-
磷(P)是组成生命物质不可缺少的元素之一,也是构成核酸与三磷酸腺苷(ATP)的重要元素,直接参与生命体能量循环。因此,磷是一切生命体的重要营养元素[1]。磷的获取主要来自于磷矿,通过化肥生产并进入农业生产与人类生活。然而,全球磷矿资源分布严重不均,主要分布于摩洛哥、中国、伊拉克和阿尔及利亚等少数几个国家,约90%的国家几乎没有磷矿储备,只能依赖进口[2]。据估算,若全球化肥消耗保持3%的年增长量,可供开采的磷资源将在未来50年内消耗殆尽[3]。现代社会人类对磷的粗放式开采利用及原生态粪尿返田习惯的逐渐废弃[4]导致磷的自然循环已被破坏。大量磷元素使用后以各种形式进入水体,或诱发水体富营养化,或流入大海沉积下来。从陆地向海洋的磷单向流动使得陆地磷资源逐渐枯竭。因此,磷的可持续利用已成为全球普遍关注的焦点。1998年,第一届磷回收国际会议在荷兰召开以来,从污水/废物中回收磷逐渐被关注和研究。
目前,欧洲、北美、日本等国家和地区已建立了磷回收国家/国际平台,旨在通过磷回收及循环利用最大限度地阻止磷从陆地向海洋的直线流动[1]。欧洲、日本等国家和地区的磷资源十分匮乏,这促使这些国家和地区未雨绸缪,提早开始了磷回收学术、技术与应用的研究与总结,使得其在磷回收技术与应用研究方面处于国际领先地位。如今,磷回收技术已不再是限制其应用的卡脖子难题[5]。未来的挑战在于如何将磷回收产品纳入市场并部分取代开采磷矿,以构建良性的磷回收产品市场[6]。本文参考欧洲、日本等国家和地区的磷回收技术应用案例及市场化经验,分析不同磷回收位点的技术特征,并总结相关国家在该领域的政策与措施,以期为我国解决磷危机提供参考。
-
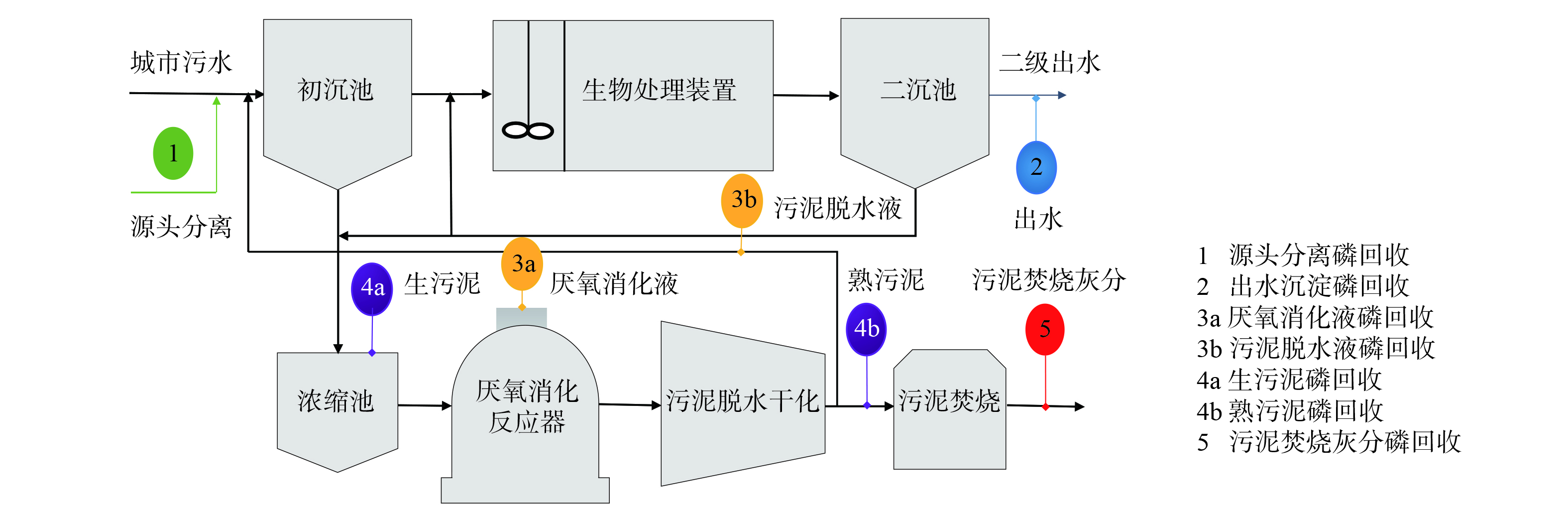
根据污水收集与处理的不同阶段,将磷回收技术分为5类(图1)[7]。1) 源头分离回收,即在污水收集系统的开端——便器端将尿液分离后直接用作肥料。2) 出水沉淀回收,即以沉淀方式去除并回收出水中磷。3) 污泥消化液或污泥脱水上清液中沉淀回收。4) 生污泥及消化熟污泥中沉淀回收。5) 污泥焚烧灰分回收,即以湿式化学萃取沉淀和热处理工艺回收磷。其中,出水磷回收方式因磷酸盐的浓度较低,回收潜力不高,故可将其目的归结为出水水质的提高,而非真正意义的磷回收。
除源分离直接利用外,不同位点磷回收技术大都以投加化学药剂沉淀方式为主。各类技术的回收产物因药剂类型不同而存在差异。其产物主要包括:鸟粪石(磷酸铵镁)、磷酸钙、磷酸镁、磷酸铝、磷酸铁、蓝铁矿等[8-9]。其中,鸟粪石与蓝铁矿可直接以肥料或其它材料形式出售,而其他磷酸盐化合物则主要用作磷矿替代物 (二级磷矿) 供下游化工/化肥工业生产化肥。
-
根据不同的磷回收位点,将欧洲、日本等地区和国家的磷回收技术案例、应用背景与市场条件等方面信息进行了汇总[10] (表1) 。
-
荷兰是畜牧大国,其有限国土面积迫使本国畜牧业朝着集约化发展。然而,过量动物粪肥回用农田导致磷(P)与氮(N)渗入地下水和流入地表水,造成地下水污染及水体富营养化等环境问题。为此,荷兰政府早已开始限制粪肥回用,本土过量粪肥还需出口至邻国处理。与此同时,欧盟硝酸盐指南(The Nitrates Directive)[11]也规定每公顷粪肥年回用量不得超过170 kg。两项法令/指南对粪肥返田的限制使得农民望肥兴叹,还需自费将粪肥外运及处理。
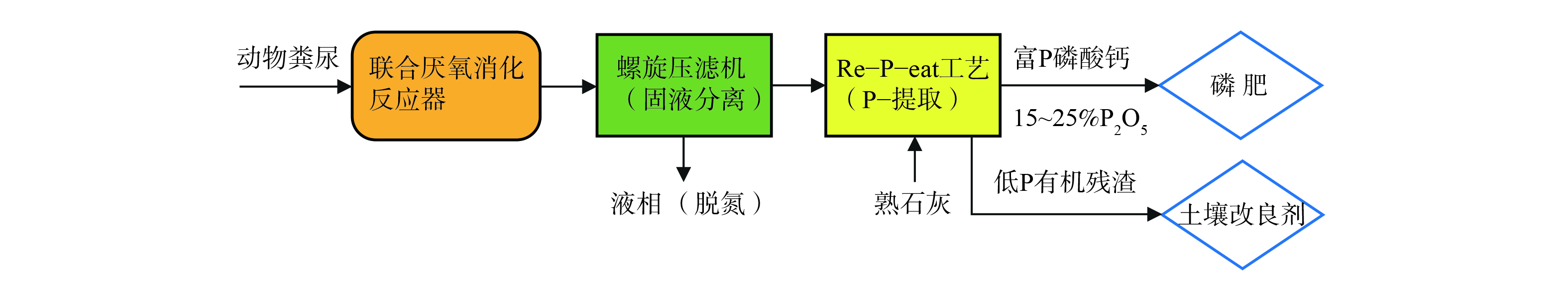
在此情形下,欧盟“Horizon2020”项目资助建设了Groot Zevert Vergisting (GZV)示范工厂[12],通过“Re-P-eat”工艺进行粪肥减量浓缩和磷回收尝试(流程见图2)。GZV位于荷兰Beltrum省,集合周边55处畜牧与屠宰场产生的猪牛粪尿联合进行厌氧消化,是荷兰最大的固体废弃物厌氧消化工厂之一。2018年,其年粪肥处理量已达135 000 t。消化液与沼渣通过螺旋压滤机实现固-液分离,并将通过气浮、微过滤、反渗透浓缩等技术将液相制成N、K营养液,直接回用于农田(自用或出口邻国)或作为化肥厂原料;固相则采用Re-P-eat工艺,即在酸化反应器中加入熟石灰,回收富磷磷酸钙(CAP)和低磷有机土壤改良剂。整个处理/回收工艺最终出水符合荷兰地表水排放标准,并可直接回补地表水资源[13]。
GZV粪肥回收技术的经济效益明显,体量巨大的粪肥可就地回收为浓缩肥料或土壤改良剂,从而可节省高昂长途运输及处理成本,而且每吨13 欧元的综合处理费用相比欧洲传统猪粪单独处理成本(每吨处理费用为20~25 欧元)要低50%~100%[13]。
-
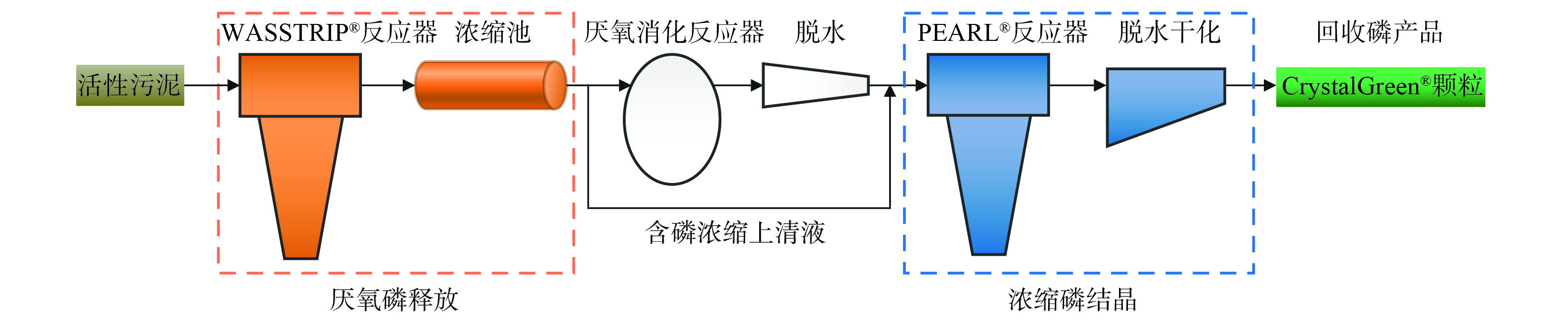
加拿大Ostara公司将工业、农业、市政污水处理厂中的营养物回收转化为一种高效且环保的颗粒肥料——Crystal Green®。其核心工艺包括WASSTRIP®和Pearl®技术,工艺流程如图3所示。其中,WASSTRIP®可实现富磷污泥厌氧释磷,并联合浓缩池为Pearl反应器提供磷浓缩液,同时可避免PO43-和Mg2+等离子进入厌氧消化反应器而导致结垢问题;而Pearl®技术主要采取添加Mg盐并控制pH条件,来实现磷沉淀、鸟粪结晶与分离。
WASSRTIP®联合Pearl®技术生产的市售鸟粪石化肥品牌称作“Crystal Green®”,是一种缓释肥料。该肥料产品符合欧洲肥料法规(EC)第2003/2003号标准,产品纯度达99.6%,且无病原体,其中的盐分和重金属含量都远低于其他市售磷肥[14]。在Crystal Green®的生产过程中,系统的进料可控性强,并可通过循环系统控制结晶过程与磷回收效率。同时,由于其反应器构造特殊,可人为控制鸟粪石的结晶尺寸。整个装置为自控系统,包括进料、反应、结晶及出料等。产物结晶体,即鸟粪石,可通过进一步脱水、干燥(热干方式)、粒径筛选、打包储存后进入出售环节[14]。
事实上,这类鸟粪石生成与回收技术在荷兰早期的BCFS脱氮除磷工艺[15-16]中便已出现。Crystal Green®案例的成功之处在于其商业销售模式。该商业模式包括技术设备销售+产品回购+产品销售,即先将核心设备和技术分包销售到厂家,再对厂家生产的鸟粪石磷肥进行回收,并销售给磷肥需求用户。该模式可保证用户端(厂家)有技术可用、有利可图、无产品销售之虞,而技术公司自身也实现了轻资产利益转化,在保证产品质量的同时专注于提供技术支持,最终为磷肥用户提供优质磷肥资源,最终实现三方共赢,保障了技术的可持续发展。
基于上述商业模式,Ostara公司自2005年成立以来,已与北美、欧洲等地区的22个污水处理厂开展合作,成为全球最大鸟粪石回收公司之一。其中,美国芝加哥斯蒂克尼(Stickney)污水处理厂装有全球最大的鸟粪石回收装置,年产量达9 000 t;荷兰Amersfoort污水处理厂(30万人口当量)[17]安装有欧洲首个结合污泥热水解技术[18]的大型鸟粪石回收装置,年产量达900 t。近期,爱尔兰Murphy Ireland水务公司宣布与Ostara公司合作,对爱尔兰最大的污水处理厂——Ringsend污水处理厂进行资源回收工艺的升级改造。该工程将于2023年完成,并由Ostara公司向欧洲、北美销售网分销工程改造后的Crystal Green®产品(日产量约为14 t)[18]。
-
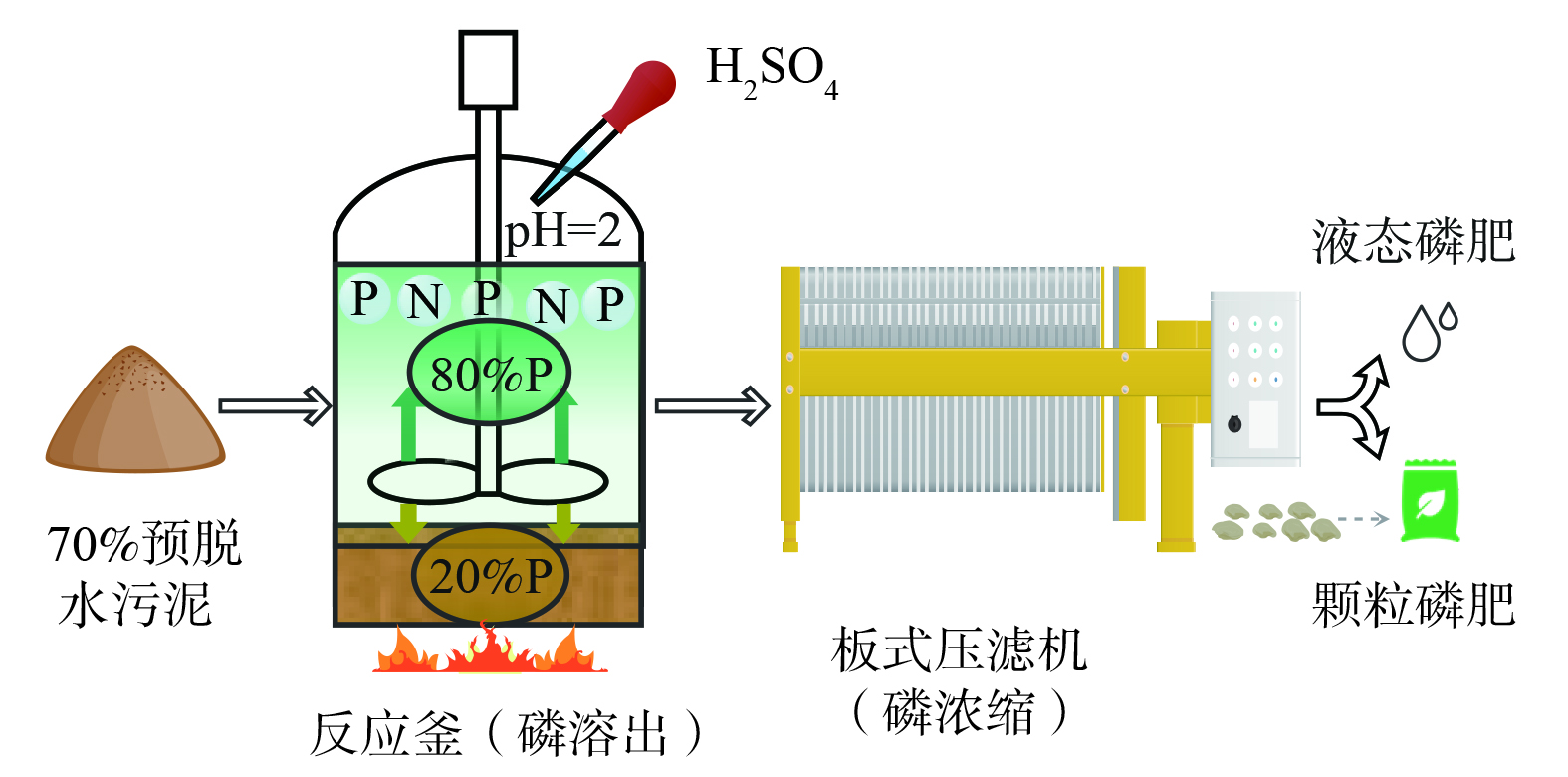
德国TerraNova Energy公司采用Terra Nova® Ultra工艺,通过水热碳化(hydrothermal carbonization,HTC)原理控制反应条件模拟并加速天然煤炭的生成过程,将活性污泥直接制成可燃烧煤,同时以液体磷肥和含磷生物炭形式实现磷回收 (见图4) 。该工艺中磷回收的主要环节在反应釜处理后,将富含N、P的溶出液经压滤脱水浓缩为液体肥料,亦有通过投加水合硅酸钙颗粒(Calcium silicate hydrate granules,CSH)转化而成的颗粒磷肥。尽管该工艺中的磷回收是污泥水热炭化制煤的副产物,但其磷回收效率仍可高达80%[19]。经种植实验比较,这种液体磷肥种植作物(番茄和小麦)干重和高度均优于对照市售液体磷肥,是一种良好的磷回收产品[20]。
目前,该工艺已应用于我国济宁污水处理厂、德国凯泽斯劳滕(Kaiserslautern)中央污水处理厂、德国杜塞尔多夫(Düsseldorf)示范污水处理厂、斯洛韦尼亚国马里博尔(Maribor)污水处理厂等[21]。中国济宁污水处理厂的TerraNova® Ultra工艺已稳定运行4年,处理规模为50万人口当量,设计年污泥处理量约为14 000 t,磷的年回收产量约为200 t∙a-1 [21-22]。
-
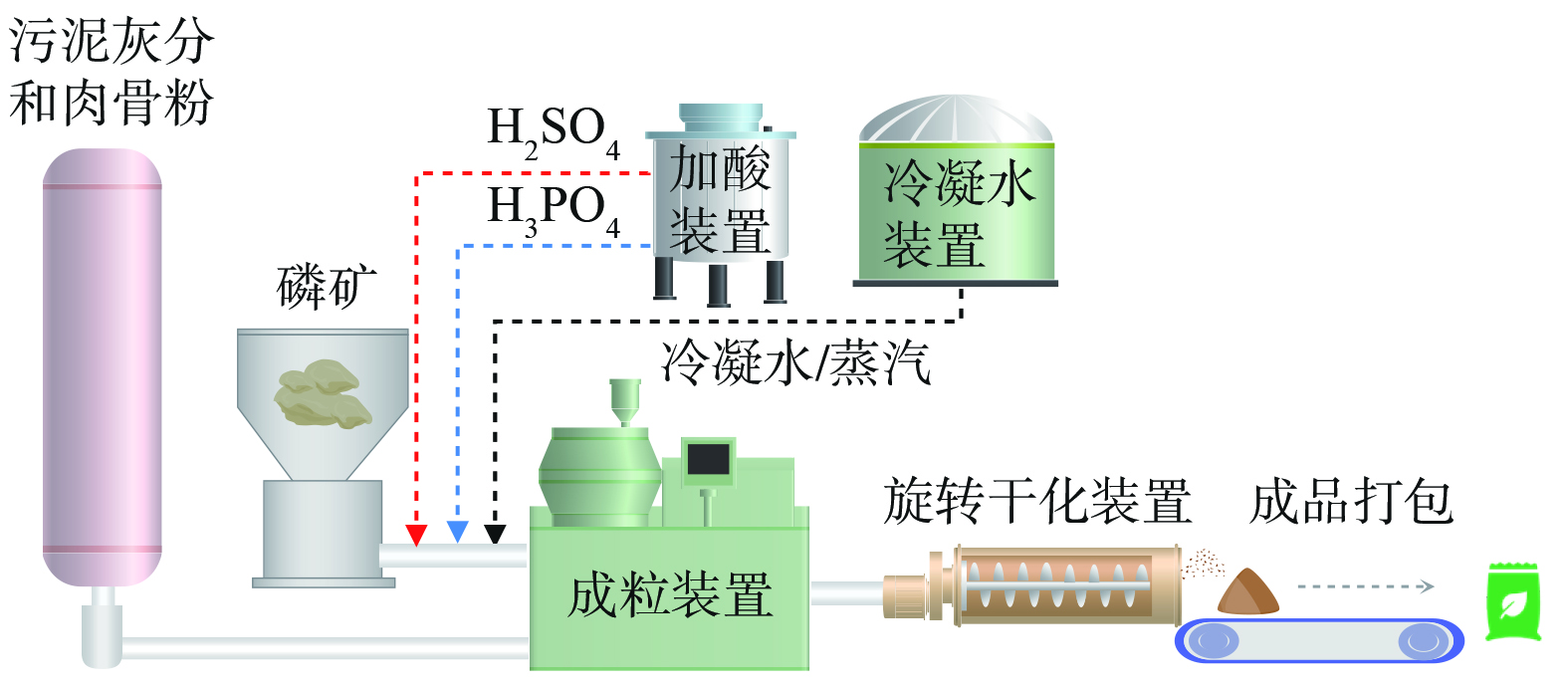
1) 荷兰ICL Fertilizers。ICL Fertilizers于2011年与荷兰政府签约,计划在2025年实现用污泥焚烧灰分回收磷技术来取代磷矿的使用[23]。ICL Fertilizers作为磷肥生产商,主要研发针对污泥焚烧灰分、待回收磷酸盐及肉骨粉灰等次级磷酸盐原料使用技术(图5)。ICL欧洲工厂所在国家(德国、荷兰)并不缺少磷资源,甚至存在过剩的磷矿产量,因此,该公司主要将大部分回收磷酸盐产品出口到缺磷国家,在赚取一定利润的同时转移国内磷过剩问题[24],以达到“可持续发展与环境保护并行”的目的。
ICL Fertilizers旗下阿姆斯特丹化肥生产厂的磷矿年消耗量为250 000 t、磷产品年总产能为800 000 t,其中二次回收的磷可替代10%原磷矿[25]。该工厂先通过单次或多次磷酸酸蚀来释放磷元素,再继续添加氯化钾(MOP)、硫酸钾(SOP)或其他微量金属元素(Cu、Mg、Mn、Mo、Zn等)生产不同形式的复合化肥,最后加入磷酸铵生产NPK化肥。除此之外,ICL公司还在欧洲和美国发展下游业务,如已准备在荷兰特尔纽岑建立试点工厂通过Recophos工艺和Tenova工艺生产白磷(P4),以及正在开展可行性分析的食品级磷酸生产项目[24, 26]。
2) 日本Metawater。与欧洲磷资源状况不同,日本没有足够磷矿,所有磷矿依赖进口。然而,日本法规对污泥无害化处理要求极为严苛,法律禁止污水处理剩余污泥直接农用[10]。因此,出于降低污泥处理成本考虑,为解决本国的磷资源短缺问题,日本提倡从厌氧消化污泥、脱水液或污水处理厂污泥焚烧灰分中回收磷[9]。目前,该国已开展针对污泥、污水、动物粪便和工业废水等资源的磷回收技术研究,拥有众多的大规模磷回收工厂及长期的运营经验[27]。
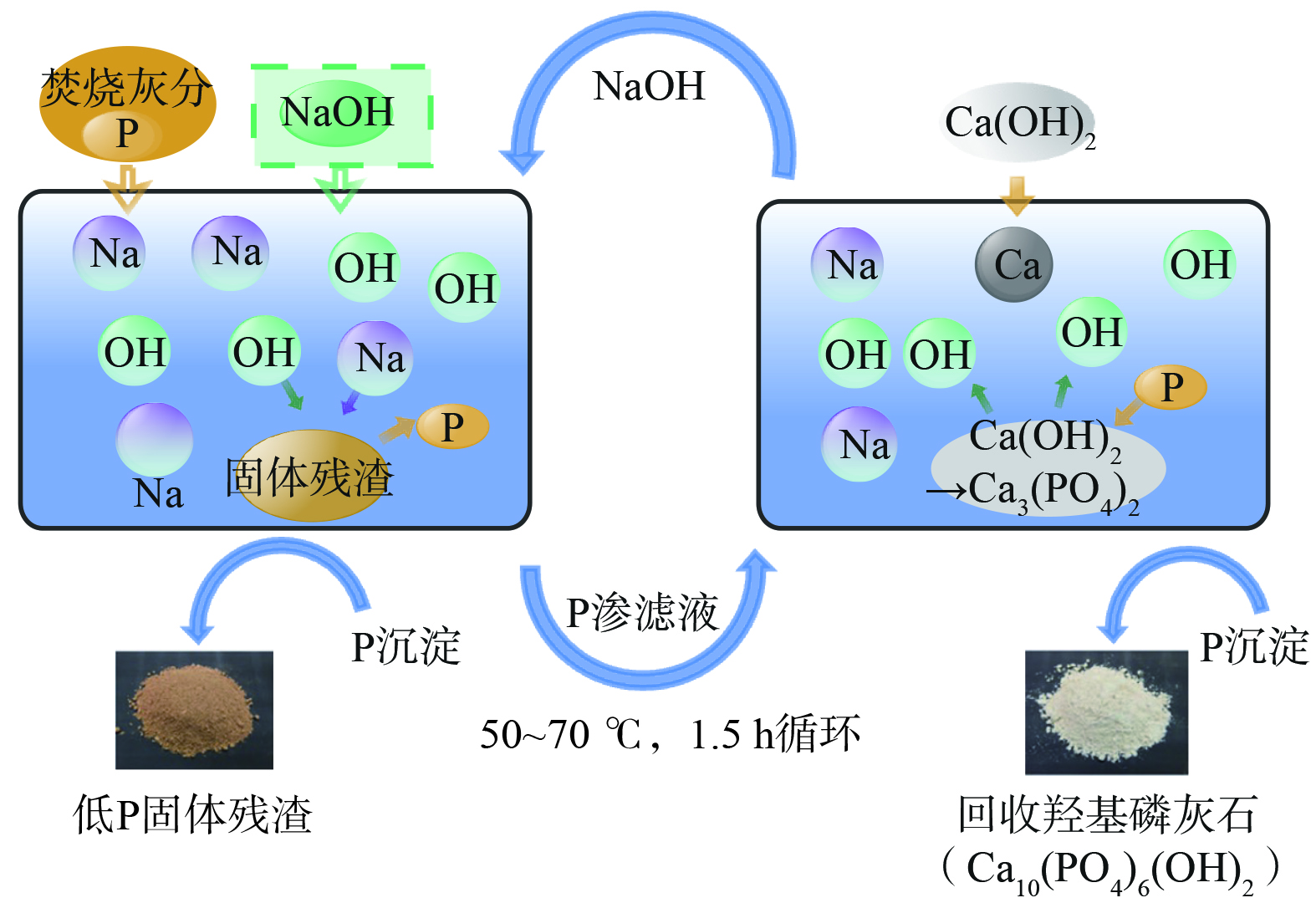
日本Metawater集团运营的歧阜(2010年)和鸟取(2013年)两座污泥焚烧灰分磷回收工厂的年磷肥产量分别为300 t及150 t[19]。其磷提取工艺(图6)为:先用NaOH淋洗灰分磷;再通过投加Ca2+以羟基磷灰石钙(HAP)沉淀形式回收磷;最后将回收产物脱水、干燥、颗粒化后形成磷肥供当地农民使用。灰分剩余残渣通过弱酸清洗去除重金属,转化成无臭味的棕色颗粒,符合土壤污染防治标准,可作为路基材料或沥青填料中石粉替代品,亦可作为土壤改良剂[28]。
歧阜磷回收厂每年可回收全厂30%~40%的灰分,每年为当地农民提供约300 t的磷肥,故其磷回收成本仅占总运行成本的3%。为纪念歧阜市在磷循环中的贡献,当地政府将回收的磷肥命名为“Gifu-no-daichiR”(岐阜之地)。该项目的回收产物由歧阜市JA-ZEN-NOH(全国农业合作协会联合会的分支)负责销售,获得良好的市场评价。目前,当地已建立稳定的羟基磷灰石分销渠道,且随着磷回收过程的逐渐稳定、回收效率的逐步提高,其磷肥销售量也在不断增长,可为歧阜市带来不菲的经济收益[28]。
-
以上案例表明,城市污水及有机固废的体量巨大,其中所含的磷资源大都未被开发和利用。目前,各种磷回收技术已相对成熟,并逐渐进入商业化应用阶段[29]。然而,理想的磷回收技术应该是低成本、高效率、产物俏、风险小的工艺[30],因此对比不同点位磷回收技术的应用模式、可行性、经济性与前景等内容,可为工艺选择提供参考。
1) 粪肥直接磷回收的产物等同于中品位磷矿,可用作化肥生产原料,而且可实现粪肥原位减量化无害化处理,具有生态环保效益和经济价值。然而,这种方法只适宜农村地区分散式应用。
2) 液相(厌氧池上清液、污泥厌氧消化上清液和污泥脱水液)磷回收,因其可直接在污泥厌氧消化等单元实施,适用于污水处理厂等集中污水处理设施,为当前全球磷回收最广泛手段之一[31]。但是,这种磷回收方式效率往往不高,通常只能回收磷负荷的10%~30%[29],且成分复杂需进一步纯化产物。通过合适工艺优化可以获得高含量、高品质磷产物,如加拿大的Crystal Green®技术。
3) 从污泥中直接磷回收通常以污泥减量化为目的,所回收的营养浓缩液具有较高的农业利用价值。该工艺亦适用于污水处理厂等集中污水处理设置。
4) 焚烧灰分磷回收具有较高的磷回收效率(~90%),在相同污泥负荷情况下,灰分磷回收相当于5~10倍液相磷回收量[29, 31]。而且,污泥或固废经高温完全燃烧,灰分中不含有机成分和致病菌,产物纯度较高。灰分磷回收技术的产物因工艺的不同也有差异。该技术适用于有污泥焚烧炉的污水处理厂或相关设施。
在焚烧正逐渐演变为污泥终极处理、处置的大趋势下[32],灰分磷回收成为当前最具前景的磷回收方式。日本的国土面积优先,使得该国优先建设中心污泥焚烧厂来承担周边污水处理厂的磷回收任务[28]。波兰波美拉尼亚省的2个污泥焚烧厂甚至承担了周边220多个污水处理厂60%的污泥焚烧任务[31]。这表明由于“中心辐射周边”的“污泥焚烧+磷回收”模式可降低污水处理厂的磷回收成本,有潜力成为未来污水处理磷回收的主要方式。
-
磷矿资源的不均匀分布和过度开采会引发地缘政治风险和环境污染,必将影响未来世界可持续性发展[33]。随着全球人口的继续增加,为获得足够食物来养活所有人类,全球磷矿石需增产70%来填补未来30%的粮食赤字[31, 34]。据估算,1961—2050年,全球磷矿供应量和需求量的动力模型表明,磷肥需求量呈直线上升趋势,到2045年磷需求将超过磷供应[35],因此,若继续放任有限磷资源的无节制消耗,人类终将步入无磷可用的危险境地。以上主要回收技术应用案例表明,尽管磷回收技术还有待发展,但已足以支撑回收污水、固废中大部分的磷。因此,磷回收技术的应用已不存在技术上的“硬件”问题。然而,由于磷回收产品与原磷矿市场竞争力较弱,政策/法律、税收/补贴等管理层面的“软件”问题仍很突出。以下梳理相关国家采取的政策与措施。
1) 从政策与法律层面支持回收磷产品。相对于天然磷矿,消费者一般首先对从污水、污泥和粪肥中回收磷的安全性和可用性持怀疑态度。为此,欧盟重新审视这一问题,修订了相关法律,以保障磷回收产品在市场中的一席之地。如2019年6月5日,欧盟修订了欧盟肥料条例(EU)2019/1009),三种磷回收产物STRUBIAS(鸟粪石、生物炭和焚烧灰分合称)已被列为化肥生产的二次磷原料,满足使用和安全要求的肥料可在欧洲市场自由出售[36]。修订条例技术报告表明[6],STRUBIAS材料在安全性方面不会对人类、动植物和环境构成风险。在使用效果方面,技术评估和生命周期分析表明回收磷肥相比传统肥料的农业使用效率相当,但重金属、有机污染物含量更低,更有利于应对全球变暖、富营养化和人类癌症等问题。新条例将于2022年7月16日实施,届时将为回收的磷产品进入市场提供法律依据和保护。
除上述欧盟总揽全局打通磷回收市场贸易壁垒外,各成员国还配合制定了相应的法律、法规。瑞士、荷兰为2个先行探索的国家,分别提出“瑞士磷元素闭合循环构建”与“2050荷兰循环计划”,旨在实现境内营养物全回收与闭合循环。随后,英、法、德也提出以磷回收法律框架和网络系统构建为目标,促进磷回收产业良性发展。其他北欧也陆续出台相关政策以扩大磷回收维度与深度[37]。欧洲各国创建了欧洲可持续磷回收平台(European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform),以实现欧洲磷回收技术的学术成果、管理经验共享,为管理者、消费者和市场提供交流平台,促进磷回收市场多维度发展[38]。
2) 对销售回收产品的税收与补贴政策。虽然政策与法律手段可保障磷回收产品进入市场无行政障碍。但客观来看,磷回收成本仍高于传统磷矿,导致磷回收产品市场竞争能力变弱。天然磷矿国际市场价格在二十世纪呈现不断攀升趋势:1950—2000年磷矿石价格上涨10倍;2007年又上涨了200%;2007—2008年的不到14月里,磷肥价格飙升了800%[39]。尽管如此,磷回收产品价格总体上也难与天然磷矿抗衡,这主要表现为磷回收产品在磷矿石涨价时市场存量太少,难以以量取胜。
面对市场现状,各国政府应以保护天然磷矿石的角度,对其开采、销售行为课以重税,用其来补贴或减免磷回收产品的税收。瑞典和丹麦便采取了相关措施。如瑞典自1984年征收磷矿开采税(1994年以磷肥镉含量衡量,税收最低标准依据每吨磷肥中镉的单位质量来征收,按每克3.3 欧元计,以间接限制开采磷矿[40]。2021年3月24日瑞典政府赠款5 100万克朗(约3 850万人民币),以支持该国磷回收公司“EasyMinings”的计划,表彰其在污水污泥磷回收和减少欧洲磷矿开采等自然资源保护方面作出的贡献[41]。丹麦从2005年起征收市场动物磷饲料销售税,税率为0.53 欧元/kg P[42];并于2018年提出实现80%污泥中磷回收的目标,以通过征收污水排磷税(每排放1 kg P征收22欧元)和污泥填埋税(每吨污泥征收63欧元)来促进磷回收技术进步和应用发展[43]。
-
磷矿资源的短缺性和分布不均会诱发人类于地球生存的不可持续性。磷危机的出现会使得磷元素逐渐成为地球上真正的“稀土”。因此,决策磷资源合理利用并及时对其进行回收已成为当务之急。国际上许多地区、国家,如欧洲、日本等,已于20年前先行探索了从政府管理角度对磷资源回收的政策、措施。这些地区和国家在磷回收技术及应用方面已走在世界前列,并积累了许多磷回收成功应用案例。
相关经验及案例表明:1) 磷回收位点分别为源分离、浓缩液/污泥脱水上清沉淀、生熟污泥分离,以及污泥焚烧灰分提取,相应技术均已有成熟案例,虽不完美,但可应用于工程实际;2) 而若以污泥的完全处理、处置为目标,污泥焚烧灰分磷提取是较有潜力的磷回收方式,其技术相对简单但磷回收效率最高(~90%),且杂质含量相对较少;3) 磷回收的难题主要不在技术或设备等,关键在于磷回收产品进入市场的软件壁垒。欧洲和日本等地区、国家的经验表明,政府相关部门应高屋建瓴,出台便于磷回收技术应用及其产品顺利进入市场,并获得市场竞争力的政策/法律条例和税收/补贴手段,从而以经济手段抑制磷矿石过度开采,并通过减税/补贴磷回收产品将其变废为宝,以缓解世界性的磷危机。
国际上主要污水磷回收技术的应用进展及与之相关的政策措施
Global applied cases and technical summary of phosphate recovery from wastewater
-
摘要: 欧洲、日本等国家和地区率先开启从污水及固体废弃物中回收磷的技术研发与工程应用,在政策/法律等层面也相继出台或修订了一系列有利于磷回收产品顺利进入市场的法规/条例。从磷的源分离、浓缩液沉淀、污泥分离以及污泥焚烧灰分提取几类技术,梳理分析了全球已研发并应用的污水处理磷回收技术的主要案例,并对比了各类技术的适用条件。分析了磷回收产品进入市场并获得竞争力的软性障碍,并从政策、法律及税收、补贴等层面介绍了个别国家和地区所采取的具体管理措施,以期为污水磷回收技术的应用与推广提供参考。Abstract: Prompt phosphorus crisis makes its techniques and engineering extended globally, which is associated with a community of shared future for mankind. European countries and Japan with scarce phosphorus rocks have started up developing techniques and applying engineering on phosphate recovery from wastewater and waste solids, and also they have correspondingly launched and/or revised a series of laws/regulations to promote the recovered phosphate products into commercial markets. Based on the applied cases and techniques from these countries, major applied cases of phosphate recovery are first summarized and evaluated; next, appropriate sites of phosphate recovery in wastewater and sludge processes and identified, including source separation, concentrated supernatant precipitation, sludge and incinerated sludge ashes; finally, the gap between recovered phosphate products and the markets is discussed, and some political and economic measures taken by EU countries are introduced.
-

-
图 1 从污水或污水处理过程中回收磷的位点详解[4]
Figure 1. Detailed sites of phosphate recovery from wastewater and sludge treatment processes
表 1 欧洲、日本污水磷回收应用案例汇总
Table 1. Cases summary of phosphate recovery from wastewater in Europe and Japan
回收点位 国家及地区 原料 产物 名称 规模 源头分离回收 荷兰霍斯特文洛
(Horst-Venlo)农场液态及固态猪粪 生物炭 Agro America
(VP Hobe)工程规模 荷兰格鲁特泽维特(Groot Zevert)厌氧消化厂 液态粪肥消化物 N、K化肥溶液;富含磷的有机肥料;清水 GENIAAL (Nijhuis) 工程规模 德国库普弗采尔(Kupferzell)和佐尔鲍尔(Zorbau) 液体肥料;液体消化物 磷酸盐沉淀;硫酸铵;有机土壤改良剂(生物炭) BioEcoSim (Suez) 中试规模 工程规模
(计划)英国、挪威、瑞典、芬兰、丹麦和南非的农场 粪肥浆液;沼渣沼液 硝酸铵基液体肥料 N2-Applied 中试规模 灰分磷回收 荷兰ICL、德国ICL 污泥焚烧灰分;动物灰分 矿物肥料 ICL 工程规模 西班牙Fertiberia化肥集团 小试规模 法国敦刻尔克(Dunkerque)DCP 污泥焚烧灰分 磷酸; 磷酸氢钙 Ecophos 工程规模 柏林比特菲尔德-沃尔芬(Bitterfeld-Wolfen) 污泥焚烧灰分 磷酸钙;N、P、K原料;氯化铁絮凝剂; Ash2Phos
(EasyMining)工程规模 瑞典乌普萨拉(Uppsala);柏林赫尔辛堡(Helsingborg) 氢氧化铝、絮凝剂或工业应用;磷酸盐饲料 中试规模 德国汉堡(Hamburg)(在建) 污泥焚烧灰分 磷酸;石膏;铁盐和铝盐;矿物灰渣 TetraPhos(Remondis) 工程规模 德国埃尔弗林森(Elverlingsen) 中试规模 日本30多个污泥焚烧炉 干化污泥;污泥焚烧灰分 含P泥渣 Kubota (KSMF) 工程规模 德国哈尔登斯勒本(Haldensleben) 污泥焚烧灰分 P或NPK肥料 PHOS4Green(Glatt) 工程规模 德国魏玛(Weimar)格莱特技术中心 小、中试规模 日本岐阜(Gifu)、鸟取(Tottori) 污泥焚烧灰分 磷酸钙;用作肥料生产 Metawater 工程规模 瑞士索洛图恩(Solothurn);西班牙马德里( Madrid) 污泥焚烧灰分 工业级磷酸;水泥/混凝土工业用二氧化硅 Phos4Life 工程规模
(计划)滤饼;重金属精矿;氯化铁混凝剂 中试规模 奥地利莱奥本(Leoben) 污泥焚烧灰分 白磷 RecoPhos thermal (Italmatch) 中试规模 德国弗赖贝格(Freiberg) TU Bergakademie工厂 污泥及其他焚烧灰分;磷矿及其它二级磷;鸟粪石 磷酸 Parforce 中试规模 污泥消化液/
脱水上清液全球约100个工业规模鸟粪石回收装置实际应用于污水处理厂或其它废水处理,其中一些装置已经运行10年以上;世界最大鸟粪石回收装置位于芝加哥斯蒂克尼污水处理厂:Ostara装置;北欧最大鸟粪石回收工厂丹麦Marselisborg 污水处理厂:Phosphogreen装置 各种方式回收的可溶性磷溶液:污水(仅适用于强化生物除磷)、食品加工业、矿业或工业、粪肥、沼气池、源分离尿液等; 鸟粪石 Pearl (Ostara) 工程规模 NuReSys Struvia (Veolia) Phosphogreen (Suez) AirPrex (CNP) 污泥消化液/
脱水上清液全球12个污水处理厂 浓缩污泥;污泥消化液 Crystal Green® WASSTRIP (Ostara) 工程规模 丹麦奥胡斯Åby、Marselisborg污水处理厂 浓缩污泥;污泥消化液 鸟粪石 Phosphogreen (Suez) 工程规模 荷兰Nieuwveer污水处理厂 污泥消化液 蓝铁矿 ViViMAG (WETSUS) 中试规模 生污泥/消化熟污泥(脱水) 中国济宁TerraNova 工厂 脱水、消化污泥 镁/钙磷盐 TerraNova(HTC) 工程规模 德国Ruhrverband/Duisburg工厂 示范规模 瑞士伯尔尼(Bern) 消化污泥 磷酸钙 Extraphos (Budenheim) 工程规模
(计划)德国Dinslaken (Emschergenossenschaft)、奥芬巴赫(Offenbach)(在建)、曼海姆(Mannheim)(在建);瑞士Offtringen、Uvrier 消化脱水污泥;
富磷生物质含磷灰分 EuPhore 工程规模 德国温克尔(unkel)、汉堡(Homburg);美国雷德伍德(Redwood);瑞典哈门赫格(Hammenhög) 80%干重污泥;
生物质材料派热格生物炭(Pyreg biochar),在瑞典注册为肥料(PYREGphos); Pyreg (pyrolysis) 工程规模 意大利梅佐科罗纳(Mezzocorona) Ecoopera污水处理厂 10~15% 干重消化
脱水污泥磷酸盐沉淀 CarboREM 中试规模 -
[1] 郝晓地, 王崇臣, 金文标. 磷危机概观与磷回收技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011. [2] U. S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY. Mineral commodity summaries 2021[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/mcs2021, 2021. [3] HAO X D, WANG C C, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, et al. Looking beyond struvite for P-recovery[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(10): 4965-4966. [4] 郝晓地, 于晶伦, 付昆明, 等. 农村污水处理莫轻视“肥水”资源[J]. 中国给水排水, 2019, 35(20): 5-12. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.20.002 [5] DESMIDT E, GHYSELBRECHT K, ZHANG Y, et al. Global phosphorus scarcity and full scale P-recovery technique: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 45(4): 336-384. [6] EUROPEAN COMMISSION. Amending to Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 for the purpose of adding precipitated phosphate salts and derivates as a component material category in EU fertilizing product[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04].https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=PI_COM%3AC%282021%294743, 2021. [7] 柴春燕, 冯玉杰. 污水能源资源回收利用全球工程应用进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(24): 14-19. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2016.24.003 [8] JUPP A R, BEIJER S, NARAIN G C, et al. Phosphorus recovery and recycling-closing the loop[J]. Chemical Society reviews, 2021, 50(1): 87-101. doi: 10.1039/D0CS01150A [9] 郝晓地, 周健, 王崇臣, 等. 污水磷回收新产物——蓝铁矿[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(11): 4223-4234. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0236 [10] NÄTTORP A, KABBE C, MATSUBAE K, et al. Development of phosphorus recycling in Europe and Japan[J]. OHTAKE H, TSUNEDA S. Phosphorus Recovery and Recycling. Singapore:Springer Singapore, 2019: 3-27. [11] EUROPEAN COMMISSION. The Nitrates Directive[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://ec.europa.eu/environment/water/water-nitrates/index_en.html, 2018. [12] SYSTEMIC. Flow diagrams of our demonstration plants: Groot Zevert Vergisting plant[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://systemicproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/Systemic-GZV-Poster_EN_LR.pdf, 2020. [13] SYSTEMIC. Groot Zevert Vergisting, Beltrum (Netherlands)[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://systemicproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/Factsheet-1-Groot-Zevert_year3_final.pdf, 2020. [14] GYSIN A, LYCKE D, WIRTEL S. The Pearl® and WASSTRIP® processes (Canada)[J]. SCHAUM C. Phosphorus:Polluter and Resource of the Future Removal and Recovery from Wastewater. London:IWA Publishing, 2018: 359-365. [15] VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, BRANDSE F A, VRIES A. Upgrading of wastewater treatment processes for integrated nutrient removal the BCSF(r) process[J]. Water Science & Technology, 1998, 37(9): 209-217. [16] 郝晓地, 汪慧贞, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M. 可持续除磷脱氮BCFS工艺[J]. 给水排水, 2002, 28(9): 7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2002.09.003 [17] OSTARA. Ostara inaugurate 900 t/y struvite-recovery in Amersfoort[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://phosphorusplatform.eu/scope-in-print/news/1219-ostara-struvite-recovery-amersfoort, 2016. [18] OSTARA. Ostara and Murphy partner to deliver part of Ringsend wastewater treatment plant up - grade project for Irish water[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://ostara.com/project/ostara-and-murphy-partner-to-deliver-part-of-ringsend-wastewater-treatment-plant-upgrade-project-for-irish-water/, 2021. [19] BUTTMANN M. Industrial scale plant for sewage sludge treatment by hydro-thermal carbonization in Jining/China and phosphate recovery by TerraNova® Ultra HTC process[C]. European Biosolids and Organic Resources Conference, 2017. [20] TERRANOVA. Growth tests with TerraNova® Ultra liquid fertilizer showed better results than com-mercial liquid fertilizer[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. http://s232856347.online.de/pdf/Ergebnisse-Wachstumstest-mit-Tomate-und-Weizen.pdf, 2015. [21] TERRANOVA. Terranova-energy projects[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://terranova-energy.com/projekte/, 2010. [22] 仲璐, BUTTMANN M, 王君琦. 污泥水热碳化处理技术及其工程化应用——以济宁中山污泥处理工程项目为例[J]. 环境卫生工程, 2020, 140(2): 70-72. doi: 10.19841/j.cnki.hjwsgc.2020.02.014 [23] EUROPEAN SUSTAINABLE PHOSPHROUS PLATFORM. Dutch phosphate value chain agreement[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/images/download/Dutch_phosphate_value_chain_agreement_-_Oct_4th_2011.pdf, 2011. [24] LANGEVELD K. Phosphorus recovery into fertilizers and industrial products by ICL in Europe[J]. OHTAKE H, TSUNEDA S. Phosphorus Recovery and Recycling. Singapore:Springer Singapore, 2019: 235-255. [25] ICL. ICL the Netherlands Amfert opened its innovative phosphate recycling unit[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://icl-group-sustainability.com/reports/producing-fertilizers-with-recycled-phosphate/, 2019. [26] LANGEVELD K. The Recophos/Inducarb process (the Netherlands)[J]. SCHAUM C. Phosphorus:Polluter and Resource of the Future Removal and Recovery from Wastewater. London:IWA Publishing, 2018: 443-446. [27] OHTAKE H, OKANO K. Development and implementation of technologies for recycling phosphorus in secondary resources in Japan[J]. Global Environmental Research, 2015, 19(1): 49-65. [28] NAKAGAWA H, OHTA J. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash: a case study in Gifu, Japan[J]. Phosphorus Recovery and Recycling. OHTAKE H, TSUNEDA S. Singapore:Springer Singapore, 2019: 149-155. [29] EGLE L, RECHBERGER H, ZESSNER M. Overview and description of technologies for recovering phosphorus from municipal wastewater[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 2015, 105: 325-346. [30] EGLE L, RECHBERGER H, KRAMPE J, et al. Phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater: an integrated comparative technological, environmental and economic assessment of P-recovery technologies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 571: 522-542. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.019 [31] CIELIK B, KONIECZKA P. A review of phosphorus re-recovery methods at various steps of wastewater treatment and sewage sludge management: the concept of "no solid waste generation" and analytical methods[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 142: 1728-1740. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.116 [32] HAO X D, CHEN Q, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, et al. Sustainable disposal of excess sludge: incineration without anaerobic digestion[J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115298. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115298 [33] WITHERS P J, FORBER K G, LYON C, et al. Towards resolving the phosphorus chaos created by food systems[J]. AMBIO:A Journal of the Human Environment, 2019, 49(5): 1076-1089. [34] SAMIR K, WOLFGANG L. The human core of the shared socioeconomic pathways: population scenarios by age, sex and level of education for all countries to 2100[J]. Global environmental change:human and policy dimensions, 2017, 42: 181-192. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.06.004 [35] CORDELL D, WHITE S. Peak phosphorus: clarifying the key issues of a vigorous debate about long-term phosphorus security[J]. Sustainability, 2011, 3(10): 2027. doi: 10.3390/su3102027 [36] EUROPEAN COMMISSION. Published initiatives-fertilizing products-technical update[EB/OL]. [2021-09-04]. https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12135-Fertilising-products-technical-update_en, 2021. [37] EUROPEAN SUSTAINABLE PHOSPHROUS PLATFORM. Summary of the 3rd European Sustain-able Phosphorus Conference (ESPC3) [EB/OL]. [2021-09-07]. https://phosphorusplatform.eu/images/scope/scopenewsletter127.pdf, 2018. [38] 郝晓地, 宋鑫, VANLOOSDRECHT M C M, 等. 政策驱动欧洲磷回收与再利用[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(8): 35-42. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2017.08.007 [39] NEDELCIU C E, KRISTINSDOTTIR K, STJERNQUIST I, et al. Global phosphorus supply chain dynamics: assessing regional impact to 2050[J]. Global Food Security, 2020, 26: 100426. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100426 [40] ANDERSEN M S. The nitrogen mineral fertilizer tax in Sweden [EB/OL]. [2021-09-05]. https://ieep.eu/uploads/articles/attachments/cd57d2c2-6c74-4244-8201-10c8fff4b7f6/SE%20Fertilizer%20Tax%20final.pdf?v=63680923242, 2017. [41] EASYMINING. Our phosphorus recovery solution receives multi-million grant[EB/OL]. [2021-09-05]. https://www.easymining.se/newsroom/articles-news/51-msek-grant/, 2021. [42] ANDERSEN M S. The animal feed mineral phosphorus tax in Denmark[EB/OL]. [2021-09-05]. https://ieep.eu/uploads/articles/attachments/ccbf12fc-48fa-4ddf-8d6d-4413357ae01e/DK%20Phosphorus%20Tax%20final.pdf?v=63680923242, 2017. [43] GAARD J J. Danish national taxes on phosphorous discharges and on sludge ash landfill[EB/OL]. [2021-09-05]. https://phosphorusplatform.eu/images/download/P-removal-workshop-2019/Gaard_Denmark_Ministry_9_11_19_Liege.pdf, 2019. -



 下载:
下载: