-
我国是世界上最大的煤炭生产与消费国,2019年,全国原煤产量为38.5亿吨,消费总量为22.2亿吨,占全国一次能源消费总量的57.7%[1-2]。《中国可持续能源发展战略专题》中指出到2050年煤炭在我国能源结构消费比例中仍占50%以上,短期内,煤炭作为主体能源的地位不会发生改变[3]。然而,我国多数煤矿水文地质条件复杂,矿井水害时有发生,据统计从2000年到2014年,4500人死于矿井突水事故,造成了巨大的经济损失与人员伤亡。煤矿一旦发生突水事故,准确快速地进行突水水源识别是水害治理的关键[4]。
我国煤矿区地下水系统一般由多个含水层组成,且各含水层之间存在着不同程度的水力联系[5]。受采煤活动的影响,地下水系统的输入、输出与系统结构将会发生变化,从而诱发矿井水害[6]。地下水水化学成分及组成是地下水流动过程中与周围环境相互作用的产物[7],通常可利用煤矿区地下水水化学成分及特征示踪地下水循环途径,进一步研究其形成因素可阐明地下水演化本质,准确识别矿井突水水源。因此研究煤矿区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用对矿井突水水源识别及水害防治具有重要的意义。
地下水水化学成分的组成主要受大气降水、地表水、地下水含水层性质、水动力条件及人类活动等多种因素控制,因此其演化过程需要多组变量综合刻画[8]。目前,Piper三线图、同位素、Gibbs图、离子比例系数法等成为研究地下水水化学特征及其形成作用的重要方法[9-10]。许多学者借助这些方法对矿区地下水的水化学特征及形成作用开展了研究。王剑等[11]利用Piper三线图及同位素研究了滇东北毛坪矿区地下水化学特征及控制因素,揭示了研究区各含水系统特征的差异;潘玥等[12]借助Gibbs图分析了徐州东部废弃矿井地下水化学的控制因素;张妹等[13]综合Piper三线图、同位素及离子比例分析出顾北矿区地下水化学性质主要受蒸发及岩石风化作用影响;刘凯旋等[14]利用同样的手段分析了孙疃矿地下水水化学特征以及其形成作用,为孙疃矿矿井水水源判别及煤炭开采安全提供了依据。
伊敏矿区隶属呼伦贝尔大型煤电基地,位于国家生态保护区呼伦贝尔草原,目前关于该矿区的地下水特征、分布规律、形成作用等方面的研究少有报道。因此,本文在掌握矿区水文地质条件的基础上,采集该区不同类型水样,综合运用Piper三线图、同位素、Schoeller图、Gibbs图、离子组合比例图来分析伊敏矿区地下水及矿井水水化学特征、形成作用及主要离子来源,以期为伊敏矿区矿井水防治提供依据与理论基础。
-
伊敏矿区行政区域隶属内蒙古自治区呼伦贝尔市鄂温克族自治旗,位于大兴安岭西坡,伊敏河中下游的东部,包含敏东一矿及二矿两个矿区,目前主采敏东一矿,其面积约49.1422 km2,主要煤种为褐煤,井田设计规模500 万t·a−1。矿区可采煤层大部分属于伊敏组,其中主采煤层为16-3上煤及16-3煤。
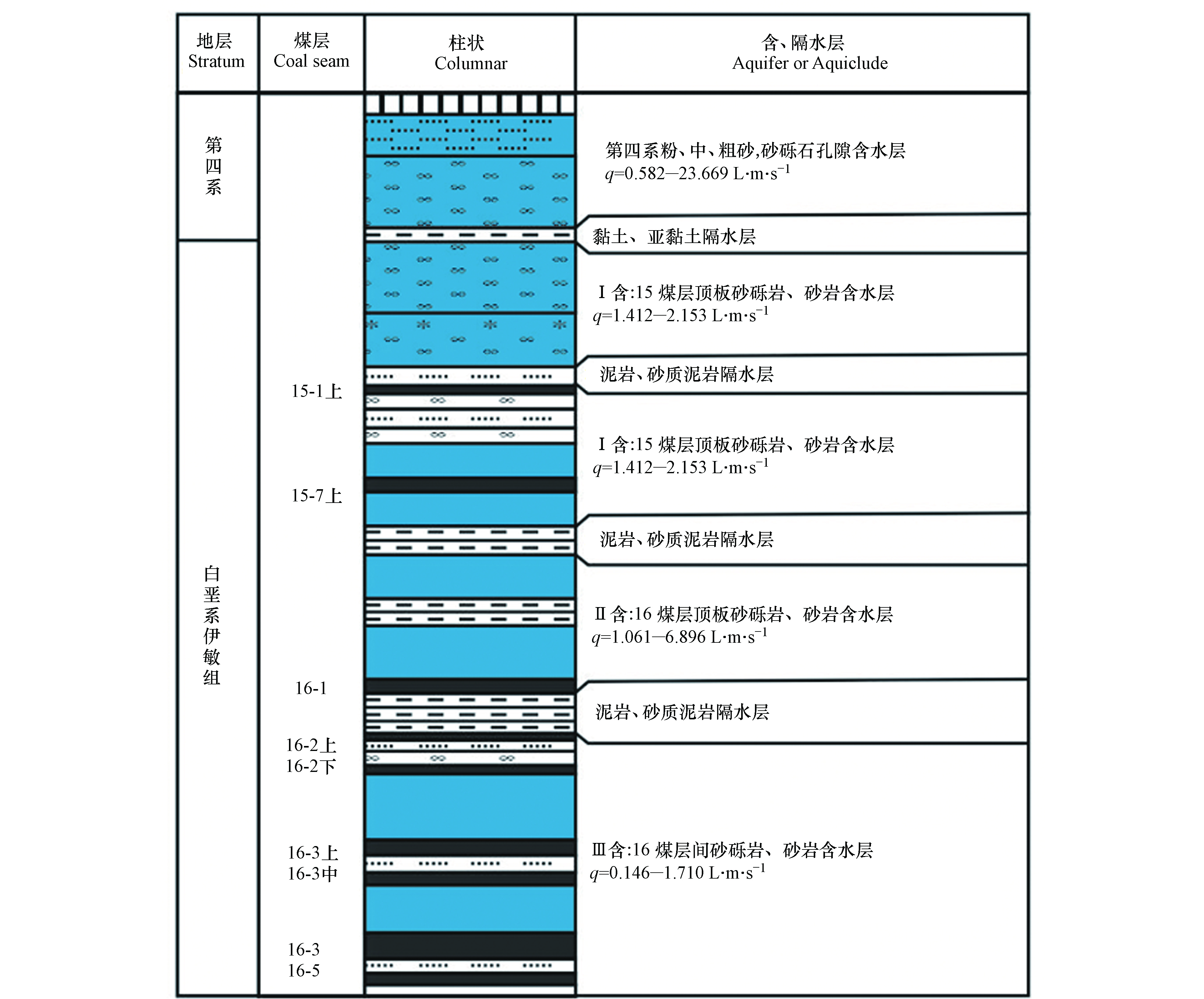
矿区地表水系主要有伊敏河和锡泥河,分别流经矿区的西部及东部,地下水主要含水层从上至下依次为:第四系粉中、粗砂、砂砾石孔隙含水层(第四系),15煤层组顶板及层间砂砾岩、砂岩含水岩组(Ⅰ含水层,简称Ⅰ含),16煤层组顶板砾岩、砂砾岩含水岩组(Ⅱ含水层,简称Ⅱ含),16煤层间砾岩、砂砾岩含水岩组(Ⅲ含水层,简称Ⅲ含)。其中第四系为潜水层,距离主采煤层16-3距离较远;Ⅰ含水层厚度为0—136.5 m,平均厚度46.36 m,渗透系数为1.62—3.37 m·d−1;Ⅱ含水层厚度为0—133.45 m,平均厚度55.00 m,渗透系数为1.26—4.66 m·d−1;Ⅲ含水层厚度为0—135.41 m,平均厚度38.13 m,渗透系数为0.19—1.71 m·d−1;Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ含水层均为承压含水层。研究区综合水文地质柱状图,如图1所示。
-
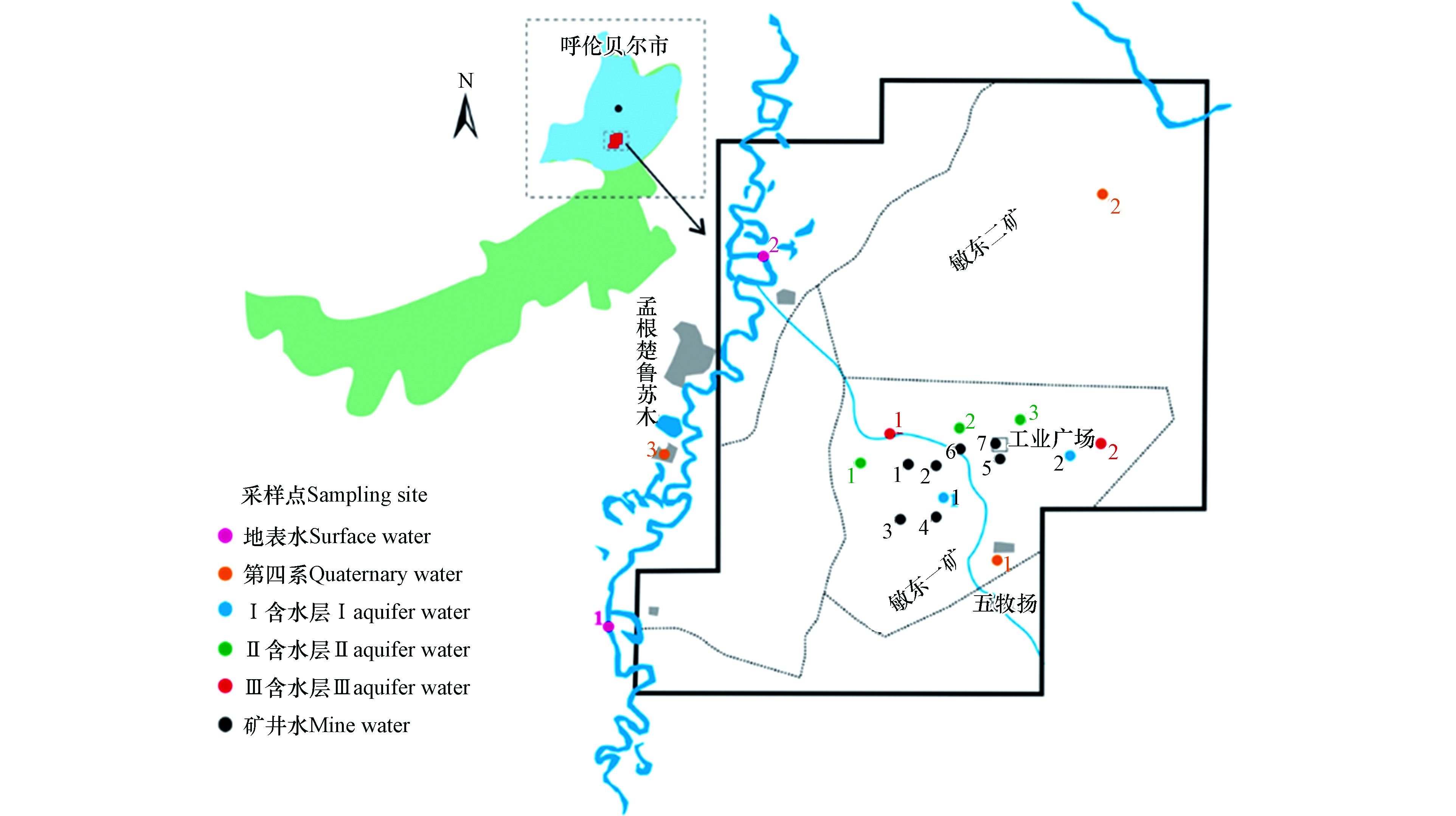
为了解研究区地下水水化学特征,准确识别伊敏矿区矿井水补给水源,分别采集区域大气降水、伊敏河地表河流水、第四系潜水、Ⅰ含、Ⅱ含、Ⅲ含承压水及矿井水水样21组,水样类型及具体取样位置如图2所示。水样采集选用2.5 L塑料瓶,采样前先润洗3—5次,采样后立即密封,标注地点与日期,送往陕西省煤矿水害防治技术重点实验室进行检测,检测项目包括K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO42-、Cl−、HCO3−、pH值、溶解性总固体(TDS)及δD和δ18O同位素。其中K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO42-、Cl−采用离子色谱检测;HCO3−采用化学滴定法;pH及TDS使用便携式检测仪器检测;δD和δ18O采用波长扫描光强衰荡光谱技术测试,结果采用VSMOW 标准。
-
此次共采集水样21组,其中大气降水2组,地表水2组,第四系潜水3组,Ⅰ含、Ⅱ含、Ⅲ含承压水7组及矿井水7组,各组水样水化学参数检测结果见表1。
研究区水样阳离子以Na+为主,浓度为2.90—271.42 mg·L−1,平均为75.67 mg·L−1,其次为Ca2+、Mg2+、K+;阴离子主要为
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ ,浓度为21.33—663.14 mg·L−1,平均为257.17 mg·L−1,其次为Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 。其pH值为7.43—8.33,平均为7.92,属于弱碱性水。其TDS的值为36.90—1003 mg·L−1,平均为420.59 mg·L−1,该区地下水及矿井水均属于淡水(TDS<1000 mg·L−1)。根据表1绘制7种离子Piper三线图(图3).大气降水、地表水、第四系水、Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ含及矿井水均靠近HCO3+CO3端元,远离SO42-和Cl−端元,阴离子以HCO3−为主(阴离子三角图),在阳离子三角图中,大气降水、地表水、第四系水、Ⅰ含水样品分布在Ca端元,而Ⅱ含水样在Na+K端元及Ca端元均有分布,Ⅲ含水及矿井水样主要分布在Na+K端元。大气降水、地表水、第四系水、Ⅰ含水水化学类型为HCO3-Ca型,Ⅱ含水层水化学类型主要为HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型,Ⅲ含水及矿井水水化学类型主要为HCO3-Na型。水化学类型分析结果表明,大气降水、地表水、第四系水以及Ⅰ含水层之间联系密切,Ⅱ含水层为过渡层,与上部含水层联系稍弱,Ⅲ含水及矿井水水化学类型主要为HCO3-Na型,矿井水与Ⅲ含水联系密切。
-
水中δD和δ18O一般受水岩作用影响较弱,是确定不同水源与成因的有效手段[15-16]。检测21组水样δD和δ18O同位素值,并计算不同类型水样δD和δ18O的平均值(表2)。
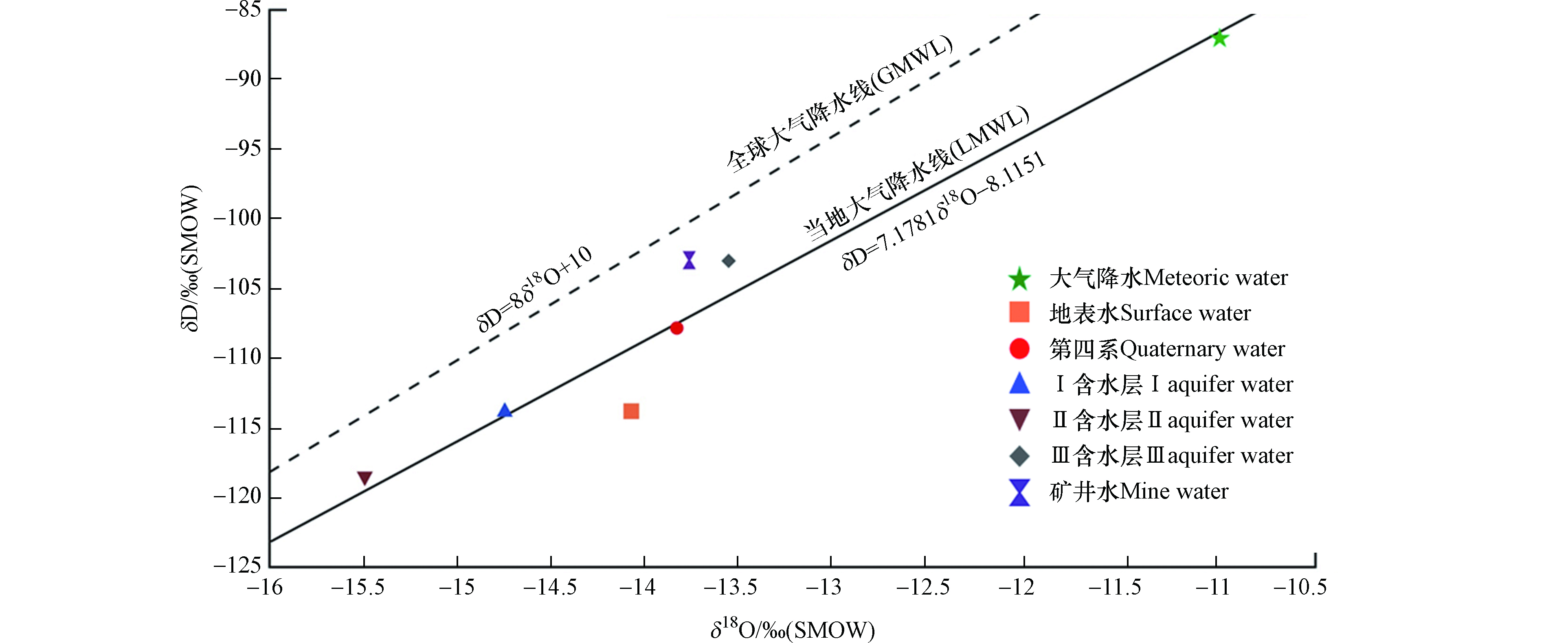
不同含水层地下水稳定同位素δD(VSMOW)在−118.50‰— −87.15‰之间,δ18O(VSMOW)在−15.50‰— −11.01‰之间,据文献报道若δD<−400‰—10‰,δ18O在−60‰—0‰之间,主要来源为大气降水。根据大气降水、地表水、地下水及矿井水δD、δ18O平均值绘制δD—δ18O关系图(图4)。
因缺少本地大气降水线,故选择距离最近气候相似地区大气降水方程代替:δD=7.1781δ18O−8.1151[17],所取大气降水样品基本落在此线上,验证了所引方程适用。显然,第四系水、Ⅰ含水和Ⅱ含水δD和δ18O平均值均落在当地大气降水线附近,说明其主要补给来源为大气降水;而Ⅲ含水偏离当地大气降水线较多,介于全球和当地大气降水线之间,且矿井水样的δD和δ18O接近Ⅲ含水,对比表2中δD和δ18O平均值发现,矿井水δD和δ18O的平均值与Ⅲ含水样δD和δ18O平均值差距最小,说明矿井水主要来源于Ⅲ含承压水补给,这与水化学类型分析结果一致。
-
(1)岩石风化作用
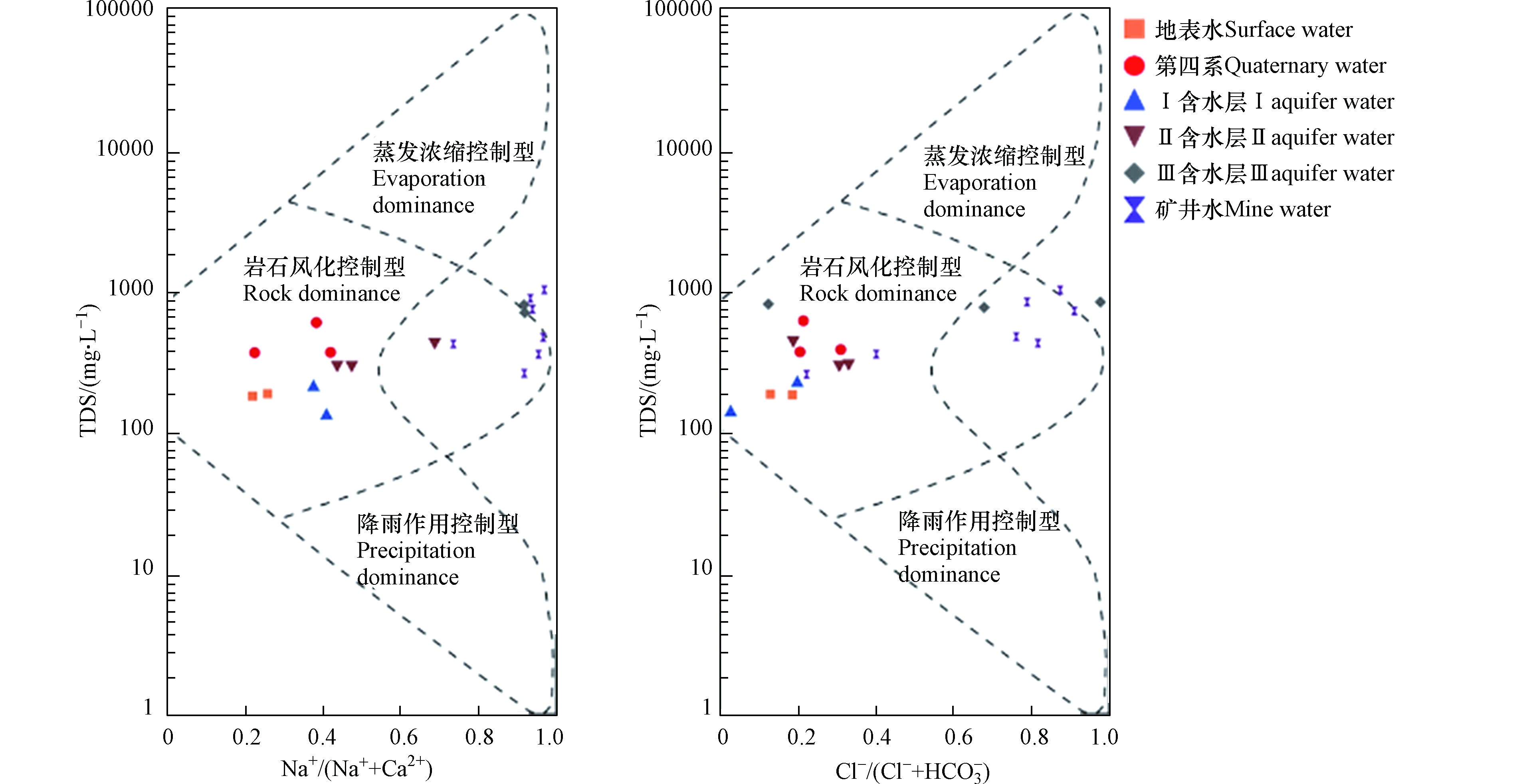
Gibbs图是利用水中Na+、Ca2+、Cl−、HCO3−与TDS之间的关系来研究地下水中主要离子形成的控制因素,包括蒸发浓缩控制型、岩石风化控制型、降水作用控制型3种[18-19]。近年来,国内外学者广泛利用Gibbs图来研究地表水及地下水的形成作用[20-21]。
利用Gibbs对研究区地下水及矿井水的形成作用进行分析(图5),地下水及矿井水TDS均小于1000 mg·L−1,Na+/(Na++Ca2+)值在0.22—0.97,Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)值在0.03—0.99,且水样均落在岩石风化区域,说明该区地下水及矿井水主要离子形成作用均为岩石风化控制。此外,在Gibbs图中,第四系水、Ⅰ含水和Ⅱ含水与矿井水分布较远,Ⅲ含水与矿井水分布靠近,进一步佐证了Ⅲ含水层与矿井水联系密切。
(2)离子交换作用
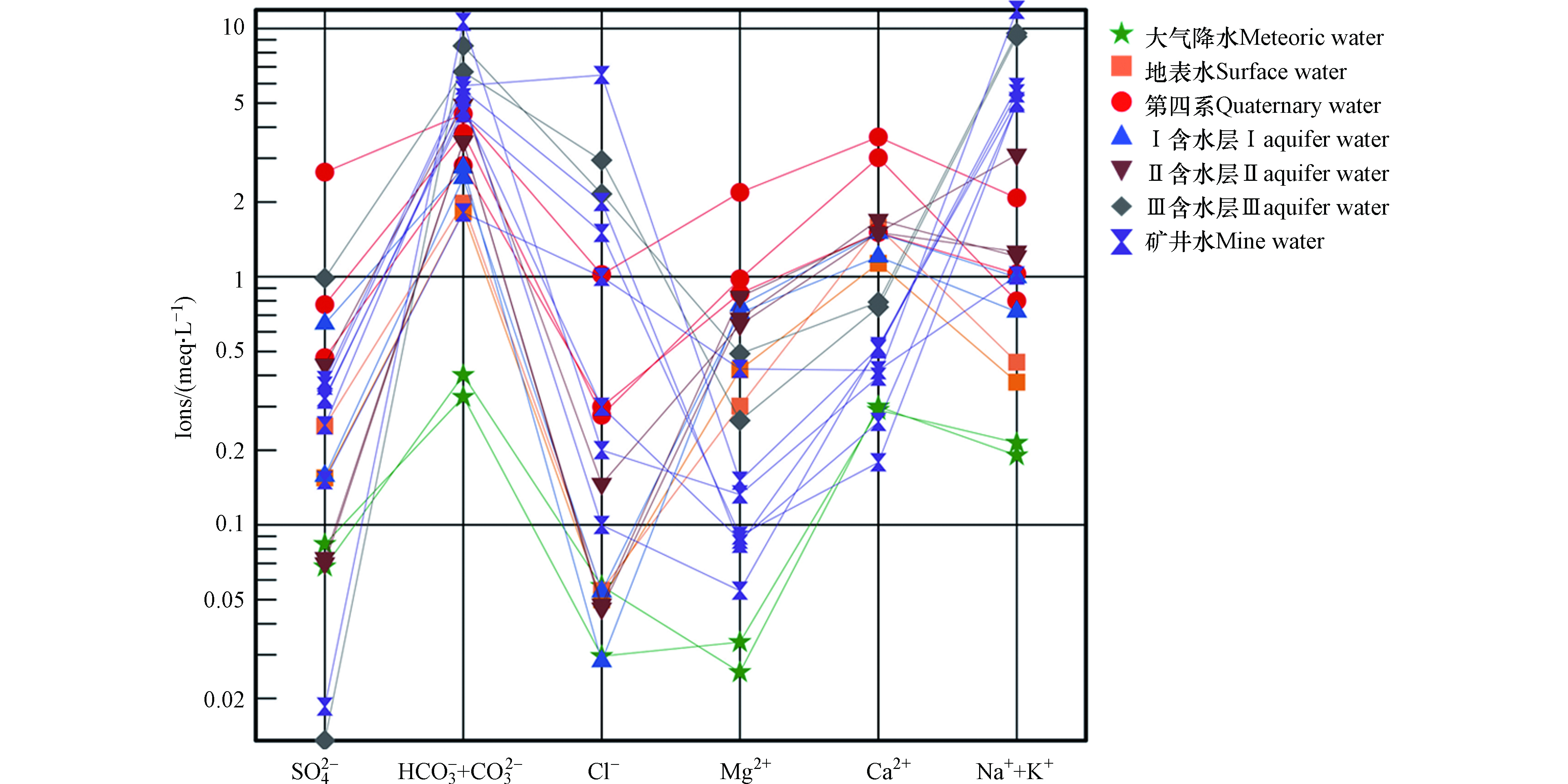
绘制研究区水样Schoeller图(图6),分析离子总体变化特征,判断是否存在阳离子交换作用。地下水中阴离子以HCO3−为主,其变化呈现出由地表水、第四系至承压含水层增加的趋势,阳离子Na++K+浓度(meq·L−1)也有相同的趋势。而阳离子Ca2+和Mg2+浓度呈现出相反的趋势(Ca2+更为明显),即随着深度的增加,由地表水、第四系至承压水,Ca2+和Mg2+浓度逐渐减小。这是由于阳离子Ca2+和Mg2+较浓的浅层地下水向深层补给过程中与有含有Na+和K+的岩土发生阳离子交替吸附作用,使得深层地下水中Na++K+浓度含量上升,Ca2+和Mg2+浓度含量下降,阳离子交换反应化学方程如下式:
-
伊敏矿区地下水主要受岩石风化作用控制及离子交换作用影响,地表水及地下水中主要离子的比例关系可进一步分析主要离子的来源。根据研究区地表水、地下水及矿井水的离子浓度,绘制不同离子间关系图,分析追踪伊敏矿区地下水主要离子来源(图7)。
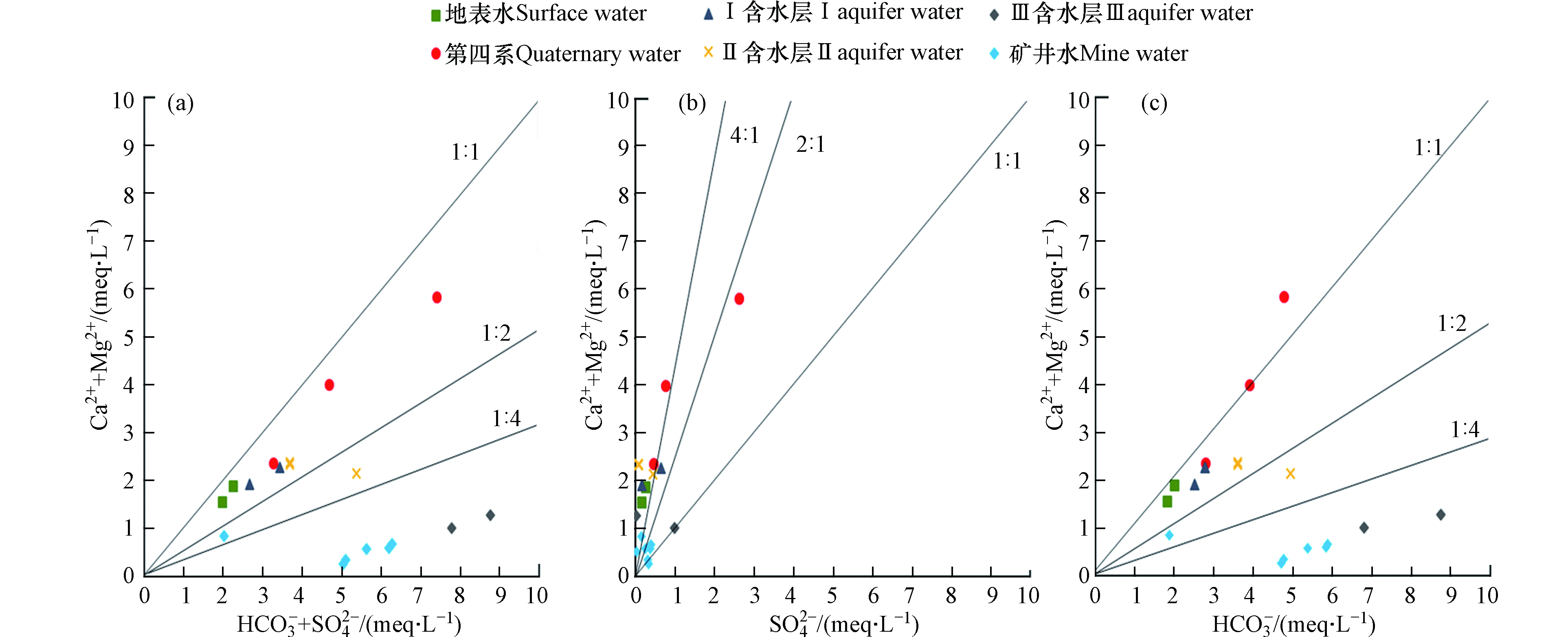
利用(Ca2++Mg2+)/(HCO3−+SO42-)可以分析水中主要矿物来源,若比值大于1,则表明水化学形成作用主要是以碳酸盐类溶解为主,若比值小于1,则主要是以硅酸盐类溶解为主,若比值约等于1,则证明水化学的形成主要以碳酸盐和硅酸盐溶解为主[22]。由7(a)可知,所有水样点均落在1∶1直线下方,说明该矿区各层水中主要离子主要来源于硅酸盐的溶解作用,同时表明水中
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ +${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的含量大于Ca2++Mg2+含量,这是由于地下水中的Ca2+、Mg2+与含水介质表面吸附的Na+、K+发生了离子交换,使水中Ca2+、Mg2+减少,进一步证实了Schoeller图的分析结果。另外,从图中可以发现地表水、第四系含水层和Ⅰ含水层更接1∶1直线,Ⅱ含水层稍有偏离,Ⅲ含水层、矿井水偏离较大(小于1∶4),进一步说明地表水、第四系含水层与Ⅰ含水层联系紧密,与Ⅱ含水层减弱,而Ⅲ含水层与上部含水层联系较弱,与水化学类型分析结果一致。由(Ca2++Mg2+)/
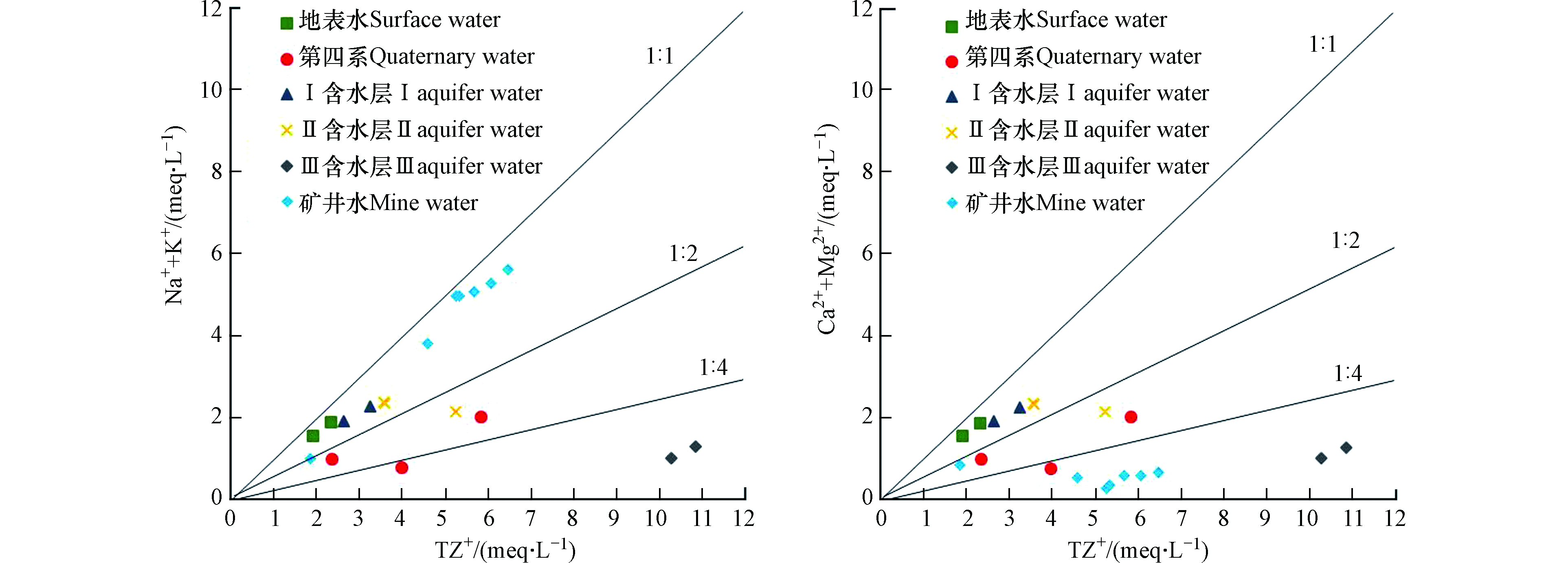
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 比例(图7(b))可知,所有水样点均落在1∶1直线上方,只有部分Ⅲ含水层(包括矿井水)水样接近1∶1直线,其余均大于1∶1直线,表明水中的Ca2++Mg2+大于${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的含量,说明岩层中硫酸盐岩含量较少。由(Ca2++Mg2+)/HCO3−(图7(c)比例可知,大多数水样落在1∶1直线下方,表明硅酸盐物质的溶解在水化学形成作用中占主导地位,并有大量的${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 存在,可以说明游离的CO2溶于水中形成${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 或少量的碳酸盐岩溶解。地下水主要离子成分的多数与硅酸盐的溶解作用有很大的关系。硅酸盐在地下水中的溶解强弱可以用(Na++K+)/TZ+、(Ca2++Mg2+)/TZ+进行估算,其中TZ+为总阳离子含量[23],如图8所示。
从图8(a)可以看出,(Na++K+)/TZ+均在(1∶1)与(1∶4)直线之间,表明地下水中化学成分的形成作用包括硅酸盐的溶解作用,Na+与K+来源于硅酸盐(钾长石、钠长石等)的溶解(式3、4)。从图8(b)可以看出,(Ca2++Mg2+)/TZ+均在(1∶1)直线下方,表明地下水中的Ca2+和Mg2+大多来自于硅酸盐(钙长石)的溶解作用(式5)。通过对(a)与(b)的对比可知,(Na++K+)/TZ+中Ⅲ含水层、矿井水、第四系更接近1∶1直线,其次为Ⅱ含水层、Ⅰ含水层与地表水,而(Ca2++Mg2+)/TZ+中规律相反,而各层最初来源均为大气降水,进一步证明地下水在径流的过程中发生了离子交换的作用,离子交换作用也是Mg2+的主要来源。
综上所述,伊敏矿区地下水及矿井水中主要离子来源于硅酸盐包括钾长石、钠长石及钙长石的岩石风化溶解,并受到Ca2+、Mg2+、K+、Na+阳离子交换作用的影响。
-
(1)伊敏矿区不同类型水样主要阳离子为Na+,其次为Ca2+、Mg2+、K+;阴离子主要为
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ ,其次为${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、Cl−;pH值平均7.92,属于弱碱性水;TDS平均420.59 mg·L−1,属于淡水。(2)大气降水、地表水、第四系水以及Ⅰ含水水化学类型均为HCO3-Ca型,Ⅱ含水水化学类型为HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型,上部含水层之间水力联系紧密;Ⅲ含水和矿井水水化学类型为HCO3-Na型,且Ⅲ含水与矿井水δD、δ18O平均值最接近,介于全球和当地大气降水线之间,矿井水主要源于Ⅲ含承压水补给。
(3)伊敏矿区地下水及矿井水主要离子形成作用受岩石风化控制,主要离子来源于钾长石、钠长石、钙长石等硅酸盐矿物的溶解,并受到阳离子交换作用的影响。
伊敏矿区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用分析
Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation process of groundwater in Yimin mining area
-
摘要: 煤矿区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用对矿井突水水源识别及水害防治具有重要的意义。本文采集伊敏矿区水样21组,综合利用Piper三线图、同位素、Schoeller图、Gibbs图及离子比例关系分析了地下水化学特征及其控制因素。结果表明,矿区不同类型水样主要阳离子为Na+,阴离子主要为HCO3−,平均pH值为7.92,TDS平均值为420.59 mg·L−1;大气降水、地表水、第四系水以及Ⅰ含水层水化学类型均为HCO3-Ca型,它们之间联系密切,Ⅱ含水层水化学类型为HCO3-Ca型和HCO3-Na型,Ⅲ含水层水与矿井水水化学类型为HCO3-Na型,且Ⅲ含水层水与矿井水δD和δ18O平均值最接近,矿井水主要来源于Ⅲ含水层补给;伊敏矿区地下水及矿井水主要离子形成作用受岩石风化控制,主要离子来源于钾长石、钠长石、钙长石等硅酸盐矿物的溶解,并受到Ca2+、Mg2+、K+、Na+阳离子交换作用的影响.Abstract: Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation process of groundwater are of great significance to the mine water inrush identification and prevention of water disaster. This paper studied hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation process of groundwater in Yimin mining area using Piper trilinear diagram, isotopic characteristics, Schoeller graph, Gibbs diagram and ion ratio. The results show that Na+ is the main cation while HCO3− is main anion in the study area water. The average pH of water is 7.92, and the average TDS is 420.59 mg·L−1. The atmospheric precipitation, surface water, quaternary water and confined aquifer I groundwater is predominantly of the HCO3-Ca type, and they are closely related. The major hydrochemical types of confined aquifer Ⅱ groundwater are HCO3-Ca type and HCO3-Na type. The confined aquifer Ⅲ groundwater and mine water are of HCO3-Na type, besides, δD and δ18O average value of confined aquifer Ⅲ groundwater is closed to mine water. Thus, mine water is mainly recharged from confined aquifer Ⅲ groundwater. The formation process of groundwater and mine water is mainly controlled by rock weathering, and main ions are derived from dissolution of silicate minerals including potassium feldspar, sodium feldspar, calcium feldspar and affected by Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+ ion exchange.
-

-
表 1 研究区水样主要离子分析表(mg·L−1)
Table 1. Main ion concentration of water samples from study area(mg·L−1)
序号
Serial number水样类型
Sample type取样点位
Sampling pointK+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42- HCO3− Cl− pH TDS 1 大气降水
Meteoric waterMe-1 3.06 3.12 5.82 0.41 4.02 21.33 1.05 7.54 45.46 2 Me-2 2.52 2.90 6.01 0.31 3.26 26.59 2.01 7.43 36.90 3 河流水
Surface waterS-1 2.20 9.10 31.69 3.66 12.01 122.6 1.93 8.03 183.00 4 S-2 1.06 8.01 22.70 5.12 7.43 111.18 1.77 8.33 188.00 5 第四系潜水
Quaternary waterQ-1 2.29 46.40 73.18 26.54 126.50 292.30 36.17 7.55 606.00 6 Q-2 1.26 17.60 60.36 11.90 37.04 238.90 9.80 7.76 377.00 7 Q-3 1.81 22.53 30.15 10.40 22.65 171.12 10.60 8.31 368.00 8 Ⅰ含承压水
Ⅰ aquifer waterⅠ-1 3.05 14.80 24.14 8.69 7.57 154.00 1.91 8.10 215.00 9 Ⅰ-2 2.81 21.22 30.02 9.30 31.03 170.01 1.00 8.06 132.00 10 Ⅱ含承压水
Ⅱ aquifer waterⅡ-1 2.22 70.00 30.18 7.78 21.23 301.7 5.18 8.22 440.00 11 Ⅱ-2 1.45 26.90 33.95 8.24 3.53 220.00 1.63 7.81 296.00 12 Ⅱ-3 1.56 28.10 30.18 10.07 3.36 220.00 1.69 7.80 295.00 13 Ⅲ含承压水
Ⅲ aquifer waterⅢ-1 2.87 211.00 15.09 3.20 47.39 414.90 104.4 7.97 800.00 14 Ⅲ-2 3.29 218.00 15.84 5.95 0.65 534.30 76.27 7.80 855.00 15 矿井水
Mine waterMi-1 1.18 114.14 5.21 1.06 15.36 291.64 10.60 8.23 352.00 16 Mi-2 1.03 116.52 10.52 0.66 12.08 328.68 3.54 7.94 252.00 17 Mi-3 8.21 128.80 10.34 1.83 18.39 359.47 230.00 8.27 708.00 18 Mi-4 7.11 121.70 10.21 1.02 17.47 356.45 70.90 7.74 800.00 19 Mi-5 1.24 113.98 3.58 1.10 15.67 287.47 53.20 7.78 460.00 20 Mi-6 2.62 271.42 7.93 1.61 0.89 663.14 7.09 7.91 1003.00 21 Mi-7 0.60 22.91 8.40 5.16 7.26 114.70 35.4 7.75 420.00 表 2 研究区各类型水样δD、δ18O平均值
Table 2. δD、δ18O average value of each various-type water samples from study area
序号
Serial number水样类型
Sample typeδD/‰平均值
δD/‰mean valueδ18O/‰平均值
δ18O/‰mean value1 大气降水Meteoric water −87.15 −11.01 2 地表河流Surface water −114.00 −14.10 3 第四系潜Quaternary water −108.00 −13.85 4 Ⅰ含水层Ⅰ aquifer water −113.65 −14.75 5 Ⅱ含水层Ⅱ aquifer water −118.50 −15.50 6 Ⅲ含水层Ⅲ aquifer water −103.00 −13.60 7 矿井水Mine water −102.95 −13.81 -
[1] 2019煤炭行业发展年度报告[C]. 煤炭工业协会. 2019 annual report on the development of coal industry[C]. Coal Association (in Chinese).
[2] 谢和平, 吴立新, 郑德志. 2025年中国能源消费及煤炭需求预测 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(7): 1949-1960. XIE H P, WU L X, ZHENG DZ. Prediction on the energy consumption and coal demand of China in 2025 [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(7): 1949-1960(in Chinese).
[3] 中国科学院能源战略研究组, 中国能源可持续发展战略专题研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. Energy Strategy Research Group, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Thematic study on China's energy sustainable development strategy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006(in Chinese).
[4] 王甜甜, 靳德武, 刘基, 等. 动态权-集对分析模型在矿井突水水源识别中的应用 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(9): 2840-2850. WANG T T, JIN D W, LIU J, et al. Application of dynamic weight-set pair analysis model in mine water inrush discrimination [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(9): 2840-2850(in Chinese).
[5] 陈陆望, 许冬清, 殷晓曦, 等. 华北隐伏型煤矿区地下水化学及其控制因素分析—以宿县矿区主要突水含水层为例 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(4): 996-1004. CHEN L W, XU D Q, YIN X X, et al. Analysis on hydrochemistry and its control factors in the concealed coal mining area in North China: A case study of dominant inrush aquifers in Suxian mining area [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(4): 996-1004(in Chinese).
[6] 陈陆望, 殷晓曦, 刘鑫, 等. 华北隐伏型煤矿地下水水化学演化多元统计分析 [J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2013(6): 43-48. CHEN L W, YIN X X, LIU X, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis on hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in the concealed coal mines in North China [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2013(6): 43-48(in Chinese).
[7] 张小文, 何江涛, 彭聪, 等. 地下水主要组分水化学异常识别方法对比: 以柳江盆地为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(8): 3225-3234. ZHANG X W, HE J T, PENG C, et al. Comparison of identification methods of main component hydrochemical anomalies in groundwater: a case study of Liujiang Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(8): 3225-3234(in Chinese).
[8] GULER C, THYNE G D, MCCRAY J E, TURNER A K. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2002, 10(4): 455-474. doi: 10.1007/s10040-002-0196-6 [9] RAJMOHAN N, ELANGO L. Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India [J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 46(1): 47-61. [10] STOTLER R L, FRAPE S K, RUSKEENIEMI T, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of ground waters in and below the base of thick permafrost at Lupin, Nunavut, Canada [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 373(1-2): 80-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.04.013 [11] 王剑, 罗朝晖, 陈植华, 等. 滇东北毛坪铅锌矿区水化学特征及成因 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(6): 1421-1431. WANG J, LUO Z H, CHEN Z H, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of water chemistry in Maoping lead-zinc mine area, Northeastern Yunnan, China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(6): 1421-1431(in Chinese).
[12] 潘玥, 刘勇, 徐红霞, 等. 徐州东部废弃矿井地下水化学及其时空演化特征分析 [J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(2): 113-118. PAN Y, LIU Y, XU H X et al. Characteristics of groundwater chemistry and its spatio-temporal variation in abandoned mine in eastern Xuzhou [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2018, 24(2): 113-118(in Chinese).
[13] 张妹, 刘启蒙, 刘凯旋. 顾北矿区地下水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 煤矿安全, 2018, 49(5): 193-196. ZHANG M, LIU Q M, LIU K X. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of groundwater in Gubei Mining District [J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2018, 49(5): 193-196(in Chinese).
[14] 刘凯旋, 刘启蒙, 柴辉婵, 等. 孙疃矿区地下水化学特征及其控制因素研究 [J]. 煤炭工程, 2019, 51(4): 74-79. LIU K X, LIU Q M, CHAI H C, et al. Chemical Characteristics and Control Factors of Groundwater in Suntuan Coal Mine [J]. Coal Engineering, 2019, 51(4): 74-79(in Chinese).
[15] THOMAS J, ROSE T. Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology [J]. Environmental Geology, 2002, 43(5): 532-532. [16] 汪集旸, 陈建生, 陆宝宏, 等. 同位素水文学的若干回顾与展望 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(5): 406-413. WANG J Y, CHEN J S, LU B H, et al. Review and prospect of isotope hydrology [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 43(5): 406-413(in Chinese).
[17] 贾伟光, 邸志强, 金洪涛, 等. 东北平原西部山前台地区地下水环境同位素分析-以洮儿河流域中上游为例 [J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 25(10): 1013-1016. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2004.10.026 JIA W G, DI Z Q, JIN HT, et al. Analysis of environmental isotopes for groundwater in pediment Tableland Region of China’s Western Northeast Plain- exemplified with the middle upper reach of Taoer River Basin [J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2004, 25(10): 1013-1016(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2004.10.026
[18] XING L, GUO H, ZHAN Y. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70-71(1): 250-264. [19] 高楹, 田原. 山东济南东南部狼猫山水库上游山区地下水化学特征 [J]. 资源科学, 2018, 40(2): 359-368. GAO Y, TIAN Y. Groundwater chemical characteristics in the upper reaches of the Langmaoshan Reservoir, Shandong [J]. Resources Scence, 2018, 40(2): 359-368(in Chinese).
[20] LI P, QIAN H, WU J, et al. Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China [J]. Mine Water and Environment, 2013, 32(3): 195-206. doi: 10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8 [21] 华琨, 李洲, 李志. 黄土区长武塬地下水水化学特征及控制因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(8): 2065-2073. HUA K, LI Z, LI Z. The hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater in the Changwu loess tableland [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(8): 2065-2073(in Chinese).
[22] SUBBA R N, MARGHADE D, DINAKAR A, et al. Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(21): 747. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-7093-8 [23] WEN X, WU Y, SU J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinity of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, Northwestern China [J]. Environmental Geology, 2005, 48(6): 665-675. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-0001-7 -



 下载:
下载: