-
地膜主要使用聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)材料制作而成,在自然条件下极难降解[1]. 厚度为0.004—0.008 mm的地膜被广泛使用,因其力学性能较低,耕作后期破损严重,容易形成碎膜[2],长期残留将污染土壤[3],威胁土壤质量的可持续性,当地膜残留超过200 kg·ha−1会影响作物产量[4]. 相对于肉眼可见的碎膜,微米、纳米微塑料则能产生更大的潜在危害[5]. Liu等认为农田地膜的使用可产生微塑料[6]. 当微塑料被土壤动物如蚯蚓、虫类等取食后,会随着食物链传递[7].
我国高度重视耕地保护,不仅要保数量还要提质量[8]. 新疆天山山脉以北,冬季持续时间较长,给当地的种植业和反季节提供新鲜蔬菜带来不便. 为提高作物、蔬菜和果树的产量,我国农用塑料在2019年使用量达到2.4×106 t[9],而新疆是我国地膜使用最多的省份之一,特别是棉花覆盖率已达到100%[10]. 1980年,新疆兵团第八师石河子已经开始使用地膜覆盖栽培技术[11],到2021年新疆地膜使用量和覆盖面积已经稳居全国榜首,农用地膜使用量已高达2.404×105 t[12]. 新疆报道的农用地膜情况大多以露天覆膜为主,但忽略了设施农业用膜状况.
设施农业因其独特的保温作用,解决了新疆冬季无法种植作物这一难题,因此在新疆得到快速推行. 因地膜在新疆的大量使用,从而导致的残留及污染问题备受关注. 为填补新疆设施农业中土壤微塑料的污染情况,本次实验选取北疆某典型县设施农业集中区域,通过野外采样结合室内分析,探讨微塑料在设施农业的土壤深层分布特征及其来源,为新疆设施农业可持续发展提供参考,也可为我国设施农业土壤中微塑料的现状评估和治理保护提供基础数据支撑.
-
该县属温带大陆性干旱半干旱气候[13],地势南高北低,呈现山地、平原、沙漠等地貌形态,南部山地最高海拔为5290 m,北部沙漠最低海拔为360 m,全境高差为4930 m. 平原地区平均气温6.7 ℃,年降水量167 mm,无霜期平均180 d[14],5月至8月是平原地区作物生长旺盛的时间段. 该县南部为山地,海拔较高,温度较低,该区域多种植玉米及小麦等耐寒、生长周期短的作物;北部海拔较低,温度较高,多种植喜温耐旱的作物,以棉花、玉米、蔬菜等作物较为常见. 为应对冬季新鲜蔬菜的供应,规模较大的设施农业大多分布在县城周边低海拔位置.
-
2023年5月经实地调查,挑选非客土、全年无休的规模化设施农业大棚作为采样对象,按照规模>40个的随机选取5个设施农业大棚作为采样区域,规模<40个的随机选取3个设施农业大棚作为采样区域,本研究采样区有3块,A设施农业区(按照规模选择5个)、B设施农业区(按照规模选择5个)、C设施农业区(按照规模选择3个),共选取了13个样品采集区.
-
每个设施农业采用S型采样法进行采样,每个点挖取50 cm×50 cm×60 cm的土壤样品,对每10 cm土层分层混匀后使用四分法采样,土样分6层分别装入布袋并编号,共采集土壤样品78份. 设施农业采样点的分布情况详见于表1.
-
土壤微塑料使用饱和氯化钠溶液-密度分离法提取[15]. 土样带回实验室在白纸上风干,过5 mm金属筛,称50 g置于三角瓶. 加入30%的NaClO·KOH混合溶液[16],烘箱60 ℃消解48 h后加入150 mL饱和NaCl溶液,振荡30 min,静置5 h,收集上清液,重复3次. 上清液离心后用0.45 µm的玻璃纤维滤膜抽滤,取滤膜置于培养皿中阴干. 为保证实验的准确性,实验服及采样布袋均使用纯棉材料,实验均使用清洗干净的玻璃仪器. 借助体视显微镜(SMZ 25,Nikon)观察微塑料数量、粒径、颜色、形状等. 借助扫描电子显微镜(SEM-EDS)分析微塑料表面特征. 借助显微激光拉曼光谱仪(LABRAM HP EVOLUTION)鉴定微塑料成分.
-
Tomlinson等[17]提出的污染物负荷指数(pollution load index,PLI)模型,以研究区域样点微塑料的丰度为主要指标,点面结合评价总体的污染情况. 评估模型定义如下:
式中,CFi表示各个采样点微塑料的污染系数;Ci表示单个样点的微塑料丰度;Coi表示微塑料丰度的参考值,选择Everaert等[18]利用数学模型所估算出的对生物体无效应安全浓度540 个·kg−1. PLIi为单个样点的微塑料污染负荷指数;n为样点个数;PLIzone为该区域内微塑料污染负荷指数. PLI值的不同范围对应着不同污染程度:小于1为轻度,1到2之间为中度,大于2为重度.
-
微塑料的丰度表示为单位风干土中微塑料的个数(个·kg−1),数据处理采用Microsoft Excel 2016处理,使用SPSS 26进行数据分析,使用Origin 2022进行作图.
-
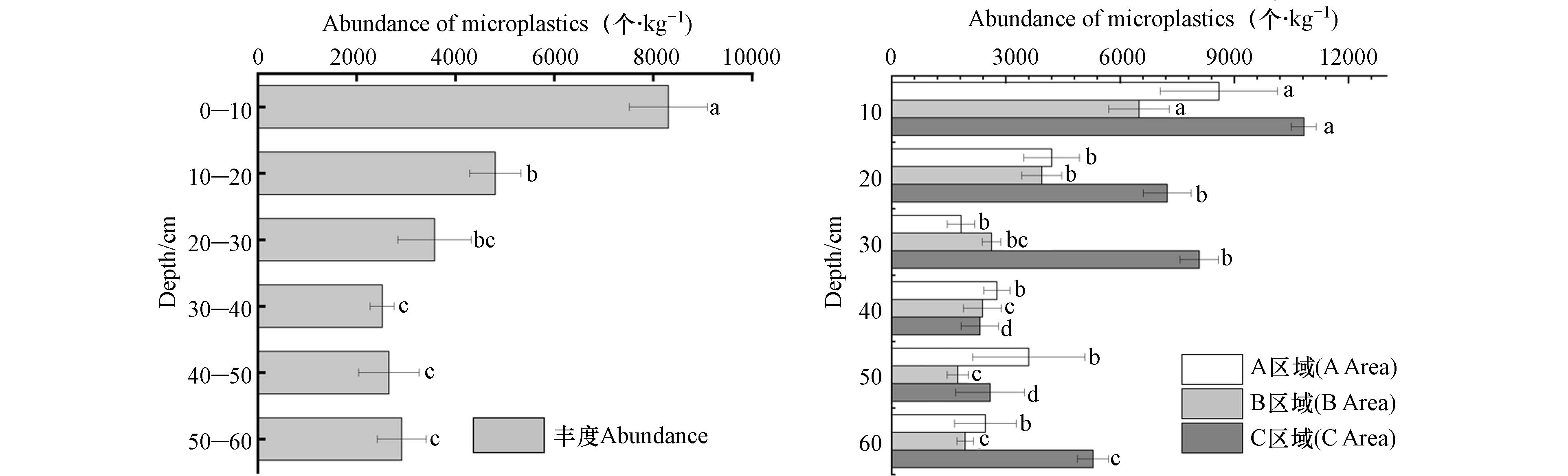
如图1所示,本研究3个典型区域设施农业土壤样品中均检测到微塑料,土壤微塑料的丰度范围为1.442×104—3.882×104 个·kg−1,平均丰度在2.4763×104 个·kg−1. 表2总结了不同地区设施农业土壤微塑料丰度情况. 本研究中的设施农业微塑料丰度最高值低于云南省滇池河岸设施农业缓冲带土壤微塑料丰度[19]. 但本研究设施农业土壤微塑料丰度高于山东省寿光市设施农业土壤微塑料[20]、陕西省渭河平原大棚区土壤微塑料[21]、杭州湾设施农业土壤微塑料[22]、江苏省徐州市土壤微塑料[23]、北京郊区设施农业土壤微塑料[24 − 26]. 说明该县设施农业土壤微塑料丰度比全国大部分已经报道省市地区高.
本次研究中在0—10 cm处微塑料丰度最高,从土层深度来看0—30 cm微塑料丰度比30—60 cm高,微塑料在0—30 cm丰度与土层深度呈反比,在30—60 cm处微塑料丰度随土层深度有逐渐累积现象. 这与陈荣龙等[21]、Hu等[27]在陕西关中农田与新疆阿拉尔市棉田得出的结论一致,土壤微塑料量与土层深度有关,0—10 cm处微塑料丰度最高与环境和人为因素有关,表层0—30 cm高于深层含量,微塑料的深层迁移可能与灌溉有关. 本研究的灌溉用水源为地下水,在灌溉方式上,A和B区域实行的是喷灌,而C区域实行的是滴灌. 李尤亮等[28]结果显示灌溉方式不同,其土壤平均储水量不同,覆膜滴灌大于微喷灌,覆膜滴灌方式增加土壤温度提高产量,并且土壤温度随着深度而增加. 由此表明,在农田环境中微塑料耕层的迁移可能与长期机械翻耕有关,非耕层微塑料的迁移可能与水和土壤性质及管理模式有关.
通过对3个区域的设施农业进行分析,结果表明3个区域土壤微塑料丰度与土层深度均不同. 如图1所示3个区域设施农业微塑料丰度从土层总体来看,0—10 cm丰度值最高,平均总丰度值C区域>A区域>B区域. 在0—30 cm的土层范围内,A和B区域的微塑料丰度随着深度的增加而逐渐减少. C区域微塑料丰度在0—20 cm处逐渐降低,20—30 cm处微塑料丰度增加11.6%. 30—60 cm处3个区域微塑料丰度有不同程度增加. A区域微塑料丰度在30—50 cm处呈增加趋势,随后在60 cm处呈下降趋势. B区域微塑料丰度在30—50 cm处下降后增加11.29%. C区域30—40 cm处微塑料丰度降低了71.28%,该区域30—60 cm处土壤微塑料丰度随土层深度有累积现象. 各区域之间微塑料丰度不同,与吴亚梅等[24]对北京市设施农业调查结果一致. 这与种植模式与种植频次和种类有关,本研究C区域中微塑料丰度较大,该区域种植成熟期较短的白菜类蔬菜,使用地膜频次较高. A、B区域因上半年使用穴盘育苗,下半年种植辣椒、西红柿使用地膜频次较少. 不同品种蔬菜其根系深度分布也不一样,辣椒根系分布于地面以下16.24—30.69 cm[29]. 白菜根系主要分布在表层即0—20 cm处[30],西红柿的根系深度主要分布在30 cm处[31]. 由此可见,不同区域设施农业耕层微塑料丰度的不一致现象可能与种植作物种类有关.
由此得出,在耕作层0—30 cm处不同土层微塑料丰度随着土层深度呈减少趋势,这与区域内种植作物类型、种植频次和灌溉方式有关. 30—60 cm处不同区域微塑料丰度在不同土层中呈现不规律性富集. 微塑料丰度在0—30 cm土层比30—60 cm土层高出106.55%.
-
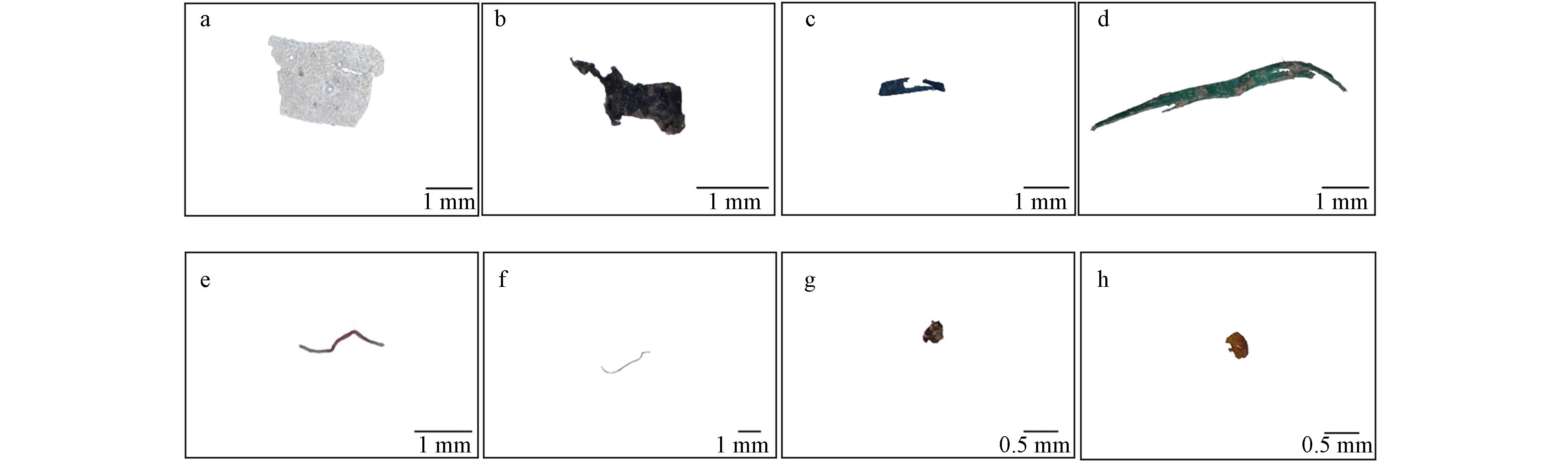
鉴于微塑料形状特征的多样性,将其划分为薄膜、纤维、碎片和颗粒4种,详情如图2所示. 薄膜类微塑料表面较为光滑薄,边缘较不规则,表面会出现空缺和塌陷现象. 碎片类微塑料的边缘破损较为显著,同时其厚度也相对较大. 纤维类微塑料呈线性,表面有卷曲不规则的情况. 颗粒状微塑料体积小,形态不规则.
-
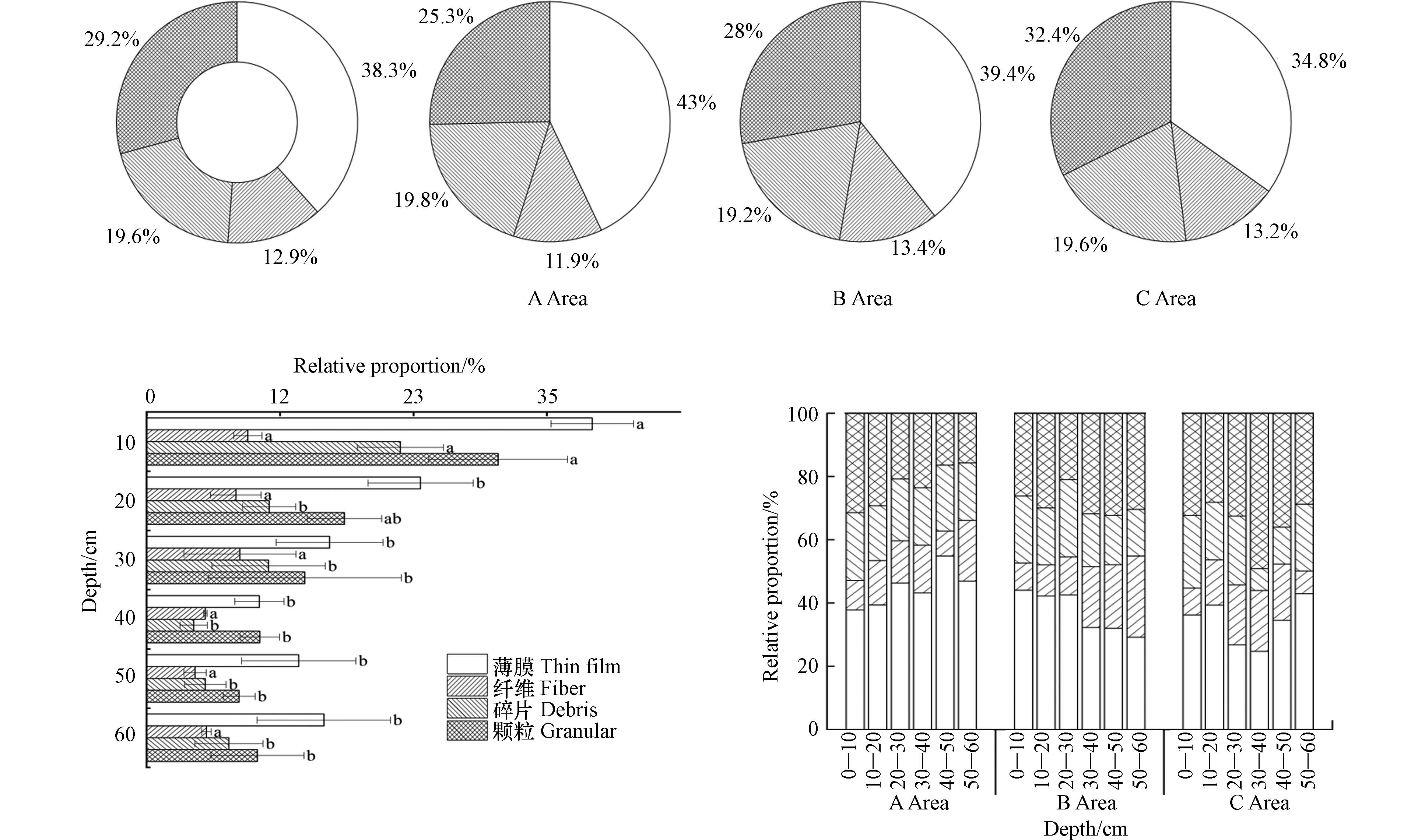
如图3所示,3个区域设施农业的微塑料类型在不同土层均有不同. 该地区设施农业微塑料形状主要为薄膜38.3%、颗粒29.2%、碎片19.6%、纤维12.9%. 如图3所示3个区域大棚微塑料类型占比均有不同,其中薄膜检出量占比最大是A区域43%,占比最小是C区域34.8%;纤维检出量占比最大的是B区域13.4%,占比较小的是A区域11.9%;碎片检出量占比最大的是A区域19.8%,占比较小的是B区域19.2%;颗粒检出量占比最大的是C区域32.4%,占比较小的是A区域25.3%.
按照不同土层微塑料形状所示,每10 cm土层微塑料种类含量较多的是薄膜类,其次为颗粒类. 0—30 cm处每10 cm土层土壤的微塑料种类含量均呈下降趋势. 30—60 cm土层中,薄膜型、碎片型、纤维型微塑料含量随着深度有不断累积的趋势;颗粒型微塑料含量在50—60 cm处有不断累积的趋势.
本研究中的土壤微塑料主要以薄膜为主,颗粒次之. 吴思齐等[32]对辽宁冻融地区的微塑料调查显示薄膜占比56%、纤维37%、碎片8%. 费禹凡等[22]对杭州湾设施农业调查表明土壤微塑料主要为薄膜类. Feng等[33]对青藏高原某地区调查显示微塑料在地表水、沉积物中以纤维为主,土壤中以薄膜为主. 边淑贞等[34]对黄淮海与渤海地区设施蔬菜优势区的调查表明54%的农户使用厚度为0.004 mm的地膜,因成本问题没有使用国家标准规定的0.008 mm地膜,这种更薄的地膜极易破碎且难以清理,问卷中53%的废弃处置方式是随地丢弃. 不同类型的微塑料可能与所应用的微塑料种类、厚度和管理方式存在关联.
-
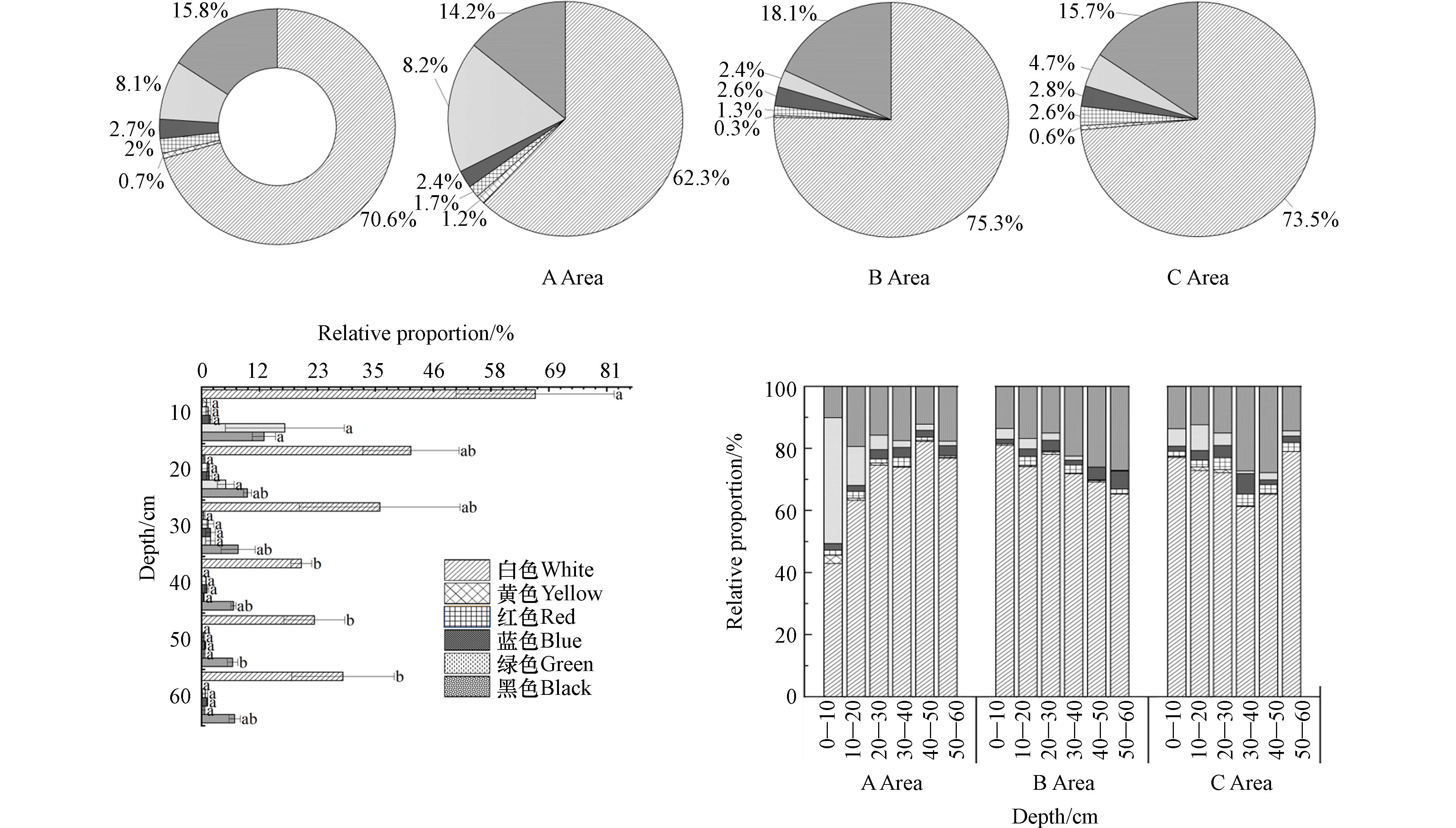
通过体视显微镜的观测发现,主要的微塑料颜色为白色、黄色、红色、蓝色、绿色和黑色. 如图4所示,该地区设施农业中微塑料以白色为主占70.6%,其次是黑色15.8%、绿色8.1%、蓝色2.7%、红色2.0%、黄色0.7%. 各区域设施农业中,微塑料的颜色占比存在差异,其中白色微塑料B区域75.3%>C区域73.5%>A区域62.3%;绿色微塑料A区域18.2%>C区域4.7%>B区域2.4%;黑色微塑料B区域18.1%>C区域15.7%>A区域14.2%;黄色、红色、蓝色微塑料占比均在3%以下.
在不同的土层中,微塑料的颜色分布呈现出差异性. 其中,白色微塑料在各土层中的占比相对较高,为主要成分;黑色和绿色微塑料的占比次之,为次要成分;而其他颜色的微塑料在不同土层中的占比并没有明显差异. 30—60 cm处白色、黑色、绿色微塑料占比例随深度增加呈减少趋势,其他颜色占比不明显;30—60 cm处白色微塑料含量占比随着土壤深度呈增长趋势,黑色占比在此土层无明显差异,绿色占比较小.
在3个不同区域中,各土层的微塑料占比均存在差异性. 白色微塑料在3个区域的不同土层均占比例最多. A区域在0—30 cm绿色微塑料比其他区域含量高,且含量随着土层深度增加呈反比. 黑色微塑料在不同区域的不同土层均有分布,其中黑色微塑料在30—60 cm比0—30 cm处占比高.
本研究区域的土壤微塑料以白色微塑料为主,黑色微塑料为次之,与吴亚梅等[24]、马贵等[35]对北京市设施农业与固原市农田调查结果一致. 白色微塑料主要来源可能与通常使用的普通白色农膜残留有关;黑色微塑料可能与育苗的穴盘材料或者使用黑色的地膜残留有关;绿色微塑料与当地设施农业篷布颜色相符. A区域0—10 cm处绿色微塑料丰度高,可能受到设施农业篷布的影响较大.
-
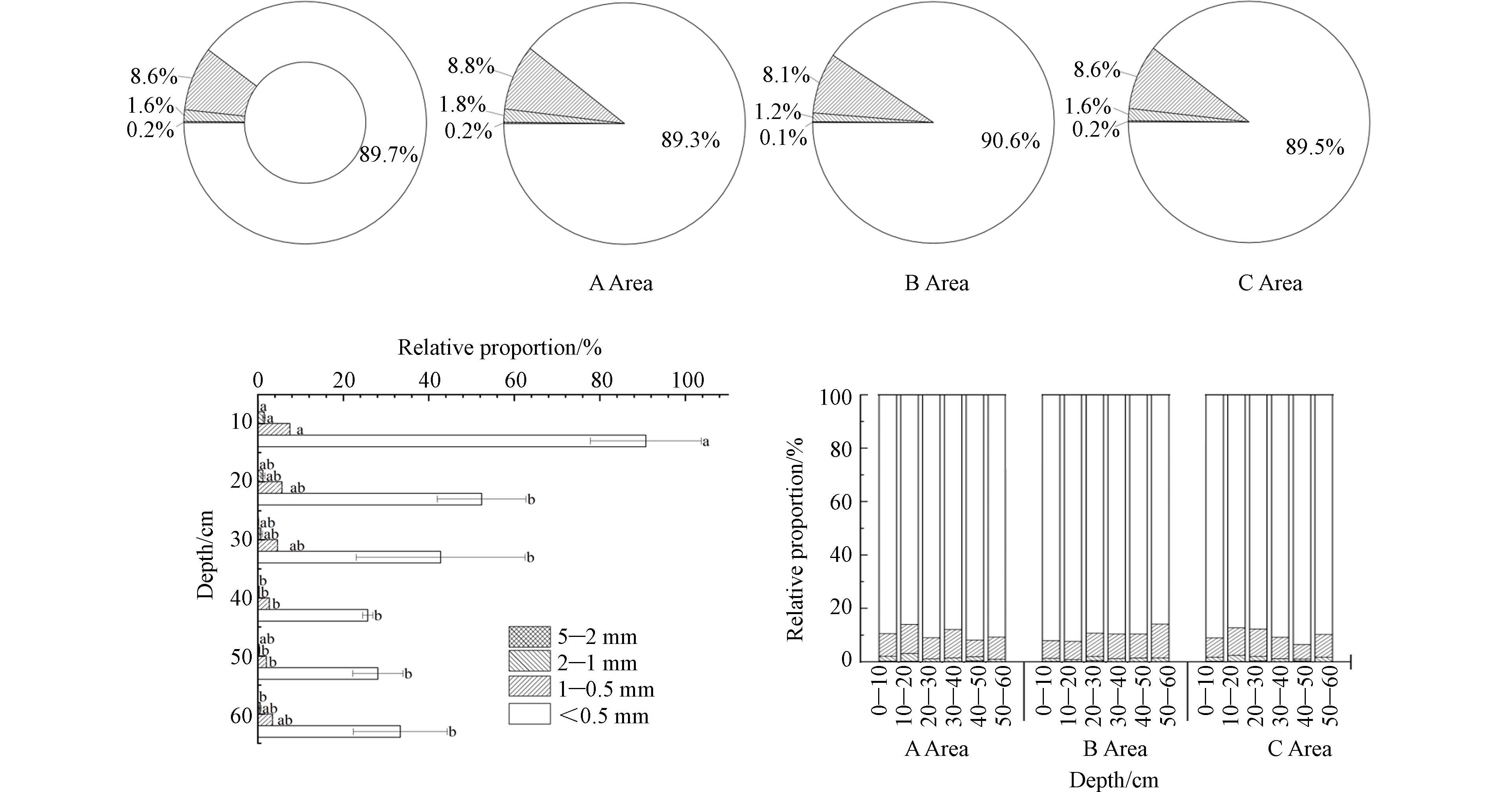
微塑料的粒径分为5—2、2—1、1—0.5、0.5—0 mm 的4个等级. 由图5所示,该地区设施农业土壤微塑料粒径分布为0.5—0(89.7%)、1—0.5(8.6%)、2—1(1.6%)和5—2 mm(0.2%). 在3个不同区域中,微塑料的粒径占比相差不大,且该地区0.5—0 mm粒径的微塑料占比普遍高于89%以上. 各土层微塑料粒径占比以0.5—0 mm(85.92%—93.56%),1—0.5 mm(5.79%—14.70%).
如图5所示,各区域各土层中土壤微塑料粒径以0.5—0 mm为主. 在0—30 cm处0.5—0 mm微塑料在占比呈持续下降趋势,30—60 cm处占比呈现持续上升趋势. 1—0.5 mm微塑料占比在0—50 cm处持续降低,在50—60 cm处占比增加.
本研究显示,粒径小于0.5 mm的土壤微塑料占比达到了89%. Ding等[36]研究表明我国陕西农田微塑料以<0.5 mm为主. 宋宁宁等[37]研究表明山东花生农田中微塑料粒径<1 mm占77.30%. Yu等[20]研究表明山东蔬菜大棚粒径大小以0—0.5 mm为主. 由此可见微塑料的粒径大小大部分均在0.5 mm以下并在土壤中大量存在,这与本研究结果一致. 有报道称微塑料粒径小于1 mm会被土壤动物摄入[38]. 生菜可以吸收PS(200 nm)并在根、茎、叶均检出[39]. 由此可见,随着土壤中微塑料的不断累积将会摄入动植物体内,并随着食物链传递. 由于塑料的降解受到生物因素(动物、植物、酶、微生物)与非生物因素(热、化学、光、机械)[40]的影响,致使北疆设施农业农用塑料的降解速率的影响有待探究.
-
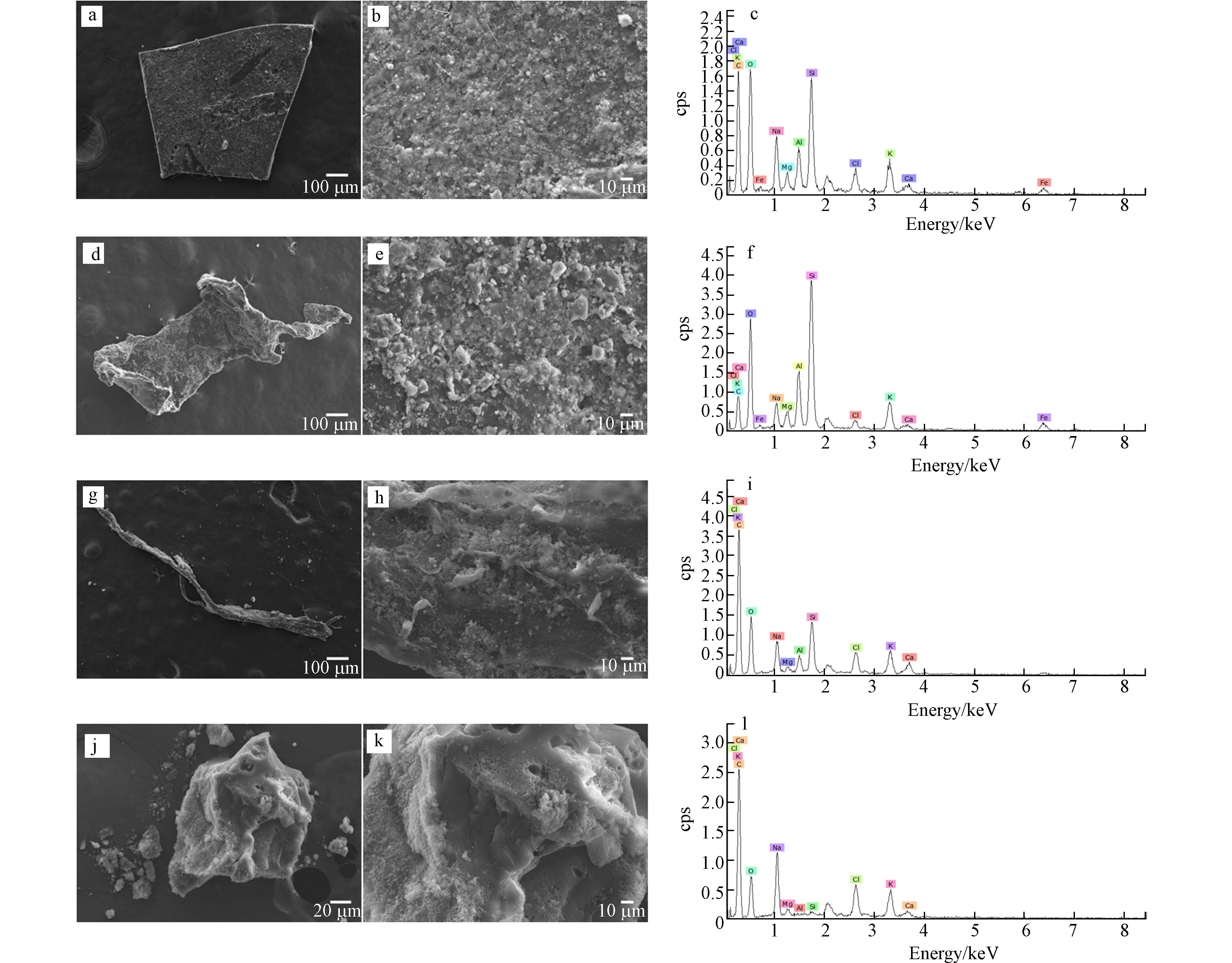
设施农业中分离出的土壤微塑料使用扫描电子显微镜,情况如图6所示,Si、Al元素的含量碎片>薄膜>纤维>颗粒,Ca元素含量纤维>薄膜>颗粒>碎片,Mg元素含量碎片>薄膜>颗粒>纤维,Fe元素碎片>薄膜. 由此可知微塑料可以吸附一定量的矿物质,并且吸附能力大小取决于微塑料的形态和类别[41]. 考虑到塑料成分主要为C、O元素,密度分离法中有Na、Cl元素,故该元素不进行对比.
从调查可知该县设施农业微塑料大小以0.5 mm以下为主,因此无法被回收,导致大量滞留在土壤中,并在土壤中呈现不同空间状态,微塑料会吸附重金属及矿物质,小颗粒物质会随着根部被吸收到植物体[42]对食品安全造成一定影响. 通过观察可看到微塑料表面有凹坑,为微生物提供繁衍居所,并将其作为碳源分解,其特殊形态会改变土壤的性质,影响土壤微生物量及微生物群落结构功能[43]. 现阶段农田中大量微塑料残留会成为新“碳库”[44].
-
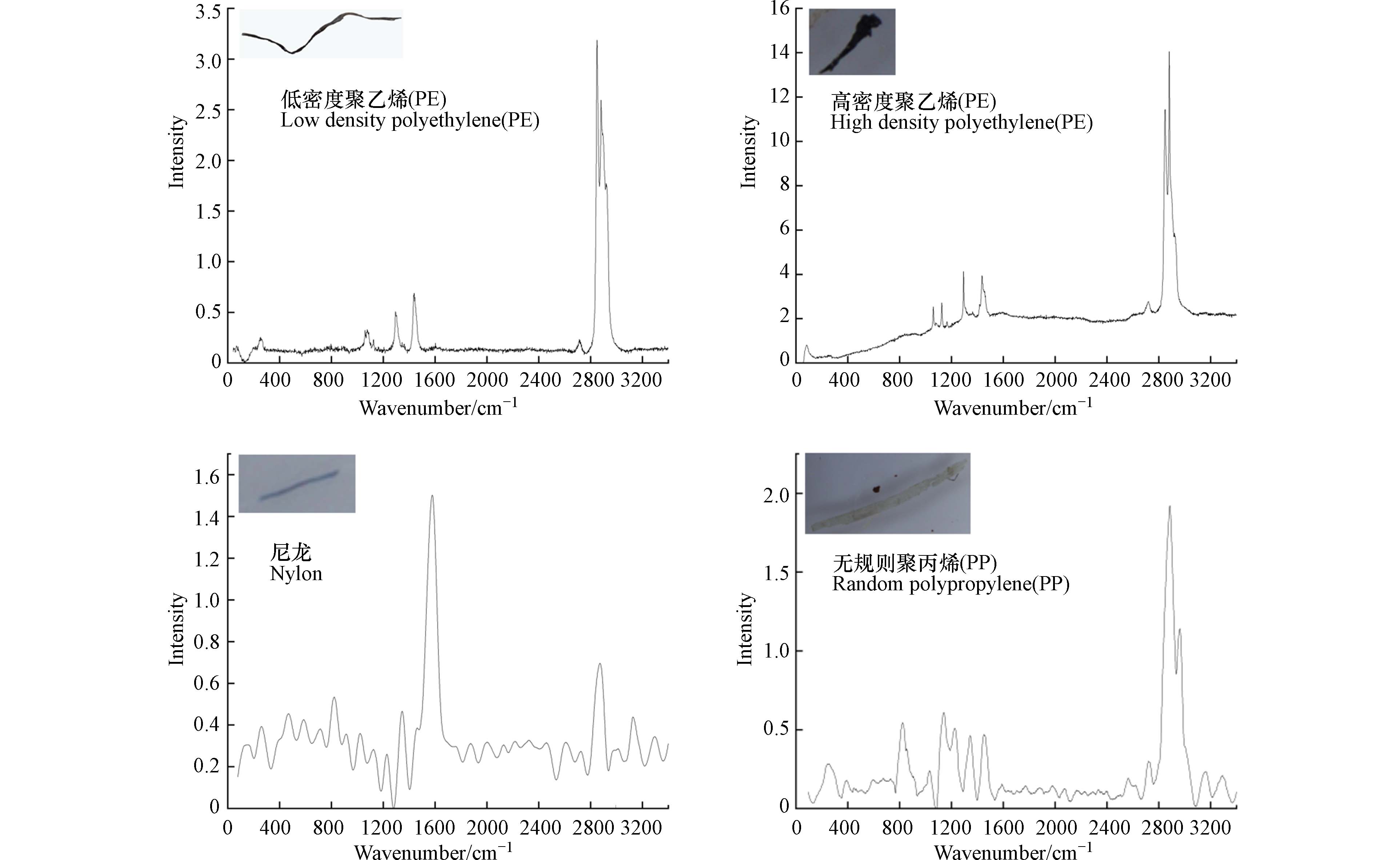
从3个区域设施农业浮选出的微塑料,每个区域通过镜检后选出典型微塑料5个,共计挑选15个. 使用显微激光拉曼光谱仪分析,其结果减去基线平滑处理并参比《微塑料污染物》[45]中拉曼图谱中的特征峰进行分析. 如图7所示,该地区设施农业中样品微塑料图谱对比一致的主要种类有聚乙烯(PE)5个、聚丙烯(PP)3个、尼龙1个,其中6个微塑料碎片无对应类型. 本研究结果表明,检出的土壤微塑料以PE和PP为主要类型.
Ren等[46]对农田微塑料研究表明,农田中微塑料的主要成分PE、PP、PES、PS、PA,其中农用地膜由PE制成. 冯三三等[47]对青藏高原典型区微塑料调查表明,其主要成分为PP、PE,其次为PET、PS. 在采样过程中,现场可见的塑料制品来源有大棚塑料篷布、地膜、育苗穴盘、编织绳、滴灌带、肥料等. 设施农业中的土壤因有篷布的存在,大气沉降导致的微塑料可能性较小. 本研究区的微塑料来源与设施农业生产过程密切.
-
根据土壤微塑料负荷指数由表3可知,各区域设施农业均为不同程度重度污染,3个设施农业土壤微塑料污染符合指数PLI在2.31—3.2之间,C区域的重度污染指数达到了最高水平. 该地区微塑料污染负荷指数平均数值达到PLIzone=2.65,该地区设施农业微塑料污染程度达到重度.
-
(1)北疆某县设施农业土壤微塑料丰度范围1.442×104—3.882×104 个·kg−1,整体平均丰度在2.4763×104 个·kg−1. 0—30 cm的土壤微塑料丰度与深度呈负相关性,30—60 cm土壤微塑料随深度有不断累积的趋势.
(2)北疆某县的设施农业土壤微塑料以薄膜状为主38.3%,颜色以白色为主占70.6%、黑色占15.8%,粒径以小于0.5 mm为主89.7%;PE和PP是微塑料的主要来源.
(3)不同形状的土壤微塑料会吸附矿物质.
(4)根据污染负荷指数,北疆某县的设施农业土壤微塑料污染程度达到重度,需引起重视.
北疆某县典型设施农业土壤微塑料分布特征
Distribution characteristics of microplastics in typical facility agriculture soil in North Xinjiang
-
摘要: 以北疆某县为例,研究典型设施农业土壤微塑料的污染分布特征,2023年5月采集该地区3个区域不同土层深度(0—10、10—20、20—30、30—40、40—50、50—60 cm)的土壤样品. 使用饱和氯化钠溶液-密度分离法提取微塑料并用体视显微镜观察. 结果表明,该地区设施农业土壤中微塑料丰度范围为1.442×104—3.882×104 个·kg−1,0—30 cm的土壤微塑料丰度与深度呈负相关性,30—60 cm土壤微塑料随深度有不断累积的趋势;该区域土壤微塑料形状主要有薄膜状、颗粒状、碎片状、纤维状等4种;微塑料颜色有白色70.6%、黑色15.8%、绿色8.1%、蓝色2.7%、红色2.0%、黄色0.7%;微塑料的粒径小于0.5 mm的占比最大;使用拉曼光谱鉴定微塑料的到主要成分以聚乙烯(PE)、聚丙烯(PP)为主;该区域土壤微塑料污染指数达到2.65,微塑料污染程度达到重度. 研究表明,该研究区设施农业微塑料污染普遍较高,需引起重视.Abstract: The distribution characteristics of soil microplastics in a typical facility agriculture in North Xinjiang were studied in the present study. Soil samples at different soil depths (0—10, 10—20, 20—30, 30—40, 40—50, 50—60 cm) were collected from three regions in May 2023 in the study area. The soil microplastics were observed using a stereomicroscope after extracting by saturated sodium chloride solution-density separation method. Results showed that the abundance of soil microplastics in the facility agriculture area ranged from 1.442×104—3.882×104 items·kg−1, The soil microplastics abundance was negatively correlated with the depth at the 0—30 cm depth, while the soil microplastics accumulated continuously at the depth of 30—60 cm. There were four shapes of soil microplastics in the study area including thin film, granular, debris and fiber. The proportions of white, black, green, blue, red and yellow soil microplastics in the study area were 70.6%, 15.8%, 8.1%, 2.7%, 2.0% and 0.7%, respectively. The main components of soil microplastics were polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), and the soil microplastics with particle size less than 0.5 mm was larger than other particle size. The degree of microplastic pollution was severe in the study area with the pollution index of 2.65. Our results indicated that the we should pay attention to the soil microplastic pollution in the study area because the soil microplastic pollution was generally high in facility agriculture in North Xinjiang.
-

-
表 1 土壤采样点分布及基本情况
Table 1. Distribution and basic situation of soil sampling sites
区域
Area样点数量
Number of sample sites耕作周期
Cultivation cycle种植作物
Raise crops灌溉方式
Irrigation method覆膜时长/a
Coating duration种植频次/(茬·a−1)
Planting frequencyA 5 常年 辣椒、西红柿 喷灌 11 1 B 5 常年 辣椒、西红柿 喷灌 13 1 C 3 常年 辣椒、西红柿、小白菜 滴灌 10 2 表 2 不同地区设施农业土壤微塑料丰度特征
Table 2. Abundance characteristics of microplastics in soil of facility agriculture in different regions
采样点
Sampling sites土壤类型
Soil type微塑料丰度/(个·kg−1)
Abundance of microplastics参考文献
References云南省滇池河岸 设施农业缓冲带 7100—42960 [19] 山东省寿光市 设施农业0—5 cm 1443±977 [20] 设施农业5—10 cm 1313±857 设施农业10—25 cm 1362±829 陕西省渭河平原 蔬菜地 100—18000 [21] 大棚区 100—500 杭州湾设施农业 设施农业 20—1560 [22] 山东省寿光市 设施农业 1000—3786 [23] 江苏省徐州市 1300—3400 北京市设施农业 设施农业 440±179.63—2366.67±347.21 [24] 北京郊区 设施农业0—10 cm 896.5±80.4(160—2120) [25] 设施农业10—20 cm 630.6±47.2(180—1340) 设施农业20—30 cm 445.3±47.8(80—1480) 北京郊区 废弃温室 2215.56±1549.86 [26] 普通温室 891.11±316.71 简易温室 632.50±566.93 表 3 设施农业各区域土壤微塑料污染负荷指数
Table 3. Soil microplastic pollution load index in each region of facility agriculture
设施农业区域
Facility agriculture area微塑料污染系数CF
Microplastic pollution coefficient CFPLI指数
PLI indexA 7.24 2.43 B 5.90 2.31 C 11.22 3.20 -
[1] 姜晓旭, 封雪, 周笑白, 等. 土壤中微塑料污染现状与检测技术研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(1): 163-175. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022070301 JIANG X X, FENG X, ZHOU X B, et al. Research progress on pollution status and analysis method for microplastics in soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(1): 163-175 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022070301
[2] 曹鹏飞, 刘泽星, 陈梅, 等. 新疆兵团滴灌技术应用现状、问题与推广启示[J]. 水利发展研究, 2022, 22(5): 114-119. CAO P F, LIU Z X, CHEN M, et al. Current status, problems and recommendations of the application of drip irrigation technology in the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps[J]. Water Resources Development Research, 2022, 22(5): 114-119 (in Chinese).
[3] HUO L, PANG H C, ZHAO Y G, et al. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from Northwest China[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2017, 165: 286-293. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2016.09.006 [4] WEN Y, LIU J, DHITAL Y, et al. Integrated effects of plastic film residues on cotton growth and field carbon sequestration under drip irrigation in arid oasis regions[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2022, 339: 108131. [5] 王烨, 安舒玉, 刘蕾, 等. 水体微塑料与重金属的相互作用及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2023,DOI: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20231031.008. WANG Y, AN S Y, LIU L, et al. Research progress on the interaction and composite toxicity effects of microplastics and heavy metals in water bodies [J]. Applied Chemistry, 2023,DOI: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20231031.008(in Chinese).
[6] LIU M T, LU S B, SONG Y, et al. Microplastic and mesoplastic pollution in farmland soils in suburbs of Shanghai, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 855-862. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.051 [7] 许铭宇. 湿地生态系统中微塑料污染及迁移转化研究进展[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2023, 19(4): 92-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2023.04.19 XU M Y. Research progress on microplastic pollution, migration and transformation in wetland ecosystems[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 2023, 19(4): 92-96 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2023.04.19
[8] 郭永田. 加强耕地保护建设筑牢粮食安全基础[J]. 农业发展与金融, 2022(10): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-690X.2022.10.009 GUO Y T. Strengthening the Protection and Construction of Farmland and Building a Solid Foundation for Food Security[J]. Agricultural Development and Finance, 2022(10): 11-14 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-690X.2022.10.009
[9] 武凤霞, 张淑彬, 刘建斌. 中国农田土壤微塑料污染现状及其对土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中南农业科技, 2022(5): 193-200 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-273X.2022.05.048 WU F X, ZHANG S B, LIU J B. The current situation of microplastic pollution in farmland soil in China and its impact on soil microorganisms[J]. South-Central Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(5): 193-200 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-273X.2022.05.048
[10] 岳东波. 南疆棉农残膜回收效益认知及行为的影响因素研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2023. YUE D B. A study on the cognitive and behavioral factors influencing the benefits of cotton farmer's residual film recycling in Southern Xinjiang[D]. Alaer: Tarim University, 2023 (in Chinese).
[11] 朱桓, 沈明亚, 施献松. 蔬菜地膜复盖栽培技术研究初报[J]. 新疆农业科技, 1981(5): 8-15. ZHU H, SHEN M Y, SHI X S. Preliminary report on the cultivation technology of vegetable plastic film covering[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology, 1981(5): 8-15 (in Chinese).
[12] 张静. 新疆棉花种植农户绿色农业技术采纳行为研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2023. ZHANG J. Research on the adoption behavior of green agricultural technologies by cotton farmers in Xinjiang[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2023 (in Chinese).
[13] 国家统计局农村社会经济调查司. 中国县域统计年鉴-2020-县市卷[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. Rural Social and Economic Survey Department of the National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook 2020 (County-level)[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021(in Chinese).
[14] 新疆维吾尔自治区人民政府网[EB/OL] 2023-06-28
[15] 王志超, 孟青, 于玲红, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区农田土壤中微塑料的赋存特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(3): 204-209. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.03.025 WANG Z C, MENG Q, YU L H, et al. Occurrence characteristics of microplastics in farmland soil of Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(3): 204-209 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.03.025
[16] 孙霞, 苟燕如, 严涵, 等. 北疆典型棉区土壤微塑料污染现状及分布特征[J].农业环境科学学报,2024,43(3):571-580. SUN X, GOU Y R, YAN H, et al. Soil microplastic pollution and distribution characteristics in a typical cotton field in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,,2024,43(3):571-580(in Chinese).
[17] TOMLINSON D L, WILSON J G, HARRIS C R, et al. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index[J]. Helgolä nder Meeresuntersuchungen, 1980, 33(1): 566-575. [18] EVERAERT G, VAN CAUWENBERGHE L, DE RIJCKE M, et al. Risk assessment of microplastics in the ocean: Modelling approach and first conclusions[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 1930-1938. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.069 [19] ZHANG G S, LIU Y F. The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.004 [20] YU L, ZHANG J D, LIU Y, et al. Distribution characteristics of microplastics in agricultural soils from the largest vegetable production base in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 756: 143860. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143860 [21] 陈荣龙, 陈延华, 黄珊, 等. 陕西关中农田土壤中塑料碎片和微塑料残留及其累积特征研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(10): 1649-1658. doi: 10.12357/cjea.20220137 CHEN R L, CHEN Y H, HUANG S, et al. Residues and accumulation characteristics of plastic fragments and micro-plastics in farmland soil of Guanzhong Plain, Shaanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(10): 1649-1658 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12357/cjea.20220137
[22] 费禹凡, 黄顺寅, 王佳青, 等. 设施农业土壤微塑料污染及其对细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(13): 1592-1601. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0685 FEI Y F, HUANG S Y, WANG J Q, et al. Microplastics contamination in the protected agricultural soils and its effects on bacterial community diversity[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(13): 1592-1601 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0685
[23] LI Q L, ZENG A R, JIANG X, et al. Are microplastics correlated to phthalates in facility agriculture soil?[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 412: 125164. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125164 [24] 吴亚梅, 王育鹏, 王康, 等. 北京市设施农业土壤微塑料的污染特征及潜在来源[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(4): 333-344. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20211118002 WU Y M, WANG Y P, WANG K, et al. Pollution characteristics and potential sources of microplastics in facility agricultural soil in Beijing[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(4): 333-344 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20211118002
[25] GUO S, ZHANG J J, LIU J W, et al. Organic fertilizer and irrigation water are the primary sources of microplastics in the facility soil, Beijing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 895: 165005. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165005 [26] WANG K, CHEN W, TIAN J Y, et al. Accumulation of microplastics in greenhouse soil after long-term plastic film mulching in Beijing, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 828: 154544. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154544 [27] HU C, LU B, GUO W S, et al. Distribution of microplastics in mulched soil in Xinjiang, China[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2021, 14(2): 196-204. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20211402.6165 [28] 李尤亮, 张雷, 王杰, 等. 不同灌溉方式对土壤水热及生菜产量的影响[J]. 人民长江, 2023, 54(9): 114-118. LI Y L, ZHANG L, WANG J, et al. Effects of different irrigation methods on soil water-thermal condition and yield of Lactuca sativa[J]. Yangtze River, 2023, 54(9): 114-118 (in Chinese).
[29] KULKARNI M, PHALKE S. Evaluating variability of root size system and its constitutive traits in hot pepper (Capsicum annum L. ) under water stress[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2009, 120(2): 159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2008.10.007 [30] 杨庆娥, 任振江, 高然. 污水灌溉对土壤和蔬菜中重金属积累和分布影响研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2007(5): 74-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2007.05.027 YANG Q E, REN Z J, GAO R. Research on the effect of sewage irrigation on the accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in soil and vegetables[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2007(5): 74-75 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2007.05.027
[31] 张阳阳. 基于智能控制技术的灌溉系统研究[D]. 西安: 西安工程大学, 2020. ZHANG Y Y. Research on irrigation system based on intelligent control technology[D]. Xi'an: Xi'An Polytechnic University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[32] 吴思齐. 冻融地区农业土壤微塑料分布及归趋研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2022. WU S Q. Research on the distribution and fate of microplastics in agricultural soils in freeze-thaw regions[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2022 (in Chinese).
[33] FENG S S, LU H W, TIAN P P, et al. Analysis of microplastics in a remote region of the Tibetan Plateau: Implications for natural environmental response to human activities[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 739: 140087. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140087 [34] 边淑贞, 柳晓娟, 安子扬, 等. 我国典型设施蔬菜种植区农用地膜污染分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(11): 76-81. BIAN S Z, LIU X J, AN Z Y, et al. Pollution status of film mulching in Chinese protected vegetable areas[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(11): 76-81 (in Chinese).
[35] 马贵, 丁家富, 周悦, 等. 固原市农田土壤微塑料的分布特征及风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9): 5055-5062. MA G, DING J F, ZHOU Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of microplastics in farmland soil in Guyuan[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(9): 5055-5062 (in Chinese).
[36] DING L, ZHANG S Y, WANG X Y, et al. The occurrence and distribution characteristics of microplastics in the agricultural soils of Shaanxi Province, in north-western China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720: 137525. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137525 [37] 宋宁宁, 李梦佳, 王学霞, 等. 覆膜年限和有机肥施用对花生田耕层土壤微塑料赋存特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2024,45(3):1684-1691. SONG N N, LI M J, WANG X X, et al. The effects of mulching years and organic fertilizer application on the occurrence characteristics of microplastics in the topsoil of peanut fields[J]. Environmental Science, 2024,45(3):1684-1691(in Chinese).
[38] 朱芷宏, 张琎, 高晓丹, 等. 微塑料参与下的土壤碳循环过程评述[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2024,32(2):252-261. ZHU Z H, ZHANG J, GAO X D, et al. Review of soil carbon cycling processes involving microplastics[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2024,32(2):252-261(in Chinese).
[39] 金灿, 王毅, 代知广, 等. 土壤中微塑料污染及其防治措施的探讨[J]. 环境科技, 2021, 34(2): 73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2021.02.017 JIN C, WANG Y, DAI Z G, et al. Exploration on the pollution and control measures of soil microplastics[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 34(2): 73-78 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4829.2021.02.017
[40] 孙文潇, 杨帆, 侯梦宗, 等. 环境中的微塑料污染及降解[J]. 中国塑料, 2023, 37(11): 117-126. SUN W X, YANG F, HOU M Z, et al. Microplastic pollution and degradation in environment[J]. China Plastics, 2023, 37(11): 117-126 (in Chinese).
[41] 闫协民. 聚苯乙烯微塑料/四环素复合污染物对AGS细胞损伤机理研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2020. YAN X M. Mechanism of damage to AGS cells by polystyrene microplastics/tetracycline composite pollutants[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[42] 黄硕霈, 谭长银, 涂晨, 等. 土壤微塑料与重金属复合污染机理及其植物生理效应研究进展[J/OL]. [2023-10-16]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2023, HUANG S P, TAN C Y, TU C, et al. The combined pollution mechanism of microplastics and heavy metals in soil and physiological effects on plants: A review[J/OL]. [2023-10-16]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2023,
[43] ZHANG M J, ZHAO Y R, QIN X, et al. Microplastics from mulching film is a distinct habitat for bacteria in farmland soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 688: 470-478. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.108 [44] 黎鹏. 微塑料与磷添加对玉米生长及土壤特性的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. LI P. The effects of microplastics and phosphorus addition on maize growth and soil characteristics[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[45] 克里斯托弗·布莱尔·克劳福德, 布莱恩·奎因. 微塑料污染物[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2016. CHRISTOPHER B C, BRIAN Q. Microplastic pollution [M]. Beijing: China Environment Publishing House, 2016 (in Chinese).
[46] REN S Y, WANG K, ZHANG J R, et al. Potential sources and occurrence of macro-plastics and microplastics pollution in farmland soils: A typical case of China[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2023,54(7): 533–556. [47] 冯三三, 卢宏玮, 姚天次, 等. 青藏高原典型区微塑料分布特征及来源分析[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(9): 2130-2141. FENG S S, LU H W, YAO T C, et al. Distribution and source analysis of microplastics in typical areas of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(9): 2130-2141 (in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: