-
在经济迅猛发展和社会不断进步过程中,突发性的环境事故也层出不穷。近年来,《中国统计年鉴》中有关全国性突发环境事件的数据,见表1[1-6]。
表1可知,自2014年起,突发环境事件的次数逐年下降,而在所有类型中,一般环境事件所占的比例超过95%。从数量上看,重大环境事件和较大环境事件的发生次数已经控制到很低的水平,但一般环境事件的发生次数依然处于较高的水平。实际上,在频发的环境污染事件中,水体污染事件在其中所占的比例不容小觑[7]。
目前,面对水体污染事件,尤其是突发性水体污染事件,对污染源的追溯最常用的方法有硝酸盐氮氧双稳定同位素溯源技术[8]、水化学特征分析技术[9]、水质模型与地理信息系统相结合技术[10]、多元统计分析技术[11]和三维荧光光谱特征分析技术[12]等。硝酸盐氮氧双稳定同位素溯源技术对污染源的定性和定量评估较为可靠,但是测试成本高,操作难度大[13]。水化学特征分析技术由于其分析结果的准确性较高,且该方法较为经济,被众多学者广泛使用,但此项技术依赖于分析水体的离子组成以定性分析污染源,不能进行污染源的定量评估[14]。水质模型与地理信息系统相结合技术虽能对水中污染物的迁移和转化过程进行较为精确的模拟,但实测数据需求量大、水质变量模拟具有一定局限性、复杂情况下模型的稳定性差,难以在无资料地区普遍应用和推广[15]。多元统计分析技术能够针对分析过程中产生的大量复杂的数据进行简化处理,从而挖掘分析出潜在的污染源特征,但该方法也存在无法定量评估污染源的问题[16]。
一种新型水污染分析检测和溯源技术,三维荧光光谱技术近年来逐渐发展成熟,与其他技术相比,其操作简单且检测过程快速无污染。另外,随着三维荧光光谱技术在水污染溯源案例中的使用以及三维荧光技术的不断更新与发展[17],以三维荧光光谱技术为基础的指纹图谱库逐步建立并完善[18],结合当今世界大数据与人工智能在环境管理中的广泛应用,一种流域指纹图谱和人工智能相结合的水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系正在逐渐构建完善,见图1。
文章综合近年来国内外的相关研究和实际水污染溯源案例,综述了指纹图谱与人工智能结合形成的水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系的构建过程与其在水污染分析检测和溯源领域的研究应用进展。
-
在线监测-预警技术体系主要分为以下几大模块:在线监测网络布设、水污染预警、水污染风险评估分析及应急处置等系统。在水污染事故发生后,利用在线监测-预警技术体系能够在短时间内进行预警并采取相关手段进行溯源工作不仅能将污染事故的后续影响降到最低,而且也是后续污染风险评估以及污染物的处理处置的前提和基础。在线监测-预警技术体系是通过在线监测手段进行水质异常检测,对可能出现的水质异常现象进行及时的发现和预警,其水质异常的检测手段主要分为两类,一类以统计理论为基础,一类以AI算法为基础。
-
以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测利用了统计学的相关算法和模型进行计算和拟合,比较理论计算得出的理论值与现场测定所得的实际数据之间的残差或者阈值,以此来判别水质异常事件。自回归模型(AR)、3δ法以及时间序列递增算法(TSI)是应用最为广泛的几种统计算法模型[19-20],以上几种算法模型都能在出现水质异常的第一时间通过高效的算法进行识别[21]。
目前国内外所采用的以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测手段,大多将多参数指标权重法与统计概率相结合,算法与算法之间相互弥补其自身的漏洞,在很大程度上提高了水质异常检测的准确性。BYER et al[22]提出在对生物和化学污染物进行测定和研究基础上,大力发展连续监测的水质在线预警系统。BARZEGAR et al[23]使用多种系统和算法模型,如小波-ANFIS、自适应神经模糊推理系统(ANFIS)和ANN,多种算法相结合运算,以高达99%的准确度求得伊朗西北部某流域中的盐度。HIMANSHU et al[24]和MOHAMMADPOUR et al[25]对比了小波变换和SVM两种变换模型在对河流水质预测时的准确度和适用性。结果表明,在准确度和适用性方面,小波变换都略胜一筹,并且小波变换模型相较传统的支持向量机更能体现出其优越性。毛莺池等[26]也运用同样的小波变换方法且结合贝叶斯模型,进行复杂变量的模拟和计算以判别水质异常。
-
随着人工智能的不断发展,AI智能算法已经在各大行业广泛应用,水污染预警与防治领域也不例外。运用AI智能算法应对水质波动及突发水污染事件的案例也越来越多。而在AI算法中,机器学习是其核心。机器学习能够按照既定的算法模型进行不断学习的同时进行优化,预测水质的变化并且提取其中异常数据。机器学习的异常检测学习算法可分为两类,分别是有监督异常检测学习算法和无监督异常检测学习算法[27]。前者中的贝叶斯网络、回归算法、神经网络、最大熵模型、SVM等最为常见且最具代表性,后者主要为降维算法和聚类算法等[28]。
无监督的聚类算法与有监督的算法相结合从而进行水质在线高频监测以挖掘和分析复杂的水质数据是水质异常检测常用的方法。聚类算法依赖于对复杂数据的分类,通过分析数据与数据之间的隐含关系找到其潜在问题。PHUNG et al[29]针对点源与非点源污染的识别问题使用了多元统计技术分析相关水质参数,达到能够准确区分和识别的效果。德国海姆霍研究中心牵头的来自欧洲和美洲十几所世界顶级院校的研究者联合发表了水质在线监测领域的综述[30],对用于水质检测中的物理和化学传感器的应用做出了高度评价。
可见,在水污染分析检测和溯源领域,在线监测-预警技术体系已经被众多研究者开发、应用并趋于成熟。无论是以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测还是以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测都在河流突发水污染应急响应领域发挥了重要的作用。而随着大数据和AI智能算法的发展,以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测逐渐取代了其他检测手段并逐渐成为今后发展的主要方向。而在实际的河流突发性水污染案例中,一旦在线监测-预警技术体系发现水质异常,便以发现异常的水质断面为节点进行由下而上的水污染溯源工作,这就需要依靠建不同类型的受污染水体的水质指纹以支持后续的溯源工作。
-
水质指纹图谱即三维荧光光谱(excitation-emissionmatrix,EEM),其原理是建立以发射光波长和激发光波长为纵横坐标的二维平面,将待测水体的荧光强度以类似“等高线”的形式投影在坐标平面所形成的谱图。每种荧光有机物(fluorescence organic matter,FOM)激发光和发射光的波长都是固定的,在一定浓度范围内,其荧光强度与有机物浓度线性相关[31]。不仅三维荧光光谱中的波长和强度可以作为有机物的种类和浓度的判别依据,而且通过不同有机物的不同三维荧光光谱特点可以展现水样中的有机物组成[32-36],这就如同每个人的“指纹”一样。三维荧光光谱和水体一一对应,因此被形象地称为水质指纹[37],简称水纹。
FOM的种类有很多,对于自然界的常见水体,蛋白质、腐殖质以及叶绿素等最为普遍,而对于成分复杂并且类型多变的污水而言,蛋白质、表面活性剂、油脂、维生素等其他芳香族化合物、以及药品残余及其代谢产物等最为常见[38-41]。每种FOM都有其特定的发光位置[42],将含有不同种类有机污染物的废水的指纹收集起来便形成了一套指纹图谱。指纹图谱数据库从构建的物质类型上大体分为两类,一类是纯物质化学品指纹图谱库,一类是相对应的研究区域工业园区或流域内企业等实际水体荧光图谱库。
-
纯物质化学品指纹图谱是在一定的实地考察调研基础上,对研究区域中的主要工业企业污染物排放点所排放的污染物种类有大致了解或者有一定的推断,据此选取若干种具有代表性且可以产生荧光响应的纯化学品,按照不同的浓度梯度和污染物配比,建立的指纹图谱。
王宝玉[43]根据研究区域的实际情况,选取了3种有代表性的纯化学品,水杨酸(带苯环的酸类),罗丹明B(染料类)和丙酮(脂肪族酮类)。通过配置不同浓度的纯化学品溶液以及两三种按照不同配比的混合溶液,测定其三维荧光光谱,构建了纯化学品的指纹图谱数据库。研究发现,以上3类纯化学品的荧光指纹特征各不相同,并且不同浓度纯化学品溶液的荧光峰的位置和轮廓变化不明显,但是其强弱会发生明显变化。按照不同配比比例将其中任意两种物质混合后的荧光光谱与其中任意一种单独的荧光光谱进行对比发现,混合作用仅仅是将二者的荧光光谱中的峰进行叠加。
综上,通过选取若干种具有代表性的纯化学品以构建单独一种和若干种混合溶液的指纹图谱对成分和构成比较简单的水样较为适用。混合后的若干种物质的荧光光谱彼此之间影响较小,混合后的荧光光谱为若干种纯物质荧光峰的叠加,虽然不同的FOM之间有几率发生荧光猝灭和荧光反应耦合作用,导致其中某种物质的光谱信息被覆盖,甚至直接导致此物质的消失,但是可以在后续的荧光解谱等工作中解决此类问题。但是这种由纯物质化学品构建指纹图谱的方法仅适用于对污染源产生的具体污染物有一定的了解,并且可以明确污染物的具体种类的水体。
-
不同的行业企业,其生产原料、中间产物、特征污染物、工艺、管理水平等都有所不同,最终排放到水体中的残留污染物也是不同的,每家企业的废水中都包含自己独特的信息。除此之外,即便是同一生产企业的不同地区的生产厂房,即便其运用相同的原料和生产工艺,其排放的废水水文也有差异。当企业废水以不同途径排入河道、湖泊或者其他系统时,就形成了其在不同流域环境下的指纹图谱。
-
汤久凯等[44]针对某制药废水的水质指纹展开研究,发现该制药厂的青霉素废水的指纹特征较为鲜明,存在4个明显的荧光峰,并且每个峰的峰强与污染物浓度的相关性较为明显。胡远等[45]针对同样的问题,选择某兽药的抗生素废水展开研究,发现6个主要的水纹荧光峰,并且其中某些峰与峰之间存在一定的关系。吴静等[46]研究发现某制药厂废水的水纹中包含六个水纹峰,将其按照波长分为两组进行特性研究,发现在同一组的水纹峰当中,激发波长与峰强呈现负相关的关系。吴静课题组还研究了我国南、北方城市污水[47]、炼油废水[48]等水质指纹图谱。此外,王士峰等[49]研究某印染废水处理厂废水水纹特征时发现其水质指纹中两个峰的峰强和波长范围都较为稳定,并且二者的正向相关性系数超过0.9。而对于涂装生产废水,张梦怡等[50]进行了研究,结合指纹图谱分析、常规指标分析和有机物的定性分析进行了水纹特征的分析,建立了涂装废水中的有机物的识别技术。以上特定行业企业的水质指纹特征可作为水体快速识别其对应源头废水的新方法。
-
河道水、湖水等与工业废水不同,其属于自然水体,指纹特征有明显的差异。谢超波等[51]的研究选择了某条大流量的河道,建立其水纹荧光图谱后发现其3个荧光峰的强度变化非常明显,并且伴随着突变现象。刘传旸等[52]以某河流A为主要研究对象,建立了A河及其上游来水方向J河D水质荧光指纹图谱。A河水质荧光指纹主要包括3个特征荧光峰,其激发波长,其上、中、下游水质指纹之间相似度均大于99%,具有典型的印染废水污染特征。A河上游由J河分流汇入,J河水质荧光指纹与A河相似度低于60%,且强度不超过A河的40%。J河对A河水质荧光指纹形成过程的影响较小,A河的荧光强度主要由A河上游区域贡献。MOSTOFA et al[53]研究了日本琵琶湖以及与其相连的河流,从河流的上游到下游开展为期1年的采样,构建了其指纹图谱并分析了其荧光峰的变化情况。BAKER et al[54]选择了多达6条河流,对其进行密集采样后分析其指纹特征并构建对应河流的水质指纹图谱。
综上,无论是工业废水还是河道水,由于工业企业等污染源的存在,实际水体的指纹图谱都具有独特的水文特征,其水纹峰的个数、峰位置(即激发波长/发射波长)、每个峰的强度以及峰与峰之间相关性都存在差异。在实际水体的指纹图谱中,每种物质的荧光峰都不一样,物质浓度越高,在图谱中就越突出。因此,从指纹图谱中不仅可以定性地找出具体污染物的种类,还能通过构建不同浓度梯度的指纹图谱以定量确定出污染物的具体含量。不难看出,无论是纯物质化学品还是实际水体的指纹图谱,都包含着污染源特定的水质指纹信息。纯化学品指纹图谱的构建具有一定的约束性,只适用于对污染源有一定的调研基础,能够明确污染物的主要成分的水体。而实际水体的指纹图谱的应用相对较为广泛,且没有太多限制,可适用于工业企业废水、河道水、管网污废水,甚至可以达到江河湖海。但无论哪种类型的指纹图谱,其指纹库的构建只是后续水质分析和污染物溯源中的基础步骤。三维荧光光谱的信息含量很大,仍存在荧光信号叠加等问题,因此,很多学者研究了三维荧光光谱解析的问题,这就需要结合大数据等人工智能及诸多算法程序进行指纹图谱的解析以确定污染源。
-
近几年,我国大数据分析体系不断建立与完善,人工智能也蓬勃发展,如今大数据分析与人工智能相互结合,相辅相成,在越来越多领域逐渐得到应用,并展现出其独特的优势。我国也将此项技术拓展到了污染溯源领域,并且随着技术体系的不断革新,已经越来越接近国际先进水平。以实际水体河流等为代表,其污染溯源工作中所采用的三维荧光指纹图谱法融入大数据分析与AI后,不仅在指纹图谱的特征提取、分析方面有极大的提升,还在污染源匹配、相似污染源的辨识问题中也发挥了其独特的优势,提升了溯源工作的速度和效率,节约了成本,在精确度和准确度上有了质的提高。在此基础上,完成污染物定性溯源的同时进行定量的解析也是非常有必要并且利于解决更多的实际问题。
进行水体污染溯源的过程包括自上游到下游沿水流方向定性的源解析(Source apportionment,SA),同时也包括由下游向上游逆流而上的污染物的定量源反演(Source inversion,SI),而源解析是通过对指纹图谱的解析以获取河流污染物来源等信息,并根据解析出的各类信息复原污染物动态的过程[55]。
-
在工业污水的污染源解析方面,BAKER et al[56]对某造纸工厂排放的废水进行指纹图谱的解析工作,针对指纹图谱的特征进行详细分析,开创了工业污水源解析的先例,为工业污水的源解析提供了参考依据。在实际污染案例中,BORISOVER et al[57]利用源解析相关技术对以色列某条河流沿岸的有可能排入河流的工业企业为研究对象开展研究,成功解析出该河流的主要工业污染来源,定位到其废水排放的标记物,通过对水样特征成分的分析锁定了污染企业。而在农业面源的污染源解析方面,NADEN et al[58]在实际农田中开展试验,将荧光组分的强度与农田废水量进行相关性分析,发现二者的相关性较强,发现废水中蛋白质组分和腐殖质组分的含量比值存在显著的差异,进而说明了水体指纹特征的差异。在油料类污染物的污染源解析等方面,CARSTEA et al[59]将某条河流的指纹图谱进行分析,针对其中腐殖质的荧光组分的含量解析出和柴油相同的类色氨酸荧光信号,创新性地进行了油料类污染物的溯源工作。而对于油料等污染物的鉴别,杨子臣[60]使用3种统计学模型对各种类矿物油的指纹图谱进行解析,达到了矿物油种类鉴别的目的。
在进行污染源解析的过程中,依赖模型和算法程序是远远不够的,其指纹特征的提取分析、信息挖掘以及特征拟合乃至准确度都有很大的提升空间。为了既能保证计算结果的精确又能够快速高效地实现污染物源解析,需要借助大数据与人工智能领域的一些技术,如指纹识别技术、图像特征提取与特征匹配技术等。陈友明[61]进行了有关指纹图谱前的预处理方面的研究,创建了一套相对完整的指纹图谱解析预处理系统,为指纹特征的快速高效提取与对比工作的进行奠定了基础。而在指纹特征提取与匹配研究领域,徐梅花[62]运用两种检测和特征提取算法对指纹图谱的特征进行细节性的捕捉和检测,完成了对指纹特征的准确快速提取。汤海林[63]在对指纹特征进行准确提取的基础上,提出以方向场均值为基础的Poinacre索引算法,进一步提升了指纹信息提取的效率。
-
而在实际的水污染事件溯源案例中,单纯的源解析工作往往不能达到很好的效果,通常将源反演与源解析结合使用,以互相弥补彼此方法中的缺陷和短板。污染源解析的工作能够解决对污染源的追溯、污染位置的确定、污染贡献度的计算等问题,但这对于整个污染评估工作来说并不完整,还需要对下游断面数据进行监测,利用污染物源反演技术反演和重新构建所研究污染物的排放信息等。源反演技术与源解析技术在技术指标的依赖性上略有差异,不仅依赖于指纹图谱的构建,而且需要其他水质参数作为辅助。程伟平等[64]对地表水的污染情况进行了源反演模拟,运用反向概率密度识别法对地表水的污染源进行了反向的识别。DATTA et al[65]将污染物迁移模型与分类非线性优化模型相耦合,构建了一种基于源反演的污染物动态监测网络,有效提高了污染源识别的效率。朱嵩等[66]和王家彪等[67]借助两种不同的水污染溯源模型以及马尔科夫蒙特卡洛方法分析计算出了污染源的具体位置和污染物的强度等信息。
从以上的研究与实际的水污染案例中可以看出,无论是污染物的源解析还是源反演,国内外都有众多学者进行了深入研究,并将此类技术推广应用。总的来说,源解析从定性的角度对水质指纹图谱的特征进行深层的信息挖掘和提取分析,而源反演则是从定量的角度重构污染物的排放历史,为下一步污染物来源的分析和推演奠定基础。源解析与源反演相辅相成,源解析是源反演的前序工作,指导着源反演工作的进行,而源反演所求得的量化的源信息不仅可以提高源解析的准确定,并且为后续应急处置工作提供指导性建议。
-
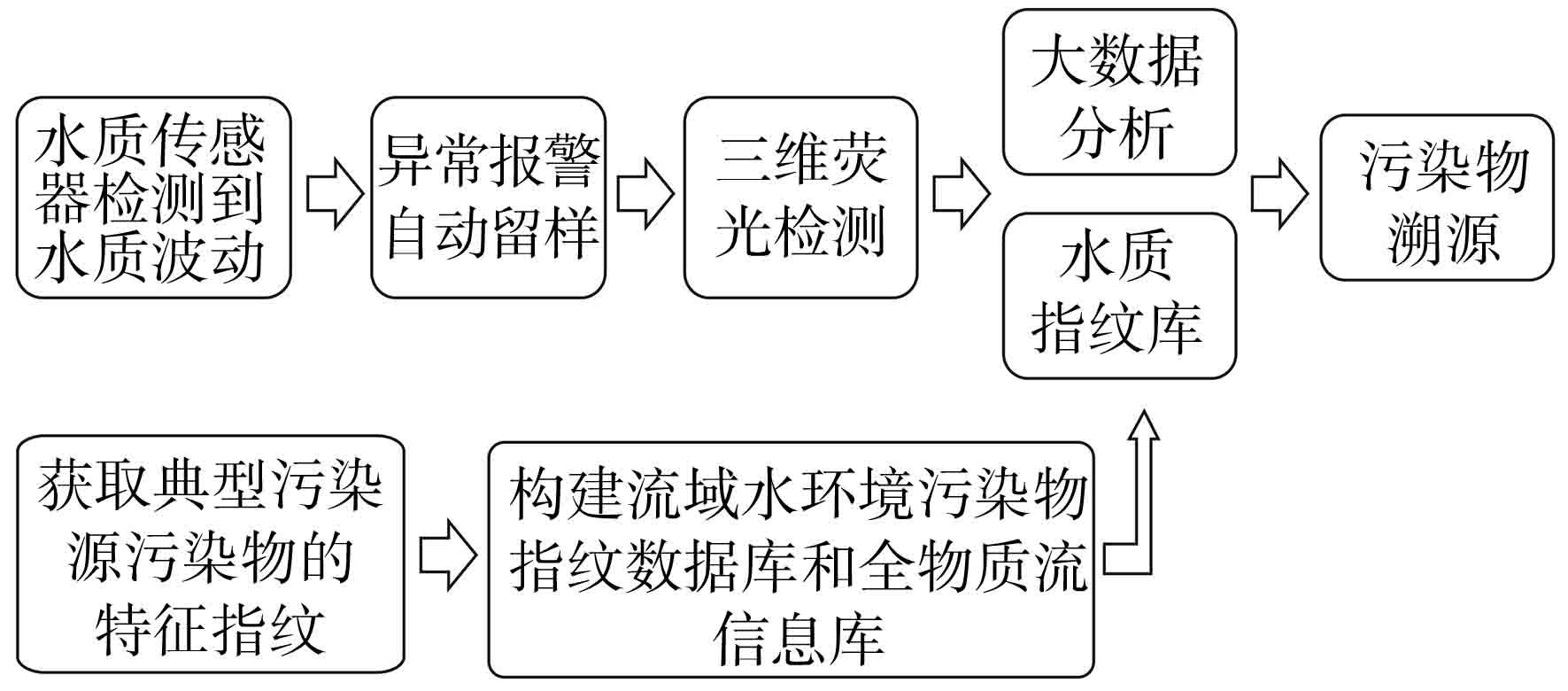
(1)水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系在水污染溯源,尤其是突发性水环境污染事件的溯源中起到了至关重要的作用。水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系的过程包括:水质在线监测-预警体系的构建、指纹图谱库的构建、大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系的构建。当水污染事件发生时,该系统通过在线水质传感器检测到水质波动,对波动进行评估后进行水质异常预警并且自动留样,运用大数据和人工智能分析算法将水样与水质指纹图谱库进行对比分析和模拟,最终判断污染物的来源。
(2)水质在线监测-预警体系能够进行实时在线对水质监测数据进行分析和异常检测,并指导前期预警和后期溯源及应急处置工作。其主要分为以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测和以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测,而后者由于其算法和模型的优越性使其成为今后研究的热点。
(3)水质指纹图谱库包括纯物质化学品和实际水体的指纹图谱,两种类型的指纹图谱都包含着污染源特定的水质指纹信息。前者由于需要预先明确污染物的主要成分,因此使用时有一定的局限性,而后者通过获取流域典型的工业源、农业源、生活源和城市面源中有机污染物的特征指纹构建其流域指纹图谱库,其适用性较为广泛。
(4)大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系是在水质指纹图谱构建完成的基础上将大数据与人工智能相结合,对指纹图谱的特征进行识别、提取、匹配和分类,通过源解析和源反演将污染物定性和定量的有机结合,最终达到污染物溯源的目的。
指纹图谱技术与人工智能在污染物溯源解析中的应用研究
Research and application of fingerprint technology and artificial intelligence in pollutant tracing and analysis
-
摘要: 水污染在线监测-预警-溯源体系在水环境污染事件的溯源中起到了至关重要的作用,而指纹图谱技术与人工智能的有机结合是污染物解析中重要的一环。文章通过水质在线监测-预警体系的建设、指纹图谱库的构建、大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系的完善以完成对污染物进行分析和溯源。对上述体系的构建以及该领域的研究应用进展进行全面综述,并对现有技术方法的优缺点进行比较和分析。
-
关键词:
- 水质指纹图谱 /
- 大数据 /
- 人工智能 /
- 在线监测-预警-溯源体系
Abstract: The online monitoring-early warning-traceability system for water pollutions plays an important role in the traceability of water pollution events. The combination of fingerprint technology and artificial intelligence (AI) is an important part in the traceability of pollutants. The analysis and traceability of pollutants could be achieved by the construction of the water quality online monitoring-early warning system, the establishment of the fingerprint database, and the improvement of the pollution traceability system with big data analysis and AI analysis. In this paper, the construction of the above systems and the research and application progress in this field are reviewed, the advantages and disadvantages of the existing methods are compared and analyzed. -
在经济迅猛发展和社会不断进步过程中,突发性的环境事故也层出不穷。近年来,《中国统计年鉴》中有关全国性突发环境事件的数据,见表1[1-6]。
表 1 《中国统计年鉴》2014~2019年全国突发环境事件情况t/a 突发环境事件次数 特别重大环境事件 重大环境事件 较大环境事件 一般环境事件 2014 471 0 3 16 452 2015 334 0 3 5 326 2016 304 0 3 5 296 2017 302 0 1 6 295 2018 286 0 2 6 278 2019 261 0 0 3 258 总计 1958 0 12 41 1905 表1可知,自2014年起,突发环境事件的次数逐年下降,而在所有类型中,一般环境事件所占的比例超过95%。从数量上看,重大环境事件和较大环境事件的发生次数已经控制到很低的水平,但一般环境事件的发生次数依然处于较高的水平。实际上,在频发的环境污染事件中,水体污染事件在其中所占的比例不容小觑[7]。
目前,面对水体污染事件,尤其是突发性水体污染事件,对污染源的追溯最常用的方法有硝酸盐氮氧双稳定同位素溯源技术[8]、水化学特征分析技术[9]、水质模型与地理信息系统相结合技术[10]、多元统计分析技术[11]和三维荧光光谱特征分析技术[12]等。硝酸盐氮氧双稳定同位素溯源技术对污染源的定性和定量评估较为可靠,但是测试成本高,操作难度大[13]。水化学特征分析技术由于其分析结果的准确性较高,且该方法较为经济,被众多学者广泛使用,但此项技术依赖于分析水体的离子组成以定性分析污染源,不能进行污染源的定量评估[14]。水质模型与地理信息系统相结合技术虽能对水中污染物的迁移和转化过程进行较为精确的模拟,但实测数据需求量大、水质变量模拟具有一定局限性、复杂情况下模型的稳定性差,难以在无资料地区普遍应用和推广[15]。多元统计分析技术能够针对分析过程中产生的大量复杂的数据进行简化处理,从而挖掘分析出潜在的污染源特征,但该方法也存在无法定量评估污染源的问题[16]。
一种新型水污染分析检测和溯源技术,三维荧光光谱技术近年来逐渐发展成熟,与其他技术相比,其操作简单且检测过程快速无污染。另外,随着三维荧光光谱技术在水污染溯源案例中的使用以及三维荧光技术的不断更新与发展[17],以三维荧光光谱技术为基础的指纹图谱库逐步建立并完善[18],结合当今世界大数据与人工智能在环境管理中的广泛应用,一种流域指纹图谱和人工智能相结合的水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系正在逐渐构建完善,见图1。
文章综合近年来国内外的相关研究和实际水污染溯源案例,综述了指纹图谱与人工智能结合形成的水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系的构建过程与其在水污染分析检测和溯源领域的研究应用进展。
1. 在线监测-预警技术体系
在线监测-预警技术体系主要分为以下几大模块:在线监测网络布设、水污染预警、水污染风险评估分析及应急处置等系统。在水污染事故发生后,利用在线监测-预警技术体系能够在短时间内进行预警并采取相关手段进行溯源工作不仅能将污染事故的后续影响降到最低,而且也是后续污染风险评估以及污染物的处理处置的前提和基础。在线监测-预警技术体系是通过在线监测手段进行水质异常检测,对可能出现的水质异常现象进行及时的发现和预警,其水质异常的检测手段主要分为两类,一类以统计理论为基础,一类以AI算法为基础。
1.1 以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测
以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测利用了统计学的相关算法和模型进行计算和拟合,比较理论计算得出的理论值与现场测定所得的实际数据之间的残差或者阈值,以此来判别水质异常事件。自回归模型(AR)、3δ法以及时间序列递增算法(TSI)是应用最为广泛的几种统计算法模型[19-20],以上几种算法模型都能在出现水质异常的第一时间通过高效的算法进行识别[21]。
目前国内外所采用的以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测手段,大多将多参数指标权重法与统计概率相结合,算法与算法之间相互弥补其自身的漏洞,在很大程度上提高了水质异常检测的准确性。BYER et al[22]提出在对生物和化学污染物进行测定和研究基础上,大力发展连续监测的水质在线预警系统。BARZEGAR et al[23]使用多种系统和算法模型,如小波-ANFIS、自适应神经模糊推理系统(ANFIS)和ANN,多种算法相结合运算,以高达99%的准确度求得伊朗西北部某流域中的盐度。HIMANSHU et al[24]和MOHAMMADPOUR et al[25]对比了小波变换和SVM两种变换模型在对河流水质预测时的准确度和适用性。结果表明,在准确度和适用性方面,小波变换都略胜一筹,并且小波变换模型相较传统的支持向量机更能体现出其优越性。毛莺池等[26]也运用同样的小波变换方法且结合贝叶斯模型,进行复杂变量的模拟和计算以判别水质异常。
1.2 以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测
随着人工智能的不断发展,AI智能算法已经在各大行业广泛应用,水污染预警与防治领域也不例外。运用AI智能算法应对水质波动及突发水污染事件的案例也越来越多。而在AI算法中,机器学习是其核心。机器学习能够按照既定的算法模型进行不断学习的同时进行优化,预测水质的变化并且提取其中异常数据。机器学习的异常检测学习算法可分为两类,分别是有监督异常检测学习算法和无监督异常检测学习算法[27]。前者中的贝叶斯网络、回归算法、神经网络、最大熵模型、SVM等最为常见且最具代表性,后者主要为降维算法和聚类算法等[28]。
无监督的聚类算法与有监督的算法相结合从而进行水质在线高频监测以挖掘和分析复杂的水质数据是水质异常检测常用的方法。聚类算法依赖于对复杂数据的分类,通过分析数据与数据之间的隐含关系找到其潜在问题。PHUNG et al[29]针对点源与非点源污染的识别问题使用了多元统计技术分析相关水质参数,达到能够准确区分和识别的效果。德国海姆霍研究中心牵头的来自欧洲和美洲十几所世界顶级院校的研究者联合发表了水质在线监测领域的综述[30],对用于水质检测中的物理和化学传感器的应用做出了高度评价。
可见,在水污染分析检测和溯源领域,在线监测-预警技术体系已经被众多研究者开发、应用并趋于成熟。无论是以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测还是以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测都在河流突发水污染应急响应领域发挥了重要的作用。而随着大数据和AI智能算法的发展,以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测逐渐取代了其他检测手段并逐渐成为今后发展的主要方向。而在实际的河流突发性水污染案例中,一旦在线监测-预警技术体系发现水质异常,便以发现异常的水质断面为节点进行由下而上的水污染溯源工作,这就需要依靠建不同类型的受污染水体的水质指纹以支持后续的溯源工作。
2. 指纹图谱库的构建
水质指纹图谱即三维荧光光谱(excitation-emissionmatrix,EEM),其原理是建立以发射光波长和激发光波长为纵横坐标的二维平面,将待测水体的荧光强度以类似“等高线”的形式投影在坐标平面所形成的谱图。每种荧光有机物(fluorescence organic matter,FOM)激发光和发射光的波长都是固定的,在一定浓度范围内,其荧光强度与有机物浓度线性相关[31]。不仅三维荧光光谱中的波长和强度可以作为有机物的种类和浓度的判别依据,而且通过不同有机物的不同三维荧光光谱特点可以展现水样中的有机物组成[32-36],这就如同每个人的“指纹”一样。三维荧光光谱和水体一一对应,因此被形象地称为水质指纹[37],简称水纹。
FOM的种类有很多,对于自然界的常见水体,蛋白质、腐殖质以及叶绿素等最为普遍,而对于成分复杂并且类型多变的污水而言,蛋白质、表面活性剂、油脂、维生素等其他芳香族化合物、以及药品残余及其代谢产物等最为常见[38-41]。每种FOM都有其特定的发光位置[42],将含有不同种类有机污染物的废水的指纹收集起来便形成了一套指纹图谱。指纹图谱数据库从构建的物质类型上大体分为两类,一类是纯物质化学品指纹图谱库,一类是相对应的研究区域工业园区或流域内企业等实际水体荧光图谱库。
2.1 纯物质化学品指纹图谱
纯物质化学品指纹图谱是在一定的实地考察调研基础上,对研究区域中的主要工业企业污染物排放点所排放的污染物种类有大致了解或者有一定的推断,据此选取若干种具有代表性且可以产生荧光响应的纯化学品,按照不同的浓度梯度和污染物配比,建立的指纹图谱。
王宝玉[43]根据研究区域的实际情况,选取了3种有代表性的纯化学品,水杨酸(带苯环的酸类),罗丹明B(染料类)和丙酮(脂肪族酮类)。通过配置不同浓度的纯化学品溶液以及两三种按照不同配比的混合溶液,测定其三维荧光光谱,构建了纯化学品的指纹图谱数据库。研究发现,以上3类纯化学品的荧光指纹特征各不相同,并且不同浓度纯化学品溶液的荧光峰的位置和轮廓变化不明显,但是其强弱会发生明显变化。按照不同配比比例将其中任意两种物质混合后的荧光光谱与其中任意一种单独的荧光光谱进行对比发现,混合作用仅仅是将二者的荧光光谱中的峰进行叠加。
综上,通过选取若干种具有代表性的纯化学品以构建单独一种和若干种混合溶液的指纹图谱对成分和构成比较简单的水样较为适用。混合后的若干种物质的荧光光谱彼此之间影响较小,混合后的荧光光谱为若干种纯物质荧光峰的叠加,虽然不同的FOM之间有几率发生荧光猝灭和荧光反应耦合作用,导致其中某种物质的光谱信息被覆盖,甚至直接导致此物质的消失,但是可以在后续的荧光解谱等工作中解决此类问题。但是这种由纯物质化学品构建指纹图谱的方法仅适用于对污染源产生的具体污染物有一定的了解,并且可以明确污染物的具体种类的水体。
2.2 实际水体指纹图谱
不同的行业企业,其生产原料、中间产物、特征污染物、工艺、管理水平等都有所不同,最终排放到水体中的残留污染物也是不同的,每家企业的废水中都包含自己独特的信息。除此之外,即便是同一生产企业的不同地区的生产厂房,即便其运用相同的原料和生产工艺,其排放的废水水文也有差异。当企业废水以不同途径排入河道、湖泊或者其他系统时,就形成了其在不同流域环境下的指纹图谱。
2.2.1 工业废水
汤久凯等[44]针对某制药废水的水质指纹展开研究,发现该制药厂的青霉素废水的指纹特征较为鲜明,存在4个明显的荧光峰,并且每个峰的峰强与污染物浓度的相关性较为明显。胡远等[45]针对同样的问题,选择某兽药的抗生素废水展开研究,发现6个主要的水纹荧光峰,并且其中某些峰与峰之间存在一定的关系。吴静等[46]研究发现某制药厂废水的水纹中包含六个水纹峰,将其按照波长分为两组进行特性研究,发现在同一组的水纹峰当中,激发波长与峰强呈现负相关的关系。吴静课题组还研究了我国南、北方城市污水[47]、炼油废水[48]等水质指纹图谱。此外,王士峰等[49]研究某印染废水处理厂废水水纹特征时发现其水质指纹中两个峰的峰强和波长范围都较为稳定,并且二者的正向相关性系数超过0.9。而对于涂装生产废水,张梦怡等[50]进行了研究,结合指纹图谱分析、常规指标分析和有机物的定性分析进行了水纹特征的分析,建立了涂装废水中的有机物的识别技术。以上特定行业企业的水质指纹特征可作为水体快速识别其对应源头废水的新方法。
2.2.2 河道水
河道水、湖水等与工业废水不同,其属于自然水体,指纹特征有明显的差异。谢超波等[51]的研究选择了某条大流量的河道,建立其水纹荧光图谱后发现其3个荧光峰的强度变化非常明显,并且伴随着突变现象。刘传旸等[52]以某河流A为主要研究对象,建立了A河及其上游来水方向J河D水质荧光指纹图谱。A河水质荧光指纹主要包括3个特征荧光峰,其激发波长,其上、中、下游水质指纹之间相似度均大于99%,具有典型的印染废水污染特征。A河上游由J河分流汇入,J河水质荧光指纹与A河相似度低于60%,且强度不超过A河的40%。J河对A河水质荧光指纹形成过程的影响较小,A河的荧光强度主要由A河上游区域贡献。MOSTOFA et al[53]研究了日本琵琶湖以及与其相连的河流,从河流的上游到下游开展为期1年的采样,构建了其指纹图谱并分析了其荧光峰的变化情况。BAKER et al[54]选择了多达6条河流,对其进行密集采样后分析其指纹特征并构建对应河流的水质指纹图谱。
综上,无论是工业废水还是河道水,由于工业企业等污染源的存在,实际水体的指纹图谱都具有独特的水文特征,其水纹峰的个数、峰位置(即激发波长/发射波长)、每个峰的强度以及峰与峰之间相关性都存在差异。在实际水体的指纹图谱中,每种物质的荧光峰都不一样,物质浓度越高,在图谱中就越突出。因此,从指纹图谱中不仅可以定性地找出具体污染物的种类,还能通过构建不同浓度梯度的指纹图谱以定量确定出污染物的具体含量。不难看出,无论是纯物质化学品还是实际水体的指纹图谱,都包含着污染源特定的水质指纹信息。纯化学品指纹图谱的构建具有一定的约束性,只适用于对污染源有一定的调研基础,能够明确污染物的主要成分的水体。而实际水体的指纹图谱的应用相对较为广泛,且没有太多限制,可适用于工业企业废水、河道水、管网污废水,甚至可以达到江河湖海。但无论哪种类型的指纹图谱,其指纹库的构建只是后续水质分析和污染物溯源中的基础步骤。三维荧光光谱的信息含量很大,仍存在荧光信号叠加等问题,因此,很多学者研究了三维荧光光谱解析的问题,这就需要结合大数据等人工智能及诸多算法程序进行指纹图谱的解析以确定污染源。
3. 大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系
近几年,我国大数据分析体系不断建立与完善,人工智能也蓬勃发展,如今大数据分析与人工智能相互结合,相辅相成,在越来越多领域逐渐得到应用,并展现出其独特的优势。我国也将此项技术拓展到了污染溯源领域,并且随着技术体系的不断革新,已经越来越接近国际先进水平。以实际水体河流等为代表,其污染溯源工作中所采用的三维荧光指纹图谱法融入大数据分析与AI后,不仅在指纹图谱的特征提取、分析方面有极大的提升,还在污染源匹配、相似污染源的辨识问题中也发挥了其独特的优势,提升了溯源工作的速度和效率,节约了成本,在精确度和准确度上有了质的提高。在此基础上,完成污染物定性溯源的同时进行定量的解析也是非常有必要并且利于解决更多的实际问题。
进行水体污染溯源的过程包括自上游到下游沿水流方向定性的源解析(Source apportionment,SA),同时也包括由下游向上游逆流而上的污染物的定量源反演(Source inversion,SI),而源解析是通过对指纹图谱的解析以获取河流污染物来源等信息,并根据解析出的各类信息复原污染物动态的过程[55]。
3.1 污染源解析
在工业污水的污染源解析方面,BAKER et al[56]对某造纸工厂排放的废水进行指纹图谱的解析工作,针对指纹图谱的特征进行详细分析,开创了工业污水源解析的先例,为工业污水的源解析提供了参考依据。在实际污染案例中,BORISOVER et al[57]利用源解析相关技术对以色列某条河流沿岸的有可能排入河流的工业企业为研究对象开展研究,成功解析出该河流的主要工业污染来源,定位到其废水排放的标记物,通过对水样特征成分的分析锁定了污染企业。而在农业面源的污染源解析方面,NADEN et al[58]在实际农田中开展试验,将荧光组分的强度与农田废水量进行相关性分析,发现二者的相关性较强,发现废水中蛋白质组分和腐殖质组分的含量比值存在显著的差异,进而说明了水体指纹特征的差异。在油料类污染物的污染源解析等方面,CARSTEA et al[59]将某条河流的指纹图谱进行分析,针对其中腐殖质的荧光组分的含量解析出和柴油相同的类色氨酸荧光信号,创新性地进行了油料类污染物的溯源工作。而对于油料等污染物的鉴别,杨子臣[60]使用3种统计学模型对各种类矿物油的指纹图谱进行解析,达到了矿物油种类鉴别的目的。
在进行污染源解析的过程中,依赖模型和算法程序是远远不够的,其指纹特征的提取分析、信息挖掘以及特征拟合乃至准确度都有很大的提升空间。为了既能保证计算结果的精确又能够快速高效地实现污染物源解析,需要借助大数据与人工智能领域的一些技术,如指纹识别技术、图像特征提取与特征匹配技术等。陈友明[61]进行了有关指纹图谱前的预处理方面的研究,创建了一套相对完整的指纹图谱解析预处理系统,为指纹特征的快速高效提取与对比工作的进行奠定了基础。而在指纹特征提取与匹配研究领域,徐梅花[62]运用两种检测和特征提取算法对指纹图谱的特征进行细节性的捕捉和检测,完成了对指纹特征的准确快速提取。汤海林[63]在对指纹特征进行准确提取的基础上,提出以方向场均值为基础的Poinacre索引算法,进一步提升了指纹信息提取的效率。
3.2 污染源反演
而在实际的水污染事件溯源案例中,单纯的源解析工作往往不能达到很好的效果,通常将源反演与源解析结合使用,以互相弥补彼此方法中的缺陷和短板。污染源解析的工作能够解决对污染源的追溯、污染位置的确定、污染贡献度的计算等问题,但这对于整个污染评估工作来说并不完整,还需要对下游断面数据进行监测,利用污染物源反演技术反演和重新构建所研究污染物的排放信息等。源反演技术与源解析技术在技术指标的依赖性上略有差异,不仅依赖于指纹图谱的构建,而且需要其他水质参数作为辅助。程伟平等[64]对地表水的污染情况进行了源反演模拟,运用反向概率密度识别法对地表水的污染源进行了反向的识别。DATTA et al[65]将污染物迁移模型与分类非线性优化模型相耦合,构建了一种基于源反演的污染物动态监测网络,有效提高了污染源识别的效率。朱嵩等[66]和王家彪等[67]借助两种不同的水污染溯源模型以及马尔科夫蒙特卡洛方法分析计算出了污染源的具体位置和污染物的强度等信息。
从以上的研究与实际的水污染案例中可以看出,无论是污染物的源解析还是源反演,国内外都有众多学者进行了深入研究,并将此类技术推广应用。总的来说,源解析从定性的角度对水质指纹图谱的特征进行深层的信息挖掘和提取分析,而源反演则是从定量的角度重构污染物的排放历史,为下一步污染物来源的分析和推演奠定基础。源解析与源反演相辅相成,源解析是源反演的前序工作,指导着源反演工作的进行,而源反演所求得的量化的源信息不仅可以提高源解析的准确定,并且为后续应急处置工作提供指导性建议。
4. 结论与展望
(1)水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系在水污染溯源,尤其是突发性水环境污染事件的溯源中起到了至关重要的作用。水污染在线监测-预警-溯源技术体系的过程包括:水质在线监测-预警体系的构建、指纹图谱库的构建、大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系的构建。当水污染事件发生时,该系统通过在线水质传感器检测到水质波动,对波动进行评估后进行水质异常预警并且自动留样,运用大数据和人工智能分析算法将水样与水质指纹图谱库进行对比分析和模拟,最终判断污染物的来源。
(2)水质在线监测-预警体系能够进行实时在线对水质监测数据进行分析和异常检测,并指导前期预警和后期溯源及应急处置工作。其主要分为以统计理论为基础的水质异常检测和以AI算法为基础的水质异常检测,而后者由于其算法和模型的优越性使其成为今后研究的热点。
(3)水质指纹图谱库包括纯物质化学品和实际水体的指纹图谱,两种类型的指纹图谱都包含着污染源特定的水质指纹信息。前者由于需要预先明确污染物的主要成分,因此使用时有一定的局限性,而后者通过获取流域典型的工业源、农业源、生活源和城市面源中有机污染物的特征指纹构建其流域指纹图谱库,其适用性较为广泛。
(4)大数据分析与AI相结合的污染溯源体系是在水质指纹图谱构建完成的基础上将大数据与人工智能相结合,对指纹图谱的特征进行识别、提取、匹配和分类,通过源解析和源反演将污染物定性和定量的有机结合,最终达到污染物溯源的目的。
-
表 1 《中国统计年鉴》2014~2019年全国突发环境事件情况
t/a 突发环境事件次数 特别重大环境事件 重大环境事件 较大环境事件 一般环境事件 2014 471 0 3 16 452 2015 334 0 3 5 326 2016 304 0 3 5 296 2017 302 0 1 6 295 2018 286 0 2 6 278 2019 261 0 0 3 258 总计 1958 0 12 41 1905 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2015中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2015. [2] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2016中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2016. [3] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2017中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2017. [4] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2018中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2018. [5] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2019中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2019. [6] 中华人民共和国国家统计局.2020中国统计年鉴[M].北京: 中国统计出版社,2020. [7] CAMP J S, ABKOWITZ M D, LEBOEUF E J. Inland waterway resource and spill management needs in Southeastern USA[J]. Disaster Prevention & Management, 2010, 19(4): 483 − 497. [8] ROGERS K M, NICOLINI E, GAUTHIER V. Identifying source and formation altitudes of nitrates in drinking water from Réunion Island, France, using a multi-isotopic approach[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2012, 138: 93 − 103. [9] ANSHUMALI, RAMANATHAN A L. Seasonal variation in the major ion chemistry of Pandoh Lake, Mandi District, Himachal Pradesh, India[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2007, 22(8): 1736 − 1747. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.03.045 [10] NAS B, BERKTAY A. Groundwater contamination by nitrates in the city of Konya, (Turkey): A GIS perspective[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2006, 79(1): 30 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.05.010 [11] SHRESTHA S, KAZAMA F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2007, 22(4): 464 − 475. [12] INAMDAR S, SINGH S, DUTTA S, et al. Fluorescence characteristics and sources of dissolved organic matter for stream water during storm events in a forested mid-Atlantic watershed[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 2011, 116: G03043. [13] 徐志伟, 张心昱, 于贵瑞, 等. 中国水体硝酸盐氮氧双稳定同位素溯源研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(8): 3230 − 3238. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.08.056 [14] VUAI S A, NAKAMURA K, TOKUYAMA A. Geochemical characteristics of runoff from acid sulfate soils in the northern area of Okinawa Island, Japan[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2003, 37(5): 579 − 592. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.37.579 [15] PRAHARAJ T, SWAIN S P, POWELL M A, et al. Delineation of groundwater contamination around an ash pond: geochemical and GIS approach[J]. Environment International, 2002, 27(8): 631 − 638. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00121-0 [16] Bu H M, Tan X A, Li S Y, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of water quality in the Jinshui River of the South Qinling Mts. China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2010, 73(5): 907 − 913. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.11.007 [17] 史斌. 水污染动态预警监测模型构建与应急处置工程风险分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. [18] 吕清, 顾俊强, 徐诗琴, 等. 水纹预警溯源技术在地表水水质监测的应用[J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(1): 152 − 156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.01.030 [19] 朱炜玉, 史斌, 姜继平, 等. 基于水质时间序列异常检测的动态预警方法[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(12): 131 − 137. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2018.12.019 [20] DARIANE A B, AZIMI S. Streamflow forecasting by combining neural networks and fuzzy models using advanced methods of input variable selection[J]. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 2018, 20(2): 520 − 532. doi: 10.2166/hydro.2017.076 [21] 周俊临. 基于数据挖掘的分布式异常检测[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2010. [22] BYER D. Real-time detection of intentional chemical contamination - In the distribution system[J]. Journal American Water Works Association, 2005, 97(7): 130 − 133. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.2005.tb10938.x [23] BARZEGAR R, ADAMOWSKI J, MOGHADDAM A A. Application of wavelet-artificial intelligence hybrid models for water quality prediction: a case study in Aji-Chay River, Iran[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2016, 30(7): 1797 − 1819. doi: 10.1007/s00477-016-1213-y [24] HIMANSHU S K, PANDEY A, YADAV B. Ensemble wavelet-support vector machine approach for prediction of suspended sediment load using hydrometeorological data[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2017, 22(7): 05017006. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001516 [25] MOHAMMADPOUR R, SHAHARUDDIN S, CHANG C K, et al. Prediction of water quality index in constructed wetlands using support vector machine[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2015, 22(8): 6208 − 6219. [26] 毛莺池, 齐海, 接青, 等. M-TAEDA: 多变量水质参数时序数据异常事件检测算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2017, 37(1): 138 − 144. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2017.01.0138 [27] SINGH K P, MALIK A, MOHAN D, et al. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study - Science Direct[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(18): 3980 − 3992. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011 [28] NAGHIBI S A, POURGHASEMI H R, ABBASPOUR K. A comparison between ten advanced and soft computing models for groundwater qanat potential assessment in Iran using R and GIS[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2018, 131(3): 967-984. [29] PHUNG D, HUANG C, RUTHERFORD S, et al. Temporal and spatial assessment of river surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a study in Can Tho City, a Mekong Delta area, Vietnam[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(5):1-13. [30] RODE M, WADE A J, COHEN M J, et al. Sensors in the Stream: The High-Frequency Wave of the Present[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 50(19): 10297 − 10307. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b02155 [31] 陈国庆, 顾正建, 朱拓, 等. 太湖水荧光光谱分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2006(6): 16 − 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2006.06.004 [32] MOSTOFA K, F WU, LIU C Q, et al. Characterization of Nanming River (southwestern China) sewerage-impacted pollution using an excitation-emission matrix and PARAFAC[J]. Limnology, 2010, 11(3): 217 − 231. doi: 10.1007/s10201-009-0306-4 [33] CARSTEA E M, BAKER A, BIEROZA M, et al. Continuous fluorescence excitation–emission matrix monitoring of river organic matter[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(18): 5356 − 5366. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.036 [34] HAMBLY A C, HENDERSON R K, STOREY M V, et al. Fluorescence monitoring at a recycled water treatment plant and associated dual distribution system – Implications for cross-connection detection[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(18): 5323 − 5333. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.003 [35] HENDERSON R K, BAKER A, MURPHY K R, et al. Fluorescence as a potential monitoring tool for recycled water systems: A review[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(4): 863 − 881. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.027 [36] GALINHA C F, CARVALHO G, PORTUGAL C, et al. Two-dimensional fluorescence as a fingerprinting tool for monitoring wastewater treatment systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2011, 86(7): 985 − 992. [37] WU J, PONS M N, POTIER O. Wastewater fingerprinting by UV-visible and synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Water Science & Technology A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2006, 53(4-5): 449 − 456. [38] 王忠东, 武金玲, 李东明, 等. 基于荧光机制的光纤式农药残留测量系统[J]. 中国激光, 2006(7): 1003 − 1008. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2006.07.029 [39] 陈茂福, 吴静, 律严励, 等. 城市污水的三维荧光指纹特征[J]. 光学学报, 2008(3): 578 − 582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2008.03.033 [40] 吴静, 曹知平, 谢超波, 等. 石化废水的三维荧光光谱特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(9): 2437 − 2441. [41] 李宏斌, 刘文清, 张玉钧, 等. 三维荧光光谱技术在水监测中的应用[J]. 光学技术, 2006(1): 27 − 30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2006.01.033 [42] 戴春燕, 吴静, 向熙, 等. 工业废水为主的城市污水的荧光指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(2): 414 − 417. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)02-0414-04 [43] 王宝玉. 基于谱分析与荧光响应的水污染预警溯源技术基础研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [44] 汤久凯, 吴静, 程澄, 等. 某半合成青霉素制药废水的水质指纹特性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(11): 3602 − 3607. [45] 胡远, 柴一荻, 刘博, 等. 某兽药抗生素废水的荧光水质指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(10): 3144 − 3147. [46] 吴静, 赵宇菲, 曹炯准, 等. 某头孢制药废水的水质指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(4): 1075 − 1079. [47] 吴静, 崔硕, 苏伟, 等. 北京城市水体的三维荧光特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(6): 1562 − 1566. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2011)06-1562-05 [48] 吴静, 谢超波, 曹知平, 等. 炼油废水的荧光指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(2): 415 − 419. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)02-0415-05 [49] 王士峰, 吴静, 程澄, 等. 某印染废水的水质指纹特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(12): 3440 − 3443. [50] 张梦怡, 付海娟, 池勇志. 指纹图谱法解析涂装废水中的有机污染物[J]. 山西建筑, 2021, 47(7): 166 − 169. doi: 10.13719/j.cnki.1009-6825.2021.07.059 [51] 谢超波, 吴静, 曹知平, 等. 大流量河道的水质荧光指纹变化[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(3): 695 − 697. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)03-0695-03 [52] 刘传旸, 柴一荻, 徐宪根, 等. 南方某河水质荧光指纹特征及污染溯源[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(7): 2142 − 2147. [53] MOSTOFA K, YOSHIOKA T, KONOHIRA E, et al. Three-dimensional fluorescence as a tool for investigating the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in the Lake Biwa watershed[J]. Limnology, 2005, 6(2): 101 − 115. doi: 10.1007/s10201-005-0149-6 [54] BAKER A. Fluorescence excitation - emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(5): 948 − 953. [55] 周慧平, 高燕, 尹爱经. 水污染源解析技术与应用研究进展[J]. 环境保护科学, 2014, 40(6): 19 − 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2014.06.004 [56] BAKER A. Fluorescence excitation - Emission matrix characterization of river waters impacted by a tissue mill effluent[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(7): 1377 − 1382. [57] BORISOVER M, LAOR Y, SAADI I, et al. Tracing organic footprints from industrial effluent discharge in recalcitrant riverine chromophoric dissolved organic matter[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2011, 222(1-4): 255 − 269. doi: 10.1007/s11270-011-0821-x [58] NADEN P S, OLD G H, ELIOT-LAIZE C, et al. Assessment of natural fluorescence as a tracer of diffuse agricultural pollution from slurry spreading on intensely-farmed grasslands[J]. Water Research, 2009, 44(6): 1701 − 1712. [59] CARSTEA E M, GHERVASE L, PAVELESCU G, et al. Real-time monitoring of an urban river contaminated with petroleum products[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2012, 11(2): 279 − 283. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2012.035 [60] 杨子臣. 基于三维荧光谱技术的矿物油种类鉴别[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2013. [61] 陈友明. 基于纹理分析的指纹图像预处理算法研究[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2009, 5(30): 8499 − 8501. [62] 徐梅花. 指纹图像奇异点检测及特征提取算法研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2010. [63] 汤海林. 指纹图像奇异点提取算法的研究与实现[J]. 电脑开发与应用, 2013, 26(7): 7 − 9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5850.2013.07.003 [64] 程伟平, 廖锡健. 基于逆向概率密度函数的一维污染源排放重构[J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2011, 26(4): 460 − 469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-4874.2011.04.010 [65] DATTA B, CHAKRABARTY D, DHAR A. Optimal dynamic monitoring network design and identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources[J]. Water Resources Management, 2009, 23(10): 2031 − 2049. doi: 10.1007/s11269-008-9368-z [66] 朱嵩, 刘国华, 王立忠, 等. 水动力-水质耦合模型污染源识别的贝叶斯方法[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2009, 41(5): 30 − 35. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2009.05.003 [67] 王家彪, 雷晓辉, 廖卫红, 等. 基于耦合概率密度方法的河渠突发水污染溯源[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(11): 1280 − 1289. doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20150405 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: