-
近年来,我国高铁事业迅猛发展,运营里程预计在2025年达到3.8×104 km[1-2]。高铁采用真空集便器代替传统沿线直排的如厕方式[3],集中收集和处理列车运行过程中产生的集便器污水[4]。而粪便、尿液及部分洗漱用水较常规市政污水来说具有高有机物、高氨氮、低碳氮比[5-6]等特点,极大增加了站段污水处理设施的压力。因此,在铁路段污水排放需满足《污水排入城镇下水道水质标准》 (GB/T31962-2015) B级标准[7]情况下,选择更高效的工艺对集便器污水中污染物,特别是氨氮、总氮的去除,成为铁路运输行业的水污染治理的重要内容。
集便器污水水质与黑水水质相近,有机物及悬浮固体浓度较高,且氨氮远大于有机物浓度,还可能含有病原微生物[8-9],多采用化学脱氮方法及传统硝化反硝化工艺进行处理。部分国家采用化学脱氮方法,如电解法、地面焚烧法等,但需对处理后水质及处理装置内产生的悬浮性固体进行二次分离,操作流程较复杂[10]。而传统硝化反硝化工艺脱氮往往需要足够碳氮比,在碳源不足情况下会大大影响生物脱氮处理效果,导致总氮去除效果偏低[11]。如采用单级与多级A/O-SBR工艺处理黑水,在未加碳源情况下,单级处理总氮平均去除率为51.5%;而多级处理虽有所提升,但最高仅为87.8%[12]。
厌氧氨氧化反应指在厌氧或缺氧的环境条件下厌氧氨氧化菌以氨氮为电子供体,以亚硝态氮为电子受体作用产生氮气[13]。相较于常规的生物脱氮工艺,厌氧氨氧化反应及其耦合工艺过程无需碳源消耗且可降低50%的曝气量[14-15],目前已成功应用于多种低碳氮比污水的处理。本研究采用以厌氧氨氧化反应为核心的一体式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺对高铁动车段内实际集便器污水中的氨氮、总氮及耗氧有机物 (以COD计) 进行去除研究,在实验进行的不同阶段取样分析观察系统内微生物群落多样性,以了解污染物去除性能在各个阶段的变化及耦合系统的去除机制,从而为该工艺扩大研究及现场应用提供参考。
-
本研究选取武汉某动车站段作为实验地点,取站段内厌氧化粪池出口处的集便器污水作为实验用水。污水水质指标:氨氮为750~1 000 mg·L−1,总氮为800~1 100 mg·L−1,COD为800~1 800 mg·L−1,亚硝态氮及硝态氮均<1 mg·L−1,pH为7.8~8.2。装置内接种悬浮污泥为含厌氧氨氧化菌 (anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria,AnAOB)的颗粒污泥,取自北京高碑店污水处理厂内高氨氮废水处理反应器,MLSS为2 000~2 500 mg·L−1。生物膜填料取自实验室成功运行的厌氧氨氧化耦合反应器,该反应器脱氮性能良好。
-
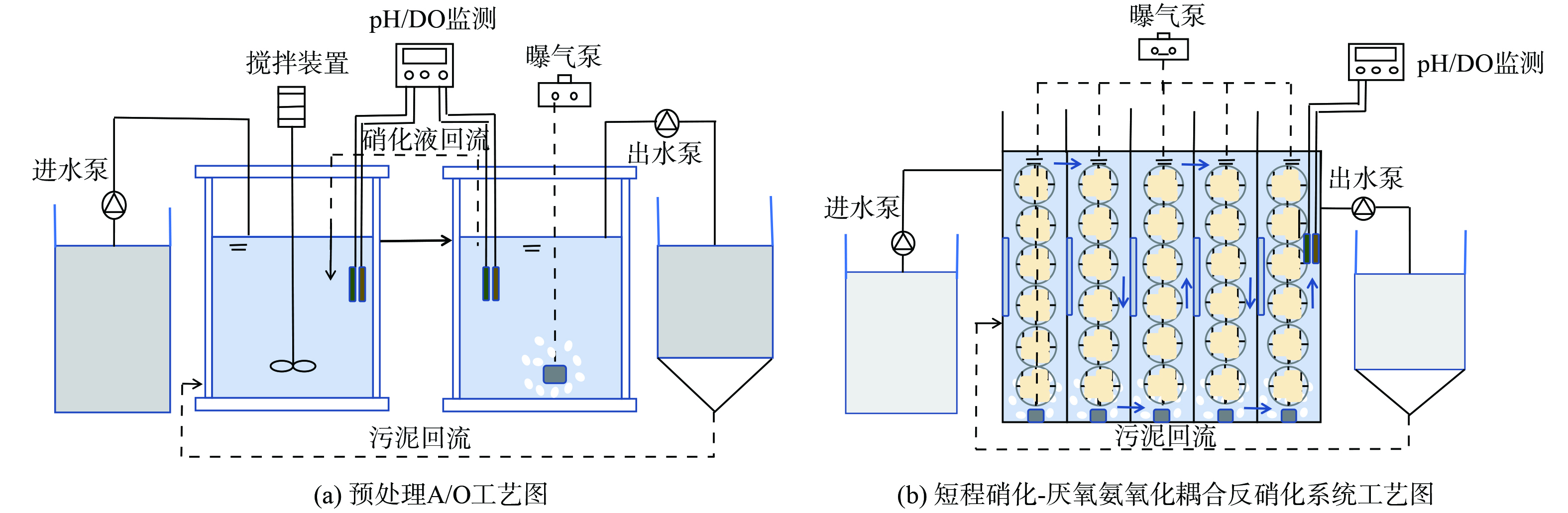
为减轻水质波动变化及高负荷水质对后续耦合反应系统所承受的冲击负荷、增强微生物活性,采用A/O工艺进行预处理。A/O工艺装置包含集便器污水进水水箱、厌氧反应池、好氧反应池及沉淀池。进水箱为塑料圆柱形水桶,容积约50 L;厌氧池为直径25 cm、高20 cm的圆柱形容器,容积为10 L、有效容积为6 L;好氧池为直径32 cm、高30 cm的圆柱形容器,容积为25 L、有效容积为18 L;沉淀池容积约20 L。其中,厌氧池设电动搅拌器,使反应池中的活性污泥能充分混合;好氧池由曝气机供气,曝气石曝气。短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化实验装置由有机玻璃制成,其长、宽、高分别为50 cm、10 cm、115 cm,容积为57.5 L、有效容积为50 L。内置1 cm×1 cm×1 cm的立方体聚氨酯海绵生物膜填料,填料填充比为85%。沉淀池容积约15 L。预处理及耦合装置中分别放置加热棒以提供适宜微生物生长的温度条件。配置实验设备型号如下:蠕动泵 (YZ1515x,兰格恒流泵有限公司) 、曝气泵 (ACO-004,森森集团股份有限公司) 、加热棒(AR-4,森森集团股份有限公司)、搅拌机(DJ-120,上海予星仪器设备有限公司)及便携式pH、DO测定仪 (Multi 3620,上海世禄仪器有限公司) 。具体工艺流程如图1所示。
预处理及耦合工艺设置适宜的实验环境,使集便器污水中的氨氮及COD在氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria,AOB)、厌氧氨氧化菌(AnAOB)和反硝化菌的协同作用下被反应去除,具体参数如表1所示。同时,实验启动过程由人工配水与经预处理后的集便器污水混合作为实验进水,采用分阶段不同比例的进水方式,具体进水方式如表2所示。
-
实验过程中氨氮、亚硝态氮、硝态氮和总氮的检测均参照《水和废水监测分析方法》[16]。COD的测定采用哈希快速消解法。微生物分析样品取自系统添加集便器污水前及稳定运行后2个阶段,随机取单块海绵生物膜填料,剪碎后加入50 mL离心管中,经超纯水超声处理后得到生物膜样品。采用NEXTflexTM Rapid DNA-Seq Kit (Bioo Scientific,美国)进行建库,利用Illumina公司的Miseq PE300/NovaSeq PE250平台进行测序 (上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司) 。
-
短程硝化厌氧氨氧化脱氮贡献率A采用公式 (1) ,反硝化脱氮贡献率采用公式 (2) 进行计算[17]。
式中:(NH4+-N)rem、TNrem分别为耦合反应器中氨氮和总氮去除量,mg·L−1。
-
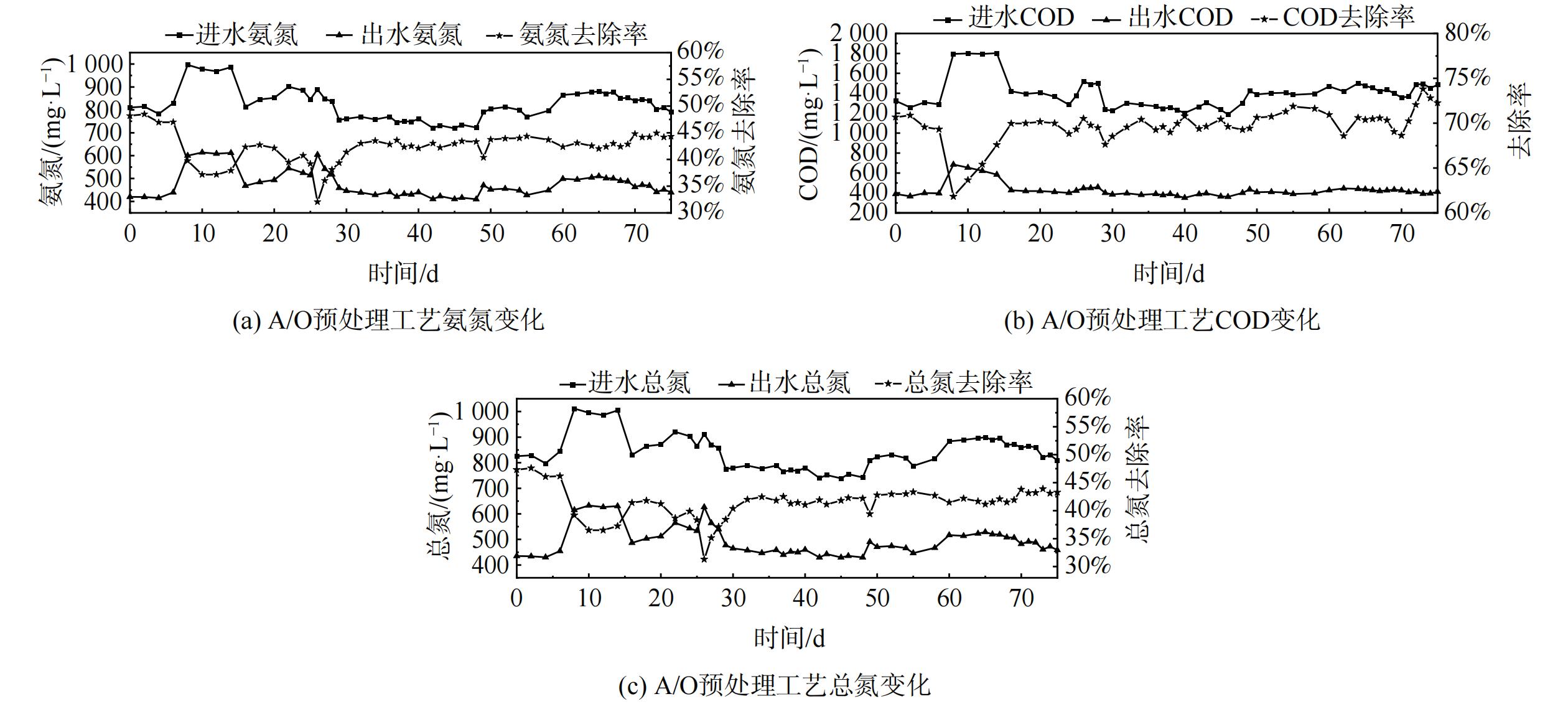
采用A/O工艺对厌氧池中的集便器污水进行初步降解,为后续一体式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统提供适宜的水质条件。反应器运行期间的污染物去除性能具体如图2所示。
在为期75 d的集便器污水处理过程中,出水中的氨氮、COD和总氮随着进水水质的波动存在一定差异性,但整体较为稳定。第1~51天溶解氧为1.50~2.00 mg·L−1,氨氮、COD及总氮去除率始终保持在约43%。从第52天开始,将溶解氧提升至2.00~2.50 mg·L−1,氨氮降解速率有所提升。但由于进水中碳氮比较低, O池在持续曝气下将大部分有机物消耗并产生少量亚硝态氮,A池缺乏额外基质来促进反硝化菌的生长,总氮的去除效率较之前有所降低。而在曝气提升作用下,COD进一步降低。这与林明等[18]的研究一致,采用A/O-MBBR组合工艺对生活污水进行实验研究,在未添加碳源的情况下,出现总氮处理不达标情况。最终,预处理后的氨氮在400~500 mg·L−1,去除率约为44%;COD降低的速率较快,进水COD在(1 400±50) mg·L−1的条件下出水COD约为400 mg·L−1,降低了约73%;由于集便器污水中存在少量有机氮及A/O工艺生成的亚硝态氮、硝态氮,总氮的去除效率约为43%。
污染物的降解效果表明,A/O预处理工艺的运行状况稳定且良好,为后续短程硝化厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺的运行提供了保证。因短程硝化厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化装置内接种生物膜填料曾在低氨氮、无COD环境中培养,可能无法承受进水中过高氨氮及COD。则A/O工艺对进水预处理后出水降低部分氨氮及COD,可在一定程度上减少对耦合装置内菌种的冲击破坏作用,最大程度保证后续实验的准确性。同时,出水水质仍属低碳氮比污水,无大量硝态氮积累,仅含有少量亚硝态氮,可为后续厌氧氨氧化反应的进行提供反应基质[19]。
-
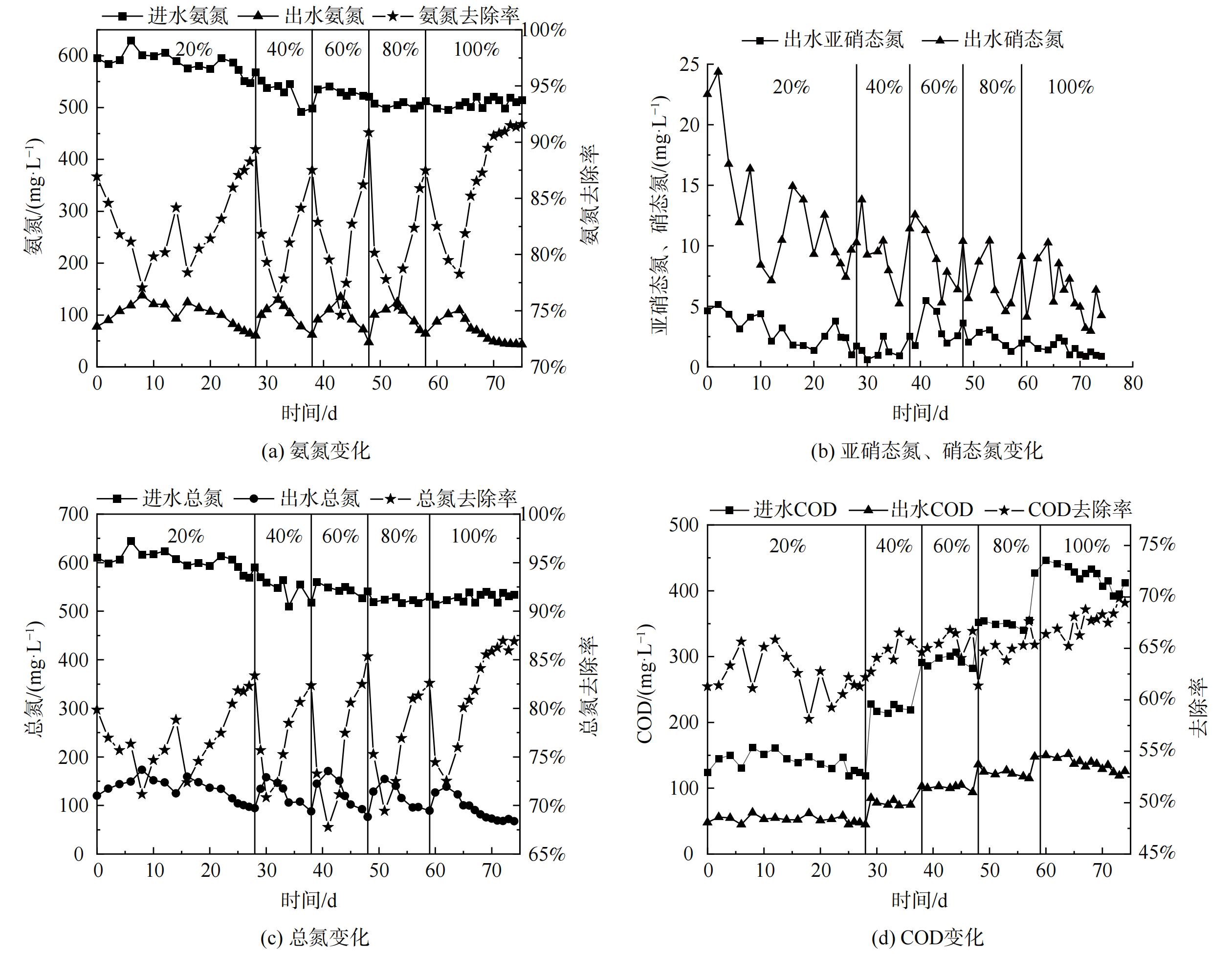
按照集便器污水所占比例分别为20%、40%、60%、80%和100%的原则进水。在75 d的运行过程中,短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺的进水全部替换为经预处理后的集便器污水,污染物去除效果较好,如图3所示。
第Ⅰ阶段 (第0~28天) 以20%比例集便器污水作为实验进水。在第1~7 天,出水氨氮升高,由最初的77 mg·L−1逐渐升至137 mg·L−1,总氮去除负荷由0.144 kg·(m3·d)−1降至0.129 kg·(m3·d)−1,氨氮去除率由87.03%下降为77.06%。按比例在进水中增加集便器污水会导致系统性能出现短暂的波动,且反应初期所需恢复时间较中后期长。这是由于采用配水启动反应器时系统内有机物较低,反硝化菌生长量较少。观察耦合系统的波动现象分析,这可能是由于系统中增加一定量的耗氧有机物 (以COD计) ,使短期内反硝化菌生长速度加快。因此,突增过高的COD表明过多耗氧有机物可能会加强自养反硝化和异养反硝化脱氮,促进异养微生物生长而抑制AnAOB活性,使厌氧氨氧化脱氮受到抑制[20]。由于本研究采用逐步增加进水比例方式,虽进水COD呈升高趋势,但耦合系统保持了较为平稳地增加。系统内反硝化菌增长速度及趋势也受到控制,并未保持像刚添加集便器污水时的状态。实验添加20%比例集便器污水过程中,由于AOB对氧的亲和力高于亚硝酸盐氧化细菌(nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, NOB),采用低氧曝气策略,控制溶解氧为0.10~0.25 mg·L−1。在溶解氧浓度不足的情况下,促使系统内氧气优先与AOB结合,以达到减缓NOB的好氧速率来抑制其生长的目的[21-23],同时促进耦合系统内短程硝化反应的发生。观察发现出水亚硝态氮值呈逐步降低趋势,这说明此时系统内NOB可能已完全被洗脱出,AOB菌种已成为优势菌种。进水中的氨氮在AOB的作用下利用系统提供溶解氧部分氧化为亚硝态氮,之后AnAOB利用产生的亚硝态氮及水中剩余氨氮发生厌氧氨氧化反应降解污染物,并生成硝态氮。同时,进水中COD持续增加说明耗氧有机物被反硝化菌消耗,将系统内可能存留的少量亚硝态氮、厌氧氨氧化生成的硝态氮还原生成氮气从系统中逸出。不同功能菌群在协同作用下对集便器污水中的污染物进行降解,实现短程硝化厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化脱氮。经过为期28 d的适应运行,出水氨氮为60.2 mg·L−1,去除率为89.4%,总氮去除负荷达0.141 kg·(m3·d)−1,出水COD为45 mg·L−1,降低了约62%。
第Ⅱ阶段 (29~38 d) 添加40%比例集便器污水后,由于进水中COD进一步升高,系统波动导致氨氮去除率提升变化较小。但经一段时间水质适应后,系统很快恢复至较高处理水平,这说明采用按比例添加集便器污水可保证系统内微生物保持平衡状态。为加强短程硝化作用,同时提升厌氧氨氧化反应速率,溶解氧提升至0.25~0.35 mg·L−1。此时,出水亚硝态氮变化趋势较为平稳,这说明耦合系统内AOB活性得到增强,AnAOB获得充足的生长基质,抵消亚硝酸盐积累现象则未产生AnAOB受抑制情况[24-26],体现了AOB及AnAOB间协同生长作用优势。同时,研究表明,NOB最适宜的溶解氧为0.7~1.4 mg·L−1,此时系统溶解氧低于该范围,故NOB活性将受到抑制,这表明该阶段耦合系统内短程硝化反应稳定发生[27-29]。同时,出水硝态氮呈持续降低趋势可知其已被反硝化菌利用,但由于进水中COD较低,造成COD降低程度较小。此阶段最终出水氨氮为57.02 mg·L−1,去除率为88.5%,总氮去除负荷为 0.136 kg(m3·d)−1,出水COD为75 mg·L−1,降低了66%。
之后,第Ⅲ (第39~48天) 、Ⅳ (第40~59天) 、Ⅴ (第60~75天) 阶段,逐步添加60%、80%及100%比例集便器污水,保持耦合系统内溶解氧为0.25~0.35 mg·L−1。系统始终保持较好的抗冲击负荷能力和恢复能力,出水氨氮去除趋势与前2个阶段相似。此现象说明耦合工艺在逐步添加定比例的集便器污水后,系统对水质的适应性已逐步增强,恢复时间逐步变短,促使耦合系统的氨氮、COD及总氮处理率随之增加。因此,在第Ⅲ、Ⅳ阶段,出水氨氮分别为47.62 mg·L−1和54.21 mg·L−1,氨氮去除率分别为90.86%和89.41%,总氮去除负荷分别为0.139 kg·(m3·d)−1和0.137 kg·(m3·d)−1,出水COD分别为94 mg·L−1和115 mg·L−1,分别降低了67%、68%。直至添加进水比例至100%,出水亚硝态氮含量变化趋势基本保持一致,未出现逐步升高现象,这说明耦合系统内的短程硝化及厌氧氨氧化反应稳定协同发生。在第Ⅰ至Ⅴ阶段采用多阶段逐步采用低氧曝气(<0.4 mg·L−1)并根据运行情况调整固定至适宜范围,对调节集便器污水处理耦合系统内的氧环境、对短程硝化反应的发生和强化及促进厌氧氨氧化反应与其耦合发生均有促进作用[30-31]。另外,对应COD处于适宜水平,可实现短程硝化厌氧氨氧化作用与反硝化作用有效耦合[32],共同提升耦合系统的脱氮效能。
最终,系统稳定运行100%比例的集便器污水后,出水氨氮、总氮和COD仅为40.25 mg·L−1、67.40 mg·L−1和120 mg·L−1,去除率分别达90.84%、86.90%和70.02%,最高总氮去除负荷为0.141 kg·(m3·d)−1。同时,系统生成亚硝态氮和硝态氮随着COD的升高呈下降趋势,与反应运行初期相差20 mg·L−1以上,这表明在第Ⅰ~Ⅴ阶段中耦合系统的反硝化过程良好,且硝态氮优先被反硝化菌利用。因此,观察第Ⅰ~Ⅴ阶段发现,在进水COD逐步升高情况下,系统内反硝化菌增长速度较稳定,未像初步添加20%比例集便器污水时出现大量增长趋势。这说明耦合系统已完全适应该水质,且短程硝化、厌氧氨氧化及反硝化反应已形成平衡状态。出水氨氮、COD及总氮的降解效果可达到《污水排入城镇下水道水质标准》 (GB/T31962-2015) B级标准。这说明耦合系统的运行良好,对集便器污水的处理性能较优。
-
在逐步添加集便器污水进水比例时,短程硝化厌氧氨氧化和反硝化作用对脱氮的贡献也发生了不同变化。当进水比例为20%,由于耦合系统内初步增加一定量COD,导致反硝化作用较未添加时有所增强。系统内短程硝化厌氧氨氧化脱氮贡献率低于反硝化脱氮贡献率,分别为31.22%和68.78%,出水氨氮及COD分别平均降低了77.06%和62.01%。耦合系统在适应进水水质变化后,增加进水比例为40%、60%时,短程硝化厌氧氨氧化的脱氮贡献率出现上升趋势,提升至45.64%和46.72%,反硝化脱氮贡献率降低至54.36%和53.28%,耦合系统平均出水氨氮及COD分别为62.31 mg·L−1、47.62 mg·L−1和75 mg·L−1、94 mg·L−1。由于亚硝酸盐可同时作为厌氧氨氧化反应和反硝化反应的电子供体[33],二者作用可共存且对亚硝酸盐存在竞争关系[34]。但进水碳氮比较小,无法为反硝化作用提供足够驱动力与厌氧氨氧化反应争夺利用亚硝酸盐,因此厌氧氨氧化反应较反硝化反应竞争力更强[35-36]。因此,在后期进水比例加大时,进水氨氮充足的条件下逐渐形成耦合系统内AnAOB生长及对亚硝酸盐竞争均大于反硝化菌的局势[37],系统内短程硝化厌氧氨氧化作用的脱氮贡献率也逐步大于反硝化脱氮作用。因此,在进水比例增加至80%及100%,短程硝化厌氧氨氧化及反硝化对脱氮的平均贡献率基本保持在77.90%和22.10%。这说明耦合系统已完全适应水质变化,实现最佳的耦合脱氮效果。
-
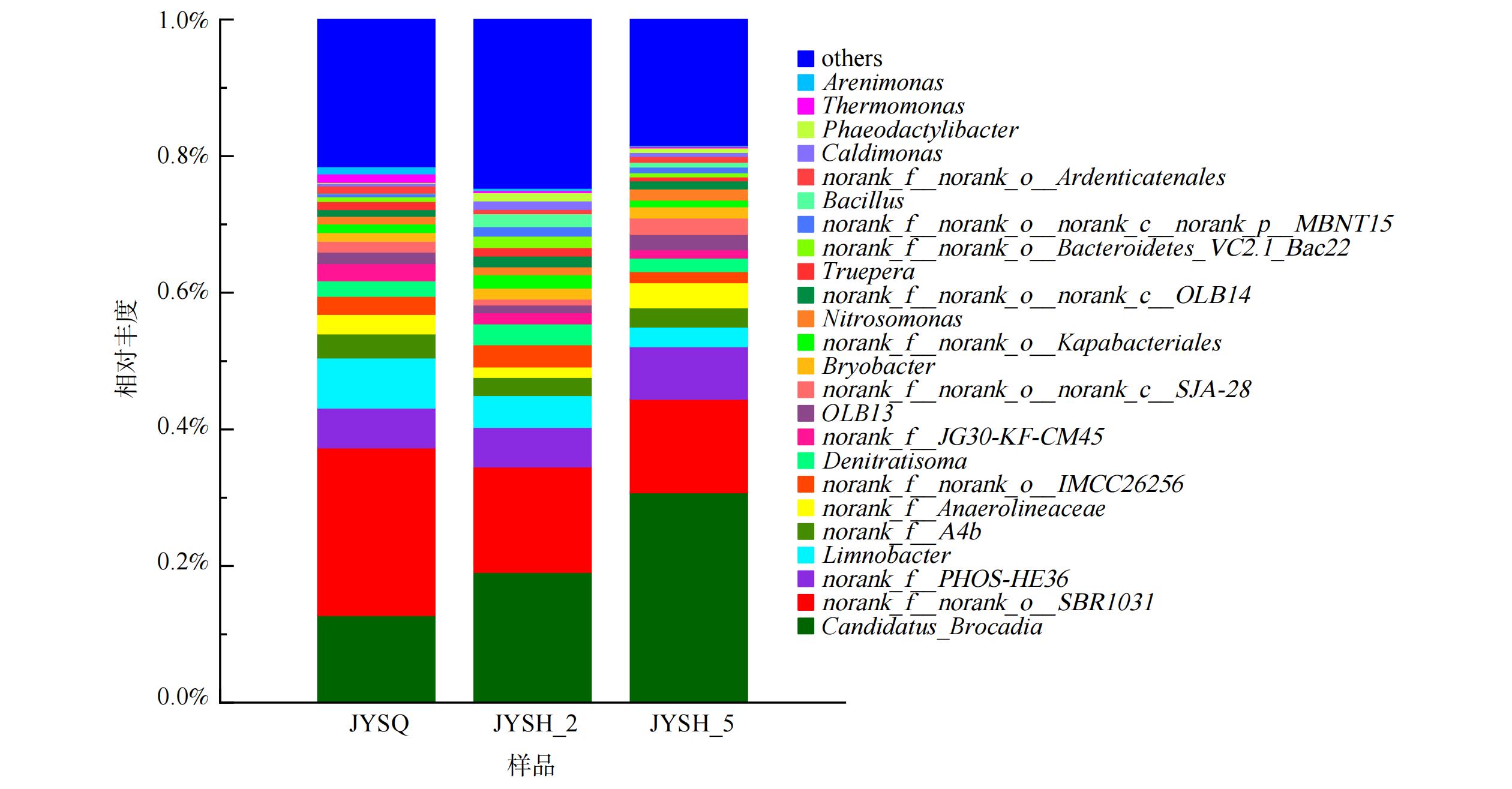
为更加清楚地了解污染物去除性能的变化与系统的去除机制,对短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺不同运行时期的微生物进行群落多样性分析。分别取进集便器污水前第5格 (JYSQ) 、处理实际集便器污水且运行稳定后第5格 (JYSH_2) 和第2格 (JYSH_5) 内的海绵填料进行16sRNA高通量测序,以了解工艺运行过程中属水平上的微生物群落结构变化,从而获得厌氧氨氧化耦合工艺高效运行的策略。
由图4可知,Candidatus_Brocadia始终是反应器内的AnAOB优势菌属且随工艺的运行,其相对丰度逐渐升高。第5格填料( (JYSQ) 内所占比例在运行集便器污水前为13%,耦合工艺稳定运行后升高至约30.70%。这证明AnAOB在填料内较好生长,与系统脱氮性能的逐渐优化相对应。另外, AOB菌属亚硝化单胞菌Nitrosomonas和反硝化菌属Denitratisoma均被检出,而无亚硝酸盐氧化菌(NOB)相关菌属。启动前Nitrosomonas及反硝化菌属Denitratisoma丰度分别为1.37%和2%;启动后增加至1.62%及3.2%。从微生物的角度证明了耦合系统的作用机制,即在短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化协同作用下去除集便器污水中的污染物。
同时,由于反应器递进式的运行方式,第2格中 (JYSH_2) 的污染物浓度远高于第5格 (JYSH_5) 。第2格与第5格填料中差异最大的菌属为Candidatus_Brocadia,两者相差11.60%。这说明进水污染物浓度会影响该菌种的丰富度,该菌属更适合在低基质浓度中生存[38]。而norank_f__norank_o__SBR1031、Limnobacter等菌属的相对丰度差异说明不同菌属对底物浓度的耐受程度不同。
-
1) 可行性。短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统采用逐步提升进水中的集便器污水比例可减少系统处理效能波动及冲击,保证系统启动及运行所需恢复时间的稳定。同时,AOB、AnAOB及反硝化菌保持协同生长作用,维持AOB及AnAOB的增殖趋势,避免异养菌过量繁殖抑制AnAOB的活性,以减少对进水水质状况变化的适应时间。因此,采用逐步增加集便器污水进水比例,虽提升了各阶段有机物浓度,但系统已具备一定量的反硝化菌和抗冲击负荷能力,减缓 AnAOB的抑制作用,系统能更快适应新的进水水质,达到稳定的去除效果。
2) 应用性。传统SBR工艺处理粪便污水,氨氮去除率基本保持在61.00%~65.40%,鲁帅等[39]对SBR工艺进行改良提升后,平均氨氮去除率提升至67.10%~72.90%。同时,需采用在线控制,对工艺中搅拌、曝气、停曝搅拌、沉淀、排水这几个阶段进行合理且精密控制[40-41]。本研究采用一体式连续流装置,仅需对系统内曝气量及温度进行控制,控制方式较为简便,同时可以达到更优的出水处理效果。另外,采用一体式部分硝化-厌氧氨氧化 (PNA) 工艺处理低碳氮比污水可改善SBR等传统工艺的缺点,其中颗粒污泥及生物膜工艺处理效果更为突出。颗粒污泥在应用方面存在一定限制性,颗粒尺寸大小及溶解氧的控制对AnAOB菌种活性及系统脱氮性能均有影响[42]。而本研究采用生物膜工艺,相较颗粒污泥提升了对菌种的保留度,来抵抗水质变化的冲击。同时,形成AOB生长在外层,AnAOB生长在内层的稳定生物结构,可为功能菌提供适宜的溶解氧浓度环境。
3) 经济性。比较传统工艺及厌氧氨氧化耦合工艺对低碳氮比污水脱氮的实际应用,传统硝化反硝化工艺在运行成本及控制成本等方面要求较高,需要较多的曝气量并外加碳源,同时生成大量污泥[43]。本研究采用短程硝化厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺,无需补充碳源、曝气量低、污泥产量低。由表3可知,不论是污泥处置和补充药耗等产生的运行成本,还是系统的控制难度及运行维护,均优于传统硝化反硝化工艺[44]。但本工艺中所需厌氧氨氧化菌种倍增时间长,需要对生长环境进行维护 (保证工艺运行的适宜水温) ,故是否需要增加对菌种的补充及维护成本需结合各因素进行考虑。
其中,干污泥处理费用以400 元·t−1计,补充药耗费用以处理每吨水量计,电耗费用以处理设施运行设备所需的电费计,加热所需费用以武汉地区提升水温所产生电加热费用的平均值计 (传统工艺所需费用需根据实际情况是否在冬季进行生物处理后进行考虑) 。
-
1) 在为期75 d的运行过程中,A/O预处理工艺的运行良好且稳定,对氨氮和COD的去除率分别达到44%和73%,为后续耦合工艺提供了水质条件。
2) 按照分阶段进水的原则向系统内添加集便器污水,工艺运行稳定后出水氨氮及总氮为40.25 mg·L−1、67.40 mg·L−1,去除率分别高达90.84%和86.90%,最高氮去除负荷达0.141 kg·(m3·d)−1。同时,反应器内亚硝态氮、硝态氮含量保持在5 mg·L−1以下,较反应初期明显减少。这证明系统在短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺的协同作用下对污水中的各项污染物进行降解。
3) 厌氧氨氧化菌Candidatus_Brocadia始终是系统内的厌氧氨氧化优势菌属,证明Candidatus_Brocadia对此类水质的适应性高。同时,系统内检测出氨氧化菌AOB菌属Nitrosomonas和反硝化菌属Denitratisoma存在,未检测出NOB相关菌属。这证明短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统处理集便器污水的成功建立及运行。
4) 采用A/O工艺+短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺集便器处理污水,实现了系统成功启动及稳定的运行效果。但实施运行过程中是否存在其他影响厌氧氨氧化耦合工艺的因素而影响系统的处理效果,如DO、温度、COD、pH等变化,有待进一步研究。
短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统处理集便器污水
Treatment of toilet sewage by coupled denitrification system of short-cut nitrification and anammox
-
摘要:
集便器污水具有高有机物、高悬浮物、高氨氮、高磷及低碳氮比的特点。采用一体式短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统进行集便器污水的污染物去除效能研究。结果表明,将氨氮为400~500 mg·L−1、COD约400 mg·L−1的集便器污水作为实验进水,按照分阶段分比例的进水方式,经过约75 d运行,最终出水氨氮及总氮仅为40.20 mg·L−1和67.40 mg·L−1,去除率分别为90.84%和86.90%,总氮去除负荷为0.141 kg·(m3·d)−1。微生物分析结果表明,Candidatus_Brocadia始终是系统内的厌氧氨氧化优势菌属,且运行稳定后其相对丰度达到约30.70%。本研究可为集便器污水脱氮工艺应用技术提供参考。
Abstract:The toilet sewage has the characteristics of high organic matter, high suspended matter, high ammonia nitrogen, high phosphorus and low carbon nitrogen ratio, the integrated short-cut nitrification and anammox coupled denitrification system was adopted in this paper to study the pollutant removal efficiency of the toilet sewage. The results showed that the sewage water with ammonia concentration of 400~500 mg·L−1, COD concentration of about 400 mg·L−1 after pretreatment with A/O device was used as the experimental water. In a phased and proportional way, the coupled system ran for 75 days ,then the ammonia and total nitrogen concentrations in the final effluent were only 40.2 mg·L−1 and 67.4 mg·L−1,, and the removal rates were as high as 90.84% and 86.9%, respectively. The total nitrogen removal load was 0.141 kg·(m3·d)−1,. Microbial analysis showed that Candidatus Brocadia was always the dominant anammox genus in the system and its relative abundance reached 30.7% after stable operation. This study can provide reference for the application technology of nitrogen removal of toilet sewage to achieve efficient and economical nitrogen removal.
-
Key words:
- toilet sewage /
- anaerobic ammonia oxidation /
- denitrification /
- microbial diversity
-

-
表 1 不同工艺实验环境参数
Table 1. Environmental parameters of different process test
工艺类型 温度/ ℃ 溶解氧/(mg·L−1) HRT /h pH 污泥回流比 A/O工艺 25±1 A:0.01~0.04
O:1.00~2.50A:6.00
O:28.807.60~8.30 150% 短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺 32±2 0.10~0.40 96.00 7.90~8.10 150% 表 2 短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化系统运行参数
Table 2. Running parameters of the denitrification system of short-cut nitrification and anammox
阶段 时间/d 集便器污水所占比 氨氮/(mg·L−1) COD/(mg·L−1) Ⅰ 0~28 20% 550~600 110~160 Ⅱ 29~38 40% 490~550 210~230 Ⅲ 39~48 60% 500~550 280~300 Ⅳ 49~59 80% 500~550 340~360 Ⅴ 60~75 100% 440~500 400~450 表 3 短程硝化厌氧氨氧化耦合反硝化工艺与传统硝化反硝化工艺经济性比较[44]
Table 3. Economic comparison between the coupled denitrification process of short-cut nitrification anammox and the traditional anammox process
工艺类别 产泥量 污泥处置费用 药耗 电耗 加热 系统控制 短程硝化厌氧氨
氧化耦合反硝化工艺0.013 kg·m−3
(5.13 kg·d−1)污泥可重复回收利用,
处理量较少— 32 元·d−1 3.33 元·d−1
(四季维持在32 ℃)曝气控制、温控等 传统硝化反硝化工艺 0.117 kg·m−3
(47.01 kg·d−1)70.50 元·d−1
(污泥脱水后泥饼外运)8.7 元·m−3 (甲醇) 36 元·d−1 2.18 元·d−1
(冬季,25 ℃)定时运行、内外回流等
PLC控制、曝气控制等 -
[1] 铁路资讯[J]. 铁路采购与物流, 2018, 13(3): 19-20. [2] 卢春房, 张军. 高速铁路技术创新与工程建设管理[J]. 中国安全生产, 2018, 13(4): 8-10. [3] 沈熙俫. 火车上的厕所“革命”[J]. 交通与运输, 2011, 27(5): 26. [4] 李作兴. 高铁集便器污水中氮磷元素回收技术研究 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学; 2018. [5] 陈为民, 郑莹雪. 列车集便器污水水质分析研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2012(9): 123-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2954.2012.09.032 [6] 胡明, 范彬, 曲波, 等. 列车集便器污水处理现状及对策研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(14): 20-26. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2016.14.005 [7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局;中国国家标准化管理委员会. 污水排入城镇下水道水质标准: GB/T 31962-2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. [8] VLAEMINCK S E, TERADA A, SMETS B F, et al. Nitrogen removal from digested black water by one-stage partial nitritation and anammox[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(13): 5035-5041. [9] ZEEMAN G, LETTINGA G. The role of anaerobic digestion of domestic sewage in closing the water and nutrient cycle at community level[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1999, 39(5): 187-194. doi: 10.2166/wst.1999.0238 [10] 黄焱歆, 范英宏, 张继杰. 旅客列车集便器污水处理方案探讨[J]. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, 2016, 6(1): 5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1671.2016.01.002 [11] YANG X L, JIANG Q, SONG H L, et al. Selection and application of agricultural wastes as solid carbon sources and biofilm carriers in MBR[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 283: 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.036 [12] 张静, 陈洪斌, 唐贤春, 等. 单级与多级AO-SBR工艺对黑水的处理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1409-1416. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511019 [13] MULDER A, VAN DE GRAAF A A, ROBERTSON L, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor[J]. FEMS microbiology ecology, 1995, 16(3): 177-183. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.1995.tb00281.x [14] TAL Y, WATTS J E, SCHREIER H J. Anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria and associated activity in fixed-film biofilters of a marine recirculating aquaculture system[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(4): 2896-2904. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2896-2904.2006 [15] ZHANG X, ZHANG H, YE C, et al. Effect of COD/N ratio on nitrogen removal and microbial communities of CANON process in membrane bioreactors[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 189: 302-308. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.006 [16] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法 (第4版)[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [17] XING W, ZHANG Z, ZHANG X, et al. Mainstream partial Anammox for improving nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater after organic recovery via magnetic separation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 361: 127726. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127726 [18] 林明, 刘雷, 王磊, 等. A/O-MBBR组合工艺处理生活污水实验研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2022, 48(9): 129-133. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2022.09.026 [19] 常根旺, 杨津津, 李绍康, 等. 短程反硝化耦合厌氧氨氧化强化脱氮工艺研究与应用进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(5): 1519-1527. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210578 [20] LIU Z, LIN W, LUO Q, et al. Effects of an organic carbon source on the coupling of sulfur (thiosulfate)-driven denitration with Anammox process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 335: 125280. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125280 [21] FRIEDMAN L, MAMANE H, AVISAR D, et al. The role of influent organic carbon-to-nitrogen (COD/N) ratio in removal rates and shaping microbial ecology in soil aquifer treatment (SAT)[J]. Water Research, 2018, 146: 197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.09.014 [22] GUISASOLA A, JUBANY I, BAEZA J A, et al. Respirometric estimation of the oxygen affinity constants for biological ammonium and nitrite oxidation[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2005, 80(4): 388-396. doi: 10.1002/jctb.1202 [23] SONG D, LIU C, SUN Z, et al. Tailoring the distribution of microbial communities and gene expressions to achieve integrating nitrogen transformation in a gravity-driven submerged membrane bioreactor[J]. Water Research, 2020, 187: 116382. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116382 [24] SLIEKERS A O, DERWORT N, GOMEZ J L C, et al. Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(10): 2475-2482. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00476-6 [25] YAN J, OP DEN CAMP H J M, JETTEN M S M, et al. Induced cooperation between marine nitrifiers and anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria by incremental exposure to oxygen[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2010, 33(7): 407-415. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.08.003 [26] 张杰, 成朔, 李冬, 等. AUSB中置曝气启动连续流全程自养脱氮工艺[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(2): 1-7. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201706066 [27] BERNET N, DANGCONG P, DELGENES J P, et al. Nitrification at low oxygen concentration in biofilm reactor[J]. JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING, 2001, 127(3): 266-271. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2001)127:3(266) [28] PARK S, BAE W, RITTMANN B E. Operational boundaries for nitrite accumulation in nitrification based on minimum/maximum substrate concentrations that include effects of oxygen limitation, pH, and free ammonia and free nitrous acid inhibition[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2010, 44(1): 335-342. doi: 10.1021/es9024244 [29] RUIZ G, JEISON D, CHAMY R. Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(6): 1371-1377. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00475-X [30] CHEN W B, TIAN M, WANG R R, et al. , editors. Shortcut nitrification rates at different aeration and sludge retention time. 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, RSETE 2011 - Proceedings; 2011 ; Nanjing. [31] 徐浩, 李捷, 罗凡, 等. 不同曝气控制方式对SBR短程硝化特性的影响[J]. 净水技术, 2017, 36(9): 53-56. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2017.09.011 [32] 严子春, 唐瑞祥, 吴大冰. 有机物对厌氧氨氧化生物膜反应器脱氮效能及微生物群落的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 1303-1308. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0571 [33] 王维奇, 王秀杰, 李军, 等. 部分反硝化耦合厌氧氨氧化脱氮性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(2): 641-647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.02.025 [34] 陈重军, 冯宇, 汪瑶琪, 等. 厌氧氨氧化反应影响因素研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2): 346-352. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2016.02.024 [35] FERNÁNDEZ I, DOSTA J, FAJARDO C, et al. Short- and long-term effects of ammonium and nitrite on the Anammox process[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2012, 95: S170-S174. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.10.044 [36] JIN R C, YANG G F, YU J J, et al. The inhibition of the Anammox process: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 197: 67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.014 [37] 魏思佳, 于德爽, 李津, 等. 厌氧氨氧化与反硝化耦合脱氮除碳研究Ⅰ: COD/NH4+-N对耦合反应的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(3): 759-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.03.019 [38] XIAO H, PENG Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Pre-anaerobic treatment enhanced partial nitrification start-up coupled with anammox for advanced nitrogen removal from low C/N domestic wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125434. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125434 [39] 鲁帅, 刘志强, 翟计红, 等. 多段式A/O-SBR工艺处理列车集便器污水研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2013, 39(7): 73-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2013.07.018 [40] 高大文, 彭永臻, 杨庆, 等. 应用实时控制实现和稳定短程硝化反硝化[J]. 中国给水排水, 2003, 19(12): 1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2003.12.001 [41] 张超, 吕锡武. SBR工艺中反硝化除磷特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(10): 2259-2263. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.10.019 [42] 朱雅新, 王少坡, 邱春生, 等. 部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺影响因素及控制策略[J]. 天津城建大学学报, 2022, 28(5): 359-366. doi: 10.19479/j.2095-719x.2205359 [43] LI J, PENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Improving efficiency and stability of Anammox through sequentially coupling nitritation and denitritation in a single-stage bioreactor[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(17): 10859-10867. [44] 李泽莹, 班玮璘, 王锦, 等. 高铁动车段集便器污水处理调研及优化脱氮分析[J]. 铁路节能环保与安全卫生, 2022, 12(1): 29-32. doi: 10.16374/j.cnki.issn2095-1671.2022.0006 -



 下载:
下载: