-
由于碳酸钙在造纸工艺中的大量应用,造成了造纸废水的钙离子含量高的特征,这给造纸废水的处理带来了不小的挑战。高浓度的钙离子对造纸工艺的厌氧、好氧以及深度处理等阶段均会带来不利影响,如导致厌氧污泥钙化[1-2],阻碍污泥与外界环境传质,影响废水生化处理效果[3-4];造成好氧污泥絮凝体增大,剩余污泥产量增多,抑制污泥活性, COD去除率下降[5-6];在膜表面产生粒径较小的无机颗粒物导致膜污染,影响膜的使用寿命,增加处理成本[7-8]。
目前除钙技术有物理法、化学法,生物法等。物理法主要有离子交换法、吸附法和膜分离法;化学法主要有化学沉淀法和电化学法;生物法主要是指生物矿化除钙。物理法除钙主要面临着除钙容量低,选择性较差等不利因素;化学法是目前应用最为广泛的除钙方法,但对除钙药剂的添加量有严格的要求[9-10];生物法主要是利用自然界生物矿化机理,利用微生物代谢产生脲酶催化分解尿素水解产生碳酸根离子,进而与钙离子结合生成碳酸钙沉淀[11],但生物法除钙工艺会带来氨氮含量超标等问题[12]。
应用最广的化学沉淀法除钙的原理是溶度积理论,但在实际废水处理中,理论与实际出入很大,有学者研究碳酸钙的结晶析出问题时也发现,碳酸钙结晶过程存在着一个过饱和状态,在该状态下并无沉淀生成[13]。为解决理论与实际的差异问题,预测水处理中碳酸钙的最小溶解度,有学者提出了碳酸钙条件溶度积的概念[14]。条件溶度积是利用化学平衡和数学方法进行推导,在某一温度下考察水中所能存在的难溶电解质的溶质组成,比实际的溶度积常数要大,但还未见用于指导实践。本研究对嘉兴某造纸厂废水处理工艺好氧段实际水样进行研究,结合造纸废水好氧原水高钙浓度、高无机碳含量的特点,并利用条件溶度积理论,探究了不添加化学药剂直接通过物理曝气进行除钙的可行性;考虑在好氧池之前增设曝气除钙工艺,进行曝气除钙实验研究,探寻了条件溶度积应用于实践指导的可能性,以期为造纸废水好氧段除钙工艺的改进提供参考。
-
本研究以嘉兴某造纸厂废水处理单元水样为研究对象,如图1所示,对废水水质成分进行检测分析,pH和温度采用梅特勒pH计(METTLER TOLEDO公司生产)进行测定,TDS采用便携式电导率仪进行测定。Ca2+ 的质量浓度采用EDTA滴定法(GB 7476-87)进行测定,无机碳(IC)质量浓度通过总有机碳分析仪(TOC-VCPH,日本岛津公司)测定。水样中Cl−、NO3−、SO42−、PO43−等阴离子质量浓度采用离子色谱(ICS-1000)进行测定,K+、Na+、Mg2+等阳离子质量浓度采用原子吸收法(AA6800,日本岛津公司)进行测定。
-
对实验室模拟溶液和造纸厂好氧原水(厌氧段出水)分别在曝气柱中进行曝气实验,研究曝气对钙离子的去除效果。曝气柱为有机玻璃柱,柱高1 m,内径10 cm,底部用曝气石曝气,溶液体积为2 L。采用电磁泵进行曝气,曝气流量为2 (L·min−1)。结合好氧原水中的钙离子含量,在曝气实验中设置钙离子质量浓度为800 mg·L−1,IC的浓度梯度为240、360、480和600 mg·L−1。
模拟溶液采用配制好的1 L Na2CO3溶液和1 L CaCl2溶液混合而成,IC浓度梯度的设置通过改变混合液中Na2CO3的量来控制。实验开始时,先将两溶液混合,每隔5 min测定1次pH,并取样测Ca2+浓度,当pH趋于稳定,且Ca2+浓度不再显著下降时,开始对混合溶液进行曝气,继续测定pH和Ca2+的变化。另对2 L好氧原水在相同条件下进行曝气,测定曝气过程中Ca2+浓度和pH的变化。
-
难溶电解质溶解平衡时的平衡常数为溶度积常数,简称溶度积。据此,常通过溶液中过饱和度的计算来判断沉淀是否达到完全,过饱和度的定义是离子浓度积与溶解平衡常数之比,碳酸钙的过饱和度根据式(1)[15]计算。碳酸钙条件溶度积可定义为碳酸钙溶解平衡时总碳浓度与总钙浓度的乘积(式(2)),总钙和总碳浓度分别根据式(3)和式(4)计算。
其中:S是碳酸钙的过饱和度;
$ {C}_{{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}}^{2+}} $ 、$ {C}_{{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{3}^{2-}} $ 分别为Ca2+、CO32−的浓度,mol·L−1;Ks为方解石的溶度积,在25 ℃时,Ks=8.7×10—9。当S<1时,没有沉淀生成;S=1时,为溶解平衡状态;当S>1时,有沉淀生成。式中:
$ {P}_{s} $ 为碳酸钙条件溶度积;$ {C}_{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{a}} $ 为溶液中所含有Ca元素的物质组分的浓度之和,mol·L−1;$ {C}_{\mathrm{c}}\mathrm{为}\mathrm{溶}\mathrm{液}\mathrm{体}\mathrm{系}\mathrm{中}\mathrm{所}\mathrm{含}\mathrm{有}\mathrm{C}\mathrm{元}\mathrm{素}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{物}\mathrm{质}\mathrm{组}\mathrm{分}\mathrm{的}\mathrm{浓}\mathrm{度}\mathrm{之}\mathrm{和} $ ,mol·L−1。根据化学反应方程式及相应平衡常数K值,将式(2)中右侧的两项用
$ {C}_{{\mathrm{H}}^{+}} $ (H+浓度)和$ {C}_{{\mathrm{H}}_{2}{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{3}} $ (H2CO3浓度)表示,根据亨利定律可推导得出Ps的数学表达式,在特定条件下将其转换成只和pH有关的函数。设 x = pH,则$ {C}_{{\mathrm{H}}^{+}}={10}^{-x} $ ,代入以上表达式可得式(5)。 -
对嘉兴某造纸厂废水好氧处理单元(图1)的水质进行取样分析,结果如表1所示。
对好氧原水中阳离子K+、Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+及阴离子SO42−、Cl−、NO3−、PO43−的质量浓度进行了测定,结果发现阳离子中Ca2+的质量浓度最高,为554.0 mg·L−1,其次是Na+,为366.96 mg·L−1,K+为64.95 mg·L−1,Mg2+为27.77 mg·L−1。各阴离子分别为:252.9 mg·L−1 Cl−、33.25 mg·L−1 NO3−、20.19 mg·L−1 SO42−、 6.27 mg·L−1 PO43−。
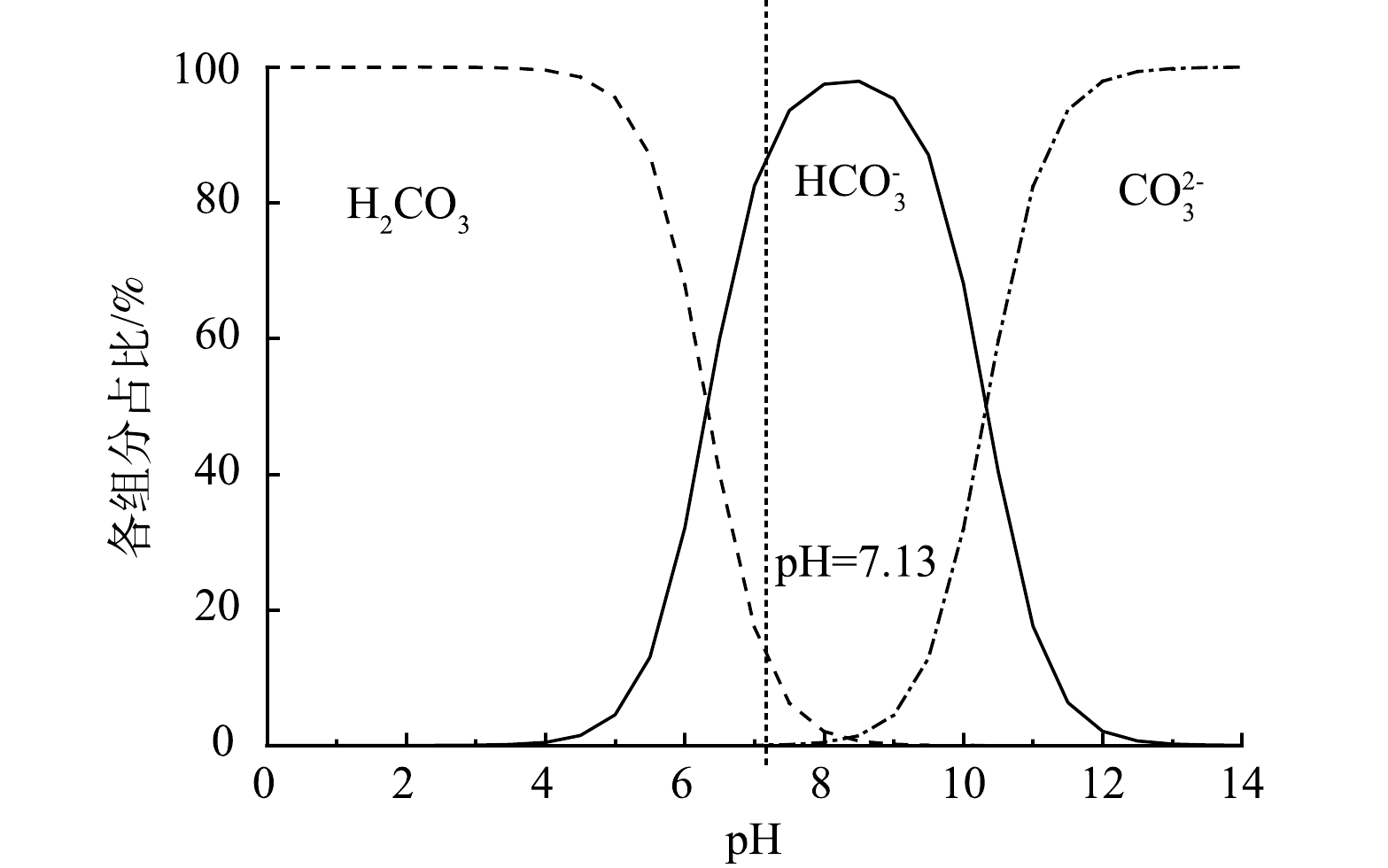
由表1可以看出,好氧原水的pH约为7,经过好氧单元的沿程处理,pH逐渐上升,温度保持在29 ℃左右,TDS和IC、Ca2+的含量均有所下降。实际工艺中Ca2+质量浓度的下降主要发生在好氧处理前段,在几个好氧池中Ca2+和IC的质量浓度略有波动。之前的研究[16]表明,造纸废水中钙离子主要通过形成CaCO3的形式而去除。但实际结果表明IC和Ca2+含量的减少若以物质的量浓度来计,并不是按照1:1的比例,这表明Ca离子去除过程中伴随着IC形式的转化。查阅该厂相关资料得知,厌氧塔中CO2分压约占30%。根据碳酸的一级、二级解离常数以及水的平衡常数进行理论推导,可以得到理想体系中不同pH条件下碳酸的组分分布,结果如图2所示。结合好氧处理段pH为7.13可知,造纸厂的厌氧出水中IC主要以HCO3−的形式存在,且含有丰富的溶解性CO2,在好氧曝气的过程中,水中的CO2被吹脱至空气中,pH有所上升,同时HCO3−大量转化为CO32−,与水中游离的Ca2+结合,生成CaCO3沉淀,而这是造成好氧颗粒污泥团聚以及剩余污泥产量大的重要原因之一。根据表1中好氧原水的水质指标,其无机碳的含量为412.9 mg·L−1,碱度为34.4 mmol·L−1,而钙的含量为554.0 mg·L−1(13.85 mmol·L−1),碱度条件满足曝气除钙要求。因此,考虑在好氧池前增设曝气除钙池,根据原水水质条件直接进行曝气除钙工艺。在曝气的过程中,原水中碱度中的部分HCO3−逐渐转化为CO32−,与水中Ca2+结合从而实现钙的沉淀与去除。
由表2可以看出,好氧原水中含量最多的无机阳离子为Ca2+,除IC外含量最高的无机阴离子为Cl−,由于离子效应的关系,其他无机离子的存在也可能会对碳酸钙的溶解度产生影响。有研究[17]表明,在SO42−存在的条件下,CaCO3的溶解度会有所增加,但造纸废水好氧原水中SO42−的含量极低,这一影响可以忽略不计。
-
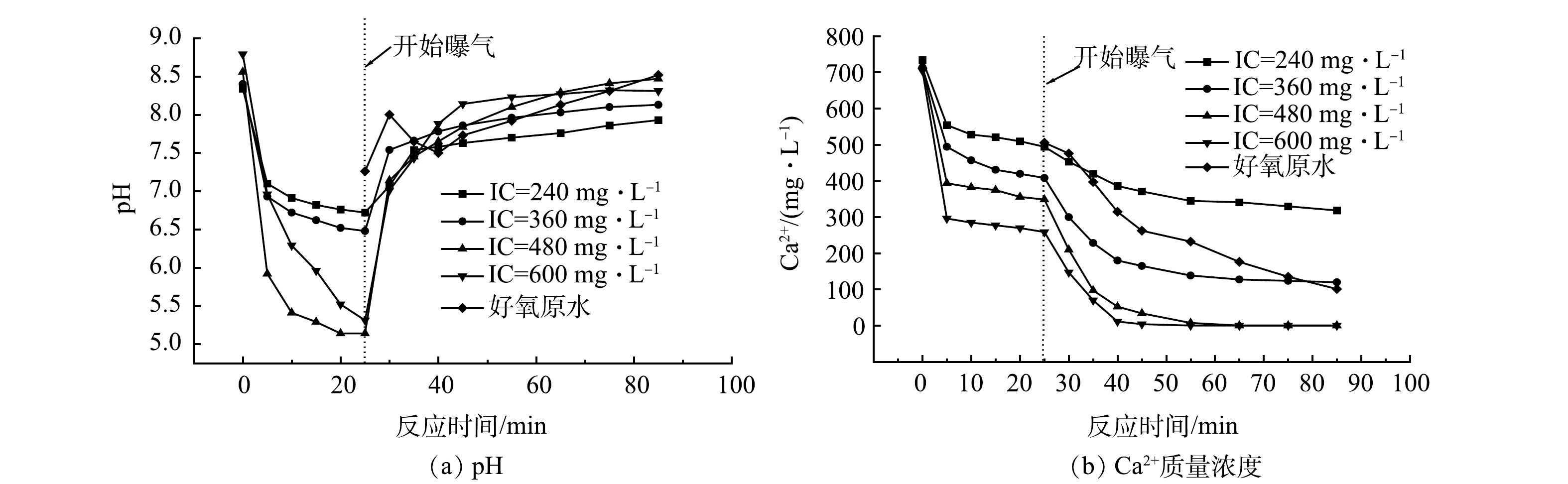
好氧原水中IC含量较高,且主要以HCO3−的形式存在,在好氧曝气池的处理中,废水中IC和Ca2+含量经过好氧1池后显著下降,pH在好氧处理段有所上升。有研究[18-20]表明,脱除废水中的CO2可以提高pH,本文进一步研究了通过曝气手段直接去除废水中钙离子的可行性。猜想通过对好氧原水进行曝气脱除CO2,改变水体pH,促进HCO3−向CO32−转化,进而与水中游离的Ca2+结合生成CaCO3。在实验室条件下对模拟废水和实际废水分别进行了曝气实验,并对实验过程中的pH、Ca2+含量进行测定,结果如图3所示。
由图3可知,对模拟溶液而言,在溶液混合约20 min后pH降至一定值,Ca2+质量浓度变化缓慢,认为此时钙的自然沉淀已达到饱和。在第25 min时对模拟溶液进行曝气,曝气后模拟溶液的pH迅速上升,Ca2+质量浓度进一步下降,一段时间后两者变化均趋缓。这说明曝气可以促进钙的沉淀,且IC含量越高,钙的沉淀效果越好。曝气开始的20 min内,好氧原水中Ca2+的去除速率基本与IC=360 mg·L−1的模拟溶液相同。但随着曝气时间的延长,在IC为240 mg·L−1和360 mg·L−1的模拟溶液中,由于IC不足导致Ca2+无法进一步沉淀,导致其质量浓度维持在一定值;在IC为480 mg·L−1和600 mg·L−1的模拟溶液中,由于IC足量或过量导致Ca2+很快沉淀完全,其质量浓度达到检测下限,去除率几乎达到100%;而好氧原水中的Ca2+质量浓度则没有稳定下来,反而是随着曝气的进行稳步持续下降。
好氧原水曝气过程中的IC与Ca2+的含量如表2所示。可以看出,好氧原水中IC含量较高,曝气60 min 后,原水中的Ca2+质量浓度由554 mg·L−1降至97.2 mg·L−1,此时IC仍有156.846 mg·L−1,好氧原水中的IC值完全满足沉淀Ca2+所需的IC含量。在足够长的曝气时间下,理论上可将钙完全沉淀。
值得注意的是,好氧原水曝气过程中pH的变化与模拟溶液中有所不同。模拟溶液在曝气后pH一直上升,但好氧原水中的pH则呈先上升后下降再上升的变化趋势,推测这是由于原水体系属于碳酸钙的过饱和溶液所致。
-
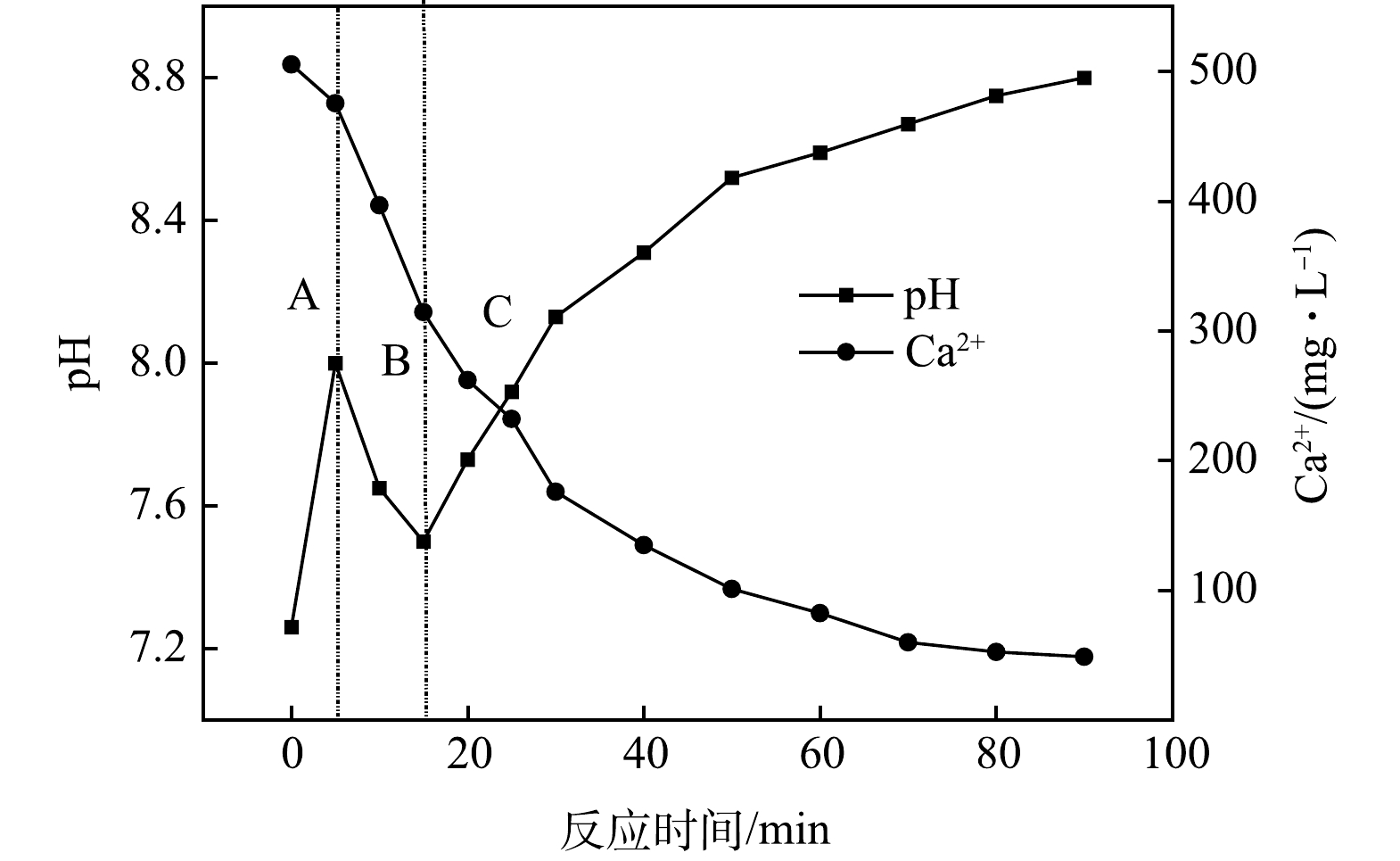
好氧原水实际曝气过程中pH和Ca2+的变化情况如图4所示。造纸厂好氧原水中富含饱和的溶解性CO2,从而导致曝气过程中pH变化呈先上升后下降再上升的趋势。根据pH变化趋势,将曝气全过程分为A、B、C阶段。由于好氧原水pH为中性,溶液中无机碳的存在形式主要以HCO3−为主,CO32−含量较低。在A阶段,曝气刚开始时, pH急剧上升。这是在 CO2饱和溶液中CO2大量脱除所致,即式(6)和式(7)均向左移动。在B阶段,当pH不断升高,式(8)开始向右移动,水溶液中钙离子与碳酸根相结合,此时发生碳酸钙的大量沉降(式(9))。钙离子的大量沉降会导致式(8)进一步向右移动,从而溶液中H+增多,导致pH短暂降低。这里需要指出的是,pH短暂降低的过程中曝气仍在进行,式(6)和式(7)所示反应仍在向左进行,只不过式(7)左移产生的OH−被式(8)右移产生的大量H+中和,最后表现为H+含量升高,pH降低。pH短暂降低的过程即为碳酸钙沉淀大量生成的过程。
在C段,经过一定时间的碳酸钙大量沉淀后,钙含量下降到一定程度,钙的沉淀速率减缓,此时随着曝气的不断进行,反应体系中式(6)和式(7)的左移作用逐渐超过了式(8)的右移效应,此时再次表现为pH上升,溶液中CO32−含量增多,碳酸钙进一步沉淀。在整个曝气除钙过程中,总反应方程式如式(10)所示。
由上述分析结果可见,对好氧原水进行曝气除钙的过程是碳酸钙过饱和溶液中CO2释放和CaCO3沉淀生成的过程,曝气过程中pH先上升后下降再上升的变化趋势是脱除CO2气体提高溶液碱性和生成碳酸钙沉淀增加溶液酸性2个过程互相竞争的结果。这一结果也与徐敬等(2004)在研究碳酸钙过饱和溶液的结晶析出过程中测得的pH变化趋势相一致,碳酸钙的结晶析出伴随有CO2气体向大气中的释放。
综上所述,无论是模拟废水还是实际废水,曝气操作均能促进钙的进一步沉降。钙去除的首要限制因素是IC含量,在IC不足的情况下很难进一步除钙;而实际废水中IC含量丰富,且含有溶解性CO2,对其进行曝气,可以改变水体pH,促进CO32−的生成,进而加快Ca2+的去除。
-
条件溶度积Ps的实际意义是量化了一定条件下水体中所有形式的Ca和所有形式的IC的共存能力的大小,Ps越大,水中所能存在的Ca和IC就越多,亦可以说,CaCO3的溶解度越大。在这个意义上,Ps和Ks均体现了CaCO3溶解能力的大小,所不同的是,就数值上来讲,Ps比Ks更大,同时也更接近水样的实际情况。当CO2浓度为大气中平均水平时,即
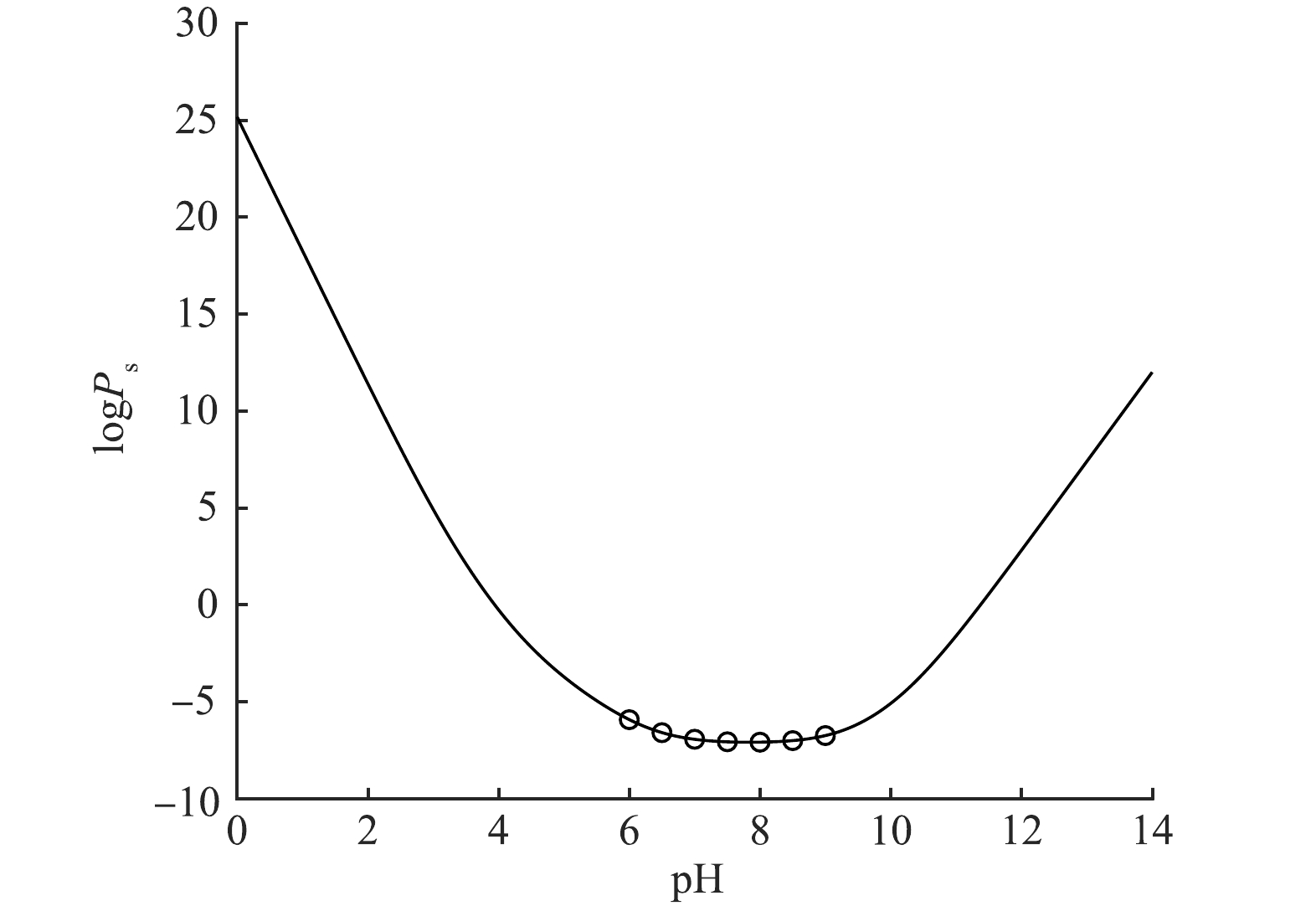
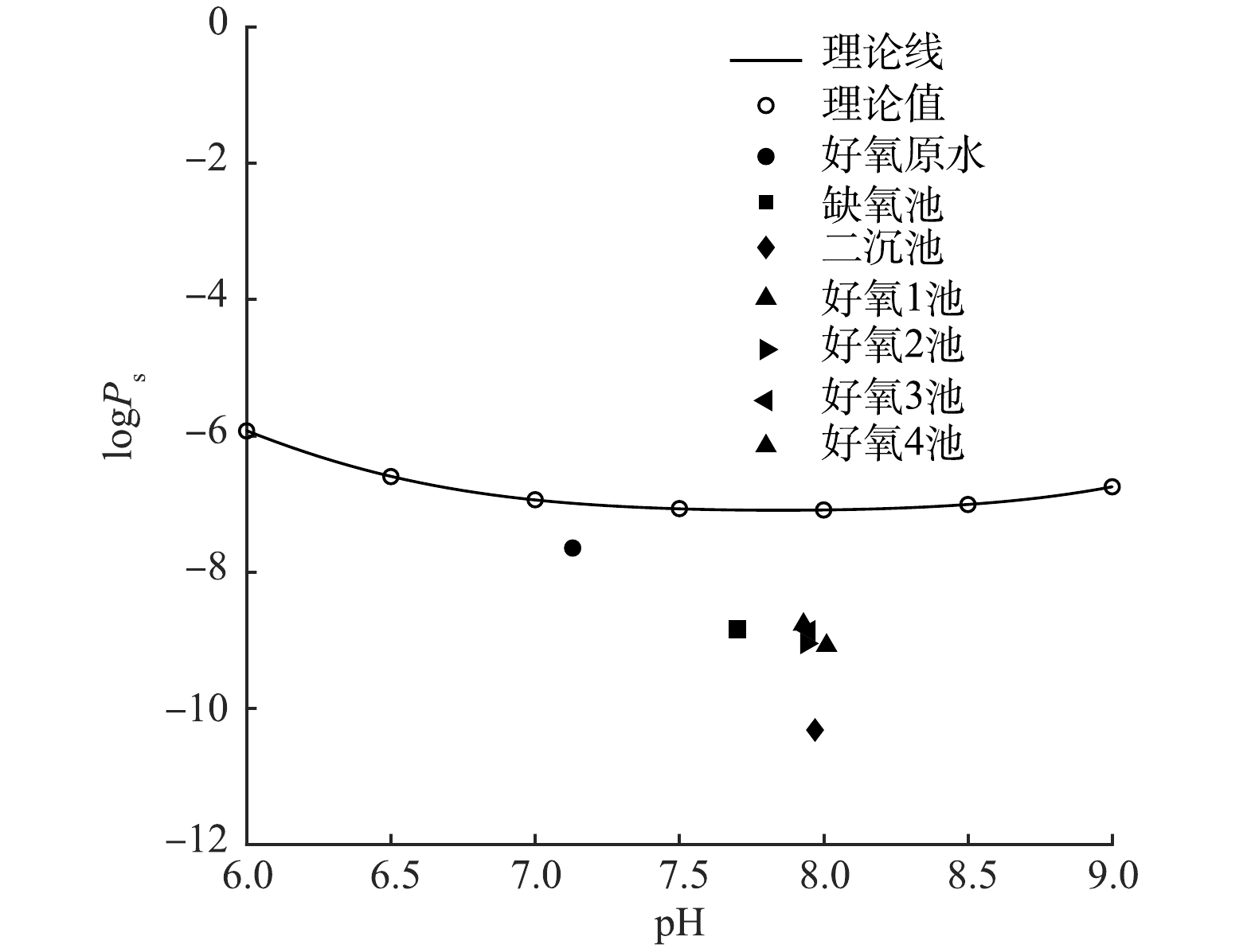
${{P}}_{{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{2}^{\mathrm{*}}}={10}^{-4.5}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a}$ ,代入式(5)中,作logPs — pH图,结果如图5所示。由图5可知,在与大气相通的体系中,当溶液pH为8左右时,logPs值最小,Ps也最小。为更好了解条件溶度积在pH=8附近的变化情况,在pH=6~9内取不同的pH,代入式(6),计算出相应的CaCO3条件溶度积的值,如表3所示。
结合图5和表3可以看出,pH在7.5~8.5时,Ps值最小,且最小值在8附近,说明在
${P}_{{\mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}}_{2}^{\mathrm{*}}}={10}^{-4.5}\mathrm{M}\mathrm{P}\mathrm{a}$ 条件下,CaCO3在pH为8左右时的溶解度最小,此时容易生成沉淀。根据好氧处理单元各工艺段的pH、Ca2+浓度以及IC浓度等数据,可以计算出实际废水的条件浓度积,将其与该pH范围内理论上的条件溶度积进行对比,相应结果如图6 所示。由图6可以看出,实际废水好氧处理段的数据值均位于理论曲线的下方,即实际水样中的“条件浓度积”并未超出理论上的“条件溶度积”,这一结果在一定程度上解释了废水中钙离子能够保持较高浓度的原因,即在该pH条件下碳酸钙的Ps较大,没有明显的CaCO3沉淀生成。比较好氧处理单元各取样点的计算结果,由图6可知,好氧池原水Ps最接近其理论计算曲线,各个曝气池位置居中,而二沉池Ps距离曲线最远,这表明好氧原水的钙沉淀趋势最明显最容易沉淀,而二沉池中钙含量最低系统最稳定钙沉淀不容易继续发生。这与也实际情况相符合。
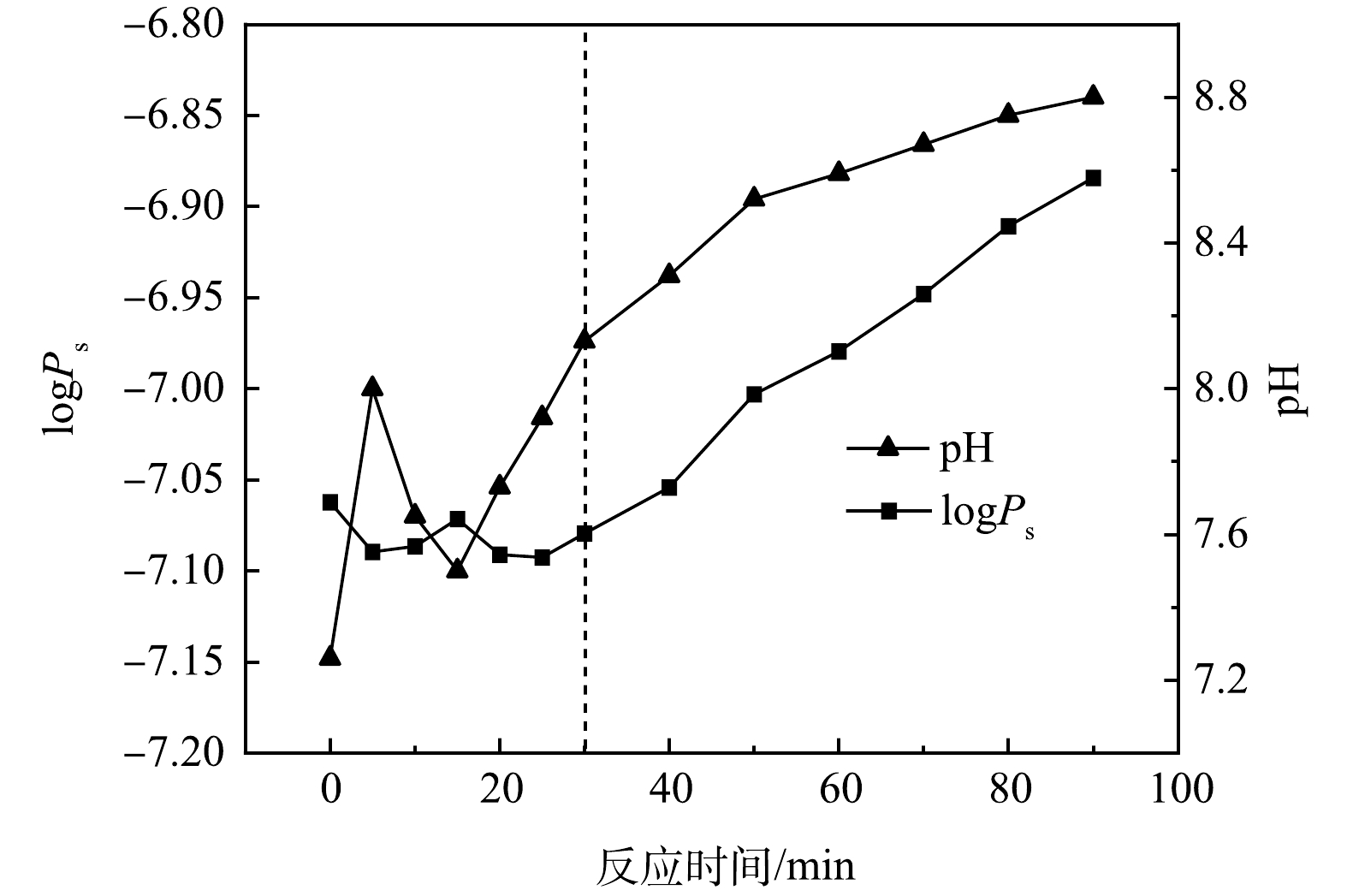
好氧原水曝气过程中的条件溶度积变化如图7所示。由图7可以看出,曝气的前30 min内pH在7.5~8.5,条件溶度积值在最小值附近,此时最有利于的钙沉淀去除。这一结果与图3(b)中好氧原水Ca2+质量浓度在曝气前段时间内下降速率较快相一致。随着曝气的进行,pH逐渐上升,条件溶度积也有所增大(图7)。
-
1)实际造纸废水好氧原水中钙离子含量高而不沉淀的原因是该pH条件下的碳酸钙条件溶度积较大。好氧原水的碳酸钙条件浓度积Ps最大,最接近理论计算曲线,钙沉淀最明显。
2)对好氧原水直接曝气可以促进碳酸钙沉淀,好氧原水曝气除钙过程是碳酸钙的过饱和溶液析出的过程,曝气过程中pH先上升后下降再上升的变化趋势与溶解性CO2气体的脱除和HCO3−的电离有关。
3) pH为7.5~8.5时碳酸钙的条件溶度积最小,此条件最有利于钙离子的沉淀去除。
基于碳酸钙条件溶度积理论的造纸废水好氧曝气除钙
Calcium removal by aerobic aeration of papermaking wastewater based on CaCO3 conditional solubility product theory
-
摘要: 造纸废水中较高的钙离子浓度会对废水处理带来很大挑战,为实现造纸废水中钙的有效快速去除,首先用条件溶度积理论分析了造纸废水钙离子浓度过高但不能及时有效沉淀的原因,然后结合模拟溶液和好氧原水曝气实验,探讨了造纸废水好氧段曝气除钙的pH变化机理,最后根据曝气过程中条件溶度积的变化情况探索了钙离子沉淀的有利条件。结果表明,好氧原水的碳酸钙条件浓度积Ps最大,最接近理论计算曲线,好氧原水的钙沉淀趋势最明显且最容易沉淀。对好氧原水直接曝气可以促进碳酸钙沉淀,pH呈现出先上升后下降再上升的趋势,这是脱除CO2气体提高溶液碱性与溶液中生成碳酸钙沉淀增加酸性互相竞争的结果。条件溶度积计算表明,pH为7.5~8.5时碳酸钙条件溶度积处于较低值,溶解度最小,该条件有利于钙的沉淀去除。Abstract: High concentration of calcium ions is a big challenge for papermaking wastewater treatment. In order to remove calcium efficiently from papermaking wastewater, the problem that the Ca2+ concentration in papermaking wastewater is high and Ca2+ cannot effectively precipitate was analyzed based on the conditional solubility product theory at first. Through the aeration experiments of simulated Ca2+ solution and raw water, the pH change mechanism of the aeration calcium removal from the aerobic section of papermaking wastewater was then discussed. Finally, the favorable conditions for calcium ion precipitation were explored according to the variation of conditional solubility product during aeration. The results showed that the conditional concentration product of CaCO3 in aerobic raw water was the highest, and the closest to the theoretical calculation curve, indicating that the calcium precipitation trend of aerobic raw water was the most obvious and the easiest to occur. The direct aeration of aerobic raw water could promote the precipitation of calcium carbonate. The pH values of wastewater increased firstly, then decreased, and increased again. The characteristic pH peak was formed due to the competitive effect of both solution alkalinity rise from the release of CO2 and solution acidity rise from the carbonate precipitation during the aeration process. The conditional solubility product calculation of the aeration process showed that the conditional solubility product of calcium carbonate was relatively lower when the pH was at 7.5~8.5, and the solubility of calcium carbonate was the minimum, which was conducive to the removal of calcium precipitation.
-

-
表 1 好氧处理单元水质情况
Table 1. Characteristic of wastewater in the aerobic treatment unit
取样点 pH TDS/(mg·L−1) T/°C IC/(mg·L−1) Ca2+/( mg·L−1) 好氧原水 7.13 2 263 29.3 412.9 554.0 缺氧池 7.70 1 935 28.9 240.7 289.4 好氧1池 7.93 1 743 29.0 237.2 314.1 好氧2池 7.94 1 610 29.0 198.8 283.3 好氧3池 7.95 1 552 29.4 206.6 328.7 好氧出水 8.01 1 544 29.0 193.2 283.0 二沉池 7.97 1 585 29.2 96.5 163.9 表 2 好氧原水曝气过程中的IC与Ca2+含量
Table 2. Concentration of IC and Ca2+ in the aerobic raw water during aeration time
mg·L−1 时间/min IC Ca2+ 0 412.92 554.0 10 265.92 343.6 20 263.04 295.2 30 228.36 212.8 60 156.84 97.2 90 126.00 52.4 表 3 pH为6~9内CaCO3的logPs
Table 3. logPs of CaCO3 between pH 6 and 9
pH Ps logPs 6 2.80×10-3 -5.93 6.5 1.40×10-3 -6.6 7 9.71×10-4 -6.94 7.5 8.49×10-4 -7.07 8 8.34×10-4 -7.09 8.5 9.04×10-4 -7.01 9 1.20×10-3 -6.75 -
[1] YU H Q, TAY J H, FANG H. The roles of calcium in sludge granulation during UASB reactor start-up[J]. Water research, 2001, 35(4): 1052-1060. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00345-6 [2] BATSTONE D. J, KELLER J, BLACKALL L L. The influence of substrate kinetics on the microbial community structure in granular anaerobic biomass[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(6): 1930-1404. [3] PEETERS B, DEWIL R, LECHAT D, et al. Quantification of the exchangeable calcium in activated sludge flocs and its implication to sludge settleability[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 83: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2011.04.008 [4] XU DD, KANG D, YU T, et al. A secret of high-rate mass transfer in anammox granular sludge: “Lung-like breathing”[J]. Water Research, 2019, 154: 189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.039 [5] DENG S, BAI R, HU X, et al. Characteristics of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus mucilaginosus, and its use in starch wastewater treatment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 60(5): 588-593. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1159-5 [6] 朱哲, 李涛, 王东升, 等. Ca(Ⅱ)在活性污泥生物絮凝中的作用研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(4): 612-616. [7] 张海丰, 王斌. 钙离子对MBR污泥混合液及膜污染层影响研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(4): 1144-1149. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2016.04.026 [8] PAULA B, FRANK V, HENK V, et al. Potential of mechanical cleaning of membranes from a membrane bioreactor[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 429: 259-267. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2012.11.061 [9] 战晓慧, 张辉, 张小红, 等. 废纸造纸废水化学沉淀法除钙研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(12): 1484-1490. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.12.009 [10] 张辉. 化学沉淀法去除造纸废水钙污染物的工艺研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. [11] 季斌, 陈威, 樊杰, 等. 产脲酶微生物诱导钙沉淀及其工程应用研究进展[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2017, 53(1): 191-198. [12] 陈逸帆, 张弛, 王书月, 等. 生物矿化促进造纸废水好氧除钙的技术研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 922-929. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0395 [13] 徐敬, 李杰. CO2释放对碳酸钙过饱和溶液析晶过程的影响[J]. 同济大学学报 (自然科学版), 2004(9): 1173-1177. [14] 朱志平. 水处理中最小碳酸钙溶解度的预测[J]. 水处理技术, 1992(5): 58-63. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.1992.05.011 [15] PATRICK H. Kinetics of CO2 stripping and its effect on the saturation sate of CaCO3 upon aeration of a CaCO3-CO2-H2O system: Application to scaling in the papermaking process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011(50): 13655-23661. [16] 崔明启, 张弛, 陈逸帆, 等. 造纸废水曝气池中钙的去除及迁移转化规律研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(6): 2128-2135. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0499 [17] 刘再华, 韩军, 李华举, 等. CaCO3-CO2-H2O岩溶系统的平衡化学及其分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2005(1): 3-16. [18] 汪惠阳, 李超群, 林金清. CO2脱除法提高废水pH值的研究现状[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2010(8): 135-139. [19] ATEF K, MERIAM T. Effect of pH and temperature on calcium carbonate precipitation by CO2 removal from iron-rich water[J]. Water and Environment Journal, 2020, 34(3): 331-341. doi: 10.1111/wej.12467 [20] 郭方峥, 解林, 刘伟京, 等. 废纸造纸废水结垢原因及防治对策研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(12): 2750-2754. -




 下载:
下载: