-
水污染和水资源短缺严重阻碍着社会和经济的可持续发展[1-2]。膜法水处理技术因具有处理效率高、出水水质好、占地面积小等优点[3],在水处理领域受到广泛关注。作为低压膜分离技术的典型代表,超/微滤技术已被广泛应用于给水处理、污水回用以及海水淡化预处理等领域[4-5]。然而,膜污染问题始终制约着膜分离技术的进一步发展[6]。
现阶段针对膜污染的控制方法主要包括膜前水质调控、膜清洗以及膜材料改性等[7]。其中,水质调控的效果较大程度上依赖于进水水质和前处理工艺参数的选择,在实际工程中控制难度较大。膜清洗是目前实际工程中控制膜污染的常规手段,无论是水/气冲刷、水力反冲洗,还是化学清洗,均可在一定程度上减缓膜污染的发展。但是,膜清洗额外增加的药剂和操控成本,及其对出水水质和膜寿命等的影响,并不利于膜技术的可持续发展[3]。膜污染本质上是一种界面现象,是待过滤料液中的溶解性有机物、胶体和颗粒物质等与膜表面之间相互作用的结果[3]。因此,膜的界面性质(如带电属性、粗糙度以及亲疏水性等),主导着膜污染的产生和发展。大量研究[5-7]表明,膜的亲疏水性是影响膜污染发展的最核心因素之一,而制备超亲水膜是从根本上控制膜污染的有效途径。
纳米材料和纳米技术的发展为新型超亲水膜的研制提供了诸多途径。氧化石墨烯(GO)作为一种表面富含羧基(—COOH)、羟基(—OH)等活性位点的二维纳米材料,已被广泛应用于水处理领域[8-10]。纳米SiO2具有易化学修饰的特点,可基于硅烷化反应灵活制备出性能丰富的有机/无机复合材料,已被广泛用于对传统有机膜材料的亲水改性[11-12]。
本研究以不锈钢网[13]为基底,以GO和氨基修饰的纳米SiO2为膜材料,利用GO表面的—COOH与纳米SiO2表面的氨基(—NH2)之间的自组装共价键反应,开展了多种新型GO/SiO2无机复合膜的制备研究。对比了4种制膜方法,即真空抽滤、多巴胺辅助抽滤、热辅助法和高温煅烧辅助抽滤法,结合对所得膜的表面官能团组成、表面形貌、表面粗糙度和亲水性的系统表征,以复合膜的亲水性和稳定性为评价指标,对超亲水GO/SiO2复合膜的制备方法进行了优选,为超亲水无机复合膜的制备提参考。
-
复合膜基底选用不锈钢网(SSM,316L型,中国安平金属有限公司),丝径为10 μm,厚度为70 μm,经5 mol·L−1硫酸溶液浸泡30 min后,用超纯水充分冲洗,于60 ℃烘干备用。制膜原材料选用2 mg·L−1 GO悬浮液(片径<500 nm,南京先丰纳米材料科技有限公司)和粒径为20 nm的SiO2纳米颗粒(Ludox HS-30,Sigma-Aldrich,美国),其中SiO2纳米颗粒经硅烷化反应修饰后制得表面含有氨基基团的SiO2(M-SiO2)[11]。M-SiO2的制备流程如下:将含有102 g·L−1纳米SiO2和35.6 g·L−1 3-氨基丙基(三甲氧基硅烷)(APTMS,97%,Sigma-Aldrich,美国)pH为5的混合溶液在氮气氛围保护下于70 ℃加热反应24 h,随后透析纯化48 h后,制得M-SiO2悬浮液,保存于4 ℃备用。其他辅助制膜的药品为:盐酸多巴胺(dopamine,98%)、三(羟甲基)-氨基甲烷盐酸盐(Tris-HCl,99%)、1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐(EDC)、N-羟基丁二酰亚胺(NHS,≥97%)以及2-(N-吗啉基)乙磺酸4-吗啉乙磺酸(MES,≥99%)。
-
将经酸洗处理后的SSM安置在抽滤器中,依次采用10 mL 0.4 mg·L−1的M-SiO2悬浮液和10 mL 2 mg·L−1的GO悬浮液作为进水进行真空抽滤,重复4次后,SSM表面即形成一层GO/SiO2复合层,即得到v-GO/SiO2复合膜。
-
将酸洗处理后的SSM浸泡于含有2 g·L−1多巴胺的Tris-HCl溶液中4、16、24 h,记为d-4、d-16和d-24,将负载有聚多巴胺的SSM安置在抽滤器中,按照上述方法进行抽滤制膜,即得到d-GO/SiO2复合膜。
-
将酸洗处理后的SSM置于底部安置有一层聚二甲基硅氧烷软模板的玻璃容器中,倒入50 mL 1 mg·L−1 GO悬浮液,于30 ℃烘箱中静置烘干;倒入100 mL含有2 mmol·L−1 EDC、5 mmol·L−1 NHS和10 mmol·L−1 MES的催化剂溶液,静置15 min后,倒出催化剂溶液;立即加入50 mL 0.4 mg·L−1 M-SiO2悬浮液,于30 ℃下静置反应至表面干燥;重复上述操作1次,即可制得h-GO/SiO2复合膜。
-
将经酸洗处理后的SSM安置在抽滤器中,采用50 mL原生SiO2纳米颗粒(HS-30)悬浮液为进水进行抽滤,将所得预负载有纳米SiO2的SSM在氮气氛围中于500 ℃煅烧4 h;随后按照上述方法进行抽滤制膜,即得到c-GO/SiO2复合膜。
-
膜表面微观形貌采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FE-SEM,JSM-7001F,日本日立)进行观察;膜表面立体形貌和粗糙度采用原子力显微镜(AFM,Multimode 8,布鲁克,德国)进行观测;膜表面纯水接触角采用视频光学接触角测定仪(OCA 20,德菲,德国)测定。测定接触角时,先将样品平整地贴在玻璃薄片上,然后将2 μL超纯水滴在干燥的膜表面,并记录液滴在膜表面的形态变化视频,从液滴振颤停止后(一般液滴低落后约0.5 s之后)开始计算膜-水接触角。膜表面官能团采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FT-IR,VERTEX 70,布鲁克,德国)进行分析。膜的纯水通量采用一套半死端过滤系统进行测定,系统由超滤杯(Amicon 8010,有效过滤面积为4.1 cm2,密理博,美国)、电子天平(ML4002,梅特勒,瑞士)、数据记录单元以及压力输出和控制装置组成。纯水通量测试步骤为:在20 kPa恒压条件对膜进行预压过滤20 min(期间膜通量逐渐趋于稳定),随后在10 kPa条件下过滤10 min,根据式(1)计算膜的纯水通量。
式中:J为纯水通量,m·(s·kPa)−1;V为过滤液体积,m3;∆P为跨膜压差,kPa;t为过滤时间,s。
-
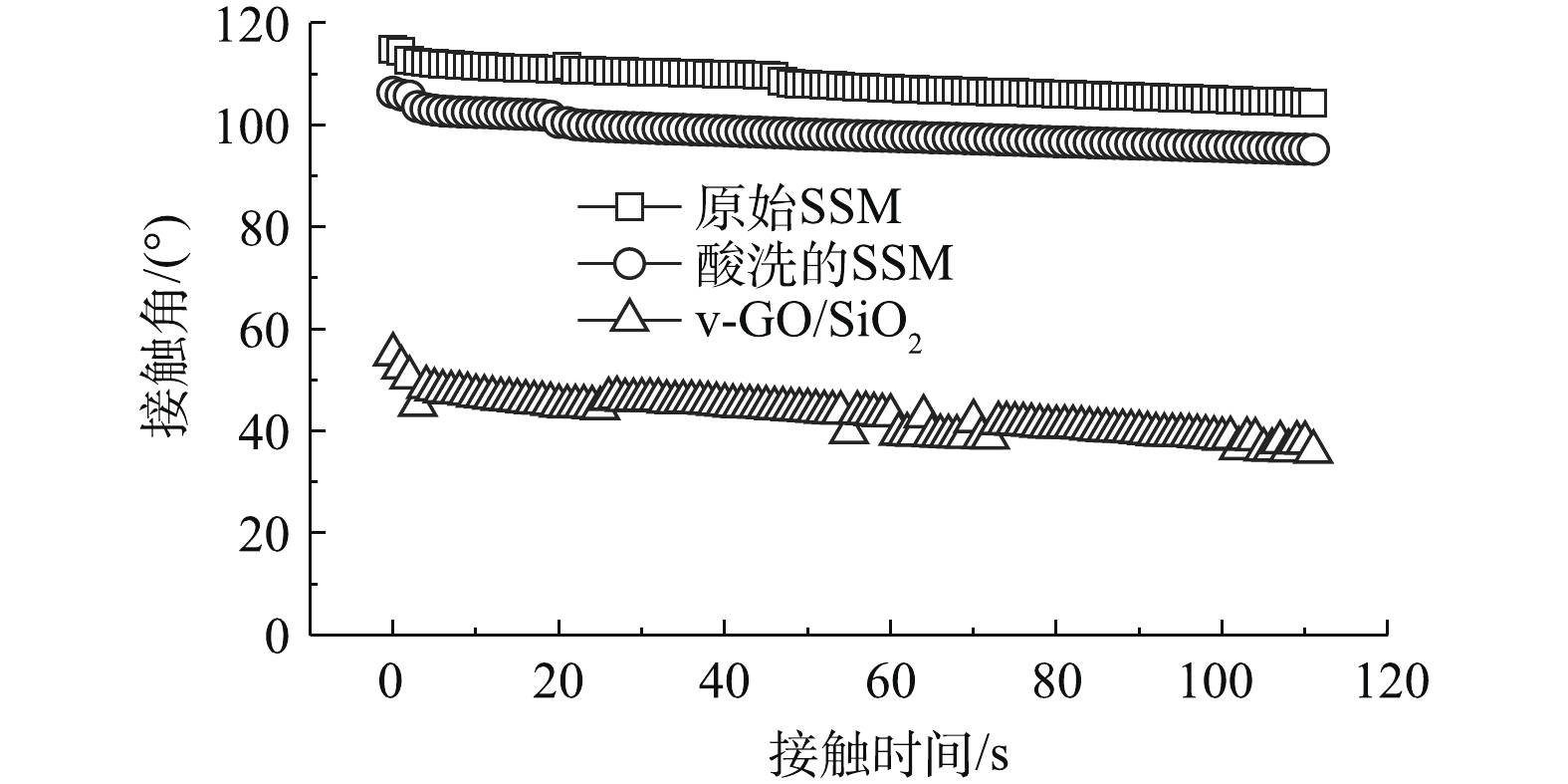
膜表面的亲疏水性由膜自身化学组成和表面微纳结构共同决定,通常使用表面纯水接触角表征膜的亲疏水性质,一般认为,膜表面纯水接触角θ<90°为亲水界面;θ<5°(或液滴能快速在膜表面铺展)为超亲水界面[14-15]。图1反映了SSM(酸洗处理前后)和v-GO/SiO2复合膜的水接触角动态变化情况。原生SSM的初始接触角为114.8°,在120 s内下降至103.8°,呈较高的疏水性,其接触角下降可能主要归因于水滴的逐渐蒸发[11]。当SSM经过酸洗预处理后,表面吸附的低表面能油类等物质被去除,其初始接触角有所降低(106.4°),但仍呈现较高的疏水性。这主要是由于SSM表面的“内凹型”微纳结构容易滞留空气,致使水滴与SSM以Cassie-Baxter模式相接触,从而呈现出较高的疏水性[15]。相比之下,v-GO/SiO2复合膜的初始接触角显著降低至55.0°,约为原生SSM的一半,这主要归因于2点原因:GO与纳米SiO2表面富含—COOH、—OH和—NH2等亲水官能团,具有较高的表面能;部分GO和纳米SiO2填充在SSM的低洼位置,减少了空气的滞留空间,从而使水滴与SSM的接触模式转换为Wenzel模式,从而呈现出亲水性[10-14]。但是,v-GO/SiO2复合膜的亲水性较低,在120 s后,依然维持在35.9°;且GO/SiO2层与SSM之间的附着力较差,强度较低。
-
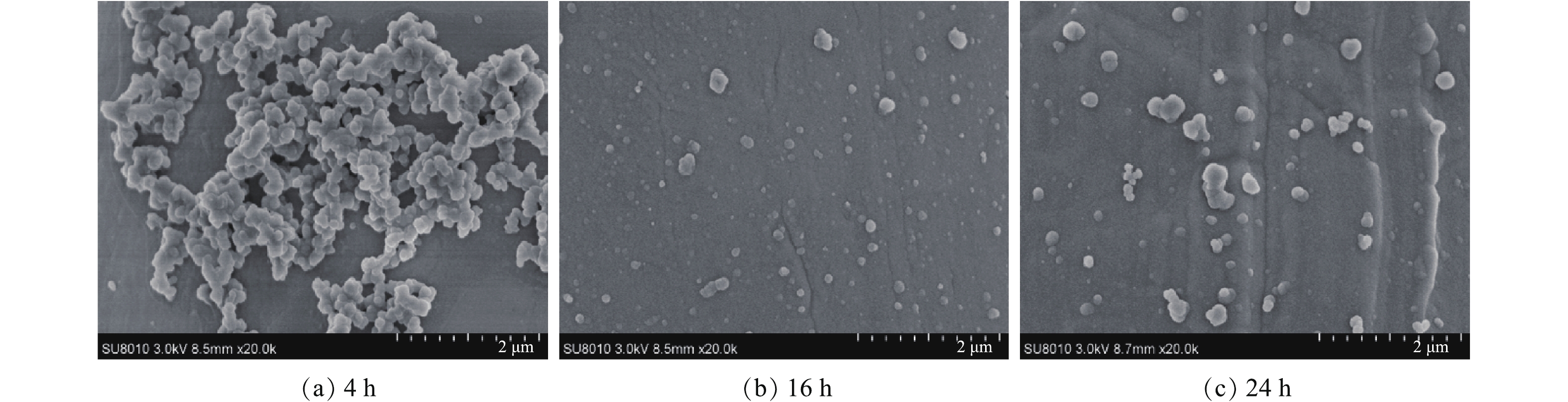
多巴胺是一种同时具有氨基和领苯二酚基官能团的生物神经物质,能在湿态条件下发生氧化自聚且可在固体表面附着[16],常被用于有机膜的亲水改性研究[17]。本研究在SSM表面预负载多巴胺以促进GO/SiO2层的黏附。图2(a)~图2(c)分别为酸洗后的SSM浸泡在0.2 g·L−1多巴胺溶液中4、16和24 h的表面SEM照片。由图2可知,经4 h浸泡的SSM表面含有一定量的多巴胺自聚产物(即聚多巴胺),而随着时间的延长,SSM表面聚多巴胺的增加并不明显。
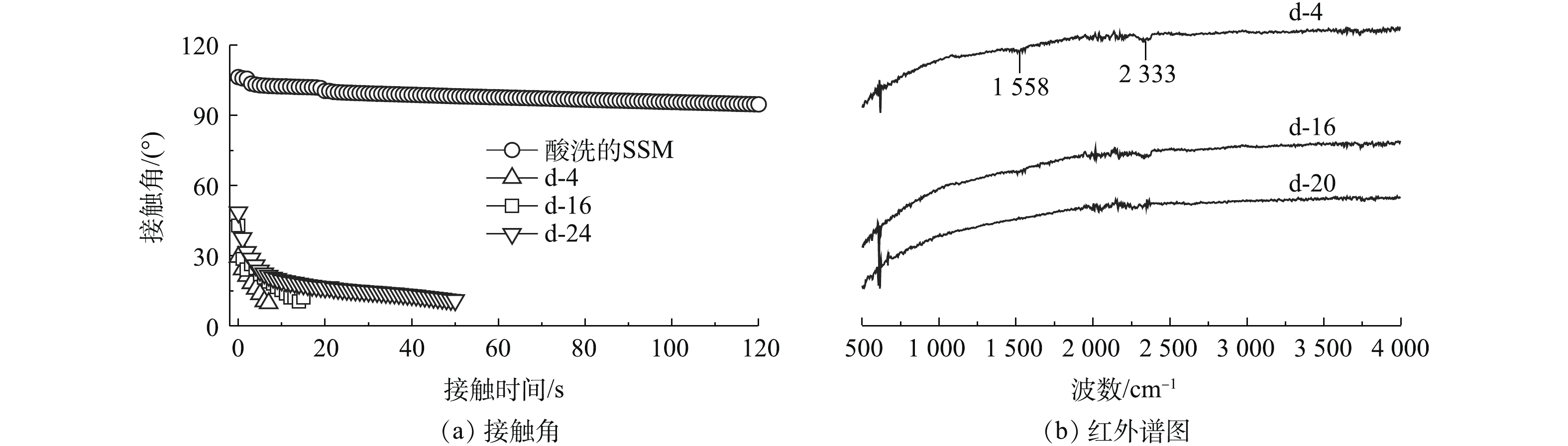
聚多巴胺的附着使SSM的亲水性明显提升。图3(a)反映了不同浸泡时间(4、16和24 h)后SSM的表面接触角对比结果。SSM表面接触角均显著减小,尤其是在多巴胺溶液中浸泡4 h后,SSM的初始接触角为29.5°,并在7 s后,完全铺展于SSM表面(即接触角为0°),表现出较强的亲水性。这可能是因为SSM表面紧密附着聚多巴胺所致,经4 h多巴胺溶液浸泡的SSM表面形貌(图2(a))已直观地证明了这一点。在经16 h和24 h浸泡后,虽然SSM表面的初始接触角略有差别,但是60 s后,均趋近于20°左右。图3(b)为不同时间浸泡后,SSM表面的红外图谱,1 558 cm−1处的吸收峰为—NH2变角振动(1 590~1 650 cm−1)吸收峰,由于芳环C=C伸缩(1 370~1 610 cm−1)和—NH2变角振动重合存在,该处的吸收峰相对较弱,但也在一定程度上证实了SSM表面聚多巴胺的存在。该图谱中并没有呈现出明显的有机官能团吸收峰,这可能是因为多巴胺层太薄或者附着量过少的缘故。
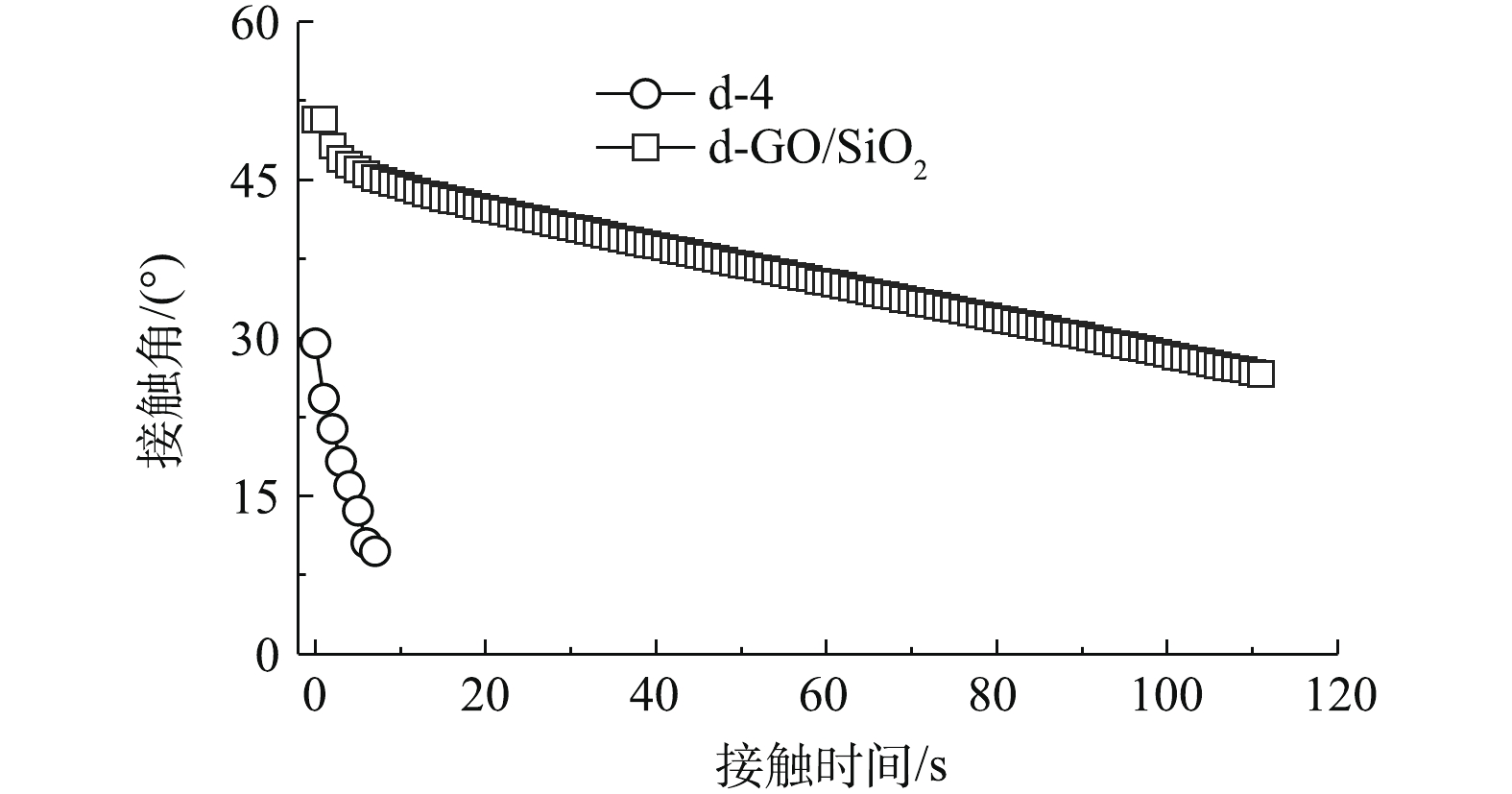
基于优选的4 h浸泡的SSM制备出d-GO/SiO2复合膜。图4反映了d-GO/SiO2复合膜与4 h多巴胺浸泡的SSM接触角动态变化的对比结果。所得d-GO/SiO2复合膜的初始接触角为50.7°,显著高于SSM。这主要归因于GO相对较低的表面能以及较为平整的表面结构[18]。SSM的表面网状纹理有利于水滴的快速铺展与吸收。与v-GO/SiO2复合膜(图1)相比,d-GO/SiO2复合膜的初始接触角更低且下降速率更高,表明亲水性有所提高,但是v-GO/SiO2复合膜的亲水性仍然较低。
-
综合上述结果发现,SSM的网状结构和钢丝的光滑表面不利于物质的附着。为了促进GO与纳米SiO2在SSM表面的附着,提升成膜负载量,研究采用热辅助法和GO/纳米SiO2层层接枝堆叠法制备出h-GO、h-GO/SiO2、h-GO/SiO2/GO、h-GO/SiO2/GO/SiO2 4种堆叠成分和层数不同的复合膜。图5(a)反映了4种膜的接触角变化结果。4种膜的接触角对比趋势呈现出明显的规律性,即随着GO层和SiO2层的依次叠加,接触角依次逐渐降低。H-GO膜的接触角最高(初始接触角为65.2°),呈相对疏水性。这是因为GO表面或边缘虽然含有一定量的—OH和—COOH等亲水官能团[9-10],但碳材料本身的表面能较低,导致亲水性有限[8]。当h-GO膜表面继续自组装接枝一层M-SiO2纳米颗粒后,所得h-GO/SiO2膜的亲水性显著提升(初始接触角降至32.5°),这主要归因于纳米M-SiO2的超亲水特性[14]。随着接枝层数的增加,膜表面亲水性获得进一步提升,但仍未达到超亲水级别[19-20]。
图5(b)为4种复合膜的红外谱图,1 100 cm−1处的吸收峰为Si—O—Si键的非对称振动吸收峰[21],1 600 cm−1处的吸收峰为—COOH官能团中—C=O的伸缩振动(1 660~1 760 cm−1)吸收峰。此外,可能是由于GO表面—COOH与氨基化SiO2表面—NH2发生了共价键合,导致了—C=O的吸收峰向低波长方向发生了偏移。综上所述,h-GO/SiO2复合膜表面亲水性有所提升,但仍未达到超亲水级别,且经烘干后膜的机械强度较弱,不利于实际应用。
-
上述多巴胺和热辅助制膜法均难以制得稳定的超亲水GO/SiO2复合膜,这2种改性策略面临一个共性问题,即复合膜难以稳定地附着在SSM上。针对这一问题,研究提出预先在SSM表面抽滤附着一次原生纳米SiO2颗粒(HS-30),随后经高温煅烧以加强对后续成膜的附着强度,制得c-GO/SiO2复合膜。
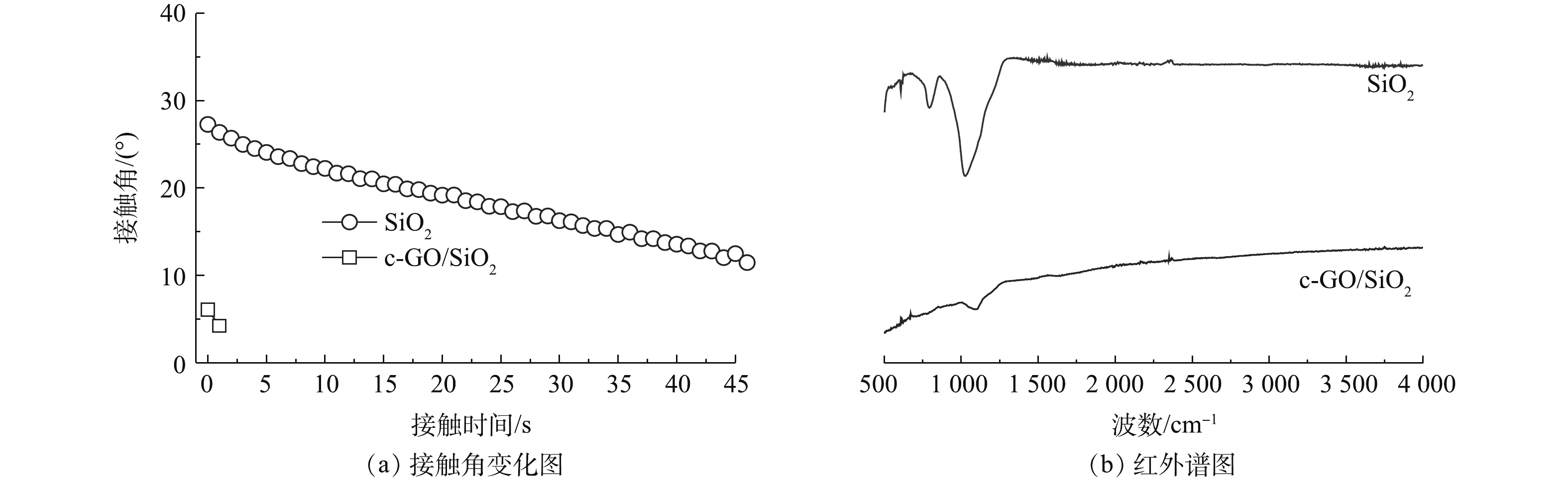
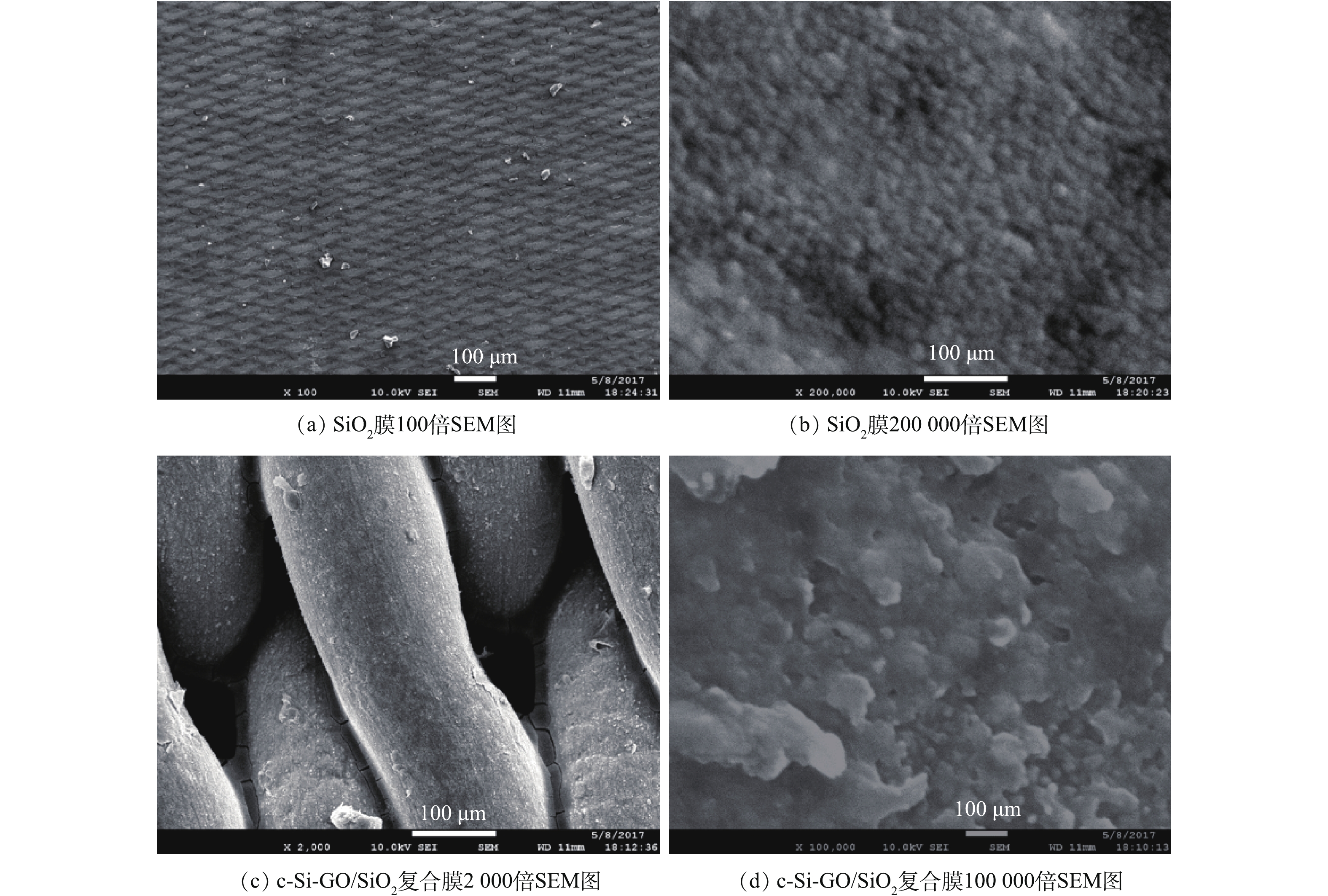
图6(a)反映了预负载纳米SiO2颗粒并煅烧后所得SiO2膜和c-GO/SiO2的接触角动态变化的对比结果。可以看出,SiO2膜的初始接触角为27.3°,并在45 s内降至12.5°,表现出较高的亲水性。由图7(a)和图7(b)可见,SiO2膜呈现出具有多层级微纳结构的复合形貌,即在SSM波浪形纹理(微米级结构)的表面覆盖着一层致密的SiO2纳米颗粒(微米级结构)。由图6(b)可知,SiO2膜中的Si—O—Si键的吸收峰(1 100 cm−1)也证实了表面覆盖的纳米颗粒为纳米SiO2。在SiO2膜基础上制备的c-GO/SiO2复合膜则表现出超亲水特性,其表面水滴初始接触角仅为6.1°,且2 s内实现完全铺展,这主要归因于膜表面的多层级微纳结构(图7(c))和超亲水M-SiO2纳米颗粒(图7(d))超亲水特性的协同作用。一方面,复合膜表面含有的大量超亲水M-SiO2纳米颗粒显著改变了膜表面的化学构成,使表面能显著提升;另一方面,多层级微纳结构也有利于水滴的吸收和铺展,从而以Wenzel接触模式强化膜表面亲水性[15]。
此外,c-GO/SiO2复合膜的红外谱图(图6(b))具有明显的碳材料谱图特征,表明了GO的存在。由图7(d)可知,片状GO与颗粒状M-SiO2也在纳米级尺度内复合形成了一定的粗糙结构,进一步促进了膜表面亲水性的提升。
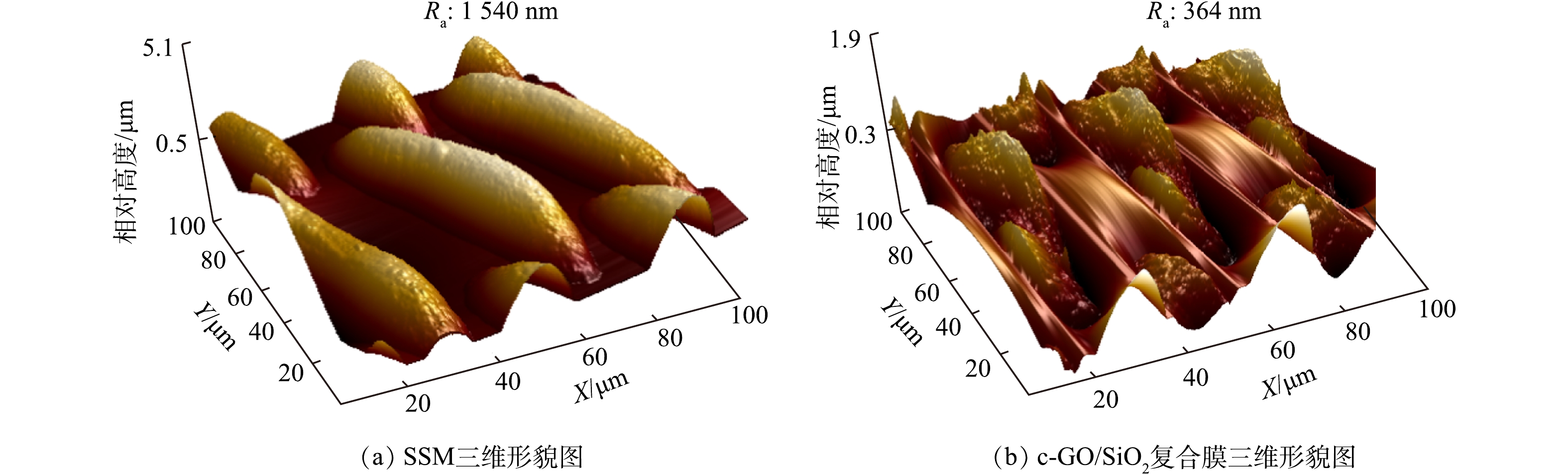
图8(a)和图8(b)分别为SSM和c-GO/SiO2复合膜的表面AFM三维形貌图。SSM和c-GO/SiO2复合膜的表面均呈现出周期性的织网状结构。由于GO和M-SiO2颗粒在表面的附着,c-GO/SiO2复合膜的平均粗糙度Ra由1 540 nm降低至364 nm,可以有效避免空气的滞留,从而有利于膜表面亲水性和过滤性能的改善。此外,由于预负载的纳米SiO2颗粒具有较高的表面能,使得制得的c-GO/SiO2复合膜与SSM基底紧密附着,具有良好的整体性和机械强度。
-
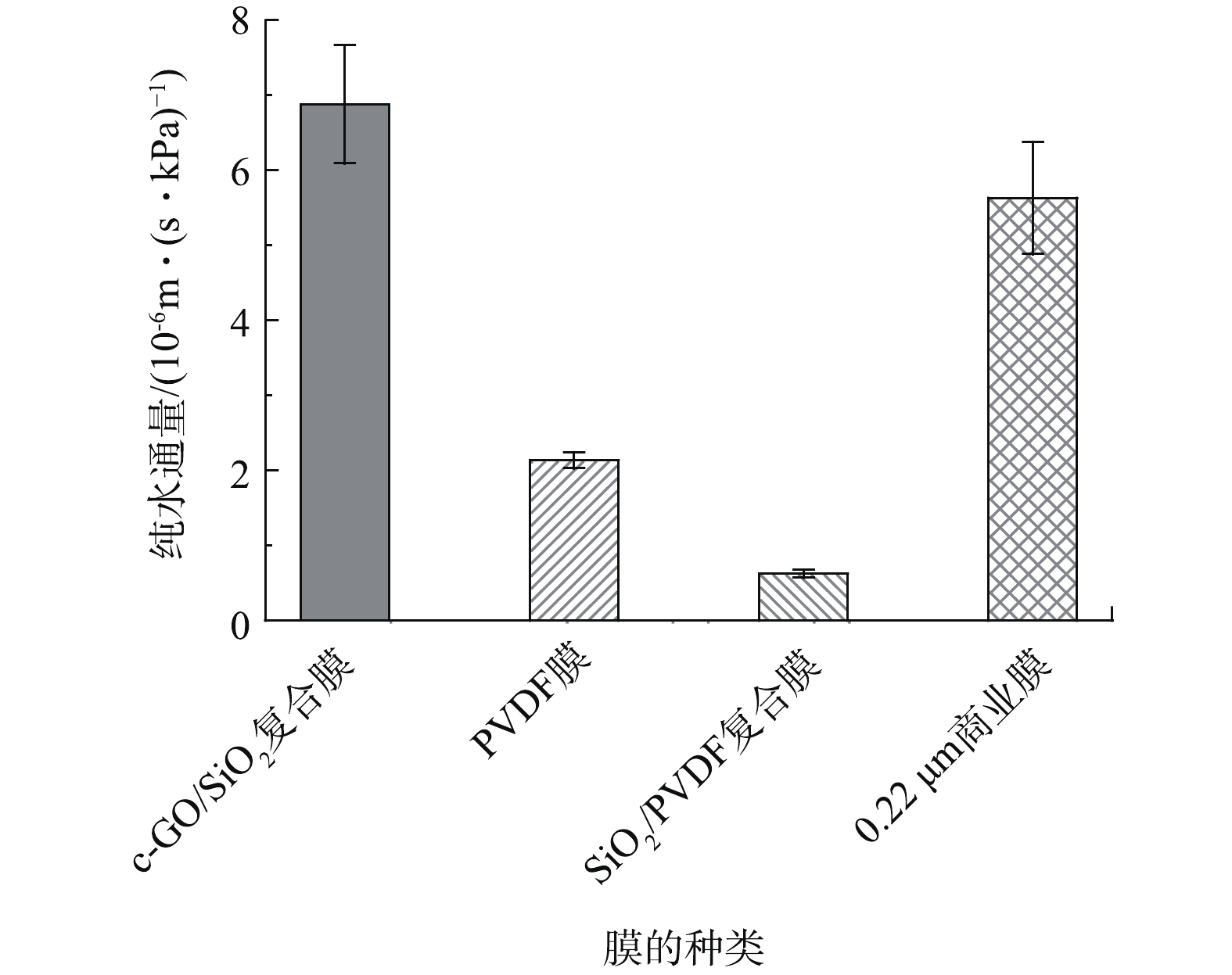
c-GO/SiO2复合膜作为一种新型无机复合膜,具有良好的应用前景。本研究以获得普遍应用的聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)有机膜材料制备了2种有机膜(PVDF超滤膜和超亲水改性的SiO2/PVDF复合超滤膜[14]),并额外选用一种孔径为0.22 μm的有机商业膜进行对比研究,纯水通量对比结果如图9所示。相比之下,超亲水c-GO/SiO2复合膜的纯水通量最高,为(6.88 ± 0.79) m·(s·kPa)−1,是0.22 μm有机商业膜的1.22倍,是普通PVDF超滤膜的3.21倍,是超亲水SiO2/PVDF复合膜的11.10倍。导致c-GO/SiO2复合膜较高纯水通量的原因可归纳于以下2点:一方面,复合膜表面具有较高的孔隙率;另一方面,复合膜的超亲水性使膜得以快速润湿,有利于膜过滤阻力的降低[22]。
-
1)研究对比了4种GO/SiO2复合膜的制备方法,其中真空抽滤法、多巴胺辅助抽滤法和热辅助法均难以制备出超亲水GO/SiO2复合膜,且成膜机械强度较弱,不利于实际应用。
2)高温煅烧辅助抽滤法可以有效地制备出具有超亲水特性的GO/SiO2复合膜,所得成膜的初始接触角仅为6.1°,且在2 s内实现完全铺展,这主要归因于表面纳米材料的高表面能和多层级微纳结构的协同效应。
3)超亲水c-Si-GO/SiO2复合膜具有较高的纯水通量,分别为普通PVDF有机超滤膜、超亲水SiO2/PVDF复合膜和0.22 μm商业膜水通量的3.21、11.10和1.22倍。
超亲水石墨烯/二氧化硅复合膜的制备优化和表征
Preparation optimization and characterization of superhydrophilic graphene/silica composite membranes
-
摘要: 膜表面亲水性是主导膜污染发生的关键因素,亲水膜的抗污染能力较强。基于氧化石墨烯(GO)和氨基修饰的纳米SiO2之间的自组装反应,分别通过真空抽滤、多巴胺辅助抽滤、热辅助法以及高温煅烧辅助抽滤法制备了多种GO/SiO2复合膜,结合纯水接触角测定、表面官能团分析以及电镜观察等,对制备方法和条件进行了优化。结果表明:高温煅烧法制备的超亲水GO/SiO2复合膜,其初始接触角为6.1°,并于2 s内,在膜表面实现完全铺展,表现出超亲水特性;此外,所制备的GO/SiO2超亲水膜的纯水通量分别是传统PVDF超滤膜、超亲水SiO2/PVDF复合膜和0.22 μm有机商业膜的3.21、11.10和1.22倍,显示出良好的应用潜力。Abstract: Membrane surface hydrophilicity is a key factor that dominates the occurrence and development of membrane fouling. A hydrophilic membrane normally performs better in antifouling. Based on the self-assembly reaction between graphene oxide (GO) and amine-terminated nano-SiO2, different kinds of GO/SiO2 membranes were prepared by the respective method of vacuum-induced filtration, dopamine-assisted vacuum filtration, heat-induced deposition, or high temperature calcination-assisted deposition. With systematic characterizations including contact angle measurement, surface functional group analyses and scanning electron microscope, the preparation methods and their corresponding conditions were compared and optimized. The superhydrophilic GO/SiO2 prepared by the calcination-assisted deposition method had the following characteristics: a low initial contact angle of 6.1°, a complete spreading on the membrane surface within 2 s, and an excellent superhydrophilic characteristic. In addition, the pure water flux of the GO/SiO2 membrane was 3.21, 11.10 and 1.22 times as much as that of the conventional PVDF membrane, superhydrophilic SiO2/PVDF composite membrane, or 0.22 μm commercial membrane, respectively, which presented promising applications in various fields.
-
Key words:
- superhydrophilic membrane /
- graphene oxide /
- SiO2 /
- self-assembly
-

-
-
[1] REZAKAZEMI M, DASHTI A, HARAMI H R, et al. Fouling-resistant membranes for water reuse[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(3): 715-763. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0717-8 [2] 曲久辉, 赵进才, 任南琪, 等. 城市污水再生与循环利用的关键基础科学问题[J]. 中国基础科学, 2017, 19(1): 6-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2412.2017.01.002 [3] MA Z B, ZHANG S, CHEN G H, et al. Superhydrophilic and oleophobic membrane functionalized with heterogeneously tailored two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheets for antifouling[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 577: 165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.01.054 [4] WU B. Membrane-based technology in greywater reclamation: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 656: 184-200. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.347 [5] HUANG Y F, FENG X S. Polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration: Fundamentals, applications and recent developments[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 586: 53-83. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.05.037 [6] XIAO K, LIANG S, WANG X, et al. Current state and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: A critical review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 271: 473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.061 [7] ZHANG R N, LIU Y N, HE M R, et al. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(21): 5888-5924. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00579E [8] 李青青, 朱振亚, 王磊, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性PVDF/PET复合膜的制备及其抗污染性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(1): 25-33. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201705167 [9] 杜锦滢, 张军, 李宁, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性PVDF膜的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(S1): 120-125. [10] 高晓琪, 梁帅, 曹俊, 等. 石墨烯在水处理膜改性中的研究与应用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(10): 82-88. [11] LIANG S, XIAO K, ZHANG S, et al. A facile approach to fabrication of superhydrophilic ultrafiltration membranes with surface-tailored nanoparticles[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 203: 251-259. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.04.051 [12] RAMASAMY D L, KHAN S, REPO E, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous and microporous amine and non-amine functionalized silica gels for the application of rare earth elements (REE) recovery from the waste water-understanding the role of pH, temperature, calcination and mechanism in light REE and heavy REE separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322: 56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.152 [13] ZHAO Z H, SHEN Y Q, YANG H D, et al. Underliquid superlyophobic copper-coated meshes for the separation of immiscible organic liquid mixtures[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2019, 11(31): 28370-28376. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b05812 [14] LIANG S, KANG Y, TIRAFERRI A, et al. Highly hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membranes via postfabrication grafting of surface-tailored silica nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2013, 5(14): 6694-6703. doi: 10.1021/am401462e [15] WANG Z, ELIMELECH M, LIN S. Environmental applications of interfacial materials with special wettability[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(5): 2132-2150. [16] DENG W, LI C, PAN F P, et al. Efficient oil/water separation by a durable underwater superoleophobic mesh membrane with TiO2 coating via biomineralization[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 222: 35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.04.019 [17] HAESHIN L, DELLATORE S M, MILLER W M, et al. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings[J]. Science, 2007, 318(5849): 426-430. doi: 10.1126/science.1147241 [18] ZHAO F, MA Z B, XIAO K, et al. Hierarchically textured superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane fabricated via nanocasting for enhanced membrane distillation performance[J]. Desalination, 2018, 443: 228-236. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2018.06.003 [19] ISMAIL M F, KHORSHIDI B, SADRZADEH M. New insights into the impact of nanoscale surface heterogeneity on the wettability of polymeric membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 590: 117-125. [20] DRELICH J, CHIBOWSKI E, MENG D D, et al. Hydrophilic and superhydrophilic surfaces and materials[J]. Soft Matter, 2011, 7(21): 9804-9828. doi: 10.1039/c1sm05849e [21] RAMASAMY D L, REPO E, SRIVASTAVA V, et al. Chemically immobilized and physically adsorbed PAN/acetylacetone modified mesoporous silica for the recovery of rare earth elements from the waste water-comparative and optimization study[J]. Water Research, 2017, 114: 264-276. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.045 [22] LIU K, VUCKOVAC M, LATIKKA M, et al. Improving surface-wetting characterization[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6432): 1147-1148. doi: 10.1126/science.aav5388 -



 下载:
下载: