微塑料是指直径<5 mm的塑料碎片和颗粒[1],包括<100 nm的纳米塑料碎片和颗粒。常见的微塑料包括聚乙烯、聚丙烯、聚苯乙烯、聚氯乙烯和聚对苯二甲酸乙酯等[2]。塑料在全世界范围内的大量生产和消费使微塑料污染问题日益严峻,其在生态系统中的广泛分布引发了微塑料对人体健康潜在风险的讨论,但目前微塑料能否对人体健康造成严重威胁尚不清楚。
由于微塑料具有化学稳定性,能够在环境当中长期存在而不易被降解,并且能够发生远距离的迁移,甚至进入动植物体内并长期积累[3]。随着微塑料不断破碎风化,其比表面积不断增大,表面容易吸附其他污染物,例如持久性有机污染物、重金属离子和抗生素等,它们之间的相互作用使污染物的毒性研究具有一定的复杂性。微塑料被证实对微生物[4]、海洋生物[5]以及其他陆地动植物[6-8]有一定的负面影响,而且微塑料亦可以通过呼吸道和消化道进入人体[9]。已有研究发现,微塑料存在于人类粪便、结肠和胎盘中[10-12],因此微塑料对人体健康的影响需要重视。但在当前阶段,由于缺乏微塑料在人体内暴露以及毒性的关键数据,微塑料对人体健康威胁的证据仍不够充分,该研究领域仍存在一些空白。本文就近年来微塑料对人体暴露途径以及毒性效应相关的研究进行了总结,并探讨了该领域未来的研究方向,以期为进一步的微塑料人体健康风险研究提供依据。
1 不同环境中的微塑料对人体的暴露途径(The pathway of human exposure to microplastics in different environments)
人类不仅是微塑料污染源,也是微塑料污染的汇[13]。环境中的微塑料对人体的暴露途径主要包括呼吸道吸入、消化道摄入以及皮肤接触。在人们日常使用的许多个人护理产品中都含有微塑料,如牙膏、洗面奶、护肤品和磨砂膏等[14-15]。这导致了皮肤与微塑料的直接接触,但由于微塑料透过皮肤需要穿透角质层,因此发生皮肤吸收的概率非常小,仅有<100 nm的纳米塑料被发现能进入角质层的表层[16]。目前几乎没有研究报道由于皮肤暴露导致的微塑料和纳米塑料的吸收。因此环境中的微塑料主要是通过呼吸道和消化道进入人体并产生效应的。
1.1 水体及相关食物中的微塑料(Microplastics in water and related foods)
水体中普遍存在的微塑料正受到全球关注,关于海洋和淡水水体中微塑料的分布已有大量的报道。其中,微塑料在饮用水以及饮用水源中的检出加重了人们对健康的担忧。有报道显示,水功能区划包括饮用水源、渔业用水在内的中国第一大淡水湖——鄱阳湖中水样和沉积物样品中微塑料的含量超过了103个·m-3[17]。另一项研究的结果显示,在长沙市的饮用水供应链中,平均每升饮用水水中含有2 753个塑料颗粒[18]。研究人员在水生植物[19]、底栖无脊椎动物[20]、鱼类[21]、水生哺乳动物[22]和鸟类[23]等不同营养级别的生物体器官内发现了微塑料的存在,摄入的微塑料逐渐向更高营养级传递[24-25],并最终通过消化道进入人体。研究发现,人们食用的海鲜产品包括鱼类[21,24]、贝类[26]和甲壳类[27]等中均检出了微塑料颗粒。这大大增加了沿海地区居民以及海产品食用人群的暴露风险。此外,食盐中微塑料的含量在某些地区十分显著,例如克罗地亚和意大利,在食盐样品中检出的微塑料颗粒分别为1.4×104~2.0×104 个·kg-1盐和1.6×103~8.2×103 个·kg-1盐[28]。美国研究人员也在12种食用盐当中检测到了微塑料[29],在我国15个品牌的盐中,海盐、湖盐和岩盐(井盐)中微塑料含量分别为550~681、43~364和7~204 个·kg-1盐[30]。
1.2 土壤及相关食物中的微塑料(Microplastics in soil and related foods)
在农业生态系统中,土壤微塑料的主要来源包括污水灌溉和污泥还田。工业废水、生活污水和洗衣废水中的塑料颗粒、纤维等通过这些方式进入土壤[31-32]。此外,温室材料、土壤调节剂以及农用地膜的应用也是微塑料的重要来源[33]。在我国新疆地区,地膜最大残留量随着时间的推移逐渐增加,达到502 kg·hm-2[34]。由于微塑料粒径小,且在环境中普遍存在,极易被土壤生物吸收,并在食物链中积累[35]。小麦、生菜、水芹和蚕豆等农作物被证明能够吸收和积累微塑料[36-40],目前已经在一些农产品加工食品当中检出了微塑料颗粒,如酒类[41-42]、添加糖和蜂蜜等[43]。最近,Oliveri Conti等[44]在从意大利卡塔尼亚市场购买的可食用水果和蔬菜中发现了纳米塑料和微塑料,并首次估算了成人和儿童的日摄入量。研究人员发现微塑料沿自然营养链的转移是一种普遍存在的现象[45],因此,对于处在食物链顶端的人类而言,通过食物链进入人体的微塑料是否会发生生物放大,是否会产生更高的暴露风险等问题亟待深入研究。
1.3 空气中的微塑料(Microplastics in the air)
空气中的微塑料能够同空气中的其他可吸入颗粒物一起通过呼吸道被人体摄入。此外,由于大气相较于水体和土壤具有更强的流动性,因此空气作为微塑料迁移的载体促进了微塑料污染的全球化迁移[46]。基于100 mg·d-1的平均粉尘暴露,研究人员估算了成年人通过空气吸入的微塑料的量为1×102~1.9×104 个·a-1[47]。此外,儿童可能通过奶嘴玩具和手直接摄入大量室内空气沉积的灰尘,根据200 mg·d-1的粉尘摄入量计算,儿童每年通过粉尘摄入的途径可能摄入超过900 mg的微塑料粒子[48]。
在人类活动较少的地区乃至人类活动范围的边界区域,即使并未发生塑料制品的生产和消费,仍能够找到微塑料的“足迹”。Bergmann等[49]发现在北极地区积雪中的微塑料浓度竟高达0~14.4×103 N·L-1。他们认为,大气输送和沉降是微塑料远距离传输的重要途径。同样,González-Pleiter等[50]发现微塑料存在于大气边界层之上,而且具有从释放点跨越遥远边界的潜在远程传输能力。微塑料通过大气运动的远距离传输无形中提高了微塑料低污染地区生物的吸入暴露风险,加速微塑料污染成为全球化的环境问题。
1.4 塑料制品在使用过程中释放的微塑料(Microplastics released from plastic products during use)
塑料制品在人类日常生活中拥有着难以替代的地位,其中食品包装塑料制品以及一次性塑料制品等与人体健康有着紧密的关联。塑料制品在使用过程中释放的微塑料颗粒能够通过消化道进入人体,例如,Hernandez等[51]的研究显示,在符合实际饮用情况的浸泡温度(95 ℃)下浸泡一个塑料茶包,会在一杯茶中释放出大约116亿个微塑料和31亿个纳米塑料。尽管这项研究中茶包释放微塑料的数量引起了争议,但毫无疑问,使用塑料茶包泡茶必定会产生微塑料的释放[52]。与成人相比,长期使用聚丙烯奶瓶的婴儿对于微塑料的暴露风险更高,其接触的微塑料数量是成人的2 600倍,而且对奶瓶的高温灭菌操作还会加剧微塑料的释放[53]。Zhang等[54]在北京青年男性的粪便中检测到了各种类型的微塑料,其中聚丙烯所占比例最高。尽管研究者并未控制受调查者食物中微塑料的摄入量,但包装水和饮料摄入量与粪便中微塑料丰度之间存在中度相关。有研究对比了一定数量的样品中自来水和瓶装水的微塑料颗粒浓度的差距,发现瓶装水中微塑料的浓度似乎更高[55]。一项分析了27个批次和11个品牌的259瓶瓶装水的研究表明,93%的包装水被微塑料污染[54]。有报道称,经过处理的自来水和瓶装水中的微塑料含量高于一些淡水水体中微塑料的含量[56]。自来水中的微塑料污染可能来自饮用水水体,也可能来自自来水塑料管道的释放[57],而这种释放作用通常会被管道中的含氯消毒剂放大[58]。瓶装水中的微塑料主要是聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯和聚酯[56],这说明瓶装水中发现的微塑料很可能来自于供水供应链或瓶盖、瓶壁等产品包装。
2 环境中的微塑料和纳米塑料对人体的影响(Effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on the human body)
研究人员普遍认为,环境中的微塑料和纳米塑料对人体健康存在着潜在的威胁,然而微塑料,特别是纳米塑料对人类是否具有重大健康风险尚无法断定,这是由于在确定微塑料对人类健康的风险时缺乏关于人体暴露的信息。目前对于微塑料的人体毒性报道仅有一些体外和比较有限的体内研究数据,因此对于微塑料的健康风险评估仍缺乏大量可靠的数据。目前对于微塑料健康风险的判断仍需依靠体外培养的人体细胞、啮齿类动物以及水生物种的毒性研究数据。微塑料对人体的暴露途径及主要影响如图1所示。
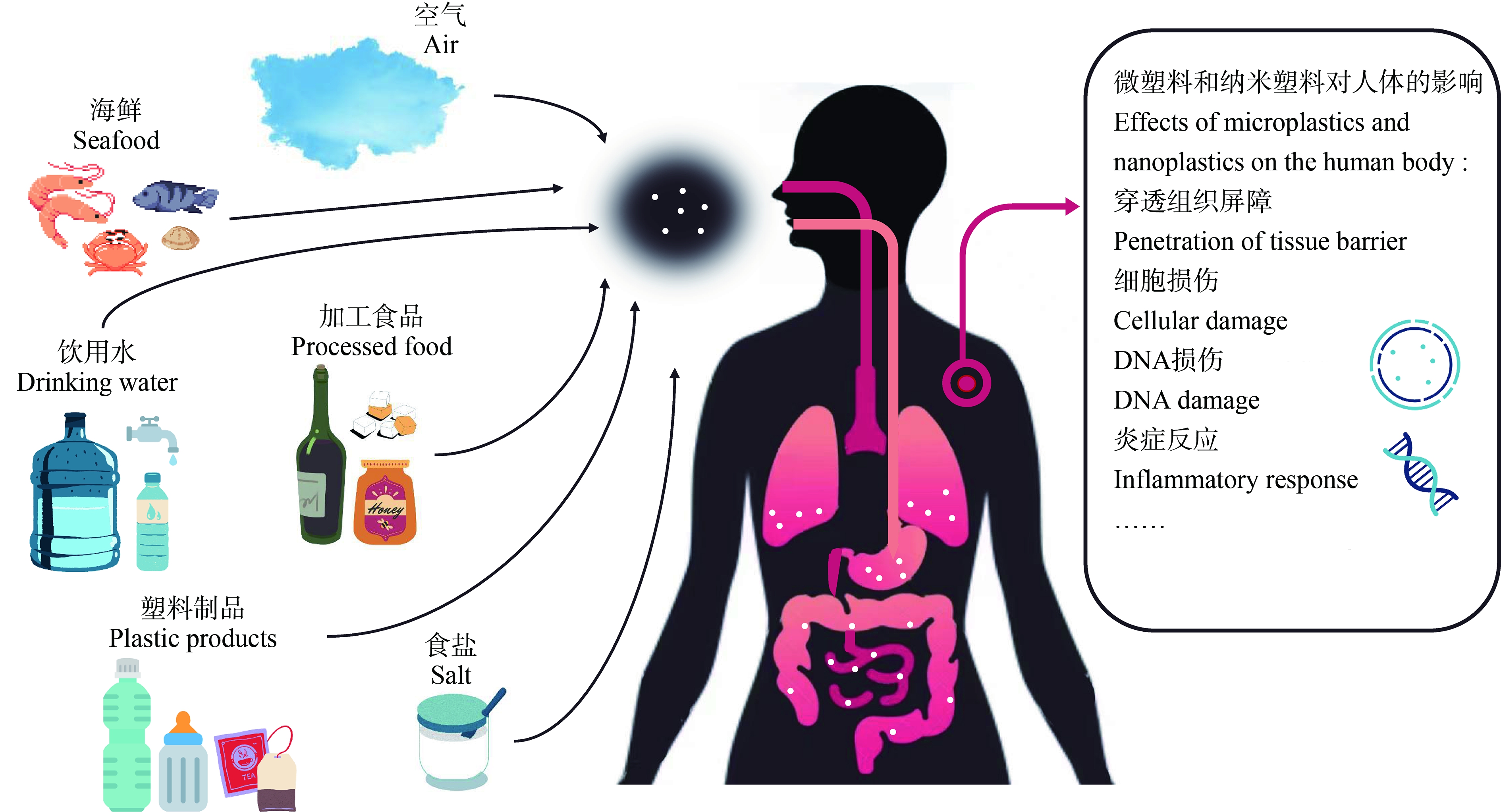
图1 微塑料和纳米塑料对人体的暴露途径及影响
Fig. 1 Exposure pathway and influence of microplastics and nanoplastics on human body
2.1 微塑料和纳米塑料对体外培养细胞的影响(Effect of microplastics and nanoplastics on cultured cells in vitro)
基于体外培养的人体细胞的数据表明,塑料颗粒可能会对人体细胞造成物理损伤、引起炎症反应、氧化应激反应、产生活性氧(ROS)、线粒体毒性、DNA损伤,还有神经毒性和代谢效应等影响。颗粒的大小、形状、粗糙度、表面性质及电荷等因素均会影响颗粒的内化迁移以及毒性效应。较大的塑料颗粒能够通过物理作用对细胞产生影响。研究显示,当聚苯乙烯塑料碎片与成纤维细胞和红细胞直接接触时,它们所引起的物理应激会导致细胞膜损伤和溶血,分别导致乳酸脱氢酶和血红蛋白释放。随着微碎片浓度和粗糙度的增加,这种物理损伤现象被放大[59-60]。一部分较小的塑料颗粒能够进入细胞,发生内化,引起细胞内的一系列反应。纳米颗粒被报道可以通过细胞膜的被动运输、通道或运输蛋白协助扩散以及胞吞几种途径被细胞吸收[61]。其中内化的主要机制是细胞的内吞性摄取,主要包括胞吞和胞饮作用,以及网格蛋白和小泡介导的内吞作用[62-63]。
一些体外研究已经证实了以聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒为主的塑料颗粒能够在人类胃、肠、肺以及免疫细胞等的单一培养物或更复杂的人类细胞模型中内化、移位以及产生毒性效应。Varela等[64]研究了人肺癌细胞A549细胞系对聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒的吸收发现,40 nm的纳米颗粒的内化速度快于20 nm和100 nm的纳米颗粒,因此他们认为聚苯乙烯纳米粒子的内化存在一个特殊的粒径范围,在这个范围内颗粒的内化速度更快。Dong等[65]发现聚苯乙烯微塑料可通过诱导ROS形成引起人正常肺上皮细胞BEAS-2B细胞系的细胞毒性和炎症效应,从而进一步导致对肺上皮屏障的破坏以及增加慢性阻塞性肺疾病的风险。Forte等[66]的研究表明,44 nm的聚苯乙烯颗粒在人胃腺癌细胞AGS细胞系的细胞质中能够较快积累,并能够诱导白细胞介素IL-6和IL-8基因的显著上调,这2种基因均与胃部疾病有关。Wu等[67]研究发现,聚苯乙烯塑料颗粒能够破坏人结肠癌细胞Caco-2细胞系的线粒体膜电位,还能够抑制ABC转运体的活性,并增加其底物砷的毒性。Cortés等[68]发现聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒会对Caco-2细胞造成包括细胞毒性、ROS增加、基因毒性、DNA氧化损伤和压力相关基因表达增加在内的不利影响。Salvati等[69]发现,40~50 nm聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒能够进入A549细胞,并在溶酶体中积累。Liu等[70]证实聚苯乙烯颗粒能够诱导ROS的产生,他们发现500 nm大小的聚苯乙烯颗粒可以刺激人肝癌细胞Huh7细胞系中ROS的产生,同样,Wang等[71]也检测到120 μg·mL-1的聚苯乙烯颗粒(300 nm、500 nm、1 μm、3 μm和6 μm)都增加了Caco-2细胞中ROS的产生。
2.2 微塑料和纳米塑料对组织、器官的影响(Effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on tissues and organs)
有限的体外和体内数据表明,随着粒径的减小,塑料颗粒对人体组织屏障的穿透能力逐渐增强[72],只有一小部分纳米塑料颗粒能够穿过肺泡和胃肠道的上皮屏障,转移到下层组织[9]。考虑到人类对塑料颗粒的长期接触以及塑料颗粒在组织和器官中可能的积累,这种低比例的颗粒内化仍然不能被忽视。微塑料颗粒进入人体后,它们可能会克服初级组织屏障,并通过血液输送到次级器官[73]。这是由于聚苯乙烯和红细胞之间的范德华力、静电力、氢键和疏水力,使羧基化聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒可以吸附并渗透到红细胞中,这使聚苯乙烯纳米颗粒避免了被肝脏和脾脏快速清除,从而增加了它们在循环系统中存留的时间[74-75]。塑料颗粒可以进一步通过血液到达次级屏障,如胎盘屏障和血脑屏障[73]。有研究证实,仍有部分更小粒径的颗粒能够穿透这些组织屏障最终到达包括肝、肾、脑和胎盘在内的全身的组织器官中[61,76]。影响塑料颗粒穿透性能的因素包括颗粒的大小、表面化学性质和电荷以及塑料颗粒与周围生物成分(如蛋白质、磷脂或碳水化合物)的相互作用[77]。研究人员将这种相互作用现象称为塑料颗粒表面的生物或生态冠状物,这类物质很可能影响着颗粒的摄取、迁移转化和毒性效应[73]。例如体液中的蛋白质吸附在纳米塑料颗粒表面,致使颗粒周围形成“蛋白冠”[78],这种冠状物能够增强细胞对颗粒的摄取以及颗粒的毒性[79]。
微塑料在进入人体细胞和组织后可能会引起物理、化学和生物毒性,这些毒性也可能会累积[9]。几项体外人类细胞培养和体内啮齿动物研究表明,吸入或摄入的微塑料有可能导致多种生物效应,包括炎症、遗传毒性、氧化应激、细胞凋亡和坏死。如果这些情况持续,一系列的结果可能会随之而来,包括组织损伤、纤维化和癌变[80]。暴露于微塑料可导致肠道的氧化损伤和炎症,以及肠道上皮细胞的破坏、黏液层的减少、微生物紊乱和免疫细胞毒性等负面影响[81]。几项研究表明,长期暴露于含有微塑料颗粒的空气中可能会对呼吸系统造成影响,增加疾病发生的风险。研究显示,吸入微塑料颗粒似乎与某些行业工人的职业病有关。接触聚丙烯微塑料颗粒的工人与在清洁环境下工作的工人相比产生呼吸道症状的风险更高[82]。慢性吸入低浓度细颗粒物也可能导致基因突变[83]。由于接触聚丙烯纤维,工龄在10~20 a的合成纺织行业工人的癌症发病率较普通人群更高[82]。随着年龄、工作年限和在工厂接触时间的延长,接触聚氯乙烯颗粒的工人患肺癌的风险也会增加[82]。此外,有报道显示塑料假体例如关节置换假体的植入会在使用过程中发生磨损,磨损后产生的塑料颗粒能够引起炎症反应,如巨噬细胞的免疫激活和相关的细胞因子的产生等,严重的甚至能够导致关节坏死[80]。
Mitrano等[72]分析总结了环境中不同粒径的颗粒物对生物体的影响,并希望为微、纳米塑料的风险评估提供思路。他们发现约104 nm以下的颗粒物能通过呼吸被吸入,并且能够跨越生物屏障,约107 nm以下的颗粒物能够通过消化道被摄取,约103 nm以下的颗粒物能够被细胞吸收并产生炎症反应,约103~106 nm的颗粒物能够导致组织纤维化,如图2所示。然而这些研究中所提到的一些负面作用多是在较高浓度的暴露下,或特殊的高风险情形下所产生的,因此,很难确定这些暴露与现实情况之间的关系。目前尚没有强有力的证据表明微纳米塑料会对人体产生任何直接的严重负面影响,这可能会导致塑料的持续生产、消费以及塑料碎片持续地泄漏到环境中,因此迫切需要对微塑料的人体健康临床效应进行更深入的研究。
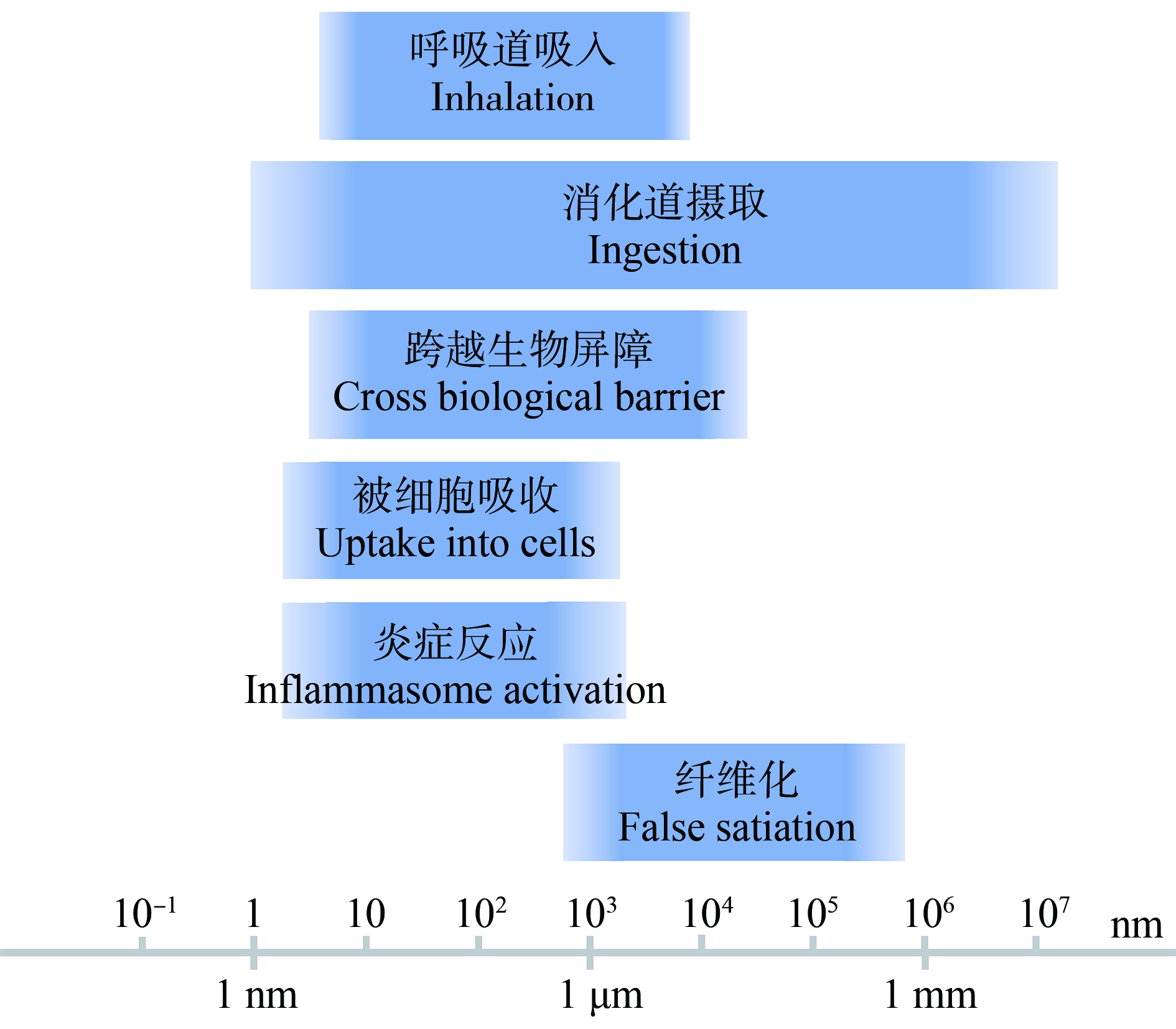
图2 不同粒径的颗粒物与生物体的相互作用
Fig. 2 Interactions between particles of different particle sizes and organisms
2.3 微塑料和纳米塑料的生物积累(Bioaccumulation of microplastics and nanoplastics)
根据体外研究数据以及模型动物体内研究数据,微塑料已被发现在胃肠道以及呼吸道内被吸收,纳米塑料颗粒可以穿透血脑屏障、胎盘,甚至细胞膜,因此进入生物体后可能产生生物积累效应。Yu等[84]发现聚苯乙烯微塑料可在幼年河蟹的鳃、肝脏和肠道组织中积累,并对其生长产生负面影响。基于小鼠模型的实验表明纳米塑料可以在肝脏、肾脏和肠道以及大脑中积累[85-86]。Ma和You[87]通过计算机模型建立了微塑料通过水生食物网积累的效应模型,结果表明,微塑料在整个食物网中迅速扩散积累,最终向高营养水平的水生生物扩散积累,其中最高营养级的生物通过食物网对微塑料的累积效应最为严重。有研究估算了不同环境中的微塑料生物积累情况发现,海水区的生物体内微塑料累计个数为(2.4±3.29) 个·kg-1,淡水区为(2.75±4.74) 个·kg-1,而河口区的生物体内微塑料个数略高,为(5.65±7.39) 个·kg-1[88]。最近,一项研究通过分析人类结肠切除样本发现了微塑料人体在肠道中的积累[10]。然而,关于微塑料和纳米塑料在人体器官中的分布和积累的直接证据仍然十分匮乏。
3 微塑料与其他污染物的联合效应及风险(Combined effects and risks of microplastics with other pollutants)
在复杂的自然环境中,特别是水环境当中,微塑料很可能以非单体的形式存在。因此微塑料往往容易和与其共同存在的污染物发生相互作用或产生联合效应。在塑料合成过程中常加入某些有机物作为添加剂,这类物质中包括一些内分泌干扰物,如双酚A、邻苯二甲酸酯等,由于这些添加剂与塑料聚合物基质之间不是通过共价键结合,所以它们在塑料老化过程中容易浸出到外部介质中,与微塑料产生联合毒性效应[89]。此外,由于微塑料具有持久性强,比表面积大等特点,其表面容易附着其他污染物如重金属离子[90-91]、有机污染物[92-96](具体包括苯系物[97-98]、多环芳烃[99-100]、多氯联苯[101-102]、全氟化合物[103]、农药[104-105]和润滑油[106-107]等)、抗生素[108]以及病原体[109-112]等。微塑料颗粒作为这些污染物的载体,使污染物发生远距离的迁移,并通过食物链将污染物转移到生态系统中[113],并且通过吸附以及生物累积和富集效应[38]增加其他污染物的生物利用度[32,114],有关微塑料和纳米塑料与其他污染物的联合效应的研究结果如表1所示。然而也有研究表明,微塑料对其他污染物的吸附作用能够降低其毒性和生物利用度[115-117]。因此微塑料与其他环境污染物共同存在的联合效应是协同还是拮抗作用尚不能一概而论,这种联合效应往往根据污染物类型、赋存环境、塑料的粒径以及受试生物等因素的差异而变化。
表1 有关微塑料与其他污染物的联合效应的文献汇总
Table 1 Summary of literature on the combined effects of microplastics and other pollutants

联合的污染物类型Pollutant type产生的联合效应Combined effec参考文献References塑料添加剂Plastic additives微塑料释放添加剂,使某些添加剂的毒性增强,并在谷物中富集Microplastics release additives, making some additives more toxic and enriched in grains[119-120]重金属离子Heavy metal ion吸附重金属离子,影响其生物利用度Adsorb heavy metal ions and affects its bioavailability[91, 116-117, 121-123]抗生素Antibiotics干预抗生素的摄取和积累,影响其毒性和副作用,协助抗性基因转移Interfere with the uptake and accumulation of antibiotics, affect their toxicity and side effects, and assists the transfer of resistance genes[124-126]有机污染物Organic pollutants在生物体内环境中解吸,影响生物利用度Desorb in the organism’s internal environment and affects bioavailability[99, 101, 104, 106, 115, 127]有害微生物Pernicious microbes增加病原体传播,协助抗性基因转移Increase the spread of pathogens and assist the transfer of resistance genes[128-130]
最近,一项关于新型冠状病毒(COVID-19)污染表面和气溶胶的研究表明,人们可能通过空气和接触受污染的物体后感染新型冠状病毒,而病毒能够在塑料上存在长达2~3 d[118]。这引发了一个值得关注的问题,即空气中的塑料颗粒有可能作为冠状病毒和流感病毒的载体传播疾病。
4 研究展望(Research prospect)
在未来很长一段时间内,人类将不可避免地接触到微塑料以及纳米塑料,因此探索微塑料对于人体健康的潜在风险显得尤为重要。针对目前已知的微塑料健康风险研究尚未解决的问题和空白,今后该领域的研究应当注意以下几方面的问题。
(1)关注纳米塑料对人体的暴露及影响。由于分析方法的局限性和对塑料颗粒的测量偏差,现有的分析通常不包括纳米塑料的暴露情况,这很可能低估了微纳米塑料对人体的暴露。由于纳米塑料具有更强的穿透性和细胞毒性,今后迫切需要足够的分析工具来检测、量化和表征纳米塑料颗粒,探究纳米塑料对人体的暴露情况及其毒性。
(2)微塑料通过食物链和空气的暴露情况仍存在研究空白。目前的报道中对空气、饮用水源的微塑料检测较少,仍缺乏较大范围的污染分布情况的数据,对食品的检测主要集中在海产品的暴露研究,对谷物、蔬菜和畜牧产品等食品中微塑料的检测仍较为缺乏。
(3)目前微塑料和纳米塑料的人体毒性研究仍存在一些问题和知识空缺。当前阶段关于人体的体内暴露及毒性数据非常有限,人体体液和组织中塑料颗粒的内部暴露检测仍处于起步阶段,环境微塑料浓度与人体内微塑料浓度之间仍待建立联系,关于吸收、分布、代谢和排泄的主要知识缺口仍然存在。今后仍需要更好地了解微塑料穿过气道、胃肠道和皮肤上皮屏障的能力,以减少目前微塑料人类风险评估的不确定性。此外,大多数的体外研究采用的是聚苯乙烯塑料微球,缺乏其他种类(如聚乙烯、聚氯乙烯等)和形状(如薄片、纤维等)的塑料颗粒的体内外毒性研究。且目前的研究数据大多基于较高的颗粒浓度,与实际环境中的浓度存在差距。关于微塑料的毒性研究还可以借鉴较为成熟的工程纳米材料的毒性研究以及可吸入颗粒物的毒性研究。
(4)需要进一步研究微塑料作为载体的能力。由于实际环境的复杂性,对微塑料毒性的评估不应局限于简单地考察微塑料单体的毒性效应,迫切需要更多关于微塑料和其他污染物的联合毒性研究以充分了解微塑料在现实环境条件下的潜在毒性、毒性机制和长期影响。微塑料表面的生态或生物冠状物尚未被充分研究,其介导颗粒吸收和毒性的潜在机制尚不清楚。
[1] Thompson R C,Olsen Y,Mitchell R P,et al.Lost at sea:Where is all the plastic?[J].Science,2004,304(5672):838
[2] Geyer R,Jambeck J R,Law K L.Production,use,and fate of all plastics ever made [J].Science Advances,2017,3(7):e1700782
[3] 陈璇,章家恩,危晖.环境微塑料的迁移转化及生态毒理学研究进展[J].生态毒理学报,2021,16(6):70-86
Chen X,Zhang J E,Wei H.Research progress and prospect on transportation,transformation and ecotoxicology of microplastics in environment [J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2021,16(6):70-86 (in Chinese)
[4] Wang J,Lv S H,Zhang M Y,et al.Effects of plastic film residues on occurrence of phthalates and microbial activity in soils [J].Chemosphere,2016,151:171-177
[5] Amelia T S M,Khalik W M A W M,Ong M C,et al.Marine microplastics as vectors of major ocean pollutants and its hazards to the marine ecosystem and humans [J].Progress in Earth and Planetary Science,2021,8:12
[6] Dong Y M,Gao M L,Qiu W W,et al.Uptake of microplastics by carrots in presence of As(Ⅲ):Combined toxic effects [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,411:125055
[7] An D,Na J,Song J,et al.Size-dependent chronic toxicity of fragmented polyethylene microplastics to Daphnia magna [J].Chemosphere,2021,271:129591
[![]() íková G.Aquatic vascular plants:A forgotten piece of nature in microplastic research [J].Environmental Pollution,2020,262:114354
íková G.Aquatic vascular plants:A forgotten piece of nature in microplastic research [J].Environmental Pollution,2020,262:114354
[9] Vethaak A D,Legler J.Microplastics and human health [J].Science,2021,371(6530):672-674
[10] Ibrahim Y S,Tuan Anuar S,Azmi A A,et al.Detection of microplastics in human colectomy specimens [J].JGH Open,2021,5(1):116-121
[11] Ragusa A,Svelato A,Santacroce C,et al.Plasticenta:First evidence of microplastics in human placenta [J].Environment International,2021,146:106274
[12] Schwabl P,Köppel S,Königshofer P,et al.Detection of various microplastics in human stool:A prospective case series [J].Annals of Internal Medicine,2019,171(7):453-457
[13] Tang Y Q,Liu Y G,Chen Y,et al.A review:Research progress on microplastic pollutants in aquatic environments [J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,766:142572
[14] Andrady A L.Microplastics in the marine environment [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2011,62(8):1596-1605
[15] Browne M A,Crump P,Niven S J,et al.Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide:Sources and sinks [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2011,45(21):9175-9179
[16] Campbell C S J,Contreras-Rojas L R,Delgado-Charro M B,et al.Objective assessment of nanoparticle disposition in mammalian skin after topical exposure [J].Journal of Controlled Release,2012,162(1):201-207
[17] Jian M F,Zhang Y,Yang W J,et al.Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in China’s largest freshwater lake system [J].Chemosphere,2020,261:128186
[18] Shen M C,Zeng Z T,Wen X F,et al.Presence of microplastics in drinking water from freshwater sources:The investigation in Changsha,China [J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2021,28(31):42313-42324
[19] Kögel T,Bjorøy Ø,Toto B,et al.Micro- and nanoplastic toxicity on aquatic life:Determining factors [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2020,709:136050
[20] Naidu S A,Ranga Rao V,Ramu K.Microplastics in the benthic invertebrates from the coastal waters of Kochi,Southeastern Arabian Sea [J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health,2018,40(4):1377-1383
[21] Barboza L G A,Lopes C,Oliveira P,et al.Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects,lipid oxidative damage,and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2020,717:134625
[22] Besseling E,Foekema E M,van Franeker J A,et al.Microplastic in a macro filter feeder:Humpback whale Megaptera novaeangliae [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,95(1):248-252
[23] Le Guen C,Suaria G,Sherley R B,et al.Microplastic study reveals the presence of natural and synthetic fibres in the diet of King Penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) foraging from South Georgia [J].Environment International,2020,134:105303
[24] Su L,Deng H,Li B W,et al.The occurrence of microplastic in specific organs in commercially caught fishes from coast and estuary area of East China [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,365:716-724
[25] Wang W F,Gao H,Jin S C,et al.The ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on aquatic food web,from primary producer to human:A review [J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,173:110-117
[26] Nalbone L,Cincotta F,Giarratana F,et al.Microplastics in fresh and processed mussels sampled from fish shops and large retail chains in Italy [J].Food Control,2021,125:108003
[27] Cho Y,Shim W J,Jang M,et al.Nationwide monitoring of microplastics in bivalves from the coastal environment of Korea [J].Environmental Pollution,2021,270:116175
[28] Renzi M,![]() A.Litter µplastics features in table salts from marine origin:Italian versus Croatian brands [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,135:62-68
A.Litter µplastics features in table salts from marine origin:Italian versus Croatian brands [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,135:62-68
[29] Kosuth M,Mason S A,Wattenberg E V.Anthropogenic contamination of tap water,beer,and sea salt [J].PLoS One,2018,13(4):e0194970
[30] Yang D Q,Shi H H,Li L,et al.Microplastic pollution in table salts from China [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2015,49(22):13622-13627
[31] Leslie H A,Brandsma S H,van Velzen M J,et al.Microplastics en route:Field measurements in the Dutch River delta and Amsterdam canals,wastewater treatment plants,North Sea sediments and biota [J].Environment International,2017,101:133-142
[32] Horton A A,Walton A,Spurgeon D J,et al.Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments:Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2017,586:127-141
[33] Ng E L,Huerta Lwanga E,Eldridge S M,et al.An overview of microplastic and nanoplastic pollution in agroecosystems [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:1377-1388
[34] Zhang D,Liu H B,Hu W L,et al.The status and distribution characteristics of residual mulching film in Xinjiang,China [J].Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2016,15(11):2639-2646
[35] Rillig M C,Ziersch L,Hempel S.Microplastic transport in soil by earthworms [J].Scientific Reports,2017,7:1362
[36] Li L Z,Luo Y M,Li R J,et al.Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode [J].Nature Sustainability,2020,3(11):929-937
[37] 李连祯,周倩,尹娜,等.食用蔬菜能吸收和积累微塑料[J].科学通报,2019,64(9):928-934
Li L Z,Zhou Q,Yin N,et al.Uptake and accumulation of microplastics in an edible plant [J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2019,64(9):928-934 (in Chinese)
[38] 李瑞杰,李连祯,张云超,等.禾本科作物小麦能吸收和积累聚苯乙烯塑料微球[J].科学通报,2020,65(20):2120-2127
Li R J,Li L Z,Zhang Y C,et al.Uptake and accumulation of microplastics in a cereal plant wheat [J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2020,65(20):2120-2127 (in Chinese)
[39] Jiang X F,Chen H,Liao Y C,et al.Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of polystyrene microplastics on higher plant Vicia faba [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,250:831-838
[40] Bosker T,Bouwman L J,Brun N R,et al.Microplastics accumulate on pores in seed capsule and delay germination and root growth of the terrestrial vascular plant Lepidium sativum [J].Chemosphere,2019,226:774-781
[41] Prata J C,Paço A,Reis V,et al.Identification of microplastics in white wines capped with polyethylene stoppers using micro-Raman spectroscopy [J].Food Chemistry,2020,331:127323
[42] Kosuth M,Mason S A,Wattenberg E V.Anthropogenic contamination of tap water,beer,and sea salt [J].PLoS One,2018,13(4):e0194970
[43] Cox K D,Covernton G A,Davies H L,et al.Human consumption of microplastics [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2019,53(12):7068-7074
[44] Oliveri Conti G,Ferrante M,Banni M,et al.Micro- and nano-plastics in edible fruit and vegetables.The first diet risks assessment for the general population [J].Environmental Research,2020,187:109677
[45] Au S Y,Lee C M,Weinstein J E,et al.Trophic transfer of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems:Identifying critical research needs [J].Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management,2017,13(3):505-509
[46] 骆永明,施华宏,涂晨,等.环境中微塑料研究进展与展望[J].科学通报,2021,66(13):1547-1562
Luo Y M,Shi H H,Tu C,et al.Research progresses and prospects of microplastics in the environment [J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2021,66(13):1547-1562 (in Chinese)
[47] Zhang Q,Xu E G,Li J N,et al.A review of microplastics in table salt,drinking water,and air:Direct human exposure [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2020,54(7):3740-3751
[48] Abbasi S,Keshavarzi B,Moore F,et al.Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County,Iran [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,244:153-164
[49] Bergmann M,Mützel S,Primpke S,et al.White and wonderful?Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic [J].Science Advances,2019,5(8):eaax1157
[50] González-Pleiter M,Edo C,Aguilera  ,et al.Occurrence and transport of microplastics sampled within and above the planetary boundary layer [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,761:143213
,et al.Occurrence and transport of microplastics sampled within and above the planetary boundary layer [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,761:143213
[51] Hernandez L M,Xu E G,Larsson H C E,et al.Plastic teabags release billions of microparticles and nanoparticles into tea [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2019,53(21):12300-12310
[52] Hernandez L M,Xu E G,Larsson H C E,et al.Response to comment on “plastic teabags release billions of microparticles and nanoparticles into tea”[J].Environmental Science &Technology,2020,54(21):14136-14137
[53] Li D Z,Shi Y H,Yang L M,et al.Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation [J].Nature Food,2020,1(11):746-754
[54] Zhang N,Li Y B,He H R,et al.You are what you eat:Microplastics in the feces of young men living in Beijing [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,767:144345
[55] Danopoulos E,Twiddy M,Rotchell J M.Microplastic contamination of drinking water:A systematic review [J].PLoS One,2020,15(7):e0236838
[56] Koelmans A A,Mohamed Nor N H,Hermsen E,et al.Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water:Critical review and assessment of data quality [J].Water Research,2019,155:410-422
[57] Fournier E,Etienne-Mesmin L,Grootaert C,et al.Microplastics in the human digestive environment:A focus on the potential and challenges facing in vitro gut model development [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,415:125632
[58] Vertova A,Miani A,Lesma G,et al.Chlorine dioxide degradation issues on metal and plastic water pipes tested in parallel in a semi-closed system [J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2019,16(22):4582
[59] Choi D,Bang J,Kim T,et al.In vitro chemical and physical toxicities of polystyrene microfragments in human-derived cells [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,400:123308
[60] Choi D,Hwang J,Bang J,et al.In vitro toxicity from a physical perspective of polyethylene microplastics based on statistical curvature change analysis [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,752:142242
[61] Yang C S,Chang C H,Tsai P J,et al.Nanoparticle-based in vivo investigation on blood-brain barrier permeability following ischemia and reperfusion [J].Analytical Chemistry,2004,76(15):4465-4471
[62] Khalil I A,Kogure K,Akita H,et al.Uptake pathways and subsequent intracellular trafficking in nonviral gene delivery [J].Pharmacological Reviews,2006,58(1):32-45
[63] Ziello J E,Huang Y,Jovin I S.Cellular endocytosis and gene delivery [J].Molecular Medicine,2010,16(5-6):222-229
[64] Varela J A,Bexiga M G,Åberg C,et al.Quantifying size-dependent interactions between fluorescently labeled polystyrene nanoparticles and mammalian cells [J].Journal of Nanobiotechnology,2012,10:39
[65] Dong C D,Chen C W,Chen Y C,et al.Polystyrene microplastic particles:in vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,385:121575
[66] Forte M,Iachetta G,Tussellino M,et al.Polystyrene nanoparticles internalization in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells [J].Toxicology in Vitro:An International Journal Published in Association with BIBRA,2016,31:126-136
[67] Wu B,Wu X M,Liu S,et al.Size-dependent effects of polystyrene microplastics on cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition in human Caco-2 cells [J].Chemosphere,2019,221:333-341
[68] Cortés C,Domenech J,Salazar M,et al.Nanoplastics as a potential environmental health factor:Effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells [J].Environmental Science:Nano,2020,7(1):272-285
[69] Salvati A,Aberg C,dos Santos T,et al.Experimental and theoretical comparison of intracellular import of polymeric nanoparticles and small molecules:Toward models of uptake kinetics [J].Nanomedicine:Nanotechnology,Biology,and Medicine,2011,7(6):818-826
[70] Liu X D,Tian X D,Xu X,et al.Design of a phosphinate-based bioluminescent probe for superoxide radical anion imaging in living cells [J].Luminescence:The Journal of Biological and Chemical Luminescence,2018,33(6):1101-1106
[71] Wang Q Q,Bai J L,Ning B A,et al.Effects of bisphenol A and nanoscale and microscale polystyrene plastic exposure on particle uptake and toxicity in human Caco-2 cells [J].Chemosphere,2020,254:126788
[72] Mitrano D M,Wick P,Nowack B.Placing nanoplastics in the context of global plastic pollution [J].Nature Nanotechnology,2021,16(5):491-500
[73] Lehner R,Weder C,Petri-Fink A,et al.Emergence of nanoplastic in the environment and possible impact on human health [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2019,53(4):1748-1765
[74] Anselmo A C,Gupta V,Zern B J,et al.Delivering nanoparticles to lungs while avoiding liver and spleen through adsorption on red blood cells [J].ACS Nano,2013,7(12):11129-11137
[75] Chambers E,Mitragotri S.Prolonged circulation of large polymeric nanoparticles by non-covalent adsorption on erythrocytes [J].Journal of Controlled Release:Official Journal of the Controlled Release Society,2004,100(1):111-119
[76] Grafmueller S,Manser P,Diener L,et al.Bidirectional transfer study of polystyrene nanoparticles across the placental barrier in an ex vivo human placental perfusion model [J].Environmental Health Perspectives,2015,123(12):1280-1286
[77] Mahmoudi M,Lynch I,Ejtehadi M R,et al.Protein-nanoparticle interactions:Opportunities and challenges [J].Chemical Reviews,2011,111(9):5610-5637
[78] Treuel L,Brandholt S,Maffre P,et al.Impact of protein modification on the protein corona on nanoparticles and nanoparticle-cell interactions [J].ACS Nano,2014,8(1):503-513
[79] Nasser F,Lynch I.Secreted protein eco-corona mediates uptake and impacts of polystyrene nanoparticles on Daphnia magna [J].Journal of Proteomics,2016,137:45-51
[80] Wright S L,Kelly F J.Plastic and human health:A micro issue?[J].Environmental Science &Technology,2017,51(12):6634-6647
[81] Huang Z Z,Weng Y,Shen Q C,et al.Microplastic:A potential threat to human and animal health by interfering with the intestinal barrier function and changing the intestinal microenvironment [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,785:147365
[82] Prata J C.Airborne microplastics:Consequences to human health?[J].Environmental Pollution,2018,234:115-126
[83] Kingsley S L,Deyssenroth M A,Kelsey K T,et al.Maternal residential air pollution and placental imprinted gene expression [J].Environment International,2017,108:204-211
[84] Yu P,Liu Z Q,Wu D L,et al.Accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in juvenile Eriocheir sinensis and oxidative stress effects in the liver [J].Aquatic Toxicology,2018,200:28-36
[85] Deng Y F,Zhang Y,Lemos B,et al.Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure [J].Scientific Reports,2017,7:46687
[86] Estrela F N,Guimarães A T B,Araújo A P D C,et al.Toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and zinc oxide to mice [J].Chemosphere,2021,271:129476
[87] Ma Y F,You X Y.Modelling the accumulation of microplastics through food webs with the example Baiyangdian Lake,China [J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,762:144110
[88] 俞海睿,陈启晴,施华宏.水生环境中微塑料自身及负载有机污染物的生物富集效应[J].科学通报,2021,66(20):2504-2515
Yu H R,Chen Q Q,Shi H H.The bioaccumulation effects of microplastics and associated organic pollutants in the aquatic environment [J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2021,66(20):2504-2515 (in Chinese)
[89] Browne M A,Niven S J,Galloway T S,et al.Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms,reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity [J].Current Biology,2013,23(23):2388-2392
[90] Godoy V,Blázquez G,Calero M,et al.The potential of microplastics as carriers of metals [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,255(Pt 3):113363
[91] Caruso G.Microplastics as vectors of contaminants [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2019,146:921-924
[92] Hernandez E,Nowack B,Mitrano D M.Polyester textiles as a source of microplastics from households:A mechanistic study to understand microfiber release during washing [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2017,51(12):7036-7046
[93] Horton A A,Svendsen C,Williams R J,et al.Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames,UK:Abundance,sources and methods for effective quantification [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,114(1):218-226
[94] Liu J,Zhang T,Tian L L,et al.Aging significantly affects mobility and contaminant-mobilizing ability of nanoplastics in saturated loamy sand [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2019,53(10):5805-5815
[95] Ter Halle A,Ladirat L,Gendre X,et al.Understanding the fragmentation pattern of marine plastic debris [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2016,50(11):5668-5675
[96] Yang J,Yang Y,Wu W M,et al.Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2014,48(23):13776-13784
[97] Kedzierski M,D’Almeida M,Magueresse A,et al.Threat of plastic ageing in marine environment.Adsorption/desorption of micropollutants [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2018,127:684-694
[98] Rehse S,Kloas W,Zarfl C.Microplastics reduce short-term effects of environmental contaminants.part Ⅰ:Effects of bisphenol A on freshwater zooplankton are lower in presence of polyamide particles [J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2018,15(2):E280
[99] Oliveira M,Ribeiro A,Hylland K,et al.Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ Group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (Teleostei,Gobiidae) [J].Ecological Indicators,2013,34:641-647
[100] Fisner M,Majer A,Taniguchi S,et al.Colour spectrum and resin-type determine the concentration and composition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in plastic pellets [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2017,122(1-2):323-330
[101] Besseling E,Wegner A,Foekema E M,et al.Effects of microplastic on fitness and PCB bioaccumulation by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L.) [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2013,47(1):593-600
[102] Velzeboer I,Kwadijk C J A F,Koelmans A A.Strong sorption of PCBs to nanoplastics,microplastics,carbon nanotubes,and fullerenes [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2014,48(9):4869-4876
[103] Wang F,Shih K M,Li X Y.The partition behavior of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanesulfonamide (PFOSA) on microplastics [J].Chemosphere,2015,119:841-847
[104] Rochman C M,Hoh E,Kurobe T,et al.Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress [J].Scientific Reports,2013,3:3263
[105] Zhang W W,Ma X D,Zhang Z F,et al.Persistent organic pollutants carried on plastic resin pellets from two beaches in China [J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2015,99(1-2):28-34
[106] Nematdoost Haghi B,Banaee M.Effects of micro-plastic particles on paraquat toxicity to common carp (Cyprinus carpio):Biochemical changes [J].International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2017,14(3):521-530
[107] Llorca M,Schirinzi G,Martínez M,et al.Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances on microplastics under environmental conditions [J].Environmental Pollution,2018,235:680-691
[108] 杨杰,仓龙,邱炜,等.不同土壤环境因素对微塑料吸附四环素的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2019,38(11):2503-2510
Yang J,Cang L,Qiu W,et al.Effects of different soil environmental factors on tetracycline adsorption of microplastics [J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2019,38(11):2503-2510 (in Chinese)
[109] Amaral-Zettler L A,Zettler E R,Mincer T J.Ecology of the plastisphere [J].Nature Reviews Microbiology,2020,18(3):139-151
[110] Zettler E R,Mincer T J,Amaral-Zettler L A.Life in the “plastisphere”:Microbial communities on plastic marine debris [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2013,47(13):7137-7146
[111] Frère L,Maignien L,Chalopin M,et al.Microplastic bacterial communities in the Bay of Brest:Influence of polymer type and size [J].Environmental Pollution,2018,242:614-625
[112] Wu X J,Pan J,Li M,et al.Selective enrichment of bacterial pathogens by microplastic biofilm [J].Water Research,2019,165:114979
[113] Kwon J H,Chang S,Hong S H,et al.Microplastics as a vector of hydrophobic contaminants:Importance of hydrophobic additives [J].Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management,2017,13(3):494-499
[114] Guzzetti E,Sureda A,Tejada S,et al.Microplastic in marine organism:Environmental and toxicological effects [J].Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2018,64:164-171
[115] Zhu Z L,Wang S C,Zhao F F,et al.Joint toxicity of microplastics with triclosan to marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,246:509-517
[116] Oliveira P,Barboza L G A,Branco V,et al.Effects of microplastics and mercury in the freshwater bivalve Corbicula fluminea (Müller,1774):Filtration rate,biochemical biomarkers and mercury bioconcentration [J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,164:155-163
[117] Yuan W K,Zhou Y F,Chen Y L,et al.Toxicological effects of microplastics and heavy metals on the Daphnia magna [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2020,746:141254
[118] van Doremalen N,Bushmaker T,Morris D H,et al.Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1 [J].The New England Journal of Medicine,2020,382(16):1564-1567
[119] Shi M,Sun Y Y,Wang Z H,et al.Plastic film mulching increased the accumulation and human health risks of phthalate esters in wheat grains [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,250:1-7
[120] Shi Q Y,Tang J C,Wang L,et al.Combined cytotoxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and phthalate esters on human lung epithelial A549 cells and its mechanism [J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,213:112041
[121] Barboza L G A,Vieira L R,Branco V,et al.Microplastics cause neurotoxicity,oxidative damage and energy-related changes and interact with the bioaccumulation of mercury in the European seabass,Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus,1758) [J].Aquatic Toxicology,2018,195:49-57
[122] Khan F R,Syberg K,Shashoua Y,et al.Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J].Environmental Pollution,2015,206:73-79
[123] Wang F L,Wang X X,Song N N.Polyethylene microplastics increase cadmium uptake in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) by altering the soil microenvironment [J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,784:147133
[124] Quan B Y,Li X,Zhang H,et al.Technology and principle of removing triclosan from aqueous media:A review [J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,378:122185
[125] Laganà P,Caruso G,Corsi I,et al.Do plastics serve as a possible vector for the spread of antibiotic resistance?First insights from bacteria associated to a polystyrene piece from King George Island (Antarctica) [J].International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health,2019,222:89-100
[126] Zhou W S,Han Y,Tang Y,et al.Microplastics aggravate the bioaccumulation of two waterborne veterinary antibiotics in an edible bivalve species:Potential mechanisms and implications for human health [J].Environmental Science &Technology,2020,54(13):8115-8122
[127] Bakir A,Rowland S J,Thompson R C.Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions [J].Environmental Pollution,2014,185:16-23
[128] Yang Y Y,Liu G H,Song W J,et al.Plastics in the marine environment are reservoirs for antibiotic and metal resistance genes [J].Environment International,2019,123:79-86
[129] Imran M,Das K R,Naik M M.Co-selection of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens in metal and microplastic contaminated environments:An emerging health threat [J].Chemosphere,2019,215:846-857
[130] Lu L,Luo T,Zhao Y,et al.Interaction between microplastics and microorganism as well as gut microbiota:A consideration on environmental animal and human health [J].The Science of the Total Environment,2019,667:94-100