-
挥发性硫化合物( volatile sulfur compounds, VSCs)能抑制所有有氧细胞线粒体呼吸链末端的细胞色素氧化酶[1],造成细胞窒息,对人体的危害性极大. 司法实践中,硫化氢(H2S)是最常见的VSCs致死毒物,每年全国会有上百人因H2S中毒致死[2 − 3]. H2S是一种较为常见的神经毒剂,主要依靠呼吸道进入身体,也可以通过皮肤、消化道进行缓慢地吸收. H2S在体内的代谢主要有3条途径:其一,H2S进入人体之后与细胞色素氧化酶等蛋白酶结合,导致蛋白酶失去其原有的作用;其二,硫离子在人体被氧化,形成硫代硫化物、硫酸盐等;其三,H2S甲基化后,生成甲硫醚(dimethyl sulfide, DMS)和甲硫醇(methanethiol, MT),之后甲硫醇会随着时间的推移,逐步转化为甲硫醚[4 − 5]. 第一条途径是导致人体硫化氢中毒的原因,后两条途径为肝脏等器官进行解毒的过程.
因DMS和MT的刺激性气味,很少发生直接摄入而急性中毒的案例,且经过初步检验也易将MT、DMS中毒与H2S中毒区分开。因此,作为H2S在人体内主要的代谢产物,DMS和MT具有一定的标识作用。目前,国内外学者主要通过研究血液中的硫离子、硫代硫酸盐以及硫化血红蛋白等鉴定H2S中毒,如强火生、罗才会、Varlet 、张震等[6 − 9]通过GC-MS或GC-FPD等方法测定血液中的S2-,褚建新、刘春霞等[10 − 11]分别通过分光光度计和荧光探针检测血中的硫化血红蛋白,同时为了提高定量的准确性,Maseda等[12]通过LC-MS方法测定血液和尿液中的硫代硫酸盐. 但是上述方法均存在重复性差、操作复杂等缺点。为了避免此类问题,需对H2S甲基化产生的DMS、MT进行分析. 基于相关文献可知[5,9],在人体内检测出H2S、DMS和MT的存在,可为H2S中毒做出判断. 国内外主要是采用气相色谱-质谱(gas chromatography mass spectrometry, GC-MS)法和气相色谱法检验DMS和MT,王芳琳、吴颖娟[13 − 14]采用GC-MS分别对血中的MT和废水中的DMS进行定性定量,张立江、Ábalos等[15 − 16]采用顶空气相色谱的方法对废水中的DMS、MT进行检验,并对挥发性硫化物性质进行较为全面的研究.
顶空气相色谱法(HS-GC)是一种联合操作技术,采用顶空萃取,可专一性收集样品中的易挥发性成分[17]. HS-GC具有较高的灵敏度和比较迅速的分析速度,可降低共提物引起的干扰,且操作简便[18]. 其简便性、快捷性和准确性满足鉴定机构的检验要求,因此本文拟建立全血中DMS和MT的顶空气相色谱检验方法,以期为公安机关处理硫化氢中毒案件和安全生产等方面提供理论依据和方法支撑.
-
Agilent 7890B气相色谱仪(美国安捷伦公司);Agilent 7697A顶空进样器(美国安捷伦公司);Agilent J&W GS-GasPro(30 m×320 μm×5 μm)毛细管柱(美国安捷伦公司).
-
甲硫醚、甲硫醇:色谱纯级,>99.7 %,上海麦克林生化公司;无氧水:实验当天将高纯N2通入到去离子水中进行脱氧 15 min 以制备无氧水;饱和硼砂(Na2B4O7)溶液:称取足量的Na2B4O7,加入无氧水100mL 溶解,充分超声振荡,自然静置后,取上层清澈溶液[19];0.1 %氢氧化钠溶液配制:用电子天平称取0.1 g NaOH固体加入99.9 mL无氧水中[20].
-
硫化氢中毒致死者的全血样本:经公安部物证鉴定中心同意,样本取自于2021年7月—2022年1月因硫化氢中毒而死亡的5起案件,检材样本为心血,并及时在-20 ℃环境下冷冻保存以延缓腐败. 15份血液样本的基本信息见表1. 空白血液样本:50份健康成年人血液,冷冻保存. 其他血液样本:选取20份其他死因中毒血样,冷冻保存.
-
在10 mL顶空瓶中依次加入0.5 mL待测血液样品、0.2 mL的20 %硫酸溶液、0.15 g 氯化钠、1 mL无氧水稀释,及时密封.
-
(1)色谱条件:进样口温度250 ℃,分流模式,分流比10:1,载气为氮气,采用gas-pro毛细管柱,流量为0.5 mL·min−1;柱温升温程序为起始温度50 ℃,保持2 min后,以20 ℃·min−1升至250 ℃,保持2 min,平衡时间1 min;尾吹气为高纯氮气,恒流60 mL·min−1;FPD检测器,温度为270 ℃;空气流量为恒流60 mL·min−1;氢气燃气流量为恒流60 mL·min−1.
(2)顶空进样器条件:加热箱温度为60 ℃,样品瓶平衡时间为15 min,定量环温度为80 ℃,传输线温度为95 ℃.
-
本次实验考察了ALC-1、gas-pro和plot-q三种色谱柱,而ALC-1对于DMS和MT的保留能力较差,plot-q的峰容易出现拖尾现象,响应值较差. 结合文献[9]和实际操作发现Agilent J&W GS-Gas-Pro(30 m×0.32 mm×5 μm)对于DMS、MT和溶剂峰有着较好地分离,且色谱柱的流失较少,所以本实验选择gas-pro强极性色谱柱.
-
本次实验比较了电子捕获检测器(ECD)、氢火焰离子化检测器(FID)和火焰光度检测器(FPD). 以往的研究表明FPD、ECD具有较高的灵敏度,其中FPD对于含硫、磷的物质具有较强的选择性;而ECD对电负性强的物质有较高灵敏度,但硫化物的电负性并不高,在实际检测中灵敏度不如FPD. 在温度较高时,易受溶剂蒸气的污染,以致于减少仪器使用寿命[5]. 所以本实验选择的检测器为FPD,经优化后将其温度参数设置为270 ℃,空气流量为恒流60 mL·min−1,氢气燃气流量为恒流60 mL·min−1.
-
随着储存时间的增加,硫化氢中毒血样会产生二硫化碳等有机物,这些硫化物会干扰FPD检测器对甲硫醚和甲硫醇的检验效果,因此,本实验决定对DMS、MT所在的酸碱环境进行研究,以期达到最优的提取效果.
分别取6份0.5 mL DMS浓度依次为0.01、0.2、0.8 μg·mL−1血样装入顶空瓶中,分别加入空白去离子水、20%硫酸溶液、10%磷酸溶液、三氯乙酸溶液、饱和硼砂溶液、0.1%氢氧化钠溶液,以满足中性、酸性、碱性的测定环境. 具体结果见表2.
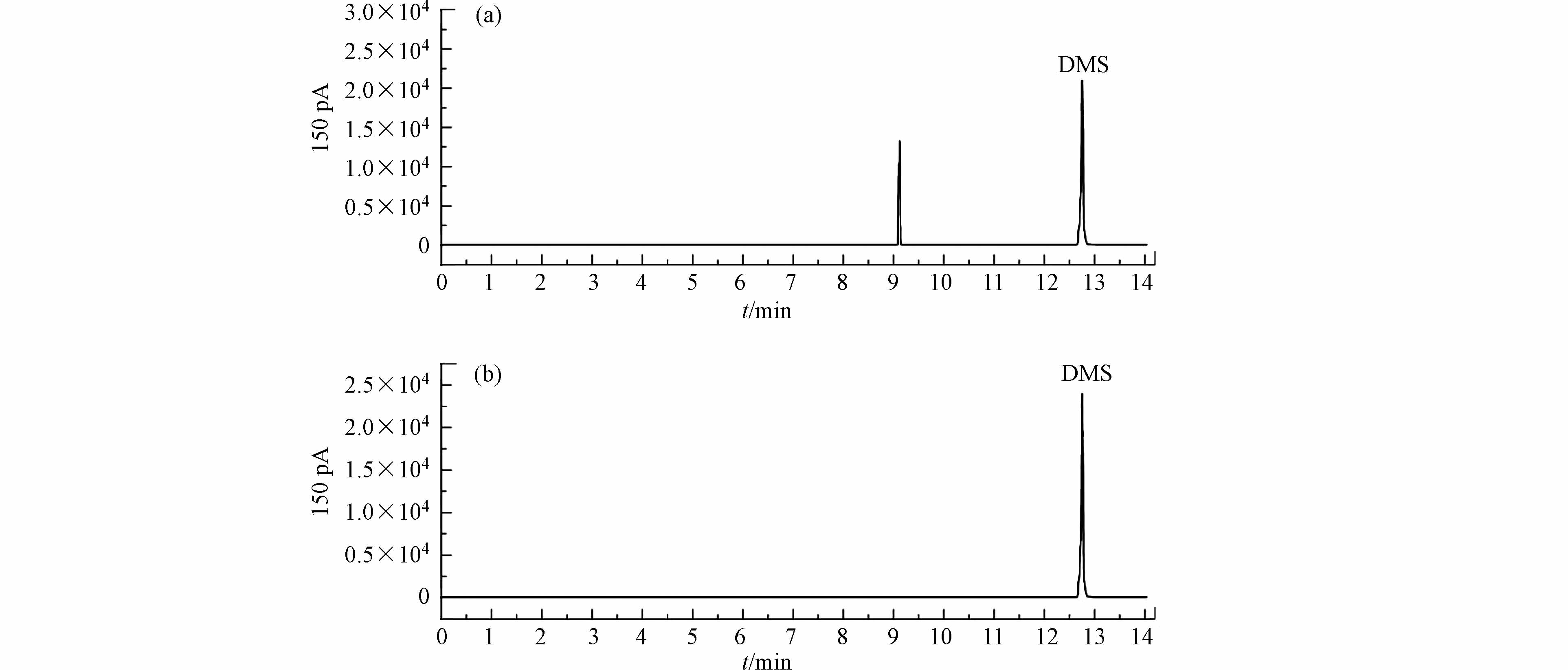
根据表2中数据所示,样品经去离子水稀释后可以显现出DMS,但是其响应值较低,灵敏度不足,实操性较差;饱和硼砂溶液和0.1%氢氧化钠溶液提供的碱性环境不利于醚类和醇类化合物的挥发造成DMS的响应值大幅度降低;磷酸为弱酸,同样不利于待测物的挥发,使得DMS的分析结果较差;三氯乙酸溶液可以很好地提高DMS的GC响应值,但高温环境会使一部分三氯乙酸生成氯仿,对检测器造成污染,具体数据和效果如表2、图1(a)所示;20%硫酸溶液可以有效地提高DMS的响应值,并且杂质峰较少,具体数据和效果如表2、图1(b)所示. 因此,本次实验选择20%硫酸溶液作为酸性介质,检验环境为酸性溶液.
此外,实际操作发现,由于MT的沸点较低(6 ℃),常温下容易挥发. 实验室常温下配制的标准溶液,准确性非常差,虽然可以使用冷藏的溶剂测得其标准曲线,但是重现效果较差,且所得数据不稳定. 结合实际检验工作的条件,含MT的H2S中毒血不可能保存完好. 因此,本实验决定不再研究MT的定量方法,但根据保留时间可以对MT进行定性.
同时,本实验对20 %硫酸溶剂加入量进行考察,发现加入0.2 mL效果最好,因此,本实验选择加入0.2 mL 20 %的硫酸溶液.
-
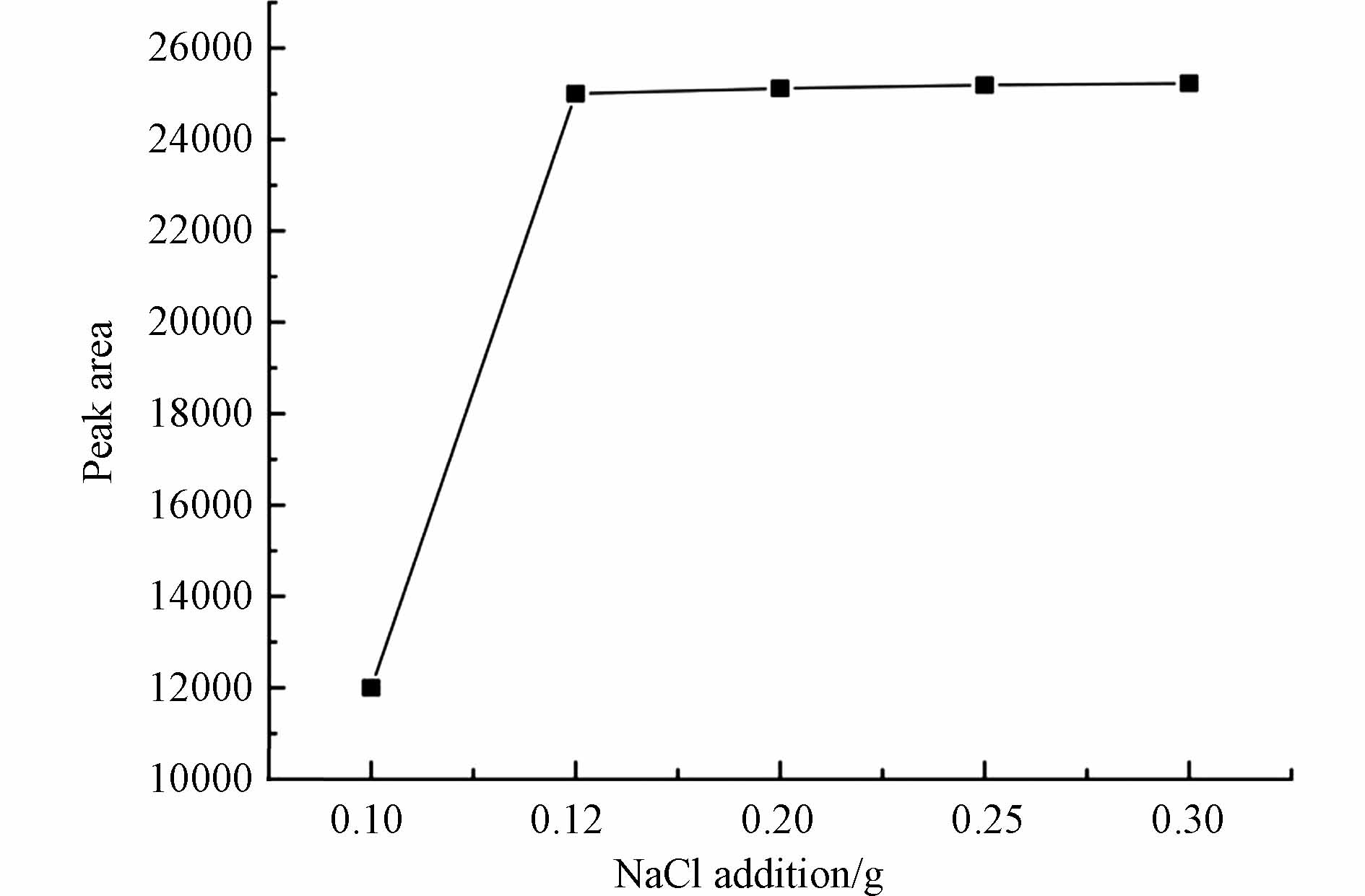
本实验就离子强度对实验结果的影响进行了考察,加入0.1—0.3 g的NaCl使得DMS的响应值得到了较好提升,当加入量在0.15 g以上时,虽然峰面积也有升高,但是提升效果不明显,且加入0.15 g NaCl的效果已达到检验工作的标准,为了减少资源浪费,本实验选择0.15 g NaCl添加量,具体见图2.
-
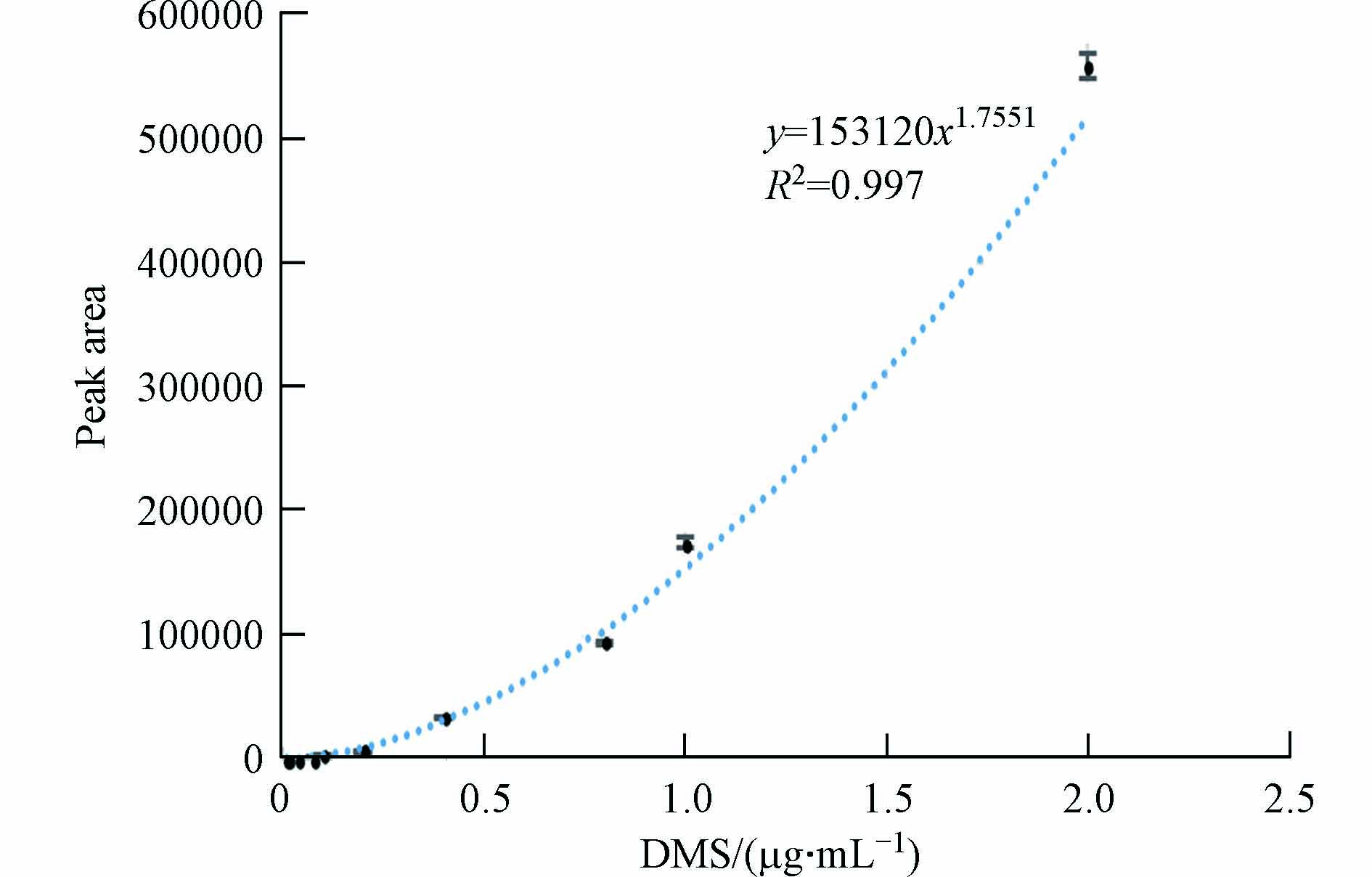
取空白血,添加DMS标准物质配制成含0.01、0.02、0.04、0.08、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.0、2.0 μg·mL−1 DMS的血液样品,使用“1.4”前处理方法处理,做3组平行实验. 以血样的DMS浓度为横坐标,所得的峰面积为纵坐标,得到DMS血样包含误差棒的标准曲线,通过测定检出限(LOD)和定量限(LOQ)来评价该方法的灵敏度,以信噪比3:1为LOD,以信噪比10:1为LOQ[21 − 22]. 结果见表3和图3. 由图3可知,在0.01—2.00 μg·mL−1 范围内呈幂指数.
-
按照考察所得的全血中DMS检测方法,使用相对标准偏差(RSD)表示精密度. 配制DMS低、中、高 3 种浓度的标准溶液,且连续7 d进行相同操作,得到日内日间精密度,结果见表4. 相对标准偏差落在1.6%—3.6%之间,表示仪器处于较为稳定的状态,满足实际工作需要.
-
使用“1.4”前处理方法处理50份健康成人血样,基于所得实验结果,50份空白血样中仅含有H2S,并未检测出DMS和MT的存在. 结合文献[5]分析其原因,随着储存血样时间的推移,腐败产生的H2S逐渐增多,但由于血样脱离人体,细胞失去活性、代谢停止,使得H2S不能进行甲基化反应得到DMS和MT. 因此,在空白血样中并未检测出DMS和MT的存在.
-
将收集到的20份其他死因中毒血样,按照本实验考察所得的最佳仪器条件、前处理条件进行检验,在其他死因血样中并未检测出DMS和MT的存在,说明其他毒物使人中毒死亡,并不会产生DMS和MT. 因此,本实验判定DMS和MT可能是H2S中毒后特定的代谢产物,研究DMS和MT作为硫化氢中毒的标志物具有重要意义.
但需特别注意的是,在特定案件中,可能存在高浓度DMS和MT的中毒致死案件,此类案件会对于硫化氢中毒起一定的干扰作用,需要结合现场环境及硫化氢中毒后的其他代谢产物,如硫代硫酸盐等进行综合分析判断.
-
采用建立的方法,对硫化氢中毒案件中的血液检材进行检验,结果见表5. 对表5检验结果分析,此五起案件共计15份血样中都存在DMS,浓度范围在0.016—0.430 μg·mL−1之间,位于DMS血样标准曲线的范围,由此证明本实验所建立的方法可以应用到硫化氢中毒案件中DMS的实际案例中.
此外,虽然MT的沸点低,以致于其在室温条件下极易挥发,使得一些H2S中毒血中没能检测出MT,但是本实验发现,其他死因的血样中,都未发现MT的存在,只有H2S中毒血中存在MT. 因此,MT的存在依旧可以作为判断H2S中毒的标志物之一.
-
(1)本实验经过分析空白血样、其他死因血样可知,DMS和MT为人体因硫化氢中毒而死亡的特定代谢物. 但需特别注意的是,在公安实践中,也会发生因吸入高浓度DMS和MT中毒致死的案件,此类血样中也可检测出DMS和MT的存在,对于此类特殊情形,检验人员需要结合相关法医学知识对其进行深入分析,以确定其死因.
(2)关于未来研究硫化氢中毒案件的展望:由于随着时间的推移,尸体、血液会逐渐腐败,因此,在检验硫化氢中毒事故中,尚需建立更加准确的内源性硫化氢、硫代硫酸盐、二硫化碳的阈值,以及研究血液腐败、尸体腐败所产生的硫化氢含量等基础数据.
顶空气相色谱法测定硫化氢中毒血中的甲硫醚和甲硫醇
Determination of dimethyl sulfide and methyl mercaptan in blood by headspace gas chromatography
-
摘要: 甲硫醚和甲硫醇作为硫化氢进入人体之后的主要代谢产物,具有一定的标识作用. 针对血液中甲硫醚和甲硫醇的检验进行研究,建立了顶空气相色谱检验方法. 实验采用对含硫化合物具有高灵敏度的火焰光度检测器(FPD),同时发现向0.5 mL血样中加入0.15 g氯化钠可使检出效率得到提升. 本方法血中甲硫醚的标准曲线范围为0.01—2.00 μg·mL−1,相关系数(R2)为0.997,检出限为0.003 μg·mL−1,定量限为0.01 μg·mL−1. 虽然甲硫醇由于自身沸点太低,不适合对其进行定量分析,但对其进行定性检测,也可为硫化氢中毒提供一定的依据. 本研究建立的方法可直接应用于血液中微量甲硫醚和甲硫醇的检测,从而为硫化氢中毒案件的检验鉴定提供依据.Abstract: Methyl sulfide and methyl mercaptan, as the main metabolites of hydrogen sulfide after entering the human body, have certain marking effects. A headspace gas chromatographic method was developed for the detection of methyl sulfide and methyl mercaptan in blood. A flame photometric detector (FPD) with high sensitivity for sulfur-containing compounds was used, and it was found that the addition of 0.15 g sodium chloride to 0.5 mL of blood sample resulted in improved detection efficiency. The standard curve range of this method was 0.01—2.00 μg·mL−1, the correlation coefficient (R2) was 0.997, the limit of detection was 0.003 μg·mL−1, and the limit of quantification was 0.01 μg·mL−1. Although methyl mercaptan is not suitable for quantitative analysis due to its low boiling point, its qualitative detection can also provide a basis for hydrogen sulfide poisoning. The method developed in this study can be directly applied to the determination of trace amounts of methyl mercaptan and methyl mercaptan in blood, thus providing a basis for the identification of hydrogen sulfide poisoning cases.
-
Key words:
- gas chromatography /
- methyl sulfide /
- methanethiol /
- hydrogen sulfide.
-

-
表 1 15份样本的基本信息
Table 1. Basic information for the 15 samples
案件编号
Sequence number简要案情
Brief case死亡人数
Number of deaths1 2022年1月某地员工矿洞内工作时中毒死亡,之后进入的两位救援人员相继中毒死亡. 3 2 2021年9月某地员工井下作业时中毒死亡. 3 3 2021年7月某地因暴雨导致井位上升,使得居住点临近井位的一家六口全部中毒死亡. 6 4 2021年11月某地梁某在猪饲料厂清理粪池时,中毒死亡. 1 5 2021年10月某地工厂员工下水道作业时中毒死亡. 2 表 2 考察酸碱介质对DMS血样峰面积的影响
Table 2. Examining the effect of acid and base media on the peak area of DMS blood samples
0.01 μg·mL−1 DMS 0.2 μg·mL−1 DMS 0.8 μg·mL−1 DMS 去离子水 0 986 5742 20%硫酸 47 6005 93505 10%磷酸 0 0 0 三氯乙酸 0 2063 19965 饱和硼砂 0 782 5320 0.1%氢氧化钠e 0 0 0 表 3 DMS的相关系数、范围、检出限及定量限
Table 3. Correlation coefficient, range, detection limits and quantification limits of DMS
回归方程
Regression equation范围/(μg·mL−1)
Range相关系数
R2LOD/(μg·mL−1) LOQ/(μg·mL−1) DMS y = 153120x1.755 1 0.01—2.00 0.997 0.003 0.01 表 4 DMS血样的回收率和精密度
Table 4. Recovery rates and precision of DMS blood samples
全血样品浓度/ (μg·mL−1)
Concentrations of whole blood samples回收率/%
Average recovery rateRSD/% 日内精密度
within-day precision日间精密度
Inter-day0.8 96 1.6 2.1 0.2 94 2.8 3.5 0.02 97 2.6 3.6 表 5 硫化氢中毒案件中DMS的含量
Table 5. Content of DMS in hydrogen sulfide poisoning cases
序号
Sequence number死亡人数
Death tollDMS/(μg·mL−1) 是否检出MT
Whether MT is detected① 3 0.430 √ 0.305 √ 0.280 √ ② 3 0.376 √ 0.296 × 0.215 × ③ 6 0.067 × 0.016 × 0.016 × 0.078 √ 0.093 × 0.027 √ ④ 1 0.247 √ ⑤ 2 0.218 √ 0.079 × -
[1] DILEK N, PAPAPETROPOULOS A, TOLIVER-KINSKY T, et al. Hydrogen sulfide: An endogenous regulator of the immune system[J]. Pharmacological Research, 2020, 161: 105119. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105119 [2] 吴凯, 杨相建, 刘春源, 等. 1起硫化氢中毒死亡案例的法医学检验分析[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2013, 28(1): 85. WU K, YANG X J, LIU C Y, et al. Forensic examination and analysis of a death case of hydrogen sulfide poisoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2013, 28(1): 85 (in Chinese).
[3] MAEBASHI K, IWADATE K, SAKAI K, et al. Toxicological analysis of 17 autopsy cases of hydrogen sulfide poisoning resulting from the inhalation of intentionally generated hydrogen sulfide gas[J]. Forensic Science International, 2011, 207(1/2/3): 91-95. [4] 吴娜, 王涤新. 硫化氢中毒机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2010, 23(6): 434-436. WU N, WANG D X. Research progress on mechanism and treatment of hydrogen sulfide poisoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Industrial Medicine, 2010, 23(6): 434-436 (in Chinese).
[5] 张震, 张云峰, 吴小军, 等. 硫化氢中毒检验技术研究进展[J]. 分析试验室, 2022, 1(13): 5-12. ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y F, WU X J, et al. Application of molecular signal detection technology for hydrogen sulfide poisoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2022, 1(13): 5-12 (in Chinese).
[6] 强火生, 陈航, 沈保华, 等. 硫化氢中毒案件中血液硫离子的测定[J]. 法医学杂志, 2017, 33(2): 148-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.02.008 QIANG H S, CHEN H, SHEN B H, et al. Determination of sulfide ion in blood from hydrogen sulfide poisoning cases[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2017, 33(2): 148-153 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.02.008
[7] 罗才会, 李剑波, 于天晓, 等. 气相色谱-质谱法测定硫化氢中毒血液中的硫化物[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2012, 37(12): 1025-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3626.2012.12.001 LUO C H, LI J B, YU T X, et al. Determination of sulfide in the hydrogen sulfide poisoned blood using gas chromatograpy-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chongqing Medical University, 2012, 37(12): 1025-1028 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3626.2012.12.001
[8] VARLET V, GIULIANI N, PALMIERE C, et al. Hydrogen sulfide measurement by headspace-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-GC-MS): Application to gaseous samples and gas dissolved in muscle[J]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 2015, 39(1): 52-57. doi: 10.1093/jat/bku114 [9] 张震, 吴小军, 魏春明, 等. 三氯乙酸酸化HS-GC-FPD法测定血液中的硫化氢[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2022, 37(5): 471-474, 484. doi: 10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2022.05.012 ZHANG Z, WU X J, WEI C M, et al. Determination of hydrogen sulfide in blood by trichloroacetic acid acidification HS-GC-FPD[J]. Chinese Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2022, 37(5): 471-474, 484 (in Chinese). doi: 10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2022.05.012
[10] 褚建新, 满勤, 包朝胜, 等. 分光光度法检测硫化氢中毒血液中的硫化血红蛋白[J]. 法医学杂志, 2003, 19(4): 212-214. CHU J X, MAN Q, BAO C S, et al. Determination of the hemoglobin in poisoned blood by spectrophotometery[J]. Journal of Forensic Medicine, 2003, 19(4): 212-214 (in Chinese).
[11] 刘春霞, 马兴, 魏国华, 等. 一种基于荧光素的高选择性硫化氢荧光探针[J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(10): 1762-1767. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.002 LIU C X, MA X, WEI G H, et al. A fluorescein-based probe for hydrogen sulfide detection with high selectivity[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(10): 1762-1767 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.002
[12] MASEDA C, HAYAKAWA A, OKUDA K, et al. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of thiosulfate in human blood and urine as an indicator of hydrogen sulfide poisoning[J]. Legal Medicine, 2017, 24: 67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2016.12.004 [13] 王芳琳, 王炯, 徐建中. 血中甲硫醇的GC-MS检验[J]. 分析测试学报, 2008, 27(增刊1): 42-44. WANG F L, WANG J, XU J Z. GC-MS analysis of methanethiol in blood[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2008, 27(Sup 1): 42-44 (in Chinese).
[14] 吴颖娟, 陈飒, 邓怡, 等. HS-SPME/GC/MS法测定水中甲硫醚和二甲基三硫醚[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(24): 124-127. WU Y J, CHEN S, DENG Y, et al. Determination of dimethyl sulfide and dimethyl trisulfide in water by headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas ChromatographyMass spectrometry[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2017, 33(24): 124-127 (in Chinese).
[15] 张立江, 冯辉, 景长勇, 等. 顶空气相色谱法测定废水中甲硫醚[J]. 河北工业科技, 2006, 23(1): 31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1534.2006.01.010 ZHANG L J, FENG H, JING C Y, et al. Determination of dimethyl sulfide in wastewater by headspacegas chromatography[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2006, 23(1): 31-33 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1534.2006.01.010
[16] ÁBALOS M, PRIETO X, BAYONA J M. Determination of volatile alkyl sulfides in wastewater by headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2002, 963(1/2): 249-257. [17] 王晓姝. 顶空气相色谱法检测尿液及血浆中亚硝酸盐[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2014. WANG X S. Determination of nitrite in urine and plasma by headspace gas chromatography[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2014 (in Chinese).
[18] 刘俊, 张珊, 闫海军. 自动顶空-气相色谱法测定胶囊中9种荷脑的含量[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2010, 19(19): 27-28. LIU J, ZHANG S, YAN H J. Determination of nine brain brains in capsules by automated headspace-gas chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2010, 19(19): 27-28 (in Chinese).
[19] 马英歌, 孙谦, 李莉, 等. 热脱附结合GC-MS测定大气总悬浮颗粒物中的半挥发性有机物[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1424-1427. MA Y G, SUN Q, LI L, et al. Determination of semi-volatile organic pollutants from atmospheric using Thermal Desorption system with Gas chromatography-mass Spectrometer[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1424-1427 (in Chinese).
[20] 郑烨. 顶空气相色谱直接测定大鼠血样中1-溴丙烷的方法及应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. ZHENG Y. Method and application research of using headspace gas chromatography to directly measure 1-BP concentrations in rats blood[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[21] 谢兰桂, 袁淑胜, 韩小旭, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定药用胶塞中的二甲基二硫代氨基甲酸锌[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3631-3634. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021.11.hjhx202111038 XIE L G, YUAN S S, HAN X X, et al. Determination of zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate in pharmaceutical rubber closures by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 3631-3634 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021.11.hjhx202111038
[22] 侯伟, 张蕾萍, 王继芬, 等. 人体毛发中氯胺酮及其代谢物的超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检验及含量统计分析[J]. 分析测试学报, 2021, 40(10): 1453-1459, 1466. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.21031604 HOU W, ZHANG L P, WANG J F, et al. Determination and statistical analysis of ketamine and its metabolites in human hair by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2021, 40(10): 1453-1459, 1466 (in Chinese). doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.21031604
-



 下载:
下载: