-
砷元素是一种有毒类金属,由于人类活动和地质活动,如采矿和冶金作业、木材处理、添加剂和化肥的应用、钢铁工业、煤炭生产、风化的基岩溶解反应、火山活动和含水层的过度开采等,砷可被引入环境,通过口腔接触、皮肤接触、呼吸等进入人体[1-3]。含砷尾渣大多是在有色金属冶炼过程中产生的,是一种通常储存在尾矿库中的有害固体废物[4-5]。砷硫化物矿物的氧化会导致砷离子的析出[6]。铜冶炼炉渣选矿后产生的矿浆自然脱水后形成尾渣这类固体矿物废料,在堆放过程中不仅会占用大量场地,其中矿物氧化释放出来的砷离子可通过离子交换进入土壤和地表水中,因此尾渣堆积带来的环境问题不容忽视[7]。
近年来国内外许多学者对尾矿渣中砷所产生的环境污染问题进行了多方面的研究。朱翔宇等[8]利用多种表征手段系统分析安徽铜陵杨山冲尾矿中砷的赋存形式,发现砷以As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的形式赋存于风化较弱的下部尾矿中,而强烈风化的表层尾矿中只存在As(Ⅴ);Kohfahl等[9]通过对芬兰Haveri Au铜矿尾矿在表生条件下淋滤过程的系统研究,探讨出尾矿中砷元素对周边生态环境的影响及潜在威胁,同时在环境治理及尾矿渣综合利用等方面取得一定研究成果;温其谦等[10]应用矿物学和化学分析方法发现半壁山金矿矿业周边的矿石、底泥、土壤中均存在含砷矿物——毒砂,且砷主要分布在道路两旁或村民聚集地的农田耕层土壤中。研究区有色金属冶炼中铜炉渣产出铜精矿后再回炉重炼产出尾渣,尾渣一天产量为3500—3600 t,呈粒砂状,黑灰色,有湿度,主要采用室内堆放,通常外售参与水泥矿浆和混凝土的制备。
为研究含砷尾渣对周围环境带来的潜在危害性,本文以安徽某有色金属冶炼厂中冶炼炉渣选矿后排放的尾渣矿浆为研究对象,应用SEM、XRF、XRD和XPS等表征手段相结合的方法,从该尾渣元素组成研究入手,通过形态提取深入了解尾渣中砷的精细化学结构及赋存形态,进而为后续尾渣中砷的风险评价及资源化利用提供理论依据。
全文HTML
-
研究区位于安徽省中南部、长江下游,北接合肥,南连池州,介于北纬30°45′—31°09′、东经117°35′—118°09′之间,是长江中下游平原与皖南山区的交接地带,以沿江丘陵为主要地貌,主要由志留系、泥盆系、石炭系、二叠系和三叠系灰岩、页岩和砂岩组成[11-13]。本次研究的含砷尾渣主要来源于安徽省某有色金属冶炼厂冶铜过程,整个厂区内渣选区布置在熔炼区南侧,主导风向的下风向,以专用运渣通道相连,渣缓冷区周边设置30—40 m宽防护隔离带,主要有炉渣缓冷场、渣堆场,渣选场布置在堆场东南侧,其中包括尾矿库等。
-
本次采样在冶炼尾渣库内选取几堆作为采样点,在尾渣垂直剖面处以0、1.5、3 m为标准共取8个样,并标记为W1—W8,为避免水分蒸发及污染,迅速放于聚乙烯塑料中袋中密封保存,以备后用。
-
pH、Eh及EC的测定:按水-渣比2∶1加入烧杯中,用磁力搅拌器搅拌1 min,静置1 h,取上清液测定其pH、Eh和EC[14]。pH、Eh及EC分别由pH计(型号PHS-3E)、电导率仪(型号DDS-11A)测定。
尾渣中As的结构分析:采用XRF(日本岛津XRF-1800)测定总混合尾渣样品主要元素含量。采用XRD(日本马克公司MXPAHF)测定主矿物及含砷矿物物相组分。通过SEM-EDS(ZEISS GeminiSEM500)观察尾渣表面微观形貌及As的分布。采用XPS(Thermo ESCALAB 250)测定As存在价态,并使用XPS PEAK41曲线拟合程序对所得光谱进行拟合[15]。
尾渣中As含量测定:总砷含量通过稀释王水消解、电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱仪(ICP-AES)测定[16]。另取样品采用Tessier提取法测定各形态As的含量。
-
采用铜精矿标准样品(ZBK338B)保证分析质量,测定结果在允许误差范围内(±5%)。采用平行样控制样品测试的精密度,随机选取一个样品进行3次平行提取实验,相对偏差小于5%,在允许误差范围内,每10个样品取一组标样和一组空白样。数据分析采用Excel、Origin、SPSS等方法。
1.1. 研究区概况
1.2. 采样与测试
1.2.1. 样品采集与预处理
1.2.2. 样品测试
1.3. 质量控制与数据处理
-
表1显示样品的pH、氧化还原电位、电导率和含水率。从表1可知,尾渣pH值介于7.97—8.28,均值为8.11,属于碱性环境,这是因为尾渣内含硫量少,同时也存在碱性元素如K、Na、Mg等。在不同高度处pH变化不大,这与堆放时间间隔较短有关。氧化还原电位为负值,表现为还原性。含水率小于1%,研究表明尾渣是有色金属在冶炼过程中冶炼炉渣选矿后排放的尾渣矿浆,是经自然脱水后形成的固体矿物废料,这是造成含水率低的主要原因。针对该种碱性尾渣中砷污染物的修复,化学修复法和土壤淋洗修复法较为合理,而电动修复法只能在酸性条件下进行,植物修复法对环境条件要求苛刻[17-18]。
表2 XRF结果表明,尾渣中所含元素种类较多较杂,主要元素Fe (51.32%),O (19.4%),Si (18.08%),还含有K、Na、Mg等碱性元素含量 (%wt)分别为1.44%、0.63%、0.98% ,进一步验证了pH分析结果。所测尾渣样品中As和S含量较低,为0.17%,结合表1发现,消解所得TAs含量最高1688 mg·kg−1,最低1131 mg·kg−1,含量范围为0.11%—0.17%。同时尾渣经过对冶炼炉渣的磨碎、浮选、脱水等工艺后不存在大量的石膏或Ca、S成分。
-
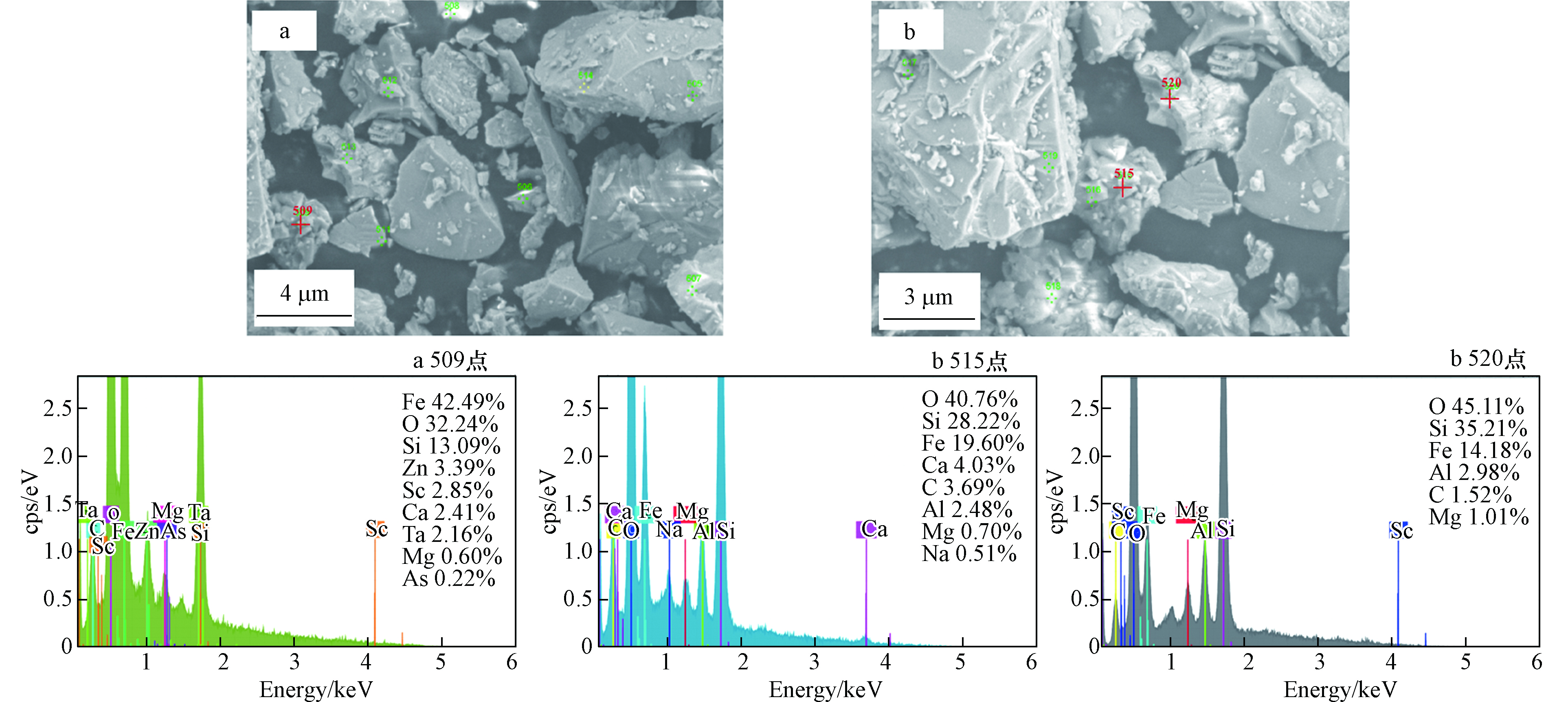
采用扫描电镜对其在不同放大倍数下的形貌进行分析,由扫描电镜图(图1)可看出,尾渣表面呈现一种不规则、大小颗粒不均匀分散的状态,空间分布间距较大,其粒径大小也不同,表面凹凸不平,高倍数下观察到颗粒表面呈侵蚀态.这是由于尾渣经熔炼炉渣选矿过程中的磨碎、浮选、脱水等工艺后,表面被破坏,小颗粒簇拥堆积吸附在大颗粒上,以层状、球状的包裹体形式存在,不规则的表面形貌说明该含砷尾渣形貌结构复杂。但仅依据扫描电镜图无法判断出砷分布的状态,需结合能谱图进一步分析。一般来说铜冶炼过程中铜精矿、熔炼烟尘及熔炼炉渣中As、Mg元素会表现高度的相关性[19],同时XRF结果发现尾渣中含0.98%Mg,根据图1中各元素面分布图发现并未检测到Mg元素,XRD中也未发现砷酸镁类矿物,这是因为As和Mg经炉渣选矿过程后含量减少,砷酸镁在高温下经失去稳定性,该处砷化合物不以砷酸镁的形式存在。由面扫描图发现O和Si有几乎重合的元素亮点,推测尾渣中存在SiO2,As元素亮点与O、Si、K、Fe、Al有重叠。
结合能谱图进行随机点扫描(图2),结果发现选取的几点中均是Fe含量最高,在509点处Fe含量为42.49%,其次是O为32.24%,在该处还发现含有部分As元素,占总量的0.22%,表明此处含有砷化物质。以该处球状体为中心,放大至8107倍数继续进行点扫描(B),可以发现该处周围均是O元素含量最高,其次为Si,在515点处O含量为40.67%,520点处O含量45.11%,尾渣中As与O共生的可能性极大,且砷化物质的粒度较小,大约在几微米粒度范围。
由表3可知,尾渣中As含量与其pH呈负相关,与Eh呈正相关关系,表明pH、Eh是影响As释放的因素之一。赵永红等[20]通过静态释放实验发现pH和温度的升高都会提高As的释放量。Eh影响吸附-解吸的平衡分配模式,还原条件下As3+的活性比As5+更高,更易于迁移[21]。表3显示As与其他重金属如Zn、Fe、Cu呈负相关性,与Al呈弱正相关,说明尾渣中主量元素含量对As含量的影响不大。一般来说,自然界中数百种含砷矿物通常以硫化物的形式存在,易与Cu、Pb以及其他金属形成合金[22],但该尾渣中As与S的相关性基本为零,SEM-EDS能谱图中As分布区域并未扫描到S的存在,结合XRD结果显示存在少量As的硫化物,可能是硫化砷在选矿浮选过程中包裹在硫化铜矿物内部进入尾渣中,造成硫化物含量低于EDS能谱检测限[23]。
-
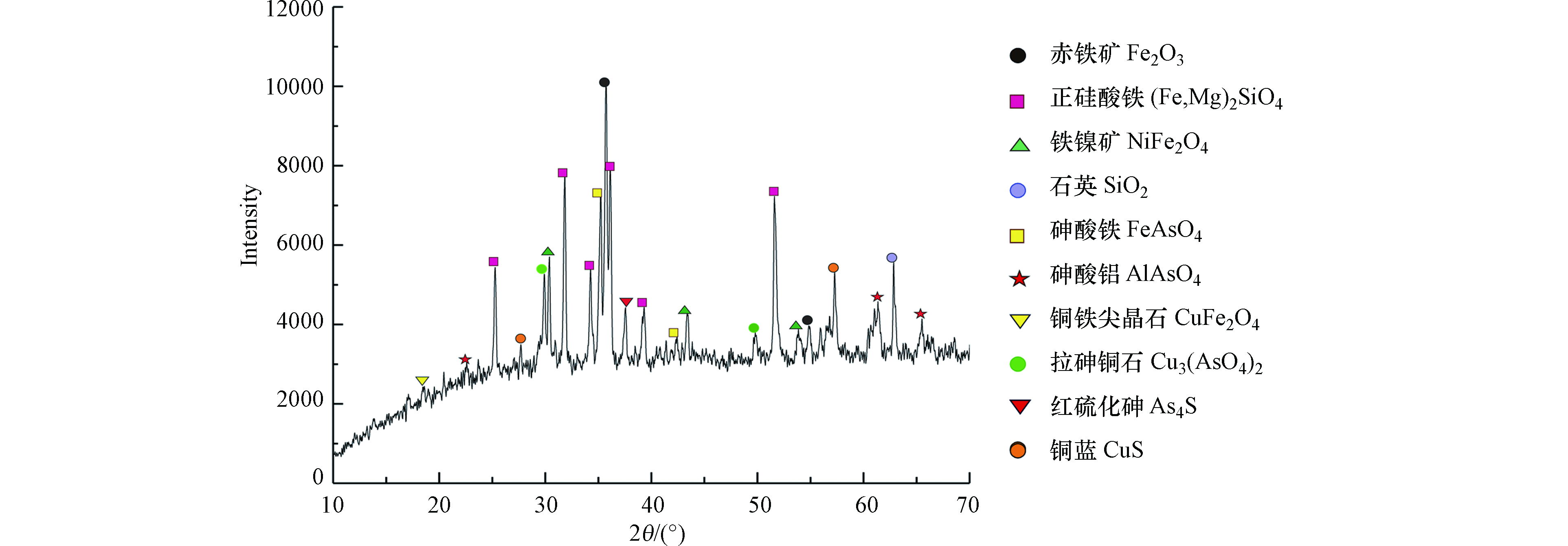
诸多学者的研究表明,尾渣中As有毒砂、含砷黄铁矿、砷酸盐及砷与铁形成的氧化物或氢氧化物等多种形态[24]。使用X射线衍射技术检测该尾渣中主要的矿物相,分析结果如图3所示,主要矿物为铁橄榄石(Fe, Mg)2SiO4和赤铁矿Fe2O3,和XRF结果中Fe含量最高相一致,含砷矿物主要为砷酸铁和拉砷铜石,伴有少量砷酸铝,属于经磨碎、浮选、脱水等工艺后形成的次生矿物相,并含有石英、铁镍矿、铜铁尖晶石、铜蓝等矿物。
-
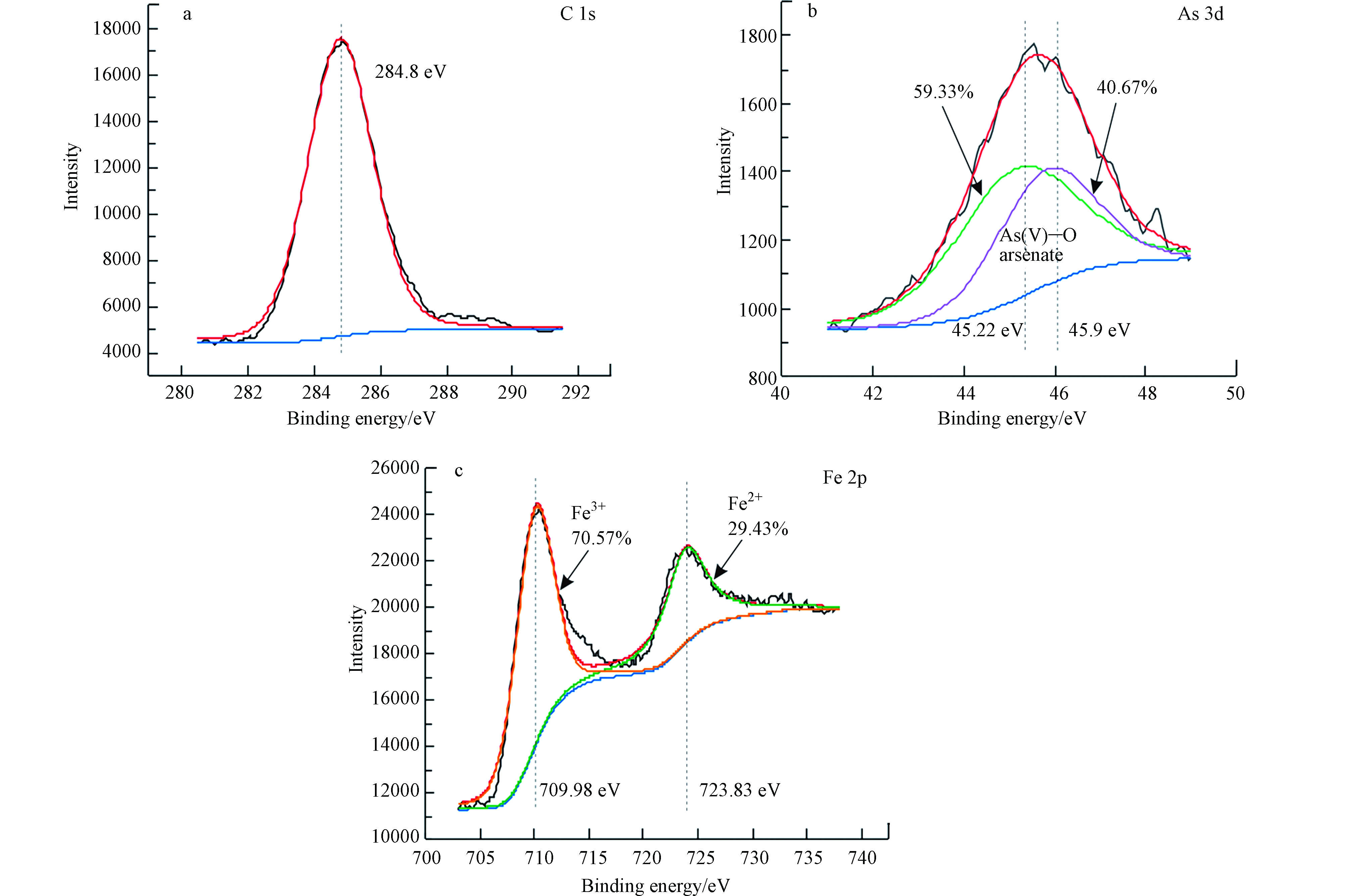
利用XPS进行光电子峰分析,使用曲线拟合程序(XPS PEAK41)对光谱进行拟合,采用标准背景,拟合参数为峰组分(电子结合能)的位置和峰面积,并得到284.8 eV处的C 1s谱峰,以此作为电荷补偿的内部标准校准所有测量到的光谱[25]。XPS属于表面分析型,由图4可知,尾渣中主要元素Fe以Fe2+和Fe3+形式存在,使用双峰拟合发现As 3d5/2对应的结合能为45.22 eV,占比59.33%,As 3d3/2对应的结合能为45.9 eV,占比40.67%,As以As(Ⅴ)形式与O结合形成金属砷酸盐[26],进一步验证了XRD结果中含铁盐和拉砷铜石等矿物,表明尾渣在熔炼炉渣选矿过程中表面被全部氧化。
-
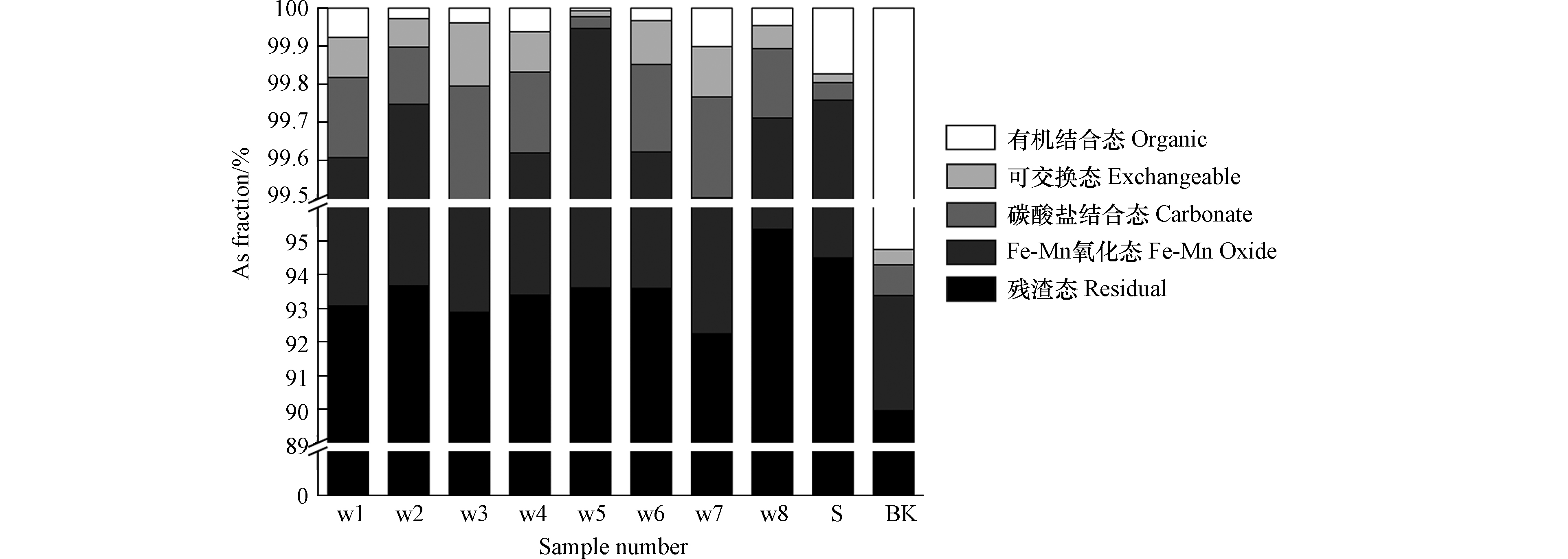
尾渣中As的赋存形态直接影响到其迁移转化及生物可利用性能力,不同的存在形态表现出不同的活泼性,进而影响As的毒性和生态风险[27]。尾渣中各形态As含量比如图5所示,结果表明As主要以残渣态存在,占90%—95%,其次为Fe-Mn氧化态占4%—7%;不同形态As含量大小依次为残渣态>Fe-Mn氧化态>碳酸盐结合态>可交换态>有机结合态。尾渣本就是经过冶炼过程中渣选矿磨碎、浮选、脱水等工艺处理后所产生的,这也是造成残渣态含量高的原因之一[28]。根据前人研究结果表明残渣态的As能稳定存在于尾矿、土壤以及沉积物中,短期内不会发生迁移转化,只有遇到极其恶劣的pH环境或存在螯合剂时才会部分进入到环境中,对生态环境造成威胁[29-30]。
2.1. 尾渣理化特征及元素组成分析
2.2. 尾渣形貌特征及砷共生元素
2.3. 含砷矿物及砷价态分析
2.3.1. 含砷矿物
2.3.2. 砷价态
2.4. 尾渣砷赋存形态
-
(1)尾渣表面呈现一种不规则、大小颗粒不均匀分散的状态,空间分布间距较大,其粒径大小也不同,表面凹凸不平,颗粒表面呈侵蚀态,小颗粒簇拥堆积吸附在大颗粒上,以层状、球状的包裹体形式存在。
(2)尾渣中所含元素较多,XRF和SEM-EDS分析结果证实了该尾渣中As的存在,S、As相关性低,As主要与O元素共生以As(Ⅴ)-O砷酸盐存在,且砷化物质的粒度范围大约在几微米。尾渣中含砷矿物为砷酸铁FeAsO4和拉砷铜石Cu3(AsO4)2,伴有少量砷酸铝和硫化砷。通过相关性分析可知,部分重金属之间存在明显的相关性,pH是影响As释放的重要因素之一。
(3)总砷含量在0.11%—0.17%之间,根据Tessier五步连续提取法可知,尾渣中As主要以残渣态为主,占90%—95%,Fe-Mn氧化态占4%—7%,不同形态As含量大小依次为残渣态>Fe-Mn氧化态>碳酸盐结合态>可交换态>有机结合态,从形态分析上有效态砷含量少,较稳定,不易进入环境中,但总砷含量高,对环境存在潜在威胁,需妥善处置。




 下载:
下载: