-
氨广泛存在于畜牧业、饲料生产、化肥工业及制冷等行业排放的污染物中,不仅会污染环境,还会对人体神经系统、消化系统、呼吸系统和内分泌系统产生不可逆的损伤,甚至致人死亡[1-3]。喷淋填料塔是常见的气态污染物处理设备,可有效消除或降低有害物质浓度[4-5]。氨气在水中溶解后会发生水解反应,使溶液呈碱性。在喷淋溶液中加入酸性物质,利用酸碱中和特性可实现氨气的有效去除。
影响喷淋填料塔效率的因素有塔内液气比、溶液浓度、喷嘴和填料等[6-7]。祝杰等[8]从喷淋塔内的液滴受力入手,推导了气相部分传质系数的计算式,建立了除氨喷淋塔的传质模型,并研究了喷淋密度和空气流速对传质效果的影响。郑文亨等[9]从微观和宏观方面推导出了喷淋室净化空气的效率。JAFARI等[10]发现,0.01%硫酸溶液的除氨效率约90%,最高可达97.92%,远高于除氨效率约70%的纯水。戴圣炎[11]将次氯酸溶液与臭氧联合除氨,氨气的去除效率可达80%以上,次氯酸溶液的有效氯浓度越高,臭氧曝光的时间越长,氨气的去除效果就越好。鞠剑锋等[12]将电解法制备的次氯酸溶液与十六烷基三甲基溴化铵等有机物复合成泡沫型次氯酸水,此种次氯酸溶液对空气中的氨气和硫化氢去除效率达70%。张晓静等[13]将恒压变频水泵应用于纺织厂中空气处理单元的喷淋室并对水泵进行变流量控制,年平均节能达22.8%。陈志强等[14]通过控制吸收塔循环泵的运行,调整喷淋的液气比,达到处理烟气的目的。王昱等[15]设计了一套废气净化的PLC控制系统,通过监测环境参数,控制泵和阀门的运行,除氨效率可达85%,且经济成本量化清晰。
本研究以氨气为处理对象,基于除氨喷淋填料塔的效率模型,用实验数据对效率模型进行验证,再将喷淋溶液循环动态模型与效率模型结合,建立除氨循环喷淋填料塔系统的动态仿真器,并利用动态仿真器模拟以次氯酸溶液为喷淋液体的氨气去除效果,提出喷淋溶液的浓、稀溶液混合配比策略,利用仿真器进行验证和对比分析,以期得到可有效减少次氯酸溶液消耗量和提升除氨效果的喷淋填料塔运行策略。
-
次氯酸(HClO)是一种易于制备、贮藏稳定、消毒杀菌能力强且安全环保的物质,它分解后不会产生对人体和环境有害的物质[16-17]。当次氯酸水溶液pH为4.5~7.0时,可与氨气(NH3)发生化学反应[18],具体见式(1)和式(2)。
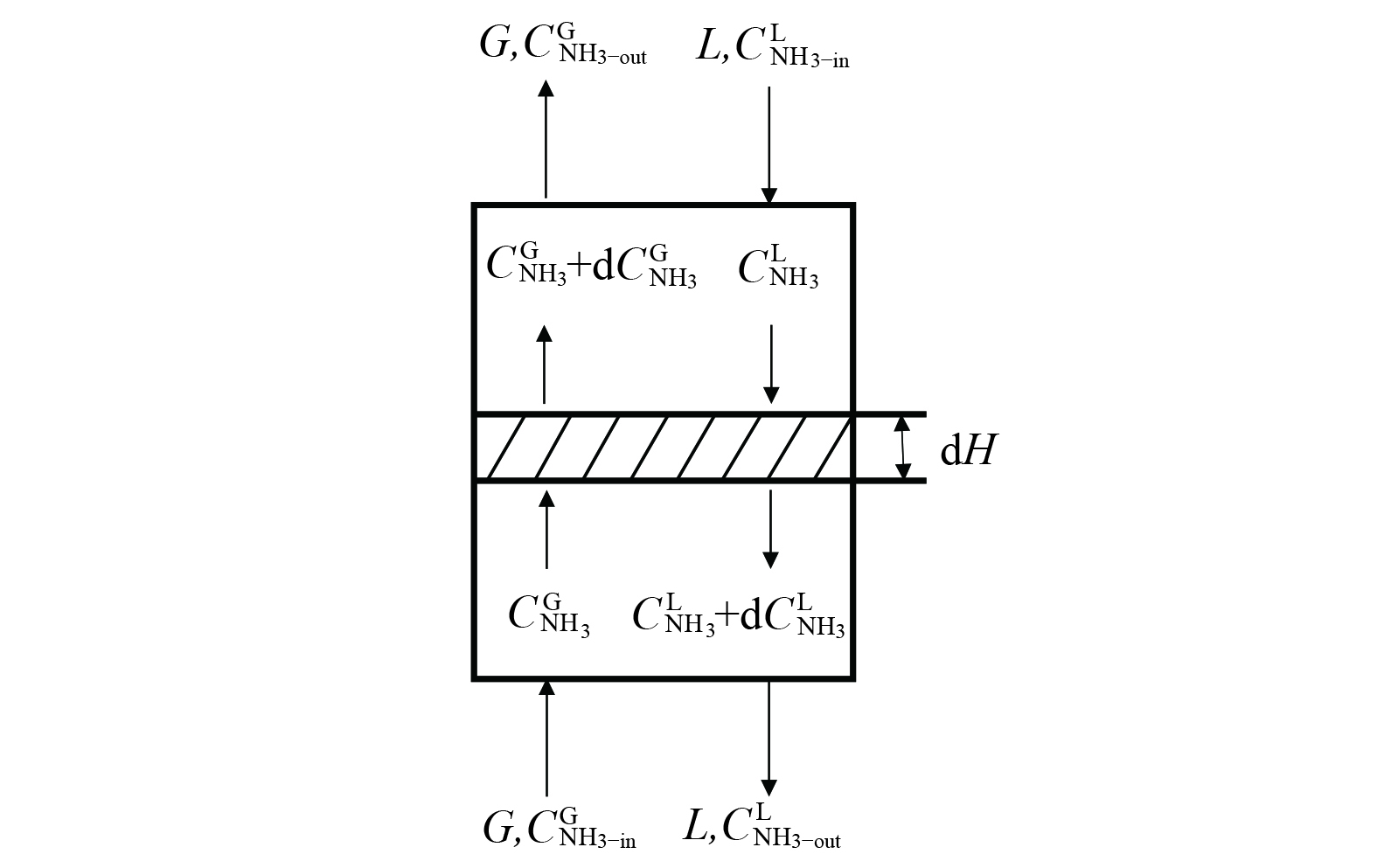
以逆流式的除氨喷淋填料塔为研究对象。如图1所示,dH为塔内填料的微元段,微元段的气相进出口处NH3浓度分别为
$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{G}} $ 和$ {\text{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{G}}\text{+}\text{d}{{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{G}} $ ,液相进出口处NH3浓度分别为$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{L}} $ 和$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{L}}\text{+}\text{d}{{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{L}} $ 。喷淋填料塔的填料微元段的传质面积见式(3)。
式中:dA为微元段内的传质面积,m2;a为填料层的单位体积内的有效传质比表面积,m2·m−3;S为喷淋填料塔的横截面积,m2;dH为填料层微元段高度,m。
对微元段进行NH3的质量守恒,可得其以气相参数表示的微元段传质面积中的平衡方程[19],见式(4)。
式中:G为单位时间内通过塔的气体流量,
$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\cdot{\text{s}}^{-1} $ ;$ \text{}{\text{K}}_{\text{G}} $ 为气相的总传质系数,${\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\cdot\text{(}{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}\cdot{\text{s)}}^{-1}$ ;$ C_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{G*}} $ 为气液两相平衡时气相中NH3的浓度,$ \text{mol}\cdot{\text{m}}^{-3} $ 。将式(3)与式(4)联立可得式(5)。
定义喷淋填料塔的除氨效率
$ \text{η} $ 计算式为式(6)。式中:
$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}\text{-in}}^{\text{G}} $ 和$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3-out}}}^{\text{G}} $ 分别为喷淋填料塔进、出口气体中的NH3浓度,$ \text{mol}\cdot{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ 。由于氨水的气液平衡关系符合亨利定律[20],可应用对数平均值法。将式(5)右侧积分可得
式中:
$ {\Delta }{{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}\text{m}}^{\text{G}} $ 为喷淋填料塔气相摩尔浓度表示的总推动力的对数平均值;m为相平衡系数;L为单位时间内通过喷淋填料塔的液体流量,$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ;。将式(5)、(6)和(7)联立可得喷淋填料塔效率η和液相出口溶液的NH3浓度
$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3-out}}}^{\text{L}} $ ,见式(8)和式(9)。王卫东等[21]利用逆流式喷淋填料塔对氨气等恶臭气体进行了处理。填料塔内径为90
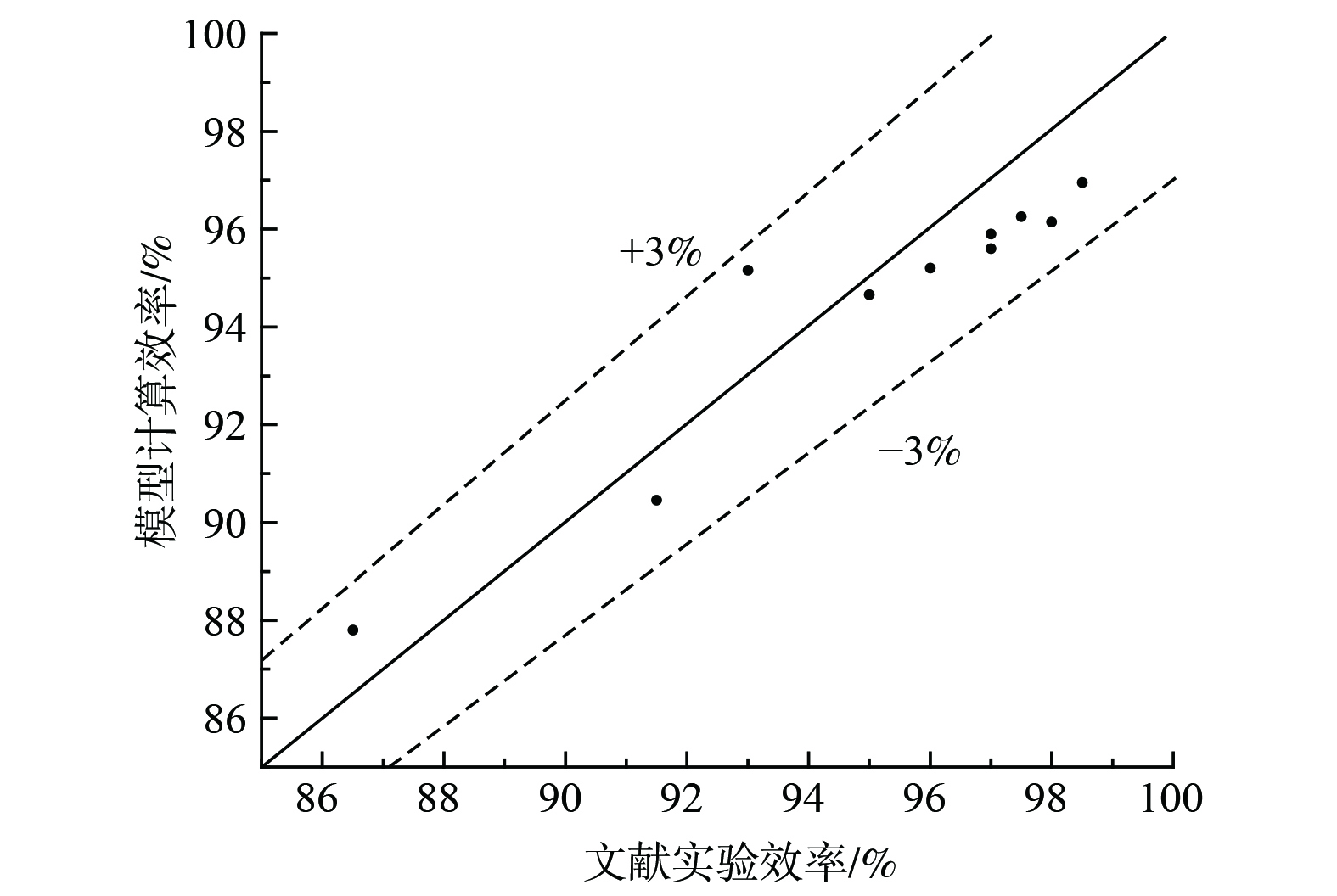
$ \text{mm} $ ,高度为850$ \text{mm} $ ,填料为不锈钢材料的拉西环,填料高度为480$ \text{mm} $ 和600$ \text{mm} $ ;实验中气体的流量为7.5~12.5$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{h}}^{\text{-1}} $ ,氨浓度为60~80$ \text{mg}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{\text{-3}} $ 。实验时喷淋的酸性液体流量不变,通过改变气体流量获得了不同液气比对氨气处理效率的实验结果。将建立的除氨喷淋填料塔效率模型各参数依照文献[21]中的实验装置和条件设置,利用实验结果对效率模型的计算结果进行验证(见图2),效率模型与结果偏差均小于±3%,模型的决定系数
$ {\text{R}}^{\text{2}} $ 为0.93。 -
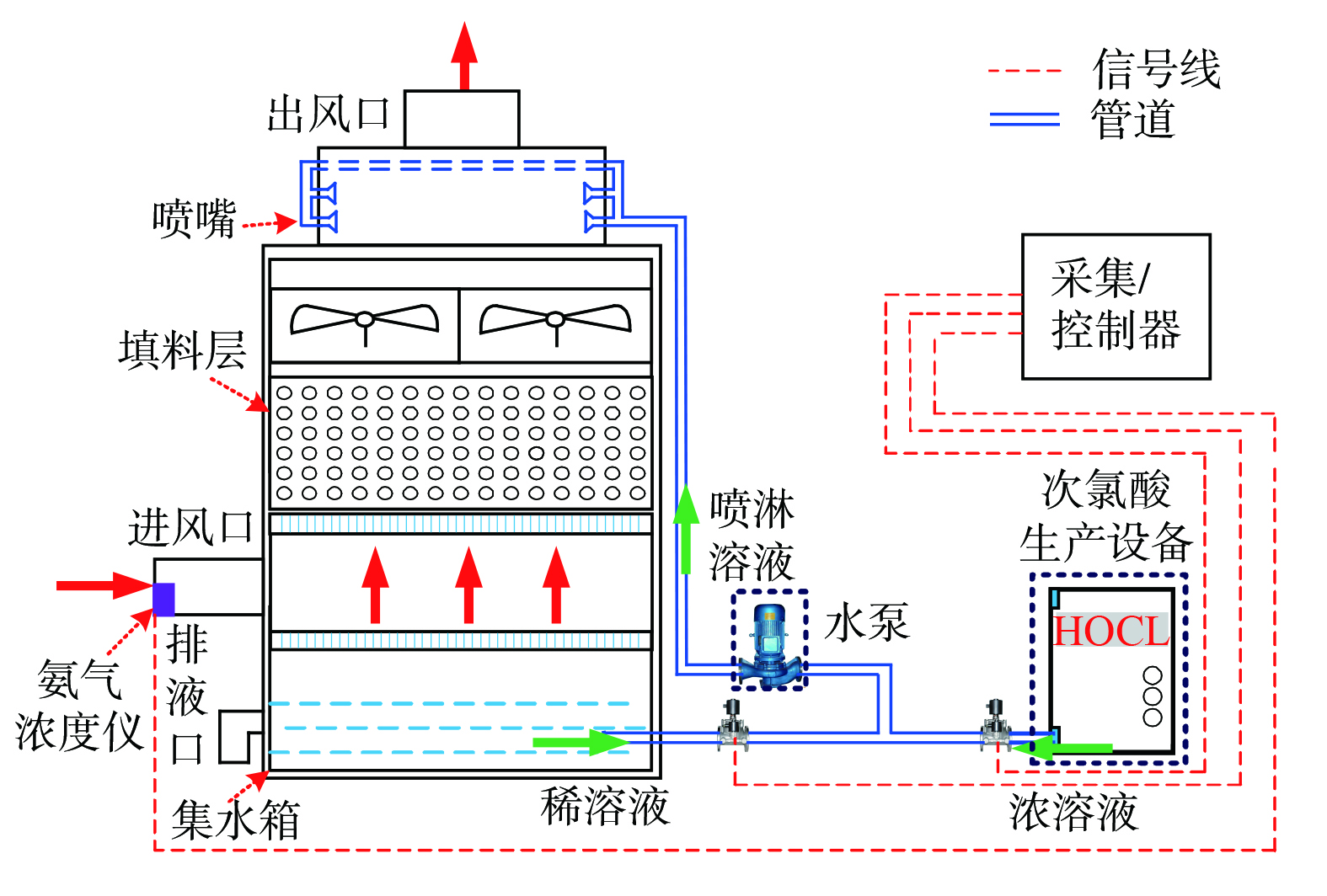
除氨喷淋填料塔及溶液循环系统由喷淋填料塔、水泵、集水箱、次氯酸生产设备、相应管道和信号线组成(见图3)。用安装在喷淋填料塔进风口处的氨气浓度仪监测氨气浓度,并通过“采集/控制器”采集数据。将次氯酸浓溶液,以及与氨气混合、吸收和反应后送入集水箱的次氯酸稀溶液混合成为喷淋溶液,再由水泵将其送入喷淋填料塔进行喷淋除氨。根据进风口处的氨气浓度,由“采集/控制器”调节浓、稀溶液的混合比例来确定喷淋溶液的浓度和流量。
建立喷淋溶液循环动态模型的假设条件有:1)浓溶液和稀溶液在喷淋前充分混合,次氯酸浓度均匀;2)由于浓、稀溶液和混合溶液中次氯酸的浓度都是ppm数量级,因此,可忽略溶液浓度对溶液密度的影响。
设t时刻塔底集水箱内的稀溶液HClO浓度为
$ \text{C} $ (t)。依据集水箱内次氯酸分子的质量守恒,则t时刻集水箱内溶液中HClO浓度的变化见式(10)。式中:
$ {{Vol}}_{\text{T}} $ 为集水箱的溶液体积,$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}} $ ;$ \text{}{{V}}_{\text{high}}({t}) $ 为喷淋液中浓溶液流量,$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ;$ {{V}}_{\text{low}}({t}) $ 为参与循环的稀溶液流量,$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ ;$ {{C}}_{\text{handle}}({t}) $ 为处理NH3后进入集水箱的喷淋溶液HClO浓度,$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ 。将1.1节所述的除氨喷淋填料塔效率模型与1.2节所述的喷淋溶液循环动态模型结合,建立了除氨循环喷淋填料塔的系统仿真器。
-
对喷淋填料塔的稀溶液进行再利用,可减少次氯酸浓溶液的补充,从而达到节水节能的目的。因此,制定控制策略的目标是对浓、稀溶液配比流量及喷淋溶液总流量进行优化。
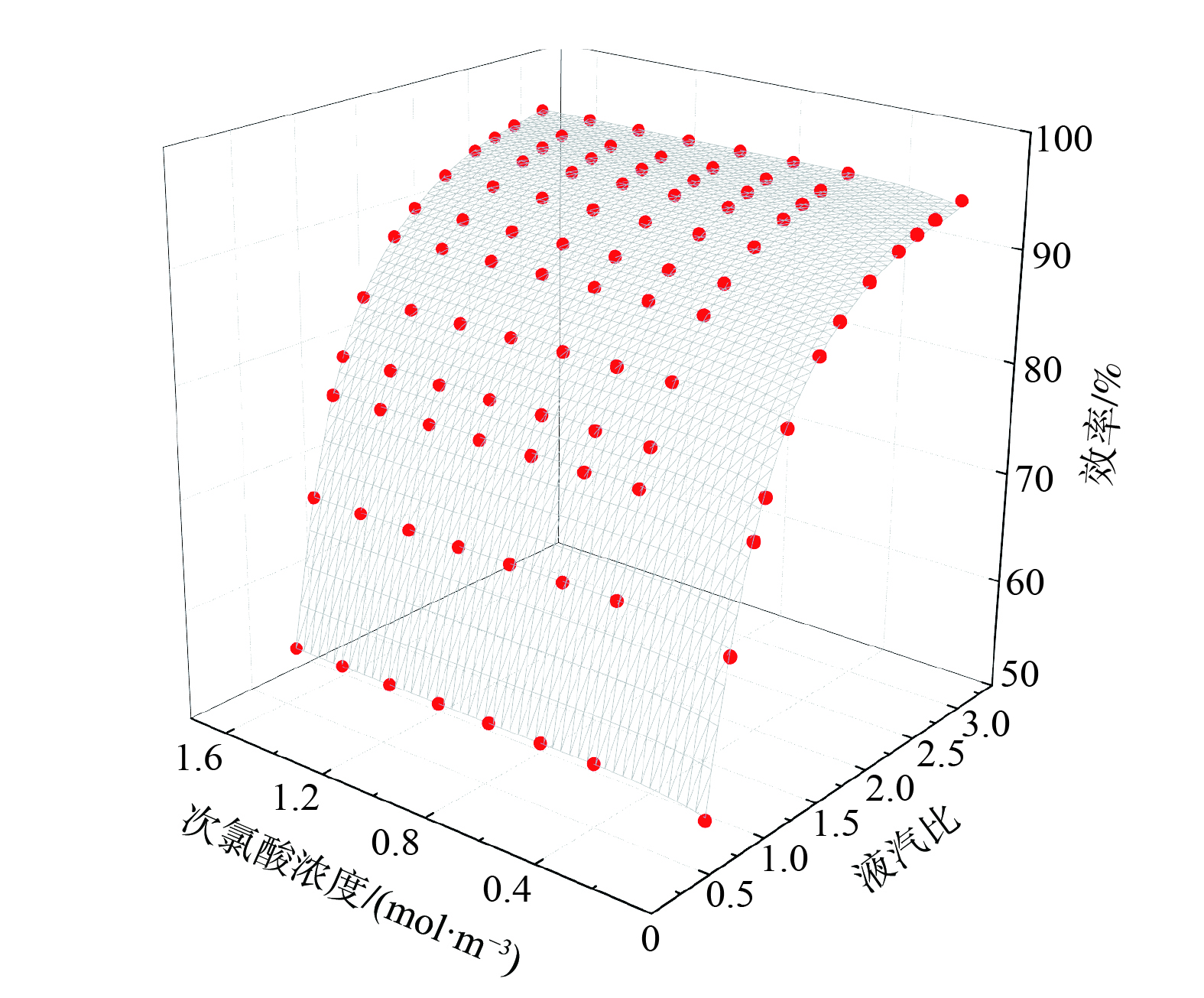
结合ZHU等[22]的结果和本研究建立的喷淋填料塔效率模型可知,喷淋填料塔的效率与液气比和喷淋溶液浓度相关。因此,利用仿真数据对喷淋填料塔效率与液气比和喷淋溶液浓度的关系进行拟合,获得喷淋填料塔的效率模型。如图4和式(11)所示,该模型的拟合决定系数
$ {{R}}^{\text{2}} $ 为0.99。式中:
$ \eta_{\text{n}} $ 为喷淋填料塔曲面函数拟合模型的效率;$ {{C}}_{\text{mix}} $ 为喷淋溶液的HClO浓度,$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ;L/G为液气比,为方便拟合函数,此处将气、液流量的单位转化为摩尔,即$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}\text{ol}}^{{-1}} $ 。本研究选取浓溶液和稀溶液的流量为优化控制参数,浓溶液消耗量的最小值为优化控制的寻优目标。该优化问题的数学表达式见式(12),约束条件见式(13)和式(14)。
式中:
$ {{V}}_{\text{}\text{high}}^{\text{}\text{i}} $ 为当前优化控制时刻的浓溶液流量,$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{s}}^{{-1}} $ 。考虑到进风侧氨浓度动态变化的因素,为保证排放能完全达标且尽可能降低排放溶液和循环溶液中的氯胺浓度,由式(13)进行约束。式中:
$ {{K}}_{\text{s}} $ 为排放安全系数,取${{K}}_{\text{s}}=0.8 $ ;$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{}\text{i}} $ 为当前时刻所测得的待处理气体中的NH3浓度,$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ;$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{GB}} $ 为国标规定的NH3排放标准浓度,$ {{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{GB}}=2\;\text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ [23]。喷淋填料塔中的氨是先被液体吸收再被次氯酸中和的。若喷淋溶液中次氯酸浓度较高,集水箱溶液中会残存一定量的次氯酸;若喷淋溶液中次氯酸浓度较低,集水箱溶液中会残存一定量的氨。由于集水箱中的部分溶液将被直接排放,这就意味着若排放液中含有较高浓度的次氯酸是浪费,而含有的氨则需进行再处理。因此,为保证集水箱溶液中氨浓度为0,需要有式(14)的约束。式中:
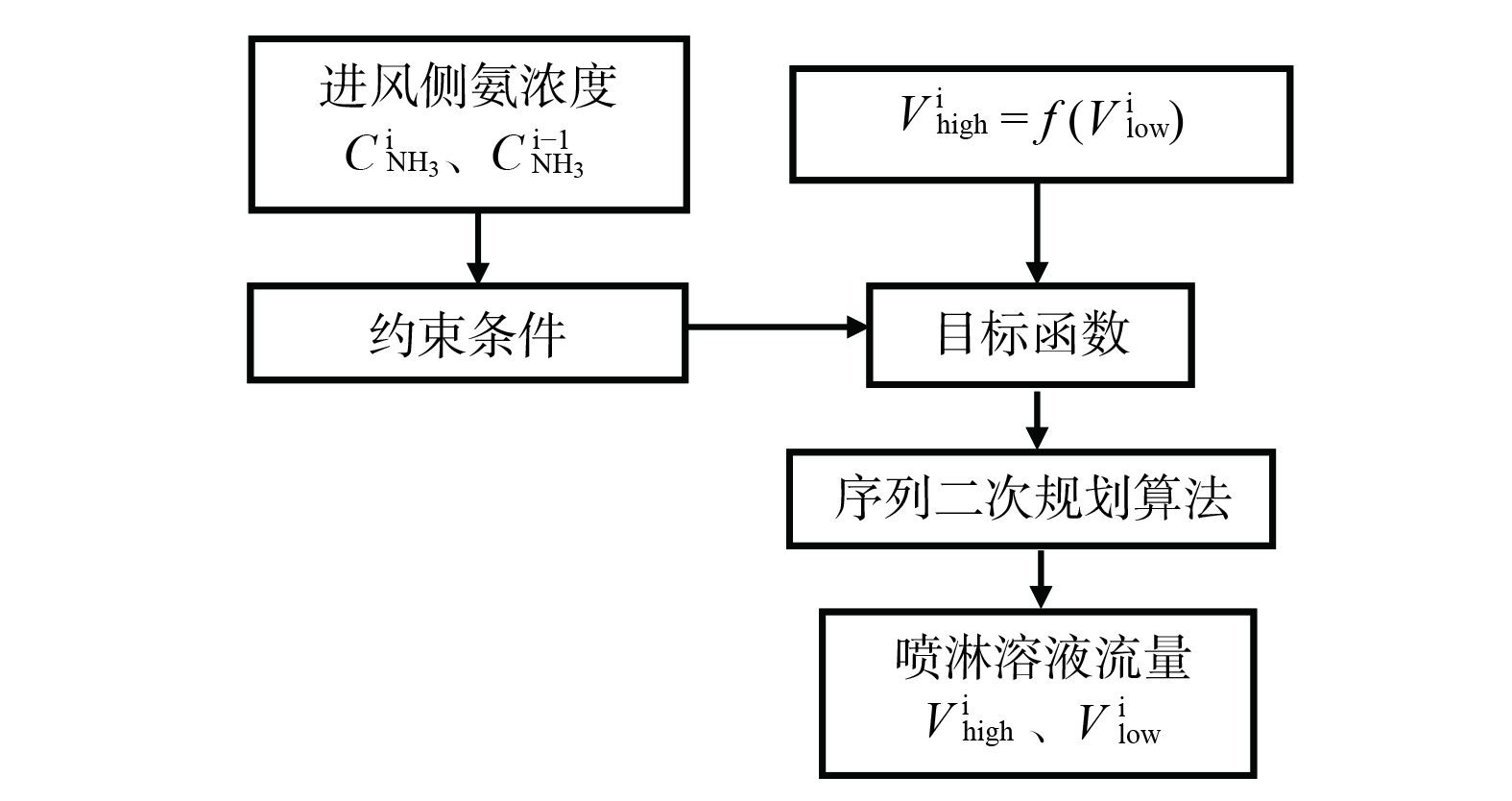
$ {{C}}_{\text{high}} $ 为浓溶液的HClO浓度,$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ;$ {{K}}_{\text{r}} $ 为HClO与NH3发生化学反应的比例系数,$ {{K}}_{\text{r}}\text{=1.5} $ ;$ \overline{{{C}}_{{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}}^{\text{}\text{i-1,}\text{}\text{i}}} $ 为上一优化时刻至当前优化时刻时间段内的进风侧NH3的平均浓度,$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ,如式(15)所示。优化控制策略的逻辑如图5所示,采用序列二次规划算法(Sequential Quadratic Programming)为寻优算法[24]。该优化控制策略实时采集进风口的氨浓度,并以次氯酸浓溶液流量为目标函数,排放气体的氨浓度和集水箱溶液的浓度为约束条件,通过序列二次规划算法,获得满足条件的次氯酸稀溶液流量和对应的最小次氯酸浓溶液流量。
-
将优化控制策略在系统仿真器中进行验证。仿真时,设定
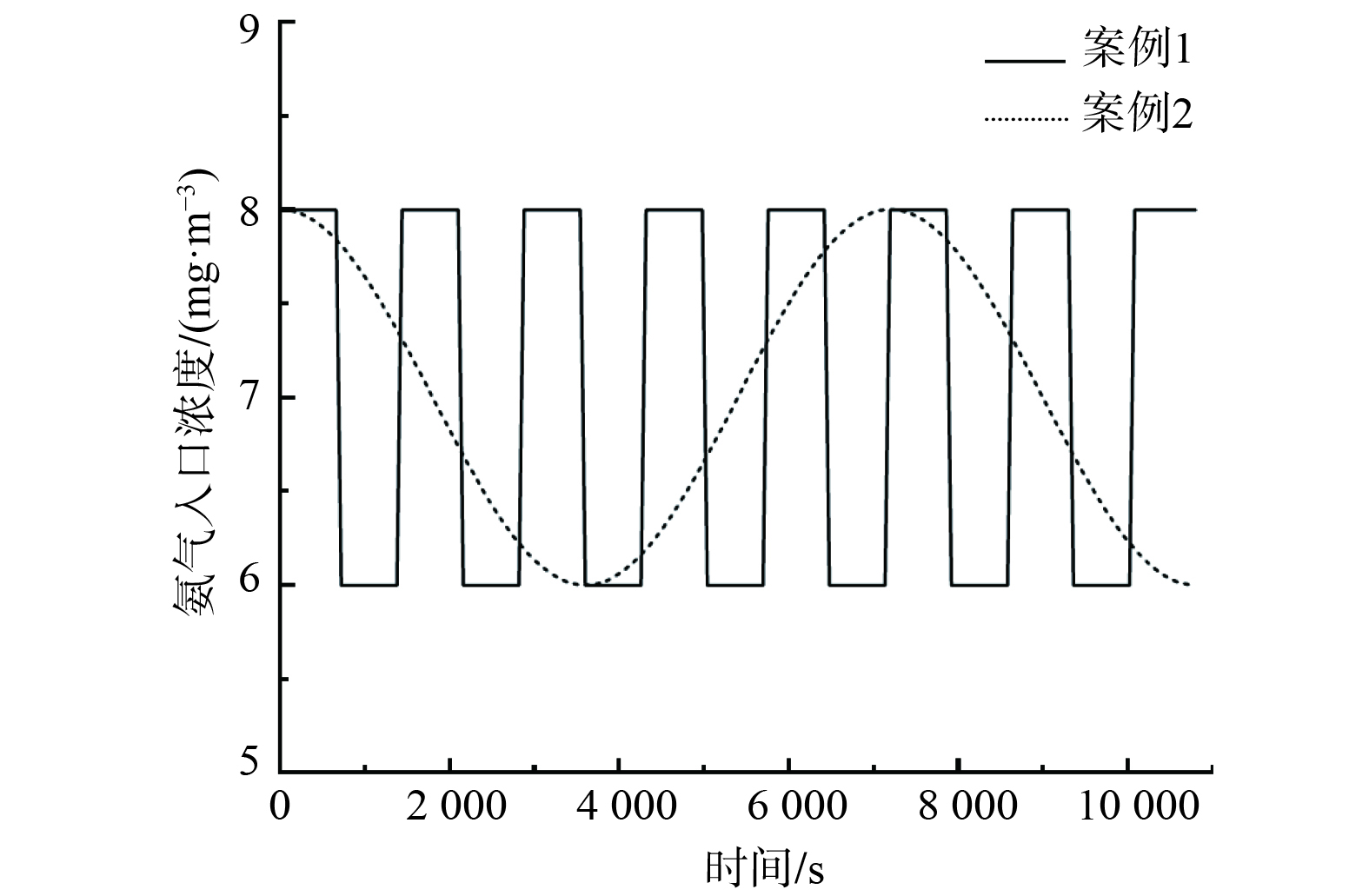
$ {{C}}_{\text{high}} $ 为1.334$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{\text{-3}} $ ,待处理气体的风量为1 800$ {\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{h}}^{{-1}} $ ,优化时间步长为180 s,集水箱溶液中次氯酸和氨初始浓度均为0。如图6所示,仿真中设定2种进风侧氨浓度的变化,分别为案例1的矩形波和案例2的正弦波变化波幅均为1
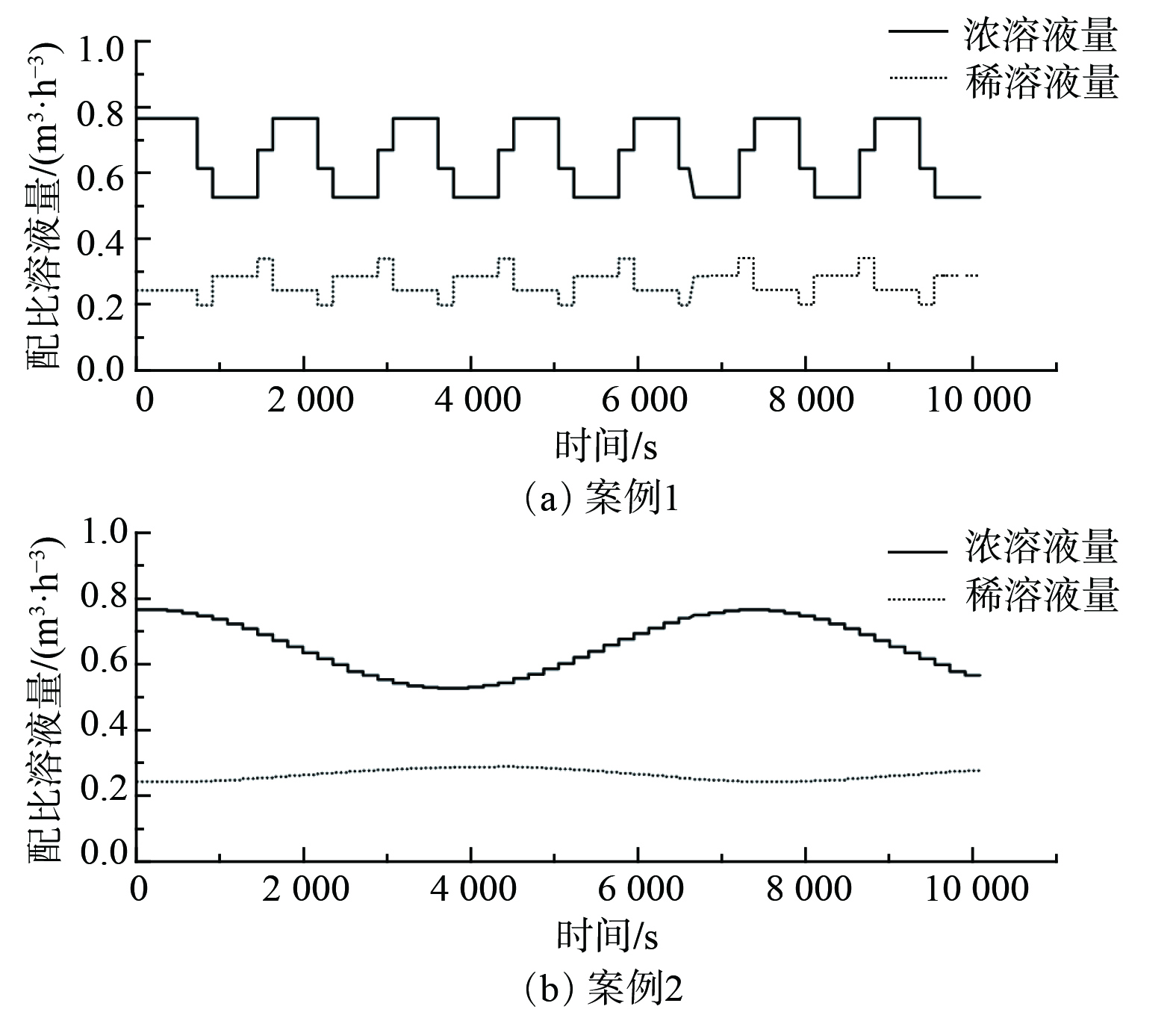
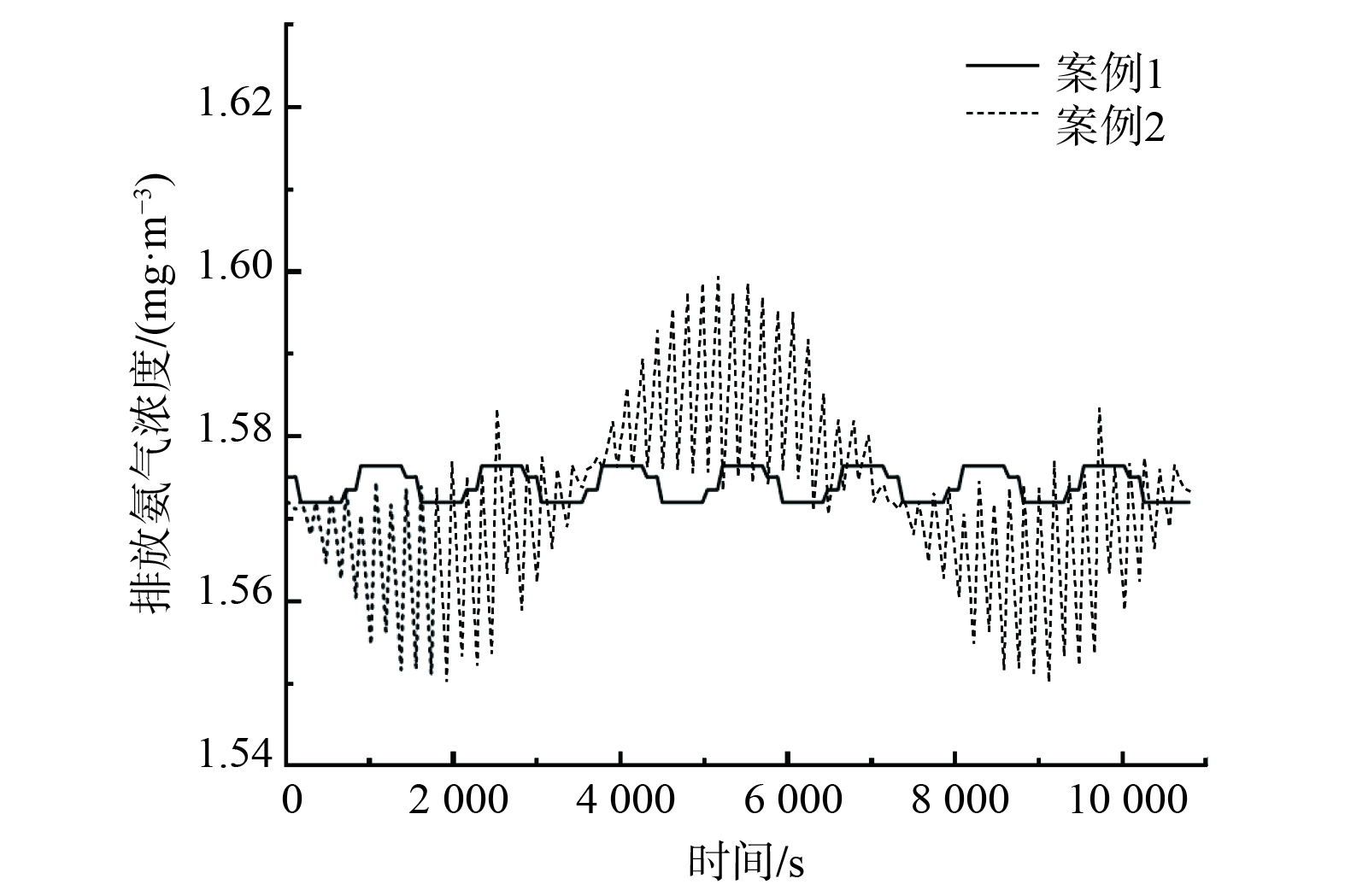
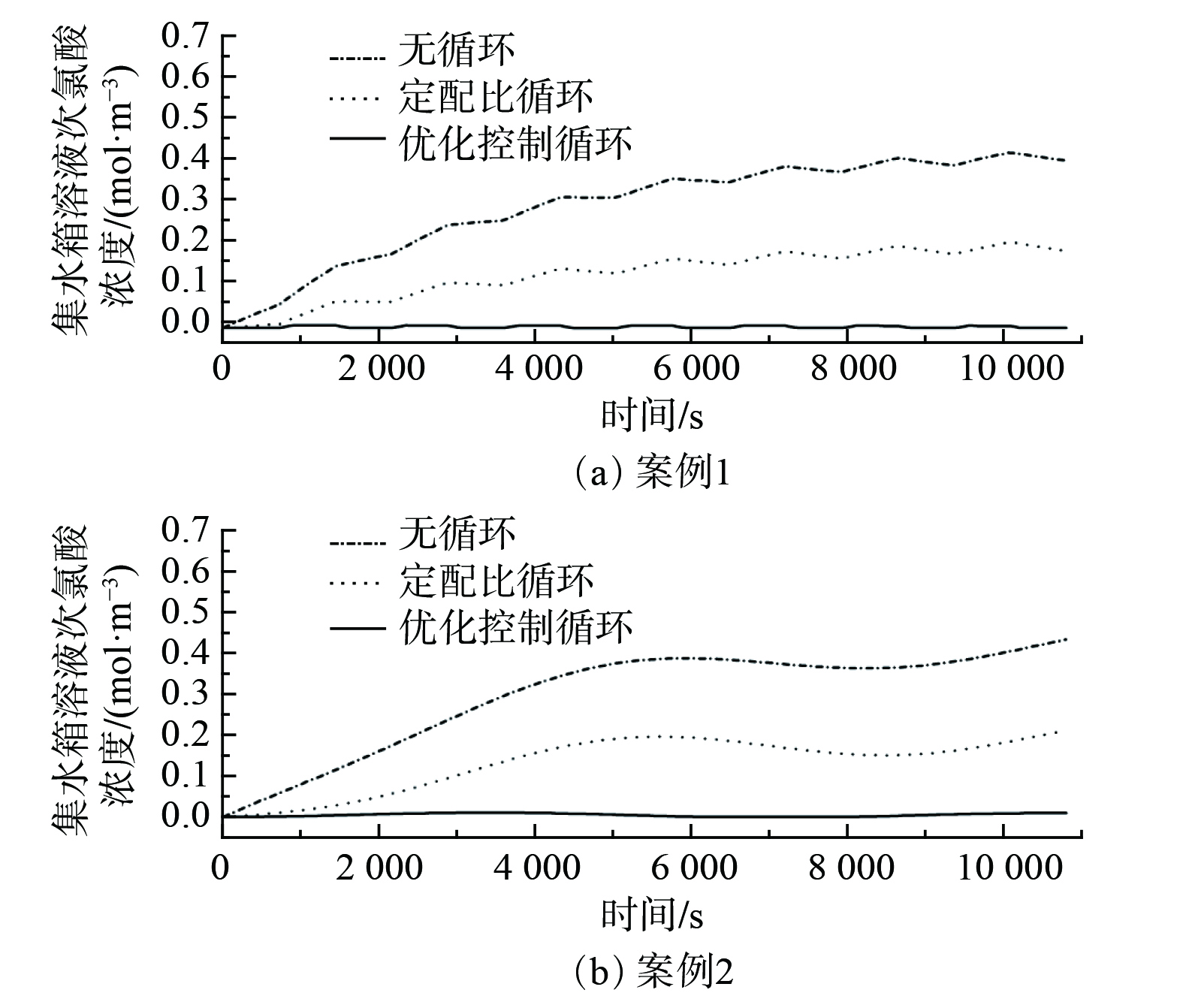
$ \text{mg}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ 。矩形波的周期为1 440 s,正弦波的周期为7 200 s。图7所示为案例1和案例2在采用优化控制策略时的浓溶液与稀溶液混合配比量。图8所示为排放气体的氨浓度。由图7和图8可见,优化控制策略可随进风侧氨浓度变化,调节浓溶液和稀溶液的配比,并均能将排放气体中的氨浓度降至国家标准规定的限值以下。
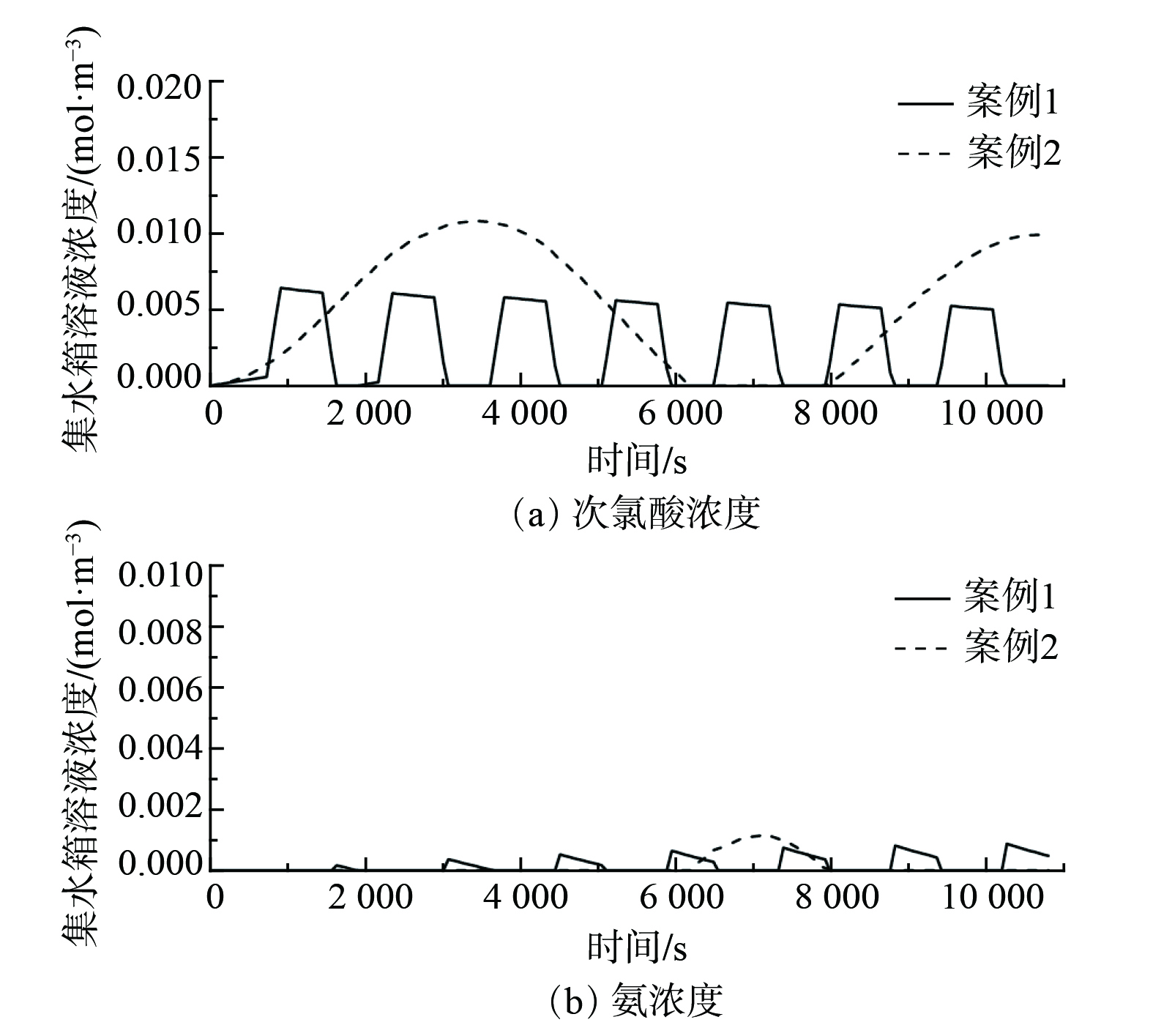
如图9所示,随着喷淋填料塔系统的持续运行,塔底部的集水箱溶液中残留的次氯酸浓度和氨浓度均较小。案例1残留的次氯酸浓度最大不超过0.006
$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ,氨浓度最大不超过0.001$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ;案例2残留的次氯酸浓度最大不超过0.012$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ ,氨浓度最大不超过0.0012$ \text{mol}\text{∙}{\text{m}}^{{-3}} $ 。为验证优化控制策略节约次氯酸需求量的效果,本研究将其与其他2个固定喷淋量的控制策略进行对比。固定喷淋量策略1为仅采用次氯酸浓溶液,无塔内稀溶液回收过程;固定喷淋量策略2为浓、稀溶液混合比固定(80%浓+20%稀)。2个控制策略的喷淋溶液流量均为1
$ {\text{}\text{m}}^{\text{3}}\text{∙}{\text{h}}^{{-1}} $ 。优化控制策略与2个固定喷淋量控制策略的除氨效果如图10所示,3个控制策略在2个案例下均可使排放气体的氨浓度达到国家排放标准规定限值以下。
图11所示2个案例下分别采用3个控制策略时,集水箱溶液内次氯酸浓度的变化状况。采用2个固定喷淋量控制策略时,集水箱溶液的次氯酸浓度持续上升,排放的液体内含有较多的次氯酸。而优化控制策略使集水箱溶液的次氯酸浓度在0附近小幅变化。
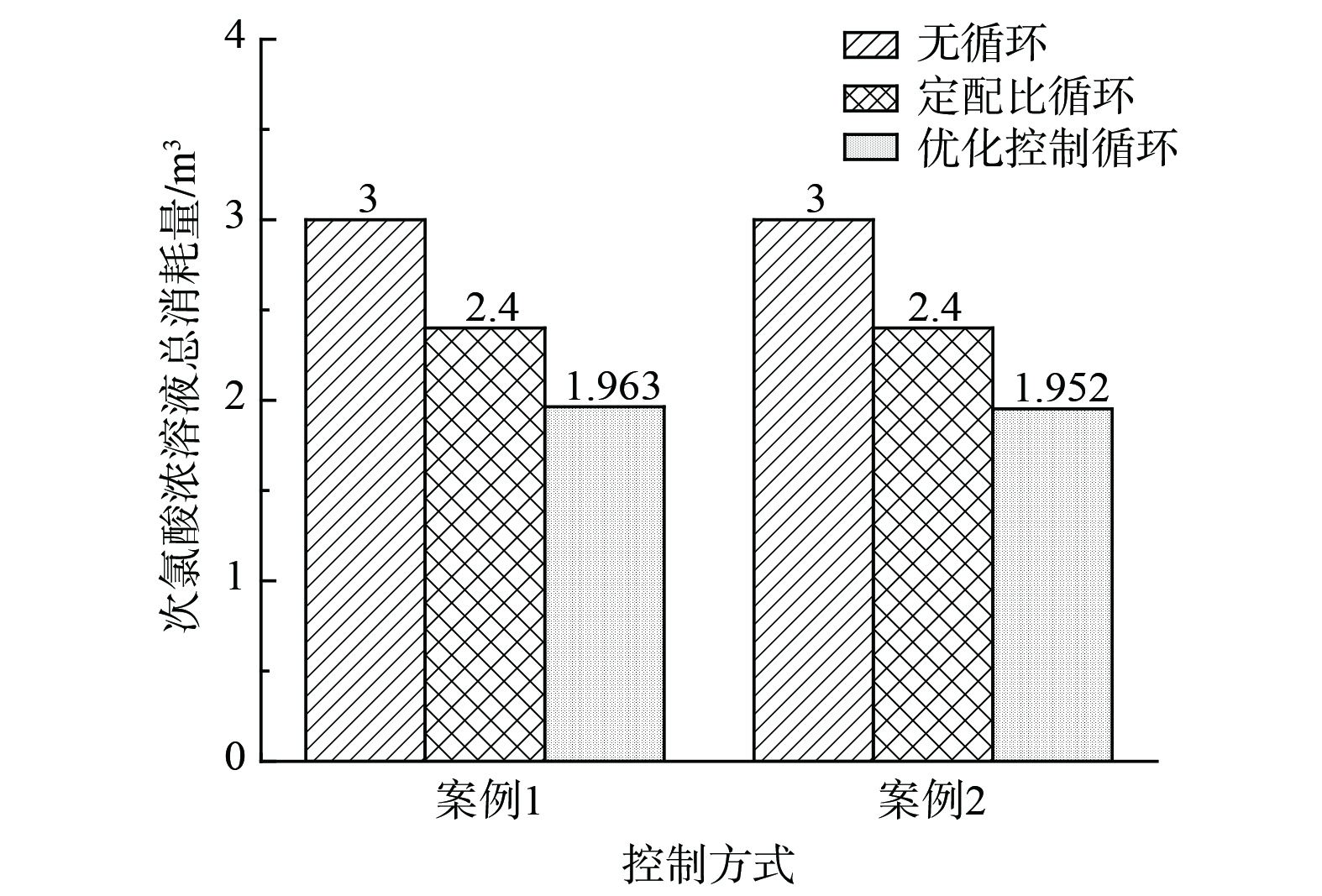
图12为3个控制策略下,系统连续运行3 h后次氯酸溶液消耗总量的对比情况。在案例1时,与固定喷淋量策略1相比,优化控制策略节约了34.57%的次氯酸量;与固定喷淋量策略2相比,优化控制策略节约了18.21%的次氯酸量。在案例2时,与固定喷淋量策略1相比,优化控制策略节约了34.93%的次氯酸量;与固定喷淋量策略2相比,优化控制策略节约了18.67%的次氯酸量。
-
1)建立的喷淋填料塔效率模型与文献中的实验数据对比,偏差在±3%以内,表明该喷淋填料塔效率模型具有较高的准确性。
2)提出的喷淋溶液循环量配比优化控制策略,在进风侧氨浓度变化的状况下可有效地将排放气体中氨浓度处理到国标GB14554的限值要求,且集水箱溶液的氨浓度很小,可直接排放。
3)与固定喷淋量的控制策略相比,优化控制策略可较大程度地节约次氯酸的消耗量。在相同运行时间内(3 h),优化控制策略相较于固定喷淋量策略1,2个案例情况下节约的次氯酸量都超过34%;相较于固定喷淋量策略2,2个案例情况下节约的次氯酸量都超过18%。
除氨循环喷淋填料塔系统建模及运行优化控制
Modeling and operational optimization control of packed tower system for ammonia removal by circulating spray
-
摘要: 喷淋填料塔是一种常见除氨设备。将喷淋除氨系统作为研究对象,以次氯酸溶液为喷淋液体,并对系统的优化运行进行研究。基于除氨逆流喷淋填料塔效率模型和系统溶液循环动态模型,建立了除氨循环喷淋填料塔系统仿真器,提出了一种以次氯酸溶液消耗量最小为目标的优化控制策略,通过仿真进行了验证,并与其他2个固定喷淋量控制策略进行了对比。与文献数据相比,喷淋填料塔效率模型的偏差在±3%以内,表明建立的仿真器精度较高。仿真验证结果表明:优化控制策略可使排放气体中氨浓度达到国标GB14554的排放限值要求,而且处理后的废液中氨含量低于其他2个控制策略;在相同的运行时长内,优化控制策略与2个固定喷淋量策略对比,次氯酸的消耗量分别节约34%和18%,说明提出的运行优化控制策略可有效节约次氯酸消耗。本研究提出的优化策略可有效提升除氨喷淋填料塔的运行效率。Abstract: Spray packed tower is a common equipment for the treatment of ammonia gas. The spray packed tower system was taken as the research object to study its optimal operation, with hypochlorous acid solution as the spray liquid.. A simulator of the spray packed tower system was established, based on the efficiency model and the dynamic model of solution circulation. An optimal control strategy was developed to minimize the consumption of hypochlorous acid solution, which was verified by simulation and compared with other two control strategies with fixed spray rate. Compared with the experimental data of the literature, the deviation of the efficiency model of spray packed tower was within ±3%, which indicated that the simulation established in this paper had high accuracy. Simulation results showed that the optimal control strategy could maintain ammonia concentration of discharge gas to satisfy the requirement of GB14554, and the ammonia concentration of the waste solution was lower than the other two control strategies. In the same running time, compared with the two fixed spray rate strategies, the consumption of hypochlorous acid could be saved by 34% and 18% respectively, indicating that the proposed optimal control strategy could effectively save the consumption of hypochlorous acid. The optimization strategy proposed in this study can effectively improve the operation efficiency of the packed column for ammonia removal.
-

-
-
[1] 戴万能, 高晓根, 计维安, 等. 含硫气田恶臭硫化物性质及阈限值研究[J]. 天然气与石油, 2015, 33(6): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2015.06.021 [2] 石志芳. 奶牛场氨和硫化氢排放特征及氨生物毒性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. [3] HADLOCON LS, MANUZON RB, ZHAO LY. Optimization of ammonia absorption using acid spray wet scrubbers[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2014, 57(2): 647-659. [4] 黄翔, 张伟峰, 郑文亨, 等. 利用喷水室对空调新风中有机物和无机物去除的实验研究[J]. 洁净与空调技术, 2004(2): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3298.2004.02.004 [5] LESON G, WINER AM. Biofiltration: an innovative air pollution control technology for VOC emissions[J]. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association. 1991, 41(8): 1045-54. [6] GUO Y, NIU Z, LIN W. Comparison of removal efficiencies of carbon dioxide between aqueous ammonia and NaOH solution in a fine spray tower[J]. Energy Procedia, 2011, 4(1): 512-518. [7] 郑毅, 赵祥迪, 杨帅, 等. 填料塔-文丘里耦合洗消设备研发与H2S洗消效率分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2020, 16(12): 111-115. [8] 祝杰, 吴振元, 叶世超, 等. 喷淋塔传质特性的实验与模型研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015(1): 317-322. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150153 [9] 郑文亨, 黄翔, 颜苏芊. 喷水室处理空调新风传质理论的研究[J]. 西安工程科技学院学报, 2004(3): 52-56. [10] JAFARI M J, MATIN A H, RAHMATI A, et al. Experimental optimization of a spray tower for ammonia removal[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2018, 9(4): 783-790. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2018.01.014 [11] 戴圣炎. 微酸性电解水与臭氧融合的减臭杀菌技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [12] 鞠剑峰, 王相伟, 于亚楠, 等. 泡沫型次氯酸水杀菌消毒剂的制备及性能[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(10): 7-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.10.005 [13] 张晓静, 王仕元, 周义德, 等. 纺织空调喷淋系统恒压变频控制设计运行探讨[J]. 棉纺织技术, 2020, 48(3): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7415.2020.03.006 [14] 陈志强, 傅钧, 刘卫华, 等. 烟气脱硫系统控制策略[J]. 水利电力机械, 2007(6): 9-11. [15] 王昱, 吴鹏, 曾志雄, 等. 规模化猪舍废气复合净化系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(4): 344-352. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.04.039 [16] DING T, XUAN X T, LI J, et al. Disinfection efficacy and mechanism of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on Staphylococcus aureus in pure culture[J]. Food Control, 2016, 60: 505-510. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.037 [17] WEI C, ZHI W Z, ZHENG X S, et al. Efficiency of slightly acidic electrolyzed water for inactivation of Salmonella enteritidis and its contaminated shell eggs[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2009, 130(2): 88-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.12.021 [18] 陈寿椿. 重要无机化学反应[J]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 1994: 1883-1584. [19] 徐崇嗣. 塔填料产品及技术手册[J]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 1995: 637-638. [20] 童志权. 大气污染控制工程[J]. 北京:机械工业出版社, 2006: 191-193. [21] 王卫东, 齐国庆, 黄其成, 等. 化学填料塔脱除恶臭气体工艺研究[J]. 石油化工应用, 2010, 29(9): 10-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2010.09.003 [22] ZHU J, ZHAO P, ZHANG Q, et al. Modeling and experimental studies on chemical absorption of sulphur dioxide with ethylenediamine-phosphoric acid solution in a θ-ring packed tower for purification of flue gas[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 255: 117764. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117764 [23] 中华人民共和国国家标准. GB14554-93. 恶臭污染物排放标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. [24] 孙远韬, 章增增, 张氢, 等. 裂纹扩展寿命多失效模式可靠度的序列二次规划计算方法研究[J]. 机械强度, 2019, 41(5): 1090-1095. doi: 10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2019.05.013 -



 下载:
下载: