-
目前,城市黑臭水体治理已经进入攻坚期[1]。对于城市河道来讲,水体黑臭与底泥污染密切相关,因此,污染底泥的异位处理或原位修复是黑臭水体治理的关键环节。河道底泥黑臭主要与酸可挥发性硫化物(AVS)、亚铁和氨氮的存在有关,其含量的高低直接反映了河流黑臭水体的污染情况[2-4]。针对这些污染物质,以往常规的物理或者化学修复方法并不能同时去除所有污染,甚至可能引起其他的二次污染[5-10]。因此,在不产生二次污染的前提下,研究出一种新型绿色环保的治理方法,以达到底泥致黑臭多污染物的同步耦合去除是目前人们关注的热点问题。
电动修复技术最初兴起于污染土壤的修复,其修复原理是在直流电场的作用下,利用电迁移、电渗析和电泳等原理去除土壤中的重金属和有机物等污染物,并成功应用于工程实践中[11-13]。随着研究的不断深入,该技术也被尝试用于去除水体中硫化物和氨氮等物质[14-19],其原理是利用电极的氧化还原作用。对于还原性物质,可以利用阳极的氧化作用,直接氧化分解污染物质,或者是利用外加电势刺激相应功能的微生物,提高微生物的活性,再利用微生物间接分解污染物质,从而达到修复的目的。因此,利用阳极的氧化作用,在一定程度上可以对底泥中硫化物、亚铁、氨氮等主要还原性污染物进行氧化,实现多污染物同步耦合去除的目标。
目前,采用电动修复技术在理论上可以实现底泥黑臭污染物质的同步氧化去除。本研究通过实验室的模拟实验,探讨了电动修复对底泥致黑臭污染物(硫化物、亚铁、氨氮)的同步去除特征,分析了电动修复治理黑臭底泥的优化条件,相关结果可为河道水体黑臭的治理提供新参考。
-
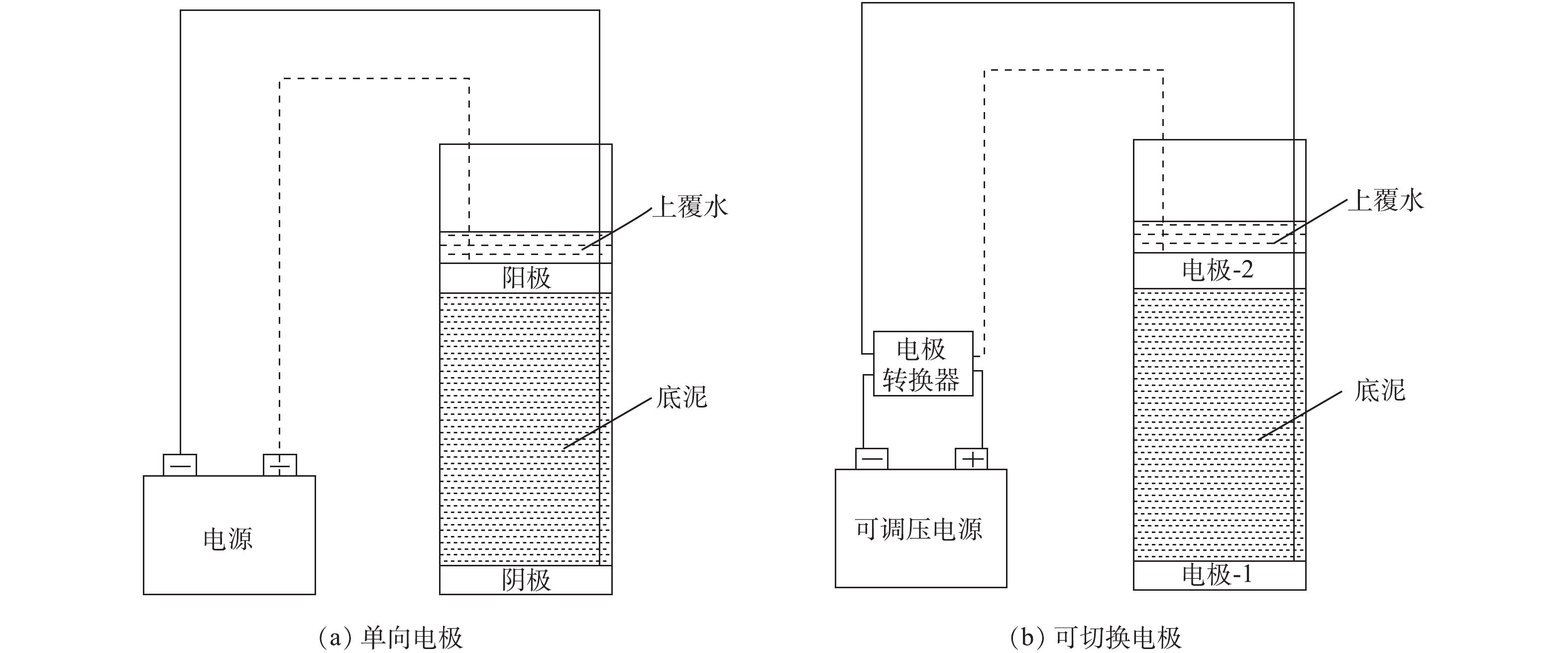
本实验所用的底泥取自东莞石排公园东北处污染河流,该河流主要受到附近居民产生的生活污水的污染,导致河道底泥黑臭严重。本实验将采集到的底泥样品先做均匀化处理,然后再用塑料箱密封遮光厌氧保存。实验原泥样品初始理化性质:AVS为(6 554.07±84.62) mg·kg−1,Fe2+为(18 810±101.85) mg·kg−1,间隙水氨氮为(272.58±25.28) mg·L−1,底泥铵态氮为(1 161.00±91.06) mg·kg−1,Eh为(−334±21.15) mV,pH=7.06±0.78。电动修复实验装置如图1所示。图1(a)为单向电极黑臭底泥电动修复实验装置。实验在15组玻璃柱(直径为8 cm,高为15 cm)中进行,每个玻璃柱中添加12 cm厚的黑臭底泥。电动修复实验装置以石墨为电极,钛丝作为导线,电极间距离为10 cm。阴极在玻璃柱下部,距离量筒底部约1~2 cm;阳极在玻璃柱上部(上面覆盖有少许底泥),加上约2 cm的上覆水,封口密封。连通正负电极后,施加15 V直流电源。接着分别在第1、3、5、7和10天取样。取样时,每次随机取出3根玻璃柱,在2个电极处,取4 cm厚度的样品,测定其还原性污染物的含量,观察在通电过程中还原性污染物含量的变化情况。图1(b)为切换电极黑臭底泥电动修复实验装置。实验在12组玻璃柱(直径为8 cm,高为15 cm)中进行,每个玻璃柱中添加12 cm厚的底泥。2个电极(石墨电极板,钛丝作为导线)之间距离为10 cm,电极-1在玻璃柱子下部,距离量筒底部约1~2 cm;电极-2在玻璃柱子上部(上面覆盖有少许底泥),加上约2 cm的上覆水。连通电极转换器和电源后,用对应定制的木制塞子塞住封口。施加直流电源,电压为12 V。接通电源后,先调电极转换器,在初始状态下,电极-1连接电源的负极,电极-2连接电源的正极。然后,分别设置电极的切换频率为1、2.5、5 d·次−1,再根据这个频率定期切换电极的极性。通电10 d后,结束通电,分别在玻璃柱的上部、中部和下部,取4 cm厚度的样品,测定其还原性污染物的含量,观察定时切换电极对还原性污染物的影响。
-
在实验过程中,间隙水中氨氮、硝态氮和亚铁的测定采用国家水与废水监测标准方法。AVS的测定参考文献中的方法[20]。底泥可交换铵态氮参照土壤农化分析方法,采用KCl浸提法测定: 称取5 g底泥(同时测含水率计算干泥质量),使用2 mg·L−1的KCl溶液,振荡40 min,浸出液按间隙水样氨氮的测定方法进行测定。电流读数为定时记录变压器上电表的实时数据。pH和Eh均采用对应的雷磁便携式测定仪进行测定。
采用Excel将实验数据先做预处理,对数据进行平均值和标准偏差的计算,再用SPSS、Origin软件进行数据分析和绘图。
-
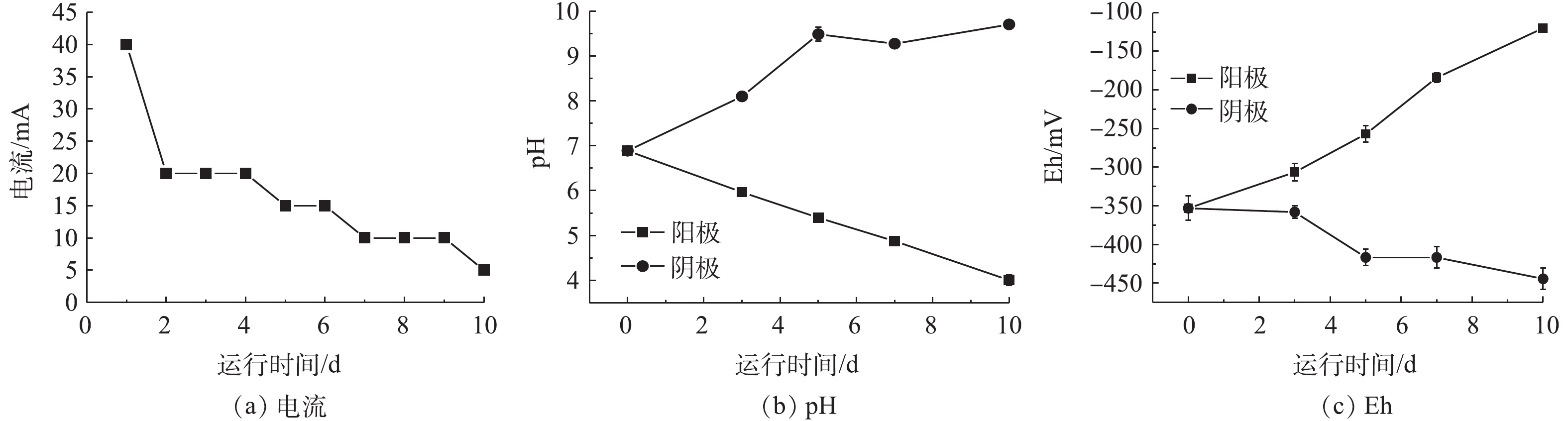
在装有黑臭底泥的玻璃装置中,分别以石墨作为电极,单向通电后,观察电动修复对底泥的影响。由图2可知,在通电过程中,底泥的pH、Eh和电流随时间均发生了不同程度的变化。电流随着通电时间的延长呈逐渐下降的趋势。通电之后,在第1天,电流达到最大值40 mA;随后电流逐渐下降,在第10天降到最低值,为5 mA。在单向电动修复过程中,阳极和阴极对于底泥的pH和Eh的变化呈现明显的两极分化,且随着通电时间的延长,差异越明显。处理后,阳极区的pH由最初的6.89下降到4.00,而阴极区的pH由最初的6.89上升到9.70,出现阳极酸化和阴极碱化的现象;在Eh变化上,阳极的氧化还原电位上升幅度较大,底泥氧化还原电位从原来的−353.00 mV上升至−120 mV,还原性明显改变。阴极的氧化还原电位稍微降低,从−353.00 mV降至−444.33 mV。
综上所述,如果在底泥中只是进行单向电极的电动修复,很可能会对底泥的pH和Eh造成较大的影响,主要体现在:在通电过程中,阳极的pH会出现较明显的下降,Eh会出现较大的上升;而阴极的pH则会出现一定程度的上升,Eh会有所下降。这个电动修复存在的一个弊端是须采取适当的方式(如切换电极)加以改进。
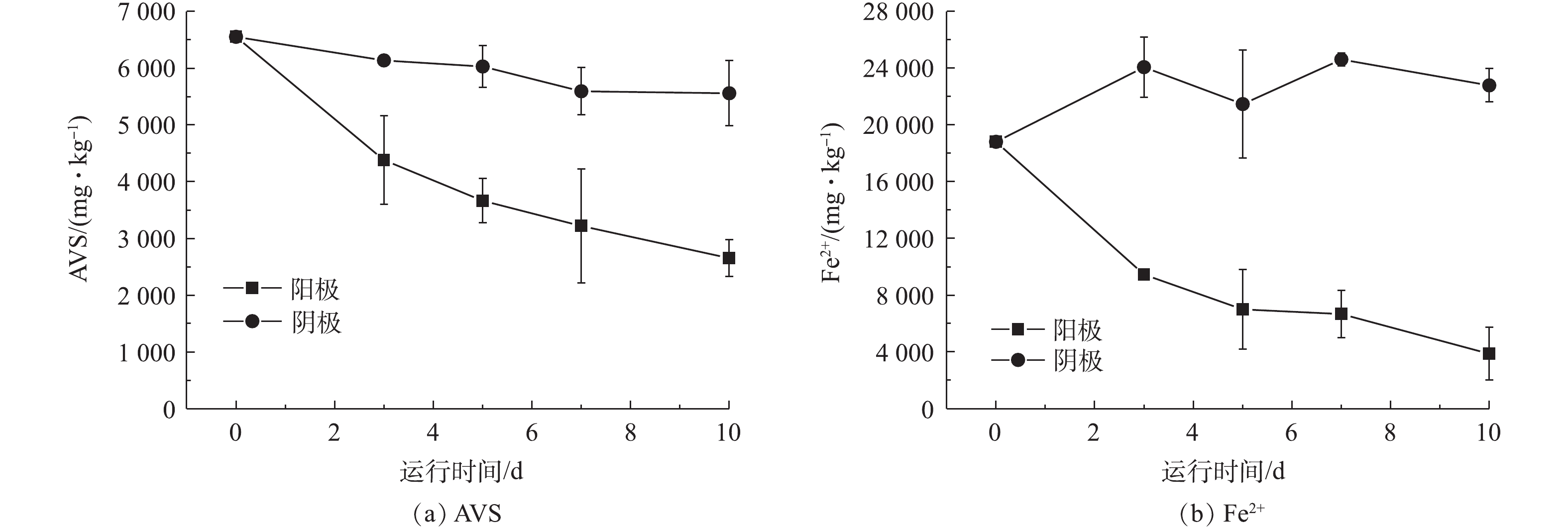
如图3所示,随着通电时间的延长,阳极处底泥中的AVS和亚铁离子浓度均呈逐渐下降的趋势,且下降的效果比较明显。而阴极区域底泥的AVS和亚铁离子的浓度变化不大,虽有所波动,但下降趋势并不明显。在通电10 d后,阳极区域底泥的AVS浓度比最初下降了60%,亚铁离子浓度比最初下降了79.41%,均显示出较好的去除效果。
如图4所示,从浓度变化趋势看,在通电过程中阳极区域间隙水中氨氮浓度与硝态氮浓度间呈负相关。随着通电时间的延长,阳极和阴极区域的间隙水氨氮浓度均呈先下降后缓慢上升的趋势,但整体趋势明显下降;阳极区域硝态氮浓度呈先上升后快速下降的趋势;而阴极区域的间隙水硝态氮则处于一个比较稳定的状态,含量很低,基本接近0。通电10 d后,阳极和阴极区域的间隙水氨氮浓度分别比最初下降了56.2%和72.3%,均取得了比较明显的去除效果。而底泥的铵态氮在通电过程中出现了不太规律的升降变化。在通电结束后,阳极处含量比通电前增加了30%左右,而阴极处比开始时略有下降,但整体的去除效果不明显。由此可见,电动修复对氨氮的去除主要发生在间隙水界面。
依照电动修复原理,底泥的电动修复过程起主要作用的为电解水过程和电极的电化学氧化还原过程,这2个过程在整个底泥修复体系中起至关重要的作用。在电解水过程中阳极区的主要反应如式(1)所示,阴极区的主要反应如式(2)所示。
此外,电化学氧化处理技术是氧化底泥的主要过程,其原理主要是利用阳极产生的羟基自由基(·OH)来氧化还原性的物质。其中,电解过程中氯离子对电化学氧化具有增效作用,起作用的原因是电解过程中有Cl2、HClO、ClO−等活性氯的生成[21]。阳极区的主要反应如式(3)~式(5)所示,阴极区的主要反应如式(6)和式(7)所示。
AVS含量的降低主要是由于电化学氧化所致。在通电过程中,阳极产生的羟基自由基(·OH)具有很强的氧化性,可以氧化AVS生成
${\rm{SO}}_4^ {2-} $ [22]。此外,由于底泥间隙水中存在Cl−,在电极的氧化作用下,会被转化成氧化性较强的活性氯,AVS在活性氯的作用下,可直接被氧化成${\rm{SO}}_4^ {2-} $ [23]。从水的电解过程来看,阳极区域在电解水过程中产生了H+,而H+可以与AVS反应,使部分AVS转化为H2S气体,从而可去除部分AVS;而阴极区在水解过程中产生了OH−,且处于还原状态,不具备去除AVS的条件,这也说明了阴极区AVS没有明显下降的原因。对于亚铁离子在2个电极上含量的变化情况,电极间的电迁移可能也起到了重要的作用[11]。在电场的作用下,阳极区域带正电荷的亚铁离子容易向阴极区域迁移,从而降低该区域亚铁离子的含量。同时,部分在阳极处由于电化学氧化从亚铁离子变成的三价铁离子也可能在电场的作用下迁移到了阴极,并在阴极处发生了还原反应重新变成了亚铁离子,且阴极pH较高,可能生成了氢氧化物并沉淀下来,使阴极的亚铁离子出现累积现象。由于受到电场作用的影响,阴极中的Cl−向阳极迁移,其含量逐渐减少,在阴极区难以产生有效的活性氯,对亚铁离子进行氧化作用,以至阴极区的亚铁离子并不能有效被氧化。所以,从整体上来看,阳极对AVS和亚铁离子均具有较明显的氧化效果,而阴极氧化效果一般,甚至可能出现亚铁离子的累积。
在氨氮去除方面,电动修复对底泥的间隙水氨氮有比较明显的去除效果。间隙水氨氮的去除可能与电极的电化学氧化性质(在Cl−促进作用下的强氧化作用)和pH的变化有关[24-25]。在阳极处,电极主要发生氧化反应。在这个过程中,阳极附近的Cl−也有可能在电场的作用下发生反应,生成了具有强氧化性的次氯酸根离子等活性氯,间接氧化水里面的氨氮[26]。具体反应过程为:阳极附近的游离态
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 很容易在活性氯或者底泥里面的氨氧化细菌(AOB)的作用下失去电子,被氧化成${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ ,而${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ 可以跟底泥中的AVS在短时间内发生反硝化反应,这个过程中通常伴随有中间产物${\rm{NO}}_2^ - $ 的生成,最终以N2的形式去除[27]。此外,阴极的pH较高,${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ 也可以在阴极与OH−发生反应,生成不稳定的氨水化合物,最终以氨气的形式去除。同时相关研究[28-29]发现,在缺氧的环境下,阴极也有可能发生硝化反硝化的脱氮过程。因此,通过实验数据可知,2个电极附近的间隙水氨氮均有很好的去除效果。而通过观察底泥铵态氮的变化规律(图4(c)),可以看出阳极与阴极的铵态氮浓度之间存在一定的负相关关系。由于底泥铵态氮可能是结合在底泥其他物质里面,同时其结合物又可能带有电荷,因此,可以判断底泥铵态氮含量的变化可能与在其在电场作用下发生的迁移有关。 -
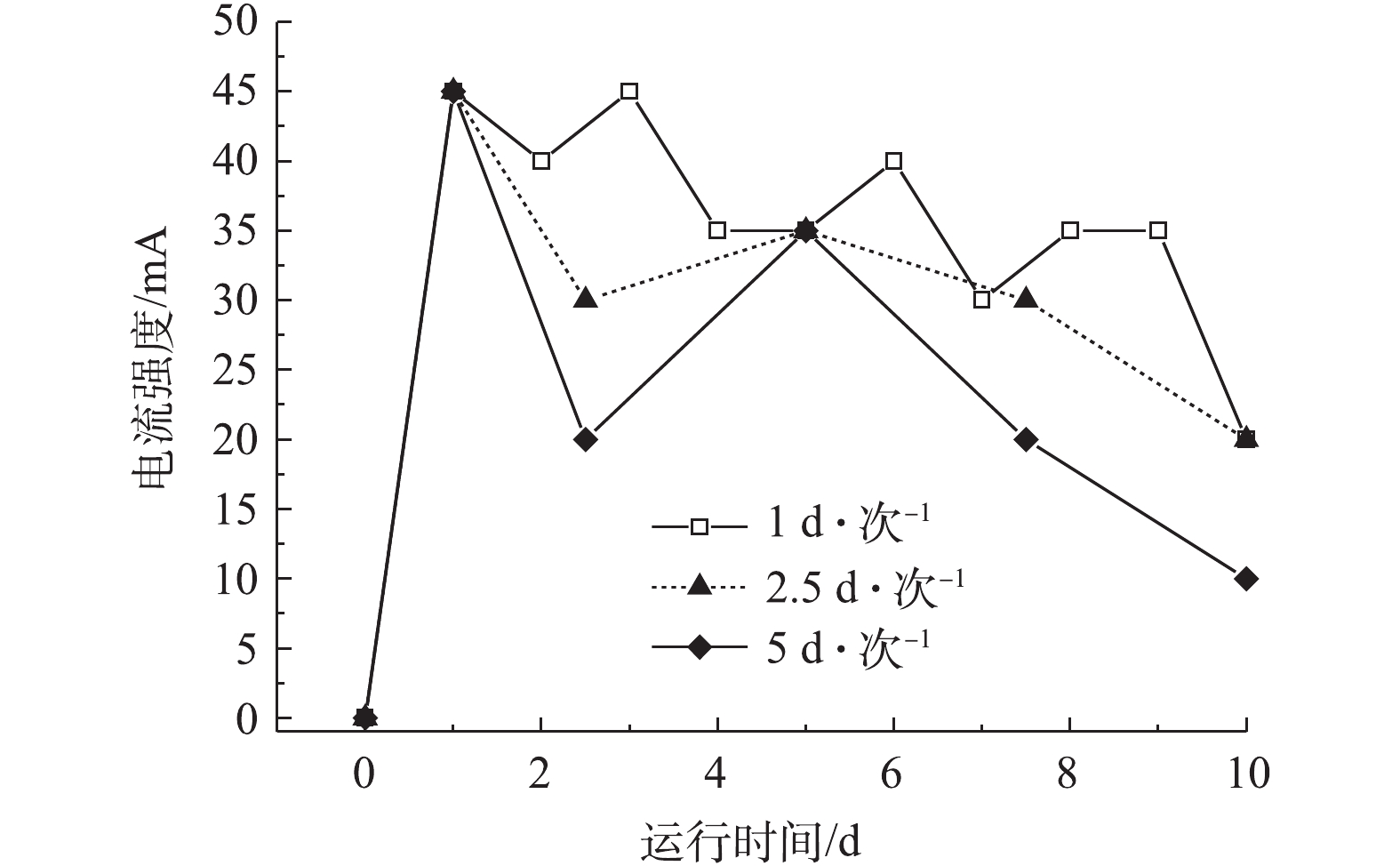
在电动修复过程中,不同电极切换频率下电流的变化情况如图5所示。由图5可知,在周期性切换电极的条件下,以1、2.5、5 d·次−1的电极切换频率的各处理系统的电流强度均呈现一定的周期性波动。在开始通电阶段,各处理组的电流均由0上升至45 mA。此后,在每次切换电极方向的过程中,各处理组的电流均表现出先增大而后逐渐降低的趋势。电流大小与底泥间隙水中的各种带电离子的迁移作用有密切关系。在初始阶段,由于底泥间隙水中有大量带电离子的存在,在电场作用下,带电离子发生迁移,使电流示数增大。在切换电极方向的过程中,电流示数突然增大,这是因为切换电极方向引起了底泥中电场的反转,激活了底泥中一部分由于沉淀等原因而处于静置状态的离子参与到定向迁移过程,促使电流增大[30]。通电10 d后,切换频率为1 d·次−1和2.5 d·次−1的底泥电流最后稳定在20 mA,切换频率为5 d·次−1的底泥电流最后稳定在10 mA。
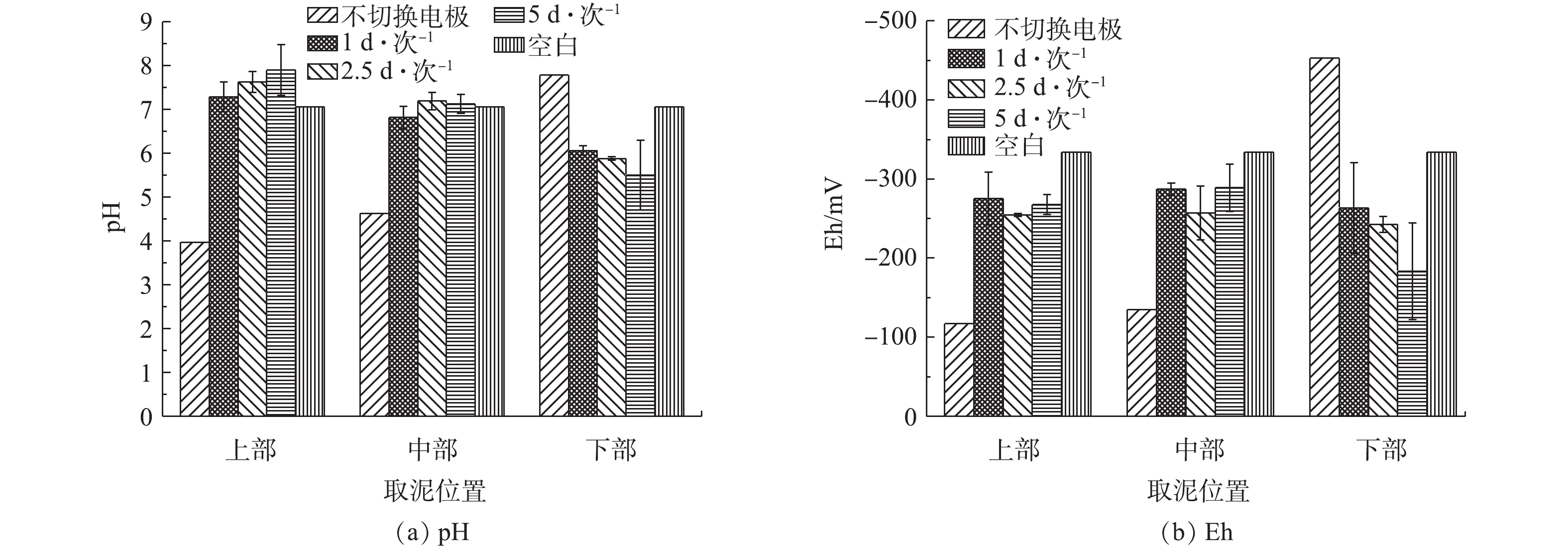
由图6(a)可知,空白对照组底泥的pH为7.06,实验组初始状态电极-2连接电源正极,电极-1连接电源负极。在电动修复10 d后,4个实验组处理的底泥均发生了不同程度的变化。对于不切换电极的处理组,在上部和中部的pH为3.97和4.63,呈现大幅度降低趋势,为酸性;而下部的pH为7.78,呈现上升趋势,为碱性。而在对底泥进行不同频率周期性切换电极的另外3组实验组中,底泥上部的pH均呈现一定程度的上升,中部的pH变化较小,下部的pH均稍微降低,但整体并没有出现过酸或过碱的现象。
由图6(b)可以看出,电动修复10 d后,底泥各处的Eh均为负值,此时底泥处于还原状态。Eh越小,表明底泥的还原性越强。在对电极进行周期性切换的条件下,除切换电极频率为5 d·次−1的底泥下部Eh较大外,其他各位置测得的Eh数值较为相近,表明底泥各位置的还原性大小相近。总体来说,经过周期性切换电极后,各实验组的Eh均有所上升。
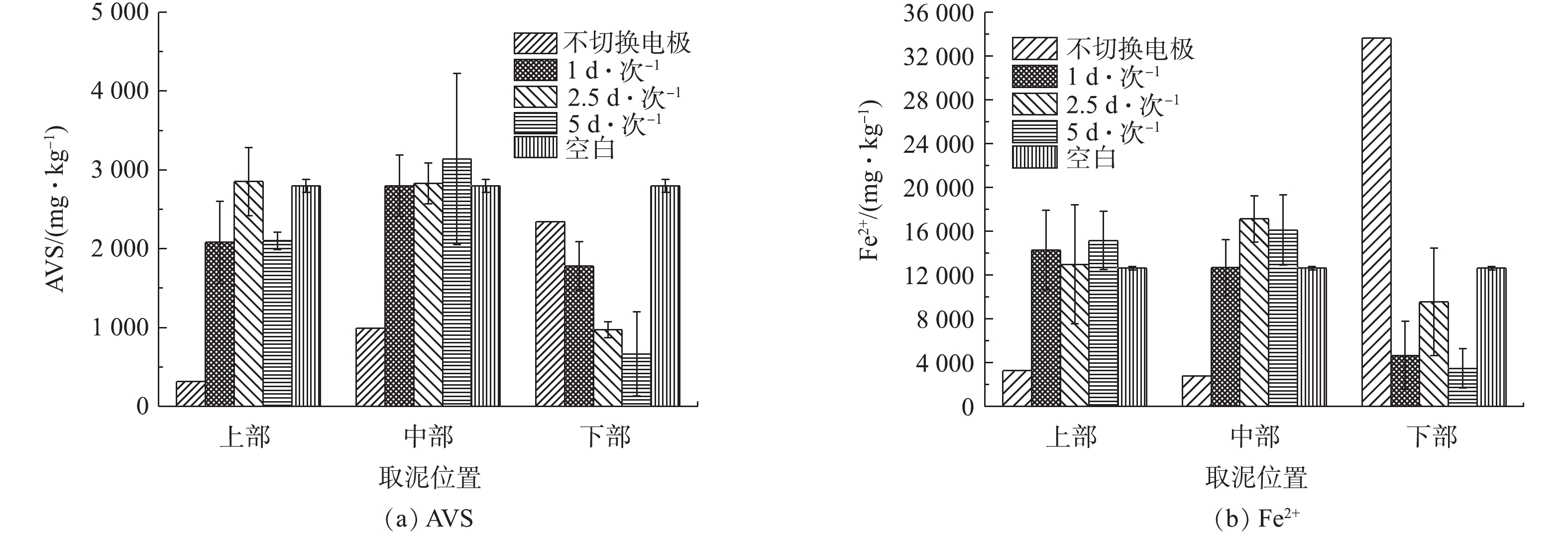
底泥经过10 d的电动修复后,不同交换频率的底泥AVS和Fe2+含量变化情况如图7所示。在AVS处理方面,由图7(a)可知,空白组的底泥AVS在上部、中部和下部均为2 797 mg·kg−1。经过氧化处理后,不切换电极组对底泥上部和中部的AVS去除效果最好,去除率分别为88.63%和64.50%。从底泥下部氧化效果来看,4组实验中底泥的AVS浓度均出现不同程度的下降,5 d·次−1的底泥下部去除率最高,为76.19%。同时,比较各处理组底泥AVS平均值可知:不切换电极时为1 218 mg·kg−1,切换频率1 d·次−1时为2 219 mg·kg−1,2.5 d·次−1时为2 217 mg·kg−1,5 d·次−1时为1 967 mg·kg−1,空白组为2 797 mg·kg−1。通过对比平均值可以看出,所有处理组整体的AVS平均值均小于空白组,这说明通电处理是可以氧化AVS的,且不切换电极处理组整体平均值最低。这证实了对于AVS的去除,切换周期越长,切换频率越低,越有利。在切换电极的电动修复处理组中,对比各位置AVS的变化,可以看出,底泥下部的AVS能取得较好的氧化效率,特别是5 d·次−1时的效果最佳。因此,对于AVS的去除,通电时间对其氧化效果有明显的影响,通电周期越长,切换频率越低,越有利于AVS的去除。在亚铁离子处理方面,由图7(b)可知,对于空白组中的底泥亚铁离子,上部、中部和下部均为12 647 mg·kg−1。在上部,不切换电极时亚铁离子含量下降,去除率为74.14%;3种交换频率下,底泥亚铁离子含量均上升。在中部,不切换电极组中的亚铁离子含量下降,去除率为77.84%;3种交换频率下亚铁离子含量均上升。在下部,不切换电极组的亚铁离子含量急剧上升,而其他切换电极组则均有下降,去除率分别为63.10%、24.50%、72.48%。其中,5 d·次−1时的处理效果最好。比较各处理组底泥亚铁离子平均值看出:不切换电极时为10 357 mg·kg−1,1 d·次−1时为10 541 mg·kg−1,2.5 d·次−1时为11 516 mg·kg−1,5 d·次−1时为11 587 mg·kg−1,空白组为12 647 mg·kg−1。结合亚铁离子整体的变化数据可以看出,通电处理均小于空白组,这说明通电可以促使对亚铁离子进行部分氧化。同时,亚铁离子是阳离子,其在电场作用下具有迁移能力[31]。因此,结合图7(b)中各处理组亚铁离子在上部、中部和下部含量的变化,可以推测,亚铁离子在电场作用下发生的离子迁移对其含量变化也有影响。
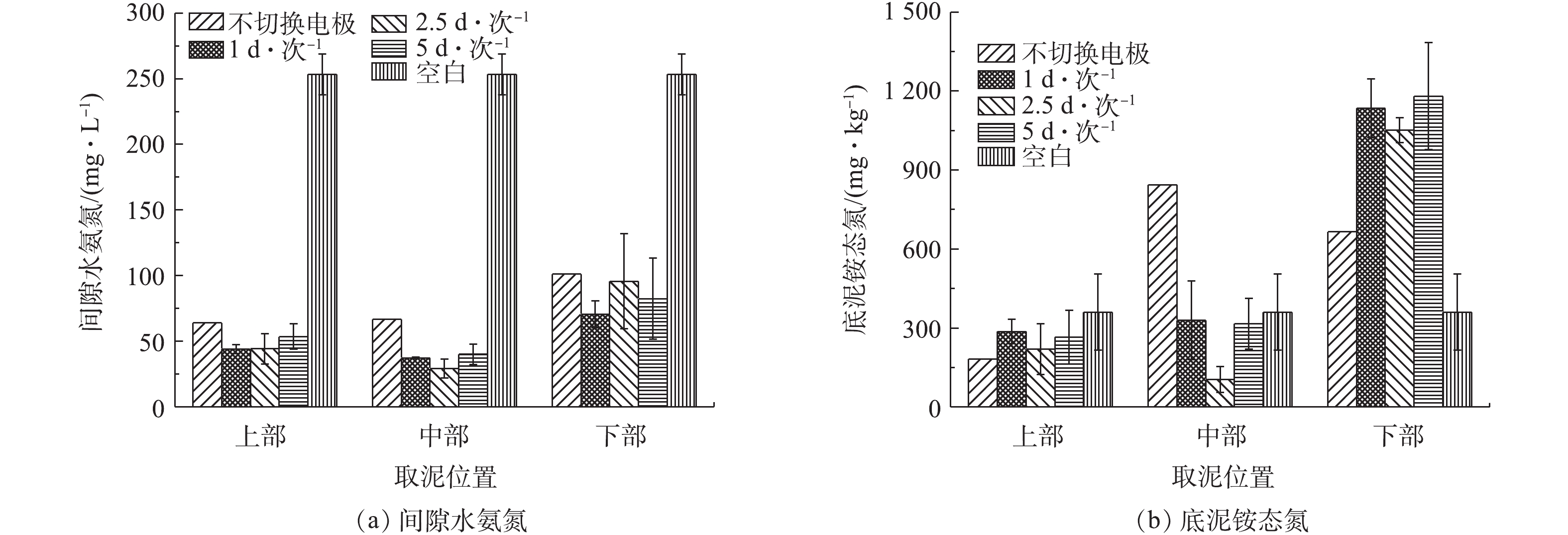
由图8(a)可知,底泥在经过10 d的电动修复后,各实验组各位置的间隙水氨氮浓度均有大幅度下降。取泥位置为上部和中部的实验组中,间隙水氨氮浓度下降幅度最为明显。从间隙水氨氮的去除效果来看,空白组的间隙水氨氮浓度为253.35 mg·L−1。电动修复10 d后,对上部底泥而言,各实验组间隙水氨氮的去除率分别为74.75%、82.86%、82.59%、78.92%;对中部底泥而言,各实验组间隙水氨氮的去除率分别为73.68%、85.3%、88.57%、84.19%;对下部底泥而言,各实验组间隙水氨氮的去除率分别为60.12%、70.27%、64.88%、61.33%。由此可见,在对底泥采用不同切换频率进行电动修复中,以切换频率为1 d·次−1和2.5 d·次−1的底泥中间隙水氨氮去除效果最佳。
对底泥采用周期性切换电极进行电动修复时,底泥在通电10 d后,各处的铵态氮浓度变化如图8(b)所示。由图8(b)可以看出:底泥上部的铵态氮浓度均呈现一定程度的下降趋势,切换电极频率为2.5 d·次−1的底泥中下降幅度最为明显;底泥中部的铵态氮浓度除切换电极频率为2.5 d·次−1的底泥呈下降趋势外,其他均呈现上升趋势;底泥下部的铵态氮浓度均呈现上升趋势。由此可见,铵态氮在底泥中各位置含量的变化可能是由于通电过程中电场的迁移所造成的。
针对单电极电动修复存在的两极pH出现过酸过碱、阴极还原性污染物去除效果不明显、电流强度持续不久等问题,后期补充了周期性切换正负极的实验,以解决单电极电动修复存在的不足。分别通过1、2.5、5 d·次−1电极切换频率与不切换电极和空白组相比较,处理结果有明显的提高。
单电极电动修复最容易出现的问题就是出现电极两端的酸碱不平衡,从而引起极化现象,进而使通电的电流强度不能长时间保持。通过周期性切换电极可以明显看到,每次切换电极都在一定程度上提高了电流的强度,效果明显,且切换的频率越高,效果越好。出现这种现象的一个很重要的原因在于,底泥两极的pH能够恢复正常,稳定在中性附近,使离子交换能稳定进行。因此,通过定期切换电极是可以解决酸碱破坏和电流强度不持久的问题。
与单向电极电动修复相比,在切换电极的电动修复过程中,电极的切换会影响底泥不同位置黑臭污染物的氧化效果,主要体现在对AVS和亚铁离子的氧化方面。在电极切换过程中,底泥上部和下部2个电极均轮流发生氧化作用,底泥上部和下部的AVS和亚铁离子氧化效果明显。因为底泥中部没有直接跟电极接触,所以氧化效果一般。在底泥间隙水氨氮的氧化过程中,切换电极比单电极的氧化效果更好。除了能够氧化底泥上部和下部的间隙水氨氮外,底泥中部的间隙水氨氮也能够被去除。这可能是由于电场的作用,使底泥中部的间隙水氨氮向两极迁移,而间隙水氨氮在两极处容易受到电化学氧化,因此,其能够整体被去除。与间隙水氨氮不同,底泥铵态氮没有出现显著的去除效果,而是出现了明显的迁移累积过程。利用底泥铵态氮在电动修复过程中类似于重金属的迁移累积特性,可以针对底泥铵态氮提出2种不同的处理方案:第1种方案,利用电场的作用将底泥铵态氮引导向下层底泥迁移,避免氨氮向上覆水体释放;第2种方案,利用电场的作用引导铵态氮富集于上层底泥,然后疏浚移除。
综上所述,以定期切换正负电极的电动修复方式可以在不产生严重酸碱破环的前提下,实现黑臭底泥中多污染物的同步耦合去除。通过实验可以发现,去除的主要污染物包括AVS、亚铁离子和底泥中间隙水氨氮,而对底泥中铵态氮的去除效果则不明显。然而,该修复方法目前还存在一些不足:只是在实验室中进行的模拟实验,实际河道中的情况较为复杂,电动修复过程中所需要的能源消耗也是一个需要考虑的问题,如何合理提高能耗比以提高修复效率是后面需要解决的问题。
-
1)采用电动修复技术去除黑臭底泥硫化物、亚铁和氨氮等还原性污染物,结果表明,电动修复对底泥硫化物和亚铁离子具有明显的氧化效果,但氧化主要发生在阳极区;电极切换频率越低,氧化效果越明显。
2)电动修复对间隙水氨氮具有明显的去除效果;而对底泥铵态氮去除效果不显著,但其在阳极和阴极间出现明显的来回迁移现象,可以利用该特性对底泥铵态氮进行富集和后续处理。
3)通过切换电极,可以避免单向电极出现的明显的阳极酸化和阴极碱化现象,同时也可以减缓电流骤减,增加处理时间和效果。电动修复具备同步去除底泥中致黑臭多污染物质的潜力,但去除率有待进一步优化提高。
利用电动修复技术原位氧化去除黑臭底泥还原性污染物的室内模拟实验
Indoor simulation experiment of in-situ oxidation removing the reductive pollutants in black-odorous river sediment with electrokinetic remediation
-
摘要: 城市河道底泥致黑臭多污染物的同步耦合去除是当前研究的热点。为实现河道底泥致黑臭污染物的同步去除,采用电动修复技术开展了氧化去除黑臭底泥硫化物、亚铁和氨氮等还原性污染物的室内模拟实验。实验结果表明:在单向通电(1.5 V·cm−1)10 d后,阳极区对底泥硫化物(AVS)、亚铁有明显的氧化效果,去除率分别达到59.51%和79.41%,但阴极的去除效果不明显;阳极区和阴极区均对间隙水氨氮有明显的去除效果,去除率分别为56.5%和73.9%。在氧化过程中,阳极和阴极出现明显的酸化和碱化现象,而这种两极酸碱化可以通过周期性切换电极的方式加以避免。在电极切换频率为1、2.5和5 d·次−1时,对黑臭物质的氧化效果差别明显;在切换频率为5 d·次−1时,对硫化物、亚铁氧化去除效果最好;在切换频率为2.5 d·次−1时,对氨氮去除效果最佳。硫化物、亚铁、氨氮最大去除率可分别达到76.19%,72.48%和88.57%。由此可见,电动修复可以同步去除底泥中的致黑臭污染物质,改善水体水质,但其去除率有待进一步优化提高。Abstract: Synchronous removal of multi-pollutants in black and odorous sediment in urban rivers is a hot research topic nowadays. To achieve synchronous removal of multi-pollutants in black and odorous sediment, the indoor simulation experiments of oxidation removing the reductive pollutants in black and odorous sediment, such as sulfide, ferrous and ammonia nitrogen, were conducted with electrickinetic remediation technology. The results showed that after 10 days treatment by one-way electrode electrolysis (1.5 V·cm−1), acidic volatile sulfide (AVS) and ferrous iron could be obviously oxidized in the anode sediment area, with the removal rates of 59.51% and 79.41%, respectively; but their removal effects in the cathode area was not significant. In addition, the ammonia nitrogen concentrations in interstitial water could be significantly reduced in both anode and cathode area, and the corresponding removal rates were 56.5% and 73.9%, respectively. However, during the oxidation process, obvious acidification in anode area and alkalinization in cathode area occurred, which could be avoided by periodically switching the electrodes. At the electrode switching frequencies of 1-, 2.5-, and 5-day per cycle, the oxidation efficiencies of black-odorous pollutants were significantly different during the electrokinetic remediation. In addition, the optimized electrode switching frequency for sulfide and ferrous iron removal was 5-day per cycle, while for ammonia nitrogen removal was 2.5-day per cycle. The maximum removal rates of sulfide, ferrous iron and ammonia nitrogen could reach 76.19%, 72.48% and 88.57%, respectively. The above findings indicated that electrickinetic remediation technology could simultaneously remove multi-pollutants in the black-odorous sediments and improve the water quality, but the corresponding removal efficiencies may require further improvement.
-
Key words:
- black-odorous sediments in river /
- electrokinetic remediation /
- sulfide /
- ferrous /
- ammonia nitrogen /
- oxidation
-

-
-
[1] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 生态环境部. 住房城乡建设部 生态环境部关于印发城市黑臭水体治理攻坚战实施方案的通知[EB/OL]. [2019-09-06]. http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201810/t20181015_237912.html. [2] 刘晓玲, 徐瑶瑶, 宋晨, 等. 城市黑臭水体治理技术及措施分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(3): 519-529. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201812181 [3] 孙韶玲. 水体黑臭演化过程及挥发性硫化物的产生机制初步研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017. [4] 王旭, 王永刚, 孙长虹, 等. 城市黑臭水体形成机理与评价方法研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(4): 1331-1340. [5] HE Z H, HUANG R, LIANG Y H, et al. Index for nitrate dosage calculation on sediment odor control using nitrate-dependent ferrous and sulfide oxidation interactions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 226: 289-297. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.037 [6] HE Z H, LONG X X, LI L Y, et al. Temperature response of sulfide/ferrous oxidation and microbial community in anoxic sediments treated with calcium nitrate addition[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 191: 209-218. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.01.008 [7] LIU X N, TAO Y, ZHOU K, et al. Effect of water quality improvement on the remediation of river sediment due to the addition of calcium nitrate[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 575: 887-894. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.149 [8] LIU T Z, YUAN J J, DONG W Y, et al. Effects on inorganic nitrogen compounds release of contaminated sediment treatment with in situ calcium nitrate injection[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(2): 1250-1260. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3421-7 [9] 余光伟, 余绵梓, 种云霄, 等. 投加硝酸钙对城市黑臭河道底泥氮迁移转化的影响机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(8): 82-89. [10] 张慧妍. 原位注射硝酸钙修复污染底泥过程中无机氮的迁移与转化[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015. [11] MOGHADAM M J, MOAYEDI H, SADEGHI M M, et al. A review of combinations of electrokinetic applications[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2016, 38(6): 1217-1227. doi: 10.1007/s10653-016-9795-3 [12] CANG L, FAN G P, ZHOU D M, et al. Enhanced-electrokinetic remediation of copper-pyrene co-contaminated soil with different oxidants and pH control[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(8): 2326-2331. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.062 [13] PAZOS M, IGLESIAS O, GÓMEZ J, et al. Remediation of contaminated marine sediment using electrokinetic-Fenton technology[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2013, 19(3): 932-937. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2012.11.010 [14] 刘钊, 党岩, 田皓中, 等. 外加电势强化厌氧氨氧化工艺处理垃圾焚烧渗沥液短程硝化出水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(7): 1670-1677. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201902093 [15] LIN H J, WILLIAMS N, KING A, et al. Electrochemical sulfide removal by low-cost electrode materials in anaerobic digestion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 297: 180-192. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.086 [16] QU B, FAN B, ZHU S K, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation with an anode as the electron acceptor[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2014, 6(1): 100-105. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12113 [17] SHU J C, SUN X L, LIU R L, et al. Enhanced electrokinetic remediation of manganese and ammonia nitrogen from electrolytic manganese residue using pulsed electric field in different enhancement agents[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 523-529. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.025 [18] 郭迪. 电化学技术去除海水养殖废水中氨氮的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. [19] 宋协法, 边敏, 黄志涛, 等. 电化学氧化法在循环水养殖系统中去除氨氮和亚硝酸盐效果研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(11): 127-135. [20] 林玉环, 郭明新, 庄岩. 底泥中酸性挥发硫及同步浸提金属的测定[J]. 环境科学学报, 1997, 17(3): 97-102. [21] MOREIRA F C, BOAVENTURA R A R, BRILLAS E, et al. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 202: 217-261. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037 [22] 张宁. 电化学阳极氧化硫化物的研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2012. [23] WANG Y C, LIN H J, HU B. Electrochemical removal of hydrogen sulfide from swine manure[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.171 [24] DING J, ZHAO Q L, JIANG J Q, et al. Electrochemical disinfection and removal of ammonia nitrogen for the reclamation of wastewater treatment plant effluent[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(6): 5152-5158. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6618-0 [25] LI L, LIU Y. Ammonia removal in electrochemical oxidation: Mechanism and pseudo-kinetics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(2/3): 1010-1016. [26] GARCIA-SEGURA S, OCON J D, CHONG M N. Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents: A review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 113: 48-67. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.014 [27] 蒋沁芮, 杨暖, 吴亭亭, 等. 生物电化学脱氮技术研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(2): 408-414. [28] NANCHARAIAH Y V, VENKATA MOHAN S, LENS P N L. Recent advances in nutrient removal and recovery in biological and bioelectrochemical systems[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 215: 173-185. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.129 [29] 胡承志, 刘会娟, 曲久辉. 电化学水处理技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(3): 677-696. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201801179 [30] LU P, FENG Q Y, MENG Q J, et al. Electrokinetic remediation of chromium- and cadmium-contaminated soil from abandoned industrial site[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2012, 98: 216-220. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012.07.010 [31] 魏树和, 徐雷, 韩冉, 等. 重金属污染土壤的电动-植物联合修复技术研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(1): 154-160. -



 下载:
下载: