-
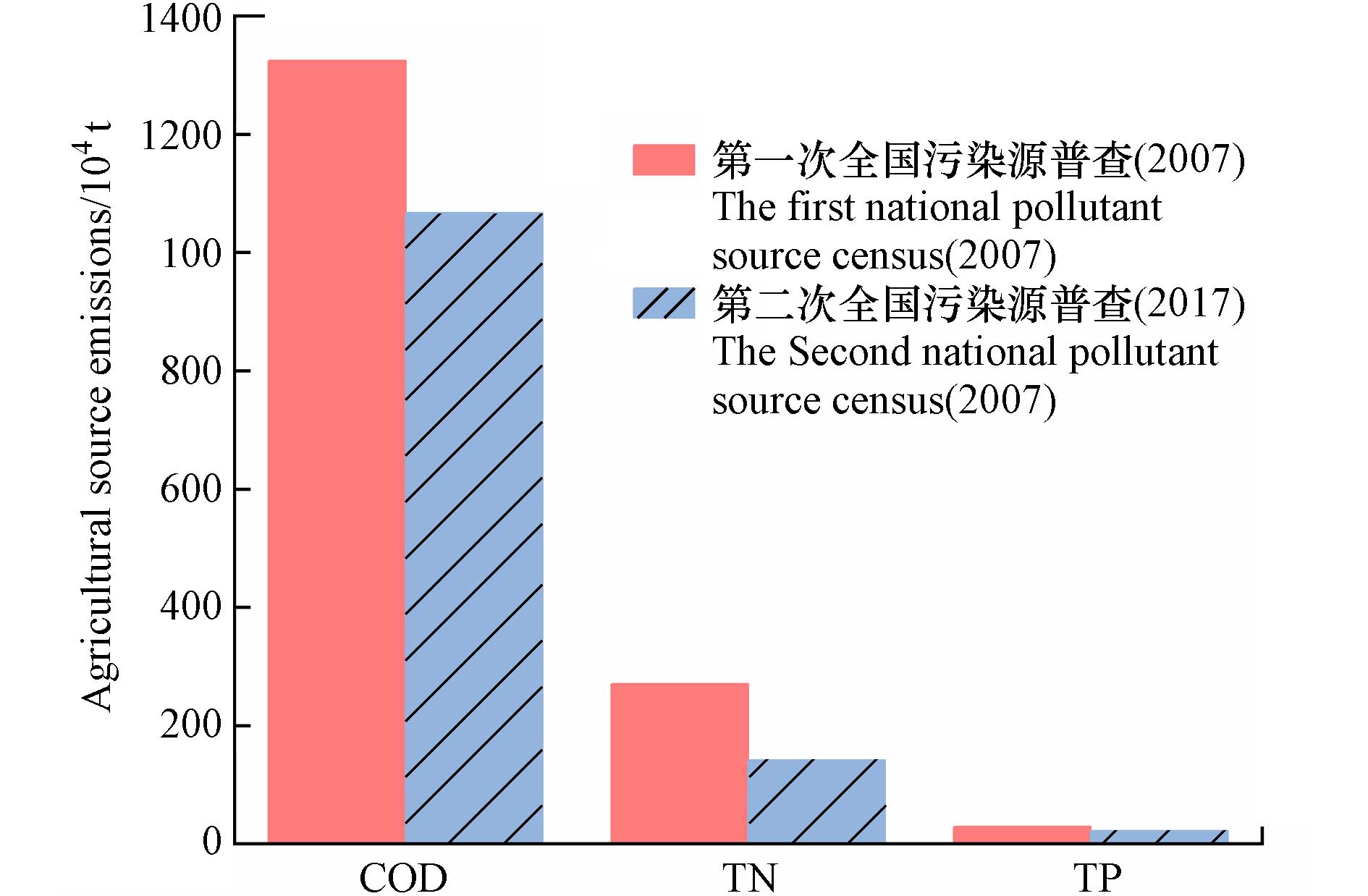
农业面源污染,从狭义上讲,是指在农业生产活动中,氮、磷等物质在降水或灌溉过程中,通过农田地表径流、壤中流、农田排水和地下渗漏,进入水体而造成的水体污染[1],农业面源污染已成为影响水环境质量的主要污染形式之一. 2020年发布的《第二次全国污染源普查公报》显示,我国农业源水污染物排放量中化学需氧量、总氮、总磷分别为
1067.13 万t、141.49 万t、21.20 万t,分别占全国水污染物排放量的49.8%、46.5%、67.2%. 与10年前相比,农业源化学需氧量、总氮、总磷排放分别下降了19%、48%和25%(见图1),农业生产实现了“增产又减污”,但农业源排放占比仍然较高. 需要指出的是,以上农业源排放量并不等于实际入河湖的量.不同于点源污染,农业面源污染有其自身的特点:一是排放形式具有分散性. 与点源污染集中排放不同,农业面源污染来源分散多样,没有明确的排污口,地理边界和位置难以识别和确定;二是随机性和不确定性强. 农业面源污染的发生受自然地理条件、水文气候特征等因素影响,水污染物向土壤和水体运移过程中,呈现时间上的随机性和空间上的不确定性;三是进入环境过程具有间接性. 农业面源污染受到生物地球化学转化和水文传输过程的共同影响,农业生产残留的氮磷等元素通常会在土壤中累积,并缓慢向外环境释放,对受纳水体环境质量的影响存在滞后性;四是具有资源性. 以畜禽粪污为例,1 t畜禽粪污有机质含量约25 kg,氮磷含量约4 kg,若能很好利用对农业生产是一种资源,处理不当进入受纳水体或在土壤中过量累积,才是污染物[2].
近年来,农业农村部聚焦重点区域和关键环节,不断加强农业面源污染治理工作. 2021年,印发实施《“十四五”重点流域农业面源污染综合治理建设规划》,围绕化肥农药减量化、秸秆综合利用、畜禽粪污资源化利用、地膜科学使用回收开展行动试点,特别是,在长江经济带、黄河流域实施农业面源污染综合治理示范项目,推动源头减量、过程拦截、末端治理、循环利用全链条防治,减少农业面源污染排放. 2021年,生态环境部、农业农村部印发《农业面源污染治理与监督指导实施方案(试行)》,明确了深入推进农业面源污染防治、加强农业面源污染治理监督管理. 各项工作取得积极成效,我国农业生态环境持续改善,但农业面源污染量大面广的基本态势尚未根本扭转,治理工作还处在“治存量、遏增量”的关口,个别地方和典型流域农业面源污染问题依然突出. 同时,地方和科研院所关于农业面源污染形成过程、监测核算方法等的试验研究逐渐增多[3 − 8],认识逐步深入,但现行的监测方法手段,特别是从流域尺度的监测能力还比较薄弱、本地化模型及参数还需要进一步完善优化,为说清楚农业面源污染入水体负荷以及流域农业面源污染综合治理提供技术支撑. 本文梳理了农业面源污染形成过程、监测核算常用的研究方法,探讨了当前研究存在的技术问题并对未来的研究方向进行了展望,以期为农业面源污染治理实践提供科学参考.
-
农业面源污染进入环境过程具有间接性,“排放量”不等于实际“污染量”,流失的氮磷经过农田沟渠、缓冲带、湿地或下级农田陆续消纳利用,最终进入水体的实际量是少于排放量的. 农业面源污染形成过程可概括为原位流失和迁移转化两个过程. 其中,种植业氮磷原位流失主要指种植业氮磷离田量,迁移转化主要指原位流失的氮磷在沟渠、湿地等迁移过程中发生的沉积、微生物转化等过程.
-
我国是世界上最大的化肥生产和消费国,化肥施用量约占全球的1/3. 为推进农业发展方式转变,农业农村部于2015年起组织实施化肥使用量零增长行动,大力推广测土配方施肥、有机肥替代化肥、水肥一体化等减肥增效技术. 经科学测算,2022年水稻、小麦、玉米三大粮食作物化肥利用率为41.3%[9],比2015年提高6.1个百分点. 尽管我国化肥利用率不断提高,但仍存在不合理使用的问题,部分氮磷等营养成分未被农作物有效利用,进入水体影响水质. 《第二次全国污染源普查公报》显示,种植业总氮、总磷排放量分别为71.95 万t、7.62 万t.
对于氮素来说,施入农田中氮肥除被植物吸收利用和残留在土壤中外,其余部分以挥发、淋溶、径流、硝化反硝化等途径损失[10, 11]. 不同地区和不同种植方式的农田氮素损失特征不尽相同. 华北平原小麦-玉米体系氮肥损失主要以氨挥发、硝酸盐淋溶、反硝化和地表径流为主[12, 13]. 对于长江中下游典型稻-麦轮作区,投入稻-麦体系的氮素除被作物吸收利用外,主要通过反硝化、氨挥发、径流和渗漏损失,残留土壤的氮素较少. 杨林章等[7]指出,江苏省太湖流域稻-麦轮作体系周年氮肥使用量约为600 kg· ha−1(按N算),其中作物吸收、氨挥发损失、渗漏和地表径流损失、反硝化损失分别占48%、17%、15%、20%. 相比于氮素,磷素在土壤中较为稳定,主要通过径流和淋溶等途径损失. 通过地表径流流失的磷可分为溶解态磷和颗粒态磷,颗粒态磷是土壤磷径流损失的主要形态[14 − 15].
影响农田氮磷流失的因素很多,主要包括降雨、土壤结构、肥料种类及用量、施肥方式、灌溉、耕作及轮作制度等[16 − 20]. 降雨是氮磷流失的主要驱动力,降雨强度大,径流中氮磷流失浓度和流失负荷高[21]. 土壤的质地、酸碱度、氮磷本底含量、有机质含量等会影响氮磷在土壤中的残留和累积,甚至改变径流和土壤侵蚀的条件,进而影响氮磷流失[22]. 肥料的种类、施用方式、施用水平等也会对氮磷损失产生影响,如Dong 等[3]指出施氮量在180—315 kg·ha−1时其对水稻产量差异不显著,但随着施氮量的增加,氮肥利用率降低,田面水总氮浓度显著升高,流失风险加大. 华玲玲等[6]发现,施肥后稻田的田面水氮磷浓度迅速达到峰值,一周内快速下降,沟渠水两周即可接近地表水Ⅱ类标准,即施肥后两周是以灌排单元为主要管理模式的稻田氮磷流失风险期,因此加强稻田的水分管理对于防治农业源水污染物排放至关重要.
-
氮磷在河流或沟渠迁移中发生的转化过程是氮磷流失与流域输出之间的重要环节,包括滞留和释放过程. 其中,滞留是指受吸附、沉积、吸收、气化(如氨挥发、反硝化等)等影响,经河流或沟渠迁移后输出的氮磷负荷减少,即污染物发生了衰减;释放是指受解析、溶解、降解等影响,滞留在河流或沟渠中氮磷重新释放出来使输出的氮磷负荷增加. 氮磷迁移转化过程既受水生生物等生物因素影响,还受到沟渠坑塘、河道地质、地形、河流形态、水文状况、流域面积、土地利用类型、陆地氮素输入量、水温、光照等非生物因素影响[23].
研究发现,流域氮磷的输出负荷与径流量显著相关,不同流域的氮输出与输入的比值为10%—35%,且径流量越大的流域氮输出占输入的比值越高[24],这主要是因为随着径流量增加,土壤氮溶出增多,流域氮输出负荷增加[25]. 因此,一年内降雨集中的月份即雨季,氮输出负荷较高,占全年总输出负荷的比例也较高. 降雨类型、降雨强度也会对土壤氮素流失产生一定的影响[26 − 27].
沟塘系统连接着农田及田外水系,不仅是农田水体排放的初级汇合段,也是下游的水体、物质的外输口,具有蓄水、节流、过滤、净化等作用. 研究发现,经过人为改造的生态沟渠对水体氮的去除率达到31.4%—64.3%[28 − 30]. 尹澄清等[31]发现, 人工沟塘系统能截留大部分的无机态的氨态氮和正磷酸根态磷,使污染物有效沉降. 目前,沟塘作为重要的农业环保工程,得到广泛研究,生态沟渠建设也成为农业农村部组织实施的重点流域农业面源污染综合治理项目中农田面源污染防治工程的重点内容之一. 浙江省平湖市围绕“源头减量”实施化肥农药减量增效,以农田氮磷生态拦截沟渠系统为主要工程,以构建生态塘或断头浜实现“末端净化”,配套节水灌溉、循环利用等技术,创建了稻田退水“零直排”模式,据监测分析,核心污染防控区氮磷排放量平均分别削减18%—24%,取得了较好效果[32].
此外,流域内农业土地的空间分布对氮素的输出具有重要影响. 源的位置及空间分布是河道氮素衰减的重要影响因子,当源距离流域出口的距离(或迁移距离)大于10 km,约有60%—80%的原位流失的氮素可以在河道迁移过程中被去除[33].
-
农业面源污染监测方法多样,与监测尺度、监测目的等相关,通常包括实地监测和模型模拟等手段.
-
种植业氮磷流失监测核算的实测研究可通过水文监测和同位素示踪等手段,适用于田块、河道和流域尺度. 田块尺度监测主要通过设置灌排小区或灌排单元,监测降雨或灌溉条件下地表径流产生量和污染物流失情况,揭示农业源水污染排放的关键时期及主要影响因素. 2005年后,我国大量专家学者在长江、黄河等流域进行了长期野外监测,积累了丰富数据. 王桂苓等[34]采用田间径流池法研究巢湖流域麦稻轮作种植条件下农田径流氮磷流失特征,其中总氮的66%以上是在麦季流失的,总磷的89%以上是在稻季流失的. 刘方谊等[35]采用流失系数法分析了湖北省三峡库区4县(区)18种主要种植模式农田地表径流情况,当季施肥造成的氮、磷流失量占农田流失总量29.6%和26.3%. 平地、缓坡地、陡坡地三类坡度农田中,平地氮磷流失量最高,分别占库区流失量56.1%和57.1%,缓坡地次之,陡坡地最低.
农业农村部在第二次全国污染源普查工作基础上,于2019年起组织实施农田氮磷流失原位国控监测,该监测体系综合考虑农田氮磷污染的发生规律和地形、气候、土壤作物种类与布局、种植制度、耕作方式、灌排方式等情况,在全国布设241个氮磷流失原位监测点,其中地表径流点位165个,地下淋溶点位76个,监测产流量、总氮、总磷等指标,获取全国六大分区54类种植模式的氮磷流失系数. 结合抽样调查,核算全国农田氮磷流失量. 2021年度农田氮磷流失监测报告显示,我国农田氮磷流失量具有明显的空间差异性,南方地表径流流失量明显高于北方,其中南方湿润平原区是地表径流氮磷流失的重点区域,以20%的耕地面积占全国氮、磷径流流失总量的62%和68%;黄淮海半湿润平原区地下淋溶总氮流失量高于其它地区流失量,占全国总量的45%.
河道、流域尺度监测主要通过布设监测点或监测断面,利用野外设施设备测量水量并采集水样,结合测试分析,解析氮磷形态和来源. 比如《NY/T
3824 -2020 流域农业面源污染监测技术规范》明确规定了监测断面(控制断面和背景断面)布设、监测时期及频率、采样方法、监测指标及方法等要求,通过监测断面的流量和水质,核算流域农业面源输出负荷.另外,同位素示踪法常用于监测氮磷的吸收、转化和分配情况,如张晴雯等[8]利用15N示踪法研究黄河上游稻田氮肥去向,发现残留化肥氮主要富集在表层0—30 cm. 高月香等[36]利用同位素示踪等方法,定量解析了北澄子河流域硝态氮污染来源,其中生活污水源和水产养殖源贡献率最高,畜禽养殖源次之,种植业贡献最低. 但需要注意的是,野外实测法受自然和人为因素影响较大,实验条件和样品采集、保存、测试各环节均可能导致实验误差,且通常需要大量人力财力.
-
(1)经验模型 经验模型主要分为两类:一是输入输出模型,包括净氮/磷输入模型及其改进模型,输出系数模型及其改进形式、PLOAD模型、通用土壤流失方程USLE、RUSLE、MUSLE等[37]. 在基础研究较少、实地监测数据较为缺乏的地区,可将净氮/磷输入模型和输出系数模型相结合,流域的养分循环及污染风险进行评估. 二是污染指数模型,包括APPI、NI、PI等[38]. Howarth等[39]首先提出“人类活动净氮/磷输入(NANI/NAPI)”的概念,用于估算流域中由人类活动导致的不同氮磷来源的输入强度. 目前,NANI/NAPI及其衍生方法在美国、欧洲及亚洲地区得到了广泛应用,结果表明人类活动导致的区域氮磷输入中约有15%—30%的氮、2%—10%的磷通过径流、淋溶和点源排放等过程输出至流域出口,剩余养分存留于流域内部[40- 41].
输出系数模型根据土地利用与水质、水量等实测数据的相关统计关系,获得不同土地利用方式下氮磷等污染物的输出系数[42],通过系数及各统计量估算得到流域污染物输出负荷,并解析主要污染物、污染源和污染区. 胡晴等[5]基于流域输出系数模型,考虑区域自然地理、水文气象以及人类活动影响等因素的差异性,建立了“驱动因子—传输因子—下渗因子—滞留因子”为主体的全过程入水体系数核算体系. 结果表明,2016年滇池流域总氮和总磷入水负荷量分别为577 t和168 t,入水系数分别为0.447和0.342,分布特点表现为四周高,中部滇池盆地低,西部最高.
(2)机理模型 机理模型在面源污染监测评估方面的应用始于20世纪六七十年代,其通常由水文过程模拟、土壤侵蚀与产沙过程模拟、氮磷等污染物产生与迁移过程模拟、污染物进入水体对水质的影响模拟等过程模型集合而成,对数据量和数据精度要求较高,侧重研究面源污染的产生机理和迁移转化过程. 机理模型在空间污染识别方面具有明显优势,但模拟过程的复杂性和对数据的强依赖性也增加了机理模型的不确定性. 常用的机理模型包括SWAT、AnnAGNPS、HSPF等,其中SWAT模型采用日尺度作为最低模拟时间尺度单位,可模拟流域内多种污染物的不同循环过程;AnnAGNPS模型适用于较小尺度的流域污染模拟,可用于预测流域水量水质、识别面源污染的关键源以及评估最佳管理措施;HSPF模型适用于对中尺度流域污染模拟.
杨佳磊等[43]采用SWAT模型,估算了太湖流域1980—2018年的非点源氮磷污染负荷变化量及主要污染来源. 结果表明,太湖流域1980年和2018年总氮、总磷负荷量分别为9.95 万t、2.60 万t和5.89 万t、0.83 万t,总体呈下降趋势,总氮、总磷负荷变化空间分布均为西北高、西南低. 此外,农村生活、农田径流和畜禽养殖是总氮的主要来源,占比分别为50.6%、26.9%和14%;农村生活、畜禽养殖、农田径流和水产养殖是总磷的主要来源,占比分别为32.8%、23.9%、14.9%和14.9%. 胡德秀等[4]构建了渭河流域咸阳—西安段的非点源污染SWAT模型,利用2008—2016年逐月径流、水质及CMADS气象数据集等资料,对SWAT模型进行率定及验证,发现2016年区域非点源总氮和总磷负荷的入河量分别为
7654.0 t和626.5 t,时间主要集中在汛期6—10月,分别占全年总氮和总磷的72.23%和56.33%,且渭河流域南岸的非点源污染重于北岸. 通过综合实施化肥减量、集中设置沼气池和加强水土保持等3项措施,可削减9.98%—50.68%的非点源总氮负荷和5.25%—52.84%的非点源总磷负荷.(3)其他模型 随着“3S”(GPS、GIS、RS)技术发展,遥感等监测手段在流域水质、农业面源污染评估等方面得到逐步应用,比如王雪蕾等[44]基于遥感监测手段,应用DPeRS模型对巢湖流域氮磷面源污染特征进行遥感像元尺度解析和氮磷减排情景分析,指出2010年巢湖流域总氮、总磷产生量分别为
1900.3 t、244.1 t,入河量分别为846.5 t、76 t,并发现当施肥量减少30%,农村生活垃圾处理率提高到60%,畜禽粪便处理率和城市垃圾处理率提高到80%时,氮磷面源污染平均削减率可以达到50%. 2022年9月,生态环境部印发《全国农业面源污染监测评估实施方案(2022—2025年)》,以“天地协同监测、模型评估核算”为农业面源污染监测评估基本思路,兼顾地面综合监测和卫星遥感监测、指标调查和监测评估,即基于以地表冲刷的氮磷营养盐类为主的地面监测,依托DPeRS模型开展农业面源污染监测评估,提出到2025年年底,全国至少完成173个农业面源污染监测区的监测工作. -
农业面源污染成因复杂,影响因素众多,复杂性和随机性强. 为科学准确反映农业面源污染的真实状况,需要对农业面源污染进行有效监测,工作难度很大. 当前我国农业面源污染监测核算仍存在一些不足.
(1)现行的监测方法以传统的人工调查采样、物理化学分析等手段为主,由于农业面源污染排放形式分散,获取较为准确的排放数据通常需要耗费大量人力财力. 而自动监测站造价较高,相关产品装备的研发、迭代能力不足,监测软硬件设备均需要运行维护,对操作人员的技术要求较高,长期的历史数据积累还比较缺乏.
(2)农业面源污染本身具有随机性和不确定性,且进入环境过程具有间接性,而目前我国从田块到流域尺度的系统监测能力还比较薄弱,农业生产过程中氮磷在“投入—产生—排放—入湖(河)”各环节迁移转化规律不明,无法说清流失的氮磷进入最终受纳水体的实际情况. 特别是流域监测方法、手段还不完善,尽管部分地区启动了流域农业面源污染监测试点,但实际的入水体负荷还没有全面系统的报道,农业源对环境质量的贡献率估算依然不清.
(3)本地化流域农业面源污染模型及参数还不完善,目前我国主要应用国际上较为成熟的机理模型,但由于我国与国外发达国家在农业生产方式、地形地貌单元、氮磷迁移转化路径等方面存在显著差异,如在我国农田中常见的沟塘等往往不在国外模型的模拟单元中,因此简单套用现有模型无法准确解析我国农业面源污染的贡献.
-
针对农业面源污染形成特点和目前我国农业面源污染监测核算研究中存在的技术问题,提出以下建议.
(1)建立流域尺度多级监测体系. 田块尺度监测是核算种植业氮磷流失系数的基础性工作,必须切实做好长期性例行监测. 科学布设长期定位监测点,加强监测点位管理,做好监测数据质量控制,构建完善数据详实、管理高效的监测网络. 聚焦重点区域、重点问题,推动开展区域性监测,形成小区—大田块—整体排灌单元—小流域(大型灌区)多级监测体系. 以长江经济带、黄河流域为重点,以农业生产为主的小流域为单元,逐步开展小流域入水体负荷评估试点.
(2)优化监测方法和监测手段. 加强低成本、高精度、高稳定性水质和水量在线监测设备的研发、现代化智能监测手段的应用,提高监测效率和时空代表性. 研发具有自主知识产权、适合我国农业面源污染监测核算的本土化模型,优化现有机理模型及其参数,提高模拟数据的精确度. 构建包括监测技术规范、分析测试方法、质量控制等内容的农业面源污染监测评估标准体系.
(3)突破监测关键技术装备. 通过国家重大科技专项、国家重点研发计划、“揭榜挂帅”等项目开展产学研联合攻关,突破制约农业面源污染监测评估创新发展的“卡脖子”技术、关键核心技术和共性技术问题,推进技术集成创新,推动设施装备向模式化、智能化转变.
(4)深化监测结果应用. 将面源污染监测治理与农业绿色发展有效融合,通过农业面源污染监测,科学评价地方工作效果,科学评价农业面源污染治理效果,为开展精准治理提供有力支撑;基于监测评估结果,系统设计区域农业面源污染综合防治方案,促进种养业增效降耗和废弃物资源化利用,助力流域水质和农业生态环境改善,为推进乡村生态振兴、推动农业绿色发展提供有力支撑.
我国农业面源污染监测研究进展与发展建议
Research progress and development proposals for monitoring agricultural non-point source pollution in China
-
摘要: 针对农业面源污染排放形式分散、随机性和不确定性强、进入环境过程具有间接性等特点,本文梳理了农业面源污染形成过程、监测核算常用研究方法,剖析了目前农业面源污染监测评估在技术方面存在的难点和问题,并提出完善相关监测制度、统筹多尺度监测、优化监测方法、设立研发项目、深化结果应用等方面建议,以期为农业面源污染治理实践提供参考借鉴,助力乡村生态振兴和农业绿色发展.Abstract: According to the characteristics of scattered, randomness and indirect nature of agricultural non-point source pollution emissions, this paper examines the formation process and research methods for monitoring and accounting. It delves into the technical challenges and issues currently faced in monitoring and assessing agricultural non-point source pollution. Based on these insights, recommendations are made to improve monitoring systems, integrate multi-scale monitoring, optimize monitoring methods, establish research and development projects, and deepen the application of results. The aim is to provide practical guidance for the treatment of agricultural non-point source pollution, thereby supporting rural ecological revitalization and green agricultural development.
-

-
[1] 孔嘉鑫, 姜仁楠, 范贝贝, 等. 农业面源污染特征及治理对策[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2016, 41(5): 85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2016.05.021 KONG J X, JIANG R N, FAN B B, et al. Research and management of agricultural non-point source pollution[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2016, 41(5): 85-88 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2016.05.021
[2] DAI F Y, FAN B Q, LI J G, et al. Fate of 15N-labelled urea as affected by long-term manure substitution[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 893: 164924. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164924 [3] DONG Z Z, WU L H, CHAI J, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on rice grain yield, nitrogen-use efficiency, and water quality in paddy field[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2015, 46: 1579-1594. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1045595 [4] 胡德秀, 李依江, 李立, 等. 基于SWAT模型的渭河咸阳-西安段非点源污染削减措施研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(10): 127-136,145. HU D X, LI Y J, LI L, et al. Reduction scenarios of non-point source pollution in Xianyang-Xi’an section of Weihe River Basin based on SWAT[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(10): 127-136,145 (in Chinese).
[5] 胡晴, 郭怀成, 王雨琪, 等. 基于改进输出系数模型的农业源污染物负荷核算[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(4): 739-748. HU Q, GUO H C, WANG Y Q, et al. Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution loads based on improved export coefficient model[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2021, 57(4): 739-748 (in Chinese).
[6] 华玲玲, 张富林, 翟丽梅, 等. 江汉平原水稻季灌排单元沟渠中氮磷变化特征及其环境风险[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2715-2723. HUA L L, ZHANG F L, ZHAI L M, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration dynamics in natural ditches under an irrigation-drainage unit in the Jianghan Plain[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2715-2723 (in Chinese).
[7] 杨林章. 我国农田面源污染治理的思路与技术[J]. 民主与科学, 2018(5): 16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0026.2018.05.004 YANG L Z. Thoughts and technologies of farmland non-point source pollution control in China[J]. Democracy & Science, 2018(5): 16-18 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0026.2018.05.004
[8] 张晴雯, 张惠, 易军, 等. 青铜峡灌区水稻田化肥氮去向研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(8): 1707-1714. ZHANG Q W, ZHANG H, YI J, et al. The fate of fertilizer-derived nitrogen in a rice field in the Qingtongxia irrigation area[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(8): 1707-1714 (in Chinese).
[9] 农民日报. 种植业高质量发展成效显著 [EB/OL]. [2022-12-24]. [10] SOARES J R, CANTARELLA H, de CAMPOS MENEGALE M L. Ammonia volatilization losses from surface-applied urea with urease and nitrification inhibitors[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 52: 82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.019 [11] 田玉华, 尹斌, 贺发云, 等. 太湖地区水稻季氮肥的作物回收和损失研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(1): 55-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2009.01.008 TIAN Y H, YIN B, HE F Y, et al. Recovery by crop and loss of nitrogen fertilizer applied in rice season in Taihu Lake Region[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(1): 55-61 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2009.01.008
[12] JU X T, XING G X, CHEN X P, et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 3041-3046. [13] 赵荣芳, 陈新平, 张福锁. 华北地区冬小麦-夏玉米轮作体系的氮素循环与平衡[J]. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(4): 684-697. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.04.017 ZHAO R F, CHEN X P, ZHANG F S. Nitrogen cycling and balance in winter-wheat-summer-maize rotation system in Northern China Plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2009, 46(4): 684-697 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.04.017
[14] COX F R, HENDRICKS S E. Soil test phosphorus and clay content effects on runoff water quality[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2000, 29(5): 1582-1586. [15] WEI Q S, ZHU G F, WU P, et al. Distributions of typical contaminant species in urban short-term storm runoff and their fates during rain events: A case of Xiamen City[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(4): 533-539. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60138-8 [16] HAN C W, XU S G, LIU J W, et al. Nonpoint-source nitrogen and phosphorus behavior and modeling in cold climate: A review[J]. Water Science and Technology: a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2010, 62(10): 2277-2285. doi: 10.2166/wst.2010.464 [17] PAN S H, LIU D D, WANG Z L, et al. Runoff responses to climate and land use/cover changes under future scenarios[J]. Water, 2017, 9(7): 475. doi: 10.3390/w9070475 [18] 贾海燕, 雷阿林, 雷俊山, 等. 紫色土地区水文特征对硝态氮流失的影响研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2006, 26(10): 1658-1664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2006.10.013 JIA H Y, LEI A L, LEI J S, et al. Nitrate-N loss effected by the runoff process in purple soil-a simulation study[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(10): 1658-1664 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2006.10.013
[19] 李琪, 陈利顶, 齐鑫, 等. 流域尺度农业磷流失危险性评价与关键源区识别方法[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(9): 1982-1986. LI Q, CHEN L D, QI X, et al. Catchment scale risk assessment and critical source area identification of agricultural phosphorus loss[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(9): 1982-1986 (in Chinese).
[20] 梁新强, 田光明, 李华, 等. 天然降雨条件下水稻田氮磷径流流失特征研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(1): 59-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.01.015 LIANG X Q, TIAN G M, LI H, et al. Study on characteristic of nitrogen and phosphorus loss from rice field by natural rainfall runoff[J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2005, 19(1): 59-63 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.01.015
[21] 付月君, 王昌全, 李冰, 等. 稻田氮磷养分损失途径及影响因素研究进展[J]. 四川环境, 2015, 34(6): 162-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2015.06.029 FU Y J, WANG C Q, LI B, et al. An overview on losing path of fertilizer nitrogen and phosphorus and their influencing factors in paddy field[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2015, 34(6): 162-167 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2015.06.029
[22] 李高明, 铁柏清, 李杰峰, 等. 湖南典型土壤类型和耕作方式的氮磷损失特征研究[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2009(4): 52-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2009.04.017 LI G M, TIE B Q, LI J F, et al. Study on nitrogen and phosphorus loss character of typical agrotype and cultivation in Hunan[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2009(4): 52-54 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-060X.2009.04.017
[23] BIRGAND F, SKAGGS W, CHESCHEIR C, et al. Nitrogen removal in streams of agricultural catchments literature review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2007, 37: 381. doi: 10.1080/10643380600966426 [24] HOWARTH R, SWANEY D, BILLEN G, et al. Nitrogen fluxes from the landscape are controlled by net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs and by climate[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2012, 10(1): 37-43. doi: 10.1890/100178 [25] BETTEZ N D, DUNCAN J M, GROFFMAN P M, et al. Climate variation overwhelms efforts to reduce nitrogen delivery to coastal waters[J]. Ecosystems, 2015, 18(8): 1319-1331. doi: 10.1007/s10021-015-9902-9 [26] WU L, PENG M L, QIAO S S, et al. Assessing impacts of rainfall intensity and slope on dissolved and adsorbed nitrogen loss under bare loessial soil by simulated rainfalls[J]. Catena, 2018, 170: 51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.06.007 [27] YANG T, WANG Q J, WU L S, et al. A mathematical model for soil solute transfer into surface runoff as influenced by rainfall detachment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 557: 590-600. [28] 王晓玲, 乔斌, 李松敏, 等. 生态沟渠对水稻不同生长期降雨径流氮磷的拦截效应研究[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(12): 1406-1413. WANG X L, QIAO B, LI S M, et al. Studies on the interception effects of ecological ditch on nitrogen and phosphorus in the rainfall runoff of different rice growth period[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(12): 1406-1413 (in Chinese).
[29] 余红兵, 肖润林, 杨知建, 等. 灌溉和降雨条件下生态沟渠氮、磷输出特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(5): 686-692. YU H B, XIAO R L, YANG Z J, et al. Study on the characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus transportation through ecological ditch during irrigation and rainfall[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2014, 23(5): 686-692 (in Chinese).
[30] 张树楠, 肖润林, 刘锋, 等. 生态沟渠对氮、磷污染物的拦截效应[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(12): 4516-4522. ZHANG S N, XIAO R L, LIU F, et al. Interception effect of vegetated drainage ditch on nitrogen and phosphorus from drainage ditches[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(12): 4516-4522 (in Chinese).
[31] 尹澄清, 毛战坡. 用生态工程技术控制农村非点源水污染[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(2): 229-232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.025 YIN C Q, MAO Z P. Nonpoint pollution control for rural areas of China with ecological engineering technologies[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(2): 229-232 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.025
[32] 李中利, 燕燕, 邵正浩. 基于稻田退水“零直排” 模式的农业面源污染治理路径[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(12): 2513-2515. LI Z L, YAN Y, SHAO Z H. Government way of agricultural non-point source pollution based on zero-direct discharge for rice field water[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 62(12): 2513-2515 (in Chinese).
[33] WOLLHEIM W M, BERNAL S, BURNS D A, et al. River network saturation concept: Factors influencing the balance of biogeochemical supply and demand of river networks[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2018, 141(3): 503-521. doi: 10.1007/s10533-018-0488-0 [34] 王桂苓, 马友华, 孙兴旺, 等. 巢湖流域麦稻轮作农田径流氮磷流失研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(2): 6-10,29. WANG G L, MA Y H, SUN X W, et al. Study of nitrogen and phosphorus runoff in wheat-rice rotation farmland in Chao Lake basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(2): 6-10,29 (in Chinese).
[35] 高月香, 李想, 高田田, 等. 同位素示踪解析北澄子河流域硝态氮污染贡献[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(10): 2269-2276. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2022-0205 GAO Y X, LI X, GAO T T, et al. Isotopic tracer analysis of nitrate nitrogen pollution contribution in the Beichengzi River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(10): 2269-2276 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2022-0205
[36] 刘方谊, 夏颖, 黄敏, 等. 湖北省三峡库区不同种植模式下农田地表径流氮磷流失特征[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2018, 35(6): 550-558. LIU F Y, XIA Y, HUANG M, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus losses from farmlands through surface runoff under different cropping patterns in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2018, 35(6): 550-558 (in Chinese).
[37] 马力, 卜兆宏, 梁文广, 等. 基于USLE原理和3S技术的水土流失定量监测方法及其应用研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(3): 602-614. doi: 10.11766/trxb201805310168 MA L, BU Z H, LIANG W G, et al. Method for quantitative monitoring of soil erosion based on USLE principle and 3S technology and its application[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(3): 602-614 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11766/trxb201805310168
[38] 管飞, 马友华, 张东红, 等. 农业面源污染负荷空间分布及风险评价研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(30): 61-66. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16090062 GUAN F, MA Y H, ZHANG D H, et al. Agricultural non-point source pollution loads: Spatial distribution and risk assessment[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(30): 61-66 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16090062
[39] HOWARTH R W, BILLEN G, SWANEY D, et al. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: Natural and human influences[J]. Biogeochemistry, 1996, 35(1): 75-139. doi: 10.1007/BF02179825 [40] HONG B, SWANEY D P, McCRACKIN M, et al. Advances in NANI and NAPI accounting for the Baltic drainage basin: Spatial and temporal trends and relationships to watershed TN and TP fluxes[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2017, 133(3): 245-261. doi: 10.1007/s10533-017-0330-0 [41] 张汪寿, 苏静君, 杜新忠, 等. 1990—2010年淮河流域人类活动净氮输入[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(6): 1831-1839. ZHANG W S, SU J J, DU X Z, et al. Net anthropogenic nitrogen input to Huaihe River Basin, China during 1990-2010[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(6): 1831-1839 (in Chinese).
[42] JOHNES P J. Evaluation and management of the impact of land use change on the nitrogen and phosphorus load delivered to surface waters: The export coefficient modelling approach[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1996, 183(3/4): 323-349. [43] 杨佳磊, 张瑞, 张银意, 等. 1980—2018年太湖流域非点源氮磷负荷变化研究[J]. 环境保护科学, 2022, 48(6): 93-101. YANG J L, ZHANG R, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Study on change of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus load in Taihu Lake Basin from 1980 to 2018[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2022, 48(6): 93-101 (in Chinese).
[44] 王雪蕾, 王新新, 朱利, 等. 巢湖流域氮磷面源污染与水华空间分布遥感解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(5): 1511-1519. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.05.031 WANG X L, WANG X X, ZHU L, et al. Spatial analysis on diffuse pollution and algal bloom characteristic with remote sensing in Chao Lake Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(5): 1511-1519 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.05.031
-



 下载:
下载:

