-
地下水是地球自然资源中淡水的主要来源之一,具有分布广泛、变化稳定、水质良好和便于应用等优点. 在我国西北内陆干旱区,地下水往往成为诸多地区不可替代的供水水源[1]. 在漫长的地质演化过程中,地下水与周围的环境(大气、地表水、岩石)进行长期的相互作用从而逐渐形成了与地表水有明显不同的水化学成分[2]. 依据地下水中各项检测指标,结合水文地质条件,综合运用数理统计[3]、piper三线图[4]、Gibbs图[5]、离子比值[6]等方法是研究地下水水化学特征及成因的常用方法,被国内外诸多学者采用. 近年来,随着人类活动的影响加剧,使得地下水化学组分来源趋于复杂化,大多学者采用多元统计分析的方法来探讨影响地下水水化学的主要因子,但因子分析与主成分分析的结果难以定量分析出各指标的贡献程度. Thurston 与 Spengler[7]在1985年提出的绝对主成分得分(APCS)的概念,能够对每个主成分分析结果中各因子的贡献程度进行定量解析,并被广泛运用于大气科学领域[8]、土壤学领域[9]和地下水科学领域中[10].
新疆渭干河流域以农业为主、农牧结合,是新疆重要的粮食与棉花的产地之一. 流域内气候干旱,蒸发强烈,伴随着人类活动加剧,使得渭干河流域盐碱地面积扩大,严重影响当地生产生活. 近年来,相关学者主要对渭干河流域地下水埋深时空变化特征[11]、地下水资源评价[12]和地下水盐化特征[13]等方面进行研究,且目前与地下水相关的研究大多集中在渭干河-库车河三角绿洲处,而针对整个渭干河流域地下水水化学特征及成因的具体论述尚显不足.
因此,本文基于65组浅层地下水样品的水质检测数据对流域浅层地下水水化学类型进行划分,采用绝对主成分得分-多元回归受体模型、Gibbs图解法和离子比值等方法查明研究区浅层地下水中主要离子的来源及影响因素. 全面分析研究区浅层地下水水化学成因,对保护流域地下水环境,实现区域水资源可持续发展有着现实意义.
-
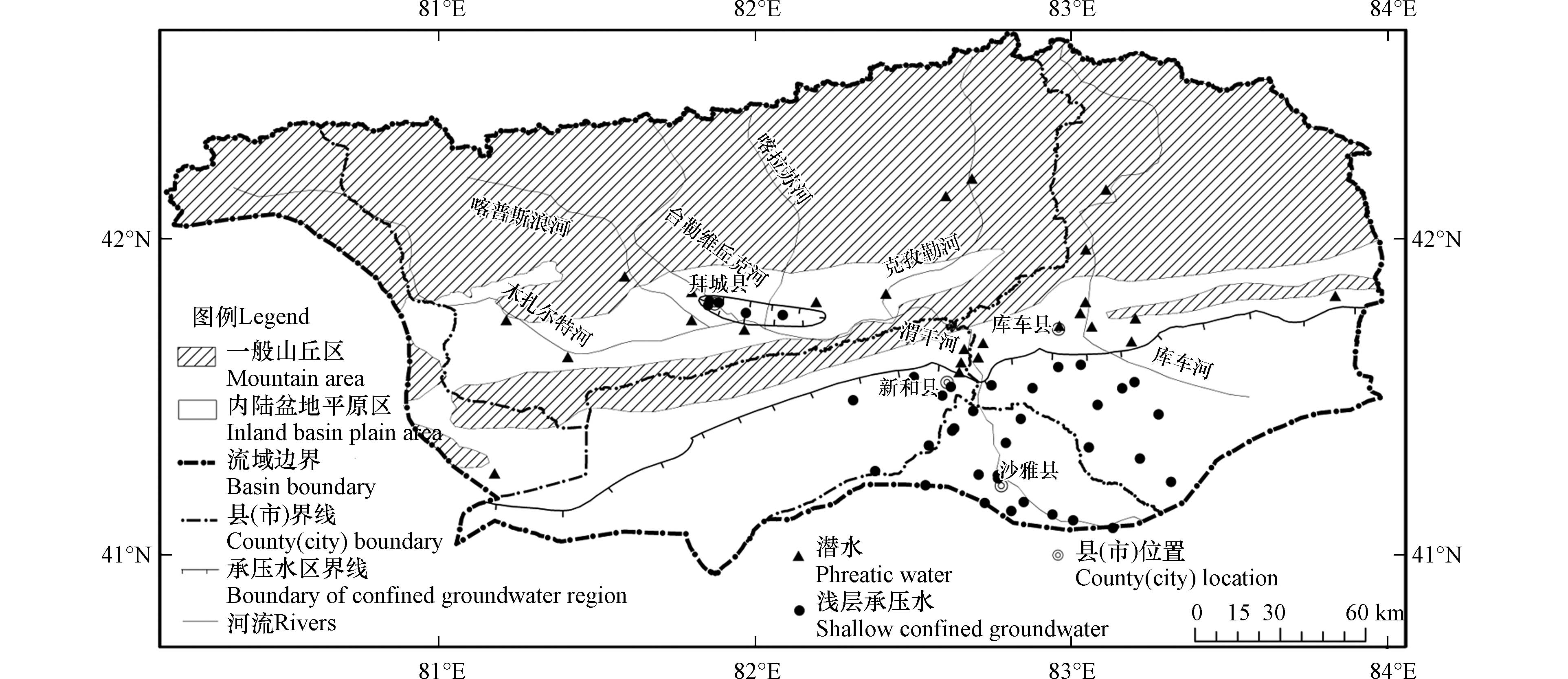
渭干河流域位于塔里木盆地北部,地理坐标位于东经80°13′—84°00′,北纬40°93′—42°65′之间,包括库车县西部、新和县北部、拜城县南部、沙雅县北部和温宿县东部. 流域北部以却勒塔格山为主体,走向自西向东,主要由第三系上新统地构成;中部主要以渭干河冲洪积平原为主;南部则以塔里木河泛滥平原为主,村庄城镇主要分布在流域中南部. 流域内地下水广泛分布于第四系孔隙含水层,其地下水含水结构由北部的单一结构逐渐过渡至南部的多层结构. 北部山区主要被砂卵砾石覆盖,并逐渐向南部的粉细砂过渡. 研究区的弱透水层岩性主要为亚砂土与亚黏土,局部区域存在黏土[13]. 研究区北部山区地下水主要补给途径为山区大气降水、冰雪融水及基岩裂隙水,南部平原区地下水主要补给途径为沿岸渗漏补给[14]. 地下水的排泄方式主要以植物的蒸发蒸腾作用、人为的生活灌溉开采为主.
流域内能源矿产十分丰富,油气田主要分布于塔里木盆地北缘库车-沙雅-拜城一带,煤炭资源主要分布在库车-温宿一带,经过多年发展改造,该地区已成为塔里木盆地开发石油的重要基地. 在土地利用方面主要以农业为主,流域中下游渭-库绿洲耕地面积占总面积62.5%[15].
-
2018年在研究区采集浅层地下水水样65组(其中潜水26组,浅层承压水39组,潜水均为单一结构潜水,承压水区所取水样均为浅层承压水)(图1). 依据《地下水环境监测技术规范(HJ 164-2020)》对水样进行采集、保存与送样. 研究区地下水指标测试由新疆地矿局第二水文地质工程大队实验室完成,各指标检测方法及检出限见表1.
-
利用SPSS 26.0软件进行描述性统计分析,确定地下水中各项水化学指标的特征值. 利用Grapher 11软件绘制Gibbs图、SPSS 26.0软件进行绝对主成分得分-多元线性回归受体模型(APCS-MLR)分析,确定研究区地下水化学成因. 利用Origin 2022软件绘制Durov图对地下水水化学类型进行分类,绘制离子比值图分析各离子来源.
-
APCS-MLR是在因子分析的基础上,将因子分析的各组分得分转变为绝对真实得分(APCS),在通过多元线性回归(MLR)计算确定主因子对各个指标的贡献率[16],其具体过程如下:
(1)对各指标数据进行标准化:
式中,
${Z_{ij}}$ 为标准化后各指标浓度值;${C_{ij}}$ 为各指标浓度实测值;$\overline {{C_i}} $ 为各指标浓度实测平均值;${S_i}$ 为标准偏差.(2)引入一组各指标浓度为0的样本,其公式为:
(3)运用因子分析法,提取出各指标实测数据的主成分,得到取样点的主成分因子得分;结合引入样本
${\left( {{Z_0}} \right)_i}$ 值,得到各指标对应的主成分得分系数;再将各指标实测组分得分减去引入各指标浓度为0的样本的主成分得分系数即得到APCS.(4)将各指标浓度作为因变量,APCS作为自变量进行MLR分析,即可确定各个指标对主成分的贡献率,其公式为:
式中:
${B_{0i}}$ 为第i项的多元线性回归常数项;${{\rm{APCS}}_p}$ 为绝对主成分得分;${{\rm{APCS}}_p} \times {B_{pi}}$ 为组分p对指标浓度${C_i}$ 的贡献值. -
渭干河流域潜水pH变化范围为7.1—8.2,平均值为7.6,浅层承压水pH变化范围为7.1—8.8,平均值为7.7,总体呈现弱碱性(表2). 潜水与浅层承压水中阳离子浓度Na++K+>Ca2+>Mg2+,潜水中阴离子浓度SO42−>HCO3−>Cl−>NO3−,浅层承压水中阴离子浓度SO42−>Cl−>HCO3−>NO3−. 流域内潜水TDS范围为206.0—3476.3 mg·L−1,均值为869.8 mg·L−1,淡水(TDS<1 g·L−1)、微咸水(1 g·L−1<TDS<3 g·L−1)和咸水(3 g·L−1<TDS<10 g·L−1)分别占潜水水样的76.9%、19.2%和3.9%. 浅层承压水TDS范围在276.1—7105.0 mg·L−1,均值为1277.5 mg·L−1,淡水、微咸水和咸水分别占浅层承压水水样的61.5%、28.2%和10.3%. 研究区内浅层地下水以淡水为主,且TDS沿地下水流向呈递增趋势.
流域内浅层地下水TH总体较高,潜水TH范围为138.1—1272.0 mg·L−1,均值为452.1 mg·L−1,浅层承压水TH范围为40.5—2272.0 mg·L−1,均值为519.9 mg·L−1. 流域内潜水中软水(75 mg·L−1 <TH<150 mg·L−1)、微硬水(150 mg·L−1 <TH<300 mg·L−1)、硬水(300 mg·L−1 <TH<450 mg·L−1)和极硬水(TH>450 mg·L−1)分别占潜水水样的11.5%、19.2%、46.2%和23.1%,浅层承压水中占比分别为12.8%、20.5%、20.5%和46.2%.
-
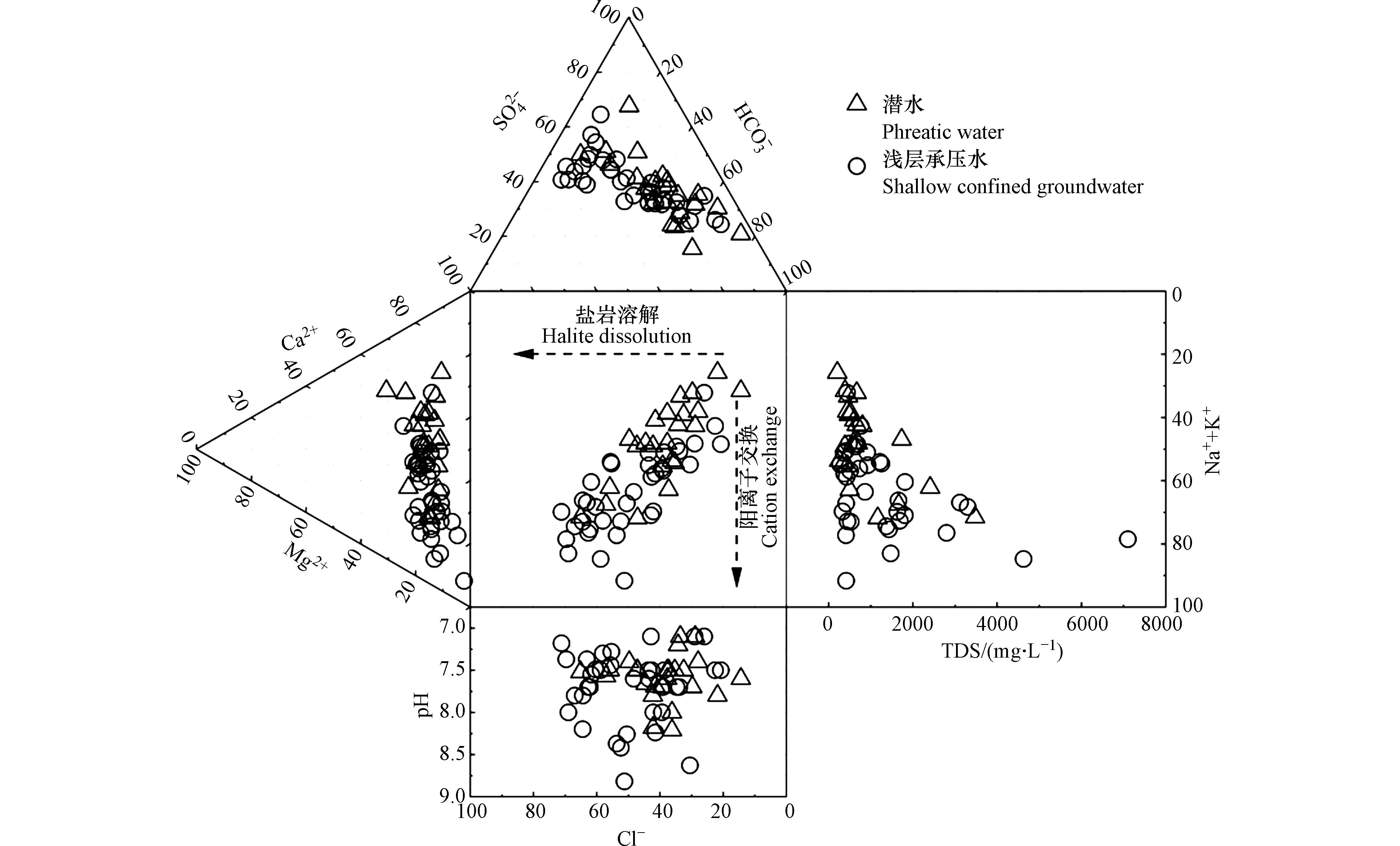
通过渭干河流域地下水化学Durov图(图2)可以看出,潜水水样分布较为分散,水化学类型复杂多样,潜水水化学类型主要为HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca、HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg、HCO3·SO4-Ca和SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型. 浅层承压水阳离子主要靠近Na++K+轴,阴离子则主要靠近SO42−与Cl−轴,从潜水到浅层承压水,水样点逐渐趋向岩盐溶解与阳离子交换,Na+和Cl−逐渐呈主导趋势,浅层承压水水化学类型以SO4·Cl-Na 和HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型为主.
-
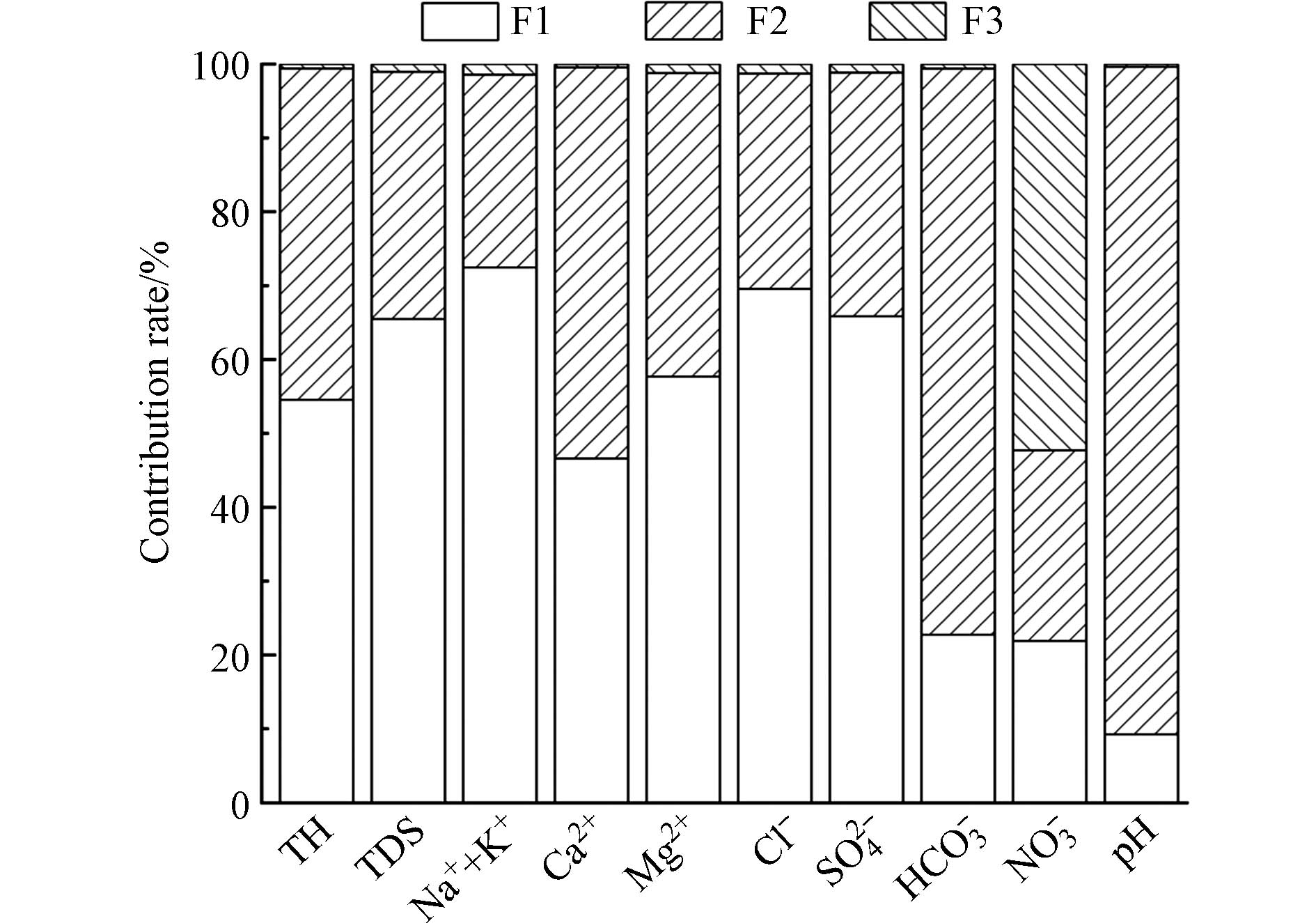
对流域内65组浅层地下水水样的10项指标进行KMO和Bartlett球形检验,检验值为0.674和0,满足KMO>0.50和Bartlett显著性<0.05的标准,表明变量间存在一定的相关性,可以做主成分分析[17]. 在水样中提取出了3个特征值大于1的主成分,贡献率分别为62.81%、20.29%和10.19%,解释累积贡献率93.29%,可基本反映原始样本信息. 使用ACPS-MLR能进一步量化得到各指标的贡献率,研究区浅层地下水的预测值与实测值的R2介于0.692—0.999之间,表明模型基本可靠. 由水化学组分主成分荷载值(表3)与地下水各组分贡献率(图3)可以看出,研究区浅层地下水的F1因子中主要荷载为TH、TDS、Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−和SO42−,各组分贡献率分别为54.6%、65.5%、72.5%、46.6%、57.7%、69.6%和65.9%. 其中TDS的荷载最高,表明水化学组分受天然水文地球化学影响较大,碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩矿物在地下水沿途流动的过程中发生溶解,控制着TDS的大小. 此外,渭干河流域位于西北内陆干旱区,水位埋深较浅,一般为2—6 m[15],潜水蒸发强烈,使得地下水中TDS升高. 因此将F1命名为蒸发浓缩-岩石溶滤因子.
浅层地下水的F2因子中主要载荷为HCO3−和pH,且两者之间呈较强的负相关关系,其水化学组分贡献率分别为76.6%和90.4%. 地下水中的HCO3−主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解,当地下水处于碱性或偏碱性环境时,会促使HCO3−向CO32−转化,即碳酸盐岩的溶解作用受到地下水酸碱度的影响[18]. 因此将F2命名为酸碱环境影响因子.
浅层地下水的F3因子中主要荷载为NO3−,贡献率为52.3%. NO3−能反映人类活动的影响,研究区作为新疆主要的农耕区,农业生产中氮肥的过量使用,以及人类生活中所排放的污水均会导致地下水中NO3−含量增大,因此将F3命名为农业-生活污染因子.
-
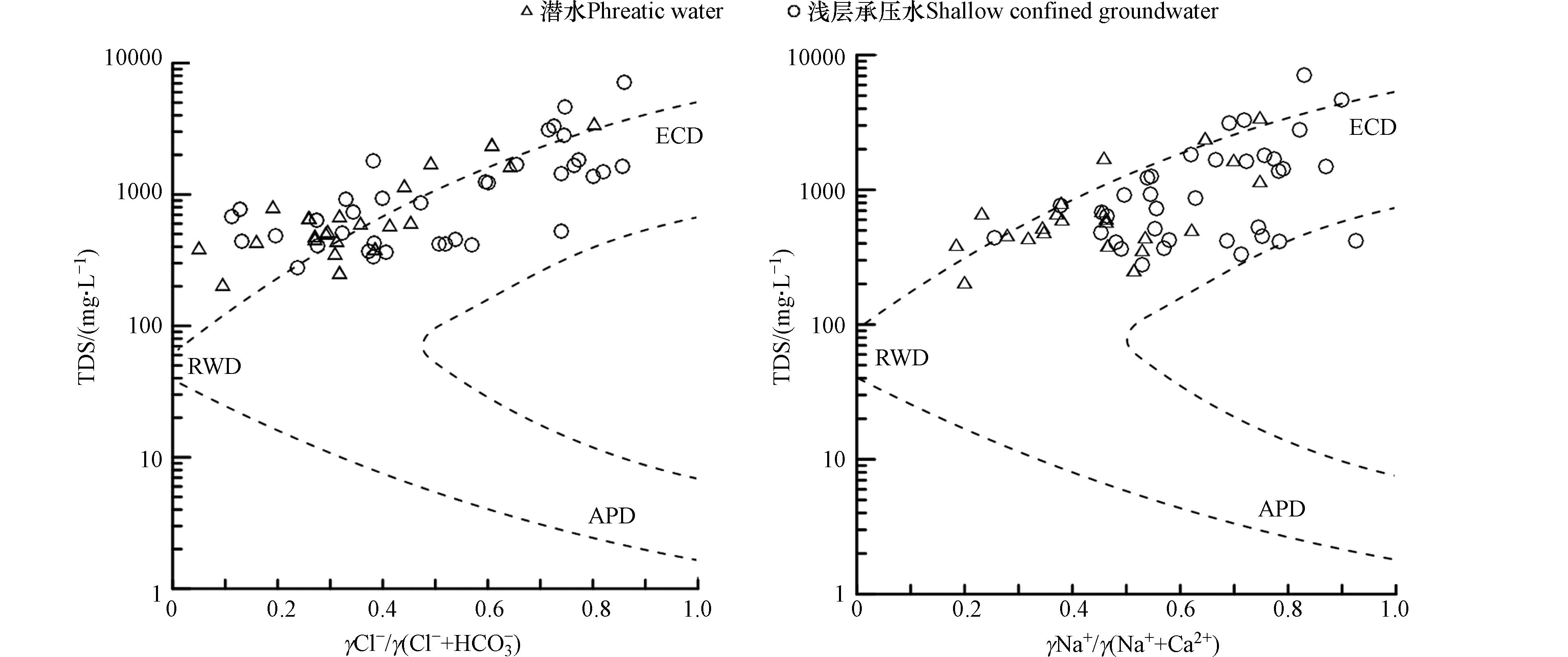
地下水化学组成有多种成因,运用Gibbs图可以判断地下水在演化过程中受到大气降水(APD)、蒸发-浓缩作用(ECD)和岩石溶滤作用(RWD)的影响[19]. 大部分取样点落于ECD区域中,个别取样点落于RWD区域内(图4),表明该区地下水化学主要受到蒸发-浓缩作用,其次受到岩石溶滤作用,这与APCS-MLR源解析中F1因子分析结论一致. Gibbs图中,γNa+/γ(Na++Ca2+)相较于γCl−/γ(Cl−+HCO3−)具有较好的聚集性,且部分样点位于Gibbs图模型范围外,表明研究区在受到蒸发浓缩和岩石溶滤影响以外,还可能受到人类活动和阳离子交换作用的影响.
-
离子比值可以对地下水水化学组分的补给来源做出判别,不同岩石风化会产生不同的离子,通过对各类离子的比值关系进行分析,可以有效的判别出其水文地球化学过程. 通常用混合图来揭示化学风化作用产生的离子[20].
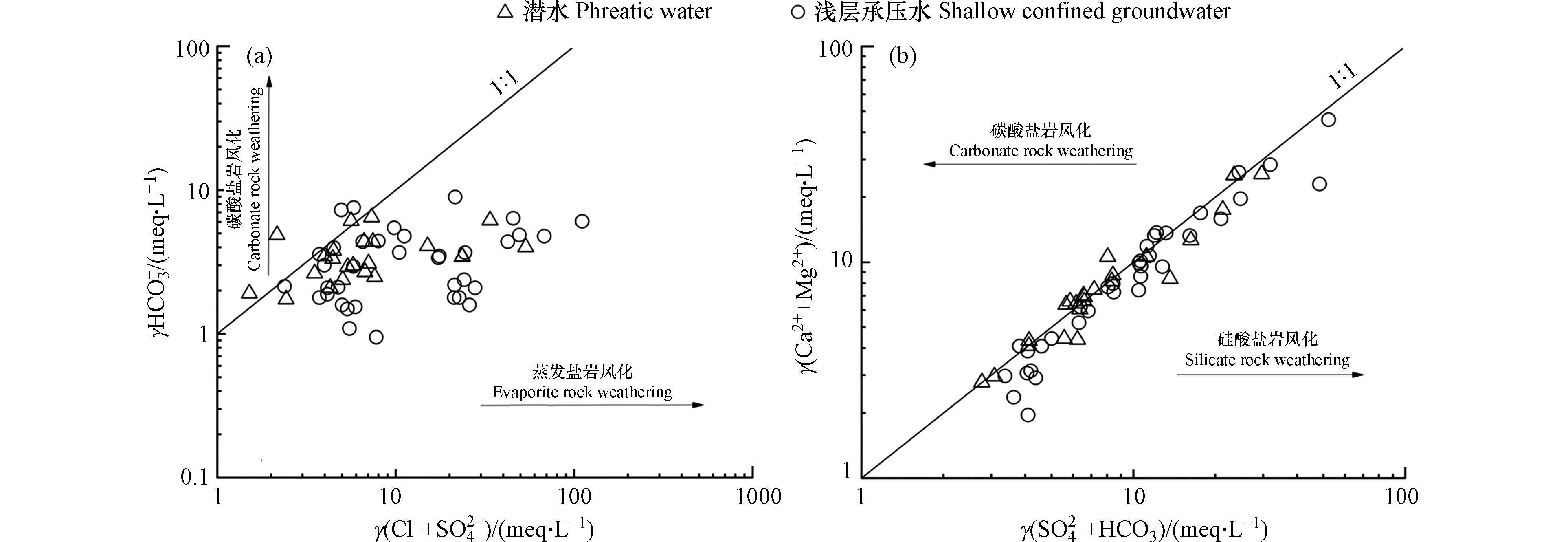
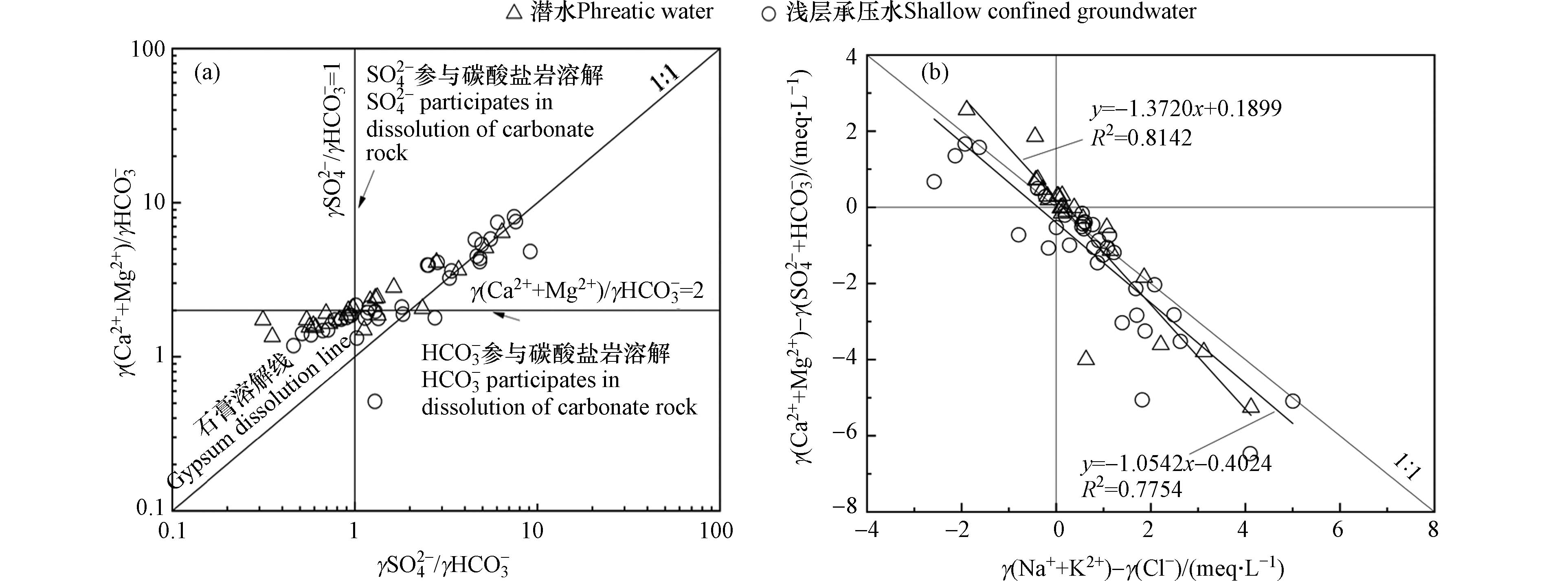
通过γ(Cl−+SO42−)与γHCO3−和γ(SO42−+HCO3−)与γ(Ca2++Mg2+)的离子比例关系能够识别出研究区地下水化学成分所受硅酸盐岩、蒸发盐岩以及碳酸盐岩风化的影响大小[21]. 由图5(a)可知,研究区取样点多数位于蒸发盐岩控制区域,少部分位于碳酸盐岩控制区域,且浅层承压水相较潜水更远离1:1等值线,表明研究区地下水水化学主要成分来源于蒸发盐岩溶解,部分来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解,浅层承压水受蒸发盐岩风化影响程度要高于潜水. 由图5(b)可知,取样点基本位于1:1等值线附近,部分取样点位于硅酸盐岩控制区域,若地下水中的Ca2+、Mg2+、SO42−和HCO3−来源于碳酸盐岩与蒸发盐岩溶解,则阴阳离子之间应当存在电荷平衡,而1:1等值线以下取样点的Ca2+和Mg2+的含量要低于SO42−和HCO3−,则存在其他阳离子(如Na+)来平衡多出来的阴离子的量,表明硅酸盐岩的溶解也会对研究区地下水主要组分的含量起到一定的影响.
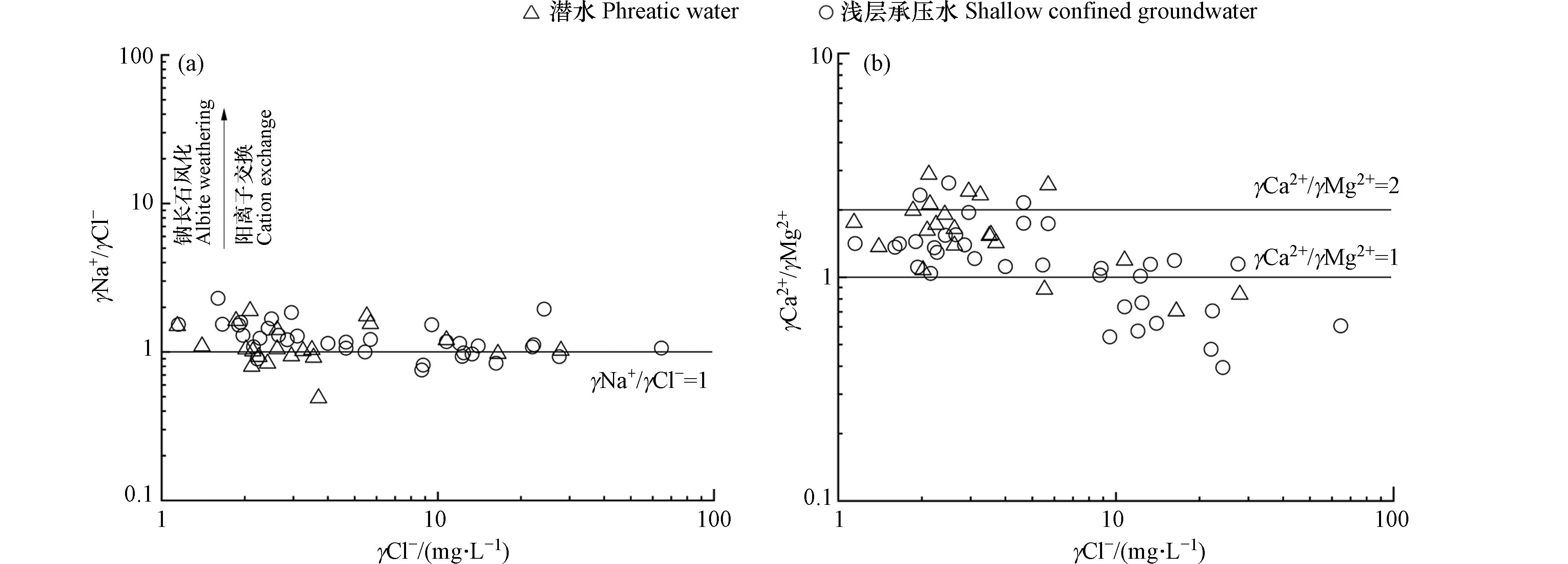
通过γCl−与γNa+/γCl−的离子比关系可以对研究区地下水中的Na+的来源做出判别. 地下水中Na+主要来源于大气降雨与蒸发盐岩和硅酸盐岩的溶解,海水和大气降水的Na+与Cl−比值大约为0.86左右,在未受人类活动影响下岩盐溶解的Na+与Cl−比值大约为1左右[22]. 由图6(a)可知,研究区取样点大多位于γNa+/γCl−=1直线之上,表明研究区Na+除了来源于岩盐溶解之外,还来源于阳离子交换作用和含钠硅酸盐岩的溶解. 部分取样点位于γNa+/γCl−=1直线之下,Cl−在地下水中较为稳定,一般只会在与其他水体混合时才会发生改变,研究区存在大量的灌溉用地,其所属的渭干河-库车三角洲绿洲更存在着大量机井,部分地区单井设计不合理,成井质量不高,使用年限短,报废率高,使隔水层破坏,且长期缺乏维护的机井会使浅层地下水沿井壁下渗,从而导致不同含水层间混合. Ca2+和Mg2+的来源可以通过γCl−与γCa2+/γMg2+的离子比关系判断,若γCa2+/γMg2+=1,则说明Ca2+与Mg2+来源于白云石的溶解;若1<γCa2+/γMg2+<2,则说明有更多的方解石溶解;若γCa2+/γMg2+>2,则说明有硅酸盐岩或石膏溶解[23]. 由图6(b)可知,研究区大部分取样点位于1<γCa2+/γMg2+<2之间,表明方解石的溶解是地下水中Ca2+的主要来源. 部分取样点位于γCa2+/γMg2+=1附近,且浅层承压水相较于潜水更加接近,表明浅层承压水受白云石溶解影响的程度要高于潜水,此外还存在个别取样点位于γCa2+/γMg2+=2之上,表明研究区地下水中的部分Ca2+和Mg2+来源于硅酸盐岩或石膏的溶解. 通过γSO42−/γHCO3−与γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γHCO3−的离子比例关系可以对地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+的来源做出进一步判别. 若γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γHCO3−=2,表明地下水中HCO3−参与碳酸盐岩的溶解;若γSO42−/γHCO3−=1,表明地下水中SO42−参与碳酸盐岩的溶解[24]. 由图7(a)可知,研究区取样点大多位于γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γHCO3−=2附近,表明Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解,部分取样点位于石膏溶解线附近,表明部分Ca2+来源于石膏等蒸发盐岩的溶解.
阳离子交换作用主要发生在Ca2+、Mg2+和Na+之间,通过γ(Na++K+−Cl−)与γ(Ca2++Mg2+-SO42−-HCO3−)之间的比值可以对研究区地下水中的阳离子交换作用做出判别,当两者比值呈负相关时,表明地下水中发生阳离子交换作用[25]. 当取样点趋向于第二象限时,表明Ca2+和Mg2+释放,Na+吸附,即地下水中发生了正向阳离子交换作用;当取样点趋向于第四象限时,则反之. 如图7(b)所示研究区取样点大多位于第四象限,部分位于第二象限,表明研究区地下水中主要发生反向阳离子交换作用. 结合APCS-MLR源解析F2因子,弱碱性环境促进碳酸盐岩的溶解,从而使得Ca2+、Mg2+在水中含量上升,而Ca2+、Mg2+吸附亲和力要高于Na+,导致地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+置换出周围岩土颗粒表面的Na+,使得地下水中Na+相对富集. 潜水分布在斜率为-1.37(R2=0.81)的直线附近,浅层承压水分布在斜率为 -1.05(R2=0.78)的直线附近,表明浅层承压水中的阳离子交换作用要高于潜水.
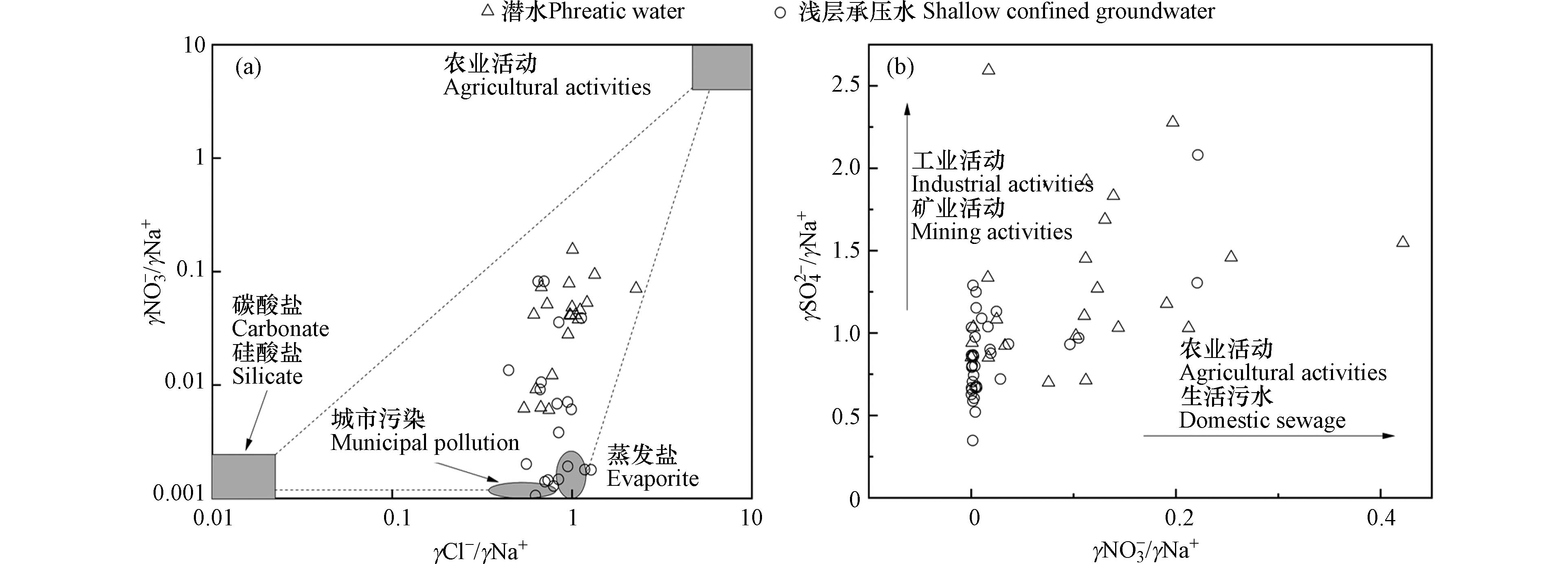
流域内的渭-库三角洲绿洲是新疆的主要粮棉产地之一,更是阿克苏地区最大的灌溉区,农业产业较为发达,此外其上游区域还分布着丰富的矿产资源[26]. 随着地区经济的发展与人口的增长,流域内地下水的化学组分受人类活动的影响越来越大. 一般来说,地下水中γCl−/γNa+和γNO3−/γNa+的比值愈大,地下水化学组成所受人类活动的影响就愈强烈[27]. 研究区浅层地下水水样中Cl−含量相较于Na+含量较高(图8(a)),表明人类活动对该区浅层地下水的化学组分造成了一定的影响,且水样的分布趋向于城市污染的区域,该区城镇人口集中,使浅层地下水受到生活污水的影响较为突出. 这与APCS-MLR源解析F3因子分析结论一致,各类肥料的使用和生活污水的不当处理会对流域内地下水化学组分的形成造成一定的影响. 研究区潜水的γSO42−/γNa+和γNO3−/γNa+明显高于浅层承压水(图8(b)),潜水埋藏较浅,人类活动产生的生活污水、工业废水以及过量使用的农业肥料等,会对潜水的水化学组成造成更大的影响.
-
(1)渭干河流域内地下水总体呈现弱碱性,优势阳离子和阴离子分别是Na++K+和SO42−,潜水水化学类型较为复杂,主要有HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca、HCO3·SO4−Ca、HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg和SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型;浅层承压水水化学类型以SO4·Cl-Na 和HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型为主.
(2)离子比值法与APCS-MLR模型结果表明,渭干河流域中地下水的主要化学组分受到蒸发浓缩作用和岩石溶滤作用的影响. 研究区地下水中Na+主要来源于岩盐的溶解,Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐岩溶解,部分来源于石膏等蒸发盐岩和硅酸盐岩溶解. 此外,Ca2+、Mg2+还与Na+发生了阳离子交换作用,对地下水化学组分产生了一定的影响,且从潜水到浅层承压水的阳离子交换作用呈现增强趋势. 人类活动对流域内浅层地下水的水化学组分产生了一定的影响,且对潜水的影响程度大于浅层承压水.
渭干河流域浅层地下水水化学特征及成因分析
Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in Weigan River Basin
-
摘要: 为探明新疆渭干河流域浅层地下水的水化学特征及其主要离子来源,综合运用数理统计、Durov图、Gibbs图、离子比例系数、绝对主成分得分-多元线性回归受体模型(APCS-MLR)等方法对渭干河流域2018年65组浅层地下水水样的检测数据进行分析. 研究结果表明,流域内多数地下水取样点总硬度偏高,溶解性总固体中等,地下水以淡水为主. 潜水水化学类型种类复杂多变,主要有HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca、SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg、HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg和HCO3·SO4-Ca型;浅层承压水水化学类型以SO4·Cl-Na型与HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg型为主. 流域内地下水形成主要受到蒸发-浓缩作用,其次为岩石溶滤作用,其中Na+主要来自岩盐的溶解,少量来自于硅酸盐岩的溶解,Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解,部分来源于蒸发盐岩和硅酸盐岩的溶解. 此外,阳离子交换作用与人类活动影响对流域内地下水中化学组分的形成也有一定贡献.Abstract: Based on 65 groups of shallow groundwater investigation datas in 2018, mathematical statistics, Durov diagram, Gibbs diagram, ion ratio, and absolute principal component score-multiple linear regression receptor model (APCS-MLR) were used to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics and main ion sources. Results showed that the total hardness of most groundwater samples in the basin was high, the total dissolved solid was medium, and the groundwater was mainly freshwater. The hydrochemistry types of phreatic water were complex and varied, mainly HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca, SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg, HCO3·SO4-Ca and HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg. The hydrochemistry types of shallow confined groundwater were mainly SO4·Cl-Na and HCO3·SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg. The groundwater formation was mainly affected by evaporation-concentration, followed by rock leaching, of which Na+ was mainly derived from the dissolution of halite, and a small amount derived from the dissolution of silicate. Ca2+ and Mg2+ were mainly derived from the dissolution of carbonate rocks, and partly from the dissolution of evaporite rocks and silicate rocks. In addition, cation exchange and human activities had a certain contribution to the formation of chemical components in groundwater.
-
Key words:
- shallow groundwater /
- hydrochemical characteristics /
- ion sources /
- Weigan River Basin.
-

-
表 1 地下水样品检测方法及检出限
Table 1. Test methods and detection limit of groundwater samples
指标
Indexes检测方法
Test methods检出限
Detection limitCl− 硝酸银容量法 0.05 mg·L−1 Ca2+、Mg2+、Mg2+、总硬度(TH,以CaCO3计) 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 K+、Na+ 火焰原子吸收分光光度法 SO42− 硫酸钡比浊法 溶解性总固体(TDS) 电子天平MP8-1测定 0.10 mg·L−1 NO3− 紫外分光光度法 0.20 mg·L−1 pH 玻璃电极法 0.01 表 2 地下水主要水化学指标特征值统计
Table 2. Characteristic value statistics of main hydrochemical indexes of groundwater
地下水类型
Groundwater types统计值
StatisticsTH TDS Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− NO3− pH 潜水
Phreatic water
(n=26)最小值 138.1 206.0 14.1 32.1 7.3 12.3 49.5 106.3 — 7.1 最大值 1272.0 3476.3 714.1 252.6 178.1 990.2 1229.6 394.6 25.2 8.2 均值 452.1 869.8 133.3 102.1 47.9 173.1 285.3 218.0 6.4 7.6 标准差 332.7 794.7 159.4 60.1 48.2 219.6 309.6 85.5 6.7 0.3 变异系数 0.74 0.91 1.20 0.59 1.01 1.27 1.09 0.39 1.05 0.04 浅层承压水
Shallow confined
groundwater(n=39)最小值 40.5 276.1 37.2 10.8 3.3 33.3 59.1 57.7 — 7.1 最大值 2272.0 7105.0 1715.4 345.8 342.0 2287.0 2217.0 546.4 15.1 8.8 均值 519.9 1277.5 255.1 100.1 65.6 314.6 415.1 222.1 1.9 7.7 标准差 427.8 1332.3 325.2 67.0 66.5 405.0 487.7 121.5 3.8 0.4 变异系数 0.82 1.04 1.28 0.67 1.01 1.28 1.17 0.55 2.00 0.05 注:pH为无量纲,其余指标单位为mg·L−1;"—"表示该指标含量低于检出限.
Note: pH value is dimensionless, the other indexes units are mg·L−1; "—" indicates that the index concentration is below the detection limit.表 3 水化学组分主成分荷载值
Table 3. Principal component load value of hydrochemical components
指标
Indexes公因子
Common factorF1 F2 F3 TH 0.914 0.378 −0.041 TDS 0.964 0.247 −0.066 Na++K+ 0.963 0.174 −0.079 Ca2+ 0.823 0.470 0.033 Mg2+ 0.942 0.311 −0.083 Cl− 0.956 0.201 −0.074 SO42− 0.939 0.236 −0.068 HCO3− 0.432 0.732 0.049 NO3− −0.101 0.060 0.993 pH −0.186 −0.917 −0.032 贡献率
Contribution rate62.81% 20.29% 10.19% 累积贡献率
Cumulative contribution rate62.81% 83.10% 93.29% -
[1] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵. 水文地质学基础[M]. 6版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 52. ZHANG R Q, LIANG X, JIN M G. Foundation of hydrogeology[M]. 6th ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011: 52 (in Chinese).
[2] 钱会, 马致远. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005: 2. QIAN H, MA Z Y. Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005: 2 (in Chinese).
[3] 曾小仙, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 石河子市浅层地下水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 68-75. ZENG X X, ZENG Y Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of the shallow groundwater in Shihezi City [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 68-75(in Chinese).
[4] 杨景燕, 杨余辉, 胡义成, 等. 新疆伊犁喀什河流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3815-3827. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042108 YANG J Y, YANG Y H, HU Y C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in Kashi River Basin, Ili, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3815-3827(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042108
[5] 鲁涵, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 新疆祁漫塔格地区地下水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2022, 33(2): 85-92. LU H, ZENG Y Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of the groundwater in Qimantage area of Xinjiang and the formation causes [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2022, 33(2): 85-92(in Chinese).
[6] 丁启振, 雷米, 周金龙, 等. 博尔塔拉河上游河谷地区水化学特征及水质评价 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(3): 829-840. DING Q Z, LEI M, ZHOU J L, et al. An assessment of groundwater, surface water, and hydrochemical characteristics in the upper valley of the Bortala River [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(3): 829-840(in Chinese).
[7] THURSTON G D, SPENGLER J D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston [J]. Atmospheric Environmen, 1985, 19(1): 9-25. doi: 10.1016/0004-6981(85)90132-5 [8] 张海霞, 蔡昂祖, 赵海萍, 等. 基于PMF和APCS-MLR模型的工业城市大气降尘金属源解析及综合污染评价 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(11): 3816-3827. ZHANG H X, CAI A Z, ZHAO H P, et al. Metal source analysis and comprehensive pollution assessment of atmospheric dust in industrial cities based on PMF and APCS-MLR models [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(11): 3816-3827(in Chinese).
[9] 卢鑫, 邝荣禧, 何跃, 等. 基于APCS-MLR模型和地统计学相结合的矿区农田土壤砷源解析 [J]. 土壤, 2022, 54(2): 379-384. LU X, KUANG R X, HE Y, et al. Source apportionment of arsenic in agricultural soils from a typical mining area based on APCS-MLR model and geostatistics [J]. Soils, 2022, 54(2): 379-384(in Chinese).
[10] 孟利, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 基于PCA-APCS-MLR的地下水污染源定量解析研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(10): 3773-3786. MENG L, ZUO R, WANG J S, et al. Quantitative source apportionment of groundwater pollution based on PCA-APCS-MLR [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(10): 3773-3786(in Chinese).
[11] 玉素甫阿吉·克尤木, 买买提·沙吾提. 渭干河灌区地下水埋深时空变化特征分析 [J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2012, 40(12): 37-38. [12] 陈雷, 陈波. 关于渭干河地下水资源评价的探究 [J]. 陕西水利, 2022, 253(2): 38-39,49. [13] 满苏尔·沙比提, 吐尔洪·依明. 渭干河―库车河三角洲绿洲地下水盐化特征及成因分析 [J]. 水文, 2009, 29(6): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2009.06.013 MANSUR S, TUERHON Y. Cause analysis: Salinization characteristics of underground water in delta oasis of the Weigan-Kuche River [J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2009, 29(6): 58-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2009.06.013
[14] 李春梅, 王书峰. 新疆塔里木河生态脆弱区渭干河灌区地下水特征分析 [J]. 中国西部科技, 2010, 9(8): 7-9,43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6396.2010.08.003 LI C M, WANG S F. Analysis of the groundwater characteristics in the Weigan River irrigation area of Tarim River in Xinjiang [J]. Science and Technology of West China, 2010, 9(8): 7-9,43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6396.2010.08.003
[15] WANG W R, CHEN Y N, WANG W H, et al. Evolution characteristics of groundwater and its response to climate and land-cover changes in the oasis of dried-up river in Tarim Basin [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 594: 125644. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125644 [16] 雷米, 周金龙, 梁杏, 等. 新疆天山北麓中段孔隙水水化学特征及苏打水的成因 [J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(2): 674-688. LEI M, ZHOU J L, LIANG X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of pore water and genesis of soda water in the middle of the northern piedmont of Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang [J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(2): 674-688(in Chinese).
[17] RAVISH S, SETIA B, DESWAL S. Groundwater quality analysis of northeastern Haryana using multivariate statistical techniques [J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2020, 95(4): 407-416. doi: 10.1007/s12594-020-1450-z [18] 雷米, 周金龙, 张杰, 等. 新疆博尔塔拉河流域平原区地表水与地下水水化学特征及转化关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 1873-1884. LEI M, ZHOU J L, ZHANG J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and transformation relationship of surface water and groundwater in the plain area of Bortala River Basin, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 1873-1884(in Chinese).
[19] 王慧玮, 郭小娇, 张千千, 等. 滹沱河流域地下水水化学特征演化及成因分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3838-3845. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080301 WANG H W, GUO X J, ZHANG Q Q, et al. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and origin analysis in Hutuo River Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3838-3845(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080301
[20] 张涛, 王明国, 张智印, 等. 然乌湖流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010. ZHANG T, WANG M G, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in ranwu lake basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010(in Chinese).
[21] 余东, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 新疆喀什地区西部潜水水化学特征及演化规律分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2493-2504. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020041301 YU D, ZHOU J L, WEI X, et al. Analysis of chemical characteristics and evolution of phreatic water in Western Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2493-2504(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020041301
[22] 孙英, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 巴楚县平原区地下水水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2601-2609. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121002 SUN Y, ZHOU J L, WEI X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of groundwater in the plain area of Bachu County [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2601-2609(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121002
[23] 鲁涵, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 喀什噶尔河下游平原区地下水咸化特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10): 4459-4469. LU H, ZENG Y Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Characteristics and causes of groundwater salinization in plain area of lower reaches of Kashigar River [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10): 4459-4469(in Chinese).
[24] 吴璇, 宋一心, 王金晓, 等. 山东省柴汶河上游地区地下水化学特征分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(7): 2125-2134. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022701 WU X, SONG Y X, WANG J X, et al. Groundwater hydrogeochemical characteristics in the up reaches of Chaiwen River, Shandong Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(7): 2125-2134(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022701
[25] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159: 252-261. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.018 [26] 周军, 王刚, 王庆军, 等. 新疆戈壁绿洲地质生态环境初步分析: 以渭干河和库车河流域为例 [J]. 新疆地质, 2019, 37(4): 469-472. ZHOU J, WANG G, WANG Q J, et al. Preliminary analysis of geological ecological environment of Gobi Oasis in Xinjiang: A case study on the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis [J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2019, 37(4): 469-472(in Chinese).
[27] 沈回归, 饶文波, 谭红兵, 等. 高寒区典型流域地下水化学特征、影响因素及健康风险 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(6): 9-17. SHEN H G, RAO W B, TAN H B, et al. Chemical characteristics, influencing factors and health risks of groundwater in typical watershed in alpine region [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 50(6): 9-17(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: