-
农药在农业领域的利用已有相当长的一段历史,各种杀虫剂、杀菌剂、除草剂为减少农作物损失做出了重大的贡献[1]。我国是农业大国,农药的使用量普遍高于世界平均水平,但农药使用效率低,仅有30%左右的农药能够发挥作用,未被有效利用的农药则会进入环境中[2-4]。随着农药长期大量的使用,使长期遭受农药污染的土壤面临酸化、土壤养分流失、土壤孔隙度变小等问题,从而导致土壤质量下降[5]。土壤中生长的农作物富集、吸收农药残留进而对人体产生危害[6-7]。已有研究表明,植物根、茎、叶中的农药含量会随着土壤中农药残留浓度的增加而增加,并最终通过生态系统的物质循环而对人体造成伤害[8-9]。研究农药对土壤环境的影响机制,从而提出合理有效的土壤农药污染治理办法,成为解决当前我国土壤农药污染问题的迫切需求。
目前已有不少学者开展了土壤中农药残留对土壤环境影响方面的研究。张春秀发现土壤中的农药残留会直接影响土壤的Eh、CEC以及土壤孔隙度[10],雷雨豪等发现土壤中苯醚甲环唑、丙环唑残留会影响蚯蚓活性[11]。闫颖、李霞、杨瑞等发现农药会对土壤中的酶活性以及微生物群落结构产生影响,土壤中的酶和微生物是土壤生态系统中的重要组成部分,土壤中的农药残留会通过影响酶和微生物的活性等来间接影响土壤质量[12-14]。
本文以我国华北某农业生产基地为研究对象,通过对研究区内土壤中9种农药残留特征的分析,研究农药与土壤环境指标的相关性,并进一步研究与土壤环境指标相关性强的农药在不同残留浓度下土壤环境指标的变化。从而为今后合理喷洒农药以及农药污染土壤的治理提供科学依据。
-
研究区位于我国华北地区,总面积约900 km2,山区半山区约占全区总面积的三分之二。其主要土壤类型为棕壤、潮土和褐土等类型,属暖温带季风气候,四季分明,日照充足,优越的土壤和气候条件使其主要用地类型为果园和菜地。区内普遍施用以鸡粪、羊粪等为主的有机肥,农药施用上,果园、菜地均选用除草剂、杀虫剂以及杀菌剂。由于农药的广泛使用,且降解率较低,使当地土壤也长期受到农药的影响。对研究区果园和菜地分别采样,研究当地土壤中农药残留情况及对土壤中环境指标的影响大小。
-
利用ArcGIS软件对研究区进行布点。综合根据研究区土地利用方式与土壤类型,采用网格布点与分层采样相结合的方式,共采集土样83份,样点分布见图1。根据每个样点所在地块的大小和形状选择梅花法、“S”法、棋盘法。研究区为主要农产品基地,在采样时主要选择耕作类型为果园和菜地的地块,其中果园采样点数为63个,菜地采样点数为20个。取样重量为1 kg左右,采样深度为0—20 cm。
-
实验室测试指标包括土壤中的重金属Cu、As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb,土壤有机质、全氮、pH、CEC、有效磷、速效钾、有效钼、有效硼、有效锌、有效锰、有效铁、有效硫,以及土壤中的9中农药残留(吡唑醚菌酯、苯醚甲环唑、丙草胺、哒螨灵、异丙草胺、五氟磺草胺、嘧菌酯、己唑醇、噻虫胺)。
采用重铬酸钾容量法测定土壤有机质,凯氏定氮法测定土壤全氮,离子计法测定土壤的pH值,氯化钡法测定土壤CEC,紫外可见分光光度法测定土壤有效磷,火焰光度法测定土壤速效钾,催化极谱法测定土壤有效钼,碳酸钠熔融-甲亚胺-H比色法测定土壤有效硼,用原子光谱法测定土壤有效锌、有效锰、有效铁,离子色谱法测定土壤有效硫。Cr、Cu、Cd、Pb、Hg、As参考《土壤和沉积物无机元素的测定波长色散X射线荧光光谱法》(HJ 780-2015)、《土壤质量铅、镉的测定石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法》(GB/T 17141-1997)、《土壤和沉积物汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定 微波消解/原子荧光法》(HJ 680-2013)的方法测定。根据需要分别选择丙酮或正己烷制备各农药的标准溶液。实验室测定几种农药的检出限在0.0013—0.0024 mg·kg−1之间,其回收率在75.5%—109%之间,相对标准偏差在0.82%—16%范围内。
分析主要采用软件为Origin8.0、Canoco4.5,绘图由ArcGIS10.3完成。
-
为了解研究区内不同用地类型下土壤中农药的残留特征,对采集的土样进行农药残留测定,果园和菜地的农药残留情况见表1。
研究区果园主要种植桃树,部分桃园套作西瓜、花生、红薯等经济作物,因此区内果园也会喷洒除草剂。李春艳等发现含水率高的土壤农药降解速率快[15],菜地由于翻耕、浇灌等而使其中农药比果园更易降解,以及农药喷洒方式、次数不同等原因,可能是导致研究区内果园土壤中几种农药残留含量的最大值普遍高于菜地的原因[16-17]。分析几种农药的检出率,吡唑醚菌酯在果园和菜地上的检出率均最高,在研究区内果园的检出率为96.82%,而菜地上的检出率达到了100%。吡唑醚菌酯在研究区内应用广泛,且因其稳定性较高,不易分解[18],而苯醚甲环唑和丙草胺在研究区内检出率均在50%以上,这两种农药对区内土壤环境有较大影响。新时代基于对农业高质量发展的要求,土壤中农药残留问题也开始得到重视,许多学者针对不同用地类型下土壤中的农药残留做了相关研究,发现不同用地类型下土壤中农药残留种类及残留浓度存在差异[19-22],本文研究区内不同用地类型下农药残留特征结果与此观点一致。
-
本文中土壤环境特指土壤中部分理化性质指标、微量元素指标、重金属指标,非传统意义上的土壤环境。将所检测的18个土壤环境指标分为三类,分别为土壤理化性质指标,土壤微量元素指标以及土壤重金属指标,分别研究农药残留与土壤环境指标的相关性,其冗余分析结果如图2所示。
整体上,苯醚甲环唑、吡唑醚菌酯和嘧菌酯这3种农药与土壤环境指标存在一定的相关性,这种相关性是农药与土壤环境指标相互影响的结果。杜丽亚、李春艳等的研究得出土壤含水率、孔隙度、酸碱度等性质会直接影响土壤中农药的降解速率[23, 15],赖波、张春秀等发现农药残留会影响土壤酸碱度以及土壤肥力状况[24, 10]。图2(a)土壤中农药残留与土壤理化性质指标冗余分析结果显示,苯醚甲环唑与速效钾、有效钼、有效磷、有机质、总氮这些土壤环境指标呈现出较强的正相关性,而与pH呈现出较强的负相关性。己唑醇、丙草胺、异丙草胺、五氟磺草胺、哒螨灵、噻虫胺与土壤理化性质指标相关性不强,对土壤理化性质的影响不大。土壤中的农药残留对土壤的理化性质指标具有较大的影响,农药的使用在一定程度上会影响土壤的结构成分。研究发现,农药与大多数土壤微量元素指标有较强的相关性。图2(b)不同农药与土壤微量元素指标的冗余分析结果显示,嘧菌酯、哒螨灵与苯醚甲环唑这三种农药与土壤微量元素指标呈现出较强的相关性,相较而言吡唑醚菌酯与五氟磺草胺的相关性较弱,丙草胺、异丙草胺、噻虫胺与土壤微量元素间几乎不存在相关性。其中几种农药与有效锌的相关性最强,但是有效硼与农药之间几乎不存在相关性。综合来看,农药对土壤微量元素有着显著的影响,进而会影响土壤的持续有效利用。农药与土壤重金属指标的冗余分析结果显示(图2(c)),苯醚甲环唑与嘧菌酯对Hg和Cu这两种土壤重金属元素有着较强的正相关性,哒螨灵与其的相关性则不高。吡唑醚菌酯与Hg和Cu则呈现出负相关,但这种关系并不显著。丙草胺、异丙草胺、五氟磺草胺、噻虫胺以及己唑醇与土壤重金属之间几乎不存在相关性。
基于冗余分析结果可以发现,几种农药与土壤理化性质、土壤微量元素、土壤重金属都存在一定的相关性。苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯与土壤环境指标有着极显著的相关性,尤其是与土壤理化性质指标,而与土壤微量元素以及重金属之间只和部分指标有较强的相关性。土壤中农药残留与土壤环境是一个相互影响的过程。杜丽亚、安琼、苗辉等发现土壤环境会对农药降解产生影响[18, 25-26],赖波等发现农药残留会改变土壤的结构和功能,对土壤质量产生影响[24, 10]。本文在前人研究基础上,从土壤农药残留对土壤环境影响的角度分析,冗余分析结果显示,部分农药(吡唑醚菌酯、苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯)与土壤的一些环境指标(pH、有效磷、有效锰、有效锌、Hg、Cu)存在较高的相关性,说明土壤中农药残留会对土壤环境产生一定的影响。研究区各样点苯醚甲环唑和嘧菌酯以及土壤环境的空间含量分布特征具有一定的关联性,而嘧菌酯因整体检出含量较低而与环境指标未有明显的空间关联性,因此不易降解的苯醚甲环唑可能是影响研究区土壤环境质量的主要农药。根据农药对土壤环境指标影响的冗余分析结果,结合表1、表2研究区内几种农药检出率,可以进一步深入研究与土壤环境指标有显著相关性的苯醚甲环唑与嘧菌酯这两种农药对土壤环境指标的影响。
-
针对上述不同农药残留与土壤环境影响的冗余分析结果,苯醚甲环唑与嘧菌酯与土壤环境指标中的pH、有效磷、有效锰、有效锌、Hg以及Cu有较强的相关性。为直观体现出区内土壤中两种农药的残留情况,以及两种农药与几种土壤环境指标的空间相关性,本文在冗余分析的基础上,利用ArcGIS 10.3得到研究区两种农药以及土壤环境指标检出含量的空间分布特征图。
如图3所示,苯醚甲环唑在研究区内土壤中残留水平较高,呈现出西北高、东南低的分布现象,且西北部土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留量高于0.022 mg·kg−1的点位较多,嘧菌酯在研究区土壤中的残留量普遍较低,仅有个别点位残留量高于0.023 mg·kg−1,其它点位残留量均介于ND—0.008 mg·kg−1。结合图4,从两种农药与土壤环境指标检出含量的空间分布特征来看,苯醚甲环唑含量较高点位有效磷、有效锌、Hg以及Cu的含量也较高,土壤pH检出值的空间变化特征不明显,不能较直观的表现出苯醚甲环唑残留含量不同对其影响的差异,嘧菌酯与土壤环境指标的空间关联度未有前者明显。已有研究表明不同种类农药残留对土壤环境的影响存在差异[27],土壤中农药的不同残留量对土壤环境的影响程度不同[28-29],本文对土壤农药残留与土壤环境指标之间的空间含量分布分析也得到相同结论。
-
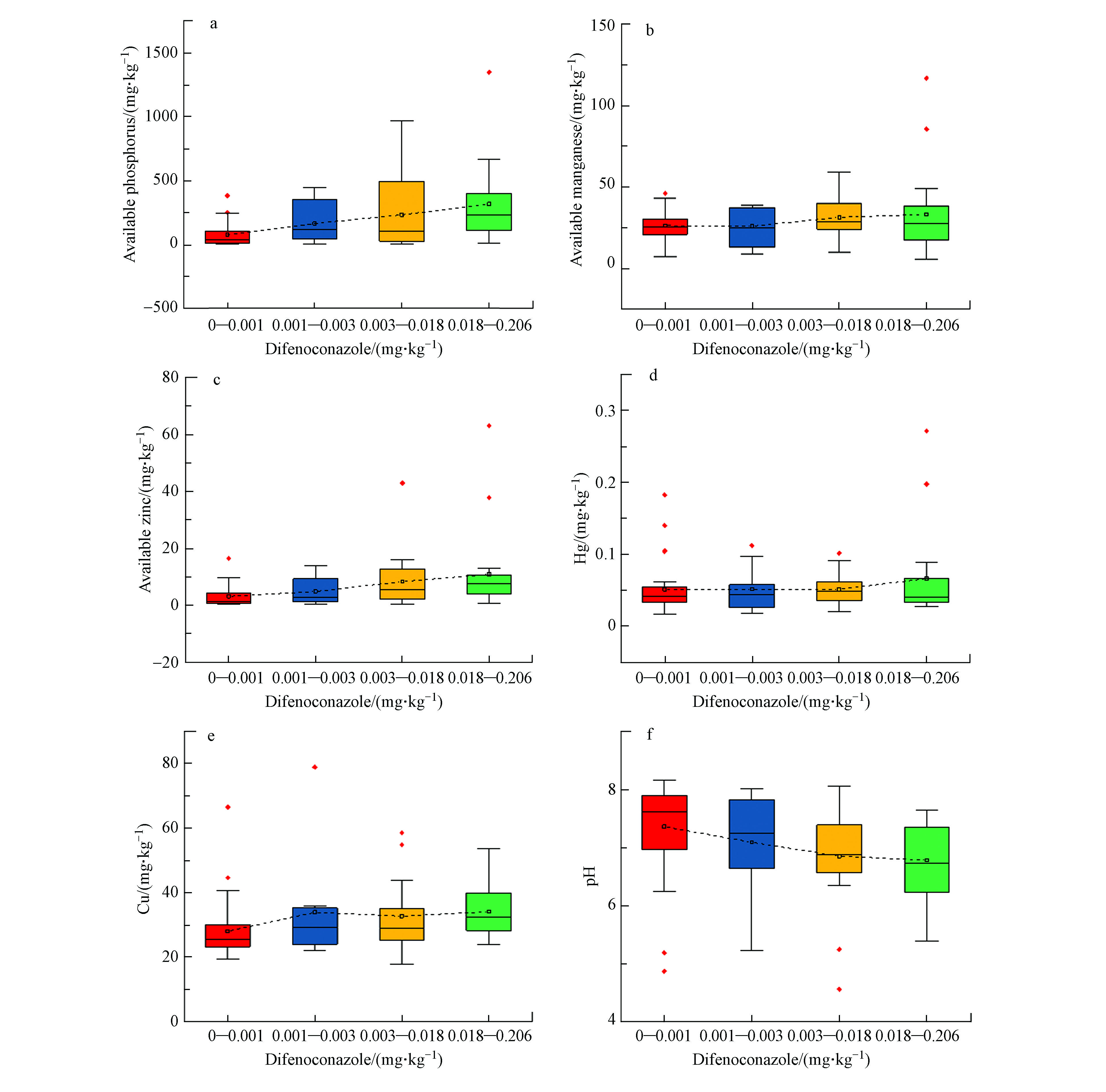
冗余分析结果显示苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯与部分土壤环境指标之间存在较强的相关性,其空间含量分布特征直观表现出苯醚甲环唑与6种土壤环境指标有较强的空间关联性。为进一步研究土壤中不同农药残留浓度下土壤环境指标的变化,本文利用概率累积曲线对区内土壤中苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯残留含量进行划分,其中嘧菌酯农药残留浓度过低,近八成样点低于0.001 mg·kg−1,对其划分梯度分析的结果差距不明显,因此只针对苯醚甲环唑做进一步的浓度分级影响分析。苯醚甲环唑广泛应用于果树和蔬菜等作物,但其在土壤中的移动性小,降解缓慢,因此在土壤中的残留浓度要略高于其他农药[30]。研究区内83个样点苯醚甲环唑的浓度介于ND—0.206 mg·kg−1。根据概率累积曲线结果将其分为4个浓度梯度,即ND—0.001 、0.001—0.003、0.003—0.018、0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1,并依次定义为残留量较低、残留量中等、残留量高、残留量过高。分析土壤中苯醚甲环唑的不同残留浓度下,有效锰、有效锌、pH、有效磷、Hg以及Cu这几种土壤环境指标含量的变化。
根据表2苯醚甲环唑的浓度分级,利用Origin软件,分析土壤中苯醚甲环唑不同残留含量下土壤环境指标的变化规律(图5)。
苯醚甲环唑是一种三唑类化合物的杀菌剂,因杀菌谱广而在农业上被广泛使用,因具有光化学稳定性、难降解性以及易在环境中转移等特点,使得苯醚甲环唑在土壤中可以长期存在,其对土壤环境的影响也较大[31]。为了解土壤中残留农药对土壤环境的影响机制,通过对研究区内土壤中苯醚甲环唑检出浓度划分等级,分析不同残留浓度下土壤环境指标(有效磷、有效锰、有效锌、Hg、Cu、pH)变化情况。根据概率累积曲线结果将其分为4个浓度梯度,即ND—0.001、0.001—0.003、0.003—0.018、0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1。随着苯醚甲环唑残留浓度的升高,几种土壤环境指标均发生变化。其中土壤有效磷、有效锰、有效锌以及土壤重金属Hg和Cu随着苯醚甲环唑浓度的升高也随之增高。土壤中这些指标的变化与土壤中微生物、酶的生命活动有关,农药通过影响土壤中微生物、酶的活性从而影响土壤中的物质转化过程[32-33]。土壤有效磷的变化最明显,随着苯醚甲环唑浓度的升高,土壤有效磷浓度增加了3倍多。土壤中的磷以无机磷和有机磷的形式存在[34],有效磷则是土壤中可被植物吸收利用的部分无机磷和有机磷,苯醚甲环唑与不可利用的有机磷、无机磷反应而将其转化为可被利用的有效态,可能是研究区土壤中有效磷含量随苯醚甲环唑残留量变化明显的原因。土壤有效锰的变化幅度相对较小,在ND—0.001 mg·kg−1浓度下,其浓度为26.23 mg·kg−1,在0.001—0.003 mg·kg−1浓度下,其浓度为25.89 mg·kg−1。土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留浓度较低时,有效锰变化并不明显,而在0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1含量下,其含量上升到了33.24 mg·kg−1,总体上的上升幅度为28.39%。土壤有效锌含量随着苯醚甲环唑含量的升高也呈现出较明显的变化,表现出243%的上升。Hg的含量波动不大,且在前三个含量梯度下其含量基本维持在0.051 mg·kg−1,在0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1含量梯度下,其含量上升至0.066 mg·kg−1。而Cu的含量虽然在0.001—0.003 mg·kg−1含量梯度到0.003—0.018 mg·kg−1含量梯度下降了3.6%,但其总体上其由27.94 mg·kg−1上升至33.98 mg·kg−1。Hg、Cu的浓度变化可能与农药组分有一定的关系[35]。
pH与土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度呈现出负相关,即随着土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留量的升高,pH值反而逐渐降低的现象。总体上,pH的变化量为0.31,根据我国《土壤环境质量 农用地污染风险管控标准》(GB 15618-2018),土壤pH值范围为6.5—7.5时,土壤重金属Hg和Cu的污染风险筛选值分别为2.4 mg·kg−1(水田为0.6 mg·kg−1)和100 mg·kg−1(果园为200 mg·kg−1)。除部分异常值外,研究区内土壤重金属Hg和Cu的浓度均未达到污染风险筛选值,区内土壤中两种农药残留的污染风险不高。
-
研究区各样点农药检出不单一,对于苯醚甲环唑对几种土壤环境指标有较大影响的情况,为排除是其它农药影响的可能,现筛选出苯醚甲环唑残留浓度呈梯度变化,但其它农药浓度大致相似的点位,从而论证苯醚甲环唑对土壤环境指标的影响是存在变化规律的(表3)。
对土壤样点数据进行分析筛选,筛选出的4个样点土壤苯醚甲环唑浓度呈梯度变化,即4个点位土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度分别位于ND—0.001 、0.001—0.003 、0.003—0.018、0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1区间内,而其它农药浓度变化量<0.01 mg·kg−1。可以看到,随着土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度的逐渐增大,而pH整体上呈现出逐渐减小的变化。当土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度未达检出限时,pH 为8.01,这与浓度为0.002 mg·kg−1时的pH值相等,土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留浓度低时,对土壤环境的影响较小。而当土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度为0.014 mg·kg−1时,pH值下降至6.80,苯醚甲环唑浓度为0.041 mg·kg−1时,pH值继续下降至6.15。结合图5土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度对土壤pH影响的变化规律可以看到,在一定浓度内,土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度与土壤pH呈负相关,且随着土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度持续升高,土壤pH下降速度趋于平缓。通过对农药残留量与土壤pH值统计发现,在基本不受其它农药干扰下,随着土壤中苯醚甲环唑浓度的升高,土壤中pH仍然会降低。研究区土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留是造成土壤环境改变的主要因素,为保证土壤质量,在农业上应控制其施用量。
-
(1)研究区内不同用地类型下土壤中农药残留量不同,吡唑醚菌酯(检出率:果园96.82%,菜地100%)和苯醚甲环唑(检出率:果园80.95%,菜地55%)在两个功能区内检出率均较高,故在农药施用过程中应控制这两种农药的使用量。
(2)冗余分析结果显示,研究区所使用的农药与土壤环境指标存在不同程度的相关性,苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯两种农药残留同时对土壤环境指标凸显出极显著的相关性,并且醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯与土壤有效磷、有效锌、有效锰、Hg和Cu等指标存在正相关,而与pH则呈现出负相关。从苯醚甲环唑、嘧菌酯检出含量与土壤环境指标检出含量的空间分布来看,其中苯醚甲环唑含量较高点位其有效磷、Cu的含量也较高,pH则相反,而嘧菌酯与土壤环境指标的空间关联度未有前者明显,或许与嘧菌酯检出含量较低有关。
(3)将研究区内土壤中苯醚甲环唑含量划分成四个浓度梯度,分析土壤中苯醚甲环唑不同残留浓度对几种相关性强的土壤环境指标的影响,发现土壤中苯醚甲环唑的残留量过高会导致土壤中Hg、Cu等有害物质含量过高,对土壤酸碱度也有较大扰动,进而降低土壤质量。所得研究成果可为今后其他地区农药合理喷洒及农药污染土壤治理方面提供参考和科学依据。
农田9种农药残留特征及对土壤环境指标影响
Characteristics of soil pesticide residues and their influence on soil environmental indicators
-
摘要:
针对当前农药广泛使用导致土壤环境严重遭受破坏的问题,本文以华北某区域土壤农药残留为研究对象,综合运用统计学、环境生态学及GIS相结合的方法,探讨土壤中农药残留对土壤环境指标的影响机制。结果表明,果园内吡唑醚菌酯、苯醚甲环唑、哒满灵、嘧菌酯等农药残留含量最大值普遍高于菜地;其中苯醚甲环唑与嘧菌酯与土壤环境指标中的pH、有效磷、有效锰、有效锌、Hg以及Cu有较强的相关性,表明这两种农药对土壤环境的影响较大;苯醚甲环唑在研究区内检出率较高(果园80.95%、菜地55.00%),其浓度梯度分析结果说明土壤中苯醚甲环唑残留量对有效磷有非常显著的影响,从ND—0.001 mg·kg−1到0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1残留浓度下,土壤中有效磷含量增加了3倍多。研究结果对于今后农业上农药种类及浓度选择上有一定的指导作用。
Abstract:To the serious damage of soil environment caused by the widespread use of pesticides, this paper takes the soil pesticide residues in a certain area of North China as the research area, and comprehensively uses the methods of statistics, environmental ecology and GIS to explore the influence mechanism of pesticide residues in soil environmental indicators. The results showed that the maximum pesticide residues of pyraclostrobin, difenoconazole, pyridaben and azoxystrobin in orchards were generally higher than those in vegetable fields; difenoconazole and azoxystrobin had a strong correlation with some soil environmental indicators, the pH, available phosphorus, available manganese, available zinc, Hg and Cu. which indicated that the two pesticides had great impact on soil environment The detection rate was high (80.95% in orchard and 55.00% in vegetable field). The results of concentration gradient analysis showed that difenoconazole residue in soil had a significant effect on available phosphorus, the available phosphorus content in the soil increased more than three times formed ND—0.001 mg·kg−1 to 0.018—0.206 mg·kg−1 residual concentration. The research results play a certain guiding role in the selection of pesticide types and concentrations in agriculture in the future.
-
Key words:
- pesticide /
- soil environmental factors /
- pertinence /
- difenoconazole /
- concentration gradient
-

-
表 1 研究区农药残留情况
Table 1. Pesticide residues in study area.
农药
Pesticide最大值 /(mg·kg−1)
Maximum最小值 /(mg·kg−1)
Minimum均值 /(mg·kg−1)
Mean检出率 /%
Check out the rate果园 吡唑醚菌酯 0.228 ND 0.007 96.82 苯醚甲环唑 0.206 ND 0.013 80.95 丙草胺 0.018 ND 0.002 63.49 哒螨灵 0.147 ND 0.004 53.97 异丙草胺 0.023 ND 0.001 52.38 五氟磺草胺 0.032 ND 0.010 57.14 嘧菌酯 0.333 ND 0.007 31.75 己唑醇 0.037 ND 0.002 36.51 噻虫胺 0.018 ND 0.001 28.57 菜地 吡唑醚菌酯 0.050 0.010 0.007 100.00 苯醚甲环唑 0.188 ND 0.025 55.00 丙草胺 0.013 ND 0.003 55.00 哒螨灵 0.050 ND 0.004 50.00 异丙草胺 0.011 ND 0.002 40.00 五氟磺草胺 0.032 ND 0.015 50.00 嘧菌酯 0.114 ND 0.008 30.00 己唑醇 0.025 ND 0.004 30.00 噻虫胺 0.008 ND 0.001 25.00 注:ND为农药残留量未达特定方法检出限.
Notes: ND means that the pesticide residue does not reach the specific method detection limit表 2 苯醚甲环唑浓度分级统计
Table 2. Difenoconazole content classification statistics
苯醚甲环唑含量范围/(mg·kg−1)
Difenoconazole content range比例/%
Proportion样品数/个
Number of samples分级
ClassificationND—0.001 39.80 33 残留量较低 0.001—0.003 13.20 11 残留量中等 0.003—0.018 22.90 19 残留量高 0.018—0.206 24.10 20 残留量过高 表 3 不同农药残留浓度(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Information on different pesticide concentration
点位
Point number苯醚甲环唑
Difenoconazole吡唑醚菌酯
Pyraclostrobin丙草胺
Pretilachlor哒螨灵
Pyridaben异丙草胺
Propolachlor五氟磺草胺
Penoxsulam嘧菌酯
Azoxystrobin己唑醇
Hexaconazole噻虫胺
ClothianidinpH 1 ND 0.001 ND ND ND ND ND ND ND 8.01 2 0.002 0.005 0.001 0.001 ND 0.001 ND 0.001 ND 8.01 3 0.014 ND 0.002 ND 0.001 ND ND ND ND 6.80 4 0.041 0.001 0.001 0.005 ND 0.002 0.008 ND ND 6.15 -
[1] 蔡键, 邵爽, 左两军. 农药知识培训: 意愿、方式与实施主体选择 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(2): 168-178. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.02.20 CAI J, SHAO S, ZUO L J. Pesticide knowledge training: Willingness, ways and choice of implementation main body [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(2): 168-178(in Chinese). doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2016.02.20
[2] 任重, 薛兴利. 粮农无公害农药使用意愿及其影响因素分析: 基于609户种粮户的实证研究 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(7): 31-36. REN Z, XUE X L. Analysis on the will of the non pollution pesticide use and its influencing factors—An empirical study based on 609 farmers [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(7): 31-36(in Chinese).
[3] 杨峻, 林荣华, 袁善奎, 等. 我国生物源农药产业现状调研及分析 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2014, 30(4): 441-445. YANG J, LIN R H, YUAN S K, et al. Survey and analysis of current situation of biologically derived pesticides industry in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2014, 30(4): 441-445(in Chinese).
[4] 刘兆征. 当前农村环境问题分析 [J]. 农业经济问题, 2009, 30(3): 70-74. LIU Z Z. Study on current rural environmental problems [J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2009, 30(3): 70-74(in Chinese).
[5] 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明. 中国农田土壤农药污染现状和防控对策 [J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(3): 417-427. ZHAO L, TENG Y, LUO Y M. Present pollution status and control strategy of pesticides in agricultural soils in China: A review [J]. Soils, 2017, 49(3): 417-427(in Chinese).
[6] 丁浩东, 万红友, 秦攀, 等. 环境中有机磷农药污染状况、来源及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 463-479. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405 DING H D, WAN H Y, QIN P, et al. Occurrence, sources and risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticides in the environment, China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 463-479(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051405
[7] 宋珍霞, 高明, 王里奥, 等. 三峡库区农业土壤重金属含量特征及污染评价: 以Cu Pb和Zn为例 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(6): 2189-2194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.06.011 SONG Z X, GAO M, WANG L, et al. Heavy metal concentrations in agriculture soils of the three-gorge reservoir area and their pollution E-valuation—taking Cu, pb, and Zn as examples [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(6): 2189-2194(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.06.011
[8] 袁欣. 有机氯农药在苏州土壤—植物间的环境迁移模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2006: 38. YUAN X. Simulation study on the environmental migration of organochlorine pesticides between soil and plant in Suzhou[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2006: 38(in Chinese).
[9] 张志勇, 余向阳, 王冬兰, 等. 小青菜对土壤中毒死蜱吸收移动特征研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2011, 48(5): 1029-1034. doi: 10.11766/trxb201004010115 ZHANG Z Y, YU X Y, WANG D L, et al. Uptake and translocation of chlorpyrifos residues in soil by Brassica chinensi [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011, 48(5): 1029-1034(in Chinese). doi: 10.11766/trxb201004010115
[10] 张春秀. 农药污染对农作物土壤的影响及可持续治理对策 [J]. 现代农业, 2017(7): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.07.030 ZHANG C X. Effect of pesticide pollution on crop soil and sustainable management countermeasures [J]. Modern Agriculture, 2017(7): 39-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2017.07.030
[11] 雷雨豪, 张翠芳, 王壮, 等. 环境激素农药三唑类杀菌剂在土壤中的残留与风险评价 [J]. 农药, 2019, 58(9): 660-663. LEI Y H, ZHANG C F, WANG Z, et al. Residues and risk assessment of environmental hormone pesticide triazole fungicides in soil [J]. Agrochemicals, 2019, 58(9): 660-663(in Chinese).
[12] 闫颖, 袁星, 樊宏娜. 五种农药对土壤转化酶活性的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(5): 588-591. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.05.019 YAN Y, YUAN X, FAN H N. Influence of five pesticides on invertase activity in soil [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(5): 588-591(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.05.019
[13] 李霞, 张小平, 喻晓, 等. 代森锰锌类农药对生姜种植地土壤酶活性及微生物群落结构的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(9): 1569-1574. LI X, ZHANG X P, YU X, et al. Effect of mancozeb on soil enzyme activities and microbial community in ginger fields [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(9): 1569-1574(in Chinese).
[14] 杨瑞, 刘帅, 王紫泉, 等. 秦岭山脉典型林分土壤酶活性与土壤养分关系的探讨 [J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(4): 1037-1046. YANG R, LIU S, WANG Z Q, et al. Relationships between the soil enzyme activity and soil nutrients in forest soils typical of the Qinling mountain [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(4): 1037-1046(in Chinese).
[15] 李春艳, 李福琴, 康頔, 等. 土壤环境因子对烯酰吗啉残留降解的影响 [J]. 贵州农业科学, 2016, 44(3): 83-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.03.020 LI C Y, LI F Q, KANG D, et al. Effects of soil environmental factors influencing the degradation of dimethomorph [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(3): 83-85(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.03.020
[16] 袁会珠, 王国宾. 雾滴大小和覆盖密度与农药防治效果的关系 [J]. 植物保护, 2015, 41(6): 9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2015.06.002 YUAN H Z, WANG G B. Effects of droplet size and deposition density on field efficacy of pesticides [J]. Plant Protection, 2015, 41(6): 9-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2015.06.002
[17] ZHANG W, HOU Y R, LIU X, et al. Wind tunnel experimental study on droplet drift reduction by a conical electrostatic nozzle for pesticide spraying [J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2017, 10(3): 87-94. [18] 闫晓阳, 徐金丽, 徐光军, 等. 高效液相色谱法检测吡唑醚菌酯在烟叶和土壤中的残留及消解动态 [J]. 农药学学报, 2013, 15(5): 528-533. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2013.05.08 YAN X Y, XU J L, XU G J, et al. Residue and dissipation of pyraclostrobin by high performance liquid chromatography in tobacco and soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2013, 15(5): 528-533(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2013.05.08
[19] 窦磊, 杨国义. 珠江三角洲地区土壤有机氯农药分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(8): 2954-2963. DOU L, YANG G Y. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface soil of Pearl River Delta economic zone [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(8): 2954-2963(in Chinese).
[20] 暴志蕾, 赵兴茹, 耿梦娇, 等. 长三角地区饮用水源地沉积物中有机氯农药污染特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(6): 1237-1245. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.06.2015111605 BAO Z L, ZHAO X R, GENG M J, et al. Characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in the sediments from the drinking water source of the Yangtze River Delta region [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(6): 1237-1245(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.06.2015111605
[21] 潘静, 杨永亮, 何俊, 等. 崇明岛不同典型功能区表层土壤中有机氯农药分布及风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(11): 2286-2292. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.11.013 PAN J, YANG Y L, HE J, et al. Distribution and ecological risk evaluation of organochlorine pesticides in surface soils from different land use areas in Chongming island [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(11): 2286-2292(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.11.013
[22] 胡春华, 周文斌, 易纯, 等. 环鄱阳湖区蔬菜地土壤中有机氯农药分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(3): 487-491. HU C H, ZHOU W B, YI C, et al. Distribution and eco-risk evaluation of organ chlorine pesticides in vegetable soil in the area around Poyang lake, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(3): 487-491(in Chinese).
[23] 杜丽亚, 章钢娅, 靳伟. 土壤含水量和胡敏酸对有机氯农药降解的影响 [J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(2): 332-336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.02.025 DU L Y, ZHANG G Y, JIN W. Effects of soil water content and humic acid on degradation of organochlorine pesticides [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(2): 332-336(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2006.02.025
[24] 赖波, 董巨河, 王飞, 等. 农药污染对土壤质量的影响及防治措施 [J]. 新疆农业科技, 2013(3): 17-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3574.2013.03.011 LAI B, DONG J H, WANG F, et al. Influence of pesticide pollution on soil quality and prevention measures [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(3): 17-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3574.2013.03.011
[25] 许静, 唐杰伟, 孔德洋, 等. 嗪吡嘧磺隆在土壤和沉积物中的降解 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(3): 461-467. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.03.2014071602 XU J, TANG J W, KONG D Y, et al. Degradation of metazosulfuron in soil and sediment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(3): 461-467(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.03.2014071602
[26] 苗辉, 杨小娟, 程丹丹, 等. 环境因子对土壤中二氯喹啉酸降解的影响 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2014, 37(4): 144-148. doi: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2014.04.021 MIAO H, YANG X J, CHENG D D, et al. Effects of environmental factors on the degradation of quinclorac in soil [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014, 37(4): 144-148(in Chinese). doi: 10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2014.04.021
[27] 张夕林, 丁晓丽, 钱允辉, 等. 不同药剂处理对土壤中农药残留量的影响分析 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2010(4): 197-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2010.04.126 ZHANG X L, DING X L, QIAN Y H, et al. Influence analysis of pesticide residues in soil by different chemical treatment [J]. Xiandai Nongye Keji, 2010(4): 197-199(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2010.04.126
[28] 万盼, 黄小辉, 熊兴政, 等. 农药施用浓度对油桐幼苗生长及土壤酶活性、有效养分含量的影响 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(1): 73-80. WAN P, HUANG X H, XIONG X Z, et al. Effects of pesticides on soil enzyme activities, available nutrients and growth of Vernicia fordii seedlings [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 42(1): 73-80(in Chinese).
[29] 李晓亮, 秦智伟, 候利园, 等. 土壤环境因素对残留农药降解的影响 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2009, 40(4): 132-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2009.04.030 LI X L, QIN Z W, HOU L Y, et al. Influence of environmental factors on degradation of residual pesticide in soil [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2009, 40(4): 132-135(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2009.04.030
[30] 吕秀亭. 苯醚甲环唑市场及在我国的登记情况 [J]. 山东农药信息, 2012(9): 36-39. LÜ|LV|LU|LYU) X T. Difenoconazole registration situation of market and in our country [J]. Shandong Pesticide News,, 2012(9): 36-39(in Chinese).
[31] 初春, 王志华, 秦冬梅, 等. 苯醚甲环唑在芹菜及其土壤中的残留测定和消解动态研究 [J]. 中国科学(化学), 2011, 41(1): 129-135. CHU C, WANG Z H, QIN D M, et al. Study on determination and dynamics of difenoconazole residues in celery and soil [J]. Science in China (Series B), 2011, 41(1): 129-135(in Chinese).
[32] 王凤花. 甲霜灵重复施用的降解动态及其对土壤微生物的生态效应[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2015. WANG F H. Biodegradation of metalaxyl and its effects on soil microbialcommunity structure with repeated applications[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2015(in Chinese).
[33] 闫车太. 三种除草剂在燕麦田土壤中的残留降解动态及对土壤微生物的影响[D]. 甘肃: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. YAN C T. Degradation dynamics of three h erbicide residues in oat field soil and their effects on soil microorganisms[D]. Gansu: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018(in Chinese).
[34] 张鹏, 谢修鸿, 李翠兰, 等. 我国几种地带性土壤中磷素形态的研究 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(10): 3210. ZHANG P, XIE X H, LI C L, et al. Forms of phosphorus in several zonal soils of China [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(10): 3210(in Chinese).
[35] WANG C, WU Q H, WU C X, et al. Application of dispersion-solidification liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of triazole fungicides in environmental water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(1): 71-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.124 -



 下载:
下载: