-
沉积物是水生态系统的重要组成部分,为水生动植物生长提供了场所[1],污染物进入水体后经过复杂的反应和转变最终沉淀于沉积物中。重金属在环境中不易降解,在水体中与悬浮颗粒共沉降于沉积物中,水环境改变时,沉积物中的重金属再次释放,造成二次污染[2-3]。孔明、罗燕等研究发现重金属在水体中积累一定的程度会对水生动植物产生严重危害,并通过食物链影响人体健康[4-6]。因此,测量重金属含量并对其污染特征进行研究和生态风险进行评价显得尤为重要[7]。表层沉积物能够蓄积大量的总磷和总氮,但当水环境改变时,二者会重新进入水体中,而水体中总氮、总磷浓度高是引起水体“水华”现象的重要因素[8-9]。
现阶段的研究对于沉积物中总磷和总氮的评价方法较多,主要包括有机氮评价方法、有机碳评价方法、有机指数法、综合污染指数评价方法等[8]。对于重金属的评价方法主要有生态风险指数法、地积累指数法、污染负荷指数和沉积物质量基准等[9-12]。而判断沉积物中重金属来源主要使用统计学分析方法,如相关分析、主成分分析和聚类分析统计等[13-14]。
洞庭湖位于湖南省东北部,长江中游荆江南岸(28°30′N—30°20′N、110°40′E—113°10′E),是我国第二大淡水湖[8],由于人类活动的影响,已经明显分化为东、西、南的3个湖区。近年来大量的学者针对洞庭湖营养盐或者重金属进行了相关研究[15-18],例如欧阳美凤等主要针对东洞庭湖及入湖口的重金属进行分析[19],王勤等针对洞庭湖湘江入湖段的重金属进行了研究[20]。张光贵等对洞庭湖近20年的氮磷进行分析[8],李芬芳等对洞庭湖及其入湖口的氮磷进行了分析[16],蔡佳等针对西洞庭湖的氮磷进行了研究[21]。但是针对洞庭湖湖体的重金属研究较少,将洞庭湖湖体的重金属和氮磷营养盐综合起来评价洞庭湖风险的研究也很少[19-23]。本研究通过对2018年洞庭湖整个湖体表层沉积物中TN、TP、Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Cd、Ni、Hg、As含量的测定,利用主成分分析TN、TP和重金属的分布特征,并借助营养盐综合污染指数、地积累指数法以及潜在生态风险指数法对沉积物中TN、TP和重金属生态风险进行评价。以期研究结果能够为洞庭湖水体污染分区、重点突出地进行管理提供依据。
-
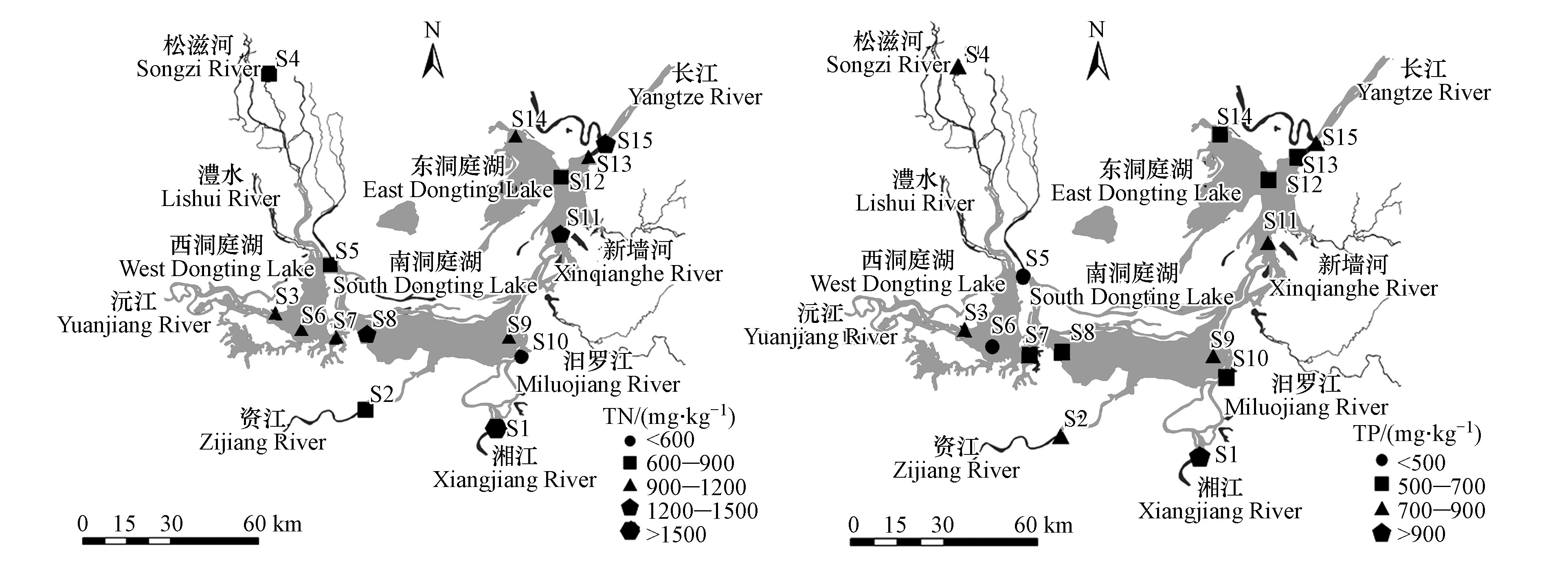
于2018年6月和9月在洞庭湖区选取15个采样点(图1),采样点包括东洞庭湖的鹿角、东洞庭湖、岳阳楼、大小西湖、洞庭湖出口,南洞庭湖的小河嘴、樟树港、万家嘴、万子湖、横岭湖、虞公庙,西洞庭湖的坡头、沙河口、南嘴、蒋家嘴。于平水期用彼得森采泥器采集底泥,采样深度约0—10 cm,每个采样点采集3个平行样现场混匀,装入封口袋。底泥样品在冷冻干燥机中烘干至恒重,研磨过100目筛,分装于密封袋中,备用。
-
沉积物中TN采用土壤质量全氮的测量凯氏法(HJ717—2014)、TP采用土壤总磷的测定碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法(HJ632—2011)。为保证分析结果的准确性,分析过程以国家一级标准物质GSS-2、GSS-8、GSS-11为质控标样,每个样品加做平行样,平行样分析误差<5%。
样品经HNO3-HClO4-HF消解后,Cd和Pb测定方法为土壤质量铅、镉的测定石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法(GB/T17141—1997),As和Hg的测定方法为土壤和沉积物汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定微波消解/原子荧光法(HJ680—2013),Cr的测定方法为土壤总铬的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法(HJ491—2009),Cu和Zn的测定方法为土壤质量铜、锌的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法(GB/T17138—1997),为保证分析结果的准确性,分析过程以国家一级标准物质GSS-25、GSS-28为质控标样,每个样品加做平行样,平行样分析误差<5%。实验数据采用SPSS25.0和Arcgis10.1进行分析。
-
评价湖泊沉积物是否受到氮污染的一个重要指标就是有机氮,其计算及标准如下:
式中,w(有机氮)为有机氮百分比,w(TN)为总氮百分比。当百分值低于0.033时,表明湖泊清洁,没有受到氮污染;当有机氮百分值在0.033到0.066之间表示湖泊较清洁;当有机氮百分值在0.066—0.133之间表示湖泊尚清洁;当有机氮百分值大于0.133则说明湖泊受到有机污染,氮污染较严重[24]。
本研究利用营养盐综合污染指数评价法(FF)评价洞庭湖沉积物中营养盐的污染程度,计算方法如下:
式中,S为单项评价指数或标准指数;C为评价因子实测值;Cs为评价因子的评价标准值;在本文中TN的Cs为1 000 mg·kg−1,TP的Cs为420 mg·kg−1;F为TN和TP污染指数平均值;Fmax为TN和TP的单项评价指数中最大者[13]。综合指数的大小与污染等级关系如表1所示。
重金属地积累指数法囊括了地球化学背景的影响、人为因素影响以及自然成岩因素的影响,集中体现沉积物中外源重金属的富积程度[17, 21, 25],其计算方法为:
其中,Igeo为地积累指数;C为重金属在沉积物中的测量浓度,mg·kg−1;B为重金属的地球化学背景值,本研究采用洞庭湖水系沉积物元素背景值作为参考值从而更加真实地反映其污染现状[17, 21];k=1.5,Igeo大小所反映的污染等级见表2.
为了考虑重金属的毒性在沉积物中的迁移转化规律、评价区域对重金属敏感性及重金属区域背景值的差异,综合反映沉积物中重金属的潜在生态影响,1980年时瑞典科学家Hakanson提出了潜在生态风险指数法[26],其计算方法如下:
式中,Er为单项重金属危害指数,RI为多项金属的综合潜在生态风险指数,Tr为重金属毒性响应系数,Ci为重金属的实测浓度值,mg·kg−1;Cn为重金属的评价参比值。本研究采用洞庭湖水系沉积物背景值作为参比更直接地评价洞庭湖沉积物中重金属的污染现状。Hg、Cd、As、Cu、Pb、Ni、Cr、Zn重金属毒性响应系数(Tr)分别为40、30、10、5、5、2、1[18, 27-29]。重金属单项潜在生态风险指数Er和综合潜在生态风险指数RI和潜在生态风险等级,如表3所示。
-
洞庭湖15个点位表层沉积物中TN含量分布如图2所示,经有机氮污染评价得出,洞庭湖流域表层沉积物有机氮污染Ⅳ级约占所有点位的20%,Ⅲ级污染点位约占所有点位的73.3%,这说明洞庭湖表层沉积物氮污染比较严重。洞庭湖TN的含量为576—1526 mg·kg−1,平均含量为1029 mg·kg−1,最大值出现在鹿角,最小值出现在虞公庙,最大值与最小值的比值为4.57。洞庭湖表层沉积物TN的含量总体表现为东洞庭湖(1146 mg·kg−1)>南洞庭湖(1040 mg·kg−1)>西洞庭湖(867 mg·kg−1)。
-
洞庭湖15个点位表层沉积物中TP含量分布如图2,洞庭湖TP的含量为482—982 mg·kg−1,平均含量为697 mg·kg−1,最大值出现在樟树港,最小值出现在万子湖,最大值与最小值的比值为2.83。总体表现为东洞庭湖(746 mg·kg−1)>南洞庭湖(710 mg·kg−1)>西洞庭湖(616 mg·kg−1)。
与2016年的研究结果[15]相比,2018年洞庭湖表层沉积物中TN含量升高8.77%,TP含量升高10.74%,表明近年来洞庭湖表层沉积物中的TN、TP内源负荷呈增加趋势,这与黄代中[30]等的研究结果一致。洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养盐的空间分布与其水文特征有关,东洞庭湖由于受藕池河沙淤积以及湘江洪道水流顶托影响,表层水体中营养盐容易沉积,所以表层沉积物中含量较高[21];而西洞庭湖离出湖口较远,受出湖口长江水流顶托的影响较小,营养物质不易沉淀,因而含量较低。其次,表层沉积物中的营养盐主要是来自水体中营养盐的沉积,有研究表明东洞庭湖水体中N、P营养盐含量高,原因主要是湘江流域、东洞庭湖周边城镇化程度较高,人类聚居活动频繁,土地利用率高导致周边水土流失、水产养殖带来的农药化肥、畜禽粪便以及人类生活的生活污水等对洞庭湖水环境污染的影响大。同时,磷元素对于泥土有较高的亲和力,而湘江、东洞庭湖区水体泥沙含量较高,这为表层沉积物中磷元素的沉降创造了一定的条件[31]。
-
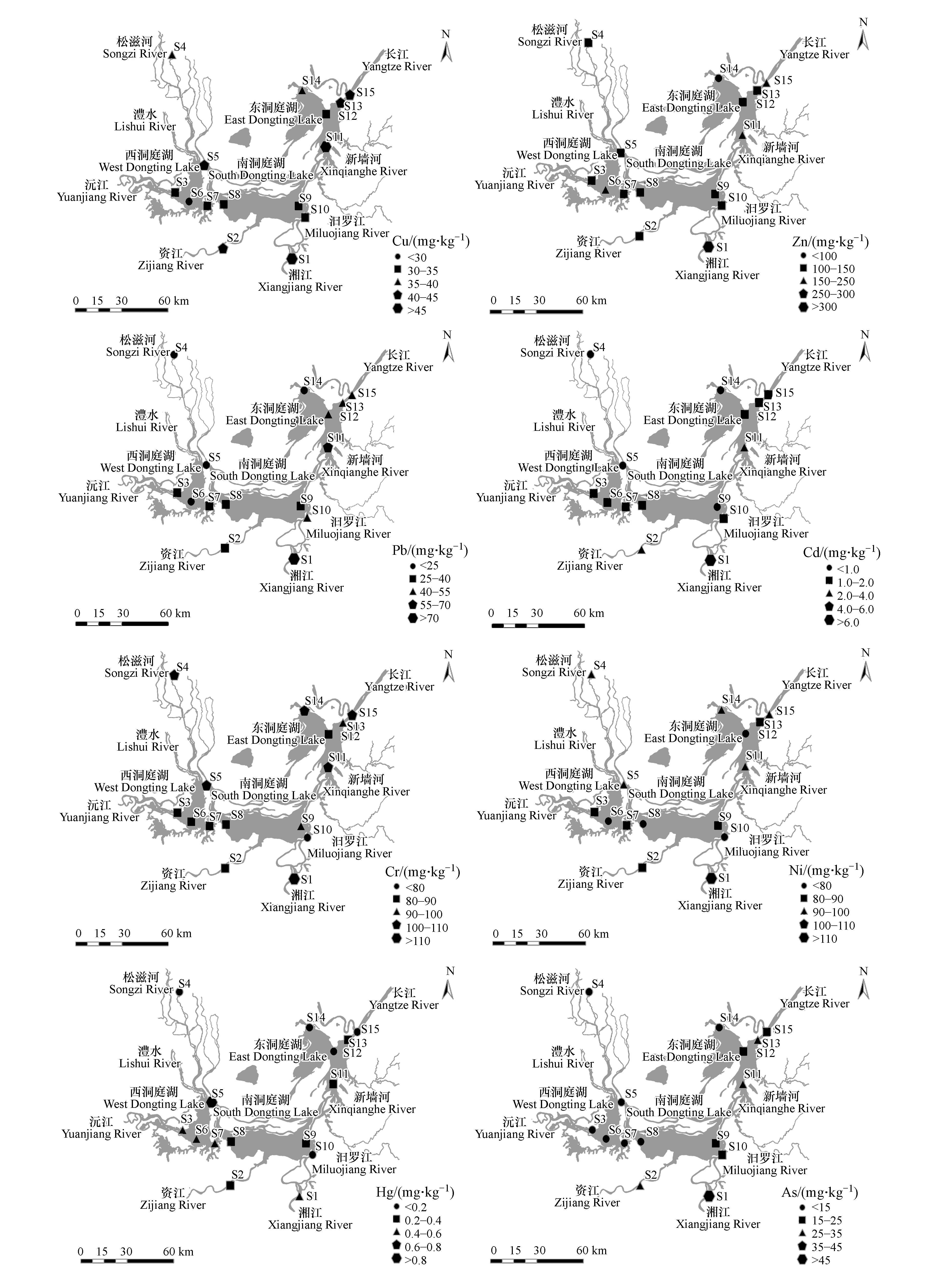
洞庭湖表层沉积物中8种重金属含量如表4所示,空间分布如图3所示。洞庭湖表层底泥8种重金属含量在0.08—378.5 mg.kg−1之间。8种重金属的变异系数在16%—117%之间,这表明不同重金属在空间分布上存在差异。其中,同一种金属在不同采样点的变异程度不同,其中Cd(1.05)的变异系数最大,Hg(0.64)、As(0.74)、Zn(0.46)、Pb(0.44)、Cu(0.21)、Ni(0.16)次之,Cr(0.12)的变异系数最小,表层沉积物在不同采样点位的含量差别大,可能是由于其不同的采样点位有不同的来源[24, 32]。
-
水体沉积物中污染物随着水流及沉积物环境的变化会重新进入水体形成二次污染,对环境造成危害及潜在风险,表层沉积物中污染物质含量水平决定危害程度及风险大小[33-34]。目前国内尚无系统的针对湖泊沉积物中营养盐生态风险评价方法。本研究采用综合污染指数法[7, 16]评价表层沉积物 TN、TP 污染程度,由单项污染指数公式计算综合污染指数(FF)。根据王佩等评价标准[35],综洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养盐生态风险分级如表5所示。
经综合污染等级计算得出洞庭湖表层沉积物营养盐污染等级呈现东洞庭湖(1.63)>南洞庭湖(1.54)>西洞庭湖(1.33)。东洞庭湖、南洞庭湖营养盐生态风险属于中度污染,西洞庭湖营养盐生态风险为轻度污染,整个洞庭湖流域氮磷营养盐生态风险为中度污染。
-
重金属单项潜在生态风险指数法评价结果表明南洞庭湖的Cd、Hg的风险等级为严重,Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni、As的风险等级为低。西洞庭湖的Cd的风险等级为较重,Hg的风险等级为严重,Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni、As的风险等级为低。东洞庭湖的Cd、Hg的风险等级为较重,Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni、As的风险等级为低。说明Hg和Cd是洞庭湖表层沉积物主要风险贡献因子。洞庭湖表层沉积物RI分布如图4所示,洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属风险RI值为483,潜在重金属生态风险为重,潜在重金属生态风险等级空间分布为南洞庭湖(547)>西洞庭湖(589)>东洞庭湖(305)。结合单项潜在风险指数评价结果可以推测,南洞庭湖风险高的原因主要是由于Hg含量的高,西洞庭湖风险高的原因主要是由于Cd的含量高。南洞庭湖受沅江影响较大,而沅江流域的汞矿较多,如万山、铜仁等汞矿,导致沅江流域的Hg含量高[36],进而导致南洞庭湖区重金属表层沉积物中Hg的含量较高。而西洞庭湖区特别是坡头和蒋家嘴表层沉积物中Cd的含量较高,从而导致其重金属风险较高。
有研究表明综合地积累指数Itot(Itot为某采样点各重金属Igeo值之和)能够更好地分析沉积物中重金属的复合污染特征,评价各采样点的污染级别[22],所以本文在地累积指数Igeo的基础上引入综合地累积指数Itot来分析洞庭湖重金属污染特征。地积累指数Igeo评价结果表明南洞庭湖表层沉积物中的Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr、Ni为轻度污染,Hg和Cd为中度污染;As为清洁;东洞庭湖表层沉积物中Cu、Pb、Cr、Ni为轻度污染,Cd和Hg为偏重度污染,Zn、As为清洁;西洞庭湖表层沉积物中Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni为轻度污染,Hg为中度污染,Cd为偏重度污染,Pb、As为清洁。洞庭湖综合地累积指数Itot值为3.45,污染等级为4,属于重度污染,空间分布结果为南洞庭湖的Itot(4.76)>东洞庭湖的Itot(2.84)>西洞庭湖的Itot(2.27),南洞庭湖为重污染,污染级别为5,东洞庭湖与西洞庭湖都是中度污染,污染级别为3。
-
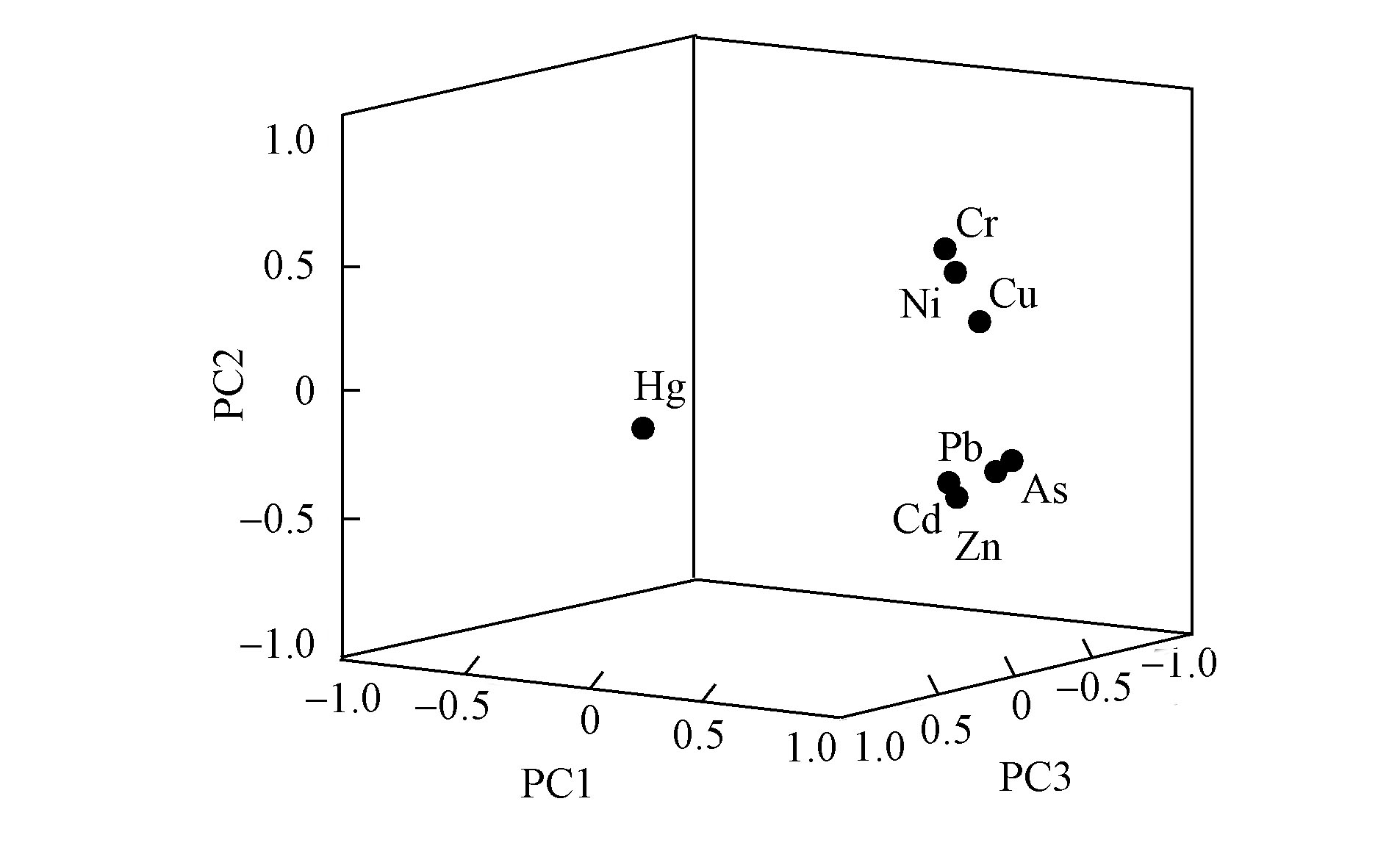
为了分辨洞庭湖沉积物中8种重金属的污染来源及相关性,本研究利用PCA分析得出因子荷载矩阵[24, 37]。洞庭湖表层沉积物重金属的主成分因子荷载图如图5,在8种重金属元素中,主成分1的贡献率为67.36%,特征因子表现在Zn、Pb、Cd和As上有较高的正荷载。主成分2的贡献率为14.83%,特征因子表现在Cu、Cr、Ni上有较高的正荷载。主成分3的贡献率为13.38%,特征因子表现在Hg上有较高的正荷载。
洞庭湖表层沉积物重金属Pearson相关分析结果如表6所示,结果表明Cu与Zn、Pb、Cd、Cr、Ni和As之间呈现极显著相关性(P<0.01),Cr和Ni之间呈现极显著的相关性(P<0.01),Ni与As之间存在显著相关性(P<0.05),Hg与其他元素的相关性都不高。这表明Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Cr、Ni、As具有相似的污染来源或产生了复合污染。而Hg的污染来源特征可能受自身的物理化学性质,沉积物中泥沙含量和有机质含量等因素的影响[24],且在沉积物中主要表现在南洞庭湖含量较高,这可能与湘江和资江是南洞庭湖主要的污染来源等因素有关[33]。
-
(1)现阶段洞庭湖表层沉积物中TN和TP污染属于中度污染,总体空间格局表现为东洞庭湖>南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。与2016年相比2018年洞庭湖表层沉积物中TN、TP呈现内源增加趋势,TN比2016年增加8.77%,TP比2016年增加10.74%。
(2)营养盐综合污染指数评价结果表明,洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养盐为中度污染,氮磷污染空间差异性较大,在空间上表现为东洞庭湖>南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。
(3)RI结果表明洞庭湖表层重金属生态潜在生态风险等级为重污染,其中南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>东洞庭湖。Er结果表明洞庭湖表层沉积物中Cd、Hg风险等级高,是造成洞庭湖流域水体沉积物生态风险的主要因素。
(4)洞庭湖表层重金属Itot值为3.45,污染级别为4,表明洞庭湖表层重金属污染程度为重污染,空间分布为南洞庭湖>东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。南洞庭湖为重污染,污染级别为5;东洞庭湖与西洞庭湖都是中度污染,污染级别为3。
(5)相关分析结果表明Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Cr、Ni、As具有相似的污染来源,来源分析结果Zn、Pb、Cd、As对于洞庭湖的重金属污染贡献较大。
洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养元素、重金属的污染特征与评价分析
Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake
-
摘要:
为了解近年来洞庭湖表层沉积物中氮、磷及重金属污染情况,对洞庭湖15个采样点表层沉积物中TN、TP和重金属(Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Ni、Cr、Hg、As)质量分数进行分析,并运用有机指数和综合营养法对TN、TP的污染程度进行评价,采用重金属潜在生态风险指数法、综合地积累指数法对重金属进行生态风险评价,利用主成分分析重金属的来源。结果表明,洞庭湖表层沉积物中w(TN)和w(TP)的范围分别介于576—1526 mg·kg−1,482—982 mg·kg−1之间。空间分布上,TN和TP总体均表现为东洞庭湖>南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属含量在0.08—378.5 mg·kg−1之间,Cu、Ni呈现东洞庭湖>南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖,Cd、Hg、Pb、As呈现南洞庭湖>东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖,Cr呈现东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>南洞庭湖,Zn呈现南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>东洞庭湖。洞庭湖表层沉积物中有机氮Ⅳ级污染点位约占所有点位的20%,有机氮Ⅲ级污染点位占比约为73.3%。营养盐综合污染指数等级为中度污染,空间分布整体呈现为东洞庭湖>南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属风险RI值为483,潜在重金属生态风险为重污染,潜在重金属生态风险等级空间整体呈现为南洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>东洞庭湖。地积累指数表明洞庭湖表层沉积物重金属总体呈现偏重污染,空间分布为南洞庭湖>东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖。研究表明,洞庭湖表层沉积物营养盐综合污染呈现中等污染,重金属污染呈现重污染状态,Cd、Hg两种重金属的风险最高,洞庭湖表层沉积物重金属生态风险主要是这两种重金属造成的。
Abstract:To study the pollution status of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals in surface sediment of Dongting Lake, the contents of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and heavy metals (including Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Ni, Cr, Hg and As) in sediment of 15 sample sites in Dongting Lake were analyzed. Comprehensive pollution index (FF)and organic index were selected to evaluate pollution grade of TN and TP. Potential ecological risk index (RI) and comprehensive geoaccumulation index (Itot) were employed to assess health risk of heavy metal pollution. The source of heavy metals was analyzed by Principal component analysis (PCA). The results indicated that the contents of TN and TP ranged from 576 mg·kg−1 to 1526 mg·kg−1 and 482 mg·kg−1 to 982 mg·kg−1, respectively. The spatial distributions of TN and TP presented similar patterns in the order of East Dongting Lake>South Dongting Lake>West Dongting Lake. The contents of heavy metals in sediments of Dongting Lake ranged from 0.08 mg·kg−1 to 378.5 mg·kg−1. Spatially, the contents of Cu and Ni ranked as an order: East Dongting Lake > South Dongting Lake >West Dongting Lake. The contents of Cd, Hg, Pb and As showed similar spatial trend, they all decreased in the order of South Dongting Lake > East Dongting Lake > West Dongting Lake. The content of Cr was ranked as an order as follow: East Dongting Lake > West Dongting Lake > South Dongting Lake. The content of Zn ranked as an order: South Dongting Lake > West Dongting Lake > East Dongting Lake. The results of organic index indicated that sampling sites evaluated as organic nitrogen Ⅳ level accounted for 20%, and sites of organic nitrogen Ⅲ level accounted for 73.3%. Comprehensive pollution index indicated moderate pollution, and the pollution level of spatial distribution ranked as an order: East Dongting Lake > South Dongting Lake>West Dongting Lake. The result of RI of Dongting Lake was 483, indicated that potential ecological risk level of Dongting Lake was heavy, and RI values decreased in the order of South Dongting Lake >west Dongting Lake>East Dongting Lake. The results of Itot indicated that contamination of heavy metals in sediments of Dongting Lake was serious, and Itot value decreased in the order of South Dongting Lake >East Dongting Lake>West Dongting Lake. The research showed that comprehensive nutrient pollution in surface sediment of Dongting Lake was moderate, and metals pollution in surface sediment of Dongting Lake was serious. Hg and Cd were the highest risk elements, and the ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake was mainly caused by these two kinds of heavy metals.
-
Key words:
- Dongting Lake /
- surface sediment /
- total nitrogen /
- total phosphorus /
- heavy metals /
- risk assessment
-

-
表 1 表层沉积物综合污染程度分级
Table 1. Classification of comprehensive pollution of surface sediments
污染程度Pollution Level 总氮单项指数STN 总磷单项指数STP 营养盐综合指数FF 清洁 STN<1.0 STP<0.5 FF<1.0 轻度污染 1.0<STN<1.5 0.5<STP<1.0 1.0<FF<1.5 中度污染 1.5<STN≤2.0 1.0<STP≤1.5 1.5<FF≤2.0 重度污染 STN>2.0 STP>1.5 FF>2.0 表 2 Igeo与重金属污染程度关系
Table 2. The relationship between Igeoand heavy metal pollution
Igeo ≤0 0—1 1—2 2—3 3—4 4—5 污染级数 0 1 2 3 4 5 程度 清洁 轻度 中度 偏重度 重度 严重 表 3 Er与RI的分级标准
Table 3. Individual induce and grades of Erand RI
Er RI 范围
Range生态风险水平
Ecological risk level级数
Grade范围
Range生态风险水平
Ecological risk level级数
GradeEr<40 低 0 RI<150 低 0 40≤Er<80 中等 1 150≤RI<300 中等 1 8≤Er<160 较重 2 300≤RI<600 重 2 160≤Er<320 重 3 RI≥600 严重 3 Er≥320 严重 4 表 4 洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属的含量(mg.kg−1)
Table 4. Contents of heavy metals in the sediments of Dongting Lake (mg.kg−1)
采样断面Sample Sections Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr Ni Hg As S1 58.55 378.5 82.05 8.71 117.5 47.50 0.45 67.54 S2 43.9 149.5 26.65 3.40 89.55 33.30 0.25 25.86 S3 30.85 146.5 26.75 1.92 85.55 30.75 0.46 12.91 S4 37.25 101.25 22.10 0.56 100.50 36.45 0.15 10.79 S5 42.25 122.00 24.85 0.67 101.05 37.35 0.81 10.10 S6 29.20 158.00 23.55 1.77 83.00 29.25 0.47 12.00 S7 32.90 140.50 30.45 1.70 89.20 33.85 0.56 14.58 S8 30.20 134.50 29.25 1.29 84.85 29.40 0.27 12.57 S9 33.20 122.50 36.75 0.84 90.00 33.65 0.25 18.91 S10 30.25 111.55 42.10 1.65 75.10 26.15 0.19 23.04 S11 45.45 160.50 52.25 2.10 105.25 38.95 0.21 32.61 S12 32.65 127.00 42.45 1.10 82.60 28.30 0.16 17.80 S13 40.20 124.00 41.15 1.20 94.30 34.90 0.24 25.78 S14 38.30 72.10 20.20 0.60 102.90 38.55 0.08 11.62 S15 44.55 159.50 40.20 1.18 100.65 38.75 0.20 22.40 平均值 37.98 147.19 36.05 1.91 93.47 34.47 0.32 21.23 东洞庭湖 40.23 172.84 38.25 1.24 97.14 35.89 9.48 12.86 南洞庭湖 38.17 131.94 24.31 2.93 91.03 33.97 5.54 6.33 西洞庭湖 34.89 172.84 41.21 1.23 92.52 34.60 13.05 14.53 表 5 洞庭湖综合污染分级
Table 5. Standard and level of comprehensive pollution in sediments
项目Items 综合污染程度分级Level of comprehensive pollution 东洞庭湖East Dongting Lake 南洞庭湖SouthDongting Lake 西洞庭湖WestDongting Lake 洞庭湖全湖Dongting Lake STN 1.03 1.04 0.87 1.03 STP 1.78 1.69 1.47 1.66 FF 1.63 1.54 1.33 1.51 污染等级 中度污染 中度污染 轻度污染 中度污染 表 6 洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养盐与重金属的皮尔逊相关性(n=15)
Table 6. Pearson correlation matrix for heavy metals(n=15)
项目Item Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr Ni Hg As Cu 1 0.695** 0.665** 0.694** 0.877** 0.901** 0.076 0.795** Zn 1 0.830** 0.953** 0.524* 0.596* 0.280 0.894** Pb 1 0.783** 0.466 0.522* -0.033 0.938** Cd 1 0.473 0.552* 0.187 0.913** Cr 1 0.985** 0.084 0.566* Ni 1 0.119 0.634* Hg 1 -0.018 As 1 *P<0.05;**P<0.01. -
[1] 李芬芳, 符哲, 李利强, 等. 洞庭湖表层沉积物重金属污染状况评估 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(11): 2462-2471. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041902 LI F F, FU Z, LI L Q, et al. Assessment on heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(11): 2462-2471(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041902
[2] RAMAMOORTHY S, RUST B R. Heavy metal exchange processes in sediment water systems [J]. Environmental Geology, 1978, 2(3): 165-172. doi: 10.1007/BF02430670 [3] ROTHW WELL J J, EVANS M G, ALLOTT T E H. Sediment-water interaction in an eroded and metal contaminated peatland catchment, Southern Pennines, UK [J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution: Foucs, 2006, 6(5/6): 669-676. [4] 刘立华. 白洋淀湿地水资源承载能力及水环境研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海冶金研究所, 2000. LIU L H. Study on water resource carrying capacity and water environment of the Baiyang Wetland[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Metallurgy, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2000 (in Chinese).
[5] 孔明, 彭福全, 张毅敏, 等. 环巢湖流域表层沉积物重金属赋存特征及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(6): 1863-1871. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.06.032 KONG M, PENG F Q, ZHANG Y M, et al. Occurrence characteristic and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Circum-Chaohu [J]. China Environment Science, 2015, 35(6): 1863-1871(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.06.032
[6] 罗燕, 秦延文, 张雷, 等. 大伙房水库表层沉积物重金属污染分析与评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(5): 987-995. LUO Y, QIN Y W, ZHANG L, et al. Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Dahuofang reservoir [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(5): 987-995(in Chinese).
[7] ZHENG N, WANG Q, LIANG Z, et al. Characterization ofheavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 154(1): 135-142. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.01.001 [8] 张光贵, 卢少勇, 田琪. 近20年洞庭湖总氮和总磷浓度时空变化及其影响因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2377-2385. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040501 ZHANG GG, LU S Y, TIAN Q. Analysis of spatial-temporal variations of total nitrogen and total phosphorus concentrations and their influencing factors in Dongting Lake in the past two decades [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2377-2385(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040501
[9] 甘树, 卢少勇, 秦普丰, 等. 太湖西岸湖滨带沉积物氮磷有机质分布及评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(9): 3064-3069. GAN S, LU S Y, QIN P F, et al. Spatial distribution and evaluation of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments from western lakeside belt of Lake Taihu [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(9): 3064-3069(in Chinese).
[10] ZHANG N N, ZANG S Y, SUN Q Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in the water environment of Zhalong Wetland, China [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2014, 23(4): 518-526. doi: 10.1007/s10646-014-1183-0 [11] IQBAL J, SHAN M H. Study of seasonal variations and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Cyprinuscarpio from Rawal Lake, Pakistan [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(4): 2025-2037. doi: 10.1007/s10661-013-3515-6 [12] KUKRER S, SEKER S, ABACI Z T, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of northern littoral zone of Lake CildirArdahan, Turkey [J]. Environment Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(6): 3847-3857. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3662-4 [13] LIU M X, YANG YY, YUN X Y, et al. Distribution and ecological assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the East Lake, China [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2014, 23(1): 92-101. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1154-x [14] GERGEN I, HARMANESCU M. Application of principal component analysis (PCA) for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments [J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(1): 137-141. [15] SINGH K P, MALIK A, SINHA S, et al. Estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in sediments of Gomti River (India) using principal component analysis [J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 2005, 166: 1-4. [16] 李芬芳, 黄代中, 连花, 等. 洞庭湖及其入湖口表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的分布及污染评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(12): 2307-2313. LI F F, HUANG D Z, LIAN H, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matters in the surface sediments of Dongting Lake and its lake inlets [J]. Ecology and Environment Science, 2018, 27(12): 2307-2313(in Chinese).
[17] 郭晶, 李利强, 黄代中, 等. 洞庭湖表层水和底泥中重金属污染状况及其变化趋势 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(1): 44-51. GUO J, LI L Q, HUANG D Z, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment of DongtingLake [J]. Research of Environment Sciences, 2016, 29(1): 44-51(in Chinese).
[18] 连花, 郭晶, 黄代中, 等. 洞庭湖表层沉积物中重金属变化趋势及风险评估 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(1): 126-134. LIAN H, GUO J, HUANG D Z, et al. Variation trend and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Research of Environment Sciences, 2019, 32(1): 126-134(in Chinese).
[19] 欧阳美凤, 谢意南, 李利强, 等. 东洞庭湖及其入湖口水域表层沉积物中重金属的分布特征与生态风险 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(7): 1195-1201. OUYANG M F, XIE Y N, LI L Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and Ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediment of East Dongting Lake and its inlet [J]. Ecology and Environmental Science, 2016, 25(7): 1195-1201(in Chinese).
[20] 王勤, 彭渤, 方小红, 等. 湘江长沙段沉积物重金属污染特征及其评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 999-1011. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101901 WANG Q, PENG B, FANG X H, et al. Characteristic and evaluation of heavy metals in sediment of Changsha. section of Xiangjiang river [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 999-1011(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101901
[21] 蔡佳, 王丽婧, 陈建湘, 等. 西洞庭湖入湖河流磷的污染特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(1): 70-78. CAI J, WANG L J, CHEN J X, et al. Characteristics of phosphorus pollution in rivers entering the West Dongting Lake [J]. Research of Environmental Science, 2018, 31(1): 70-78(in Chinese).
[22] QIAN Y, ZHENG M H, GAO L R, et al. Heavy metal contamination and its environment risk assessment in surface sediments from Lake Dongting, People’s Republic of China [J]. Bulletion of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2005, 75(1): 204-210. doi: 10.1007/s00128-005-0739-3 [23] YAO Z G. Comparison between BCR sequention extraction and geo-accumulation method to evaluate metal mobility in sediments of Dongting Lake, Central China [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008, 26(1): 14-22. doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0014-7 [24] 于佳佳, 尹洪斌, 高永年, 等. 太湖流域沉积物营养盐和重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(6): 2287-2294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.06.037 YU J J, YIN H B, GAO Y N, et al. Characteristics of nutrient and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Taihu watershed [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(6): 2287-2294(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.06.037
[25] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geojournal, 1969, 2(3): 109-118. [26] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentologicalapproach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-986. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [27] 张光贵, 谢意南, 莫永涛. 洞庭湖湘江入湖口至出口水域表层沉积物中重金属空间分布特征与生态风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(4): 803-805. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014123101 ZHANG GG, XIE Y N, MO Y T. Spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from the inlet to the outlet of Xiangjaing river in DongtingLake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(4): 803-805(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.04.2014123101
[28] HU C, DENG Z M, XIE Y H, et al. The risk assessment of sediment heavy metal pollution in the East Dongting Lake wetland [J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 2015(15): 1-8. [29] LI F, HUANG J H, ZENG G M, et al. Intergrated source apportionment, screening risk assessment, and risk mapping of heavy metals in surface sediments: a case study of the Dongting Lake, Middle China [J]. Hunan and Ecological Risk Assessment: An Internation Journal, 2014, 20(5): 1213-1230. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2013.849479 [30] 黄代中, 万群, 李利强, 等. 洞庭湖近20 年水质与富营养化状态变化 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(1): 27-33. HUANG D Z, WAN Q, LI L Q, et al. Changes of water quality and eutrophic state in recent 20 years of Dongting Lake [J]. Research of Environmental Science, 2013, 26(1): 27-33(in Chinese).
[31] 田琪, 李利强, 欧伏平, 等. 洞庭湖氮磷时空分布及形态组成特征 [J]. 水生态学杂志, 2016, 37(3): 17-25. TIAN Q, LI L Q, OU F P, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and speciation of nitrogen and phosphorus in Dongting Lake [J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2016, 37(3): 17-25(in Chinese).
[32] LU X Q, WERNER T, YOUNG T M. Geochemistry and bioavailability of metals in sediments from northern SanFrancisco bay [J]. Environment International, 2005, 31(4): 593-602. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2004.10.018 [33] 谢意南, 欧阳美凤, 黄代中, 等. 洞庭湖及其入湖口沉积物中重金属的污染特征、来源、与生态风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(10): 2253-2264. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017020303 XIE Y N, OUYANG M F, HUANG D Z, et al. Pollution characteristics, sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from Dongting Lake and its lake inlet [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10): 2253-2264(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017020303
[34] 郭掌珍, 张渊, 李维宏, 等. 汾河表层沉积物中营养盐和重金属的含量、来源和生态风险 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(3): 95-99. GUO ZZ, ZHANG Y, LI W H, et al. Concentration, sources and ecological risk of nutrients and heavy metals in surface sediments from Fenhe River [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(3): 95-99(in Chinese).
[35] 王佩, 卢少勇, 王殿武, 等. 太湖湖滨带底泥氮、磷、有机质分布与污染评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(4): 703-709. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.04.020 WANG P, LU S Y, WANG D W, et al. Nitrogen, phosphorous and organic matter spatial distribution characteristics and their pollution status evaluation of sediment nutrients in lakeside zones of Taihu Lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(4): 703-709(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.04.020
[36] 田琪, 张光贵, 谢意南, 等. 洞庭湖主要入湖口表层沉积物重金属分布特征与生态风险评价 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(2): 191-200. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160516003 TIAN Q, ZHANG GG, XIE Y N, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from main tributary entrance of Dongting Lake [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(2): 191-200(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160516003
[37] LOSKA K, WIECHUŁA D. Application of principal componentanalysis for the estimation of source of heavy metalcontamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir [J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 51(8): 723-733. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00187-5 -



 下载:
下载: