-
我国城市化进程发展迅速,市政排水管网设施仍相对落后,雨污合流管道占主体部分,这让污水处理厂面临着高无机悬浮物进水冲击的问题。在雨季,地面沙土、空气扬尘都会随着雨水冲刷进入市政管网 [1-3],温度较高的冬天或初春温度升高后的雪融也会形成地表径流,造成城市污水携带大量悬浮物进入污水处理厂 [4]。另一方面,我国许多污水处理厂为保证曝气池内充足的碳源,取消了初沉池的设置[5-6],这使得大量悬浮物(SS)在曝气池内大量积累,导致活性污泥MLVSS/MLSS的比值大幅度下降,一定程度上降低了污水处理厂的处理效果,也增加了设备运行维护的难度[7-8]。
微压内循环生物反应器(micro-pressure swirl reactor,MPSR)是一种新型多生物相反应器,反应器顶部大部分密闭,空气从反应器底部一侧进入,反应器内部活性污泥混合液成循环流态,外围流速高,内圈流速低,增加了气泡的行程,提高了氧的传质效率[9];反应器内部能够形成不同的溶解氧(DO)分区,实现了同一空间不同功能菌群共同反应,达到了同步去除COD、氮、磷的效果[10],在目前实验室阶段研究发现[11-13] MPSR对碳、氮、磷的去除能力,尤其是反硝化能力强于SBR,在超长污泥龄(50、70、90 d)下仍然有较高的脱氮除磷效果,在污泥龄为90 d阶段,系统脱氮率在80%左右,除磷率在90%以上;在对MPSR进行单周期瞬时有机负荷冲击实验中发现,可以通过调控曝气量有效应对冲击,保证污染物去除效果;有研究[14]表明,当有机负荷从0.29 g·(g·d)−1增加到1.68 g·(g·d)−1后,MPSR对于COD的去除效率平均比SBR高出10~20%。
在实验室研究的基础上,本研究考察了中试规模MPSR工艺对长春某新区城市污水处理效果,探讨了高悬浮物对MPSR工艺中污染物的去除效果和污泥特性的影响,分析了反应器中微生物菌群结构的变化,以期为该工艺在城市污水的实际应用提供参考。
-
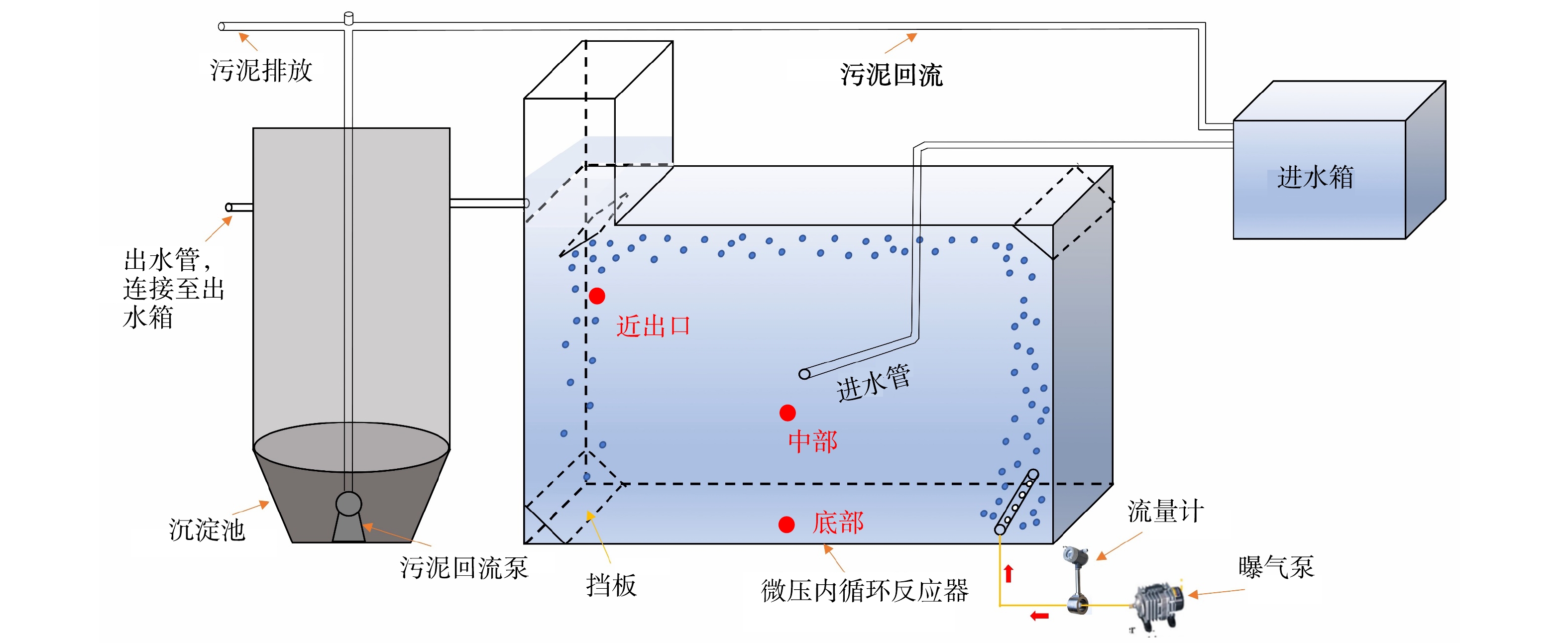
MPSR中试装置设置于长春某新区污水处理厂,工艺组成由图1所示。装置主要包括进水池、MPSR和沉淀池,总占地面积36 m2。其中,MPSR分为主反应部位和液位提升部位,主体反应部位长、宽、高为600、400、400 cm,顶部的液位提升部分长、宽、高为100、100、120 cm,总有效容积为96 m³。
污水由进水池经潜污泵提升进入主反应器中心区域,采用膜片式微孔曝气器在反应区底部单侧曝气,空气由回转式鼓风机供给。沉淀池底部设有回流泵,回流污泥与进水混合后进入主反应器。整个工艺的运行情况和控制单元由PCL中控系统进行监测与控制。
-
中试实验装置进水为长春某污水处理厂平流式曝气沉砂池出水。接种污泥取自该污水处理厂生化池好氧区,经过23 d运行反应器出水指标基本稳定,确定运行控制参数如下:进水量10 m3·h−1,MPSR水力停留时间(HRT)9.6 h,曝气量为30 m³·h−1,污泥回流比75%,污泥龄(SRT)为30 d。实验装置稳定运行共计450 d,根据进水水质特征可分为4个阶段:阶段I为稳定进水,阶段II为波动进水,阶段III为高SS进水,阶段Ⅳ为 SS回落。
-
每2 d对反应器进出水水质进行取样检测,其中,进水水样取样从早上5点至晚10点,每间隔1 h取500 mL,冷藏保存,第2天混合均匀后进行水质指标测定。COD采用快速分析法测定(Lian-hua Tech. Co. Ltd, 5B-1, China),NH4+-N、TN、TP、SS、MLSS、SV采用标准法测定,温度、DO、pH采用溶解氧仪监测(Multi340i, WTW, Germany)。
-
在实验阶段的120、248、318、399 d,采用E.Z.N.ATMMag-Bind Soil DNA Kit(OMEGA)方法提取反应器内活性污泥总基因组DNA。采用琼脂糖凝胶法(gel imaging system from UPV,USA)对DNA的完整性进行分析。第一轮PCR扩增采用Qubit3.0 DNA检测试剂盒(Q10210,Life),通用引物341F: CCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG和805R(GACTGGAGTTCCTTGGCACCCGAGAATTCCAGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC)扩增V3-V4(Miseq测序平台)。引入PCR兼容引物(Illumina)进行第2轮PCR扩增[15]。
-
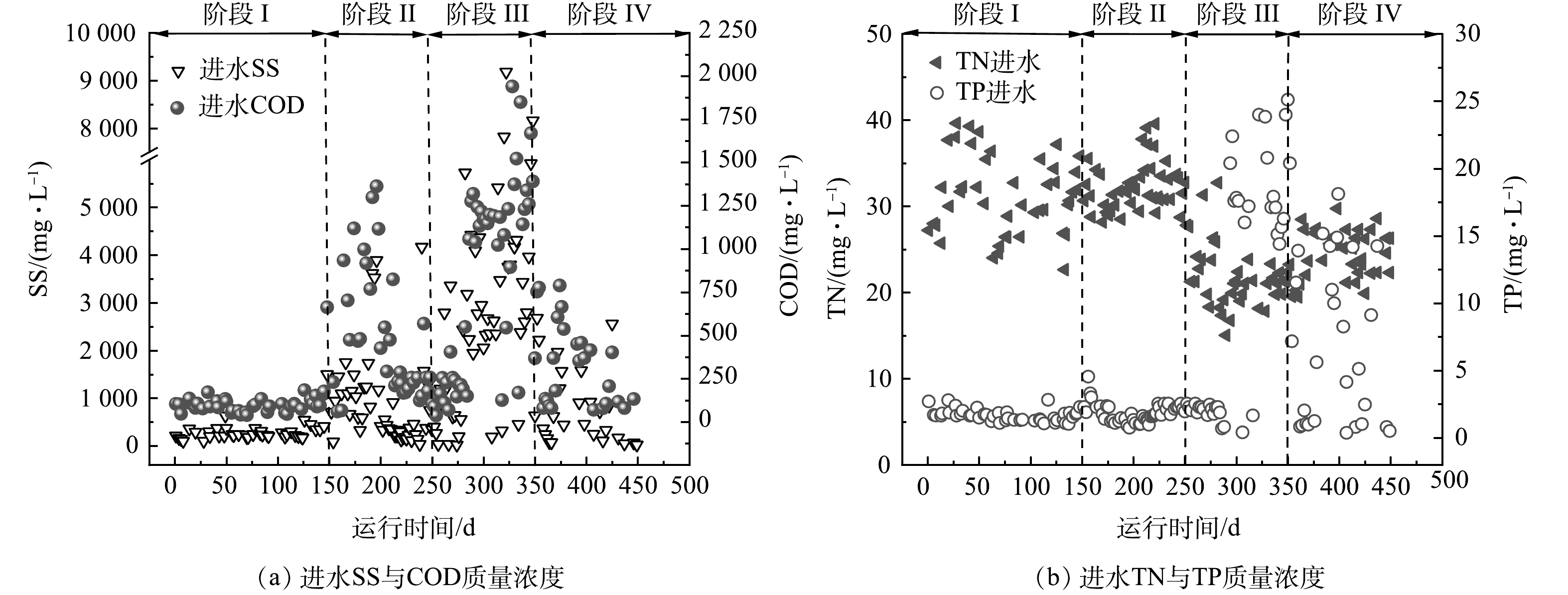
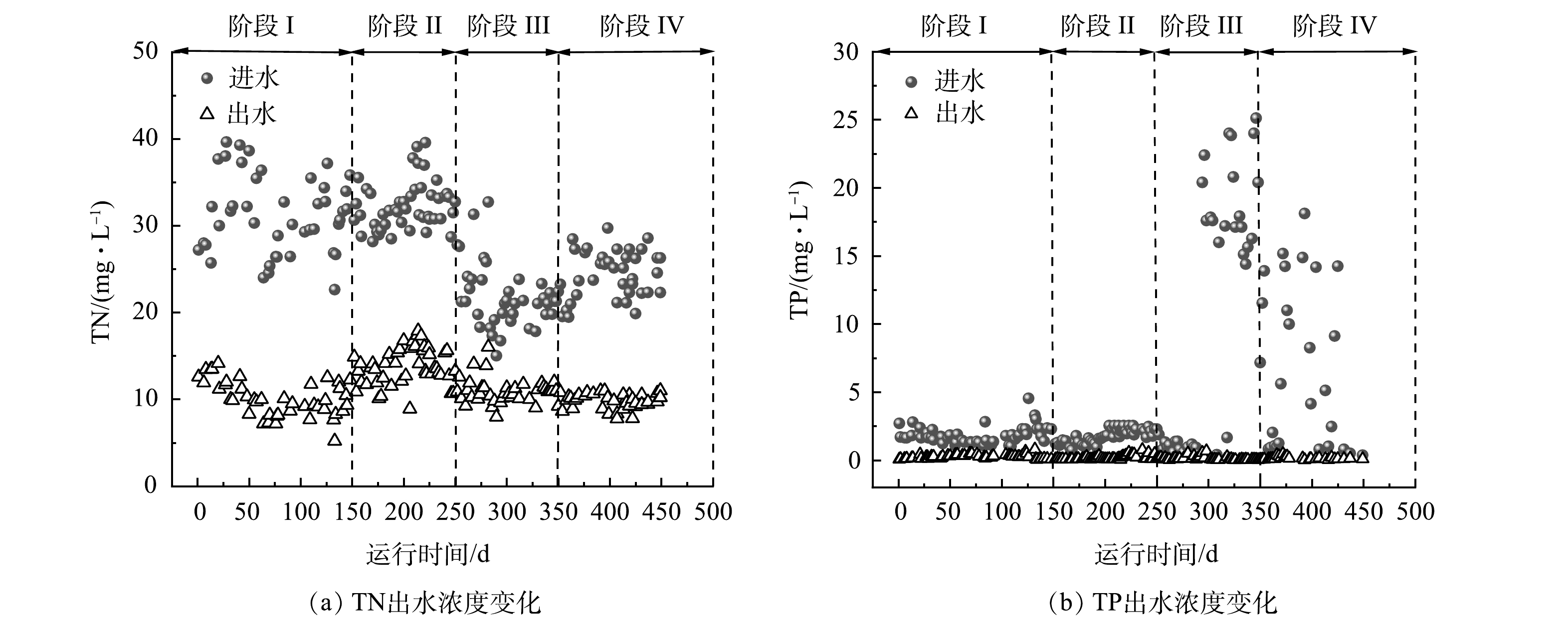
中试实验装置所在污水处理厂服务地区为城市新建的高新区,水质变化较大。污水经过曝气沉砂池处理后,粒径大的砂粒得到去除,粒径相对较小的无机质颗粒随着污水进入MPSR内。在连续运行的450 d中,进水SS和COD值变化如图2(a)所示。可以看出,随着进水SS质量浓度的增加,COD值有所升高,整个运行过程可以分为4个阶段。运行阶段I(1~150 d)反应器进水相对稳定,进水SS和COD保持在较低的水平,平均值分别为(313±246) mg·L−1和(115±103) mg·L−1;阶段II(151~250 d)为波动进水阶段,进水SS和COD平均值分别为(941±989) mg·L−1和(471±368) mg·L−1,其原因主要是由于雪水融化使携带地表有机污染物的无机质流入雨污合流管网;阶段Ⅲ(250~350 d)为高SS进水阶段,在该阶段,受降雨影响,地面无机质携带有机污染物进入管网,进水SS质量浓度最高达到9 000 mg·L−1以上,COD最高值接近2 000 mg·L−1,进水SS和COD平均值分别达到(3 174±2 037) mg·L−1和(812±561) mg·L−1;阶段Ⅳ(350~450 d)为SS回落阶段,进水SS和COD平均值回落至(790±818) mg·L−1和(324±244) mg·L−1。运用SPSS对进水SS与COD值进行双变量相关性分析,结果表明,P<0.01,皮尔逊相关系数为0.682,二者相关性为显著。
如图2(b)所示,进水中TN质量浓度相对比较稳定,在阶段I和II保持在(31±3) mg·L−1,在阶段III和IV阶段保持在(22±3) mg·L−1。进水TP质量浓度在阶段I和II保持在(1.8±0.5) mg·L−1,阶段III中期之后升高至32.2 mg·L−1,平均质量浓度为(11.5±10) mg·L−1。
-
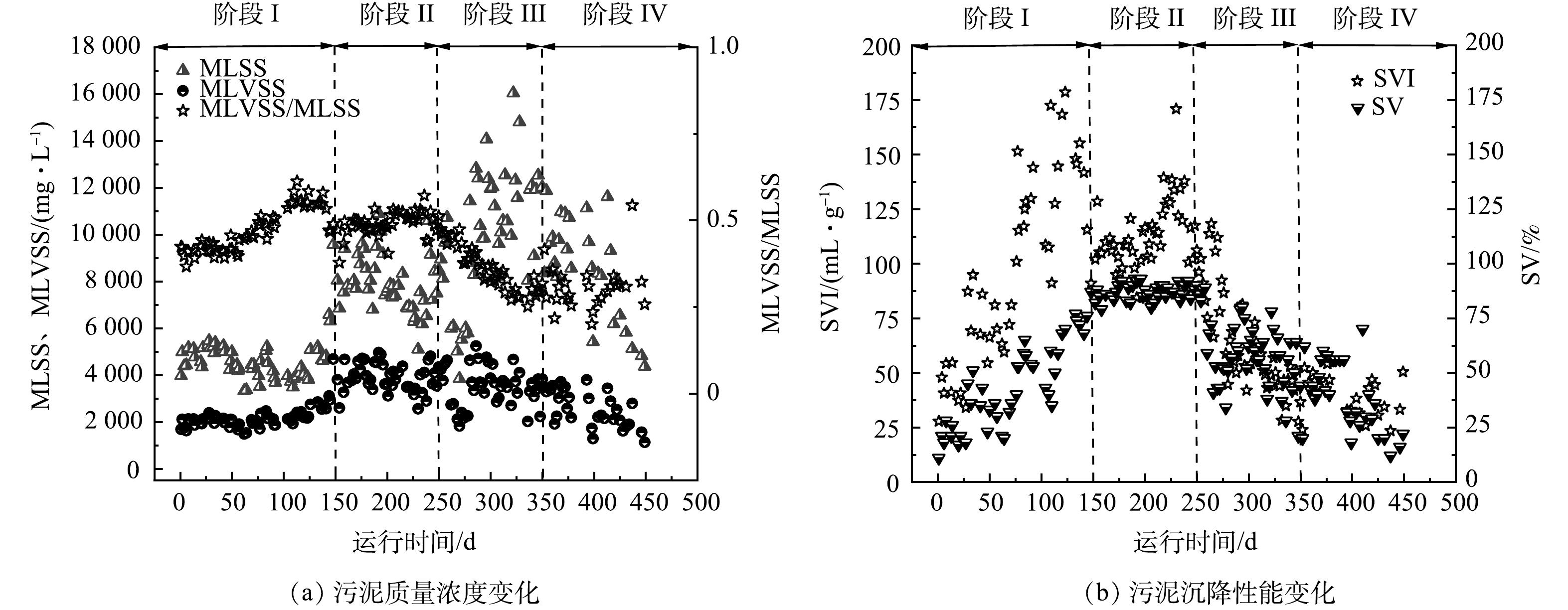
城市污水处理系统的污泥特性及活性与进水水质有关,其性能好坏关系到处理效果及运行成本。图3(a)显示了不同进水无机悬浮物条件下反应器内MLSS、MLVSS和MLVSS/MLSS变化。在阶段I稳定进水期间,MLSS保持在4 000~6 000 mg·L−1,MLVSS持续增长至约3 000 mg·L−1。在阶段II波动进水期间,污泥质量浓度升高至6 000~10 000 mg·L−1,MLVSS稳定在4 000 mg·L−1左右。在阶段III高SS进水期间,污泥质量浓度持续增加至8 000 mg·L−1以上,最高达到16 000 mg·L−1,MLVSS保持在4 000 mg·L−1左右,MLVSS/MLSS由稳定进水阶段I的0.61下降至0.29。阶段IV进水SS浓度回落后, MLVSS受高无机悬浮物冲击影响下降至2 000 mg·L−1,难以恢复至受冲击前水平,说明高悬浮物进水对系统中单位质量污泥活性有一定的影响。这与吉芳英等[16]的研究结果一致。
图3(b)为整个运行期间反应器活性污泥SV与SVI变化。可以看出,在阶段I稳定进水期间,SV和SVI随污泥浓度的增加而有所增加,SVI达到150 mL·g−1左右;在阶段II波动进水期间,泥水混合液中的活性污泥包裹着无机质使得自身比重加大,进而改善了沉降性能,SVI有所降低;在阶段III高SS进水期间,SVI由110 mL·g−1左右下降至低于50 mL·g−1,活性污泥中无机质含量高,缺乏活性和吸附性;阶段IV进水SS浓度回落后,由于仍有大量无机悬浮物截留在反应器内,SVI进一步下降至35 mL·g−1,污泥活性较差。
-
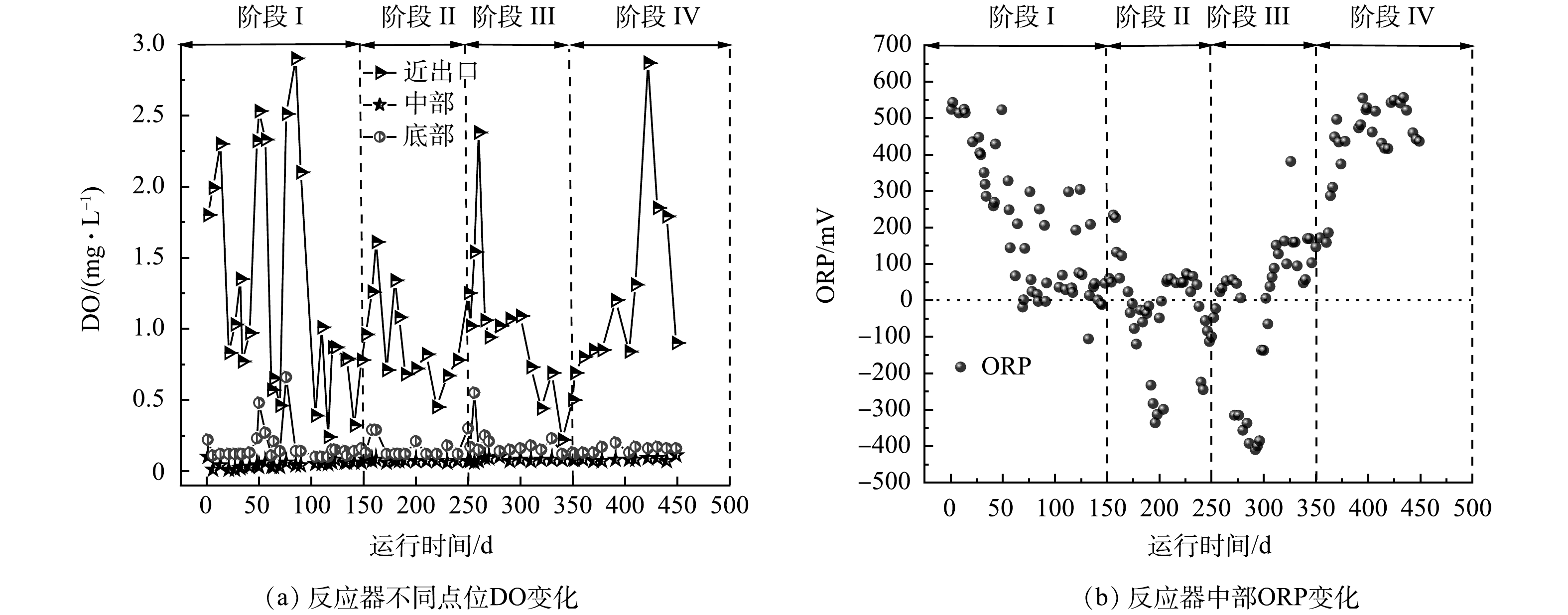
1)对MPSR内DO和ORP对处理效果的影响。同步脱氮除磷实际上是硝化菌(NOB)、反硝化菌(DNB),聚磷菌(PAO)、反硝化除磷菌(DPB)等多个功能菌群协同工作的结果,多溶解氧(DO)环境是多个功能菌群共同工作的前提。在MPSR运行的不同阶段,对反应器内不同位置(图1所示近出口、中部、底部)的DO监测结果如图4(a)所示。可以看出,整个运行阶段,反应中部DO质量浓度基本保持在0.07 mg·L−1,底部DO质量浓度在0.16 mg·L−1左右,变化不大。反应器近出口处DO浓度相对较高,DO波动大。这是因为气泡在底部沿壁上升至出口后破裂,形成的脉冲造成湍流,气、液、固三相在该区域相互作用最活跃。DO质量浓度变化、变化趋势和进水水质没有明显的相关性。
污染物去除过程实际上是一系列的氧化还原反应,氧化还原电位(ORP)与DO、COD、NH4+-N、NO3−-N的浓度有一定关系,能够反映污染物的降解状态[17-19]。在装置中部对ORP进行监测,结果如图4(b)所示。阶段Ⅰ前期ORP为300~550 mV ,反应器内氧化性强,适于硝化反应进行,后期随着污泥浓度增加耗氧量相对增加,ORP降至100 mV左右;在阶段Ⅱ、Ⅲ,由于进水COD的升高反应器内还原性状态加强,ORP在0~-400 mV;在阶段Ⅳ,进水COD降低后ORP恢复至初始状态。
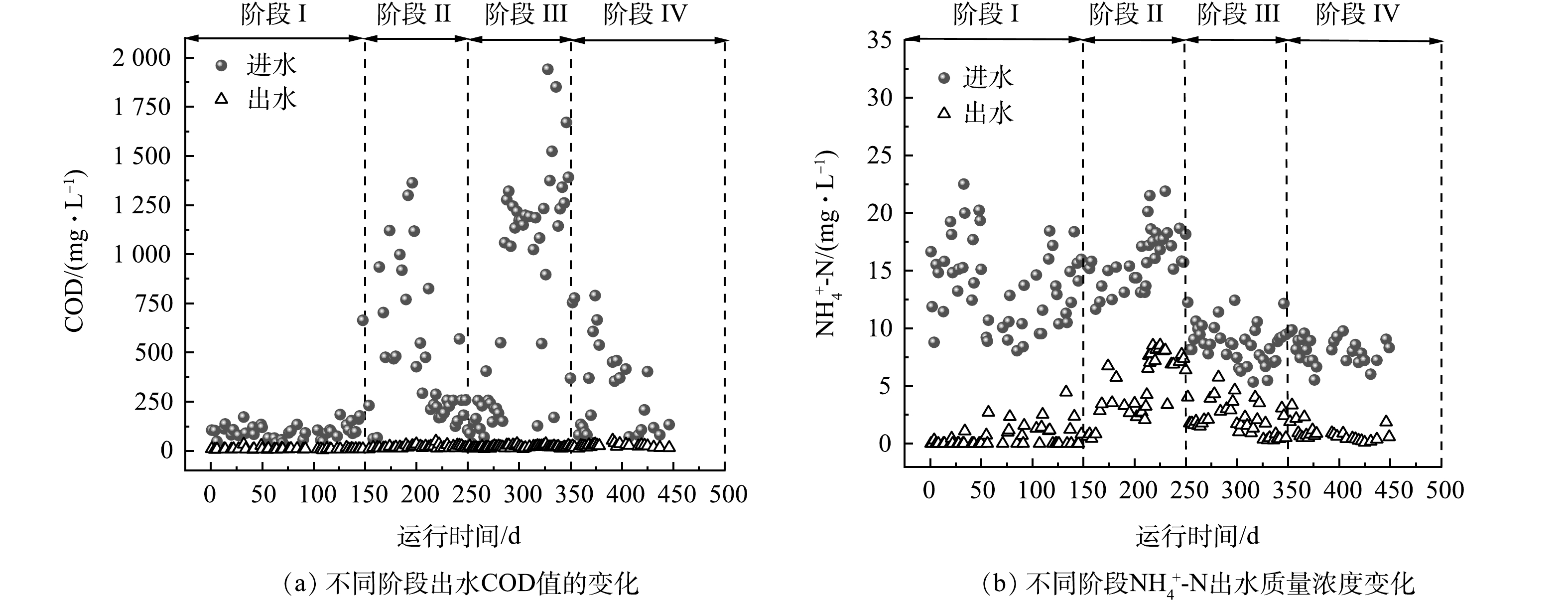
2)对COD和NH4+-N去除的影响。不同运行阶段反应器进出水COD和NH4+-N变化如图5所示。由图5(a)可以看出,反应器出水COD水质指标稳定,在阶段II和阶段Ⅲ,进水COD高达1 000~2 000 mg·L−1的条件下,出水COD值保持在26 mg·L−1以下,满足《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》GB 18918-2002的一级A标准。MPSR独特的工艺结构使得其具有良好的抗有机负荷冲击能力,反应器为中心进水的方式,有机物首先进入厌氧区被用于厌氧释磷和反硝化,扩散至硝化作用发生的外围好氧区时,有机负荷已经得到有效降低。
如图5(b)所示,在运行阶段I和II,进水NH4+-N保持在6.6~21.9 mg·L−1,NH4+-N出水质量浓度在阶段I始终低于5 mg·L−1,平均出水质量浓度仅为(0.57±0.95) mg·L−1;在阶段II质量浓度有所上升,平均出水质量浓度(5.08±2.66) mg·L−1。分析阶段II硝化效果下降的原因:一是进水SS的升高造成混合液内溶解氧扩散所限,反应器内ORP降低;二是进水温度降低,反应器平均温度为9.2 ℃,低温条件下硝化菌的活性受到了抑制[20]。在运行阶段Ⅲ,随着进水NH4+-N浓度的降低和水温的升高,出水NH4+-N平均质量浓度下降至(2.10±1.35) mg·L−1;阶段Ⅳ有机负荷都恢复至正常水平,NH4+-N去除效果恢复至最初水平。
3)对TN和TP去除的影响。如图6(a)所示,在阶段Ⅰ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ,除282 d以外,反应器出水TN质量浓度均低于15 mg·L−1,可达到GB 18918-2002的一级A标准。阶段Ⅱ出水水质出现波动,在部分时段不能保证达标排放,平均TN出水质量浓度为(13.81±2.11) mg·L−1。系统脱氮效率下降原因是由于低温和高SS影响了硝化菌群的活性,硝化是TN去除的限制步骤。如图6(b)所示,反应器除磷效果稳定,在阶段III和阶段IV,在进水TP质量浓度为15~25 mg·L−1时,出水TP始终低于0.28 mg·L−1。
MPSR采用连续运行方式,其具有良好的同步脱氮除磷效果主要归功于反应器独特的工艺结构。反应器采用单侧曝气、中心进水方式,一方面反应器内部存在一定的DO浓度分区,出口区域DO浓度较高,中心和底部区域DO浓度较低,曝气动力驱动混合液在反应器内循环流动,多种溶解氧环境和内循环有利于聚磷菌的生长和硝化液的回流,是连续运行方式下MPSR具备良好同步脱氮除磷效果的主要原因。
反硝化除磷技术的提出使得生物除磷和内源反硝化同步进行,该技术利用反硝化聚磷菌(DPAOs)在厌氧/缺氧交替的环境下,以硝酸盐代替氧作为电子受体,通过一碳两用同步实现脱氮和除磷,尤其适用于低 C/N 污水。与传统生物脱氮除磷工艺相比,MPSR具有较高的氮磷去除效率且能有效节省碳源、曝气能耗,降低污泥产量。厌氧/缺氧交替的环境利于培养出反硝化聚磷菌[21]。对反应器内微生物菌群分析表明,系统的主要除磷方式为反硝化除磷。
-
为进一步揭示MPSR工艺中污染物的去除规律,探究高无机悬浮物对微生物菌群结构影响。在不同运行阶段,对反应器不同位置中的活性污泥进行取样,通过分子生物学对反应器内微生物菌种的丰度、多样性、组成结构进行分析。阶段 Ⅰ 分别从1、2、3号点位处取样分别命名为 Ⅰ-1、Ⅰ-2、Ⅰ-3,以此类推。
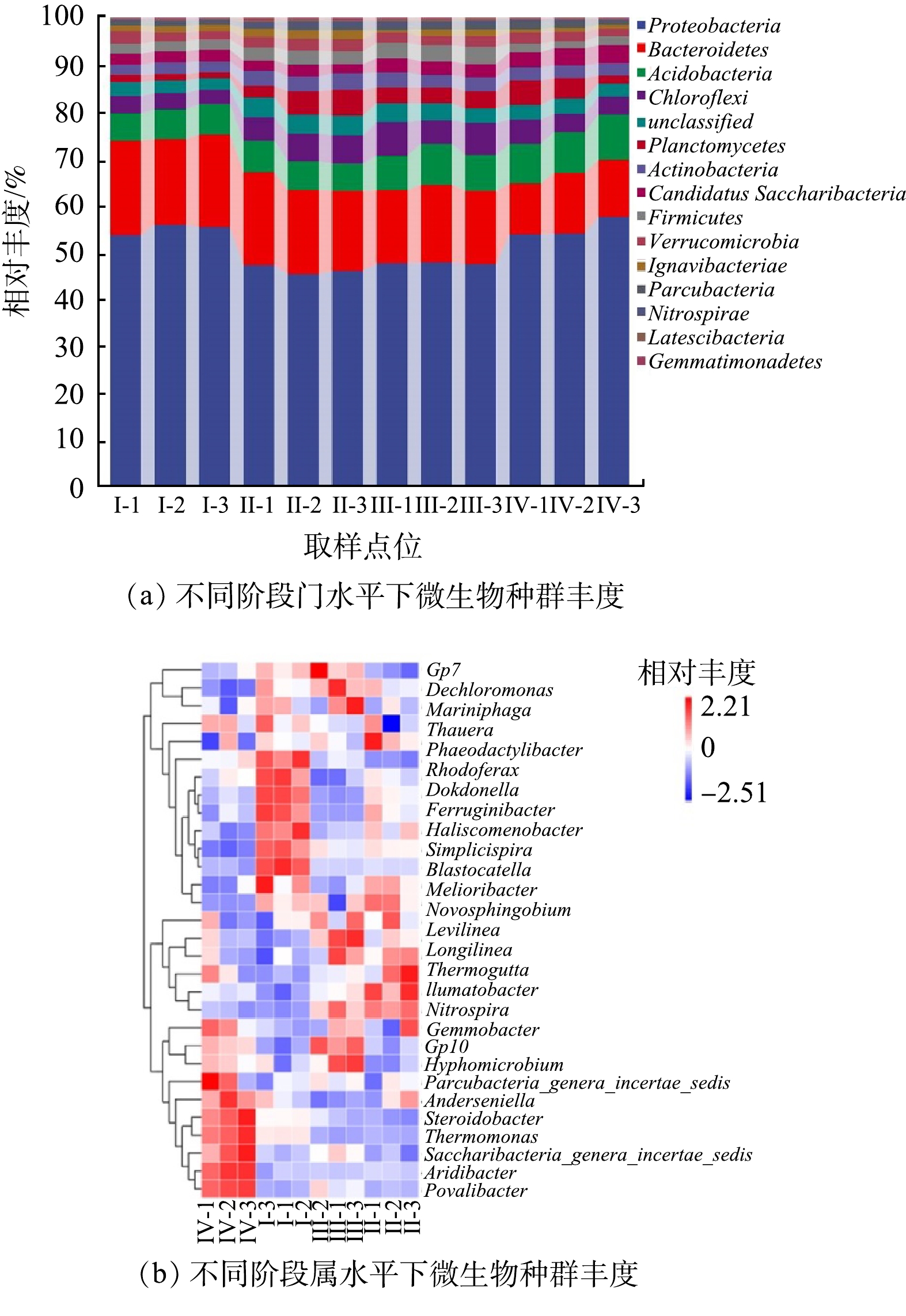
MPSR内微生物门水平上占比前15的物种分布如图7(a)所示。变形菌门(Proteobacteria) 44.86%~57.03%为主要优势菌种,其次是拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)10.8%~19.78%,酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria)5.84%~9.32%,绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi) 2.92%~6.98%,浮霉菌门(Planctomycetes)1.1%~5.46%,这5种菌群在本研究中占比达到80%以上。Proteobacteria是污水处理中最常见的菌门[22],与污染物的降解有紧密的关联,污水处理中的硝化细菌、反硝化细菌和亚硝化细菌就主要来自于Proteobacteria。整个运行过程中Proteobacteria呈现先下降后升高的趋势,这说明高SS冲击对其生存造成了一定的影响,进水SS恢复正常水平后,丰度也恢复至最初水平,变化趋势和系统脱氮效果变化表现一致。
Bacteroidetes是一种重要的异养菌,在污水处理中主要发挥有机物去除的功能,一些反硝化细菌和大多数固氮细菌也来自于该门,在厌氧降解中发挥重要作用[23]。Acidobacteria具有反硝化的功能[24-25],Chloroflexi是降解有机物的重要微生物菌群之一[26],在运行阶段Ⅲ高悬浮物浓度条件下,Bacteroidetes、Acidobacteria、Chloroflexi丰度分别达到16.2%、8.63%、6.98%,均高于正常负荷运行阶段,MPSR内丰富的微生物结构使其在高悬浮物冲击下仍可以保持稳定的处理效果。
图7(b)反映了反应器内在属水平上占比在前20的物种,趋于红色表示该物种占比较高。其中,Thermomonas(2.31%~10.04%)、Terrimonas(2.58%~4.79%)、Rhodoferax(2.40%~4.70%)、Saccharibacteria_genera_incertae_sedis(1.94%~3.88%)、Gemmobacter(1.79%~3.40%)、Dechloromonas(1.63%~3.57%)、Ferribacterium(1.73%~2.97%)、Povalibacter(1.44%~3.62%)、Phaeodactylibacter(1.74%~2.64%)、Gp7(1.31%~2.88%)、Thauera(1.35%~1.82%)在整个系统中属于相对优势菌种。
Saccharibacteria_genera_incertae_sedis、Povalibacter作为去除有机物的优势菌属[27-28],受阶段Ⅲ COD值增加的影响,丰度变化明显,增幅超过1%。这说明这2种菌属在面对COD冲击时可吸收多余有机物繁殖自身,以保证出水的稳定。Nitrospira是系统内主要的硝化菌(NOB)。有研究表明,其在低温条件下属于优势硝化菌[29]。本研究阶段Ⅱ中该菌丰度由0.39%提高至1.07%,可能跟该其在低温条件下更具竞争优势有关。Thermomonas和Terrimonas作为自养的好氧反硝化菌[30-32],受高SS进水影响,平均相对丰度由阶段Ⅰ的5.56%和4.79%下降到阶段Ⅲ的2.31%和2.69%。高SS带来COD值的提高使得自养菌在与异养菌的竞争中处于劣势,同时在曝气保持不变的情况下好氧区面积减小,使得好氧反硝化菌的丰度进一步下降。Dechloromonas为反硝化除磷菌(DPB)[33],在运行阶段Ⅰ和Ⅱ其占比分别为2.69%和2.57%。在阶段Ⅲ高TP进水条件下占比小幅上升至3.10%。阶段Ⅳ丰度下降至1.79%。这可能是由于进水SS回落以及COD值和TP浓度降低造成。此外,传统的PAOs未在系统中发现,说明反硝化除磷是MPSR系统主要的除磷途径。
以上分析结果表明,MPSR系统内同时存在硝化菌、好氧反硝化菌,反硝化除磷菌,保证了连续流运行方式下反应器能够实现同步脱氮除磷,MPSR独特的结构与曝气方式使得在单一池内同时脱氮除磷成为现实,反应器内丰富的微生物群落结构能够在进水水质剧烈变化时,出水仍然符合排放标准。
-
1)高无机悬浮物进水造成MPSR内MLSS由5 000 mg·L−1大幅升高至13 000 mg·L−1,MLVSS保持4 000 mg·L−1不变,污泥活性低,但可增强污泥在二沉池的沉降性能。
2)反应器在高无机悬浮物进水条件下对污染物降解效果仍然保持良好,整个实验出水指标均达到GB 18918-2002的一级A标准。MPSR独特的结构和单侧曝气方式在单曝气池内形成了多溶解氧分区共存,可为在单一曝气池内进行同步脱氮除磷提供合适的溶解氧环境。
3) MPSR内微生物种群结构丰富,受高无机悬浮物进水冲击时仍能保持群落结构相对稳定,存在多种反硝化菌,如好氧反硝化菌Thermomonas、Terrimonas等,主要除磷菌属为反硝化除磷菌Dechloromonas,证明了反应器内发生了同步脱氮除磷。
高悬浮物进水对中试规模微压内循环生物反应器处理效果的影响
Influence of high suspended solids influent on the treatment effect of the pilot-scale micro-pressure swirl reactor
-
摘要: 采用中试规模微压内循环生物反应器(MPSR)处理某北方城市新区污水处理厂沉砂池出水,考察了高悬浮物进水条件下反应器污染物处理效果及污染物的去除特性,利用高通量测序对微生物群落结构进行分析。MPSR 经450 d的运行结果表明,受春季冰雪融化和夏季降雨影响,反应器进水中SS质量浓度平均值在1—5月提高至约800 mg·L−1,在5—8月达到约2 700 mg·L−1,运用SPSS对进水SS与COD进行相关性分析,二者为正相关,皮尔逊相关系数为0.682。高悬浮物进水使得系统内MLSS质量浓度增加至12 000 mg·L-1,而MLVSS质量浓度基本保持在3 000~5 000 mg·L−1,SVI下降至50 mL·g−1。在不同进水负荷条件下,MPSR出水COD、TN、TP质量浓度始终保持在26、14、0.28 mg·L−1以下,达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》一级A排放标准。高通量测序结果表明MPSR内微生物结构丰富,系统内好氧反硝化菌Thermomonas、Terrimonas、反硝化除磷菌Dechloromonas等多重功能微生物共存。MPSR内丰富的微生物结构使其在高悬浮物冲击下仍可以保持稳定的处理效果。Abstract: A pilot-scale micro-pressure swirl teactor (MPSR) was used to treat the effluent from the grit chamber of a sewage treatment plant in a new district of a northern city in China, the reactor pollutant treatment effects and pollutant removal characteristics at high suspended solids influent were inspected. The high-throughput sequencing was used to determine the microbial community structure in MPSR. The 450-day operation results showed that the average SS concentration in the influent of MPSR increased to about 800 mg·L−1 from January to May and reached about 2 700 mg·L−1 from May to August due to the influences of the melting of snow and ice in spring and the summer rainfall. Based on the SPSS correlation analysis, a positive correlation occurred between water SS and COD with the pearson correlation of 0.682. The MLSS concentration in the system increased to 12 000 mg·L−1 due to high suspended solids inflow, while the MLVSS concentration basically maintained between 3 000 mg·L−1 and 5 000 mg·L−1, and SVI value decreased to 50 mL·g−1. At different influent loadings, COD, TN and TP concentrations in the effluent of MPSR were always below 26, 14 and 0.28 mg·L−1, respectively, which met the first-level A emission standards of “urban sewage treatment plant pollutant emissions standard”. The results of high-throughput sequencing showed that the microbial structure in MPSR was abundant, and multiple functional microorganisms such as aerobic denitrifying bacteria Thermomonas, Terrimonas, and denitrifying phosphorus removing bacteria Dechloromonas coexisted in the system. The rich microbial structure in MPSR enables it to maintain a stable treatment effect under the impact of high suspended solids .
-

-
-
[1] 刘志长. 合流制排水管道沉积物的沉淀状况及控制技术研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学2011. [2] 熊磊, 边德军, 吴忌, 等. 长春市新区污水水质及水量变化规律分析[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(1): 36-40. [3] 侯巧玲, 张鸿, 洋王, 等. 某高新技术工业园区污水厂的设计与运行[J]. 给水排水, 2014, 30(22): 115-118. [4] LI L Q, SHAN B Q, YIN C Q. Stormwater runoff pollution loads from an urban catchment with rainy climate in China[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2012, 6(5): 672-677. [5] ALAGHA O, ALLAZEM A, BUKHARI A A, et al. Suitability of SBR for wastewater treatment and reuse: Pilot-scale reactor operated in different anoxic conditions[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(5): 1617. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051617 [6] XIE E, XU X Y, LUO G Y. Study on a novel reactor of sludge process reduction for domestic sewage treatment[J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34: 9-12. [7] 邓仁健, 张金松, 杨靖波, 等. 高无机悬浮物进水对城市污水厂处理效果的冲击影响及机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(6): 1605-1610. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.06.018 [8] 张自杰. 排水工程: 下册[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2000. [9] 边德军. 微压内循环多生物相反应器研制及性能研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2015. [10] 万立国, 边德军, 卢文喜, 等. 微压气升循环流反应器与完全混合式反应器运行效果及微生物种群结构比较[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018, 40(1): 11-14. [11] 边德军, 王喜超, 艾胜书, 等. 微压内循环反应器与序批式反应器的污染物去除及污泥特性比较[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(11): 1315-1318. [12] 王帆, 么兴荣, 刘松林, 等. 有机负荷冲击对微压反应器的影响及调控策略[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8): 3667-3675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.023 [13] 边德军, 赵乐欣, 王宁, 等. 超长污泥龄对MPR工艺脱氮除磷效果的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(5): 1735-1743. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202010091 [14] BIAN D J, ZHOU D D, HUO M X, et al. Improving oxygen dissolution and distribution in a bioreactor with enhanced simultaneous COD and nitrogen removal by simply introducing micro-pressure and swirl[J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 99(20): 8741-8749. [15] HUANG X, DONG W Y, WANG H J, et al. Biological nutrient removal and molecular biological characteristics in an anaerobic-multistage anaerobic/oxic (A-MAO) process to treat municipal wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 969-978. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.161 [16] 吉芳英, 周卫威, 裴玲, 等. 细微泥沙对活性污泥系统的影响及其恢复特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(2): 326-332. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2015.02.22 [17] 苏高强, 彭永臻. 基于ORP的控制策略在废水生物处理中的应用[J]. 工业水处理, 2011, 31(8): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2011.08.003 [18] 高景峰, 彭永臻, 王淑莹, 等. 以DO、ORP、pH控制SBR法的脱氮过程[J]. 中国给水排水, 2001(4): 6-11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2001.04.002 [19] 王涛, 徐跃飞, 陈贵生, 等. ORP用于优化改良型Carrousel氧化沟脱氮的研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(21): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2012.21.005 [20] ZHA X, MA J, LU X W, et al. Use of a low-cost and energy-efficient device for treating low-strength wastewater at low temperatures focusing on nitrogen removal and microbial community[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 722: 137916. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137916 [21] KUBA T, SMDLDERS G, VANLOOSDRECHT M C M, et al. Biological phosphorus removal from wastewater by anaerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1993, 27(56): 241-252. [22] HU M, WANG X H, WEN X H, XIA Y. Microbial community structures in different wastewater treatment plants as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing analysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 117: 72-79. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.061 [23] SHI X Q, NG K K, LI X R, et al. Investigation of intertidal wetland sediment as a novel inoculation source for anaerobic saline wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(10): 6231-6239. [24] ZHANG Y T, DING K, YRJÄLÄ K, et al. Introduction of broadleaf species into monospecific cunninghamia lanceolata plantations changed the soil Acidobacteria subgroups composition and nitrogen-cycling gene abundances[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 467(12): 1-18. [25] 王光华, 刘俊杰, 于镇华, 等. 土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(02): 14-20. [26] MIURA Y, WATANABE Y, OKABE S. Significance of chloroflexi in performance of submerged membrane bioreactors (MBR) treating municipal wastewater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(22): 7787-7794. [27] SENGUN I Y, KARABIYIKLI S. Importance of acetic acid bacteria in food industry[J]. Food Control, 2011, 22(5): 647-656. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.11.008 [28] FU C, YUE X D, SHI X Q, et al. Membrane fouling between a membrane bioreactor and a moving bed membrane bioreactor: Effects of solids retention time[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017: 397-408. [29] CHEN M X, CHEN Y W, DONG S Y, et al. Mixed nitrifying bacteria culture under different temperature dropping strategies: Nitrification performance, activity, and community[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 195: 800-809. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.129 [30] XING W, LI J, LI D, et al. Stable-isotope probing reveals the activity and function of autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrifiers in nitrate removal from organic-limited wastewater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(14): 7867-7875. [31] XIE C H, YOLATA A. Reclassification of [Flavobacterium] ferrugineum as Terrimonas ferruginea gen. nov. , comb. nov., and description of Terrimonas lutea sp. nov. , isolated from soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2006, 56(5): 1117-1121. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64115-0 [32] MERGAERT J, CNOCLAERT M C, SWINGS J. Thermomonas fusca sp. nov. and Thermomonas brevis sp. nov. , two mesophilic species isolated from a denitrification reactor with poly(epsilon-caprolactone) plastic granules as fixed bed, and emended description of the genus Thermomonas[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2003, 53(6): 1961-1966. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02684-0 [33] TERASHIMA M, YAMA A, SATO M, et al. Culture-dependent and -independent identification of polyphosphate-accumulating Dechloromonas spp. predominating in a full-scale oxidation ditch wastewater treatment plant[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2016, 31(4). -



 下载:
下载: