-
随着工业技术的进步,工业废水污染问题日益严重。化工、电镀、印染等行业产生的工业废水中常含有较高浓度重金属离子,对人类健康和环境造成危害。如人体铜离子摄入过量,会导致肝脏器官受到损伤[1]。过量汞离子的摄入,会影响人体的中枢神经系统[2]等。因此,采用适宜的技术去除废水中的重金属离子,控制水体中有害重金属离子的含量,已经成为现阶段我国处理工业废水最严峻的挑战之一。
聚丙烯腈(PAN)膜具有成本低,易制取、化学性质稳定等优点,作为吸附剂在重金属废水处理领域应用广泛。为提高PAN膜对重金属离子的吸附性能,研究人员采用多种材料对其进行修饰改性,如壳聚糖、金属硫化物、磁性材料等[3-4]。其中金属硫化物中MoS2纳米材料具有三层原子层堆叠形成的类石墨结构,有比表面积大、表面带电性等特点,在PAN膜进行改性修饰中得到研究人员的认可。但采用MoS2改性后的PAN吸附膜对重金属离子的吸附容量达到100 mg·g−1以上却鲜有报道[4,5],膜的吸附容量仍有待提高。GO是一种比表面积大,含氧官能团(羧基、羟基、羰基、环氧基等)丰富的材料,在材料改性领域得到广泛的应用[6-7]。较大的比表面积,有利于容纳更多的重金属离子,其丰富的含氧官能团,经水解反应呈现出负电性,可提供大量吸附活性位点,通过静电作用、螯合作用、π-π共轭作用对重金属离子进行吸附,可极大提高膜对重金属离子的吸附性能[8-9]。本研究采用相转化法制备出以GO为改性材料的MoS2-PAN吸附膜,并对膜的相关性能及吸附过程进行了研究分析。
-
聚丙烯腈PAN(AR,Sigma-Aldrich);N,N-二甲基乙酰胺(DMAC)(AR,Wako);六水硝酸铜(AR,Thermo Fisher);氧化石墨烯(GO)(Sigma-Aldrich);柠檬酸氢二铵(AR,Wako);双环己酮草酰二腙(Wako);浓盐酸(AR,北京化工厂);氨水(AR,辽宁全瑞有限公司);钼酸铵(AR,Sigma-Aldrich);硫脲(Sigma-Aldrich);铜标液(Thermo Fisher);去离子水,实验室自制。
主要实验仪器:FA2204A型电子天平(Mettler Toledo);HJ-4A型数显恒温多头磁力搅拌器(巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司);356665型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Fairborn);JEOL-LV6500型扫描电子显微镜(日本电子);DL-1000D型超声振荡器(上海之信仪器有限公司);UV-7504型紫外-可见分光度计(Mettler Toledo);DXF-6065型真空干燥箱(上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂);PF-28型pH酸度计(Mettler Toledo);冷冻干燥机(Thermo Fisher);SL200B型接触角仪(Thermo Fisher);K-101型刮膜机(保定齐力恒流泵有限公司)。
-
取相应固含量的GO(GO固含量为0.005%~0.05%(质量分数),固含量差值为0.005%)加入到20 mL DMAC中,超声24 h,使GO完全分散到DMAC中;另取1 g MoS2加入到20 mL DMAC中,超声1 h,使之完全分散在DMAC中;称取18 g的PAN粉末放入锥形瓶中,倒入上述2种分散液并加入DMAC溶液至100 g。将锥形瓶用保鲜膜封好,浸泡于电恒温水浴锅中,插入电动搅拌器,在70 ℃下充分搅拌24 h制成铸膜液,待搅拌结束后,取出搅拌棒,将锥形瓶口用保鲜膜封好,静置12 h,再将铸膜液缓慢倒在洁净的玻璃板上,使用刮膜机刮制成膜,并将其放置到装有去离子水的凝固浴中24 h,使膜的一级相变、凝固及溶剂的析出过程充分进行,制得GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜。
-
1)仪器表征:采用扫描电子显微镜对GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的截面形貌进行观察,以达到了解其微观结构的目的;采用傅里叶红外变换光谱仪对吸附膜的表面官能团进行分析,研究改性吸附膜的复合情况;利用接触角仪采用静滴法测量GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的亲水性,以此研究不同GO固含量的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜亲水性变化规律。
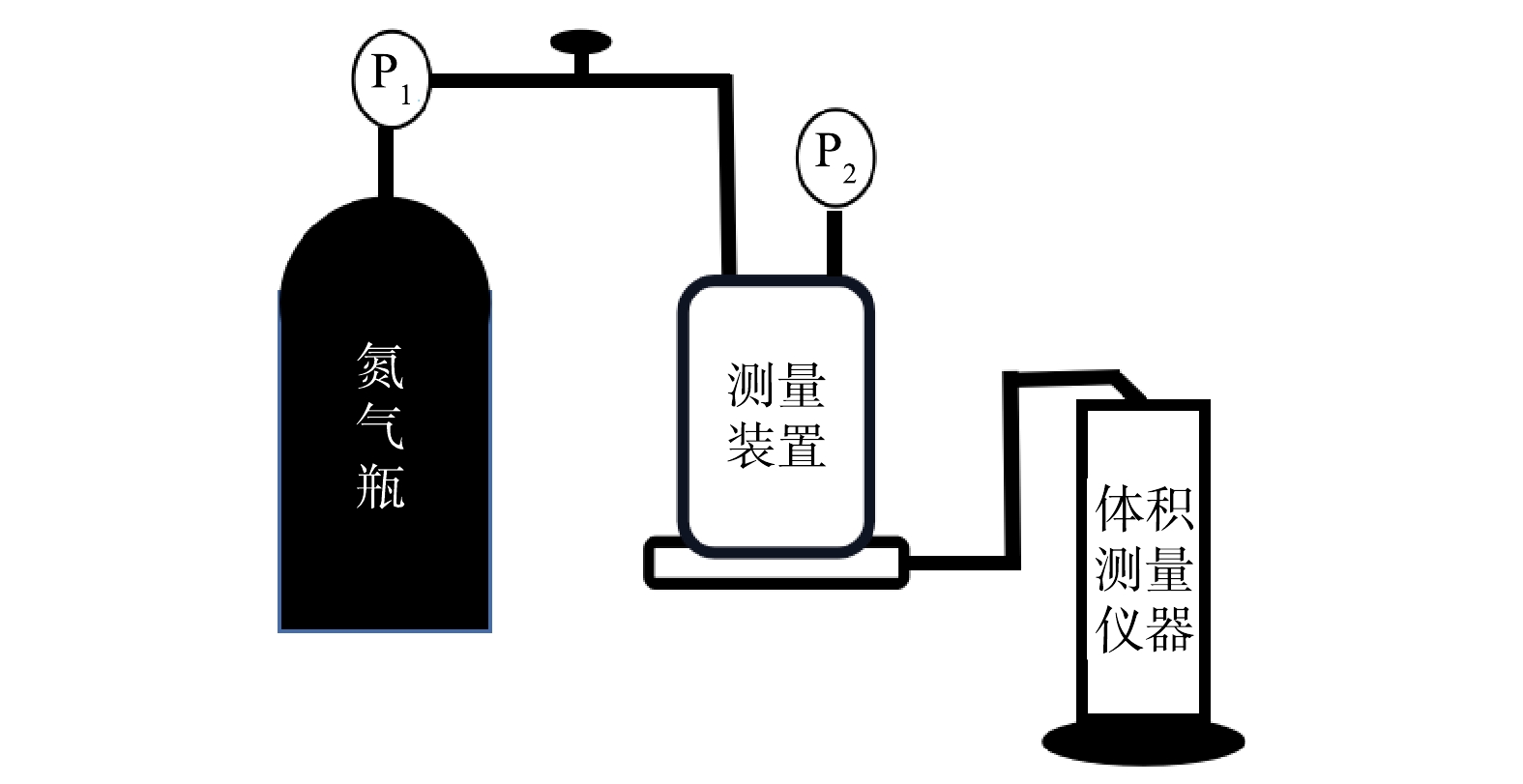
2)膜纯水通量测试:将直径为5 cm的圆形改性吸附膜置于测量装置中,调节氮气罐出口减压阀,使其出口压力P1稳定维持在0.1 MPa,并按照图1将各纯水通量测试装置连接。当测试杯中的压力P2稳定在0.1 MPa时,开始计时,并准确记录流出一定体积纯水时所需时长,根据式(1)计算出膜纯水通量。
式中:V为透过纯水的体积,L;A为膜的有效面积,m2;F为膜纯水通量,L·(m2·h)−1;t为取样时间,h。
3)膜孔隙率测试:将改性吸附膜裁剪成3 cm×3 cm的正方形,置于去离子水中1 h使其充分浸湿,取出后除去其表面水滴,并称量膜的湿质量及测量其厚度。将膜放入真空干燥箱干燥,干燥温度70 ℃,时长8 h。取出称量得到改性吸附膜的干质量,并计算膜孔隙率。根据式(2)计算膜孔隙率。
式中:Vr为膜的孔隙率,%;W1为湿膜质量,kg;W2为干膜质量,kg;ρ为水的密度,kg·m−3;A为膜的有效面积,m2;δ为膜的厚度,m。
-
将pH调为所需值的100 mL Cu2+溶液,与一定质量的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜置于烧杯中。在恒温振荡器以100 r·min−1振荡相应0~270 min(时间间隔为30 min),待吸附完成后,取上清液并测量其Cu2+浓度,重复进行3次,根据式(3)计算改性吸附膜对Cu2+的平衡吸附量。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;C为溶液初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ct为平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液的体积,L;m为膜的质量,g。
-
准备浓度为0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1的稀HCl溶液各100 mL,并按照1.4中实验方法对改性吸附膜进行静态吸附实验。待上述实验完成后,将改性吸附膜与Cu2+溶液进行过滤分离,并擦去膜表面液体。将改性膜置于相应浓度HCl溶液中,恒温振荡12 h,用去离子水对改性膜进行洗涤,采用双环己酮草酰二腙法测定[9]并计算HCl溶液与洗涤液中Cu2+浓度,计算出脱附率。
-
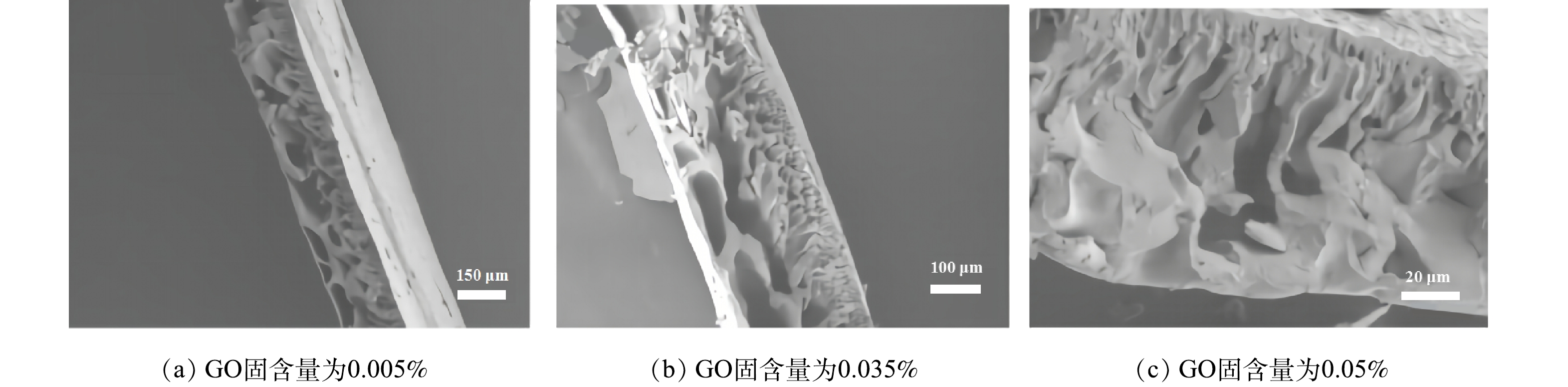
1) SEM分析。图2为不同GO固含量下制备的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜横截面SEM图。由图2可知,改性吸附膜均有狭小孔道的致密层与大孔径的多孔亚层不对称结构。当GO固含量较低时,膜孔径分布不均匀,且致密层较厚,膜孔道不平整,膜孔道贯通性效果差,当随着GO固含量的增加,膜的多孔亚层通道尺寸增加,膜孔道贯通性增强。这是由于GO具有较强的亲水性,随着GO的添加,在制膜过程中促进了铸膜液与凝固浴的交换速度,有效的缩短了铸膜液的相变时间,使膜孔道分布均匀且贯通性提高[10-11],有利于提高吸附膜与溶液中吸附质的有效接触及传质效率[12-13]。
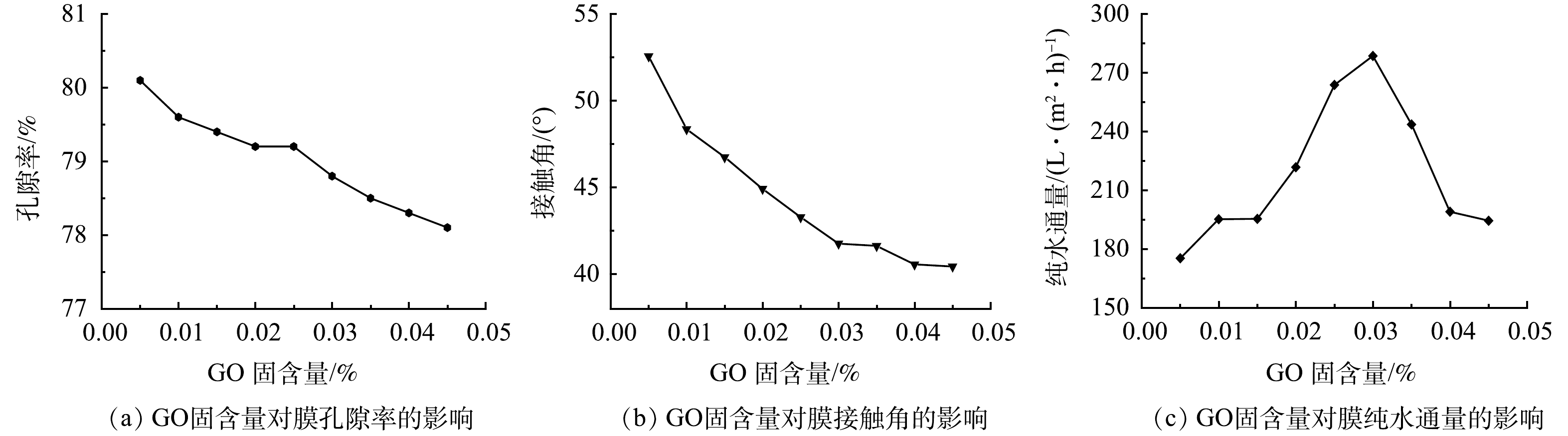
2)孔隙率、接触角及膜纯水通量分析GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的孔隙率、接触角和纯水通量分别如图3(a)~(c)所示。由图3(a)可看出,随着GO的加入,使得GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的孔隙率出现缓慢降低的趋势。该现象是由于GO与含有疏水基团C≡N的PAN相比,其亲水性较强,且GO具有较大的比表面积。在铸膜过程中,GO易向与水接触的膜孔道表面运动,进而导致膜致密顶层的狭小孔道被占据,致使孔隙率出现了该种变化趋势[11]。
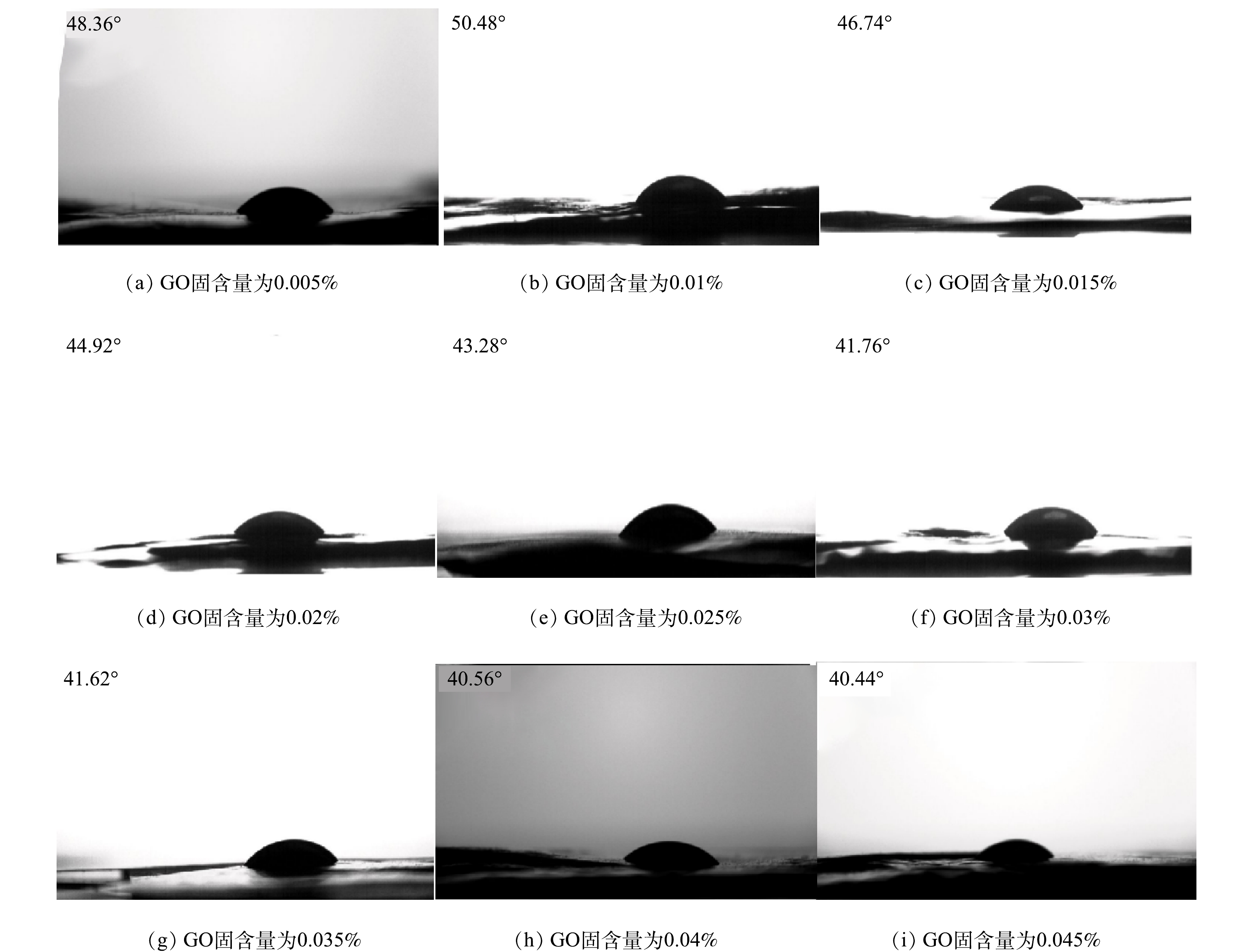
由图3(b)和图4可知,随着GO固含量的增加,GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的接触角逐渐减小。说明GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的亲水性增大。该现象是由于GO固含量的增加,改性吸附膜中的引入的亲水基团增加,使改性吸附膜亲水性得到了增强[6]。
膜的纯水通量与GO固含量的变化关系如图3(c)所示。随着GO固含量的增加,膜的纯水通量呈现出先增大后减小的趋势。出现该种变化规律是由于GO固含量的变化,使得GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的亲水性能及膜内部孔道结构出现了变化。GO固含量小于0.03%时,膜的亲水性增强为主要影响因素,孔隙率虽有所减小,但其纯水通量仍急剧增加。GO固含量大于0.03%时,由于出现GO在膜顶层孔道中的堆积,使膜孔道贯通性下降,进而出现即使孔隙率变化较小但膜纯水通量下降。因此,合理控制GO固含量可有效提高膜的亲水性及膜的纯水通量,使膜在对废水处理时提高吸附剂、吸附质及溶液之间的传质速率,从而有效提高水处理效果。
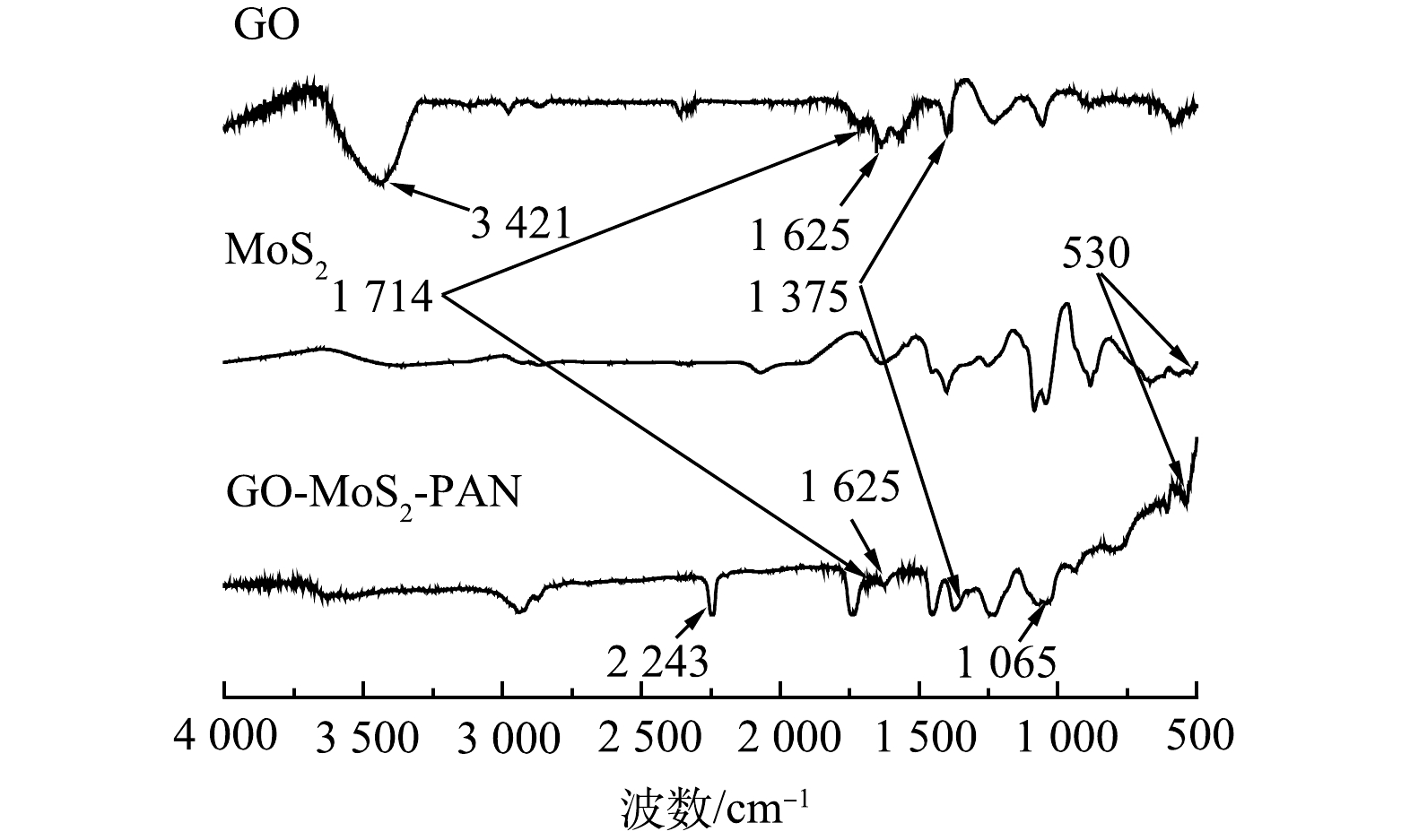
3) FTIR分析。傅里叶红外光谱对GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的结构进行了表征结果如图5所示。分析图谱可知,改性吸附膜的谱图在2 243 cm−1出现了PAN中C≡N的特征吸收峰。由于MoS2的存在,同时在530 cm−1处出现Mo—S的特征吸收峰,且在1 065 cm−1出现S=O的特征峰[4,12],表明改性吸附膜中成功的引入了MoS2,同时部分S原子与氧化基团中的O原子发生了反应。改性吸附膜材料中成功引入GO,可从谱图在1 375、1 625、1 714 cm−1处分别出现GO的C—O官能团、C=O官能团及其芳香环结构中的C=C特征吸收峰得到证实[11,13]。但GO在3 421 cm−1处O—H的特征吸收峰未在改性吸附膜谱图中明显体现,可能是由于GO固含量较低,在膜中分散度较高所致[7]。在GO-MoS2-PAN复合膜的红外谱图上出现的各特征吸收峰,表明MoS2、GO和PAN经过共混过程后,成功制备出了GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜。
-
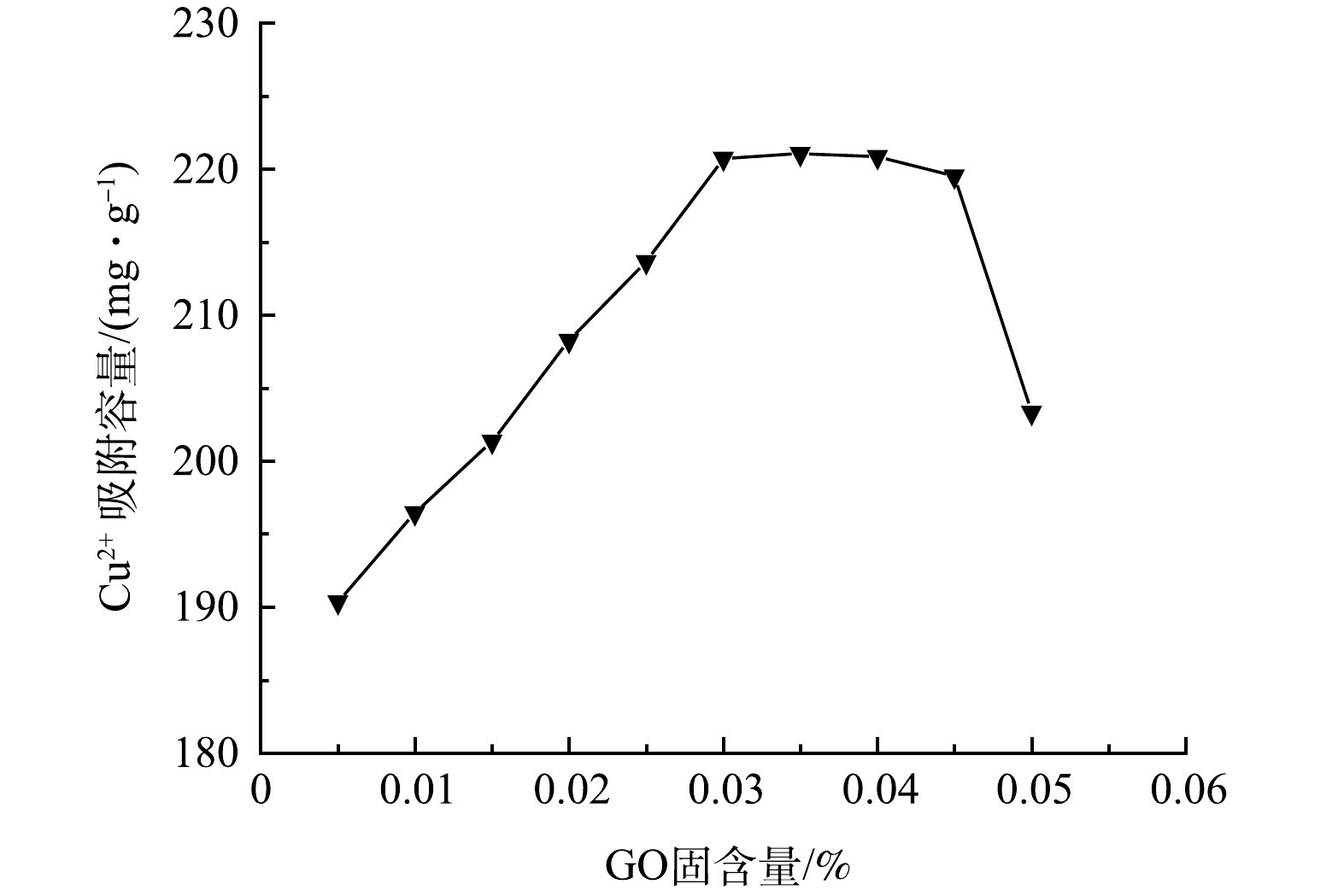
配制一定量初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的Cu2+溶液于烧杯中,将10种不同GO固含量(GO固含量为0.005%~0.05%,梯度差值为0.005%)的改性吸附膜分别称取0.05 g于烧杯中,在室温下恒温磁力搅拌180 min,得到改性吸附膜的平衡吸附量。由图6可知,吸附量在GO固含量为0.005%~0.03%时,随着GO固含量的增加平衡吸附量接近线性增长。当GO固含量大于0.03%时,随GO固含量的增加平衡吸附量基本趋于稳定,当GO固含量大于0.045%时,改性吸附膜的平衡吸附量迅速下降。出现该变化趋势是由于在GO固含量较低时,GO的引入使改性吸附膜的亲水性能提高,膜的多孔亚层厚度变大,有效促进了吸附剂与吸附质在溶液中的离子传递效率,同时引入的GO提供了可有效吸附Cu2+的活性位点及吸附表面,进而提高了改性吸附膜的平衡吸附量[8]。GO固含量达到一定比例后,GO对膜的内部结构造成了一定影响,孔隙率、膜的纯水通量下降,导致有效吸附面积变小,吸附活性位点不能得到有效利用,进而出现GO固含量占比达到一定数值后平衡吸附量下降的现象,该变化趋势与孔隙率及膜纯水通量的变化规律相关。
-
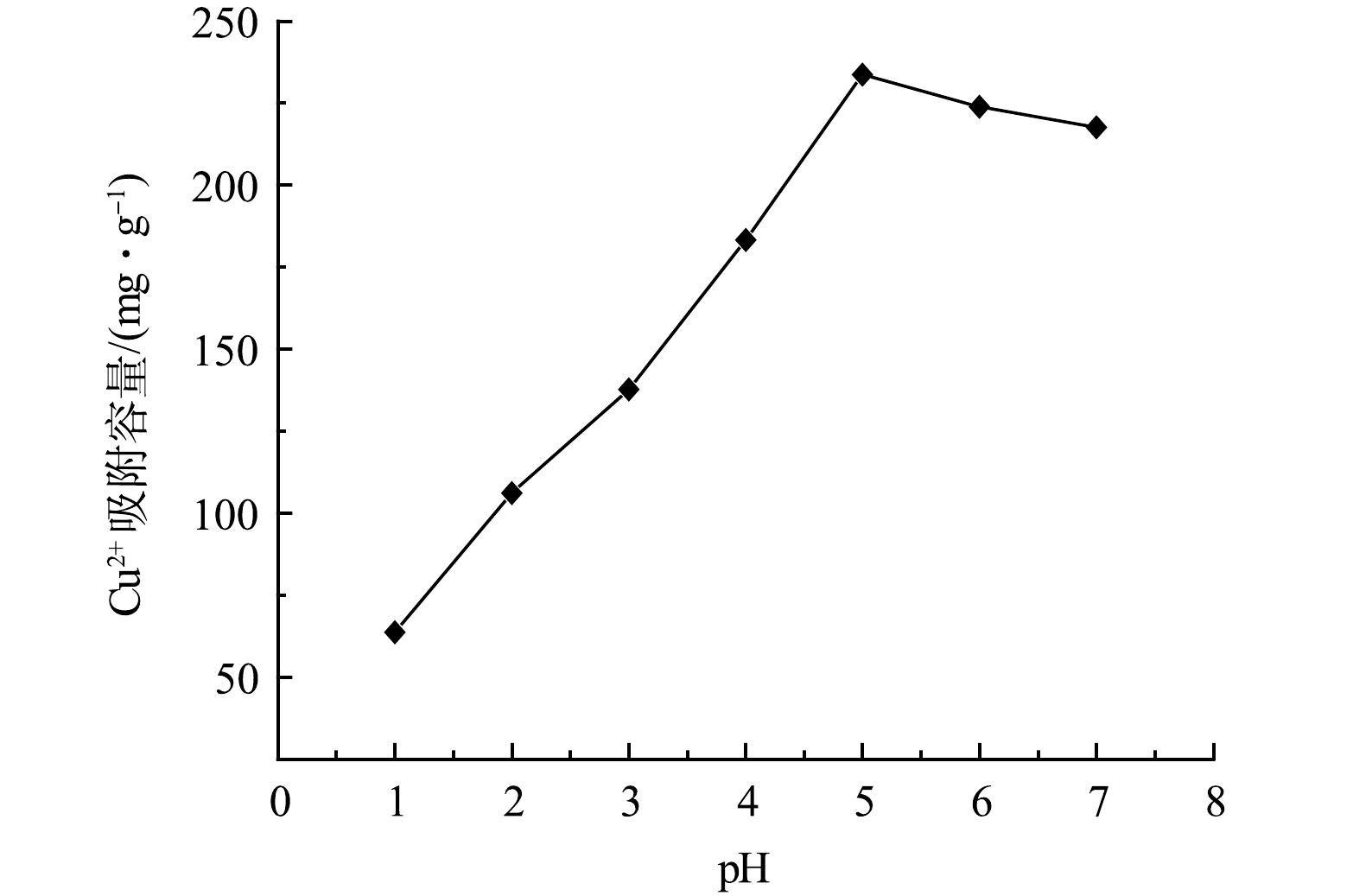
由2.2节结果可知,GO固含量为0.03%的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附量最大。选取该GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜进行pH对Cu2+的影响研究。配制一定量初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的Cu2+溶液于烧杯中,调整溶液的pH分别为1、2、3、4、5、6、7,分别称取0.05 g吸附膜材料于烧杯中,在室温下恒温磁力搅拌3 h,得到吸附膜的平衡吸附量。如图7所示,pH在1~5内逐渐增加,改性吸附膜的吸附能力逐渐增强,pH为5时平衡吸附量达到最大值。继续增大pH,呈现出下降的趋势。出现上述变化规律是由于pH的不同对膜表面官能团状态产生影响,较低的pH可使部分官能团质子化而带正电荷,对溶液中的金属阳离子产生静电排斥作用,影响吸附的传质过程[14]。同时溶液中的游离H+与Cu2+在与吸附剂相结合时,两者存在竞争关系,影响改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附能力[15-16];pH的逐渐增大,使得溶液中H+含量下降,对Cu2+的吸附过程干扰降低。当pH继续增大时,溶液中的Cu2+与水中的OH−发生反应,并以沉淀的形式析出,影响改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附[5]。
-
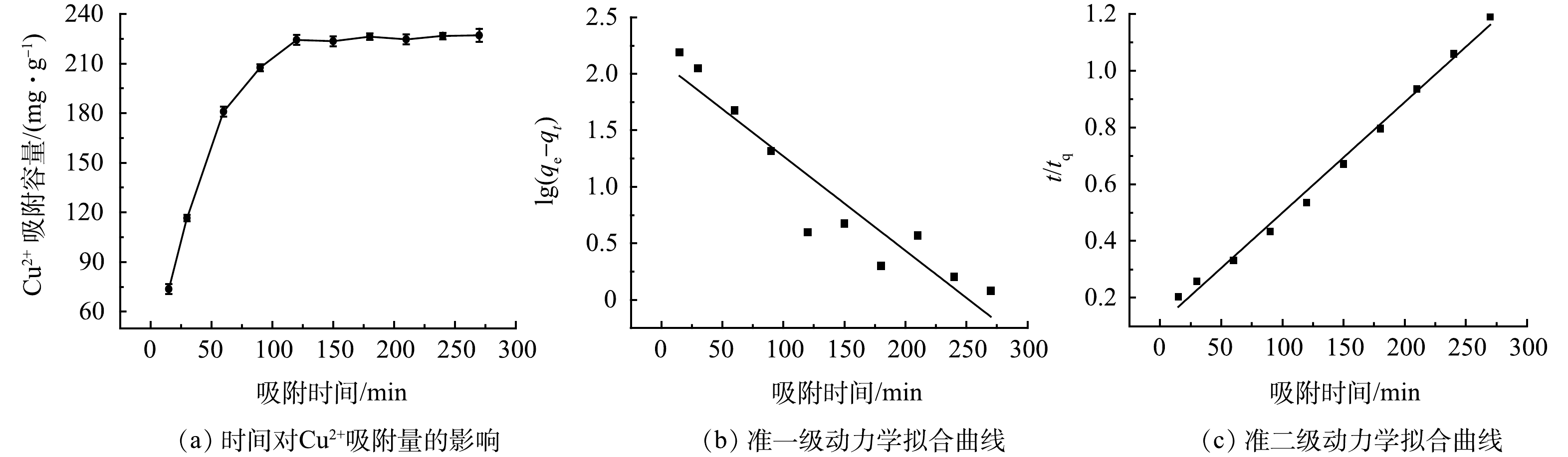
选取GO固含量为0.03%的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜,分别称取8份0.05 g备用。配制200 mL,pH为5,初始质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的Cu2+溶液于烧杯中。将改性吸附膜分别置于溶液中,调整改性吸附膜的吸附反应时间(时间为30~240 min,时间变量为30 min),分别计算不同吸附时长下的平衡吸附量,得到如图8(a)所示的曲线。由图8(a)可知,随着吸附时间的增长,改性吸附膜的平衡吸附量在出现先快速增加后趋于稳定。且当吸附时长为120 min时,改性吸附膜对Cu2+的最大平衡吸附量达到224.28 mg·g−1。出现上述变化趋势主要是因为吸附膜表面的活性位点数量一定,当达到吸附饱和后,随着时间的增长,平衡吸附量不再增加,达到最大平衡吸附量[17]。
利用准一级动力学模型(式(4))与准二级动力学模型(式(5))分析改性吸附膜的吸附动力学。
式中:qt为膜在t时刻的吸附量,mg·g−1;qe为膜平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;Kf1为准一级反应速率常数,min−1;Kf2为准二级反应速率常数,mg·(g·min)−1;t为取样时间,h。
通过对两种动力学模型拟合,得到改性吸附膜准一级、准二级动力学拟合参数,如图8(b)、8(c)。其中准一级和准二级动力学模型拟合得到的反应速率常数Kf1为0.019 2 min−1和Kf2为1.39×10−4 mg·(g·min)−1,平衡吸附量qe分别为127.46 mg·g−1和256.41 mg·g−1,可决系数R2分别为0.882 1和0.993 1。对比不同动力学模型的决定系数可以发现,准二级动力学模型的决定系数较高,说明该吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附过程符合准二级动力学模型[18]。
-
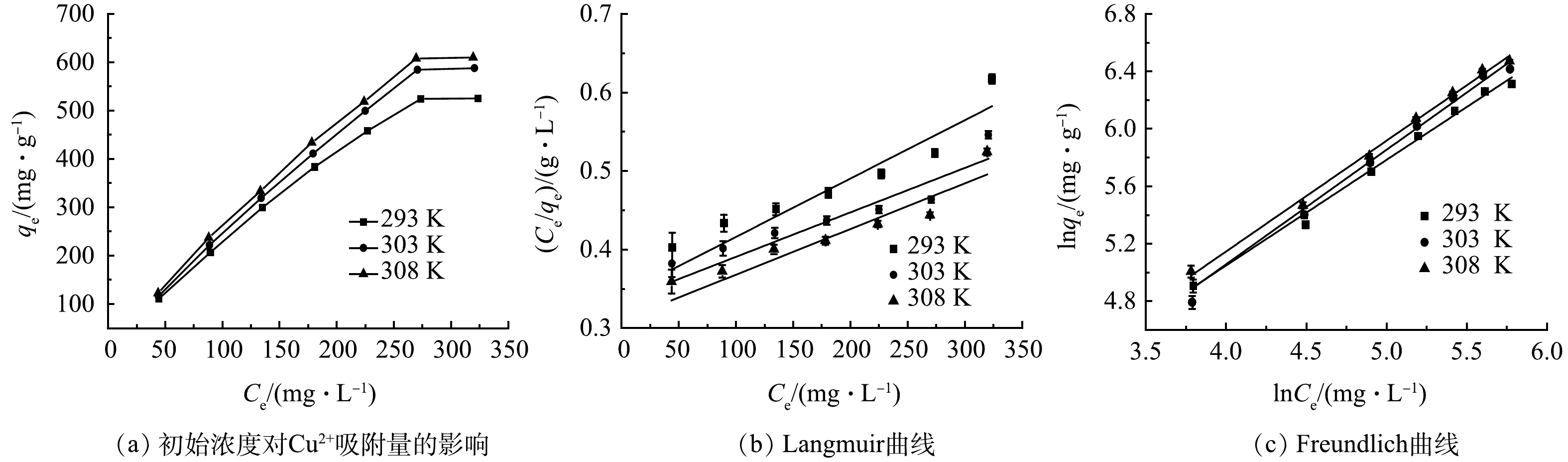
取质量浓度分别为50、100、150、200、250、300、350 mg·L−1、的Cu2+溶液100 mL于烧杯中进行吸附,调整pH为5,并分别在293、303、308 K下恒温振荡150 min后得到如图9(a)的相应变化趋势。在不同温度下,改性吸附膜的吸附量均呈现为随Cu2+质量浓度增大而增大,当Cu2+达到一定浓度后,吸附量趋于稳定的趋势。这主要是由于随着质量浓度的增大,溶液中自由移动的Cu2+与膜上吸附活性位点接触机会增多,更有利于膜的吸附作用[19]。且当Cu2+质量浓度一定时,温度越高其吸附量越大,说明温度越高越有利于改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附。为了进一步研究改性吸附膜对Cu2+的等温吸附模型,分别进行了Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型进行拟合分析。Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型方程如式(6)和式(7)所示。
式中:Ce为金属离子的平衡浓度,mg·L−1;qe为膜平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为金属离子最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir常数,mg·L−1;n和KF为Freundlich参数。
图9(b)和图9(c)分别是改性吸附膜对Cu2+的Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型拟合曲线,表1为其吸附等温常数。通过对比Langmuir等温吸附模型与Freundlich等温吸附模型的决定系数R2值发现,不同温度下Freundlich等温吸附模型的决定系数值均高于Langmuir等温吸附模型的决定系数值,证明该吸附属于多层吸附,改性吸附膜的表面为异质结构[18]。
-
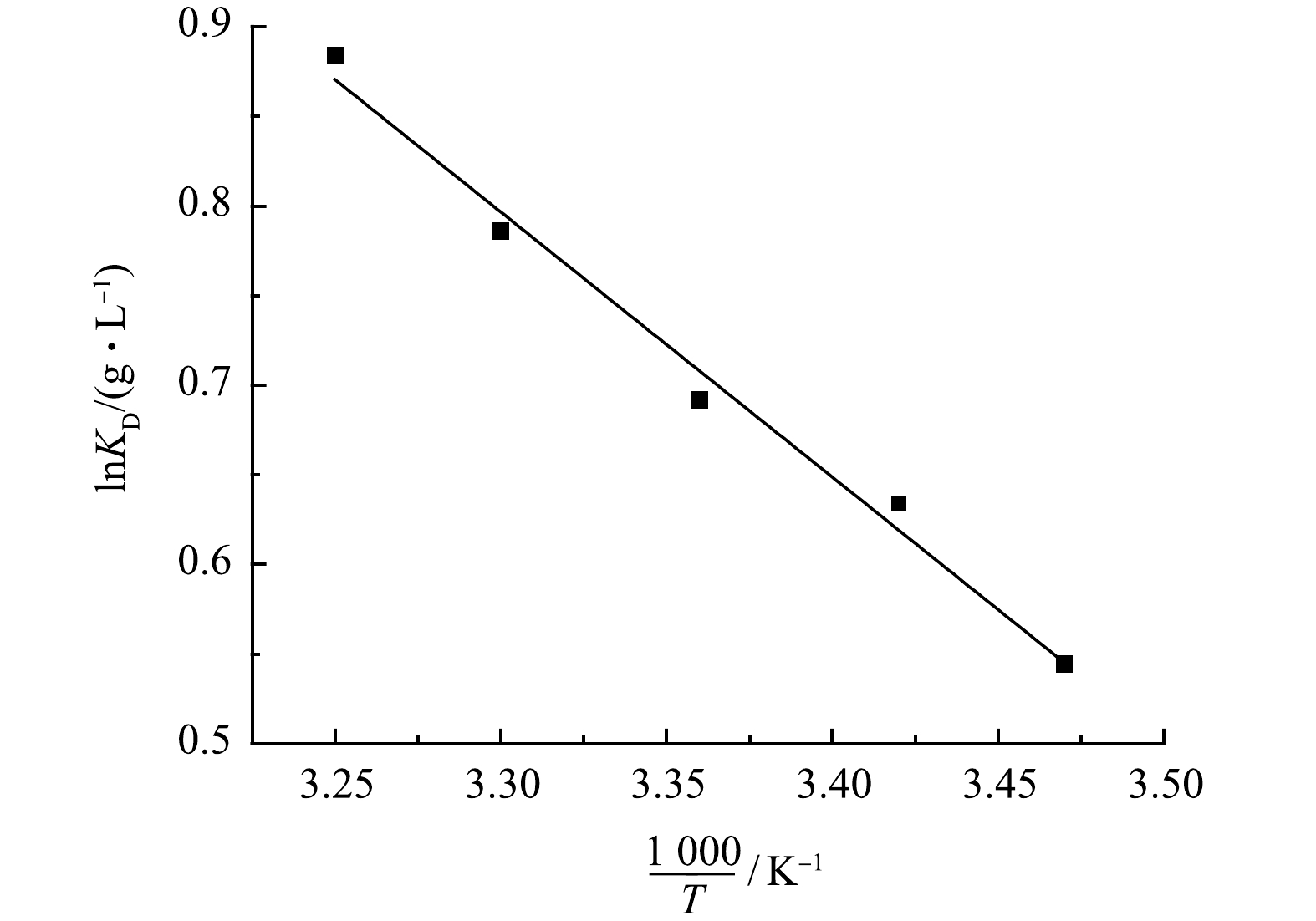
由图9(a)及等温吸附方程可知,随着溶液温度的升高,改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附性能有一定的提高,为了进一步研究其对Cu2+吸附的热力学过程,利用热力学参数进行了理论说明[19]。热力学参数计算根据式(8)~式(10)进行计算。
式中:ΔG为吉布斯自由能变,kJ·mol−1;R为理想气体常数kJ·(mol·K)−1;T为温度,K;ΔS为熵变,J·moL−1;ΔH为焓变,kJ·moL−1;qe为膜平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为金属离子的平衡浓度,mg·L−1。
由图10吸附热力学曲线及表2中相关热力学参数可知,当温度由288 K升高到308 K时,ΔG的值由−1.3 kJ·mol−1减小至−2.26 kJ·mol−1。表明温度的升高促进了改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附,温度越高更有利于吸附反应的进行。吸附反应器焓变ΔH值、熵变ΔS值均为正数,说明该吸附反应为吸热反应,且随着温度升高,溶液的自由度升高,说明该反应是一个吸热的自发反应[19]。
-
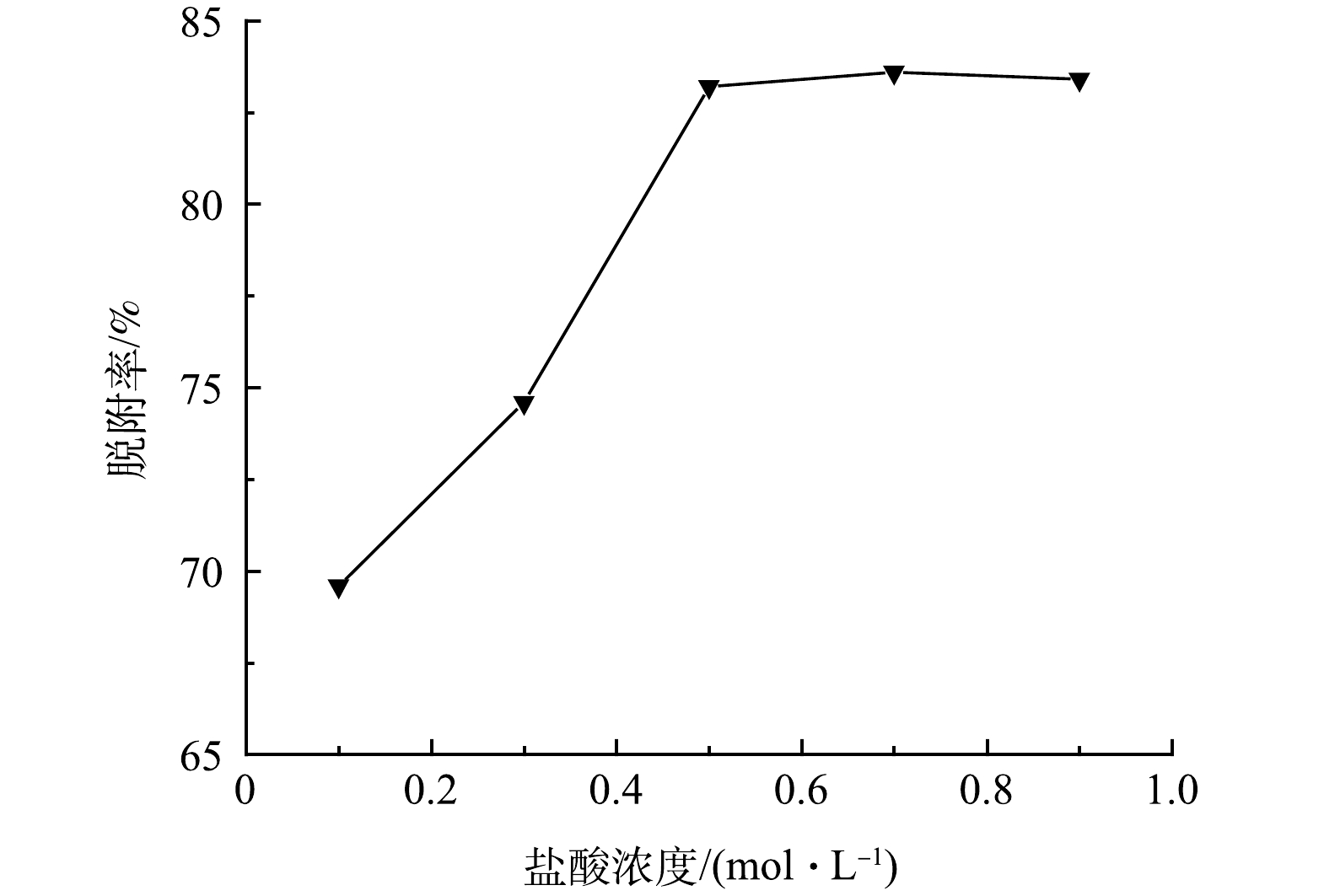
为研究GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的脱附性能,分别取浓度为0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1的稀HCl溶液对吸附后的GO固含量为0.03%的改性吸附膜进行脱附处理,脱附结果如图11所示。结果表明,随着HCl溶液浓度的升高,改性膜的脱附率迅速增大后趋于平稳。这是由于在浓度较低的时候,H+浓度与膜上活性位点接触的概率较低,发生竞争吸附的概率也随之降低,脱附效果相对较差,随着浓度的继续升高,当浓度达超过0.5 mol·L−1后,脱附率达到最大值,当继续增大浓度,脱附率无明显上升,脱附率基本维持在84%。
-
1) GO的合理添加,使GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜对Cu2+的吸附容量得到显著提高,在GO固含量为0.03%,溶液pH为5,吸附温度为35 ℃时,改性吸附膜对Cu2+平衡吸附量达到224.28 mg·g−1,且其在一定浓度的HCl溶液中脱附率可维持在84%。
2)改性吸附膜对Cu2+吸附过程的动力学数据分析表明,其符合准二级动力学模型,其等温吸附模型更符合Freundlich等温吸附模型,改性吸附膜表面为异质结构。
3)改性吸附膜对Cu2+吸附过程的的热力学数据表明,该吸附是自发吸热过程。
氧化石墨烯修饰MoS2-PAN吸附膜对铜离子吸附性能的影响
Adsorption performance of GO-MoS2-PAN membrane toward copper ions
-
摘要: 通过氧化石墨烯(GO)对硫化钼(MoS2)-聚丙烯腈(PAN)进行改性处理,采用相转化法成功制备了对水溶液中Cu2+进行吸附的GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜。通过扫描电镜(SEM)、傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)及接触角测试对该吸附剂材料进行了表征。探究了不同GO固含量对GO-MoS2-PAN改性吸附膜的孔隙率、纯水通量以及接触角的影响。在pH为5、Cu2+质量浓度为100 mg·L-1的溶液中,GO固含量为0.03%的改性吸附膜对Cu2+的最大平衡吸附量达到224.28 mg·g-1,且其脱附率为84%。结果表明,改性吸附膜对溶液中Cu2+的吸附动力学符合准二级动力学模型,等温吸附过程符合Freundlich等温吸附模型,热力学分析结果表明该吸附过程为自发吸热过程。Abstract: Molybdenum sulfide (MoS2)-polyacrylonitrile (PAN) was modified by GO, and GO-MoS2-PAN modified adsorbent membrane was prepared by phase inversion method for Cu2+ adsorption from aqueous solution. The adsorbents were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and contact angle test. The effects of different GO solid content on the porosity, pure water flux and contact angle of GO-MoS2-PAN modified adsorbent membrane were investigated. When the pH of solution was 5 and the mass concentration of Cu2+ was 100 mg·L−1, the maximum equilibrium adsorption capacity of the modified adsorption membrane with 0.03% solid content of GO toward Cu2+ was 224.28 mg·g−1, and its desorption rate was 84%. The adsorption kinetic data fitted well to the pseudo-second-order model, and the isothermal adsorption data fitted well to Frenudlich isotherm model. The thermodynamic analysis indicated that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic.
-
Key words:
- GO /
- modified adsorbent membrane /
- copper ions
-

-
表 1 吸附等温参数
Table 1. Adsorption isothermal parameters
T/K Langmuir Freundlich KL/(mg·L−1) qm/(mg·g−1) R2 KF n R2 293 2.15×10−3 1 362.76 0.835 6 8.202 1.36 0.980 5 303 1.69×10−3 1 766.44 0.759 1 6.475 1.25 0.979 4 308 1.88×10−3 1 719.40 0.795 5 7.844 1.29 0.986 9 表 2 相关热力学参数
Table 2. Relevant thermodynamic parameters
T/K ΔH/(kJ·mol−1) ΔS/(J·(mol·K)−1) ΔG/(kJ·mol−1) 288 − − −1.30 293 − − −1.54 298 12.19 46.86 −1.71 303 − − −1.98 308 − − −2.26 -
[1] YANG K, WANG G, CHEN X M, et al. Treatment of wastewater containing Cu2+, using a novel macromolecular heavy metal chelating flocculant xanthated chitosan[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 558: 384-391. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.06.082 [2] FANG L, LI L, QU Z, et al. A novel method for the sequential removal and separation of multiple heavy metals from wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 342: 617-624. [3] LI H, ZHOU F X. Efficient Adsorption of heavy metal ions by A novel AO-PAN-g-chitosan/Fe3O4 composite[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5: 8033-8039. doi: 10.1002/slct.202001965 [4] QIU J L, LIU F Q. Recyclable nanocomposite of flowerlike MoS2@hybrid acid-doped PANI immobilized on porous PAN nanofibers for the efficient removal of Cr(VI)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry Engineering, 2018, 6: 447-456. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02738 [5] 孙墨杰, 艾玉鑫, 王世杰. MoS2-PAN吸附膜对铜离子的吸附性能影响规律[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 8: 2497-2505. [6] SAIMA N, MARRIUM T. Treatment of textile wastewater containing acid dye using novel polymeric graphene oxide nanocomposites (GO/PAN, GO/PPy, GO/PSty)[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 14: 25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.007 [7] 田金光, 高小媛. 磁性氧化石墨烯材料的制备及其对重金属离子的吸附研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 11: 2812-2815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.11.031 [8] PEI J X, HUANG L. Inhibitory effect of hydrogen ion on the copper ions separation from acid solution across graphene oxide membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 209: 651-658. [9] BHARATH G, ALHSEINATl E, PONPANDIAN N, et al. Development of adsorption and electrosorption techniques for removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater using novel magnetite/porous graphene-based nanocomposites[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 188: 206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.024 [10] CHIMPALEE N, CHIMPALEE D. Thorburn Burns Flow-injection spectrophotometric determination of copper using bis( cyclohexanone) oxalyldihydrazone[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1995, 304: 97-100. doi: 10.1016/0003-2670(94)00564-3 [11] MOJTABA M, ABDOLREZA M. Fabrication of novel polyethersulfone based nanofiltration membrane by embedding polyaniline-co-graphene oxide nanoplates[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 33: 2674-2683. doi: 10.1007/s11814-016-0132-4 [12] WANG S J, QIN C. Enhanced supercapacitive performance of polyacrylonitrile derived hierarchical porous carbon via hybridizing with MoS2 nanosheets[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 40: 102695. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102695 [13] MOHAMED M. A, ALAA M. Preparation, characterization, and mechanical properties of polyacrylonitrile (PAN)/graphene oxide (GO) nanofibers[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2018, 26: 346-351. [14] ZHANG X F, YANG S J. Advanced modifed polyacrylonitrile membrane with enhanced adsorption property for heavy metal ions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 1260-1268. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19597-3 [15] LIN Y X, CAI W P, TIAN X Y, et al. Polyacrylonitrile ferrous chloride composite porous nanofibers and their strong Cr-removal performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(4): 991-997. doi: 10.1039/C0JM02334E [16] 杨焰. 氧化石墨烯功能材料的研制及其对铜、镍等离子吸附性能研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2017. [17] DENG S, YU C X, NIU J F, et al. Microwave assisted synthesis of phosphorylated PAN fiber for highly efficient and enhanced extraction of U(VI) ions from water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123815. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123815 [18] LIU D Y, NIU L L. Synthesis of poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-based dithiocarbamate magnetic composite for the adsorption of Co2+ from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Materials Science:Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30: 1161-1174. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-0385-2 [19] XU G, XIE Y, et al. Highly selective and efficient chelating fiber functionalized by Bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amino group for heavy metal ions[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2016, 7: 376-385. -



 下载:
下载: