-
制革废水经生化处理后尾水中通常含有0.3~1.0 mg·L−1的总铬[1],在制革废水生化剩余污泥中含有1~10 g·kg−1的总铬。活性污泥中微生物的胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substance, EPS)主要组分包括多糖(PS)、蛋白质(PN)和核酸等多聚物[2],因其含有大量的羧基、羟基、氨基、磷酸酯等吸附位点,能够通过离子交换、络合、电中和等作用对重金属进行有效固定 [3-4]。EPS对铬的吸附已有许多相关报道。有研究[5]认为,EPS的不同结构层、EPS含量及组分比例和外界环境均会影响重金属在EPS上的吸附。有研究[6]发现,EPS对Cr3+吸附的主要作用位点是羧基和磷酸基,并形成EPS-Cr3+配位物。
EPS一般可分为松散附着型(loosely bound EPS,LB-EPS)、紧密黏附型(tightly bound EPS,TB-EPS)和溶解型EPS(S-EPS)[7]。LASPIDOU等[7]认为,S-EPS与溶解性微生物代谢产物(soluble microbial product,SMP)属同源物质,也是在微生物的内源呼吸过程(BAP)和基质分解过程(UAP)中产生的[8]。许多研究表明,进水基质及污泥种类均影响EPS的组成,不同层EPS上存在不同的金属吸附位点[9],不同结构层中蛋白质和多糖含量的动态变化会影响污泥的吸附速率[10],可溶性EPS具有比结合态EPS更大的质子离子交换能力[11],高度可溶性EPS-Cr3+配位化合物可导致铬在环境中的迁移和蓄积[6]。
随着我国对制革废水总铬排放总量限制指标的日益严格,探索制革生化尾水中残留铬与EPS的相互关系,特别是S-EPS对出水中总铬的影响很有必要。目前,在制革废水生物处理过程中,EPS各结构层的组分变化及金属铬离子在EPS各结构层和SMP中分布情况的研究鲜有报道。本研究在对制革废水各处理阶段的不同层EPS组分定量分析的基础上,重点围绕EPS组分变化与铬的分布规律进行了研究,为制革废水铬排放总量控制和深度处理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
实验所用活性污泥及废水取自河北某制革废水处理站的主要生化处理段(水解酸化-两级好氧处理工艺),共5个采样点,分别为初沉池出水、水解酸化池污泥、一级好氧池污泥、二级好氧池污泥及二沉池出水,污泥基本性质如表1所示。水解酸化池、一级好氧池、二级好氧池的污泥沉降比(SV30)分别为30%、76%、81%。所取样品经固液分离和EPS分步提取后,储存在4 ℃冰箱中备用。
-
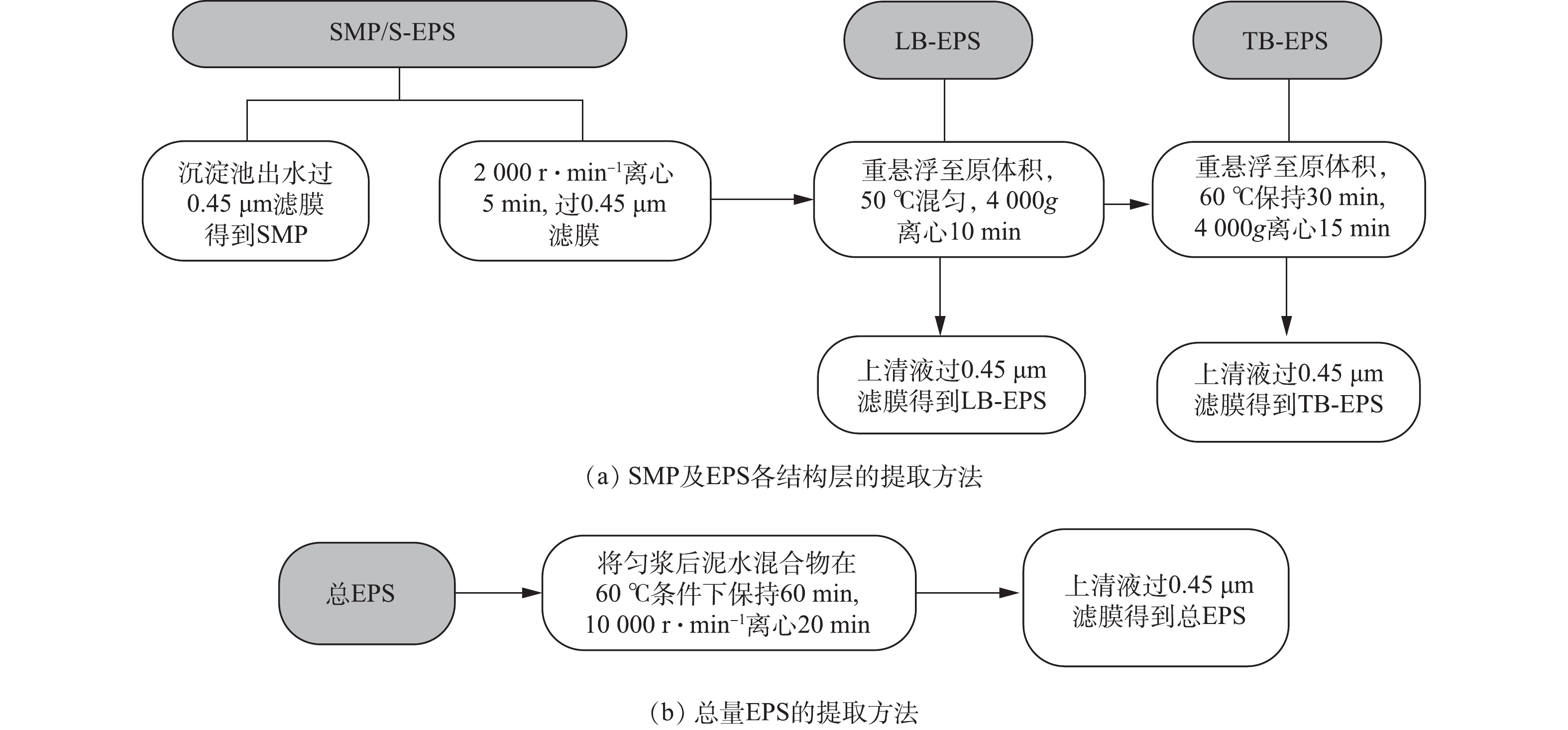
EPS 提取方法有物理法和化学法[12-13]。因化学法易造成铬离子的流失和形态改变,为保证EPS的结构完整性、物理化学性质的稳定及铬离子分布在EPS各结构层分布的相对准确性,本实验采取改良热提取法,从制革生化活性污泥中提取EPS溶液[14-15],控制温度≤80 ℃,并使加热时间≤60 min。该方法对铬离子在EPS各结构层的分布造成的影响较小,同时能更好地反映EPS各结构层蛋白质和多糖的相对组成[16-19]。EPS和SMP的提取方法如图1所示。
取均匀混合的泥水混合物50 mL,在2 000 r·min−1的离心机中离心5 min 后,取上清液,然后过0.45 μm 滤膜,得到S-EPS[20],沉淀池出水过0.45 μm滤膜,得到SMP。
-
溶解性有机碳(DOC)的测定使用德国元素分析系统公司liqui Ⅱ TOC测定仪,水样过0.45 μm滤膜,采用DOC表征SMP浓度;总铬的测定采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法(GB/T 7466-1987),每个样品平行测量3次,取平均值;挥发性悬浮物固体浓度(VSS)和悬浮固体浓度(SS)采用重量法测定。
多糖(PS)采用蒽酮-硫酸法测定,以葡萄糖作为标准品;蛋白质(PN)采用考马斯亮蓝法测定,以牛血清白蛋白(BSA)作为标准品,绘制标准曲线[21];UV254采用紫外分光光度计测定。采用蛋白质与多糖之和表征SMP及EPS总量,每个样品平行测量3次,测定结果取平均值。
1.1. 活性污泥取样及预处理
1.2. EPS与SMP的提取方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
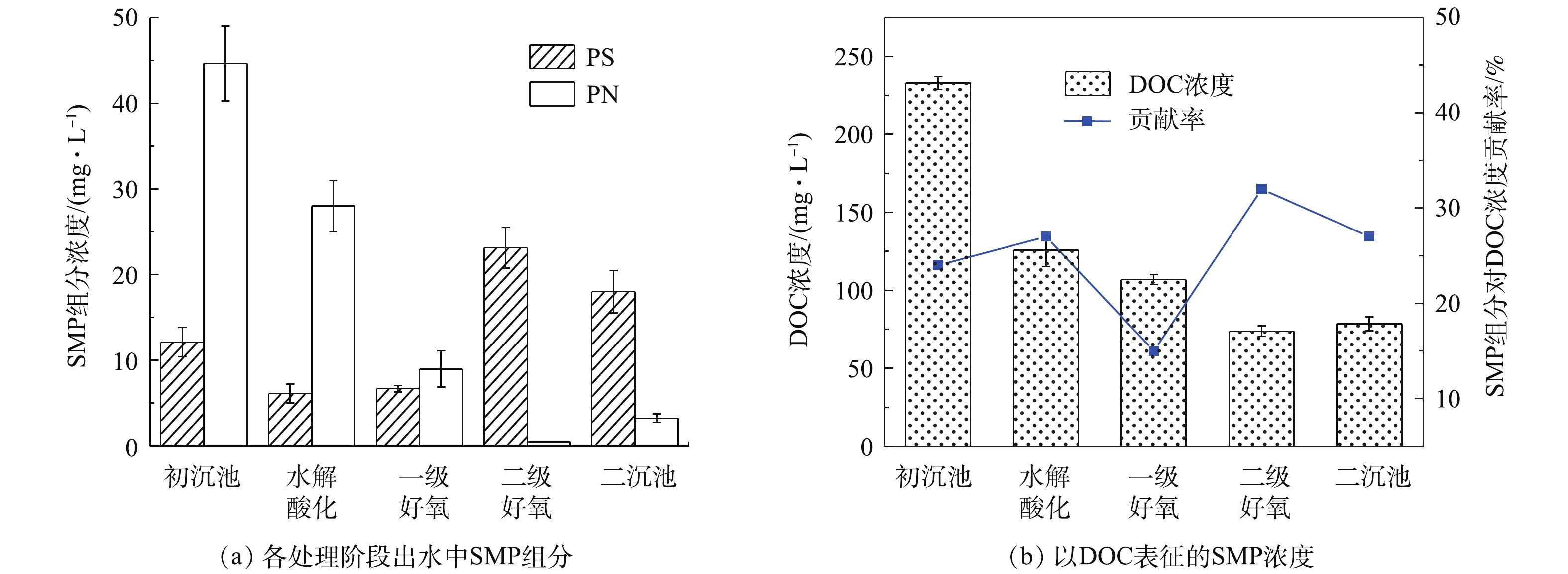
有机物在出水SMP中的分布呈下降趋势,SMP中有机碳含量逐渐降低,各处理工段出水SMP中溶解性有机物及各组分浓度比较结果见图2。SMP中有机碳浓度用DOC表征,各水样DOC浓度与组分浓度变化趋势一致,SMP中组分对有机碳的贡献率为15%~32%。在初沉池出水DOC浓度为233.1 mg·L−1时,经水解酸化-好氧生物处理,使二沉池出水DOC降低至78.54 mg·L−1,DOC去除率为66.4%,有机碳浓度变化受进水基质影响较大。在制革废水生物处理系统中,SMP中多糖变化呈先降低后升高的趋势,一级生化SMP中蛋白质和多糖的变化趋势一致,二级生化多糖含量大幅增加,二沉池出水SMP中多糖含量与二级好氧池出水SMP相似。初沉池SMP多糖含量为12.13 mg·L−1,二沉池出水中多糖含量为18.02 mg·L−1,初沉池出水SMP蛋白质含量高达44.69 mg·L−1。通过水解酸化预处理及好氧生物处理后,二沉池出水蛋白质含量削减至3.23 mg·L−1,削减92.8%,与出水DOC的削减规律相呼应。SMP组分含量呈先降低后升高的趋势,这可能是因为二级好氧池中TB-EPS外排使SMP的组分含量升高,EPS与SMP之间相互转化造成的。杨丹等[15]的研究表明,好氧颗粒污泥中SMP随底物基质消耗而缓慢增加,当底物浓度降低时,SMP来源于微生物内源呼吸及EPS水解,这验证了SMP的产生会影响出水水质的结果。
由图3可知,水解酸化池S-EPS蛋白质含量为10.61 mg·g−1(以VSS计),一级好氧池中蛋白质含量为1.347 mg·g−1,削减87.3%,二级好氧池SMP蛋白质含量未检出;一级生化后端S-EPS多糖含量为1.003 mg·g−1,二级生化多糖含量增加至18.07 mg·g−1。初沉池SMP取自初沉池后端出水,初沉池没有明显的生物处理作用,水解酸化使大分子难生物降解物质转变为易生物降解的物质。在缺氧条件下,细菌利用外源有机物合成自身细胞,导致水解酸化池中S-EPS蛋白质组分削减幅度较大。削减部分可能主要作为微生物的营养物质被消耗掉,蛋白质可为生物处理提供氮源,进而促进微生物生长。有研究[22]发现,重金属冲击浓度增加,SMP中蛋白质产生量下降。相比市政污水生物处理过程中多糖含量随生物处理过程不断削减[17],制革污水的生物处理过程则存在多糖含量增加的趋势,这可能是微生物通过增加EPS的产量来对抗微量重金属铬(Cr3+<1.5 mg·L−1)的胁迫作用造成的。AQUINO等[23]的研究表明,在铬的存在下,细胞裂解作用增强,细胞裂解产物对SMP的积累有重要贡献。康福星[24]的研究表明,在一定浓度重金属的污染水体中,微生物能分泌大量的EPS来提高净化水体的能力。
-
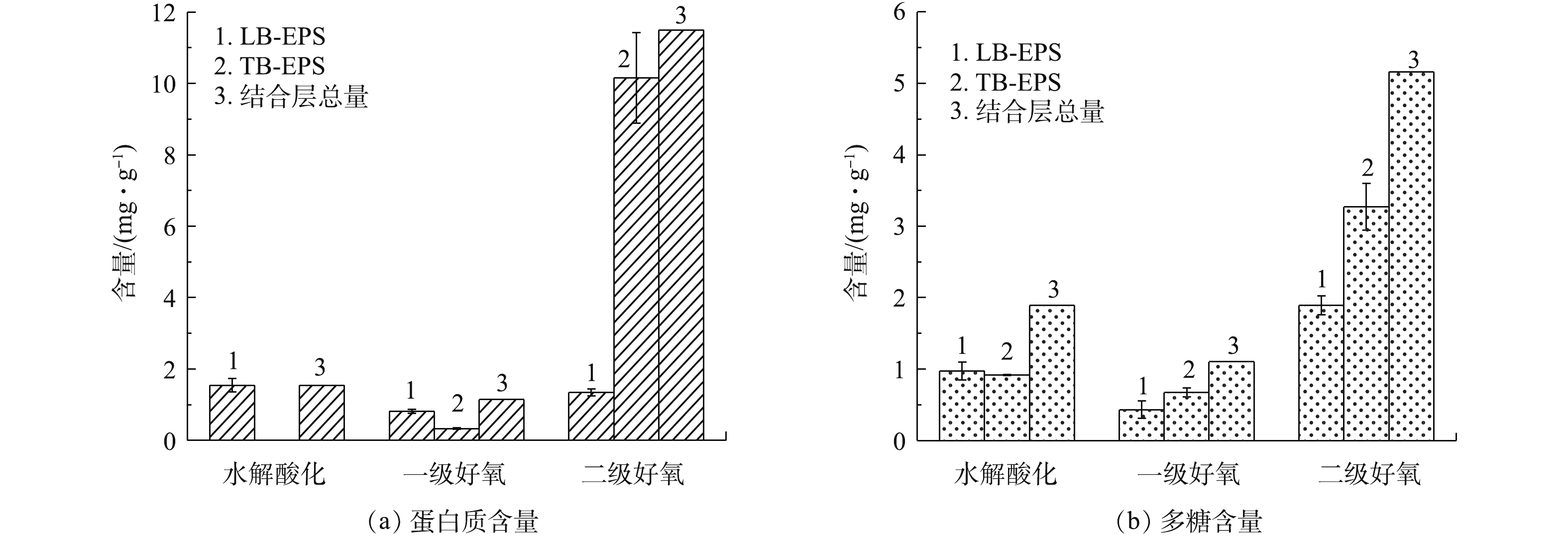
由图4可知,不同污泥样品的EPS含量变化较大。结合层EPS组分含量为2.248~16.66 mg·g−1,蛋白质占比为44.9%~69.0%,多糖占比为31.0%~55.1%。水解酸化池及一级好氧池LB-EPS主要组分为蛋白质,TB-EPS中主要组分为多糖,二级好氧池LB-EPS主要组分为多糖,TB-EPS主要由蛋白质组成。由此可见,LB-EPS层随生物处理过程的推进,蛋白质随之降低,多糖含量随之升高。LB-EPS中多糖含量从高到低依次为二级好氧>水解酸化池>一级好氧,含量依次为1.893、0.975、0.430 mg·g−1;LB-EPS中蛋白质含量从高到低依次为水解酸化池>二级好氧池 >一级好氧池,含量依次为1.544、1.346、0.817 mg·g−1;TB-EPS中多糖含量依次为0.919、0.673、3.269 mg·g−1,蛋白质含量依次为0、0.328、10.16 mg·g−1。TB-EPS与细胞表面结合紧密,稳定地附着于细胞壁外,组分变化主要是由微生物细胞自身的变化而产生的,较少受外界水体的影响;LB-EPS结构松散,是微生物细胞与液相间物质交换的场所,易受微生物活性及外界水体的影响。
樊鹏超等[9]对采用A2O工艺的城市污水处理厂研究发现,EPS中蛋白质含量高于多糖,蛋白质为6.17~43.18 mg·g−1,多糖为0.970~6.76 mg·g−1。张安龙等[25]对采用氧化沟工艺的造纸厂废水处理厂研究发现,EPS中蛋白质为47.8~124 mg·g−1,多糖为13.3~25.2 mg·g−1 。SPONZA [26]发现,皮革、染料、化学3种工业废水活性污泥EPS中蛋白质含量为24~48 mg·g−1 。在生物处理前端,进水中有机物浓度较高,污染负荷大,从而抑制EPS分泌,EPS总量为5.68 mg·g−1。SPONZA[26]研究发现,化学品、染料和皮革工业EPS中蛋白质含量低的原因是蛋白质与进水中高COD含量物质的复杂作用。在生物处理末端,结合层EPS总量大幅度增加,TB-EPS含量增幅为93%,LB-EPS增幅为22.2%。由于二级好氧处理阶段污泥负荷小,底物基质浓度较低,微生物可利用基质减少,微生物进入内源呼吸阶段,细胞的分泌及自溶使污泥中EPS含量增大[15]。胡小兵等[10]采用加热法,分层提取污水厂好氧池的活性污泥EPS,发现内层EPS的PN/PS含量高于外层EPS。周健等[27]发现,EPS及多糖含量与污泥负荷呈负相关,这与本研究中的结果相一致。
-
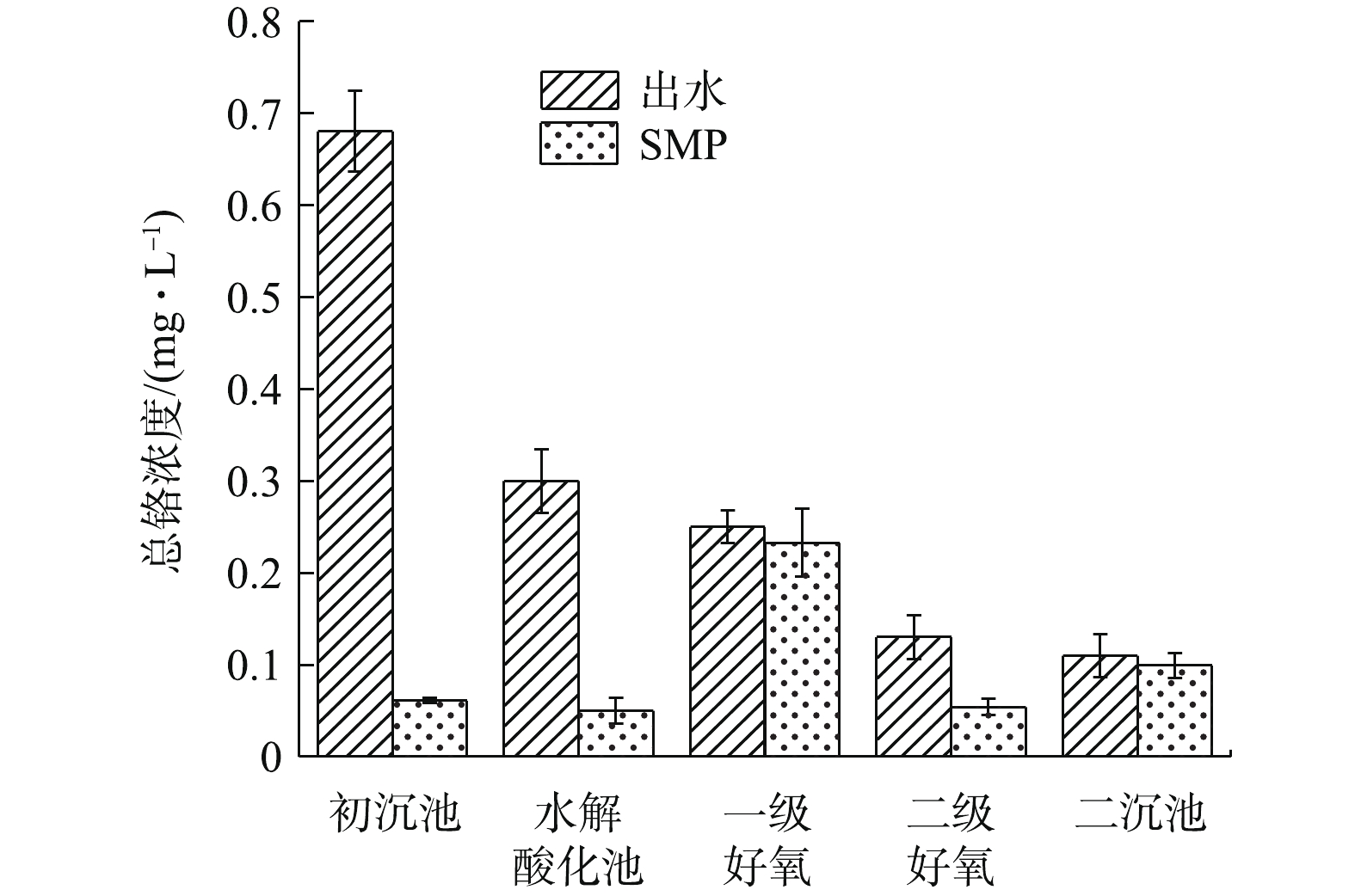
由图5可知,各处理单元的铬含量存在一定差异。以初沉池出水中铬含量为初始参照值,初沉池及水解酸化池出水经0.45 μm过滤,铬含量大幅度下降。这说明生化处理前,铬主要吸附在固体悬浮物上,大尺寸悬浮物经自然沉降附着于EPS表层,Cr3+沉淀分布在细胞表面或与EPS络合存在于微生物表面,少部分Cr3+进入细胞内部[28]。初沉池出水SMP中铬浓度为0.061 mg·L−1,经生物处理,二沉池出水SMP中铬浓度为0.099 mg·L−1,出水端中铬浓度略高于进水端。每个样品平行测定3次,基本排除了测量误差,故出水中增加的铬浓度可能是污泥中吸附累积的铬重新被释放,络合态EPS-Cr随EPS水解进入液相导致的。这与王金翠等[29]的研究结果相似,即EPS与SMP之间存在相互转化和吸附与被吸附的关系。
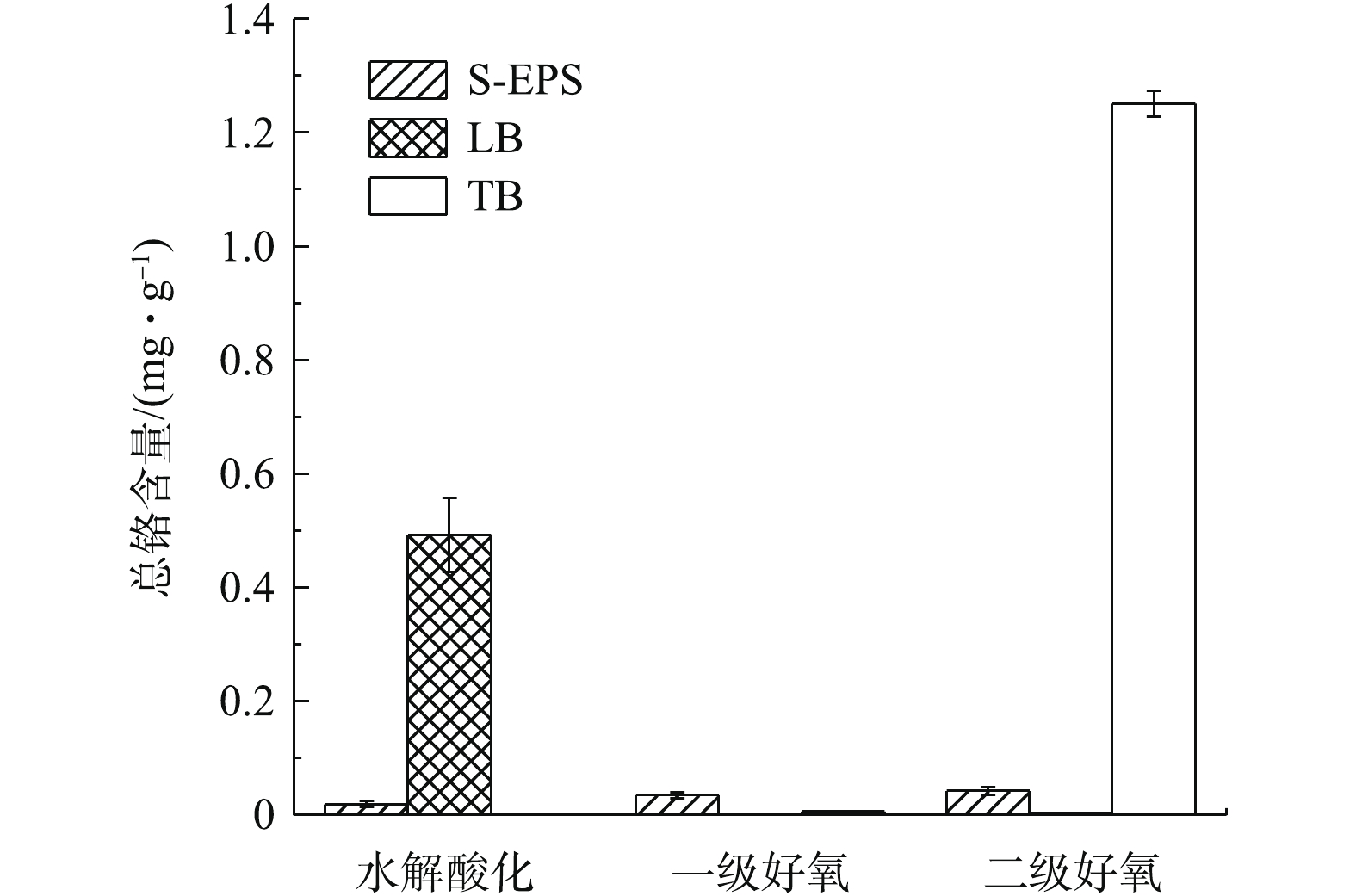
如图6所示,水解酸化池LB-EPS、二级好氧池TB-EPS中铬含量分布较多,分别为0.491 9、1.251 mg·g−1,这可能与各处理单元的污泥负荷、溶解氧含量、EPS含量等因素有关。一级好氧池中铬含量分布均很低,主要是由于该池活性污泥浓度较高造成的,MLVSS高达6.668 g·L−1(表1)。二级好氧池TB-EPS中铬含量高,主要是由于胞外聚合物结合层对Cr3+的络合能力较强造成的。这与胡小兵等[10] 的研究结果一致,即各层EPS对污泥吸附污染物的作用机制是:有机污染物通过S-EPS的吸附,经LB-EPS传输渗透到TB-EPS中储存,多糖含量的增加有利于SMP和TB-EPS对污染物的吸附。重金属铬在各池S-EPS中分布较少,主要是由于S-EPS表面结构较为光滑,结构松散,对重金属铬具有一定的吸附作用,但固定作用较弱。
利用SPSS软件,对EPS各组分的蛋白质多糖含量与DOC、总铬分布情况和多糖蛋白质进行Pearson相关性分析,结果如表2所示。从Pearson相关系数及相伴概率可知,总铬的分布与胞外聚合物中PS/PN (Pearson相关系数为0.787, P=0.036)、与PS呈显著正相关(Pearson相关系数为0.890,P=0.003);DOC与PN的含量呈显著正相关(Pearson相关系数为0.941,P=0.000);EPS总含量对污泥中总铬的分布影响不显著。
已有研究[30-32]表明,EPS中多糖比蛋白质更容易吸附金属离子,这与多糖和蛋白质中对金属离子的活性吸附点数量和吸附点位活性大小有关。EPS中多糖是络合Cr离子的主要组分,金属离子可能首先占据多糖中的活性吸附点,待饱和后再与蛋白质中的活性吸附点位结合。刘轶等[33]认为,对活性污泥脱水性能起决定作用的不是 EPS 总量而是其各组分间的比例,EPS各组分比例可影响污泥絮体表面的离子化多聚物含量和EPS亲疏水性质。PS/PN越大,污泥EPS的Zeta电位越小,对重金属阳离子的络合作用就越强,这与本研究结果一致。朱经贺[34]发现,海藻酸钠(多糖)的加入会使重金属离子(Pb2+、Cd2+)从人血清白蛋白(HSA)上脱离,并与海藻酸钠形成络合物。这可能是由于EPS中蛋白质与多糖发生静电相互作用及反应基团间的相互干扰所致[5],说明蛋白质和多糖在EPS各组分中所占比例是影响金属铬分布的重要因素。
2.1. 制革生物处理过程SMP组分特征
2.2. 制革生物处理过程EPS组分特征
2.3. 总铬在EPS、SMP组分中的分布
-
1)在制革污水生物处理过程中,EPS各组分中主要成分存在蛋白质与多糖的交替变化,结合层EPS组分含量为2.248~16.66 mg·g−1。在一级生物处理中,多糖及蛋白质含量均降低;在二级生物处理中,污泥负荷小,EPS含量显著升高,主要表现在蛋白质含量增长,SMP中多糖含量大幅升高。这一结果表明生物处理中胞外聚合物存在由内向外排放的过程。
2)在制革废水生物处理中,S-EPS吸附废水中Cr3+,经LB-EPS传输渗透到TB-EPS中储存,吸附饱和或外界条件变动会引起附着于细胞表面的铬重新被释放,EPS-Cr络合物也可能由于胞外聚合物外排过程进入液相,从而影响出水水质。
3)根据Pearson相关性分析结果,总铬与胞外聚合物中PS/PN呈显著正相关(P<0.05),总铬与PS呈显著正相关(P<0.01),DOC与PN的含量呈显著正相关(P<0.01)。这说明EPS中的不同组分含量对Cr的结合能力不同,证实了PS/PN对铬的络合起关键作用。



 下载:
下载: