-
全氟及多氟烷基化合物(per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances,PFASs)是一类人工合成的有机氟化物,其结构上至少存在一个完全氟化的甲基(—CF3)或亚甲基(—CF2—)碳[1]. 由于C-F键极高的化学键能(460 kJ·mol−1)[2],PFASs具有极强的稳定性,同时具有疏水疏脂、耐高温、耐氧化的性质,能在自然环境中长久稳定地存在[3].
据统计,人工合成的PFASs已逾4700种,仅2000年至2017年,就有超过3000 t PFASs被合成,并被用于塑料、橡胶、电子工业产品以及油漆的生产[4]. 长期的生产使用使得PFASs不断在环境中积累,目前,在中国东南部地区河流水[5]、约旦Zarqa河两岸土壤[6]、北极圈大气[7]等全球范围环境介质中内均有PFASs检出. 研究表明,环境中的PFASs可以通过饮用水和食物链传递作用进入人体,并造成生殖系统损伤[8]、免疫系统损伤[9]以及神经性伤害[10]. 全氟辛烷磺酸(perfluorooctane sulfonate,PFOS)和全氟辛酸(perfluorooctanoic acid,PFOA)是环境中最典型的两种PFASs,分别于2009年和2019年被正式列入《斯德哥尔摩公约》. 与此同时,欧盟2015年颁布的《水框架指令》中规定地表水中PFOS年平均浓度不得超过0.65 ng·L−1,最大浓度不得超过65 ng·L−1;2016年,美国环境保护署(EPA)设立了饮用水中PFOS和PFOA总浓度低于70 ng·L−1的健康标准. 2014年我国原环保部和农业部等12部委发布的文件要求,五年内确保PFOS在特定豁免用途全部淘汰. 在《重点管控新污染物清单(2021年版)》中重申,禁止PFOS类物质生产,并严禁生产、使用和进出口PFOA类物质. 尽管PFOS、PFOA等长链PFASs已被限制生产使用,仍有大量短链或含有其他新兴PFASs替代品被不断开发应用,环境中可检出PFASs种类不断增加,如何解决PFASs污染已逐渐成为当下最受关注的环境问题之一.
环境水体是环境中PFASs的重要储存库[11-12],由于PFASs分子结构的特殊性,PFASs在水环境中的分布及其与不同环境介质的结合状态相比传统疏水有机污染物差异较大[13-15]. 此外,水的地球循环过程、水力作用也会影响PFASs的环境迁移与转化过程[16-17]. 因此,厘清PFASs在水环境中的迁移转化规律,并揭示多种环境介质对该过程的影响,对于科学评估PFASs的环境污染现状并进一步有效治理PFASs污染具有重要科学意义. 在过去的数十年间,有关PFASs的综述研究已有较多,例如,Gagliano、Wei、 Bolan等[18-25] 总结比较了PFASs在大气、土壤及水环境中的修复技术,包括吸附法、水热法、超声法、光降解及生物降解法等. Podder 等[26-28]对现有研究中PFASs的潜在暴露途径及生物毒性进行了总结. 此外,Kurwadkar等[29-32]回顾了PFASs在自然水环境中的污染浓度和分布特征、暴露及现场分析方法. 上述研究总结归纳了已有研究中报道的PFASs检测分析手段、修复技术,或是针对特定区域、环境介质、单一类别PFASs进行了统计分析,而对于全球尺度上地表水中全类别PFASs的污染水平研究依然缺乏. 本文总结归纳了多种地表水体中PFASs污染现状与时空分布特征,概述了地表水体中PFASs的主要来源及迁移规律,并揭示了影响该过程的多个环境要素及作用机制,为后续研究PFASs在环境中的迁移转化过程提供理论支撑,并对未来新型PFASs研发方向与监测手段进行了展望.
-
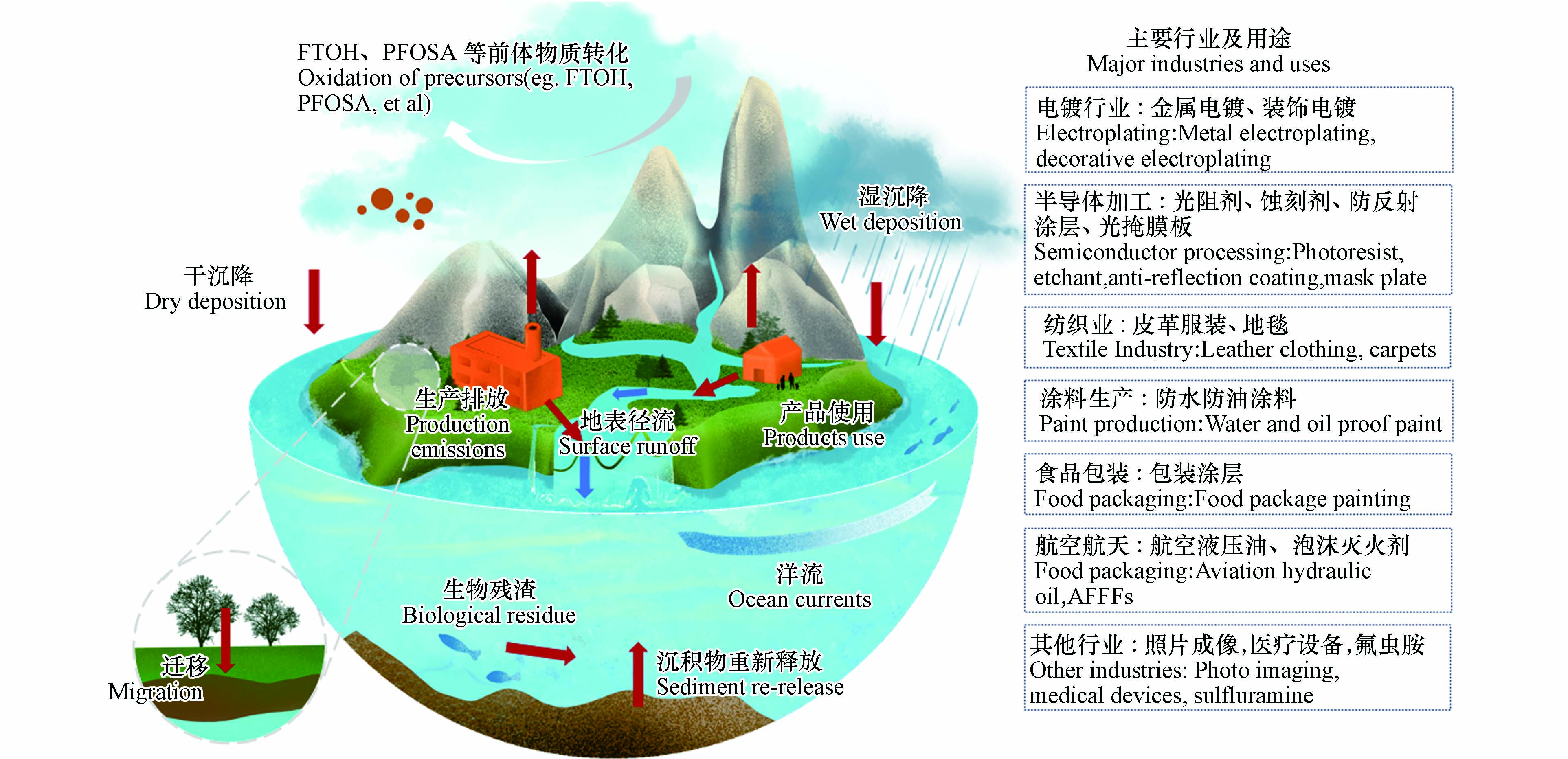
水环境中的全氟及多氟烷基化合物来源众多(图1),直接来源包括工厂生产排放和人类日常活动. 在氟化工企业生产过程中,大量含PFASs的废水直接排入地表水[33];另外,消防灭火剂、防水涂层等含氟产品的日常使用中,也会将PFASs带入环境中[34]. 除了直接排放,环境中的PFASs前体物质也可以在生物或化学作用下转化为全氟烷基酸(perfluoroalkanoic acids,PFAAs)[35]. 环境中的PFASs在植物根系吸收[36]、干湿沉降作用[37]以及地表径流[38]等自然力作用下可在不同圈层之间发生迁移转化;水圈对于PFASs,既是最主要汇同时也是潜在的源[11, 39-42]. 因此,揭示PFASs在水环境中的赋存特征和迁移转化规律对理解这类物质的地球循环过程具有重要意义.
全氟烷基羧酸(perfluorocarboxylic acids,PFCAs)和全氟烷基磺酸(perfluorosulfonic acids,PFSAs)是两类典型的PFASs,分别含有亲水性官能团羧基或磺酸基,其水溶性高于多氯联苯、多环芳烃等传统有机污染物[43],其中一些短链PFCAs在水中溶解度可以达到g·L−1级.
-
近年来,关于内陆河流中PFASs的检测报道日益增多. Li等在不同位点采集的太湖水样中均测到不同浓度的PFCAs和PFSAs,全氟丁酸(PFBA)及全氟辛酸(PFOA)浓度分别达到35.51—65.78 ng·L−1 和27.63—31.82 ng·L−1[44];Liu等监测发现,钱塘江上下游水中的PFASs总浓度为3.58—786 ng·L−1,在氟工业集中区附近水体中检测到的PFASs浓度最高[45];杜国勇等在长江流域重庆段中检出16种全氟烷基酸,包含多种链长的全氟羧酸、磺酸类物质,该流段沿岸分布着以化工行业为主的合江临港工业园、万州化工园区等多个工业园区,生产废水经由污水处理厂处理后排入河道,处理过程中大多数PFASs会转化为PFOA,导致该流域中所检出主要单体为PFOA[46]. 王鑫璇等调查了中国七大流域PFASs的污染现状,结果显示,七大流域PFASs污染程度(中位值)为:松辽(92 ng·L−1)>太湖(57 ng·L−1)>海河(18 ng·L−1)>淮河(17 ng·L−1)>长江(14 ng·L−1)>黄河(9.9 ng·L−1)>珠江(7.1 ng·L−1),其中,松辽流域年降水量居七者最少,且PFASs浓度呈现明显季节性差异,枯水期PFASs浓度最高;而太湖流域虽然面积较小,但受工业园区分布及流域内人口密集影响较大,PFASs污染也较为严重[47]. 在欧美, Pétré等在美国北卡罗来纳州开普菲尔河水系中可检出最高浓度416.8 ng·L−1的全氟己酸(perfluorohexanoic acid,PFHxA),同时含有较高浓度的全氟戊酸(perfluoropentanoic acid,PFPeA) [48].
近年来,传统长链全氟烷基化合物 PFOA和PFOS的禁止生产使用促进了一系列新兴PFASs的研发和应用(表1). 新兴PFASs代替物主要分为以下几类:(1)短链的全氟烷基磺酸或羧酸盐;(2)未被F完全取代的多氟化合物;(3)在碳链中引入醚键的全氟和多氟烷醚类化合物(per-and polyfluoropolyether substances,PFPEs),多为分为全氟和多氟烷醚羧酸、磺酸及其盐类(PFPCAs和PFPSAs); (4)含环状结构的全氟磺酸盐等.
Marchiandi 等在墨尔本工业园区临近溪水中,检测到部分新型全氟化合物,如全氟己基磷酸(PFHxPA)、N-亚甲基-全氟辛烷磺酸钾盐(MeFBSA)等,这些新兴PFASs大约可占总PFASs的20%[54]. Sun等对比了美国开普菲尔河流域2006年至2013年水样PFASs的浓度特征,结果显示2006年主要的PFCAs为C7至C9,而2013年主要PFCAs为C5至C7[55]. 2015年,Strynar等在美国北卡罗来纳州的地表水中首次检测到Gen-X[56]. 随后,在德国莱茵河支流斯赫尔河、荷兰多德雷赫特市氟化厂下游、中国渤海湾、印度洋、北极等地均检测到较高浓度的Gen-X,表明此类化合物已造成全球性污染[52, 55-59]. 现有文献中,Gen-X和同系物HFPO-TA被报道的最高污染浓度在中国山东小清河,分别为3825 ng·L−1[60]和68500 ng·L−1[61]. 有研究显示,在中国海河流域地表水中,检测到了26种PFASs,而且新兴PFASs,如F-53B,在一些沉积物样品中甚至占主导地位[62]. Lin等发现,F-53B在采集自浙江省奉化江河水样中的检出率高达100%[63]. 这些地区分布了较多电镀企业,含高浓度PFASs电镀废水的排放可能是造成该地区PFASs污染严重的主要原因.
-
陆源环境介质(土壤、江河湖水底泥及生物体)中的PFASs可随着水循环过程汇入海洋水体,造成PFASs污染逐步由近海向远海迁移.
2011年之前的监测数据显示,大西洋赤道附近的表层海水以传统的PFOA、PFOS为主,浓度仅为102—103 pg·L−1和101—102 pg·L−1,其他短链PFSAs、PFCAs浓度均小于101 pg·L−1[11]. 随着各种限制PFASs法规的推行,大西洋绝大部分海域中传统PFASs浓度均有所下降,PFOA浓度水平维持在101—102 pg·L−1[64]. 太平洋和印度洋远洋表层海水中的不同PFASs(主要包括C4—C10 PFCAs,C4—C8 PFSAs,N-甲基全氟辛基磺胺)污染水平更低(太平洋∑PFASs中位数645 pg·L−1、印度洋527 pg·L−1)[65]. 针对北冰洋和南极洲调查数据显示:检出的PFASs绝大多数为PFAAs,浓度一般为2×101—1×102 pg·L−1[66]. 可见,海洋水体中的PFASs检出总浓度的数量级一般为pg·L−1,明显低于内陆水体(ng·L−1级),其中主要污染物仍是以全氟烷基磺酸和羧酸为代表的全氟烷基酸PFAAs,表2总结了全球各大洋中的PFASs的污染特征.
-
内陆地表水中PFASs浓度的地域差异较大,以长江上、中、下游各水系中PFASs污染水平为例(表3),PFASs浓度大体呈现西低东高的趋势,与工业发达程度及人类生产活动密切相关.
长江上游工业分布较少,人口密度低,氟化产品生产量小,含氟废水排放量少,所以地表水中的PFASs浓度较中、下游浓度偏低. 宋等人在研究沱江流域典型和新兴PFASs时发现,沱江是长江上游主要的支流之一,上游PFASs污染低(12.5—48 ng·L−1),中游位置受氟工业园区影响PFASs污染严重,最高浓度点位于某氟科技有限公司附近,浓度为3.8 mg·L−1,区域内氟化工相关企业对地表水PFASs污染有重要贡献[81]. 重庆地区分布了多个电子、石化等相关涉及PFASs企业. 研究显示,在长江流域重庆地表水中PFASs检出浓度最高点为入境断面[46],地理位置与上游合江临港工业园重合.
长三角地区工业发达,是化工、纺织、印染、造纸的重要产区,拥有常熟氟化工产业园、中化太仓化工工业园等多个氟化工产业园区. 针对氟化工产业园及周边水环境中的PFASs污染,Lu等调查发现常熟氟工业园区周边地表水样品∑PFASs的浓度范围为15.6—480.9 ng·L−1,平均值为(217.1±161) ng·L−1,而园区内地表水中的 ∑PFASs 浓度范围为 281—489 ng·L−1,平均为 (352.5 ± 78.6) ng·L−1,浓度由园区中心向四周呈梯度降低[82]. 而在园区附近的太湖水体中,由北至南的6个区域中,∑PFASs有明显的从北至南的空间下降趋势(梅梁湾728 ng·L−1、竺山湾621 ng·L−1、贡湖湾491 ng·L−1以及其余28个采样点介于219—411 ng·L−1)[83]. 梅梁湾位于太湖北部,毗邻常州和无锡两个工业发达城市,这两个地区氟化工产业发达,紧靠常熟氟化工业园,生产过程中常常会造成PFASs流出[84]. 同样,位于宜兴和无锡工业城附近的竺山湾和贡湖湾也显示出相当高的∑PFASs浓度.
除长江流域外,因上游氟化企业污水排放,山东小清河中也检测出高浓度的PFOA. 在生产聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)的东岳集团以及济南3F公司附近均检测到较高浓度PFOA[85]. 在国外氟化工产业发达地区均有类似现象:美国斯宾塞海军飞行场及其周围工厂排放含有PFOS的废水,这导致了Escambia湾中PFOS重度污染[86];法国工业地区地表水中的PFHxA、PFHxS和PFOS平均含量明显较高(工业≈城市>农田)[87]. 上述研究均表明:陆源污染输入是造成江河湖泊中PFASs污染高负荷的主要原因.
此外,水力运输过程[88-89]以及河湖之间水动力差引起相对强烈的沉积作用[90],可能会导致水体中污染水平呈现沿流向逐渐降低的地域差别. Lu等在骆马湖观测到采样点的PFASs浓度沿河流—河口—湖泊方向(300.09 ng·L−1—220.40 ng·L−1—147.80 ng·L−1)连续降低的分布模式[91].
-
目前,本领域学者公认以下四个途径是海洋中PFASs的主要扩散方式:(1)挥发性PFASs(如FTOH等)经由大气中距离传输至高纬度地区,并在过程中转化为羧酸盐[92] ;(2)离子型PFASs随着洋流大范围、远距离输送至高纬度地区[93];(3)生物体内富集的PFASs通过食物链或者食物网迁移至高纬度地区[94];(4)海洋气溶胶裹夹着PFASs远距离迁移[94].
近海陆源PFASs是海洋的直接污染来源,包括土壤、内陆河流湖泊、地下水、底泥沉积物等. 近海陆源的释放会直接增加沿海水体中PFASs的浓度,排放量越大或距陆源越近,其PFASs浓度一般越高. 在人口稠密和工业化高度集中的东南亚和北海等地区,沿岸水体中的PFAAs浓度范围在0.2—20 ng·L−1[95]. 西欧、北美在大西洋沿海地区工业化发达,工业废水直接向大西洋输入,致使北大西洋PFASs浓度高于南大西洋[96]. 相反的,两极地区人为活动较少,北冰洋海域表层海水中的PFASs以传统长链PFAAs为主,且浓度基本在2×101—1×102 pg·L−1以下,大西洋以南的南大洋海域也只检测到低浓度的PFOA和PFOS[94]. 其中,河流输入是污染物由陆地至沿海的主要迁移方式,汇入河流污染水平的高低也是造成不同沿海地区水体PFASs差异性的原因之一. 泰晤士河和塞纳河中∑PFASs分别为60 ng·L−1和27 ng·L−1,这两条河流都汇入英吉利海峡,而比斯开湾的汇入河流污染水平低(如卢瓦尔河∑PFAS浓度仅为8.1 ng·L−1),这就导致了英吉利海峡PFASs污染(650 pg·L−1)高于比斯开湾(590 pg·L−1)[97]. 一项调查发现,由中国河流入太平洋西北岸的传统PFASs的陆地年排放量约为17.3—203 t[53],这导致沿海地区的较严重的PFAS污染[98]. 因此,距离陆源的远近会造成近海与远洋海域中PFASs存在明显差距.
洋流作用被认为是将离子态PFASs由近海运输至远洋地区及高纬度地区的重要途径[99],是改变海洋中PFASs分布的重要驱动力. 例如,北冰洋西半球海域中PFOA浓度有向北稀释特征,Busch等解释,这是由于北大西洋洋流将PFASs从欧洲向北运输,并在北冰洋中再分配的结果[100]. 此外,洋流会将陆源排放的PFASs混合,从而导致开阔海域中PFASs比例变化,如含有低浓度PFOA和高浓度PFOS的南大西洋环流与含高浓度PFOA、低浓度PFOS的加那利寒流在赤道附近交汇,促使大西洋赤道附近表层海水中 CPFOA/ CPFOS趋近1[67]. 因此,陆源汇入以及洋流作用的长距离运输,是造成全球海洋水体污染的直接原因.
-
研究显示,内陆江河湖泊受到水深的限制,其温度与盐度分层现象不明显,PFASs与水深没有明显的相关性[101]. PFASs在内陆水体的分布主要与其在水相-固体颗粒的吸附平衡有关. 近来,Chen等[102] 将城市水体分为三层(表层—0.1 m)、中间层(1.5—2.5 m)和底层(3—5 m),分别检测了水相和吸附在悬浮颗粒表面的PFASs的浓度,发现水中的总/单个PFAS浓度没有显著差异,表层水体中PFASs(4.1 ng ·L−1)只略低于底层(5.3 ng·L−1),Chen等认为底层水含高浓度固体颗粒,更倾向于聚集形成更大的粒子,携带更大量的PFASs,导致底层水中PFASs的浓度高于表层水. Shao等进一步探究发现,疏水性更强的长链PFCAs与PFSAs这一现象更加明显[103]. 上述结果表明,江河湖泊中的PFAS浓度在垂直方向上基本保持浓度稳定,但由于受到PFASs在水相和固相中分配平衡的影响,底层水体中的PFASs浓度略高于表层,特别是对于疏水性较强的长链PFASs.
径流被认为是含离子态PFASs在地表水和地下运输的主要机制[104-106],地表径流通常含有高浓度的悬浮颗粒,并且携带了较高浓度的PFASs [107],当进入溪流和河流,由于湍流的快速扰动,这些颗粒可以与重新悬浮的沉积物颗粒混合[108],将PFASs重新释放入水体,造成水体或沉积物的二次污染. 这被认为是内陆湖泊中PFASs竖直分布的主要成因,也将是本段内容的讨论重点.
颗粒物/沉积物上富集的PFASs与所在水体中的PFASs类型基本一致,主要为PFCAs与PFSAs,Zhao等研究了海河表面沉积物中6种全氟烷基物质(PFAS)的含量,结果表明,沉积物中PFASs的总浓度在0.52—16.33 ng·g−1(dw)之间[109]. 但与水体中PFASs的组成比例截然不同,颗粒物与沉积物上PFASs的检出频率和浓度随着碳链的增长而提高[103]. Wang等在沉积物中测得PFAS的总浓度范围为0.24—1.9 ng·g−1(dw),其中长链PFASs(C9—C14 PFCAs)在沉积物中的比例远高于在水中的比例 [110]. 同时,作为底栖生物的主要活跃区,沉积物中PFASs的并不是单纯由水相转移而来,生物转化和富集也影响着沉积物中PFASs的浓度水平[111]. 沉积物中PFASs总浓度的季节敏感性低于水体样品,Chen等分别采集了7月和12月的16个表层沉积物样品,在两个不同月份样品中的PFAS水平在一年内相当稳定[112].
现有研究普遍认为PFASs主要通过分配作用在悬浮颗粒物/沉积物上富集,经过一定时间达到分配平衡,该过程可以用线性吸附等温式描述[113],吸附能力
$ {K}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}} $ 由式(2)得出:式中,
$ {C}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{d}} $ 是PFASs在悬浮颗粒物/沉积物的浓度(pmol·kg−1);$ {C}_{\mathrm{w}} $ 是PFASs 在水相中的浓度(pmol·kg−1);$ {K}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}} $ 沉积物-水中分配系数(L·kg−1);$ {K}_{\mathrm{d}} $ 分配系数(L·kg−1);$ {f}_{\mathrm{o}\mathrm{c}} $ 表示沉积物中的有机碳含量.PFASs在水-悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中分配的影响因素复杂,主要总结如下:
(1)PFASs 结构特征
PFASs碳链长度、官能团类型和数量等对PFASs界面分配行为都具有一定的影响. 碳链长度是影响PFAS界面分配的重要影响因素. Higgins等发现,PFCAs及其盐类每增加1个—CF2—基团,分配系数(lg
$ {K}_{\mathrm{d}} $ )提高0.50—0.60个单位,而磺酸盐的lgKd会增大0.73[113],碳氟链越长在水相中的分配就越少. Lee等报道了韩国牙山湖中13种全氟化合物在水、底泥和鱼类之间的分配行为,这些PFASs的分配系数lg$ {K}_{\mathrm{d}} $ 在0.39—1.99之间,与全氟烷基链长度呈正相关性,也与生物累积系数变化趋势一致[114]. 所以,一般来说,悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中常见的PFASs均为长链,短链的PFASs分配系数较低,在沉积物中分配较少.此外,PFASs是一种离子型表面活性剂,结构中含有如羧基、磺酸基等较强极性的亲水基,官能团的种类与数量往往会影响这类有机污染物的溶解度与表面范德华力. 全氟磺酰胺、全氟磺酸盐在沉积物中的吸附能力仍然呈现链长依赖性,但相较相同碳链的全氟羧酸,二者在水中的溶解度更低、Kd值更高,也更易吸附到悬浮颗粒物/沉积物上[115]. Labadie和Chevreuil拟合ƒoc与悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中PFCAs的关系,长链与短链所得模型拟合斜率有所不同,表明长链与短链PFCAs的吸附并不是同一种作用力所致,短链PFCAs在沉积物吸附方面不遵循典型的链长依赖性[116],推测悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中的短链羧酸盐的吸附主要是羧酸基团和带电粒子在沉积物颗粒上的静电相互作用,而不是疏水作用[117].
(2)悬浮颗粒物/沉积物组成成分
悬浮颗粒物/沉积物各组成成分同样也会影响PFASs在水-悬浮颗粒物/沉积物上的分配. 不同组分有机物中,芳香性以及分子极性的巨大差异,导致了悬浮颗粒物/沉积物有机质的高度非均质性,对疏水性有机物表现出不同的吸附特征[118]. 其中,Huang认为可将有机物的吸附分成无机矿物表面、无定形的土壤有机质(软碳)和凝聚态的土壤有机质(硬碳)吸附等3类,前两者以吸附速度较快的分配为主,后者为速度相对较慢的非线性吸附[119].
悬浮颗粒物/沉积物表面吸附的有机物疏水部分,会促进PFASs的吸附. Zhang 等通过研究胡敏酸等有机质组分对PFOS在悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中吸附量的影响,揭示了PFASs在悬浮颗粒物/沉积物上的主要机制是疏水作用与界面转移过程[120]. Pan等也观察到全氟辛烷磺酸的Kd与ƒoc呈正相关(R2=0.961)[121].
无机矿物是影响悬浮颗粒物/沉积物中PFASs吸附的另一关键组分. 由于较低的pKa值,PFASs在自然水体的pH值(中性附近)下以阴离子的形式存在,容易吸附在带正电的矿物表面[122]. 其次,离子交换、表面络合和氢键作用可能对PFASs吸附到矿物表面产生重要影响. Gao和Chorover利用红外光谱研究了纳米颗粒赤铁矿(α-Fe)对PFOS的吸附作用机制,发现全氟辛烷磺酸可以通过氢键与赤铁矿相互作用[123-124]. 矿物吸附实验的证明:PFOS的单位面积吸附量按照高铁砂 > 高岭石 > 针铁矿的顺序降低[125]. 可见,水体中矿物质的表面电荷或官能团将提供表面吸附位点,而粘土矿物内部孔隙又能额外提供一部分吸附量[126],进而影响PFASs在水-悬浮颗粒物/沉积物分布.
(3)水体理化性质
pH值 pH可以改变吸附剂的表面电荷,从而影响PFASs的吸附分配. 当pH值低于7.5时,随着pH值升高,分配系数往往降低. 研究表明,水体中的盐浓度会影响PFOS在沉积物中的分配. 自然水体中,PFOA一般以阴离子形态出现. You 等发现,当溶液 pH=8 时,沉积物中 PFOS 的吸附量为 120 μg·g−1,约为 pH=7 时的4倍[127]. 在自然水体pH下,PFASs的存在形式稳定,但随着水体酸碱度的变化,沉积物的表面电性改变,从而影响沉积物与 PFASs(阴离子形态)之间的静电作用,对显著影响PFASs在沉积物上的富集吸附.
盐度 众多研究表明,盐度的增加会产生“盐析”效应,即通过水体中存在的二价阳离子(Mg2+、Ca2+)架桥,增强阴离子PFAS与正电荷表面(铁氧化物、天然有机物等)之间的吸引作用[128]. 但Higgins等提出,二价阳离子的浓度同时还有可能使得pH值变化,导致某些官能团改变质子化状态,这种趋势随着pH的上升而增强[113]. 而在最近的一项研究中,吸附剂的静电库仑电位随pH和阳离子浓度变化. 由于压缩双电层效应,随着离子强度的增加,PFOS和PFOA在氧化铝表面的吸附减少[129]. 因此,对于大范围复杂的环境,PFASs在环境介质中的分配行为同时受到pH值和盐度浓度的影响[130],因此要兼顾二者考虑其影响结果.
温度 吸附过程是自发吸热的,并受熵驱动,所以在一定温度范围内,温度的升高也会促进 PFOS在颗粒物腐殖酸上的分配[131].
-
PFASs在海水中的垂直分布呈现表层特点. Zhou等研究发现,随着采样深度增加,中国渤海、黄海近海海域水样中PFASs总浓度呈现下降趋势,表层5—10 m海水与60—70 m处相差近40%[132]. 对比近海地区,开阔海域PFASs的垂直分层同时存在“表层富集”和“深度贫化”[58]. Yamashita等收集了日本海多个深度的水柱样本,发现从表层到底层水的PFOS浓度逐渐下降,表层水中PFOS的浓度为约15 pg·L−1,深度1000 m左右降至 约2 pg·L−1,而在1500 m以下的深度低于检出限[99].
最近的研究发现,PFASs可通过海洋表面有机颗粒的垂直沉淀作用[133]或涡流扩散[134]的方式,沿纵向由表层向深海传输,从而形成污染水平沿着深度逐渐下降的趋势.
海洋表层有机颗粒的垂直沉降过程对PFASs的向下运输作用与PFASs的结构有关[135],长链PFCAs与PFSAs(PFOS 18%)通过表层有机颗粒的垂直沉降过程向下运输量较少;短链PFASs(C5—C7 PFCAs 7%)在溶液中以稳定的离子形式存在,难以吸附在颗粒上沉降,表层有机质的垂直运输贡献更小;但这一过程却是一些前体(如EtFOSAA 86%)物质向深海运输的主要方式[136] .
与表层有机颗粒的垂直沉降过程相比,“涡流扩散”是大多数PFASs向海洋深处扩散的关键途径. 过去40年间,从海洋表层向深海累计扩散的600余吨PFASs,集中在100 m以上水层中,而在100 m以下PFASs浓度快速下降,这一现象与垂直涡流扩散率的变化规律相符[137]:部分学者认为,深海水温分层会影响污染物的垂直涡流扩散:强太阳辐射加热了表层水体,降低了水体密度,阻碍了表层水与深层水之间的混合作用,从而导致污染物在表层水体富集[138]. 在北大西洋,与中间层(365—510 m)和永久温跃层周围的水层(985—1335 m)相比,正是较温暖的表层水中PFOS浓度更高[14]. 除了温度,盐度也是一大重要影响因素. Yeung等在对北冰洋的研究发现,冻结海水之下的盐跃层盐度更高、更温暖,大量由地表径流或大气沉降进入水体的PFASs在此处汇集[13]. 此外,深海独特的地貌特征(如海山,海底峡谷,海沟和热液喷口)[139]与此间形成的水团[58, 140]也会改变PFASs的运动迁移路径.
海水表层1—1000 μm水深被认为是海洋微表层(sea-surface microlayer,SML). SML被视作海洋的皮肤,是在海浪、风力作用下形成的具有纳米尺寸小液滴与气体的混合微表层,具有富集疏水性有机物和表面活性剂类物质的能力[141]. PFASs一端疏水一端亲水,有在气液界面富集的运动倾向(亲水基保留在水相内,疏水C—F链伸向气相)在气-液表面定向排列[142],这一特性使得PFASs可以SML内高浓度富集. 又因为海洋表面是一个不断受到扰动的动态气-液界面,有学者提出了海洋气溶胶(sea spray aerosol, SSA)对海洋表面PFASs富集的可能性[143]:海浪卷入空气进入水体,形成大量气泡,气泡携带次表层水体中PFASs向上迁移,与微表层接触后将PFASs带入SML或因气泡壁破裂重新释放入水体或上空(图2). Casas等测得SML、SSA对PFASs的富集因子分别为 1.2 — 5 和 522 — 4690[144].
-
水中PFAS浓度的季节性变化受到许多因素的影响,例如水流量,水质特性,气温以及集水区PFAS的使用和排放. Yu等观测到太湖水体中的PFASs,在雨季时的总浓度高达157 ng·L−1,超过旱季(72 ng·L−1)的两倍[83]. 研究人员认为,降雨多时,云滴内的PFASs可通过湿沉降进入地表水,同时冲刷附着在大气颗粒物上的PFASs,使得大气中的PFASs沉降下来,进入地表水或者土壤中,造成大气中PFASs的清除和地表水中PFASs的升高[145],同时,在雨水充沛的夏季,降雨和由此产生的地表径流将陆地上的PFASs汇入湖中,进一步加剧水体污染[80]. 此其,典型的雨季高温可以加速PFAAs前体的降解转化,在强烈的太阳辐射驱动下,太湖中高浓度PFASs前体物质生化转换加快,导致雨季太湖PFASs的总浓度上升[146]. 降水量增多的雨季,土壤中污染物随着雨水下渗的风险提高,径流量增大,水动力加快,底泥中的污染物冲进水体,从而使得PFASs的检出浓度高于旱季[147]. 水利工程等人类活动也是造成水体PFASs季节性特征的一大重要因素:“长江至太湖引水工程”流经常熟市的氟化工厂分布密集的望屿河,夏季引水将向太湖拱湖湾输入过量的PFASs [83].
在沿海地区,由于台风衍生的连续密集降雨(因此含有较少的陆地颗粒)和纳潮量的提升共同加速了雨季的海水交换能力,沿海水体中PFASs与内陆水体往往呈现相反的季节性变化[148]. Cai等发现了福建九龙口处的∑PFASs浓度呈现:旱季>雨季,雨季沿海地区PFASs浓度最低[149],胶州湾沿海海水中的PFAS浓度也在旱季呈现最高水平[148].
-
表4总结了近年来部分典型内陆水体中PFASs浓度年度变化趋势[69, 83, 150-155]. 显然, PFCAs与PFSAs是水体中PFASs污染的主体,大部分水体中PFASs总量呈现逐年波动上升的趋势. 近年来,由于氟化工相关行业向中国转移并飞速发展[156],湖泊中的PFASs流入量急剧增加,加之湖泊水力停留时间长,从而延迟PFASs生产和使用变化的响应时间,导致这类污染物在被淘汰后,浓度依然不断上升. PFCAs被证实还可通过前体物质或者其他结构的PFASs转化而来[157],这是水体中PFCAs的又一潜在来源,也是PFASs总量逐年攀升的原因之一.
不同地区湖泊中, PFOA与PFOS在浓度变化趋势有些许不同. 对于PFOA:在中国,PFOA污染逐年加重,Yu等测得太湖流域2015年的全氟烷基羧酸与磺酸总量骤升至213 ng·L−1, PFOA单体浓度在这期间同样增加[83]. Yao等比较发现,太湖中PFOA浓度由2016年的18.0 ng·L−1增长至2021年的28.2 ng·L−1 [158]. PFOA的逐年增长现象同样在加拿大的安大略湖、德国易北湖中被观察到,但增长速率更慢. 而对于PFOS,在中国湖泊中,PFOS增长率较PFOA更缓慢,而北美、欧洲国家,湖泊中的PFOS污染开始逐渐减轻,总量开始下降. 这可能得益于北美等地区对PFOS、PFOA和其他长链全氟烷基羧酸盐(PFCAs)及其前体物质的较早地采取了管控措施.
为满足持续的工业需求,大量新兴PFASs投入使用,新兴PFASs污染逐渐加重. 如在中国和韩国快速发展的沿海地区,河流中长链PFASs逐渐被短链PFASs取代,在韩国,短链C4—C7 的PFCAs 的比例由2008—2012年的46%增长到2018年的79%,主要的全氟烷基磺酸由传统PFOS转变为新兴短链型PFBS[159-160]. 多氟烷基磺酸FTSs、Cl-PFESAs等都曾作为PFOS的替代品,被投入使用后进入环境中被大量检出[52, 161]. 值得注意的是,相关政策出台带来的产业化调整,会引导企业研发更替新兴PFASs,导致在这一时期的调查中某一特定PFASs浓度的异常升高[17].
近年来,海洋水体中PFASs污染仍在加重[161-162]. 洋流源源不断地将陆源PFASs输送至全球海洋水体,加之近年的气候变化加速了PFASs迁移转化速度. PFASs污染逐年加重这一现象在极地水体中尤为明显. 极地海冰中的PFASs可能随着融冰过程重新释放到海水中,成为极地水体的PFASs新来源[40]. 同时,因气温上升,大洋绕极环流、极锋带等对极地地区的生物隔离被破坏,促使更多PFASs以生物迁移方式向极地传输,从而导致极地海洋水体PFASs浓度上升. 例如,迁徙鸟类在南极以外区域暴露和富集PFASs,回迁后通过产蛋、生物残渣、粪便使其体内的PFASs残留在南极地区[163].
-
近年来,多项限制PFASs生产与使用的措施被采纳,但传统PFASs的残余库存、转化和浸出,都有可能使得水环境中的PFASs浓度在停用几年后继续升高,这种传统PFASs污染防治的滞后性与新兴多氟及全氟替代物的不断更新生产,给未来的PFASs污染治理提出了更高要求. 目前大范围、长时间维度的监测数据的匮乏与检测手段、监测技术的不足,厘清PFASs在地表水中的赋存特征及时空差异性,对完善监测体系、深入理解PFASs的全球传输机制及后续治理PFASs具有重要意义.
本文通过概述全氟及多氟烷基化合物(PFASs)在地表水中的赋存现状,为健全PFASs监测管理体系与后续PFASs治理方案提供新思路. 本文综述了内陆河道、湖泊及海洋中的PFASs环境赋存水平,强调了点源污染对地表水PFASs污染的重要性,建议建立完善的PFASs的源头防治措施;概要分析了水体PFASs时空赋存差异性的成因以及影响因素,为提高监测数据稳定性、排除数据偶然性,宏观准确把握各水体污染现状提供了参考;同时指出:新兴 PFASs在地表水体中已普遍存在,并且已经显现出一定的替代趋势,部分研究表明这类物质的毒性已无法忽略[164].
(1)新兴PFASs替代品及其代谢产物的检测技术亟需完善整合:现有研究多基于测定具有标准试剂的物质,开发合成新兴PFASs标准品或获得该物质的公开信息,将成为这部分物质及其降解、衍生产物的成功定性分析和定量检测的关键.
(2)深入研究新兴PFASs替代品在环境中的转化产物及探明其转化路径,或有机会实现新兴PFASs替代品生物降解,相应地也可为研发新的无潜在生物蓄积性、无毒性、易降解的高性能化合物提供新方向.
(3)对PFASs在沿海/海洋沉积物中的监测调查亟待加强:沉积物是水体中PFASs的次要来源,目前在河道中水-沉积物上的分配机制研究较多,而对海洋中的研究较少. 海洋具有独有的地貌特征、洋流驱动,海洋/沿海沉积物中PFASs的沉积系数与河流沉积物具有较大差异[165],使得各预测模型对PFASs浓度预测值与实际值相差甚远. 故亟需强化监测技术并在这些地区开展持续性监测.
地表水中全氟及多氟烷基化合物(PFASs)的污染现状研究进展
Research progress on the pollution status of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water: A review
-
摘要: 近年来,全氟及多氟烷基化合物(per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances,PFASs)的大量生产使用,使得其在自然水体中的浓度日益升高. 由于PFASs的生物毒性及强稳定性,环境中的PFASs严重威胁到生态环境及人类健康. 目前,多个国家及相关国际组织开始对地表水中的PFASs展开检测,但目前的监测基本属于点源监测,大范围、长时间维度的监测依然缺乏,从而无法准确揭示PFASs的时空赋存特征. 本文概述了PFASs在地表水中的赋存水平,同时阐述了地表水环境中PFASs的水平分布和垂直分布特征,并揭示了地表水中PFASs污染水平与组成的时间变化规律,总结了影响PFASs污染的主要因素,对后续PFASs监测提出了建议,以期为准确评估水环境中PFASs的污染状况提供依据.
-
关键词:
- 全氟及多氟烷基化合物 /
- 地表水 /
- 污染特征 /
- 时空差异性.
Abstract: Recently, the mass production and usage of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) have caused the serious PFASs pollution in natural water. Due to the biological toxicity and the strong persistence, PFASs pollution is threating the ecological environment and human health. Nowadays, many countries and international organizations have begun to monitor the PFASs pollution in surface water. However, the current monitoring only focus on the point source, and there still lacking the large-scale and long-term monitoring. Therefore, it is impossible to accurately reveal the spatiotemporal characteristics of PFASs pollution. This study summarizes the occurrence level of PFASs in surface water, and expounding the distribution characteristics of PFASs in the surface water. Moreover, the temporal variation law of PFASs pollution in surface water was revealed, and some environmental factors were also discussed. Finally, the follow-up suggestions on PFASs monitoring are proposed, providing a basis for accurately assessing the pollution status of PFASs in the environment. -

-
表 1 文献中的新兴多氟及全氟烷基化合物
Table 1. Emerging polyfluorinated and perfluoroalkyl compounds reported in literatures
名称
Name简称
Abbreviation分子式
Molecular formula地点
PlaceCAS 参考文献
Reference短链全氟烷基磺酸及全氟烷基羧酸
Short chain perfluorooctane sulfonates and perfluorooctanoic acids全氟戊酸
Perfluoropentanoic acidPFBA C4F9COOH 西班牙 2706-90-3 [49] 全氟已酸
Perfluorohexanoic acidPFHxA C5F11COOH 中国 307-24-4 [50] 全氟丁烷磺酸
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acidPFBS C4F9SO3H 中国 375-73-5 [5] 多氟烷基化合物
Polyfluoroalkyl compounds1H,1H,2H,2H-全氟辛磺酸
1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctane sulfonic acid6:2FTS C6F13CH2CH2SO3H 中国 27619-97-2 [51] 全氟和多氟烷醚类化合物
Perfluoropolyethers4- 8-二氧-3H-全氟辛酸铵
Ammonium 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoateADONA CF3O(CF2)3OCHFCF2COO-NH4 + 中国 958445-44-8 [52] 全氟(2-甲基-3-氧杂己酸)
Undecafluoro-2-methyl-3-oxahexanoic acidHFPO-DA
(Gen-X)C3F7OCF(CF3) COOH
(C3F7OCF( CF3 ) COO-NH4 +)中国 13252-13-6 [52] 全氟-2,5-二甲基-3,6-二氧杂壬酸
Perfluoro(2,5-dimethyl-3,6-dioxanonanoic)acidHFPO-TA C3F7OC6F7OCF(CF3 ) COOH 中国 13252-14-7 [52] 6:2 氯代多氟烷醚磺酸盐
6:2 chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonate6:2 Cl-PFAES
(F-53B)Cl(CF2) nO(CF2)2SO3H 中国 756426-58-1 [53] 环状全氟烷基化合物
Cyclic perfluorinated acid十氟-4-(五氟乙基)环氧己烷磺酸钾盐
PerfluoroethylcyclohexanesulfonatePFECHS C2F5C6F10SO3-K+ 澳大利亚 335-24-0 [54] 表 2 五大洋中典型PFASs的赋存水平
Table 2. Spatial characteristics of PFASs around the area of the five oceans
大洋
Ocean地区
Area主要PFASs
Main PFASs检出浓度/(pg·L−1)
Concentration参考文献
References大西洋
Altantic OceanBay of Biscay of Argentia PFOA
PFOSPFOA 77—980
PFOS 40—250[67] the River Weser PFOA
PFOS∑PFAAs 120—260 [68] 太平洋
Altantic Oceanthe River Qingshui PFOA
PFOSPFOA 3—420 [69] Tokyo Bay PFOA
PFOSPFOA 48—192
PFOS 8—59[70] 印度洋
Indian OceanBay of Bengal coast PFOA
PFOS∑PFAAs 10.6—46.8 [11] Between Asia and Antarctica PFOA
PFOSPFOA 1—441
PFOS 5—23.9[71-72] 北冰洋
Arctic OceanEuropean High Arctic PFOA
PFDA∑PFAAs 0.1—3.6 [39] the Central Arctic PFOA
PFOS∑PFAAs 11—174 [13] 南冰洋
Antarctic OceanAntarctic Peninsula coast PFOA
PFOSPFOA 0—25
PFOS 25—45[64] Coastal Livingston Island PFHpA
PFOA∑PFAAs 94—420 [73] 表 3 长江流域PFASs污染状况
Table 3. Contamination status of PFASs in the Yangtze River Basin
地区
Area检出PFASs总浓度/(ng·L−1)
Concentration主要PFASs
Main PFASs主要PFASs检出浓度/(ng·L−1)
Concentration of main PFASs参考文献
Reference上游 岷江 1.54—30.2 PFBA 0.16—28.4 [74] 青藏高原峡谷区 0.272—2.224 PFBA 0.272—1.796 [75] 宜昌段 <20 PFOA <10 [76] 中游 武汉段 4.16—4.77 PFBS 1.28—1.49 [77] 洞庭湖 18.07—29.95 PFBA
PFOA4.63—11.59
3.22—8.53[78] 洪湖 25.45—63.39 PFOA
PFHxA
PFBA6.25—12.39
2.88—30.67
4.92—10.95[78] 荆州、岳阳、武汉、鄂州、黄石段 2.2—74.56 PFOA
PFBS9.9—16
1.1—40[76] 下游 太湖 10.0—119.8 PFOA
PFHxA2.2—74
<0.4—22[79] 九江至上海段 3.62—31.91 PFOA 6.8—8.2 [76] 黄浦江 39.2—576.2 PFOA
PFOS1.0—403
<286[80] 表 4 几个典型水体中PFASs年度浓度总和对比
Table 4. Comparison of total PFASs concentrations (ng·L−1) in typical surface water samples
地点
Area取样时间
Sampling timeΣPFASs/
(ng·L−1)统计物质
Statistical substancePFOA/
(ng·L−1)PFOS/
(ng·L−1)参考文献
Reference太湖
Lake Taihu2009—2010 80.3 PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS、PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA 33.2 13.8 [83] 2011—2012 67.8 25.3 9.26 2015 213 71 13.8 2021 339 120 28.5 巢湖
Lake Chao2002 15.2 PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA、PFUnA、PFDoA、PFHxS、PFOS、 PFOSA 5.9 6.6 [150] 2011 9.56 PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA、PFUdA、PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS 5.34 0.05 [151] 2012 21.19 12.68 0.25 2019 55.1 PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA、PFUnDA、PFDoDA、PFTeDA、PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS 12.6 1.15 [152] 安大略湖
Lake Ontario2012 11.86 PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA、PFUnA、PFDoA、PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS 2.37 3.95 [153] 2013 13.21 2.52 5.07 2015 15.58 2.23 5.15 易北湖
Lake Eble2011 8.1 PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS、PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA 1.9 0.91 [154] 2013—2014 16.8 PFBS、PFHxS、PFOS、PFBA、PFPeA、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFOA、PFNA、PFDA、PFUnDA、PFDoDA、6:2FTS、FOSA、HFPO-TA 1.9 ND [69] 2015 26.82 PFBA、PFPeA、PFBS、PFHxA、PFHpA、PFHxS、PFOA、PFHpS、PFNA、PFOS、PFDA、PFUnDA、PFDS、PFDoDA、PFTrDA、PFTeDA 2.37 ND [155] 注:ND,未检出,not detected. -
[1] WANG Z Y, BUSER A M, COUSINS I T, et al. A new OECD definition for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(23): 15575-15578. [2] LAU C, ANITOLE K, HODES C, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids: A review of monitoring and toxicological findings [J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2007, 99(2): 366-394. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfm128 [3] GAR ALALM M, BOFFITO D C. Mechanisms and pathways of PFAS degradation by advanced oxidation and reduction processes: A critical review [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138352. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138352 [4] GLÜGE J, SCHERINGER M, COUSINS I T, et al. An overview of the uses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2020, 22(12): 2345-2373. [5] SUN R, WU M H, TANG L, et al. Perfluorinated compounds in surface waters of Shanghai, China: Source analysis and risk assessment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 149: 88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.012 [6] SHIGEI M, AHREN L, HAZAYMEH A, et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and soil in wastewater-irrigated farmland in Jordan [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 716: 137057. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137057 [7] SHA B, JOHANSSON J H, TUNVED P, et al. Sea spray aerosol (SSA) as a source of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) to the atmosphere: Field evidence from long-term air monitoring [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(1): 228-238. [8] CHAPARRO-ORTEGA A, BETANCOURT M, ROSAS P, et al. Endocrine disruptor effect of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on porcine ovarian cell steroidogenesis [J]. Toxicology in Vitro, 2018, 46: 86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.09.030 [9] SHI G H, XIE Y, GUO Y, et al. 6: 2 fluorotelomer sulfonamide alkylbetaine (6: 2 FTAB), a novel perfluorooctane sulfonate alternative, induced developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2018, 195: 24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.12.002 [10] CAO Y X, NG C. Absorption, distribution, and toxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the brain: a review [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2021, 23(11): 1623-1640. [11] YAMASHITA N, TANIYASU S, PETRICK G, et al. Perfluorinated acids as novel chemical tracers of global circulation of ocean waters [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(7): 1247-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.079 [12] PREVEDOUROS K, COUSINS I T, BUCK R C, et al. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(1): 32-44. [13] YEUNG L W Y, DASSUNCAO C, MABURY S, et al. Vertical profiles, sources, and transport of PFASs in the Arctic Ocean [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(12): 6735-6744. [14] ZHANG X M, ZHANG Y X, DASSUNCAO C, et al. North Atlantic Deep Water formation inhibits high Arctic contamination by continental perfluorooctane sulfonate discharges [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2017, 31(8): 1332-1343. doi: 10.1002/2017GB005624 [15] NIZZETTO L, GIOIA R, LI J, et al. Biological pump control of the fate and distribution of hydrophobic organic pollutants in water and plankton [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(6): 3204-3211. [16] GONZÁLEZ-GAYA B, CASAL P, JURADO E, et al. Vertical transport and sinks of perfluoroalkyl substances in the global open ocean [J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2019, 21(11): 1957-1969. [17] TI B W, LI L, LIU J G, et al. Global distribution potential and regional environmental risk of F-53B [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 640-641: 1365-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.313 [18] GAGLIANO E, SGROI M, FALCIGLIA P P, et al. Removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration [J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115381. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115381 [19] DIXIT F, DUTTA R, BARBEAU B, et al. PFAS removal by ion exchange resins: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 272: 129777. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129777 [20] LI J N, PINKARD B R, WANG S, et al. Review: Hydrothermal treatment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135888. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135888 [21] CAO H M, ZHANG W L, WANG C P, et al. Sonochemical degradation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances - A review [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2020, 69: 105245. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105245 [22] WEI Z S, XU T Y, ZHAO D Y. Treatment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate: Status, chemistry and prospects [J]. Environmental Science:Water Research & Technology, 2019, 5(11): 1814-1835. [23] BOLAN N, SARKAR B, YAN Y B, et al. Remediation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contaminated soils - To mobilize or to immobilize or to degrade? [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123892. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123892 [24] LI F, DUAN J, TIAN S T, et al. Short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aquatic systems: Occurrence, impacts and treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122506. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122506 [25] WANNINAYAKE D M. Comparison of currently available PFAS remediation technologies in water: A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 283: 111977. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111977 [26] PODDER A, SADMANI A H M A, REINHART D, et al. Per and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as a contaminant of emerging concern in surface water: A transboundary review of their occurrences and toxicity effects [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126361. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126361 [27] DELUCA N M, MINUCCI J M, MULLIKIN A, et al. Human exposure pathways to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from indoor media: A systematic review protocol [J]. Environment International, 2021, 146: 106308. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106308 [28] SUNDERLAND E M, HU X C, DASSUNCAO C, et al. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects [J]. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 2019, 29(2): 131-147. [29] KURWADKAR S, DANE J, KANEL S R, et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 809: 151003. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151003 [30] WINCHELL L J, WELLS M J M, ROSS J J, et al. Analyses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through the urban water cycle: Toward achieving an integrated analytical workflow across aqueous, solid, and gaseous matrices in water and wastewater treatment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 774: 145257. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145257 [31] BANZHAF S, FILIPOVIC M, LEWIS J, et al. A review of contamination of surface-, ground-, and drinking water in Sweden by perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) [J]. Ambio, 2017, 46(3): 335-346. doi: 10.1007/s13280-016-0848-8 [32] XIAO F. Emerging poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review of current literature [J]. Water Research, 2017, 124: 482-495. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.024 [33] LIU Y Q, ZHANG Y, LI J F, et al. Distribution, partitioning behavior and positive matrix factorization-based source analysis of legacy and emerging polyfluorinated alkyl substances in the dissolved phase, surface sediment and suspended particulate matter around coastal areas of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 246: 34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.113 [34] RUYLE B J, PICKARD H M, LEBLANC D R, et al. Isolating the AFFF signature in coastal watersheds using oxidizable PFAS precursors and unexplained organofluorine [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(6): 3686-3695. [35] ZHAO S Y, ZHOU T, WANG B H, et al. Different biotransformation behaviors of perfluorooctane sulfonamide in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) from earthworms (Eisenia fetida) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 346: 191-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.018 [36] ZHU H K, KANNAN K. Distribution and partitioning of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids in surface soil, plants, and earthworms at a contaminated site [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 647: 954-961. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.051 [37] CASAS G, MARTINEZ-VARELA A, VILA-COSTA M, et al. Rain amplification of persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(19): 12961-12972. [38] RICHARDSON M J, KABIRI S, GRIMISON C, et al. Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in runoff and leaching from AFFF-contaminated soils: a rainfall simulation study [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(23): 16857-16865. [39] GARNETT J, HALSALL C, VADER A, et al. High concentrations of perfluoroalkyl acids in Arctic Seawater driven by early thawing sea ice [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(16): 11049-11059. [40] GARNETT J, HALSALL C, THOMAS M, et al. Investigating the uptake and fate of poly- and perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS) in sea ice using an experimental sea ice chamber [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(14): 9601-9608. [41] MACINNIS J J, LEHNHERR I, MUIR D C G, et al. Fate and transport of perfluoroalkyl substances from snowpacks into a lake in the high Arctic of Canada [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(18): 10753-10762. [42] MACINNIS J, DE SILVA A O, LEHNHERR I, et al. Investigation of perfluoroalkyl substances in proglacial rivers and permafrost seep in a high Arctic watershed [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2022, 24(1): 42-51. [43] FUJII S, POLPRASERT C, TANAKA S, et al. New POPs in the water environment: Distribution, bioaccumulation and treatment of perfluorinated compounds - a review paper [J]. Journal of Water Supply:Research and Technology-Aqua, 2007, 56(5): 313-326. doi: 10.2166/aqua.2007.005 [44] LI X Q, HUA Z L, ZHANG J Y, et al. Interactions between dissolved organic matter and perfluoroalkyl acids in natural rivers and lakes: A case study of the northwest of Taihu Lake Basin, China [J]. Water Research, 2022, 216: 118324. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118324 [45] LIU Z Z, ZHOU J Q, XU Y L, et al. Distributions and sources of traditional and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances among multiple environmental media in the Qiantang River watershed, China [J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(33): 21247-21254. doi: 10.1039/D2RA02385G [46] 杜国勇, 蒋小萍, 卓丽, 等. 长江流域重庆段水体中全氟化合物的污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(11): 2266-2272. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.11.016 DU G Y, JIANG X P, ZHUO L, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of perfluorinated compounds in surface water from Chongqing section of the Yangtze River [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(11): 2266-2272(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.11.016
[47] 王鑫璇, 张鸿, 王艳萍, 等. 中国七大流域全氟烷基酸污染水平与饮水暴露风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 703-710. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705100 WANG X X, ZHANG H, WANG Y P, et al. Contamination levels and exposure risk via drinking water from perfluoroalkyl acids in seven major drainage basins of China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(2): 703-710(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705100
[48] PÉTRÉ M A, SALK K R, STAPLETON H M, et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river discharge: Modeling loads upstream and downstream of a PFAS manufacturing plant in the Cape Fear watershed, North Carolina [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 831: 154763. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154763 [49] WANG F, ZHUANG Y R, DONG B Q, et al. Review on per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) pollution characteristics and possible sources in surface water and precipitation of China [J]. Water, 2022, 14(5): 812. doi: 10.3390/w14050812 [50] JOERSS H, MENGER F, TANG J H, et al. Beyond the tip of the iceberg: suspect screening reveals point source-specific patterns of emerging and novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in German and Chinese rivers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(9): 5456-5465. [51] QU Y X, HUANG J, WILLAND W, et al. Occurrence, removal and emission of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs) from chrome plating industry: A case study in Southeast China [J]. Emerging Contaminants, 2020, 6: 376-384. doi: 10.1016/j.emcon.2020.10.001 [52] PAN Y T, ZHANG H X, CUI Q Q, et al. Worldwide distribution of novel perfluoroether carboxylic and sulfonic acids in surface water [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(14): 7621-7629. [53] WANG T, VESTERGREN R, HERZKE D, et al. Levels, isomer profiles, and estimated riverine mass discharges of perfluoroalkyl acids and fluorinated alternatives at the mouths of Chinese Rivers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(21): 11584-11592. [54] MARCHIANDI J, SZABO D, DAGNINO S, et al. Occurrence and fate of legacy and novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in freshwater after an industrial fire of unknown chemical stockpiles [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 278: 116839. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116839 [55] SUN M, AREVALO E, STRYNAR M, et al. Legacy and emerging perfluoroalkyl substances are important drinking water contaminants in the Cape Fear River watershed of north Carolina [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2016, 3(12): 415-419. [56] STRYNAR M, DAGNINO S, MCMAHEN R, et al. Identification of novel perfluoroalkyl ether carboxylic acids (PFECAs) and sulfonic acids (PFESAs) in natural waters using accurate mass time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(19): 11622-11630. [57] LIN K, HAN T Z, WANG R, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution, ecological risk assessment and source analysis of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Bohai Bay, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 300: 134378. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134378 [58] HAN T Z, CHEN J H, LIN K, et al. Spatial distribution, vertical profiles and transport of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 437: 129264. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129264 [59] JOERSS H, XIE Z Y, WAGNER C C, et al. Transport of legacy perfluoroalkyl substances and the replacement compound HFPO-DA through the Atlantic gateway to the Arctic Ocean - is the Arctic a sink or a source? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(16): 9958-9967. [60] GEBBINK W A, van ASSELDONK L, van LEEUWEN S P J. Presence of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in river and drinking water near a fluorochemical production plant in the Netherlands [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(19): 11057-11065. [61] PAN Y T, ZHANG H X, CUI Q Q, et al. First report on the occurrence and bioaccumulation of hexafluoropropylene oxide trimer acid: An emerging concern [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(17): 9553-9560. [62] LI Y, FENG X M, ZHOU J, et al. Occurrence and source apportionment of novel and legacy poly/perfluoroalkyl substances in Hai River Basin in China using receptor models and isomeric fingerprints [J]. Water Research, 2020, 168: 115145. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115145 [63] LIN Y F, RUAN T, LIU A F, et al. Identification of novel hydrogen-substituted polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonates in environmental matrices near metal-plating facilities [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(20): 11588-11596. [64] ZHAO Z, XIE Z Y, MÖLLER A, et al. Distribution and long-range transport of polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Arctic, Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic coast [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 170: 71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.06.004 [65] GONZÁLEZ-GAYA B, DACHS J, ROSCALES J L, et al. Perfluoroalkylated substances in the global tropical and subtropical surface oceans [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(22): 13076-13084. [66] WEI S, CHEN L Q, TANIYASU S, et al. Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in surface seawaters between Asia and Antarctica [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(11): 1813-1818. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.08.002 [67] BENSKIN J P, MUIR D C G, SCOTT B F, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in the Atlantic and Canadian Arctic Oceans [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(11): 5815-5823. [68] XIE Z Y, ZHAO Z, MÖLLER A, et al. Neutral poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in air and seawater of the North Sea [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(11): 7988-8000. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1757-z [69] HEYDEBRECK F, TANG J H, XIE Z Y, et al. Alternative and legacy perfluoroalkyl substances: Differences between European and Chinese River/estuary systems [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(14): 8386-8395. [70] TANIYASU S, KANNAN K, HORII Y, et al. A survey of perfluorooctane sulfonate and related perfluorinated organic compounds in water, fish, birds, and humans from Japan [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(12): 2634-2639. [71] YAMASHITA N, KANNAN K, TANIYASU S, et al. Analysis of perfluorinated acids at parts-per-quadrillion levels in seawater using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(21): 5522-5528. [72] MARTIN J W, MABURY S A, SOLOMON K R, et al. Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2003, 22(1): 196-204. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620220126 [73] CASAL P, ZHANG Y F, MARTIN J W, et al. Role of snow deposition of perfluoroalkylated substances at coastal Livingston Island (maritime Antarctica) [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(15): 8460-8470. [74] 方淑红, 李成, 卞玉霞, 等. 岷江流域全氟化合物的污染特征及排放通量 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(7): 2983-2989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.035 FANG S H, LI C, BIAN Y X, et al. Pollution characteristics and flux of perfluoroalkyl substances in Minjiang River [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(7): 2983-2989(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.035
[75] 郑宇, 路国慧, 邵鹏威, 等. 青藏高原东部过渡区水环境中全氟化合物的分布特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(5): 1192-1201. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081506 ZHENG Y, LU G H, SHAO P W, et al. Level and distribution of perfluorinated compounds in snow and water samples from the transition zone in eastern Qinghai-Tibet [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1192-1201(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081506
[76] PAN C G, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and mass loadings of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Yangtze River of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 493: 580-587. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.033 [77] 周珍, 胡宇宁, 史亚利, 等. 武汉地区水环境中全氟化合物污染水平及其分布特征 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(3): 425-433. ZHOU Z, HU Y N, SHI Y L, et al. Occurrence and distribution of per-and polufluoroalkyl substances in waste water and surface water samples in Wuhan [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(3): 425-433(in Chinese).
[78] 李珍. 长江中游地区湖泊全氟化合物的污染特征及生态风险评估[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院武汉植物园), 2019. LI Z. Distribution and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in lakes from the middle reach of Yangtze River, China[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019(in Chinese).
[79] GUO C S, ZHANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. Distribution, source characterization and inventory of perfluoroalkyl substances in Taihu Lake, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 127: 201-207. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.053 [80] SUN Z Y, ZHANG C J, YAN H, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and potential sources of perfluoroalkyl acids in Huangpu River, Shanghai, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 174: 127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.122 [81] 宋娇娇, 汪艺梅, 孙静, 等. 沱江流域典型及新兴全氟/多氟化合物的污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9): 4522-4531. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202112227 SONG J J, WANG Y M, SUN J, et al. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of typical and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkylated substances in Tuojiang River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(9): 4522-4531(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202112227
[82] LU G H, JIAO X C, PIAO H T, et al. The extent of the impact of a fluorochemical industrial park in Eastern China on adjacent rural areas [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 74(3): 484-491. doi: 10.1007/s00244-017-0458-x [83] YU L, LIU X D, HUA Z L, et al. Spatial and temporal trends of perfluoroalkyl acids in water bodies: A case study in Taihu Lake, China (2009-2021) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 293: 118575. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118575 [84] HUA Z L, GAO C, ZHANG J Y, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in the aquatic environment of a fluorine industry-impacted region: Spatiotemporal distribution, partition behavior, source, and risk assessment [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159452. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159452 [85] ZHAO Z, CHENG X H, HUA X, et al. Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 114391. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114391 [86] DA SILVA B F, ARISTIZABAL-HENAO J J, AUFMUTH J, et al. Survey of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in surface water collected in Pensacola, FL [J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(8): e10239. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10239 [87] MUNOZ G, GIRAUDEL J, BOTTA F, et al. Spatial distribution and partitioning behavior of selected poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in freshwater ecosystems: A French nationwide survey [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 517: 48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.043 [88] GAO L J, LIU J L, BAO K, et al. Multicompartment occurrence and partitioning of alternative and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an impacted river in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 138753. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138753 [89] ZHOU Y Q, WANG T Y, JIANG Z Z, et al. Ecological effect and risk towards aquatic plants induced by perfluoroalkyl substances: Bridging natural to culturing flora [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 167: 98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.146 [90] DING J, HUA Z L, CHU K J. The effect of hydrodynamic forces of drying/wetting cycles on the release of soluble reactive phosphorus from sediment [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 992-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.016 [91] LU Y, HUA Z L, CHU K J, et al. Distribution behavior and risk assessment of emerging perfluoroalkyl acids in multiple environmental media at Luoma Lake, East China [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 194: 110733. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110733 [92] THACKRAY C P, SELIN N E, YOUNG C J. A global atmospheric chemistry model for the fate and transport of PFCAs and their precursors [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2020, 22(2): 285-293. [93] ARMITAGE J, COUSINS I T, BUCK R C, et al. Modeling global-scale fate and transport of perfluorooctanoate emitted from direct sources [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(22): 6969-6975. [94] BENGTSON NASH S. Perfluorinated compounds in the Antarctic region: Ocean circulation provides prolonged protection from distant sources [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(9): 2985-2991. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.05.024 [95] 鞠晓东. 海洋环境中全氟有机污染物研究的若干进展 [J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(7): 93-99. JU X D. Progress in research on marine environmental pollution of perfluorinated chemicals [J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(7): 93-99(in Chinese).
[96] LOHMANN R, BELKIN I M. Organic pollutants and ocean fronts across the Atlantic Ocean: A review [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2014, 128: 172-184. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2014.08.013 [97] MCLACHLAN M S, HOLMSTROM K E, RETH M, et al. Riverine discharge of perfluorinated carboxylates from the European continent [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(21): 7260-7265. [98] ZHENG H Y, WANG F, ZHAO Z, et al. Distribution profiles of per- and poly fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and their re-regulation by ocean currents in the East and South China Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 125(1-2): 481-486. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.009 [99] YAMASHITA N, KANNAN K, TANIYASU S, et al. A global survey of perfluorinated acids in oceans [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2005, 51(8-12): 658-668. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.04.026 [100] BUSCH J, AHRENS L, XIE Z Y, et al. Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the east Greenland Arctic Ocean [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2010, 12(6): 1242-1246. doi: 10.1039/c002242j [101] SCOTT B F, De SILVA A O, SPENCER C, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in Lake Superior water: Trends and sources [J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 2010, 36(2): 277-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2010.03.003 [102] CHEN H T, REINHARD M, YIN T R, et al. Multi-compartment distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in an urban catchment system [J]. Water Research, 2019, 154: 227-237. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.009 [103] SHAO M H, DING G H, ZHANG J, et al. Occurrence and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water and bottom water of the Shuangtaizi Estuary, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 216: 675-681. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.031 [104] DAUCHY X, BOITEUX V, COLIN A, et al. Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in runoff water and wastewater sampled at a firefighter training area [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2019, 76(2): 206-215. doi: 10.1007/s00244-018-0585-z [105] DAUCHY X, BOITEUX V, COLIN A, et al. Deep seepage of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances through the soil of a firefighter training site and subsequent groundwater contamination [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 214: 729-737. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.003 [106] XIAO F, SIMCIK M F, GULLIVER J S. Perfluoroalkyl acids in urban stormwater runoff: Influence of land use [J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(20): 6601-6608. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.029 [107] BORTHAKUR A, WANG M, HE M, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids on suspended particles: Significant transport pathways in surface runoff, surface waters, and subsurface soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 417: 126159. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126159 [108] CHANSON H, REUNGOAT D, SIMON B, et al. High-frequency turbulence and suspended sediment concentration measurements in the Garonne River tidal bore [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(2-3): 298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.09.012 [109] ZHAO X L, XIA X H, ZHANG S W, et al. Spatial and vertical variations of perfluoroalkyl substances in sediments of the Haihe River, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(8): 1557-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.023 [110] WANG S Q, CAI Y Z, MA L Y, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and fish from a subtropical river of China: Environmental behaviors and potential risk [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 288: 132513. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132513 [111] NAKATA H, KANNAN K, NASU T, et al. Perfluorinated contaminants in sediments and aquatic organisms collected from shallow water and tidal flat areas of the Ariake Sea, Japan: Environmental fate of perfluorooctane sulfonate in aquatic ecosystems [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(16): 4916-4921. [112] CHEN C E, YANG Y Y, ZHAO J L, et al. Legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the West River and North River, south China: Occurrence, fate, spatio-temporal variations and potential sources [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 283: 131301. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131301 [113] HIGGINS C P, LUTHY R G. Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23): 7251-7256. [114] LEE Y M, LEE J Y, KIM M K, et al. Concentration and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Asan Lake area of South Korea [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 381: 120909. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120909 [115] CAI W W, NAVARRO D A, DU J, et al. Increasing ionic strength and valency of cations enhance sorption through hydrophobic interactions of PFAS with soil surfaces [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 817: 152975. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152975 [116] LABADIE P, CHEVREUIL M. Biogeochemical dynamics of perfluorinated alkyl acids and sulfonates in the River Seine (Paris, France) under contrasting hydrological conditions [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(12): 3634-3639. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.028 [117] MUNOZ G, BUDZINSKI H, LABADIE P. Influence of environmental factors on the fate of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances along the salinity/turbidity gradient of a macrotidal estuary [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(21): 12347-12357. [118] 罗雪梅, 杨志峰, 何孟常, 等. 土壤/沉积物中天然有机质对疏水性有机污染物的吸附作用 [J]. 土壤, 2005, 37(1): 25-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2005.01.005 LUO X M, YANG Z F, HE M C, et al. Sorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants by natural organic matter in soils and sediments [J]. Soils, 2005, 37(1): 25-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2005.01.005
[119] HUANG W L, YOUNG T M, SCHLAUTMAN M A, et al. A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 9. general isotherm nonlinearity and applicability of the dual reactive domain model [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(6): 1703-1710. [120] ZHANG R M, YAN W, JING C Y. Experimental and molecular dynamic simulation study of perfluorooctane sulfonate adsorption on soil and sediment components [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 29: 131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2014.11.001 [121] PAN G, ZHOU Q, LUAN X, et al. Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in Lake Taihu (China): Impact to human health and water standards [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 487: 778-784. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.100 [122] ZHAO L X, BIAN J N, ZHANG Y H, et al. Comparison of the sorption behaviors and mechanisms of perfluorosulfonates and perfluorocarboxylic acids on three kinds of clay minerals [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 114: 51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.098 [123] GAO X D, CHOROVER J. Adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid to iron oxide surfaces as studied by flow-through ATR-FTIR spectroscopy [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 9(2): 148. doi: 10.1071/EN11119 [124] KASPRZYK-HORDERN B. Chemistry of alumina, reactions in aqueous solution and its application in water treatment [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 110(1): 19-48. [125] JOHNSON R L, ANSCHUTZ A J, SMOLEN J M, et al. The adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate onto sand, clay, and iron oxide surfaces [J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2007, 52(4): 1165-1170. [126] MUKHOPADHYAY R, SARKAR B, PALANSOORIYA K N, et al. Natural and engineered clays and clay minerals for the removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances from water: State-of-the-art and future perspectives [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 297: 102537. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2021.102537 [127] YOU C, JIA C X, PAN G. Effect of salinity and sediment characteristics on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment-water interface [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(5): 1343-1347. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.009 [128] LI Y S, OLIVER D P, KOOKANA R S. A critical analysis of published data to discern the role of soil and sediment properties in determining sorption of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 628-629: 110-120. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.167 [129] WANG F, SHIH K. Adsorption of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on alumina: Influence of solution pH and cations [J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(9): 2925-2930. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.007 [130] PAN G, JIA C X, ZHAO D Y, et al. Effect of cationic and anionic surfactants on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on natural sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(1): 325-330. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.035 [131] 贾成霞, 潘纲, 陈灏. 全氟辛烷磺酸盐在天然水体沉积物中的吸附-解吸行为 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2006, 26(10): 1611-1617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2006.10.006 JIA C X, PAN G, CHEN H. Sorption and desorption behavior of perfluorooctane sulfonate on the natural sediments [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(10): 1611-1617(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2006.10.006
[132] ZHOU Y Q, WANG T Y, LI Q F, et al. Spatial and vertical variations of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in the Bohai and Yellow Seas: Bridging the gap between riverine sources and marine sinks [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 238: 111-120. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.027 [133] AHRENS L, BARBER J L, XIE Z Y, et al. Longitudinal and latitudinal distribution of perfluoroalkyl compounds in the surface water of the Atlantic Ocean [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(9): 3122-3127. [134] LOHMANN R, JURADO E, DIJKSTRA H A, et al. Vertical eddy diffusion as a key mechanism for removing perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) from the global surface oceans [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 179: 88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.006 [135] LUTZ M J, CALDEIRA K, DUNBAR R B, et al. Seasonal rhythms of net primary production and particulate organic carbon flux to depth describe the efficiency of biological pump in the global ocean [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2007, 112(C10): C10011. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003706 [136] ZHANG X M, LOHMANN R, SUNDERLAND E M. Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in seawater and plankton from the northwestern Atlantic margin [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(21): 12348-12356. [137] WOODS J D, ONKEN R. Diurnal variation and primary production in the ocean preliminary results of a Lagrangian ensemble model [J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1982, 4(3): 735-756. doi: 10.1093/plankt/4.3.735 [138] RUDELS B, JONES E P, ANDERSON L G, et al. On the Intermediate Depth Waters of the Arctic Ocean[M]//The Polar Oceans and Their Role in Shaping the Global Environment. 1994: 33-46. [139] ROGERS A D. Environmental change in the deep ocean [J]. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2015, 40: 1-38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-102014-021415 [140] BRUMOVSKÝ M, KARÁSKOVÁ P, BORGHINI M, et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Western Mediterranean Sea waters [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 159: 308-316. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.06.015 [141] STORTINI A M, MARTELLINI T, DEL BUBBA M, et al. N-Alkanes, PAHs and surfactants in the sea surface microlayer and sea water samples of the Gerlache Inlet sea (Antarctica) [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2009, 92(1): 37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2008.11.005 [142] COSTANZA J, ARSHADI M, ABRIOLA L M, et al. Accumulation of PFOA and PFOS at the air-water interface [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2019, 6(8): 487-491. [143] SHA B, JOHANSSON J H, BENSKIN J P, et al. Influence of water concentrations of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) on their size-resolved enrichment in Nascent sea spray aerosols [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(14): 9489-9497. [144] CASAS G, MARTÍNEZ-VARELA A, ROSCALES J L, et al. Enrichment of perfluoroalkyl substances in the sea-surface microlayer and sea-spray aerosols in the Southern Ocean [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 267: 115512. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115512 [145] WANG S Q, LIN X, LI Q, et al. Particle size distribution, wet deposition and scavenging effect of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the atmosphere from a subtropical city of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153528. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153528 [146] CHEN M, WANG Q, SHAN G Q, et al. Occurrence, partitioning and bioaccumulation of emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Taihu Lake, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.301 [147] 温馨. 我国重点流域和重点地区饮用水中全氟化合物污染水平调查研究[D]. 北京: 中国疾病预防控制中心, 2020. WEN X. Investigation on the pollution level of perfluorinated compounds in drinking water in key river basins and regions in China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020(in Chinese).
[148] HAN T Z, GAO L Y, CHEN J H, et al. Spatiotemporal variations, sources and health risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in a temperate bay adjacent to metropolis, North China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 115011. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115011 [149] CAI Y Z, WANG X H, WU Y L, et al. Temporal trends and transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a subtropical estuary: Jiulong River Estuary, Fujian, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 263-270. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.042 [150] FURDUI V I, CROZIER P W, REINER E J, et al. Trace level determination of perfluorinated compounds in water by direct injection [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(1): S24-S30. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.085 [151] LIU W X, HE W, QIN N, et al. Temporal-spatial distributions and ecological risks of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in the surface water from the fifth-largest freshwater lake in China (Lake Chaohu) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 200: 24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.028 [152] CHEN S Q, YAN M, CHEN Y, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the surface water and fishes in Chaohu Lake, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(50): 75907-75920. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20753-6 [153] GEWURTZ S B, BRADLEY L E, BACKUS S, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in great lakes precipitation and surface water (2006-2018) indicate response to phase-outs, regulatory action, and variability in fate and transport processes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(15): 8543-8552. [154] ZHAO Z, XIE Z Y, TANG J H, et al. Seasonal variations and spatial distributions of perfluoroalkyl substances in the rivers Elbe and lower Weser and the North Sea [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 129: 118-125. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.050 [155] SHAFIQUE U, SCHULZE S, SLAWIK C, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in aqueous samples from Germany and Kenya [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(12): 11031-11043. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7076-4 [156] LI L, ZHAI Z H, LIU J G, et al. Estimating industrial and domestic environmental releases of perfluorooctanoic acid and its salts in China from 2004 to 2012 [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 129: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.049 [157] CHEN H R, PENG H, YANG M, et al. Detection, occurrence, and fate of fluorotelomer alcohols in municipal wastewater treatment plants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(16): 8953-8961. [158] YAO J Z, SHENG N, GUO Y, et al. Nontargeted identification and temporal trends of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a fluorochemical industrial zone and adjacent Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(12): 7986-7996. [159] SHI B, WANG T Y, YANG H F, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in rapidly developing coastal areas of China and South Korea: Spatiotemporal variation and source apportionment [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 761: 143297. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143297 [160] DU D, LU Y L, ZHOU Y Q, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in water along the entire coastal line of China: Spatial distribution, mass loadings, and worldwide comparisons [J]. Environment International, 2022, 169: 107506. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107506 [161] MENG L Y, SONG B Y, ZHONG H F, et al. Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Bohai Sea and its inflow rivers [J]. Environment International, 2021, 156: 106735. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106735 [162] SHAN G Q, QIAN X, CHEN X, et al. Legacy and emerging per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances in surface seawater from northwestern Pacific to Southern Ocean: Evidences of current and historical release [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 411: 125049. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125049 [163] SLADEN W J L, MENZIE C M, REICHEL W L. DDT residues in Adelie penguins and A crabeater seal from Antarctica [J]. Nature, 1966, 210(5037): 670-673. doi: 10.1038/210670a0 [164] JANE L ESPARTERO L, YAMADA M, FORD J, et al. Health-related toxicity of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Comparison to legacy PFOS and PFOA [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 212: 113431. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113431 [165] ZHAO Z, TANG J H, XIE Z Y, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in riverine and coastal sediments of Laizhou Bay, North China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 447: 415-423. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.095 -



 下载:
下载:










