-
双氯芬酸(DCF)属于非甾体类药物,被广泛用于人类和动物的抗炎、镇痛及解热。据统计,全球DCF年消费量约为1 400 t,每人每年的平均消费量为(0.33±0.29) g[1-2]。工业生产和动物粪便尿液导致在废水处理厂的进水和出水中频繁检测到DCF。DCF已被列入欧盟的化合物观察名单,并且在浓度低于1 μg时,痕量的DCF对几种环境物种造成了有害影响[3-4]。二价锌(Zn2+)是各种废水中最常见的重金属污染物之一。以中国养殖废水为例,每年可排放含Zn2+废水4 757 t[5]。为了预防动物疾病和刺激生长,人们经常在兽药或饲料中添加Zn2+,DCF和Zn2+以其母体或生物体产生的代谢物的形式与动物粪便和尿液一起排放,并进入废水处理系统,在废水处理系统中同时检测到DCF和Zn2+[6]。一些学者研究发现,当污水中同时存在DCF和重金属(如Zn2+)时,DCF可以通过氢键、共价键(主要是π-π相互作用)和静电引力等作用与重金属离子结合形成复合物,其复合物对细菌的毒性通常不同于DCF和重金属,导致对污染物去除的复杂影响[7-8]。因此,有必要了解重金属和DCF共存对污水处理系统性能的综合影响。
目前,对于含药物和重金属废水的处理方法有物理化学技术、生物技术以及工艺组合技术。高级氧化法处理难降解污染物质有很好的效果,具有工艺简单、去除效果好、流程短易于操作等优点,引起了众多学者的关注,Fenton试剂是一种由H2O2和Fe2+组成的反应系统,在Fe2+的催化下,H2O2迅速分解为羟基(·OH),见式(1):
由于·OH的强氧化性,使得Fenton法能够在短时间内快速去除污染物,是最实用的氧化工艺之一[9]。但UV/Fenton工艺消耗大量的Fe2+、H2O2和能量。为了降低成本,UV/Fenton通常用于生物处理法之后,作为深度处理工艺,许多研究证实,将UV/Fenton工艺作为生物处理的后续工艺能有效去除废水中的污染物。AZIZI et al[10]发现在序批式反应器(SBR)后采用Fenton工艺后,难以生物降解的偶氮染料酸性红18几乎完全被脱色,而SBR中的脱色率为88%。COD去除率接近97%,将Fenton法作为后续处理工艺较单一SBR法有明显提高。PUNZI et al[11]实验发现在生物处理后进行的UV/Fenton工艺将COD的去除率从60%提高到92%。NOUSHEEN et al[12]采用UASB和UV/Fenton工艺处理混合生活和工业废水。结果表明,生物处理降低了原进水的污染负荷,UV/Fenton去除了废水中90%以上的COD和80%以上的色度。ZHANG et al[13]将UV/Fenton作为序批式生物膜反应器(SBBR)后处理工艺用于垃圾渗滤液处理,结果发现组合工艺COD和BOD5去除率方面取得了显著的提高。在污水处理中,生物技术主要用于降低COD、TN和TP,单一的生物处理技术通常无法达到良好的去除效率。因此,生物技术与化学氧化技术相结合的组合工艺引起了众多学者的关注,UV/Fenton化学氧化可作为深度处理技术被用于进一步去除药物,不但能极大地降低处理成本,而且可以有针对性地对废水中残余的、具有生物毒性或抑制性的污染物进行降解。然而,目前关于UV/Fenton氧化技术作为深度处理方法在去除重金属和DCF复合污染方面的研究较少。因此,开发一种可靠、简便、操作难度低的污水处理方法,对解决重金属和DCF复合污染问题具有较强的现实意义。
针对含DCF和Zn2+废水生化处理存在的COD偏高和DCF不能有效去除等问题,本文以50 mg/L DCF和5 mg/L Zn2+单一及复合溶液为研究对象,采用UV/Fenton作为深度处理工艺,探究高级氧化过程中H2O2浓度、Fe2+浓度和反应时间对COD、DCF和NH4+-N去除率的影响。在综合考虑经济性和去除率后,寻求最佳高级氧化反应条件。
-
SBR中的进水化学需氧量(COD)和氨氮(NH4+-N)浓度分别为500 和40 mg/L,实验开始前保证COD和NH4+-N去除率均稳定维持在95%以上。SBR反应器进水为人工配制的模拟废水,具体配置方法,见表1。
-
取经SBR处理后的模拟废水置于锥形瓶中,H2SO4调节pH至4.5左右,加入一定量的FeSO4和H2O2,为使其充分混合,将锥形瓶放置在磁力搅拌器上,整个反应系统暗箱内进行,暗箱内置30 W紫外杀菌灯1盏,波长254 nm,锥形瓶与光源距离为10 cm(光强为860 µw/cm),开启紫外灯引发反应,反应时间120 min。反应结束关闭紫外灯,投加一定量的NaOH调节pH至10以上,关闭磁力搅拌器,静置2 h取上清液测量数据。采用单因素实验法研究H2O2浓度(c=30%,100 ~2 000 mg/L)、Fe2+浓度(10~100 mg/L)和反应时间(5~120 min)等因素对模拟废水COD、DCF和NH4+-N去除率的影响以及优化高级氧化条件。
-
采用国家规定的标准方法进行测定[14]。COD:GB 11914—89水质化学需氧量的测定-重铬酸盐法采用重铬酸钾法;NH4+-N:GB7479—87水质氨氮的测定-纳氏试剂分光光度法。
-
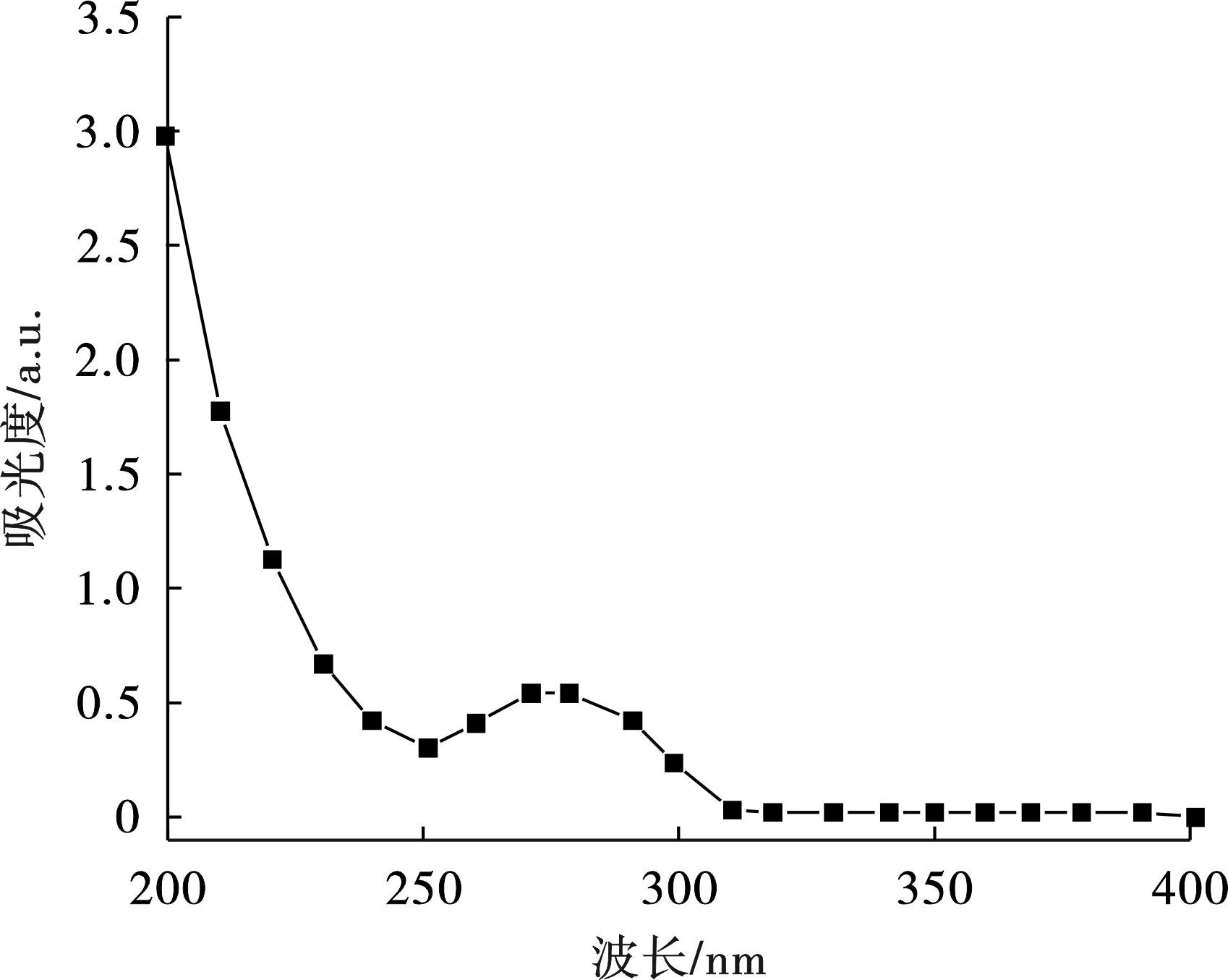
用紫外分光光度法测定DCF。首先对DCF溶液进行全波长扫描,确定DCF的最大吸收波长。DCF在200~400 nm的全波长UV-Vis扫描曲线,见图1。
确定DCF最大吸收波长为275 nm,测定DCF浓度与吸光度之间的标准曲线,定量测量DCF含量,DCF去除率计算,见式(2):
式中:η为DCF的去除率,%;c0为DCF样品处理后的剩余浓度,mg/L;ct为DCF的初始溶液浓度,mg/L。
-
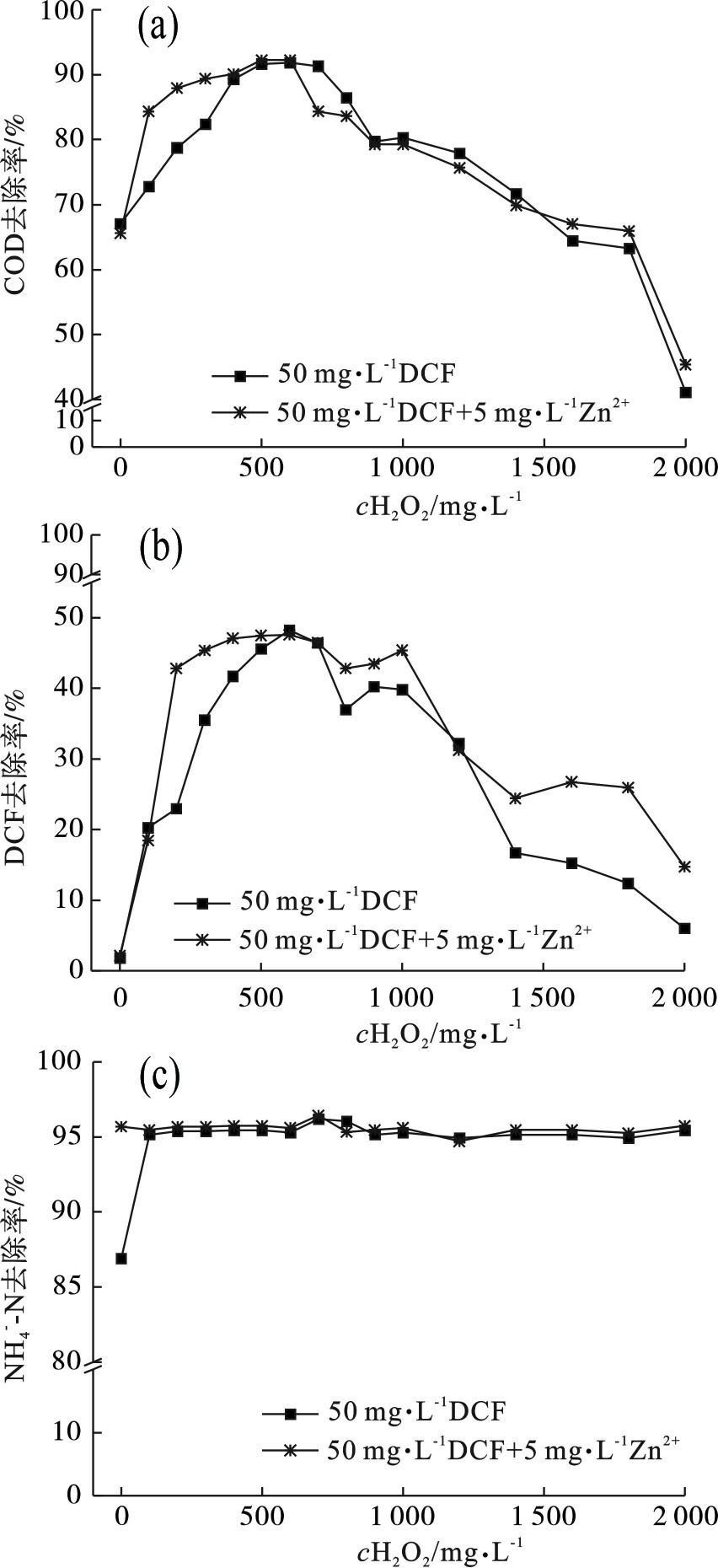
在UV/Fenton高级氧化反应中由H2O2在Fe2+的催化作用下产生的·OH是影响反应的重要因素之一,·OH可以将有机化合物氧化成易于生物降解的中间产物,因此H2O2的浓度直接影响整个反应体系的去除效果。UV/Fenton高级氧化反应选择实验条件为:光照时间为120 min,Fe2+投加量为45 mg/L,pH为4.5,考察不同浓度H2O2对50 mg/L DCF和50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+生化出水高级氧化后的各项指标的影响,见图2。
图2(a)和图2(b)可知,不同H2O2投加量对这两组(50 mg/L DCF和50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+)生化出水COD去除率和DCF去除率的影响大致相似,Zn2+的存在并不影响高级氧化各项指标。当在体系中添加较低剂量的H2O2,COD和DCF的去除率均随体系中H2O2剂量的添加而增大,当H2O2投加量增大到600 mg/L时,两组的COD和DCF的去除效果最好,去除率均达到大值,50 mg/L DCF组COD和DCF的去除率分别达到91.8%和48.2%,50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+组COD和DCF的去除率分别达到92.2%和47.8%,此后继续增大H2O2投加量,两组的COD和DCF的去除率反而呈递减的趋势。在高级氧化反应中,并非H2O2投加量越多越好,过高的H2O2投加量会影响COD和DCF的去除率。产生此现象的缘由可能是因为投加过量的H2O2会使单位时间内的•OH与其他自由基的产量增加,加剧了自由基之间的副反应,并且•OH也会与H2O2反应成H2O2反应会产生过氧化羟基自由基(HO2•),据报道,生成的HO2•活性比•OH低[15]见式(3)和(4)。另外,过量的H2O2会使Fe2+氧化成Fe3+,Fe3+与H2O2反应会产生HO2•会继续消耗•OH见式(5~7)。有学者也发现了类似的结果,LEE et al[16]发现了Fenton对牲畜废水中COD的去除率随着H2O2用量的增加先增加后下降,ACHILLEOS et al[17]发现H2O2与DCF水平之比影响DCF分解,高水平的H2O2降低了DCF降解速率。同时,COD的去除效果主要取决于DCF和乙酸盐的去除效果,见式(8)和(9)。这可能也是COD去除率的变化与DCF去除率的趋势相似的原因,实验结果表明在UV/Fenton工艺中增加H2O2用量时,DCF的去除是COD去除的主要贡献者。图2(c)可知,在UV/Fenton高级氧化实验中H2O2投加量对
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率没有产生明显影响。出现此现象是由于进入高级氧化反应中的生化出水${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率达到95%以上,反应器内的${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N值过低,难以与•OH产生有效的反应。因此,本实验中H2O2的最佳投加量为600 mg/L。过多的H2O2则浪费药剂,产生不必要的成本费用。 -
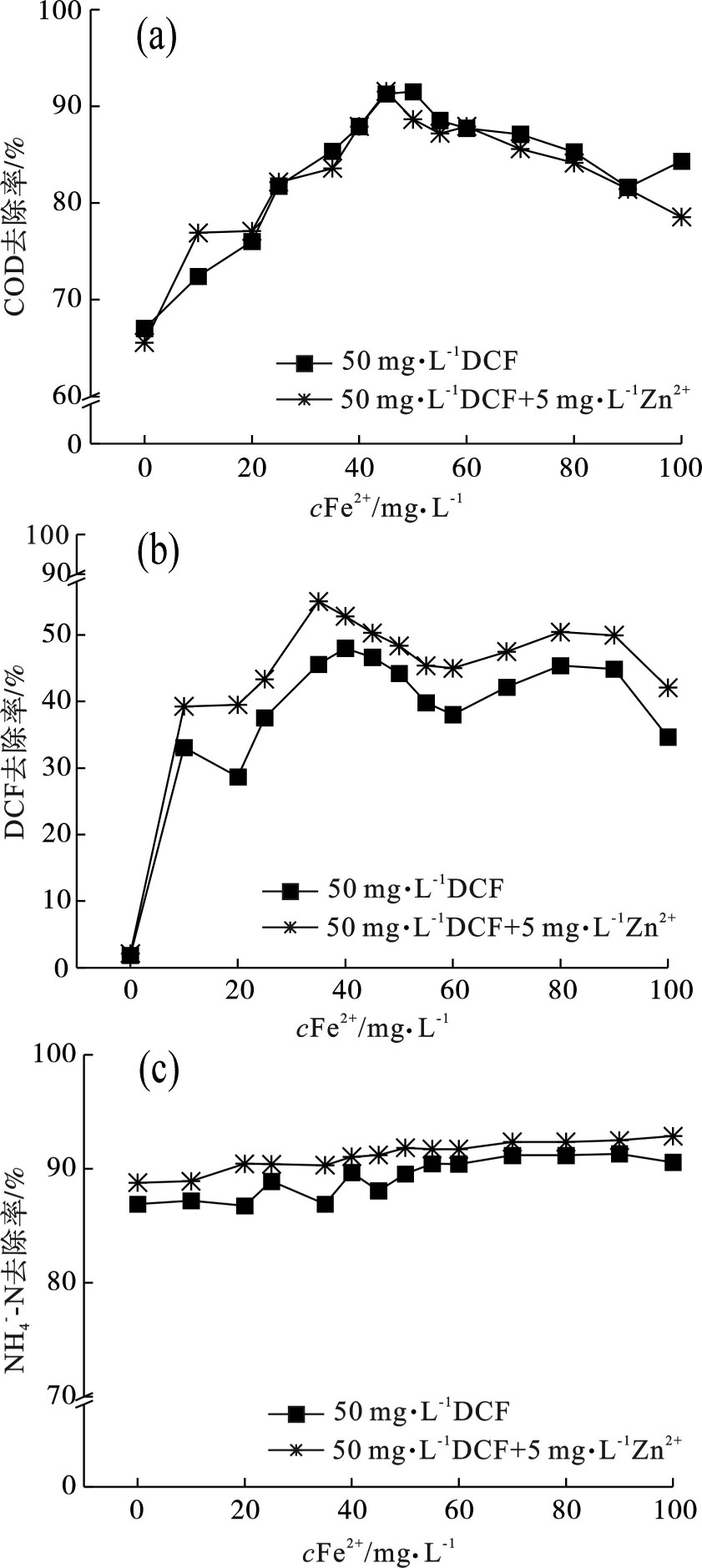
在UV/Fenton高级氧化反应过程中,Fe2+通常被认为在芬顿反应中起催化作用,因为它们可以导致H2O2产生的•OH。为光照时间为120 min,H2O2投加量为600 mg/L,pH为4.5实验条件时,考察不同Fe2+投加量对50 mg/L DCF和50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+生化出水各项指标的影响,见图3。
图3(a)和图3(c)可知,生化反应出水进入高级氧化反应体系,50 mg/L DCF组COD去除率和NH4+-N去除率的变化趋势同50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+组相似,50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+组的DCF去除率略高于50 mg/L DCF组,但总体变化趋势相同,说明了5 mg/L Zn2+的添加对高级氧化反应体系影响较小。图3(a)可知,当在体系中添加较低剂量的Fe2+,COD去除率均随体系中Fe2+剂量的添加而增大,当Fe2+投加量增大到45 mg/L时,两组对COD的去除效果最好,去除率均达到最大值,两组的组COD去除率达到92.0%左右。这是由于在Fenton过程中,Fe2+可以被H2O2或•OH氧化为Fe3+,见式(5)和(10),并且Fe3+可以在UV辐射下催化乙酸盐矿化的光反应,见式(9)。这些结果表明,在UV/Fenton工艺中,Fe2+浓度的增加有利于Fe3+和乙酸盐的反应从而提高乙酸盐的去除率,这也导致了COD去除率随着Fe2+水平的增加而增加。随后当在体系中不断添加过量的Fe2+时,则COD的去除率呈降低的趋势,这可能是由于适量的Fe2+能够促进·OH的产生,Fe2+与H2O2的反应速度很快,而过量的Fe2+会与产生了的•OH发生反应,见式(10)生成的过量Fe3+会形成难发生水解反应的配位化合物,性质稳定,从而减小•OH的利用效率。
图3(b)中DCF去除率趋势是先增加后波动减少,减少的幅度较小,其中50 mg/L DCF组中DCF去除率在40 mg/L到达最大值48.0%,50 mg/L DCF+ 5 mg/L Zn2+组DCF去除率在35 mg/L到达最大值52.8%。这可能是因为Fe2+与H2O2反应形成具有高氧化电位的•OH,见式(5),而•OH可能会进一步与DCF的进一步反应,见式(8)。P´EREZ-ESTRADA et al[18]发现•OH可以攻击DCF的芳香环结构,导致DCF降解为单羟基衍生物。之后随着Fe2+浓度逐渐增加DCF去除率逐渐下降,可能是因为Fe2+浓度的增加增强了其与DCF对•OH的竞争见式(8)和(10),进而减少了•OH与DCF的氧化反应。同时•OH也可能会与H2O2反应形成HO2•见式(4),HO2•可能转化为超氧自由基(O2−• )见式(11)和单线态氧(1O2)见式(12)和(13)。与•OH类似,O2−•和1O2也是光芬顿过程中的关键氧化物种,可直接与多种污染物分子反应。然而,1O2和O2−•得寿命都很短,这使得1O2和O2−•的产量多少依赖于催化剂。此外,Fe2+的增加会加剧H2O2和•OH的消耗,见式(5)和(10),这也可能不利于通过H2O2和•OH的反应形成和1O2。这可能是过量Fe2+不利于DCF去除的原因之一。与此同时,Fe2+过高也增加了溶液的浊度,降低紫外线的利用效率[19]。与先前的研究结果一致,ORAL et al[20]和WANG et al[21]研究发现了相似的结果,实验结果显示过量的Fe2+对Fenton工艺中DCF和CDO的去除有不利影响。图3(c)表示的
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率是随着Fe2+投加量的增加而有略微的增长,增长幅度很小,出现此现象可能是由于进水中的${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N值过小和${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N仅被很小一部高级氧化。综合分析COD和DCF的去除率可以得出当Fe2+的最佳投加量为45 mg/L时实验效果较佳,投加过多剂量的Fe2+会影响出水水质,大大增加了污水处理厂的处理成本。 -
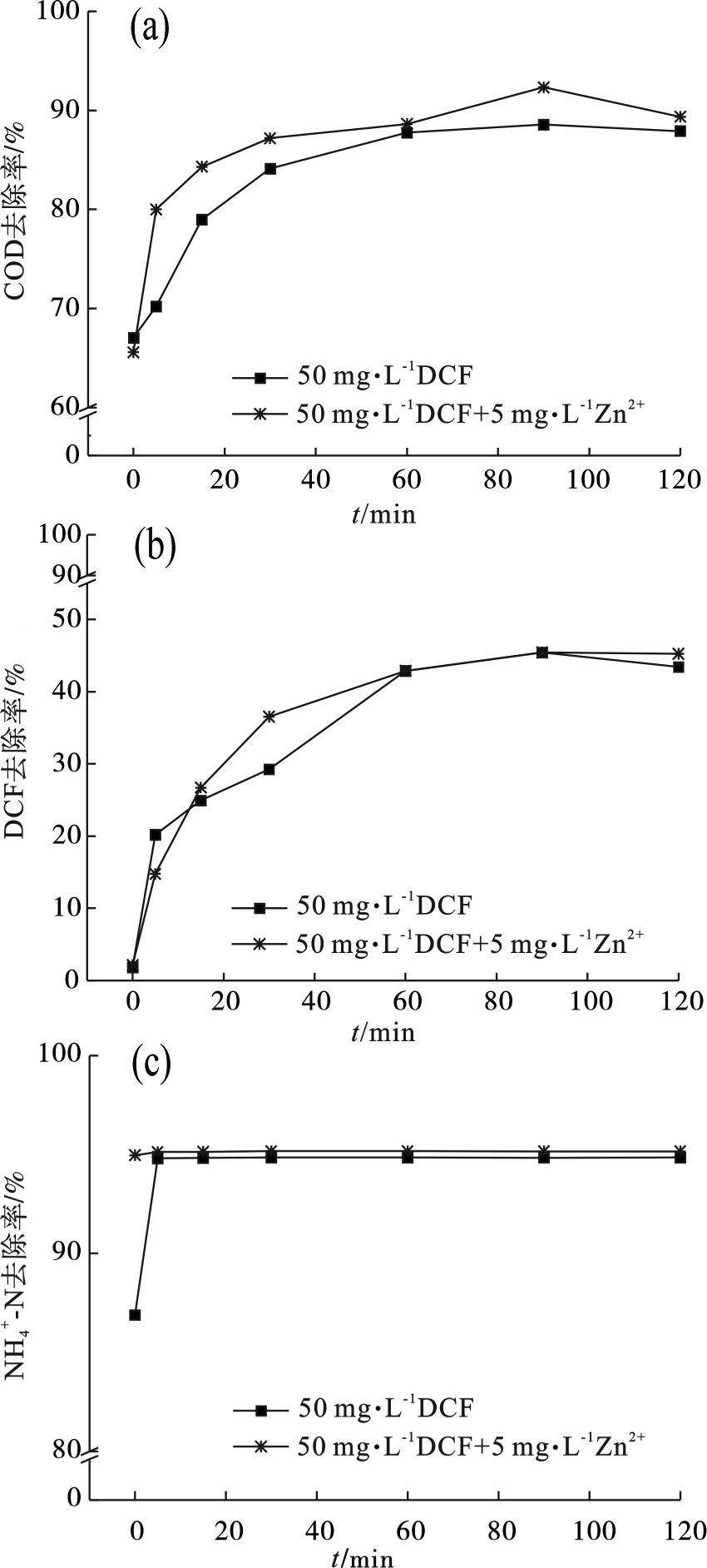
反应时间也是影响UV/Fenton高级氧化反应的一大因素,实验条件设置为H2O2投加量为600 mg/L,Fe2+投加量为45 mg/L,pH为4.5,考察不同时间因素对50 mg/L DCF和50 mg/L DCF+5 mg/L Zn2+生化出水各项指标的影响,见图4。
图4(a)和(b)可知,当高级氧化反应时间低于60 min时,COD和DCF的去除率随着反应时间的增加而增大,增速较大,在60和90 min时间段,去除率有所增加但增速减缓,反应时间90 min之后去除率稳定。这种现象是由于反应动力学上反应速率的降低缘故,前期反应速度快主要是由Fe2+催化完成的,高级氧化反应速度很快,COD和DCF的去除与反应时间成正比,均随着反应时间的增加而增大,反应会不断消耗Fe2+。当体系中Fe2+浓度过低时,Fenton体系会转换为由Fe3+催化的Fenton反应[22-23]。其次,Fenton氧化反应在Fe2 +的催化下产生大量的·OH,对目标物质进行快速降解。当反应达到一定程度后,·OH浓度下降,反应主要对象为Fe3+,降解反应变慢[24]。图4(c)表示的
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率则在10 min趋于稳定,出现此现象可能是由于${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N已在SBR生物处理阶段得到明显的去除,${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N仅被很小一部高级氧化。因此,为保证反应的充分进行,最佳反应时间应设置为90 min。 -
文中采用UV/Fenton高级氧化技术对生物处理后的含DCF和Zn2+废水进行深度处理,并采用单因素实验法分析H2O2浓度、Fe2+浓度和反应时间对UV/Fenton工艺中COD、DCF和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除率的影响,确定最佳工艺参数,为深度处理含DCF和Zn2+废水提供创新方法,结果如下。(1)H2O2的最佳投加量为600 mg/L,UV/Fenton处理工艺对COD、DCF和NH4+-N的去除效果最佳。
(2)Fe2+的最佳投加量为45 mg/L,UV/Fenton处理工艺对COD、DCF和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的去除效果最佳。(3)最佳反应时间应设置为90 min,UV/Fenton处理工艺对COD、DCF和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的去除效果最佳。
UV/Fenton法深度处理含双氯芬酸和锌废水的工艺优化
Optimization of UV/Fenton process for advanced treatment of wastewater containing diclofenac and Zn2+
-
摘要: 为研究含药物和重金属复合废水的处理方法,采用UV/Fenton工艺对经过生物处理后的含双氯芬酸(DCF)和Zn2+废水进行处理,通过单因素实验法分析了H2O2浓度、Fe2+浓度和反应时间对废水中COD、DCF和
${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N去除效果的影响。结果表明,随着H2O2浓度和Fe2+浓度投加量的升高,COD和DCF的去除率呈先上升后下降的趋势,${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N的去除率则趋于稳定。随着反应时间的增加,COD、DCF和${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N除率均为先上升后趋于平衡。结合成本和效率考虑,得出最佳处理条件为:H2O2的最佳投加量为600 mg/L,Fe2+的最佳投加量为45 mg/L,最佳反应时间应设置为90 min。Abstract: In order to study the treatment method of composite wastewater containing drugs and heavy metals, the wastewater containing DCF and Zn2+ after biological treatment was treated by UV/Fenton process. The effects of H2O2 concentration, Fe2+ concentration and reaction time on the removal of COD, DCF and${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N in the wastewater were analyzed by a single factor experiment method. The results showed that with the increase of H2O2 concentration and Fe2+ concentration, the removal rates of COD and DCF increased firstly and then decreased, while the removal rate of${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N tended to be stable. With the increase of reaction time, the removal rates of COD, DCF and${\rm{NH}}_4^ + $ -N increased firstly and then tended to its equilibrium. Considering the cost and efficiency, the optimal treatment conditions were obtained as follows: the optimal dosage of H2O2 was 600 mg/L, the optimal dosage of Fe2+ was 45 mg/L, and the optimal reaction time was 90 min.-
Key words:
- UV/Fenton /
- DCF /
- Zn2+ /
- H2O2 concentration /
- Fe2+ concentration
-

-
表 1 人工配置的模拟废水
Table 1. Artificially configured simulated wastewater
药品名称 质量浓度/mg·L−1 无水乙酸钠 573.00 氯化铵 152.00 磷酸二氢钾 44.00 双氯芬酸钠 69.83 七水硫酸锌 21.98 -
[1] NGUYEN L N, NGHIEM L D, PRAMANIK B K, et al. Cometabolic biotransformation and impacts of the anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac on activated sludge microbial communities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 657: 739 − 745. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.094 [2] YAN J, ZHANG X, LIN W, et al. Adsorption behavior of diclofenac-containing wastewater on three kinds of sewage sludge[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2019, 80(4): 717 − 726. [3] VIENO N, SILLANPÄÄ M. Fate of diclofenac in municipal wastewater treatment plant-A review[J]. Environment International, 2014, 69: 28 − 39. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.021 [4] JIANG C, GENG J, HU H, et al. Impact of selected non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals on microbial community assembly and activity in sequencing batch reactors[J]. PLOS ONE, 2017, 12(6): 0179236. [5] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 中华人民共和国国家统计局, 中华人民共和国农业部. 《第一次全国污染源调查公报》[M]. 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 北京, 2010. [6] WANG Y, WANG Z, YANG H, et al. Acute impacts of mixed heavy metals and diclofenac on sludge activity and enzyme activity involved with biological nitrogen removal[J]. Environmental Science Water Research & Technology, 2021, 7: 1852 − 1860. [7] SATHISHKUMAR P, MEENA P A A, PALANINAMI T, et al. Occurrence, interactive effects and ecological risk of diclofenac in environmental compartments and biota - a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 698: 134057. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134057 [8] XIONG T, YUAN X, WANG H, et al. Highly efficient removal of diclofenac sodium from medical wastewater by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide-poly(m-phenylenediamine) composite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 83 − 91. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.069 [9] 魏彩霞, 陈李玉, 李昕禹, 等. Fenton-SBR工艺处理盐酸溴己新生产废水运行研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(12): 89 − 92. doi: 10.11894/iwt.2018-0986 [10] AZIZI A, MOGHADDAM M R A, MAKNOON R, et al. Comparison of three combined sequencing batch reactor followed by enhanced Fenton process for an azo dye degradation: Bio-decolorization kinetics study[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 343 − 350. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.044 [11] PUNZI M, ANBALAGAN A, BÖRNER R A, et al. Degradation of a textile azo dye using biological treatment followed by photo-Fenton oxidation: Evaluation of toxicity and microbial community structure[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 290 − 299. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.042 [12] NOUSHEEN R, BATOOL A, REHMAN M, et al. Fenton-biological coupled biochemical oxidation of mixed wastewater for color and COD reduction[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2014, 45(4): 1661 − 1665. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2013.12.008 [13] ZHANG D, WU X, WANG Y, et al. Landfill leachate treatment using the sequencing batch biofilm reactor method integrated with the electro-Fenton process[J]. Chemical Papers, 2014, 68(6): 782 − 787. [14] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 210-268. [15] ERTUGAY N, ACAE F N. Removal of COD and color from Direct Blue 71 azo dye wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation: Kinetic study[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 10: 1158 − S1163. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.02.009 [16] LEE H, SHODA M. Removal of COD and color from livestock wastewater by the Fenton method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(3): 1314 − 1319. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.097 [17] ACHILLEOS A, HAOESHI E, XEKOUKOULOTAKIS NP, et al. Factors affecting diclofenac decomposition in water by UV-A/TiO2 photocatalysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 161(1-2): 53 − 59. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.04.020 [18] P´EREZ-ESTRADA L, MALATO S, GERNJAK W, er al. Photo-Fenton degradation of diclofenac: identification of main intermediates and degradation pathway[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39: 8300 − 8360. [19] 虎华, 曹艳艳, 王珍珍, 等. Fenton法降解1, 5-萘二磺酸废水及作用机制研究[J]. 化学研究, 2020, 31: 12 − 517. [20] ORAL O, KANTAR C. Diclofenac removal by pyrite-Fenton process: Performance in batch and fixed-bed continuous flow systems[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 664: 817 − 823. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.084 [21] WANG Z, YUAN S, DENG Z, et al. Evaluation of performance, extracellular polymeric substances, reactive oxygen species and lactate dehydrogenase in a combined ultraviolet/ Fenton-sequencing batch reactor at the co-selective pressure of divalent zinc and diclofenac[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8: 104479. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104479 [22] MALIK P K, SAHA S K. Oxidation of direct dyes with hydrogen peroxide using ferrous as catalyst[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2003, 31: 241 − 250. doi: 10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00200-9 [23] 王开峰, 彭娜, 李鑫, 等. UV/Fenton法处理EDTA-Cu-Ni络合废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10: 6524 − 6528. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201506160 [24] 柯水洲, 李雪瑶, 莫祺扬. Fenton法降解餐厨垃圾废水恶臭的试验研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21: 2233 − 2239. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2020.1262 -









 下载:
下载: