生相比值(RSP)等方法研究铜矿选冶渣的环境污染特性. 结果表明,铜矿选冶渣多呈团聚状,体积平均粒径为54.18 μm,主要含铁橄榄石(75.33%)、磁铁矿(12.15%)、黑云母等物相. 硫酸硝酸法测得的铜矿选冶渣Cr、Cu、Zn和Pb浓度未超过《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》规定的危废限值,该铜矿选冶渣为一类一般工业固体废物.RAC法和RSP法评价结果表明,Cu是铜矿选冶渣的主要防治对象,Fe、Zn、Pb是铜矿选冶渣的次要防治对象. 研究结果为铜矿选冶渣的安全处理和处置提供了基础数据.
-
关键词:
- 铜矿选冶渣 /
- 综合理化特性 /
- 环境污染特性 /
- 风险评估编码法(RAC) /
- 次生相与原生相比值法(RSP).
Abstract: The composition of the reselected copper smelting slag (RCSS) is complex, the environmental characteristics is unclear and the treatment and restoration are difficult. The comprehensive physicochemical properties of RCSS were determined by mineral dissociation analyzer (MLA), X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS) and synchronous thermal analyser-Fourier Transform infrared gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (STA-FTIR-GCMS). The environmental pollution characteristics of RCSS were analysed using toxic leaching procedure (TCLP) , modified BCR (three step extraction) , risk assessment coding (RAC) , phase and primary comparison (RSP). The results show that RCSS is mainly agglomerated with an average particle size of 54.18 μm. It mainly contains fayalite (75.33%), magnetite (12.15%), biotite and other phases. The concentration of Cr, Cu, Zn and Pb of RCSS measured by sulphuric acid & nitric acid method did not exceed the limit of hazardous waste specified in "Identification standards for hazardous wastes-Identification for extraction toxicity", and RCSS is a kind of general industrial solid waste. The evaluation results of RAC method and RSP method show that Cu is the main control object of RCSS, while Fe, Zn and Pb are the secondary control object. This study can provide a basis for the safe treatment and disposal of RCSS. -

-
表 1 RAC法和RSP法评价标准
Table 1. Evaluation criterion of RAC method and RSP method
等级
ClassRAC法
RAC methodRSP法
RSP methodRAC值
RAC value划分标准
Partition criterionRSP值
RSP value划分标准
Partition criterion1 RAC<1% 无风险 RSP≤1 无污染 2 1%≤RAC<10% 低风险 1<RSP≤2 轻度污染 3 10%≤RAC<30% 中风险 2<RSP≤3 中度污染 4 30%≤RAC<50% 高风险 RSP>3 重度污染 5 ≥50% 极高风险 — — 表 2 铜矿选冶渣元素组成(质量分数,%)
Table 2. Elementary composition of RCSS (mass fraction, %)
Fe2O3 SiO2 ZnO CaO Al2O3 SO3 PbO K2O MoO3 TiO3 CuO MgO 65.94 19.16 4.36 3.10 1.98 1.01 0.89 0.79 0.57 0.4 0.4 0.24 As2O3 NaO Sb2O3 P2O5 Co3O4 MnO BaO Cl IrO2 Cr2O3 ZrO2 SrO 0.2 0.16 0.16 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.01 表 3 尾矿、冶炼渣及选冶渣部分组分含量(质量分数,%)
Table 3. Partial component content of tailing, smelting slag and reselected smelting slag (mass fraction, %)
样品名称
Sample nameFe Cu Zn Pb Cr SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO 尾矿Tailing 7.66 0.04 0.0054 0.011 0.0038 52.03 13.34 5.76 2.21 冶炼渣Smelting slag 36.81 1.80 2.36 0.48 0.044 17.84 1.78 2.97 0.19 选冶渣Reselected smelting slag 44.0 0.18 2.57 0.54 0.051 19.16 1.98 3.10 0.24 表 4 铜矿选冶渣中Fe、Cu、Zn、Pb的赋存状态(质量分数,%)
Table 4. Occurrence state of Fe, Cu, Zn and Pb in RCSS (mass fraction, %)
Fe Pb 赋存矿物 铁橄榄石 磁铁矿 黑云母 黄铁矿 硅酸铅 方铅矿 含量 75.68 21.66 1.59 0.05 97.96 2.04 Cu Zn 赋存矿物 黄铜矿 硅酸铜 金属铜 孔雀石 硅酸锌 磁铁矿 闪锌矿 含量 74.10 19.58 4.71 1.57 86.90 10.56 2.54 注:铜矿选冶渣中Zn主要赋存在铁橄榄石中形成硅酸锌固溶体,其次赋存在磁铁矿中形成氧化锌固溶体;少量Cu形成硅酸铜赋存在铁橄榄石中.
Note: Zn mainly occurs in fayalite to form zinc silicate solid solution, and then occurs in magn-etite to form zinc oxide solid solution. A small amount of Cu forms copper silicate and occurs infayalite.表 5 铜矿选冶渣浸出毒性
Table 5. Leaching concentrations of RCSS
元素
ElementTCLP法浸出浓度/(mg·L−1)
TCLP leaching concentrationUSEPA危废限值/(mg·L−1)
USEPA hazardous waste limit硫酸硝酸法浸出浓度/(mg·L−1)
Sulfuric acid nitric acid leaching concentration国标危废限值/(mg·L−1)
National standard dangerous waste limit valueCr 0.509 15.00 0.122 15 Cu 26.630 NL 5.606 100 Zn 33.667 NL 19.951 100 Pb 29.158 5.00 0.302 5 注:NL指USEPA未给出相应元素的危废限值.
Note: NL means that USEPA does not give the hazardous waste limit of the corresponding element.表 6 RAC法和RSP法评价结果
Table 6. Evaluation results of RAC method and RSP method
元素
ElementRAC值
RAC value评价等级
Evaluation levelRSP值
RSP value评价分级
Evaluation classificationCr 0.78% 无风险 0.012 无污染 Fe 9.99% 低风险 0.308 无污染 Cu 40.3% 高风险 1.899 轻度污染 Zn 4.97% 低风险 0.222 无污染 Pb 10.07% 中风险 0.158 无污染 -
[1] 王林松, 高志勇, 杨越, 等. 铜渣综合回收利用研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(10): 5237-5250. WANG L S, GAO Z Y, YANG Y, et al. Research progress on comprehensive recovery and utilization of copper slag [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(10): 5237-5250(in Chinese).
[2] GORAI B, JANA R K, PREMCHAND. Characteristics and utilisation of copper slag—a review [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2003, 39(4): 299-313. doi: 10.1016/S0921-3449(02)00171-4 [3] POTYSZ A, KIERCZAK J, FUCHS Y, et al. Characterization and pH-dependent leaching behaviour of historical and modern copper slags [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 160: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.017 [4] TIAN H Y, GUO Z Q, PAN J, et al. Comprehensive review on metallurgical recycling and cleaning of copper slag [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 168: 105366. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105366 [5] 张云, 胡正生, 王艳, 等. 某氧化铜矿尾矿区重金属污染特征及农作物健康风险评价 [J]. 有色金属工程, 2021, 11(4): 125-132. ZHANG Y, HU Z S, WANG Y, et al. Heavy metals pollution characteristics and crop health risk assessment around a copper oxide tailings pond [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2021, 11(4): 125-132(in Chinese).
[6] 张卫, 魏忠义, 龙精华, 等. HTM铜矿尾矿库浅层剖面重金属赋存形态及污染特征 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(12): 6103-6109. ZHANG W, WEI Z Y, LONG J H, et al. Chemical fractions and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in surface profile of HTM copper tailings pond [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(12): 6103-6109(in Chinese).
[7] 黄长干, 邱业先. 江西德兴铜矿铜污染状况调查及植物修复研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2005, 36(6): 991-992. HUANG C G, QIU Y X. Pollution of the environment in Jiangxi Dexing cooper mine by copper and phytoremediation [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2005, 36(6): 991-992(in Chinese).
[8] MAO K X, LI L, XU M. Iron and copper recovery from copper slags through smelting with waste cathode carbon from aluminium electrolysis [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(7): 2010-2021. doi: 10.1007/s11771-021-4749-z [9] 王坤, 刘燕, 姜保成, 等. 涡流贫化法回收铜渣中的金、银、铜 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2021, 50(9): 3417-3421. WANG K, LIU Y, JIANG B C, et al. Recovery of Au, Ag and Cu from copper slag by Vortex dilution method [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2021, 50(9): 3417-3421(in Chinese).
[10] 廖亚龙, 叶朝, 王祎洋, 等. 铜冶炼渣资源化利用研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(8): 3066-3073. LIAO Y L, YE C, WANG Y Y, et al. Resource utilization of copper smelter slag—a state-of-the-arts review [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(8): 3066-3073(in Chinese).
[11] 韦宇, 母维宏, 罗中秋, 等. 铜渣基化学键合陶瓷材料吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的性能及机理 [J]. 精细化工, 2022, 39(1): 194-203. WEI Y, MU W H, LUO Z Q, et al. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by copper slag based chemically bonded ceramics: Property and mechanism [J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(1): 194-203(in Chinese).
[12] ZHANG T T, ZHI S W, LI T, et al. Alkali activation of copper and nickel slag composite cementitious materials [J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 13(5): 1155. doi: 10.3390/ma13051155 [13] 陈永明, 代杰, 胡方园, 等. 锌氧压酸浸渣赋存特性与浸出毒性评价 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(12): 3309-3320. CHEN Y M, DAI J, HU F Y, et al. Occurrence characteristics and leaching toxicity evaluation of residues from zinc sulfide oxygen-pressure leaching process [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(12): 3309-3320(in Chinese).
[14] 曾东梅. 有机—无机复合稳定剂对土壤重金属稳定化处理的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2015. ZENG D M. Research on the stabilization treatment of heavy metal contaminated soil by organic-inorganic integration amendments[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2015(in Chinese).
[15] 苗亦新. 罗平地区炼锌废渣土壤重金属污染风险及稳定化实验[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017. MIAO Y X. The risk of heavy metals pollution and laboratory study on stabilization for zinc residue in Luoping area[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[16] 高焕方, 曹园城, 何炉杰, 等. Tessier法和BCR法对比磷酸二氢钠处置含铅污染土壤形态分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(10): 5751-5756. GAO H F, CAO Y C, HE L J, et al. Speciation analysis of lead-contaminated soil treated with sodium dihydrogen phosphate using Tessier and BCR [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(10): 5751-5756(in Chinese).
[17] 张永利, 刘晓文, 陈启敏, 等. Tessier法和改进BCR法提取施加熟污泥后黄土中Cd的对比研究 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 34-38,81. ZHANG Y L, LIU X W, CHEN Q M, et al. Comparative study of Tessier method and modified BCR method for extracting Cd in loess amended by composted sludge [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(5): 34-38,81(in Chinese).
[18] 黄祥, 吴怡, 彭晓曦, 等. 典型电解锌冶炼废渣重金属形态及环境效应研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(3): 342-349. HUANG X, WU Y, PENG X X, et al. Study on heavy metal forms and environmental effects of typical electrolytic zinc smelting slag [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(3): 342-349(in Chinese).
[19] 陈江军, 刘波, 蔡烈刚, 等. 基于多种方法的土壤重金属污染风险评价对比: 以江汉平原典型场区为例 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2018, 45(6): 164-172. CHEN J J, LIU B, CAI L G, et al. Comparison of risk assessment based on the various methods of heavy metals in soil: A case study for the typical field areas in the Jianghan Plain [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(6): 164-172(in Chinese).
[20] 田恩源, 惠博, 陈小青. 拉拉铜矿尾矿工艺矿物学研究 [J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(3): 148-152. TIAN E Y, HUI B, CHEN X Q. Study on mineralogy of tailing process in Lala copper mine [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(3): 148-152(in Chinese).
[21] 卢龙, 薛纪越, 陈繁荣, 等. 黄铁矿表面溶解: 不容忽视的研究领域 [J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(6): 666-670. LU L, XUE J Y, CHEN F R, et al. Dissolution of pyrite: An important study subject [J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2005, 24(6): 666-670(in Chinese).
[22] 邓久帅, 文书明, 先永骏, 等. 黄铜矿在水溶液中的溶解特性和表面性质谱学表征 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(2): 519-524. DENG J S, WEN S M, XIAN Y J, et al. Spectroscopic characterization of dissolubility and surface properties of chalcopyrite in aqueous solution [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(2): 519-524(in Chinese).
[23] 刘庆友, 李和平, 周丽. 金属硫化物矿物原电池反应: 矿山环境启示[C]//中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第11届学术年会论文集. 北京, 2007: 521. [24] PAPARAZZO E. XPS and auger spectroscopy studies on mixtures of the oxides SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3 and Cr2O3 [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1987, 43(2): 97-112. doi: 10.1016/0368-2048(87)80022-1 [25] ALLEN G C, CURTIS M T, HOOPER A J, et al. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of iron-oxygen systems [J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions, 1974(14): 1525-1530. doi: 10.1039/DT9740001525 [26] SIRIWARDANE R V, COOK J M. Interactions of SO2 with sodium deposited on silica [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1985, 108(2): 414-422. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(85)90280-2 [27] BIRD R J, SWIFT P. Energy calibration in electron spectroscopy and the re-determination of some reference electron binding energies [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1980, 21(3): 227-240. doi: 10.1016/0368-2048(80)85050-X [28] BARR T L, YIN M P, VARMA S. Detailed X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy valence band and core level studies of select metals oxidations [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A:Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films, 1992, 10(4): 2383-2390. [29] PEDERSON L R. Two-dimensional chemical-state plot for lead using XPS [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1982, 28(2): 203-209. doi: 10.1016/0368-2048(82)85043-3 [30] 王曼祉. 内蒙古宁城县热水金矿床石英热发光和红外光谱研究 [J]. 冶金地质动态, 1992(8): 48-53. WANG M Z. Study on Shi Ying thermoluminescence and infrared spectroscopy of reshui gold deposit in Ningcheng County, inner Mongolia [J]. Metallurgical Geology, 1992(8): 48-53(in Chinese).
[31] 吴国学, 李守义, 李书法, 等. 不同石英脉型金银矿床中含矿石英脉的红外光谱对比 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(4): 527-530. WU G X, LI S Y, LI S F, et al. The comparison of infrared spectrum of quartz about different type of quartz vein AuAg deposits [J]. Journal of Jiling University (Earth Science Edition), 2004, 34(4): 527-530(in Chinese).
[32] LI M, PENG B, CHAI L Y, et al. Technological mineralogy and environmental activity of zinc leaching residue from zinc hydrometallurgical process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(5): 1480-1488. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62620-5 [33] MARTINS F M, NETO J M D R, CUNHA C J D. Mineral phases of weathered and recent electric arc furnace dust [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1/2/3): 417-425. [34] 任阳光, 熊堃. 孔雀石表面丁基黄药吸附和解吸特性研究 [J]. 金属矿山, 2014(12): 112-115. REN Y G, XIONG K. Research on the adsorption and desorption characteristics of xanthate on malachite surface [J]. Metal Mine, 2014(12): 112-115(in Chinese).
[35] 王世辉. 某铜矿铜锌分离新工艺和新药剂的研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2009. WANG S H. Study on new technology and new reagent for separation of copper and zinc in a copper mine[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2009(in Chinese).
[36] 沈刚. 黄铜矿、黄铁矿快速浮选分离新技术研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2002. SHEN G. Study on new technology of rapid flotation separation of chalcopyrite and pyrite[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2002(in Chinese).
[37] 刘丽华, 张培萍, 李献洲. 金属硫化物矿物的远红外光谱表征 [J]. 分析测试技术与仪器, 2006, 12(1): 34-37. LIU L H, ZHANG P P, LI X Z. FTIR analysis of metallic sulfide minerals [J]. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 2006, 12(1): 34-37(in Chinese).
[38] 王运敏. 中国采选技术十年回顾与展望[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012: 765-769. WANG Y M. Review and prospect of mining and dressing technology in China for ten years[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 765-769(in Chinese).
[39] 王宏宇, 孟昕阳, 侯霖杰, 等. 采用Prtrugic法制备铜渣微晶玻璃 [J]. 江西冶金, 2020, 40(6): 16-23. WANG H Y, MENG X Y, HOU L J, et al. Preparation of copper slag glass-ceramics by Prtrugic method [J]. Jiangxi Metallurgy, 2020, 40(6): 16-23(in Chinese).
[40] 王洪阳, 包焕均, 张文韬, 等. 铁橄榄石的氧化分解及碱浸溶硅 [J]. 金属矿山, 2020(10): 167-173. WANG H Y, BAO H J, ZHANG W T, et al. Oxidation roasting of fayalite together with alkali leaching of silica [J]. Metal Mine, 2020(10): 167-173(in Chinese).
[41] 阳富强, 吴超. 硫化矿自燃预测预报理论与技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2011. YANG F Q, WU C. Prediction and forecast of spontaneous combustion of sulfide minerals—Theory and technology[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011(in Chinese).
[42] 张海龙. 磁铁矿球团焙烧热分析 [J]. 冶金译丛, 1998(4): 1-5. ZHANG H L. Thermal analysis of magnetite pellet roasting [J]. Metallurgical translations, 1998(4): 1-5(in Chinese).
[43] 国家环境保护局, 国家技术监督局. 固体废物 腐蚀性测定 玻璃电极法: GB/T 15555.12—1995[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1995 State Bureau of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China, State Bureau of Quality andTechnical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. Solid waste-Glass electrade test-Method of corrosivity: GB/T15555.12—1995[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1995(in Chinese).
[44] 国家环境保护总局. 固体废物 浸出毒性浸出方法 硫酸硝酸法: HJ/T 299—2007[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2007. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People's Republic of China. Solid waste-Extraction procedure for leaching toxicity-Sulphuric acid & nitric acid method: HJ/T 299—2007[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2007(in Chinese).
[45] 国家环境保护总局. 危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别: GB 5085.3—2007[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2007. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People's Republic of China. Identification standards for hazardous wastes - Identification for extraction toxicity: GB 5085.3—2007[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2007(in Chinese).
[46] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 地下水质量标准: GB/T 14848—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T 14848—2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017(in Chinese).
[47] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People's Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Environmental quality standards for surface water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2002(in Chinese).
[48] 郑顺安. 我国典型农田土壤中重金属的转化与迁移特征研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010. ZHENG S N. Studies on the transformation and transport of heavy metals in typical Chinese agricultural soils[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: