-
清华大学张希良等[1]采用中国-全球能源经济模型 (China-in-Global Energy Model,C-GEM) ,预测中国工业二氧化碳排放约在2025—2030年左右达峰,峰值相对2020年水平上升3亿吨。为实现减污降碳,联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会 (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Chang, IPCC) 第三次评估报告[2]首次明确提出了协同效益∕协同效应 (Co-benefits) 的概念。国际上已在不同地区和行业开展了大量协同效益评估研究,证实了以减排污染物为目标的控制政策、措施不仅能够减排污染物,而且对CO2等温室气体减排具有一定的协同效益[3]。“协同效应”可以体现在3个方面:一是在控制温室气体排放过程中协同减少污染物排放;二是在控制污染物排放过程中协同减少温室气体排放;三是行业之间的跨行业协同减排温室气体。
污水处理厂是耗能大户,也是温室气体重要排放源[4],通过电力行业减碳管理措施降低水务行业碳排放量,对水务行业碳达峰碳中和具有重要意义。郝晓地等[5-6]对碳中和运行的国际先驱奥地利 Strass污水厂案例和美国Sheboygan 污水处理厂案例进行剖析,分析了剩余污泥产生、厌氧转化生物气并热电联产供热、供电方面的作法与经验。付加锋[7]针对城镇污水处理厂的污染物与温室气体如何实现协同减排核算问题提出了城镇污水处理厂污染物去除协同控制温室气体的核算边界、协同机制和核算方法。2022年6月10日,生态环境部等七部委联合发布《减污降碳协同增效实施方案》,对水环境治理协同控制提出了具体要求,污水处理行业应探索推动减污降碳协同增效的有效路径。近年来,污水处理厂经过技术升级改造能效已有较大改善,通过继续提升能效减碳的边际效益递减,亟待通过行业和领域间的协同来探索新的碳减排潜力。
近年来,江苏省能源消耗量、二氧化碳排放量及发电量均持续上涨。本课题组通过国家电网双碳支撑平台提供的实时碳排放核算管理、“电碳协同”减污降碳运行管理和绿色电力减排管理,结合污水处理运行管理规律,探讨数字化电碳管理效果,以期减少污水处理厂的二氧化碳间接排放,为污水厂减污降碳协同增效提供支持和运行指导,助力水务行业碳达峰碳中和。本研究聚焦于第三类跨行业的协同,可为污水处理、碳管理、电网3个领域的协同减污降碳提供新的合作途径。
-
在国际气候谈判中,诸多国家认为人均碳排放是关键点,并根据发达国家和发展中国家人均排放的巨大差异提出了“共同但有区别的责任”原则。日本在节能减排和环保技术上处于世界领先地位,能源效率高于多数发达国家,因此摒弃了人均碳排放的概念,提出了行业减排方法 (sectoral emission reduction approach),以能源效率作为评估节能减排效果的基本指标,认为能源效率低的国家、地区、行业或企业应当承担更大的减排义务。行业减排方法从行业入手控制温室气体减排,针对相应的产业特征进行设计,对行业实施特定节能减排需求下的监管和调整。因此,行业减排方法是一系列的政策或技术措施组合,包含行政命令、经济激励及自愿减排措施等类型。
污水处理厂的数字化电碳管理是行业减排方法中的自愿减排措施之一,聚焦用数字化方法提升污水处理厂的能源效率。数字化电碳管理主要包括污水处理厂的能源及排放数据的采集、存储、分析、处理、评估、核算、标识编码、认证、碳资产管理等内容,主要作用于污水处理厂与用电相关的5个环节:碳排放管理环节、碳减排管理环节、碳决策管理环节、碳资产管理环节和碳交易管理环节。国网数科公司拥有多家污水处理厂的用电数据同时了解用户用能特性,其绿电交易和电碳管理在碳达峰碳中和背景下可为污水处理行业提供有力支撑。数字化电碳管理数字化电碳管理可基于国家电网双碳支撑平台系统的电网数据,也可在水处理工艺流程设施之上建设光伏发电工程,推进污水处理厂的减碳管理运行控制与绿色电力管理。
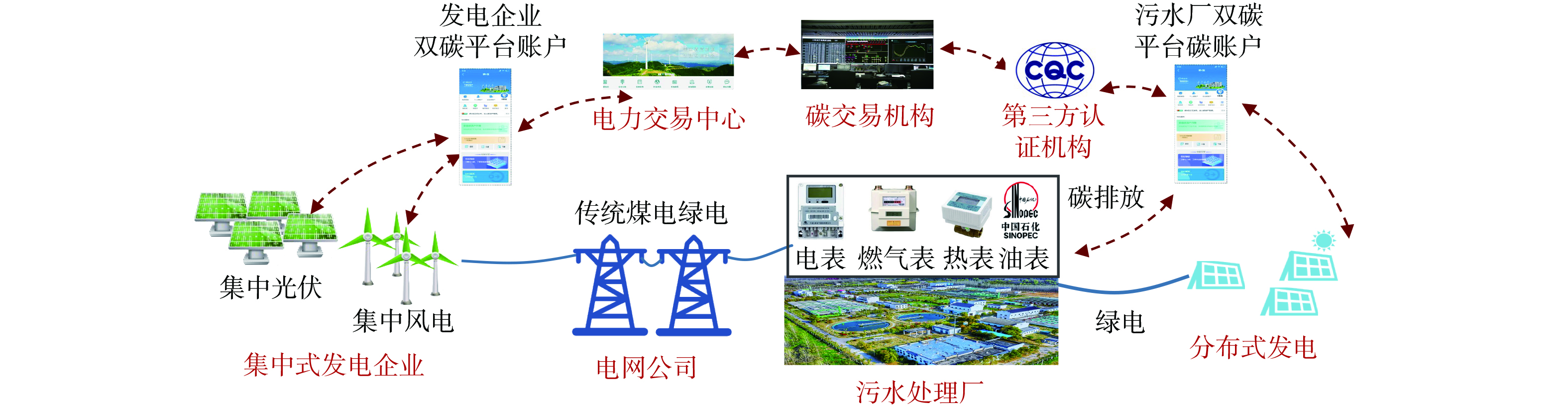
本研究通过国网数科公司的双碳支撑平台,调取江苏省某污水处理企业冬季和夏季用电尖峰时刻24 h的15 min级的用电数据,改进以往用年度数据进行碳排放管理的方法,将年度数据提升到分钟级,用实时电力数据分析和推动污水处理企业的减碳运行。以“平台+生态”的发展思路,数字化电碳管理充分发挥电网作为能源配置枢纽平台作用,连接污水处理厂等用户、风电光伏等发电企业、碳排放权注册登记与交易机构、第三方核查机构,培育共建共治共赢的电碳生态圈。污水处理厂数字化电碳管理总体架构见图1。
数字化电碳管理聚焦于污水处理厂的用电环节,在国家电网双碳支撑平台上为污水处理企业设立碳账户,为污水处理厂提供实时碳排放核算管理、日度电碳协同减碳运行管理和绿色电力减排管理。数字化电碳管理可降低污水处理厂用电产生的间接碳排放,同时降低污水处理企业的用电成本、减少能效提升的技术投资。数字化电碳管理具体应用了以下3种减排方法,分析了3类数字化电碳管理的减排潜力。
1) 实时碳排放核算方法。数字化电碳管理可直接从电力系统接入污水处理厂的用电数据,结合清华大学核算的江苏省日度实时碳排放因子,可计算该污水处理厂24 h的实时用电间接碳排放实测值,并按比例估算企业的实时碳排放量,能效较高的污水处理厂实际碳排放值将低于年电网排放因子折算的全国平均值,有利于鼓励能效先进的污水处理厂节能减排。在全国平均值计算方法下,如使用绿色电力或先进技术的污水处理企业其碳排放量较低的优势不能体现,污水处理企业有可能出现劣币驱逐良币。
在时间尺度方面,传统碳排放核算方法统计年度数据,数字化电碳管理可以提升污水处理厂用电间接碳排放的数据颗粒度,将年度数据提升为15 min级的实时数据,解决污水处理厂碳资产管理过程中成本高、难度大、精度低、周期长的问题,优化企业对用电间接碳排放的监测与核算。在电耗碳排放因子方面,因从国家电网接入数据,本研究聚焦于污水处理厂用电间接使用的碳排放量,仅针对间接排放中的用电产生的间接碳排放量进行分析,电耗为污水处理厂生产运行过程中的外购电量,不包括办公区和生活区的用电量。2022年6月中国环保产业协会发布团体标准《污水处理厂低碳运行评价技术规范》 (CAEPI 49—2022) ,规定了污水处理厂电耗碳排放因子采用官方或权威机构发布最新值,2022年电网排放因子为0.581 0 tCO2·MWh−1。城镇污水处理厂的日电耗碳排放强度计算方法如式 (1) 。
式中:Ee为电耗碳排放强度,kg CO2·m−3;fe为电耗碳排放因子,kgCO2·kWh−1,取值按国家最新标准;Wi为第i天用于生产运行的外购电量,kWh;Qra,i-污水处理厂第i天进水水量,m3。
城镇污水处理厂污水、污泥处理设备运行年耗电力产生的碳排放按照公式为式 (2) 。
式中:Ea为城镇污水处理厂污水、污泥处理设备运行年耗电力产生的折算为CO2的排放总量,t·a−1;EH为城镇污水处理厂污水、污泥处理设备运行的耗电量,MWh·a−1;EFCO2为电力CO2排放因子,t·MWh−1 (2022年电网排放因子调整为0.581 0 tCO2·MWh−1) ;GWPCO2为CO2全球增温潜势值,取值为1。
2) 日度电碳协同减碳运行策略方法。用电碳排放因子是指单位电量中内含的间接碳排放量,体现了电力用户在消费单位电能时对应在源侧产生的碳排放量。污水处理厂电耗碳排放因子采用官方或权威机构发布最新值,2022年电网排放因子为0.581 0 tCO2·MWh−1。但在工业实际生产运行中,污水处理厂实际用电的碳排放因子fe (kgCO2·kWh−1) 是随时变化的。根据电力系统碳排放流分析理论,可对电力系统中电力的碳排放来源进行追踪,得到实时变化的动态用电碳排放因子。由于不同时段不同类型机组火电、水电、风电、光伏、生物质、核电等的发电出力占比不同,用电碳排放因子在不同时段、不同日期、不同季节实际均有所不同,用电碳排放因子的大小直接反映了电能的清洁程度。日度电碳协同减碳运行通过优化用户用电时间和用电量,将污水处理厂用电行为与当地实际用电的碳排放因子协同调整,在用电碳排放因子较低的地域和时段多用电,在用电碳排放因子较高的地域和时段少用电,可推进污水处理厂用电间接碳排放量的减排。
3) 绿色电力交易减碳管理方法。绿色电力主要指风电和光伏发电企业上网电量,分布式新能源可通过聚合的方式参与绿色电力交易,绿色电力可降低污水处理厂运行过程中的间接碳排放强度。2022年中国绿电交易量持续增加,碳市场、绿电、绿证突破边界协同连接,为污水处理厂碳中和提供了新的减排路径。2022年6月10日,江苏省发展改革委等部门印发《江苏省促进绿色消费实施方案》 (苏发改就业发〔2022〕535号) ,提出建立完善绿色电力市场化交易机制,全面提升绿色电力消纳能力,研究制定高耗能企业使用绿色电力的刚性约束机制,逐年提高绿色电力消费最低占比,到2025年,高耗能企业电力消费中绿色电力占比不低于30%。随着碳达峰碳中和实施路线推进,绿色电力、绿证将成为企业电力消费的刚需,采购绿色电力将成为污水处理企业清洁低碳转型的重要措施。通过绿色电力交易减排管理,电力系统可为污水处理厂增加绿色电力供给,促进污水处理厂的绿色化、低碳化,提升减污降碳的竞争优势。
-
1) 工程情况。以江苏省某污水处理厂为例,近期设计处理规模为10 000 m³·d−1,远期设计处理规模1.5万m³·d−1,厂区设调节事故池均质均量。江苏省某污水处理厂接管废水共分为3类:确成硅废水6 000 m³·d−1,兴达泡塑废水2 000 m³·d−1,其他废水2 000 m³·d−1。确成硅废水处理采用事故调节池+高效沉淀+消毒系统,兴达泡塑废水处理采用A2/O推流式活性污泥系统,其他污水采用芬顿+沉淀+水解+AO+芬顿+沉淀+高效沉淀+活性炭吸附+消毒回用系统。进水水质见表1,出水水质执行城镇一级A标准,DB32/1072及DB32/939标准。
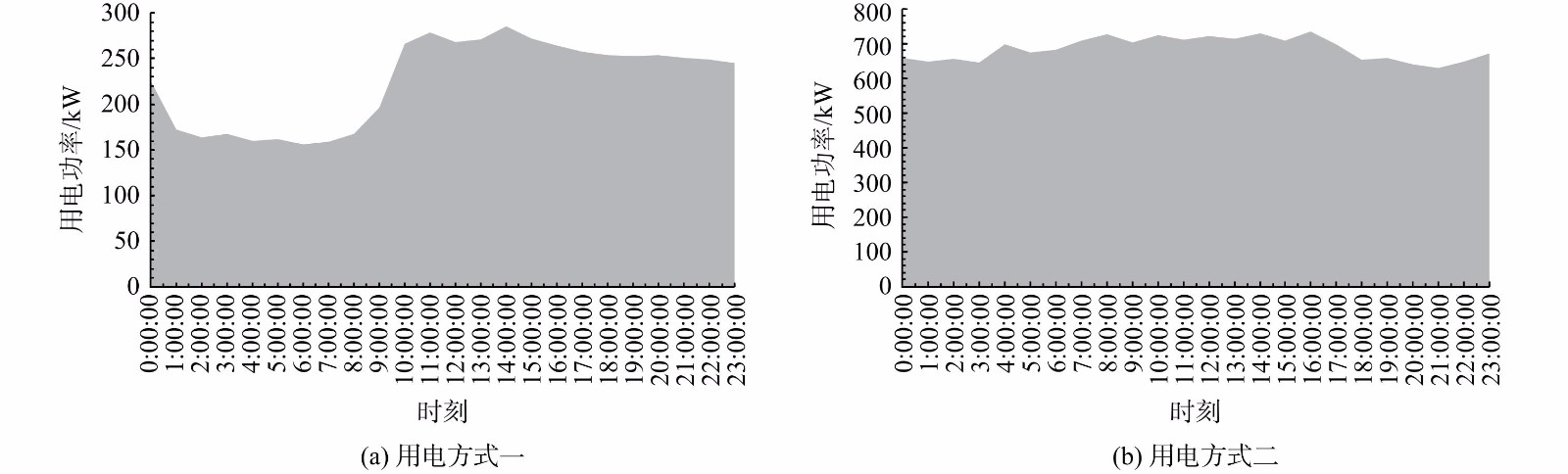
2) 运行工况及调控策略。污水处理厂用电的运行方式有2种工况。第一种工况污水处理厂仅在白天工作时间及晚间污泥浓缩脱水,凌晨至工作时间不脱泥;第二种是24 h污泥浓缩脱水。从江苏省某污水处理厂总结出2种需要调整的实际用电运行方式。方式一,0:00—9:00用电功率低,9:00—21:00用电功率高。这种策略和电网供电电价的峰谷时刻正好重合,也和江苏省6:00—10:00、16:00—21:00碳排放因子较高的时段重合,可总结为高碳排高电费的双高用电策略,需要在未来进行调整。方式二,全天24 h持续运行,用电量较为均匀,但未与电网电价的峰谷和碳排放因子高低时段相匹配,可总结为平均用电策略 (见图2) 。
3) 电碳协同减碳运行策略。在污水处理厂碳排放方面,参考江苏省某典型污水处理厂处理1 t污水平均耗电约0.3 kWh,全年污水处理设施电耗1 937 000 kWh,年处理污泥干物质量为219 t,污水处理厂污泥干物质量中好氧有机物 (以COD计) 为0.5 t·t−1、有机质为0.26 t·t−1。从温室气体排放强度来看,单位COD去除量、单位TN去除量和单位污泥处理量产生的温室气体排放量分别为0.051 3、2.435 6和0.5460 t,单位TN去除量产生的温室气体量最大,其次为污泥处理。从温室气体排放总量来看,该污水处理厂总温室气体排放量1 601.1 tCO2eq,污水处理厂用电的间接温室气体排放量为1 362.68 t,居于首位占85.1%[7]。污水处理厂能耗主要为电耗,用电间接温室气体排放是污水处理厂温室气体排放的主要来源,并且通过电网的数字化平台可以实现电碳协同调控。因此,本研究聚焦分析污水处理厂用电产生的间接二氧化碳排放,污水处理厂的直接二氧化碳排放不在电碳协同减碳管理计算范围内。
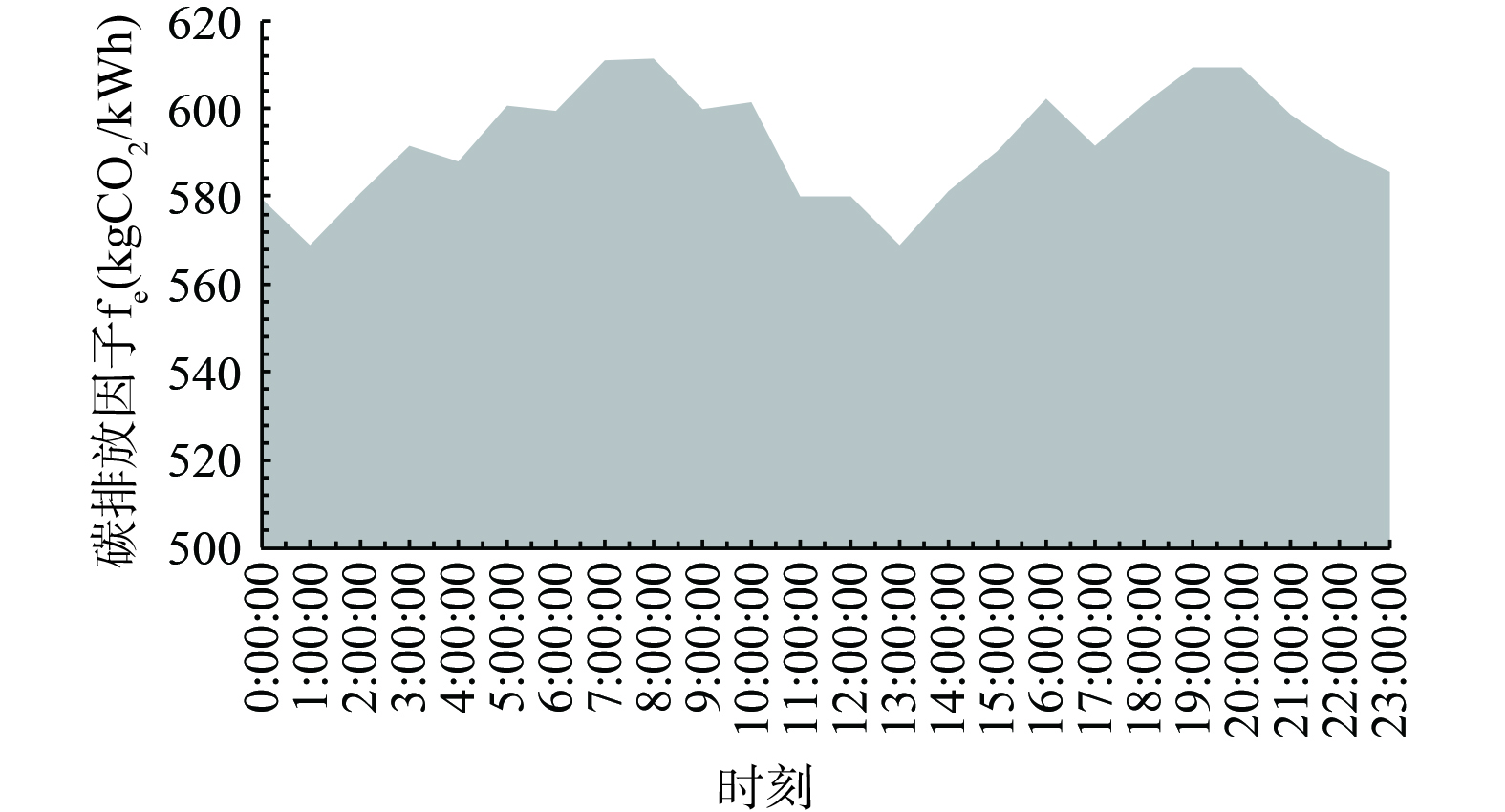
在电碳协同方面,清华大学电机系、清华能源互联网研究院与国家电网合作,对电力系统中电力的碳排放来源进行追踪,得到实时变化的动态用电碳排放因子。用电碳排放因子fe指单位电量中内含的间接碳排放量,体现了电力用户在消费单位电能时对应在源侧产生的碳排放量。清华大学电机系根据江苏省电力数据得出了省实时用电碳排放因子曲线[8]见图3。
在电碳协同方面,日度电碳协同减碳运行管理参考江苏省实时碳排放因子,将江苏省污水处理厂的实际用电曲线与用电碳排放因子曲线进行对照调整,对污水处理厂的实时碳排放行为进行电碳协同的运行调控策略调整,减少污水处理厂碳排放。江苏省日级实时碳排放因子有2个峰时和2个谷时,0:00—6:00、10:00—15:00碳排放因子较低,7:00—10:00、16:00—21:00时有碳排放因子的早晚2个高峰。通过对污水处理厂2种模式进行分析,提出污水处理厂的日度减碳运行策略:对污水处理厂实时碳排放因子进行电碳协同的运行调控策略调整,避开电碳排放因子的早晚高峰,在0:00—6:00、10:00—15:00电碳排放因子较低的2个谷时加大污水处理厂用电,有效降低污水处理厂的间接碳排放。
在经济效益方面,引入电价政策因素,根据《江苏省发展改革委关于进一步完善分时电价机制有关事项的通知》,自2022年1月将工业用电峰谷时段调整为:峰期8:00—11:00、17:00—22:00,平期11:00—17:00、22:00—24:00,谷期0:00—8:00。自2022年1月对315 kVA及以上的大工业用电实施夏、冬两季尖峰电价。每年7至8月,日最高气温达到或超过35 ℃时,10:00—11:00和14:00—15:00执行夏季尖峰电价,同时将17:00—18:00从峰期调整为平期。12月至次年1月,日最低气温达到或低于-3 ℃时,9:00—11:00和18:00—20:00执行冬季尖峰电价。夏、冬两季尖峰电价统一以峰段电价为基础,上浮20%。故电碳协同减碳运行策略选择0:00—6:00进行污水处理厂配药和污泥浓缩脱水等电耗较大的操作,可实现减碳和节约电费的双重收益。
-
1) 实时碳排放核算效果。本研究聚焦于分析污水处理厂有功功率的总体变化趋势,选取江苏省某污水处理厂,从其有功功率计算24 h 电量,从而得出污水处理厂的实时间接碳排放。通过国网双碳支撑平台调研了污水处理厂的实时用电数据,在2022年夏季尖峰时段7月、8月、9月3个月中选取了5 d 24 h的15 min的污水处理用电功率数据,在2023年冬季尖峰时段1月、2月、3月3个月中选取了5 d 24 h的15 min的污水处理用电功率数据,绘制了污水处理厂冬夏24 h功率曲线,见图4。通过调研的用电数据得到两类功率曲线。用电方式一,0:00—9:00用电功率低,9:00—21:00用电功率高。这种功率曲线和电网供电电价的峰谷时刻正好重合,高峰电价时刻用电量大,而低谷时段用电量小,污水处理厂支付高峰电费。曲线高峰也和江苏省6:00—10:00、16:00—21:00碳排放因子较高的时段重合,导致污水处理厂碳排放和电费双高。用电方式二,全天24 h用电量较为均匀,但功率曲线没有与电网电价的峰谷和碳排放因子高低时段相匹配。
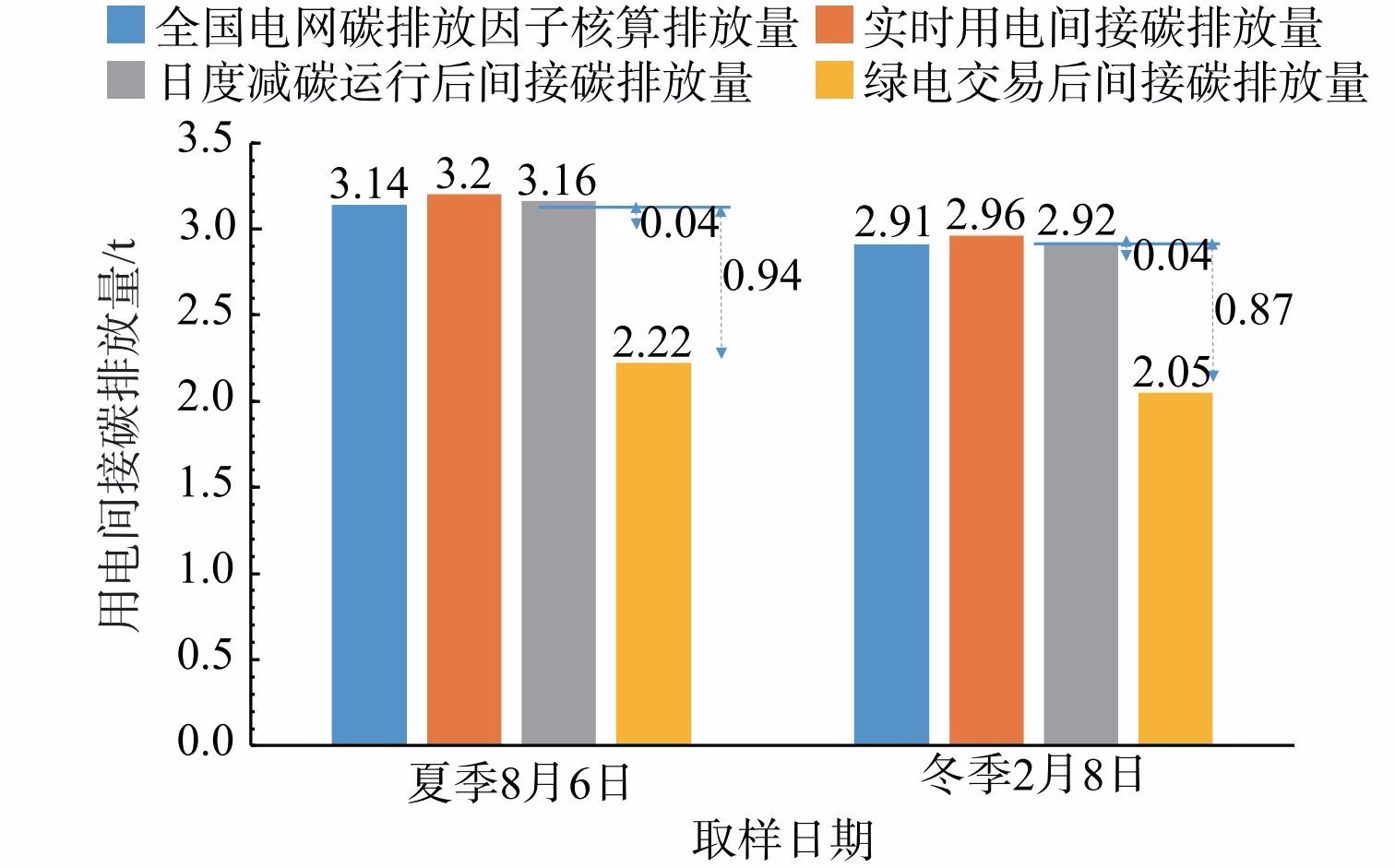
数字化电碳管理可直接从电力系统接入污水处理厂的用电数据,实现了对污水处理厂碳排放量的实时计算,与传统碳核算方法年度填报数据相比,提升了数据的采集效率和时效性,还可对污水处理厂超过全国平均值的日期提出超排减碳预警。数字化电碳管理可以计算污水处理厂24 h的实时用电间接碳排放,从而提供企业实时的碳排放量。按照电力带来的间接排放占85%,可折算总体碳排放量。根据电网提供的实时用电数据,2022年8月6日江苏省某污水处理厂的夏季日耗电量Wi为5 400 kWh,按照全国年电网排放因子计算碳排放量为3.14 tCO2eq,根据公式 (1) 计算实时日电耗碳排放量为3.2 tCO2eq,减碳潜力为-60 kgCO2eq。这说明当日实时排放量超全国平均排放因子核算值,数字化电碳管理系统可提出超排减排预警。按照电力带来的间接排放占85%,估算江苏省某污水处理厂实时日碳排放量约为3.76 tCO2eq 。2023年1月8日,江苏省某污水处理厂的冬季日耗电量Wi为5 000 kWh,按照全国年电网排放因子计算碳排放量为2.91 tCO2eq,根据公式 (1) 计算实时日电耗碳排放量为2.96 tCO2eq,减碳潜力为-58 kgCO2eq。这说明当日实时排放量超全国平均排放因子核算值,数字化电碳管理系统可提出超排减碳预警。按照电力带来的间接排放占85%,估算江苏省某污水处理厂实时日碳排放量约为3.49 tCO2eq 。
2) 日度电碳协同减碳运行效果。日度电碳协同减碳运行策略选择0:00—5:00进行污水处理厂的鼓风机运行和污水提升泵等耗电量较大设备做符合工艺的优化。针对2022年8月6日江苏省某污水处理厂夏季用电方式一,进行电碳协同减碳运行管理调整后日碳排放量为3.16 tCO2eq,可实现日减排39.3kgCO2eq,减碳比例约为1.23%。针对2023年1月8日江苏省某污水处理厂冬季用电方式二,进行电碳协同减碳运行管理调整后日碳排放量为2.92 tCO2eq,可实现日减排40 kgCO2eq,减碳比例约为1.31%。如对江苏省某污水处理厂应用日度电碳协同减碳运行策略,推广到全年该厂可减排14.6 tCO2eq。以上数据表明,电碳协同减碳运行管理对于用电方式二的污水处理厂比方式一的碳减排潜力更大,用电量越大的污水处理厂电碳协同减碳运行管理减碳效果越显著,日度电碳协同减碳运行应在污水处理厂全年推广。
3) 绿色电力交易减碳管理效果。2022年碳市场、绿电、绿证突破边界协同连接,参与绿电交易的电力用户未来有望获得由电力交易中心、碳排放权交易中心双认证的绿证,绿证标明了交易电量和等效减排二氧化碳量。2022年6月10日江苏省发改委印发《江苏省促进绿色消费实施方案》,提出充分激发全社会绿电消费潜力,研究制定高耗能企业使用绿色电力的刚性约束机制,逐年提高绿色电力消费最低占比,对符合条件的企业适度降低阶梯电价加价标准。到2025年,高耗能企业电力消费中绿色电力占比不低于30%,组织电网企业定期梳理、公布本地绿色电力时段分布。根据江苏省绿色电力政策前瞻性分析,为应对绿色电力刚性约束机制或政策升级,未来江苏省将加大绿电供应力度,可按照企业电力消费中绿色电力占比不低于30%设定绿电减排情景,推算江苏省某污水处理厂参与绿电交易将有如下减排效果。污水处理厂夏季的日耗电量Wi为5 400 kWh,若购买30%绿电为1 620 kWh,等效二氧化碳减排量0.94 tCO2eq,减碳比例约为29.4%。污水处理厂冬季的日耗电量Wi为5 000 kWh,若购买30%绿电为1 500 kWh,等效二氧化碳减排量0.87 tCO2eq,减碳比例约为29.4%。
综上所述,通过基于电碳协同的数字化电碳管理,污水处理厂可获得实时碳排放核算、日度电碳协同减碳运行和绿色电力交易减排三方面减碳管理效果,见图5。通过实时碳排放核算管理可核算污水处理厂的每日间接用电碳排放量,结合日度电碳协同减碳运行策略和绿色电力交易减碳管理2个减排措施,可为江苏省某污水处理厂夏季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.6%,冬季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.7%。
-
污水处理属于能耗密集型行业,其消耗的能源主要包括电、燃料及药剂等,电耗占总能耗的40%~70%[9]。污水处理厂电价约为700 CNY·MWh−1,高能耗、高电价导致的高污水处理成本,对中小型污水处理厂造成较大运行成本压力。江苏省是电力消耗大省,夏季用电高峰时期供电紧张。根据2021年10月15日执行的《江苏省工业用电峰谷分时电价浮动比例表》,对工业用电峰谷时段进行了调整,并启动夏、冬两季尖峰电价。大工业用电的峰谷分时电价高峰时段上浮71.96%,平期时段按市场交易购电价格,低谷时段电费下浮动58.15%。2022年5月,江苏省电力交易中心公布绿电交易均价467.04 CNY·MWh−1,可有效实现碳排放和电价双减。污水处理厂夏季的日耗电量Wi为5 400 kWh,若购买30%绿电为1 620 kWh,等效二氧化碳减排量0.94 tCO2eq,平均成交价格467.04 CNY·MWh−1,日节约电费377.5 CNY。污水处理厂冬季的日耗电量Wi为5 000 kWh,若购买30%绿电为1 500 kWh,等效二氧化碳减排量0.87 tCO2eq,平均成交价格467.04 CNY·MWh−1,日节约电费349.5CNY。按照冬夏平均计算,年可为污水处理厂节约电费约132 677 CNY。目前,污水处理企业没有纳入全国碳市场,但已纳入北京碳市场,2023年6月北京某污水处理厂因4 512 t二氧化碳未履约被北京市生态环境局罚款约245万元。未来如果污水处理厂数字化碳管理所获减排量可在全国碳市场上交易,低碳排企业可获得经济收益,超排企业也可避免收到高额罚单。
-
1) 在时间、空间和经济性3个维度上,数字化电碳管理为污水处理、碳管理、电网3个行业的减污降碳提供了新的“水-碳-电”协同合作方式,将污水处理厂间接碳排放量的计算精度从年度提升到分钟级,量化了绿色电力在污水处理厂碳减排中的贡献。污水处理厂可与电网企业、电力交易中心和碳排放交易所等主体合作进行减碳管理。
2) 数字化电碳管理可精准快速地为污水处理厂提供实时用电间接碳排放值,可为低能耗污水处理厂实时展现其低碳优势,也可为高能耗污水处理厂发出超排预警,避免污水处理企业在减碳竞争中劣币驱逐良币。通过核算,江苏省某污水处理厂夏季日度碳排放高于冬季,在0:00—6:00、10:00—15:00电碳排放因子较低的2个谷时加大污水处理厂用电,可有效降低污水处理厂的用电间接碳排放。
3) 日度电碳协同减碳运行策略选择凌晨0:00—5:00运行污水处理厂的鼓风机运行和污水提升泵等耗电量较大设备。经电碳协同减碳管理调整后,江苏省某污水处理厂夏季用电方式一减碳比例约为1.23%,冬季用电方式二减碳比例约为1.31%。用电量越大的污水处理厂电碳协同减碳运行服务管理效果越显著,日度电碳协同减碳运行可全年推广,可通过推进污水处理厂的数字化和少人化逐渐减少人员和夜间值守强度。
4) 污水处理厂选择绿色电力交易减排管理可有效实现减碳和减电费的双重收益。通过实时碳排放核算管理,日度电碳协同减碳运行管理和绿色电力交易减碳管理,可为污水处理厂夏季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.63%,为污水处理厂冬季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.71%,每年可为江苏某污水处理厂节约电费十余万元。基于电碳协同的数字化电碳管理若能在全国推广应用,可有效推进水务行业整体节能降碳与降本增效。
基于电碳协同的江苏省某污水处理厂减碳管理分析
Analysis of carbon reduction management of a wastewater treatment plant in Jiangsu Province based on electro-carbon synergy
-
摘要: 在中国“3060碳达峰碳中和”的战略背景下,绿色低碳成为污水处理厂运行评价的重要指标,污水处理厂减污降碳是大势所趋。聚焦通过电碳生态圈及数字化平台支撑,用数字化电碳管理减少污水处理厂的间接用电二氧化碳排放,在时间、空间和经济性3个维度上,为污水处理、碳管理、电网3个行业的“水-碳-电”协同减污降碳提供了新的合作模式与技术支持。针对污水处理厂碳排放及碳减排管理问题,以江苏省某污水处理厂为例,从实时碳排放核算管理、日度电碳协同减碳运行管理和绿色电力交易减碳管理3个方面,解析了该污水处理厂冬季和夏季24 h用电功率曲线,探讨了污水处理厂电碳协同的日度减碳运行策略,核算了日度电碳协同减碳运行和绿色电力交易减碳管理的效果。结果表明,通过实时碳排放核算管理可以核算污水处理厂每日间接用电碳排放量,结合日度电碳协同减碳运行策略和绿色电力交易减碳管理2个减排措施,可为污水处理厂夏季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.63%,为污水处理厂冬季日度减少间接用电碳排放30.71%,每年可为江苏省某污水处理厂节约电费十余万元。该研究结果表明基于电碳协同的污水处理厂减碳管理效果较为理想,可为水务行业推进双碳战略提供参考。Abstract: In the context of China's "3060 carbon peak carbon neutral" strategy, green and low-carbon has become an important indicator for the evaluation of wastewater treatment plant operation, and it is the trend to reduce pollution and carbon in wastewater treatment plants. This paper focused on reducing the indirect electricity CO2 emissions of wastewater treatment plants by digital electricity carbon management through the support of electricity carbon ecosystem and digital platform, which provided a new cooperation model and carbon reduction technical support in three dimensions of time, space and economy for "water-carbon-electricity" collaboration among wastewater treatment, carbon management and power grid. Taking a wastewater treatment plant in Jiangsu province as an example, the 24-hour power consumption curve of the wastewater treatment plant in winter and summer was analyzed in this work, the daily carbon reduction strategy of the wastewater treatment plant was discussed, and the daily electricity carbon reduction operation and the green power trading carbon reduction management were calculated from three aspects: real-time carbon emission accounting management, daily electricity carbon reduction operation and green power trading carbon reduction management. The effect of daily electricity carbon reduction operation and green power trading carbon reduction management was calculated. The results showed that the daily indirect electricity carbon emissions of the wastewater treatment plant could be accounted for through real-time carbon accounting management, and the combination of the two emission reduction measures of daily electric carbon synergistic carbon reduction operation strategy and green power trading carbon reduction management could reduce the indirect electricity carbon emissions of the wastewater treatment plant by 30.63% in summer and 30.71% in winter, which could save more than 100 000 CNY of electricity cost for a wastewater treatment plant in Jiangsu Province every year. The effect of carbon reduction management of wastewater treatment plant based on electricity and carbon synergy was proved to be very significant, which can provide a reference for the water industry to promote the dual carbon strategy.
-

-
表 1 江苏省某污水处理厂进水水质
Table 1. Water quality of a wastewater treatment plant in Jiangsu Province
mg·L−1 废水类型 COD BOD5 SS NH3-N TN TP 总盐 确成硅废水进水水质 ≤40 ≤10 ≤50 ≤5 ≤10 ≤2 10 000 兴达泡塑废水进水水质 ≤500 ≤50 ≤150 ≤5 ≤10 ≤8 1 500 其他废水进水水质 ≤350 ≤90 ≤250 ≤20 ≤30 ≤4 1 500 -
[1] 张希良、黄晓丹、张达, 等. 碳中和目标下的能源经济转型路径与政策研究[J]. 管理世界, 2022(1): 35-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2022.01.003 [2] 陈敏敏, 吴琼, 张震, 等. 我国城镇污水处理厂环境绩效评价研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(12): 2675-2682. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.11.12 [3] 毛显强, 曾桉, 邢有凯, 等. 从理念到行动: 温室气体与局地污染物减排的协同效益与协同控制研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021. doi:10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.285. [4] KIM D, BOWEN J D, OZELKAN E C. Optimization of wastewater treatment plant operation for greenhouse gas mitigation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 163: 39-48. [5] 郝晓地, 程慧芹, 胡沅胜. 碳中和运行的国际先驱奥地利Strass污水厂案例剖析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2014, 30(22): 1-5. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2014.22.001 [6] 郝晓地, 李季, 张益宁, 等. 污水处理行业实现碳中和的路径及其适用条件分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(12): 3857-3863. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202112158 [7] 付加锋, 冯相昭, 高庆先, 等. 城镇污水处理厂污染物去除协同控制温室气体核算方法与案例研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(09): 2086-2093. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.06.19 [8] 李姚旺, 张宁, 杜尔顺, 等. 基于碳排放流的电力系统低碳需求响应机制研究及效益分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(8): 2830-2842. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.220308 [9] 刘昊. 低碳绿色措施在污水处理技术中的应用[J]. 水电站设计, 2022, 38(3): 87-91. doi: 10.16671/j.cnki.cn51-1382/tv.2022.03.014 -



 下载:
下载: