-
近年来,我国污水处理行业发展迅速,污水处理率大幅提高,但仍存在处理效率低而处理能耗高等问题[1-2]。在城镇污水处理系统中,含氮污染物是主要的去除对象之一,相关脱氮技术一直以来备受关注。目前常用的废水生物脱氮工艺(A2/O、氧化沟等)虽然具有良好的处理效果[3],但在处理过程中需要消耗大量的能源,而且随着排放标准的不断提高,能源消耗也将进一步增加。因此,开发提质增效和节能降耗的新型生物脱氮技术一直是污水处理领域的研究热点。
在常规城市污水处理生物脱氮系统中,曝气和混合液内回流是保证系统脱氮性能的重要环节,同时也是污水处理过程中耗能最高的环节[4]。硝化-反硝化生物脱氮的第一步,即在好氧区曝气为硝化菌提供溶解氧(DO),通过硝化作用将废水中的氨氮转化为硝酸盐。随后通过内回流将硝酸盐带入缺氧区进行反硝化作用,内回流比越高,则脱氮效率越高,但是能耗也会成比例增加[5-6]。然而在实际运行过程中,曝气系统在给生物池带来溶解氧的同时,也会产生向上的水流推动力,但常规生物脱氮系统的设计与运行并未对此部分动力加以考虑和利用。若能将曝气动力作为内回流的动力[7-9],对于提高污水处理厂脱氮效率、降低运行成本具有重要的意义。
为此,本研究提出一种新型的曝气动力横向内循环反应器(ALIR),利用曝气提供的动力带动水流在好氧区与缺氧区间横向循环流动;以模拟城市污水为处理对象,考察系统的脱氮性能及功能菌活性、关键酶活性的变化特征,分析反应器的脱氮途径,并对微生物群落结构特征进行解析,以期为曝气动力横向内循环反应器的工程应用提供有效支撑。
-
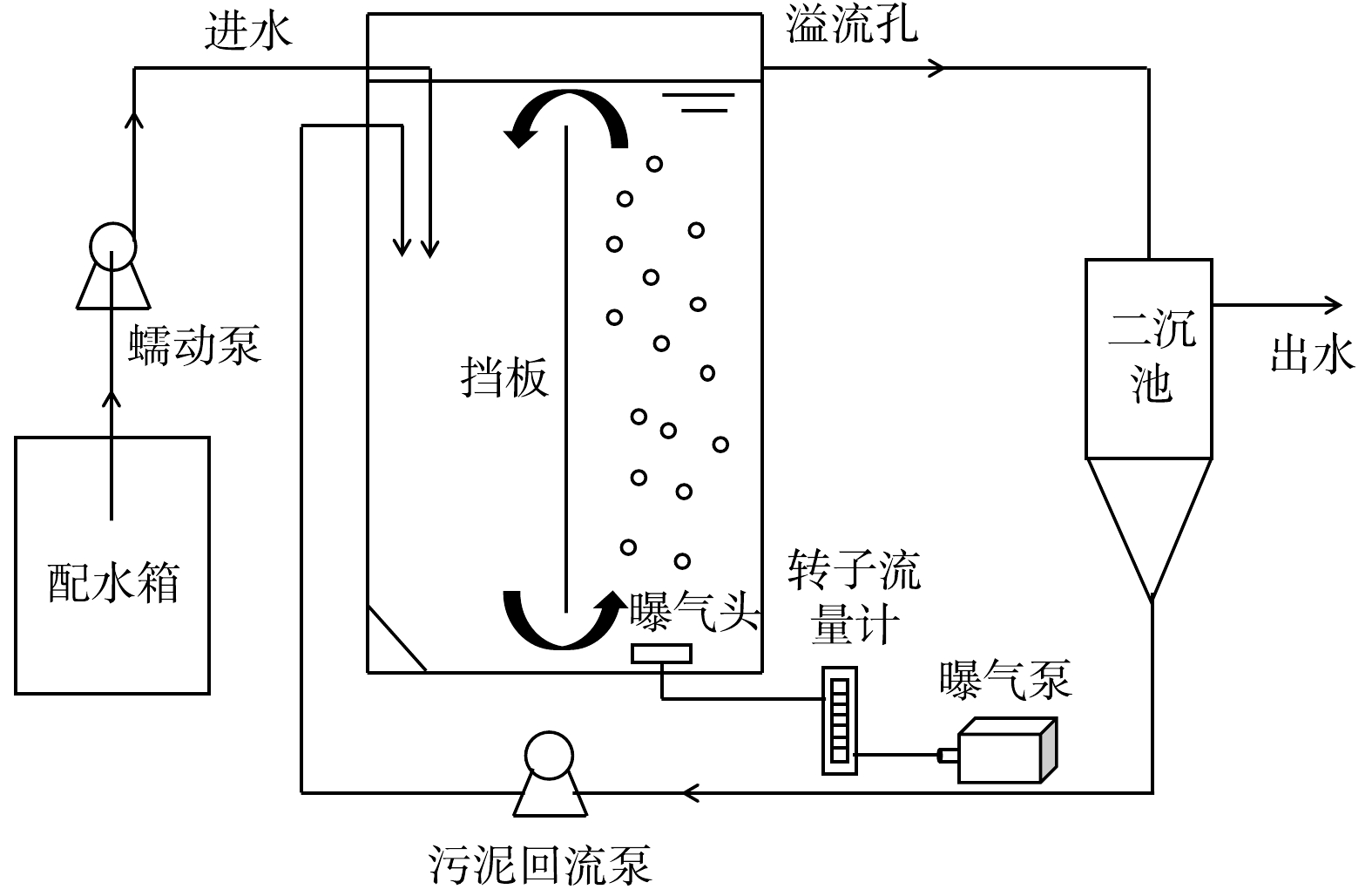
实验装置如图1所示,曝气动力横向内循环反应器由有机玻璃制成,长×宽×高为0.35 m×0.25 m×0.60 m,有效容积为30 L,内设高0.375 m的挡板,将反应器分为好氧区和缺氧区,容积比为1:1,挡板与液面的距离为85 mm,挡板与反应器底部的距离为50 mm。好氧区底部安装有曝气盘,混合液在曝气动力的推动作用下,在反应器好氧区和缺氧区间循环流动。利用转子流量计调节曝气量以控制DO质量浓度和循环液速。稳定运行期间,水力停留时间为9 h,污泥回流比为100%。
-
接种污泥取自西安市某污水厂A2O工艺好氧池,具有良好的硝化性能。进水采用模拟城市污水的合成废水,具体成分可参见已有研究[10]。进水氨氮(NH4+-N)为40 mg·L−1,化学需氧量(COD)为300 mg·L−1,以氯化铵(NH4Cl)为氮源,无水乙酸钠(CH3COONa)和可溶性淀粉(C6H10O5)n为碳源(无水乙酸钠∶可溶性淀粉=1∶1,以COD计)。为保证所培养微生物的生长繁殖需要,用NaHCO3调节pH为7.8~8.0,并加入1 mL·L−1的微量元素,各微量元素质量浓度参见已有研究[10]中的组成成分。
-
1) 常规水质分析。氨氮(NH4+-N)、亚硝态氮(NO2−-N)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)分别采用纳氏试剂分光光度法、紫外分光光度法、N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺分光光度法测定;COD使用哈希消解仪(DRB-200)消解,采用分光光度法进行测定;DO使用便携式溶解氧分析仪(JPB-607A)测定;pH使用pH计(雷磁PHS-3C)测定。
2) 活性、酶活性的测定。污泥活性包括比氨氧化活性(SAUR)、比亚硝酸盐氧化活性(SNUR)、比硝酸盐还原活性(NARR)及比亚硝酸盐还原活性(NIRR),具体测定步骤参见已有研究[11-12]中的方法。
采用低温高压细胞破碎仪(JN-02C)提取活性污泥中的粗酶,具体方法可参见已有研究[13]。酶活性包括氨单加氧酶(Amo)、亚硝酸盐氧化还原酶(Nor)、硝酸盐还原酶(Nar)和亚硝酸盐还原酶(Nir),酶活性的测定方法可参见已有研究[12-13]。使用Lowry法测定蛋白质的质量浓度,以表示粗酶的含量。
3) 同步硝化反硝化率的测定。通过批次实验研究不同DO质量浓度下的同步硝化反硝化率。取反应器中的活性污泥离心清洗(4 000 r·min−1,5 min),在密封瓶中重悬至500 mL,置于磁力搅拌器上搅拌。向密封瓶中加入无水乙酸钠、氯化铵及硝酸钠,使初始COD值为100 mg·L−1,NH4+-N和NO3−-N质量浓度为20 mg·L−1,通过调整曝气量控制DO质量浓度。反应开始后,间隔一定时间,取样并分析氮的质量浓度,根据式(1)计算同步硝化反硝化率[14]。
式中:R为同步硝化反硝化率;ΔC(NO3−-N)、ΔC(NH4+-N)分别为反应前后NO3−-N质量浓度的增加量和NH4+-N质量浓度的减少量,mg·L−1。
根据好氧区DO质量浓度的分布情况和不同DO质量浓度下的同步硝化反硝化率(R),计算好氧区的平均同步硝化反硝化率(
$ \overline{R} $ ),计算方法见式(2)。式中:
$\overline R $ 为好氧区平均同步硝化反硝化率;R(DO)为DO质量浓度下的同步硝化反硝化率;V(DO)为DO在好氧区中所占的体积,L;$ V $ 为好氧区总体积,L。4) 微生物群落结构分析。将接种污泥与运行第80天的活性污泥进行高通量测序分析。采用引物序列515F(5'-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3')和806R(5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3')对样品的16S V4区进行扩增,扩增步骤参考已有研究[15]中的方法。委托上海凌恩生物科技有限公司对扩增产物进行Illumina MiSeq高通量测序。
5) 数据相关性分析。采用SPSS 27.0对数据进行统计学分析,用r表示皮尔逊相关系数。当r>0时,各变量呈正相关;当r=0时,各变量呈非线性相关;当r<0时,各变量呈负相关;当显著性水平P<0.05时,代表两变量具有显著相关性。
-
1) 反应器对污染物的去除特性。反应器运行期间,缺氧区污泥的平均质量浓度为(2 898.16±70.44) mg·L−1,好氧区污泥的平均质量浓度为(2 900.37±30.79) mg·L−1,缺氧区与好氧区污泥质量浓度无明显差异,表明在反应器内形成了良好的内循环。图2为实验期间反应器进出水水质的变化情况,阶段Ⅰ和阶段Ⅱ分别为反应器启动过程(第1~42天)和稳定运行过程(第43~90天)。在反应器启动过程(第1~42天)中,为满足好氧区中氨氮与有机物氧化过程的DO需求,同时维持缺氧区低溶解氧环境,并实现缺氧区与好氧区自动内循环的曝气动力需求,曝气量在0.30~0.56 L·min−1以内逐步增加(图2(a))。如图2(a)所示,反应器启动后,出水NH4+-N质量浓度整体上逐渐降低,NO2−-N平均质量浓度为(0.08~0.41) mg·L−1,无明显亚硝酸积累,而NO3−-N质量浓度则有较大波动。NH4+-N质量浓度与曝气量呈显著负相关(r=−0.901,P<0.05),说明硝化菌对DO质量浓度的变化较为敏感,好氧区足够的DO是保证氨氮氧化的关键。随着曝气量的增大,好氧区DO质量浓度升高,因此NH4+-N去除效果也随之提高。而出水NO3−-N质量浓度的变化与曝气量的增加无明显相关性(P=0.28)。这可能是因为硝酸盐的反硝化过程对DO的需求与硝化过程相反,而在曝气动力横向内循环反应器中,曝气强度增加不仅会强化氨氮的氧化效果,产生更多的硝酸盐,也有可能破坏缺氧区的缺氧环境,从而抑制硝酸盐还原过程,所以启动期间出水中的NO3−-N波动较大。
反应器稳定运行期间(第43~90天),系统曝气量维持在(0.56±0.02) L·min−1,此时反应器出水NH4+-N的质量浓度为(3.20±0.93) mg·L−1,NH4+-N去除率达到(92.29±2.13)%;出水NO2−-N和NO3−-N的质量浓度分别为(0.19±0.05) mg·L−1和(8.30±1.12) mg·L−1;出水总氮(TN)为(11.68±1.31) mg·L−1,TN去除率达到(71.81±3.13)%。此外,由图2(b)可知,反应器运行期间COD的去除效果保持稳定,出水COD值平均为(11.19±1.84) mg·L−1,COD平均去除率为(96.22±0.67)%,说明系统具有良好的COD去除性能。
因此,实验在不设置内回流泵的条件下,利用曝气动能可以推动反应器内硝化液内回流,创造适宜的缺氧和好氧环境,满足城市污水脱氮的硝化和反硝化需求。实验条件下,反应器出水NH4+-N、TN和COD均可满足《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)中规定的一级A标准(NH4+-N<5 mg·L−1,TN<15 mg·L−1,COD<50 mg·L−1)。
2) 污泥活性变化。图3为实验期间比硝化活性和比反硝化活性的变化情况。由图3(a)可知,第1天(接种污泥)的SAUR与SNUR分别为(4.41±0.07)、(5.03±0.10) mg·(g·h)−1,与接种污泥相比,进入稳定期(第50天)后,污泥的SAUR和SNUR分别提高了119%和122%,稳定运行期间活性污泥的SAUR和SNUR没有明显变化。
如图3(b)所示,NARR由第1天的(17.08±0.13) mg·(g·h)−1逐渐降至第50天的(16.29±0.03) mg·(g·h)−1和第80天的(15.88±0.08) mg·(g·h)−1,运行80 d仅降低了7%,NIRR整体变化不大,从(7.6±0.05) mg·(g·h)−1(第1天)变为(7.5±0.02) mg·(g·h)−1(第80天)。不难看出,系统中比反硝化活性仅出现小幅降低,这可能是由于启动期间曝气量逐步增加(图2(a)),缺氧反硝化菌受DO质量浓度升高的影响导致其生长受到抑制,因此缺氧反硝化菌的比反硝化活性略有降低。
值得注意的是,结合图2和图3可知,稳定运行期间的比反硝化活性虽然有所下降,但TN去除率一直保持稳定。这可能是由于反应器中培养了好氧反硝化菌,从而产生同步硝化反硝化现象[16-17],并提高了系统的脱氮效果。而这一类微生物的反硝化活性无法被异位缺氧反硝化活性测定的方法检出,因此,实验期间所测的异位缺氧反硝化活性可能无法完全代表系统的反硝化性能。
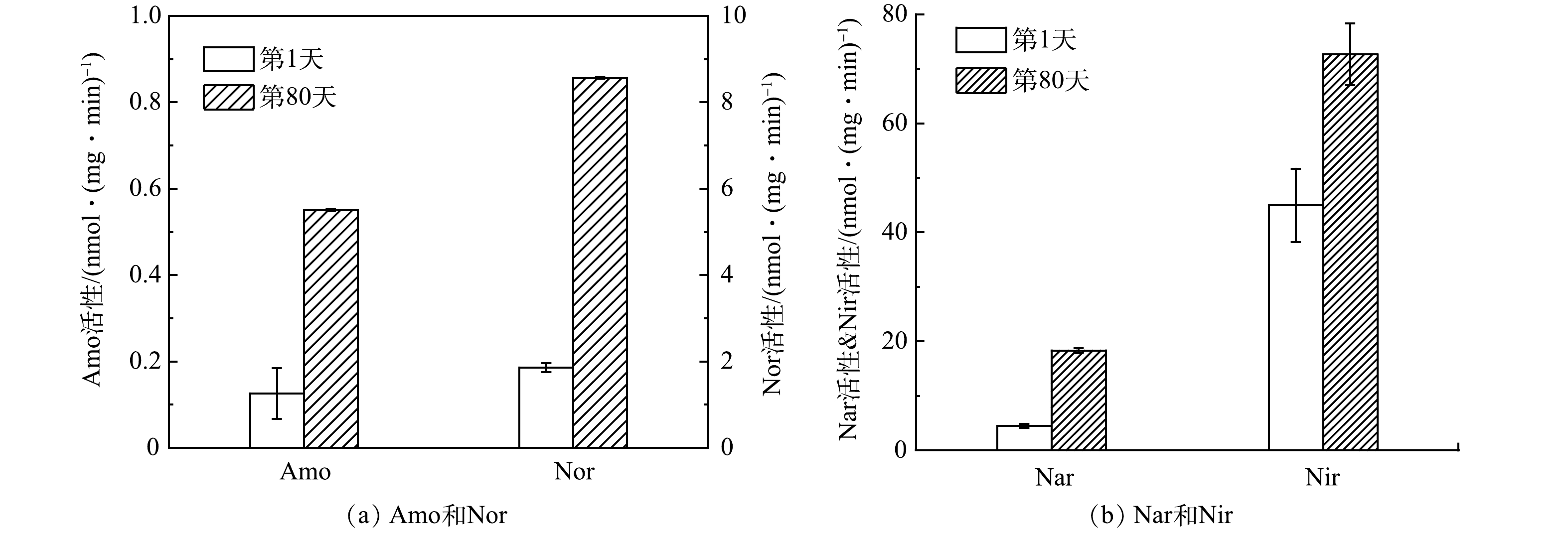
3) 污泥酶活性的变化。图4为第1天和第80天的酶活性变化。由图4(a)可知,硝化酶活性(Amo,Nor)显著上升,随着反应器的运行,Amo活性从0.13 nmol·(mg·min)−1增至0.55 nmol·(mg·min)−1,Nor活性从1.86 nmol·(mg·min)−1增至8.56 nmol·(mg·min)−1。Amo和Nor是硝化过程中催化NH4+-N转化为NO3−-N的关键酶[18],其活性对氨氧化菌(AOB)、亚硝酸盐氧化菌(NOB)活性有直接影响。实验期间,Amo和Nor活性的上升与SAUR和SNUR的升高趋势一致(图3(a))。
为进一步探究系统的反硝化性能,本研究对反应器运行前后的反硝化酶活性(Nar和Nir)进行了测定。如图4(b)所示,Nar和Nir活性明显升高,与第1天相比,Nar活性增长了308%,Nir活性增长了62%(第80天)。实验期间,硝化活性的升高促使更多NH4+-N转化为NO2−-N和NO3−-N(图2、图3),反硝化酶活性会随着基质浓度的增大而升高[19],因此Nar和Nir活性显著升高。值得注意的是,由图3(b)与图4(b)可知,反硝化酶活性与比反硝化活性具有不同的变化趋势。这可能是由于系统中逐渐培养出了好氧反硝化菌,使得在缺氧条件下测定的反硝化活性会低于实际活性,而好氧反硝化菌的反硝化酶活性则不受影响,因此,反硝化酶活性的增加趋势更能反映出系统反硝化能力的变化情况。
-
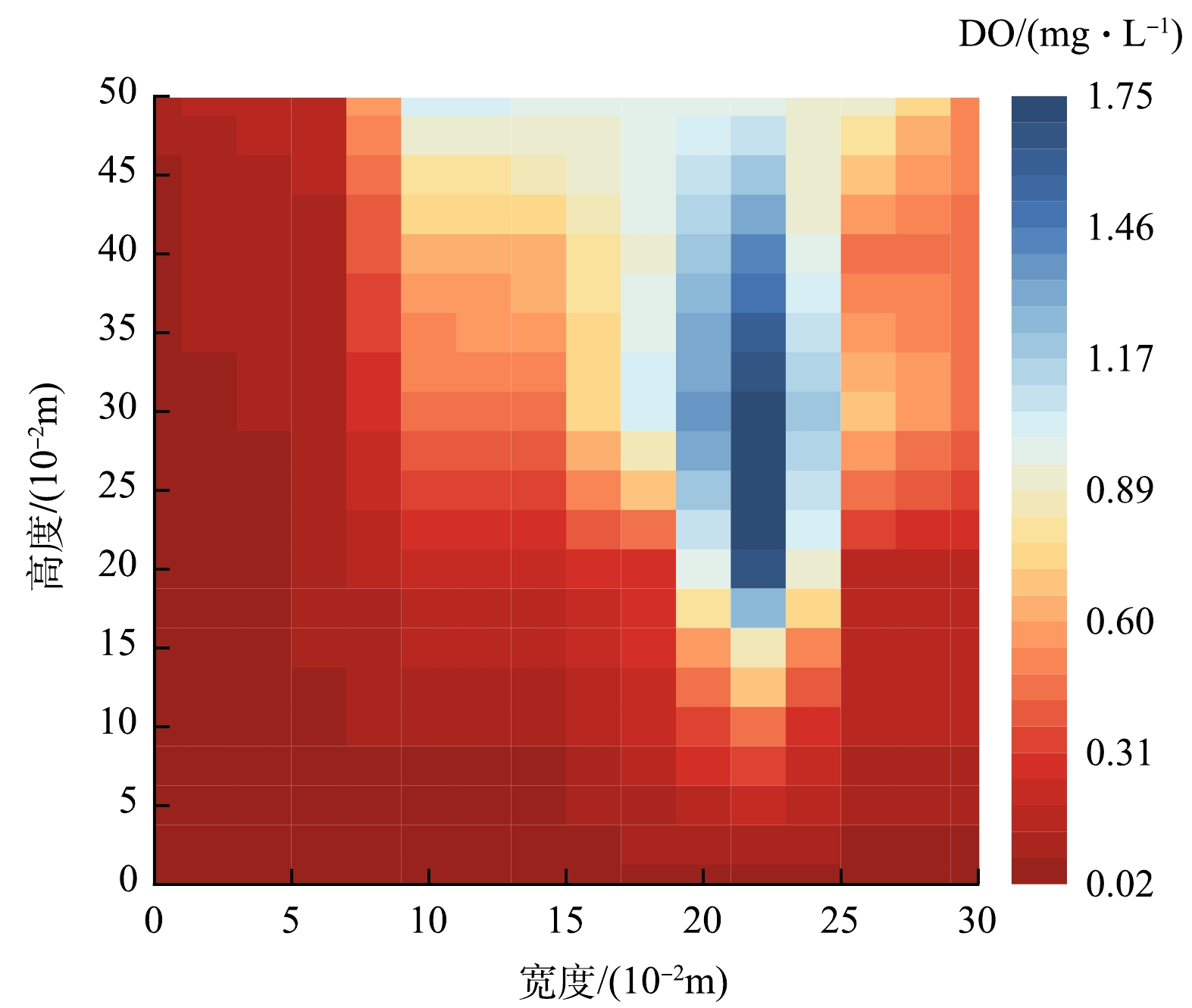
1) 反应器内DO质量浓度的分布规律。与常规A/O工艺中好氧池、缺氧池的溶解氧分布不同,由于混合液在反应器内不断循环,DO会从好氧区顶部进入缺氧区顶部,而好氧区底部也会存在缺氧状态。为探究DO质量浓度的分布规律,在本研究中测定了稳定运行期间反应器纵截面上不同位置的DO质量浓度(垂直方向测量间距为5 cm,水平方向测量间距为4 cm),并采用插值法预测反应器整体的DO分布情况(图5)。
如图5所示,反应器的DO质量浓度分布在0.02~1.75 mg·L−1,缺氧区的DO质量浓度集中在0.02~0.15 mg·L−1,上部部分区域的DO质量浓度大于0.15 mg·L−1;好氧区的DO质量浓度集中在0.10~1.10 mg·L−1,底部部分区域的DO质量浓度小于0.10 mg·L−1,DO质量浓度整体呈现出好氧区沿水流路径逐渐增加,缺氧区沿水流路径逐渐降低的分布规律。在好氧区内,通过底部的曝气装置对混合液进行曝气充氧,由于在好氧区中充氧速度大于需氧菌消耗DO的速度,故在混合液上升过程中DO质量浓度逐渐升高;当曝气产生的气泡到达好氧区顶部时会直接进入到空气中,不会被水流携带至缺氧区,所以充氧过程只在好氧区内进行[20],但充氧后的混合液很快流入缺氧区,导致缺氧区上部也存在一定的溶解氧;在缺氧区内,混合液中的DO在需氧菌的消耗下逐渐减少,最终形成缺氧环境。DO质量浓度的分布情况表明反应器内分别形成了适宜硝化菌和反硝化菌生长的环境,为含氮污染物的去除提供了必要条件[21]。
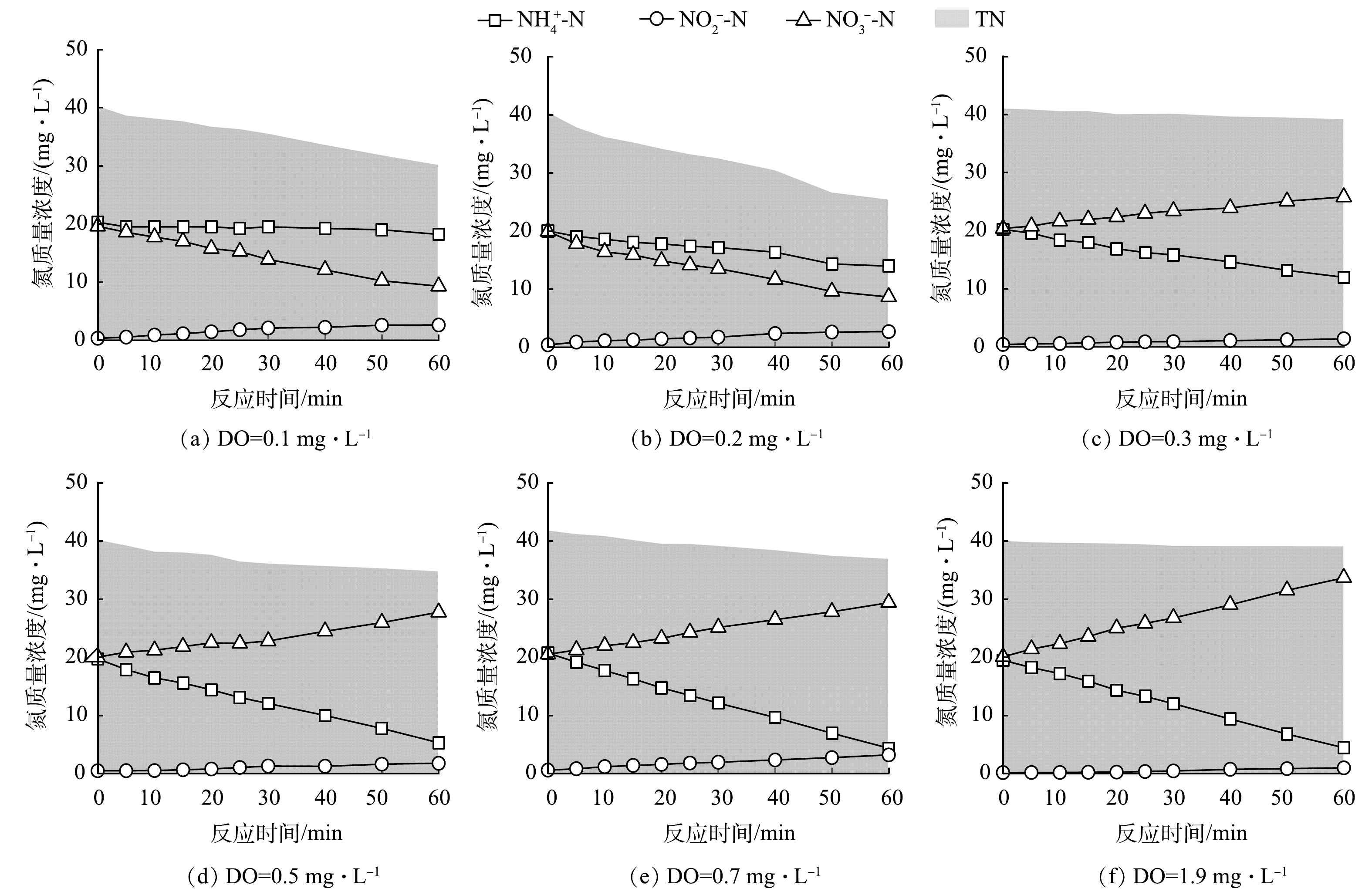
2) 脱氮途径分析。为进一步验证反应器稳定运行期间的脱氮机制,在探明系统内DO分布情况的基础上,通过批次实验研究了在DO质量浓度为0~2 mg·L−1内活性污泥对NH4+-N、NO2−-N、NO3−-N的降解情况(图6)。
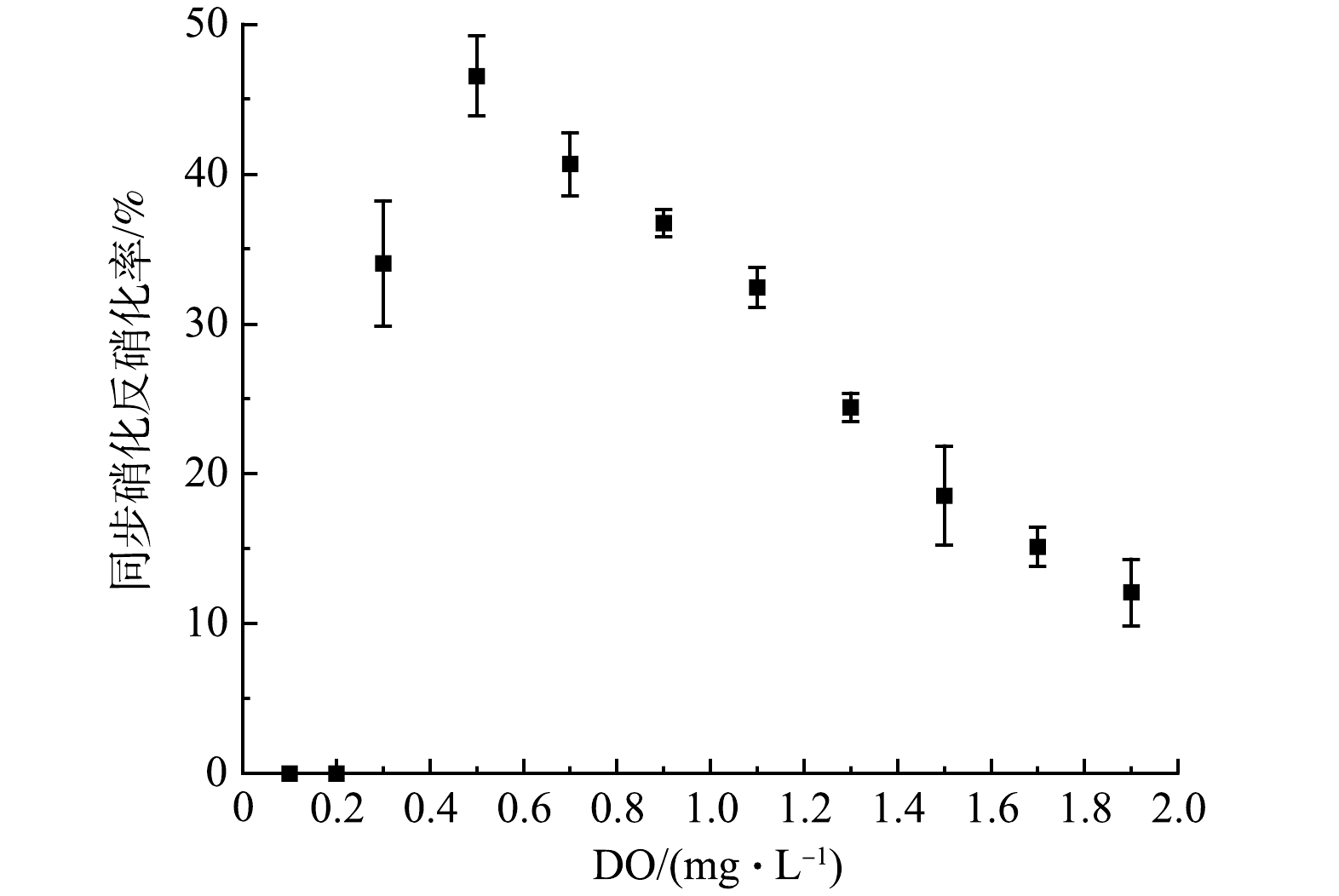
如图6所示,在不同的DO质量浓度下,氮组分呈现出不同的变化趋势。当DO小于0.1 mg·L−1时,NH4+-N基本保持不变,NO3−-N与TN显著下降,其下降速率分别为0.18、0.16 mg·(L·min)−1,表明DO过低会导致硝化菌被完全抑制,而在此DO质量浓度下系统主要进行反硝化脱氮(图6(a));当DO提高到0.2 mg·L−1时,NH4+-N、NO3−-N和TN质量浓度均降低,这说明此时系统中硝化和反硝化过程在同时进行,但反硝化速率大于硝化速率(图6(b));当DO提高至0.3 mg·L−1时,NH4+-N、TN质量浓度降低,而NO3−-N升高,即在此DO质量浓度下实现了同步硝化反硝化,同步硝化反硝化率为34.04%(图6(c))。进一步提高DO质量浓度,发现当DO为0.5 mg·L−1时,同步硝化反硝化率最大,最大值为46.54%(图6(d));但是当DO继续升高时,同步硝化反硝化率逐渐下降到12%(图6(e)、图6(f)和图7)。其原因是,在好氧条件下,当DO质量浓度较低时,由于氧的穿透力弱,污泥絮体外部会进行好氧硝化,而絮体内部会形成缺氧环境为反硝化提供溶解氧条件,实现硝化、反硝化的同步进行;随着DO质量浓度的升高,氧的穿透能力会逐渐增强,这时活性污泥絮体内部难以形成缺氧环境,反硝化会受到抑制,从而导致同步硝化反硝化率逐渐降低。结合图5中DO质量浓度的分布情况,计算出好氧区平均同步硝化反硝化率为26.49%,这表明好氧区出现了明显的同步硝化反硝化现象。综上所述,在曝气动力横向内循环反应器中,氮的主要去除途径包括好氧硝化-缺氧反硝化及同步硝化反硝化。
-
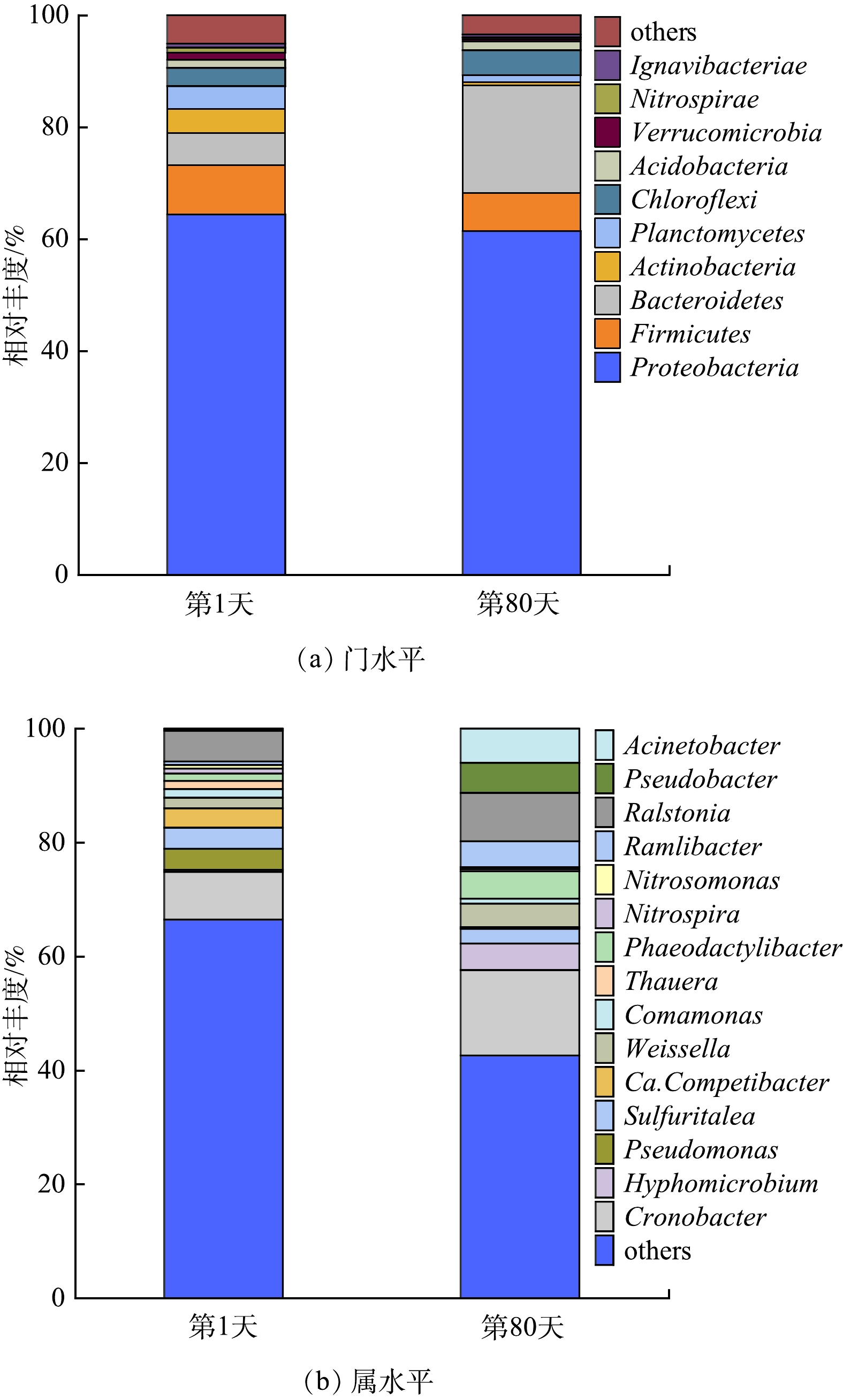
图8(a)为实验期间活性污泥的门水平微生物群落变化。如图8(a)所示,接种污泥(S1)与第80天活性污泥样品(S2)的主要门均为Proteobacteria、Bacteroidetes、Firmicutes、Chloroflexi和Planctomycetes,与常规污水生物处理研究中报道的主要菌门[22]相近。Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes是S1与S2的优势门,相对丰度分别为64.40%和5.74%(S1)、61.44%和19.17%(S2),Proteobacteria对于氮的去除起着重要作用,大多数参与脱氮的微生物(如AOB、NOB和反硝化菌)都属于Proteobacteria[23],Bacteroidetes参与分解蛋白质、多糖等大分子有机物,也能参与脱氮过程[24],这2个门的相对丰度较高,说明系统具有脱氮、去除有机物的能力。此外,Firmicutes、Chloroflexi和Planctomycetes门类对于氮和有机物的去除也起着一定的作用[25-26],广泛存在于各种废水生物处理系统中。
图8(b)为实验期间活性污泥的属水平微生物群落变化。如图8(b)所示,S1和S2微生物群落中主要的AOB和NOB分别为Nitrosomonas和Nitrospira,Nitrospira的丰度始终大于Nitrosomonas,表明在反应器内硝化完全,与实验期间未出现NO2−-N积累的现象相一致。S1样品中丰度较高的反硝化菌属包括Pseudomonas(3.73%)、Sulfuritalea(3.69%)、Ca. Competibacter(3.42%)、Comamonas(1.54%)、Thauera(1.44%)等[27],而上述反硝化菌属丰度在S2样品中均减小,这可能导致污泥比反硝化活性呈下降趋势(图3)。
值得注意的是,本研究中Hyphomicrobium属和Acinetobacter属分别从0.33%和0.07%增至4.64%和6%。有研究[28]认为,Hyphomicrobium丰度与氨氧化活性呈正相关关系,也有研究[29-30]认为Acinetobacter和Hyphomicrobium在好氧条件下仍具有反硝化的能力。在本实验中,Hyphomicrobium丰度的升高与系统硝化性能上升的变化趋势相一致(图3(a))。从Acinetobacter和Hyphomicrobium丰度的变化可以推断反应器好氧区中的SND不仅通过传统的好氧硝化-缺氧反硝化进行,也可能通过好氧反硝化进行,这也是本实验中同步硝化反硝化率高的主要原因。因此,反应器中Acinetobacter和Hyphomicrobium的富集与增殖有利于系统维持较高的脱氮效率(图2和图4)。
-
1)利用曝气动力横向内循环反应器可以在取消混合液循环泵的条件下实现良好的脱氮效果,在A/O比为1:1,HRT为9 h时,TN去除率高达(71.81±3.13)%,出水COD、NH4+-N和TN可以达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)中规定的一级A标准水质。
2)好氧区存在明显的同步硝化反硝化过程,当DO质量浓度为0.5 mg·L−1时同步硝化反硝化率最大,最大值为46.54%,好氧区的平均同步硝化反硝化率为26.49%。
3)反应器运行稳定后,具有好氧反硝化功能的Acinetobacter属和Hyphomicrobium属的丰度分别从0.33%和0.07%增长至4.64%和6%,有利于系统生物脱氮效率以及同步硝化反硝化率的提升。
曝气动力横向内循环反应器脱氮途径与性能分析
Nitrogen removal pathway and performance analysis of aeration-power lateral internal-circulation reactor
-
摘要: 为降低城市污水生物脱氮系统处理能耗、提高脱氮效率,使用一种新型曝气动力横向内循环反应器(ALIR)来处理模拟城市污水并对该反应器的脱氮途径与性能进行了研究,采用16S rRNA基因高通量测序技术对微生物群落结构进行了分析。结果表明:反应器在A/O比为1:1、水力停留时间为9 h、污泥龄为20 d、污泥回流比100%的条件下,连续运行90 d后,出水NH4+-N质量浓度低至(3.20±0.93) mg·L−1,平均去除率为92.29%,出水总氮(TN)质量浓度为(11.68±1.31) mg·L−1,TN去除率达到71.81%,同时好氧区平均同步硝化反硝化(SND)率达到26.49%;接种污泥与第80天活性污泥的优势门均为Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes;与接种污泥相比,第80天污泥中Pseudomonas、Sulfuritalea等反硝化菌属丰度呈下降趋势,具有好氧反硝化功能的Acinetobacter属和Hyphomicrobium属的丰度则明显增加。综上,实验条件下,曝气动力横向内循环反应器可以免除内回流能耗,并获得良好的脱氮效果。该研究结果可为内循环反应器在实际工程中的应用提供参考。Abstract: In order to reduce the energy consumption and improve the nitrogen removal efficiency of biological nitrogen removal system for urban sewage, a new type of aeration-power lateral internal-circulation reactor (ALIR) was used to treat artificial urban sewage, and the nitrogen removal pathway and performance of the reactor was investigated. 16 S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing technology was used to analyze microbial community structure. The results showed that at A/O ratio of 1:1, hydraulic retention time of 9 h, sludge age of 20 d and sludge return ratio of 100%, the effluent concentrations of ammonia and total nitrogen (TN) were as low as (3.20±0.93) mg·L−1 (92.29%, ammonia removal efficiency) and (11.68±1.31) mg·L−1 (71.81%, TN removal efficiency) after long-term operation for over 90 days, respectively, and the simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) rate was 26.49%. The results of the high-throughput sequencing showed that the dominant phyla in the inoculated sludge and the activated sludge on the 80th day were Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes. Compared with the inoculated sludge, the relative abundances of denitrifying bacteria in the activated sludge on the 80th day, such as Pseudomonas and Sulfuritalea, showed a decreasing tendency, while these of Acinetobacter and Hyphomicrobium with an aerobic denitrifying function increased significantly. Thus, the aeration dynamic transverse internal circulation reactor had a good nitrogen removal performance without the energy consumption of internal circulation under the experimental operating conditions. This will provide a reference for the application of this reactor in practical engineering.
-

-
-
[1] LU J Y, WANG X M, LIU H Q, et al. Optimizing operation of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: The remaining barriers and future implications[J]. Environment International, 2019, 129: 273-278. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.057 [2] SHI L L, MA B, Li X Y, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal without addition of external carbon source in an anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic sequencing batch reactor[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 42(9): 1507-1515. doi: 10.1007/s00449-019-02148-z [3] ZHANG J, SHAO Y, WANG H, et al. Current operation state of wastewater treatment plants in urban China[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 195(1): 110843. [4] DREWNOWSKI J, SKWAREK A R, DUDA S, et al. Aeration process in bioreactors as the main energy consumer in a wastewater treatment plant: Review of solutions and methods of process optimization[J]. Processes, 2019, 7(5): 311. doi: 10.3390/pr7050311 [5] 郑俊田, 郑俊, 程洛闻, 等. 混合液回流比对多点进水新型A/O/A/A/O泥膜耦合工艺脱氮除磷的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(5): 1744-1752. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202011119 [6] FOLADORI P, VACCARI M, VITALI F. Energy audit in small wastewater treatment plants: Methodology, energy consumption indicators, and lessons learned[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2015, 72(6): 1007-1015. doi: 10.2166/wst.2015.306 [7] SULC R, DYMAK J. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer in a concentric internal jet-loop airlift bioreactor equipped with a deflector[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(14): 1-28. [8] BURLUTSKII E, FELICE R D. Experimental and numerical study of two-phase flow mixing in gas-liquid external-loop airlift reactor[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2019, 119: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2019.07.007 [9] YANG T, GENG S J, GAO F, et al. Investigation of hydrodynamics and mass transfer in an internal loop airlift slurry reactor integrating mixing and separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 259: 118209. [10] DUAN H R, WANG Q L, ERLER D V, et al. Effects of free nitrous acid treatment conditions on the nitrite pathway performance in mainstream wastewater treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644(10): 360-370. [11] 李韧, 于莉芳, 张兴秀, 等. 硝化生物膜系统对低温的适应特性: MBBR和IFAS[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(8): 3691-3698. [12] 于莉芳, 张兴秀, 张琼, 等. 生物膜系统中部分反硝化实现特性[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4390-4398. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202102063 [13] YU L F, LI R, MO P C, et al. Stable partial nitrification at low temperature via selective inactivation of enzymes by intermittent thermal treatment of thickened sludge[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 418(3): 129471. [14] 张智, 刘亚琴, 傅斌, 等. DO和填料对多级A/O工艺同步硝化反硝化的影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2013, 29(17): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4602.2013.17.003 [15] 于莉芳, 汪宇, 滑思思, 等. 城市污水处理厂进水氨氧化菌对活性污泥系统的季节性影响[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1923-1929. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008075 [16] 赵骥, 王晓霞, 李夕耀, 等. DO浓度对EBPR耦合SND处理低C/N污水的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(1): 120-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.01.015 [17] 梁潇, 姚新运, 李亮, 等. 城镇污水AAOA高标准除磷脱氮技术开发与应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(2): 612-620. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202111074 [18] GE S J, WANG S Y, YANG X, et al. Detection of nitrifiers and evaluation of partial nitrification for wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 140: 85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.004 [19] 邓璐, 何江涛, 邹华, 等. 洛美沙星对水中反硝化过程的影响模拟试验[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(7): 2934-2942. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.07.017 [20] ZHENG Z Y, CHEN Y Q, ZHAN X B, et al. Mass transfer intensification in a novel airlift reactor assembly with helical sieve plates[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 342: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.039 [21] YAN L L, LIU S, LIU Q P, et al. Improved performance of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification via nitrite in an oxygen-limited SBR by alternating the DO[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 275: 153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.054 [22] 贺赟, 李魁晓, 王佳伟, 等. 不同季节城市污水处理厂微生物群落特性[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1488-1495. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202007015 [23] IBARBALZ F M, FIGUEROLA E L M, ERIJMAN L. Industrial activated sludge exhibit unique bacterial community composition at high taxonomic ranks[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(11): 3854-3864. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.010 [24] MENG F G, HE X. Effects of naturally occurring grit on the reactor performance and microbial community structure of membrane bioreactors[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 496: 284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2015.09.015 [25] CHEN D, WANG H Y, JI B, et al. A high-throughput sequencing study of bacterial communities in an autohydrogenotrophic denitrifying bio-ceramsite reactor[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(11): 1904-1910. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.07.006 [26] WANG Y Y, CHEN J, ZHOU S, et al. 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing reveals shift in nitrogen conversion related microorganisms in a CANON system in response to salt stress[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 512-521. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.096 [27] HUANG W, GONG B Z, WANG Y M, et al. Metagenomic analysis reveals enhanced nutrients removal from low C/N municipal wastewater in a pilot-scale modified AAO system coupling electrolysis[J]. Water Research, 2020, 173: 115530. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115530 [28] FUKUSHIMA T, WHANG L M, CHEN P C, et al. Linking TFT-LCD wastewater treatment performance to microbial population abundance of Hyphomicrobium and Thiobacillus spp[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 141(4): 131-137. [29] 王永刚, 王旭, 张俊娥, 等. 好氧反硝化细菌研究及应用进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2017, 37(2): 6. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2017.37(2).012 [30] GU X, LENG J T, ZHU J T, et al. Influence mechanism of C/N ratio on heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 343: 126116. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126116 -



 下载:
下载: