-
底泥是湖泊及其流域中重金属等污染物的重要归宿和蓄积库,在很大程度上避免了外源输入后水体重金属含量的剧烈变化,但是底泥作为重金属“汇”的角色并非稳定不变[1-2]。在风浪等动力扰动下,底泥-水界面的物理平衡被打破,氧化还原条件发生改变,加速有机质在界面处的迁移和转化,从而使一些有害重金属活化并发生“二次污染”[3]。研究表明,7 m·s−1风浪与2 m·s−1风浪相比,太湖水体中溶解态Mn、Cr、Zn和Cu含量大幅度增加2—15倍,11 m·s−1风浪与7 m·s−1风浪相比,Cr和Ni含量分别增加68.8%和31.2%[4]。然而,目前关于风浪扰动下底泥重金属的释放研究主要集中在重金属浓度和含量变化上[5-6],而对重金属的动态迁移过程,尤其是悬浮后的沉降过程则少有涉及。南四湖地处山东省西南部,自北向南由南阳、独山、昭阳和微山4个湖泊相互串联成一体,平均水深1.46 m,是我国华北平原上面积最大的淡水湖泊湿地。近20年来,随着地方经济的高速发展和能源消费结构的影响,南四湖底泥中Hg、Pb 和As的含量呈快速增长趋势,尤其是Hg的污染最为严重[7]。南四湖南阳湖区表层底泥中Hg的含量高达0.15 mg·kg−1,高出环境背景值约11倍,属重污染程度[8-9]。作为南水北调东线工程最重要的输水通道和京杭大运河最重要的航运路段,南四湖底泥-水界面受到风浪和船只的扰动非常频繁,底泥经常发生再悬浮和沉降运动,在此开展风浪等动力扰动下典型重金属Hg的动态迁移过程研究具有重要意义。
目前关于底泥再悬浮的研究方法主要有现场观测和室内模拟,现场观测受到各种不可控因素的影响,难以推广[10],室内模拟主要有振荡法、波浪水槽法[11]、环行槽法[12]和Y型再悬浮装置法[13]等。Y型再悬浮装置模拟水深可达1.6 m,能克服底泥原状破坏和模拟水深较浅的问题,是目前较为适用的浅水水体底泥再悬浮模拟方法[2,10]。
本文以Hg污染最为严重的南四湖南阳湖区为研究对象,应用Y型再悬浮发生装置及现场获取的风况资料,模拟研究底泥再悬浮和沉降过程下,典型重金属Hg在底泥-水界面的动态迁移过程,并估算其迁移量,为南水北调东线工程的输水水质保障与治理提供科学依据。
-
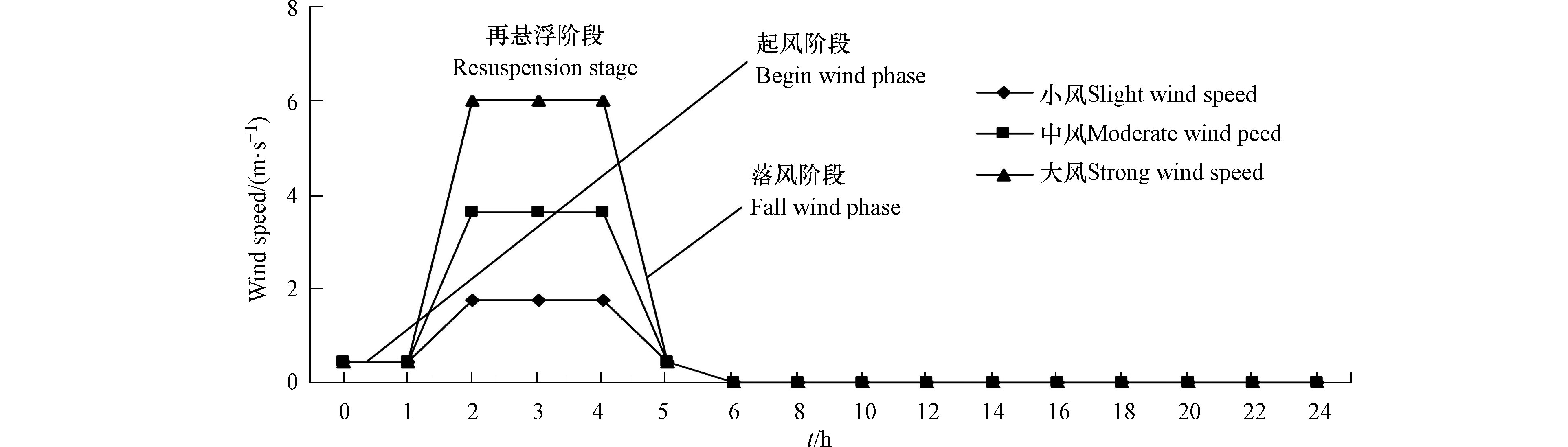
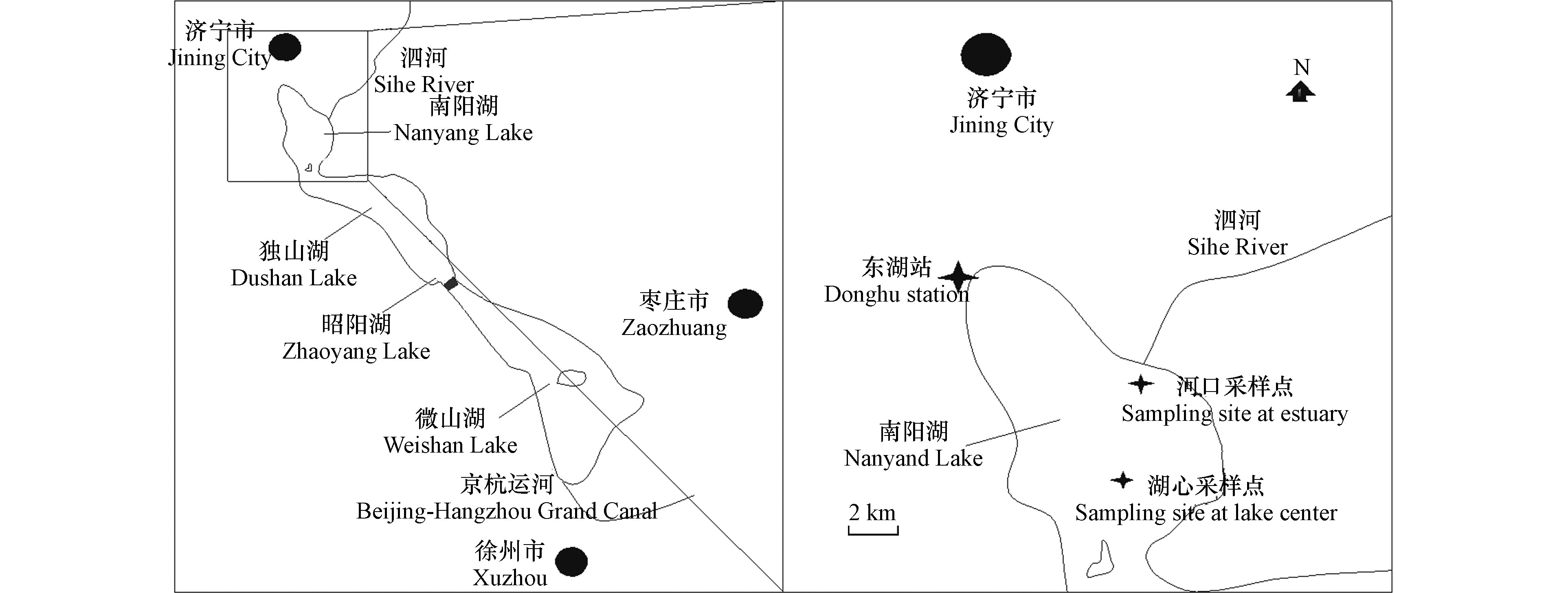
在南四湖南阳湖区东湖站(35°19′38″N,E116°35′04″)设立全自动风速测定仪(MODAS),具体位置见图1。选用2012年10月1日至2013年9月31日每10 min一次的风速自动记录数据进行统计,南阳湖区全年最大风速为9.1 m·s−1,平均风速为2.1 m·s−1,0—1.0 m·s−1低风速占比较大,约占全年风速出现频率的38.9%,6 m·s−1以上的大风速相对较少,仅占全年的2.4%。考虑到低风速对湖泊的水动力影响较小,较难对底泥产生再悬浮,本研究特设立了背景风速。选出累积频率95%以上的风速为大风速,累积频率小于95%的风速平均3等分,对落入每等份频率的风速分别进行累积加权统计,分别记为背景风速、小风速和中风速,具体结果见表1。0.42、1.75、3.63、6.02 m·s−1的平均风速分别对应于背景风速、小风速、中风速和大风速。南阳湖区背景风和小风居多,历时很长,难以进行准确统计,风速在3.0—3.5 m·s−1间的中风过程全年有435次,最长和最短历时分别约为600 min和30 min,平均历时约150 min,风速在6.0—6.5 m·s−1间的大风过程60次,最长和最短历时分别为800 min和30 min,平均历时约为120 min。不同风速的起落时长亦有差别,其过程也并非简单的单调增加或减小过程,背景风和小风的起风落风过程可在10 min内完成,中风和大风过程相对复杂,起风过程一般在3 h左右完成,落风过程一般在2—4 h完成。
-
Y型旋浆式底泥再悬浮发生装置由Y型聚乙烯管、侧位搅拌电机、上部扰动电机和调频电机等主件组成[13],具体装置示意图见文献[10]。根据尤本胜[14]对模拟水柱再悬浮垂向分布的研究结果,确定了本实验模拟风速在小风1.75 m·s−1、中风3.63 m·s−1和大风6.02 m·s−1时所分别对应的下部电机扰动频率为5.83 Hz、6.54 Hz和7.43 Hz,上部电机扰动频率均为10 Hz。依照南四湖南阳湖区不同风速所呈现的历时规律,确定各典型风速时长均为3 h,完整的风速模拟过程包括起风阶段、风速过程(再悬浮阶段)、落风阶段和沉降过程4个阶段,时长分别为1 h、3 h、1 h和19 h,总时长为24 h,具体模拟过程如图2所示。
-
2014年8月(夏季)和2015年2月(冬季)分别在南四湖南阳湖区湖心(35°9’26.7”N,116°39’50.9”E)和泗河河口(35°13’11.0’’N,116°39’51.1”E)利用大口径原位柱状采样器(Rigo Co.,Φ110×500 mm)采集原位柱状样(泥深不小于20 cm),具体采样点位置见图1,每个点位采集柱状底泥12根,分别用于对照、小风、中风和大风扰动模拟,上部用原点位湖水注满后两端橡胶塞塞紧,垂直放置,小心带回实验室。另外,在采样点采集原位湖水,作为实验过程中的上覆水。同时现场采集柱状样,按表层5 cm以上1 cm为间隔,5 cm以下2 cm为间隔进行分层,共分8层(表层11 cm),离心法(5000 r·min−1,30 min)获取间隙水,浓HNO3固定,用于间隙水Hg浓度的分析。
实验室内,按Y型再悬浮发生装置的操作步骤,将柱状底泥(高20 cm)慢慢移入Y型再悬浮发生装置,根据南阳湖常规风情(小风、中风和大风状态)对应的电机扰动频率进行不同风浪下的底泥扰动实验,每实验组均设3次平行。实验过程中,分别于2、4、6、10、24 h(0—4 h为扰动过程,4—24 h为自然沉降过程)在距离底泥-水界面5、15、30、55、105、135 cm处采集水样50 mL,便携式溶解氧测定仪(HQ30d)测定溶解氧(DO)后,0.45 μm滤膜过滤,浓HNO3固定。美国热电公司(Thermo Fisher)电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(iCAP Q ICP-MS)测定Hg浓度,测定前用双内标Rh和Re对分析信号进行校正,RSD在3%以下,全程采用空白样品进行对照,用以验证数据的准确性。
-
选择水柱垂向3个样点进行Hg浓度分析,距离泥-水界面分别为1.05、0.30、0.05 m,计算时代表水层厚度分别为1.1、0.40、0.10 m,共1.60 m。单位面积水柱Hg总增量(FHg,mg·m−2)可通过下式进行计算[15]:
式中,FHg, t为风浪过程中t时刻水柱中汞的总增量FHg(mg·m−2);THg, t为风浪过程中t时刻水柱总汞量THg(mg·m−2);THg, 0为风浪过程起始时水柱总汞量THg(mg·m−2)。其中:
式中,THg为单位面积水柱中总汞量(mg·m−2);CHg, i 为第i水层汞浓度(μg·L−1);Δhi为第i水层的厚度(m)。
-
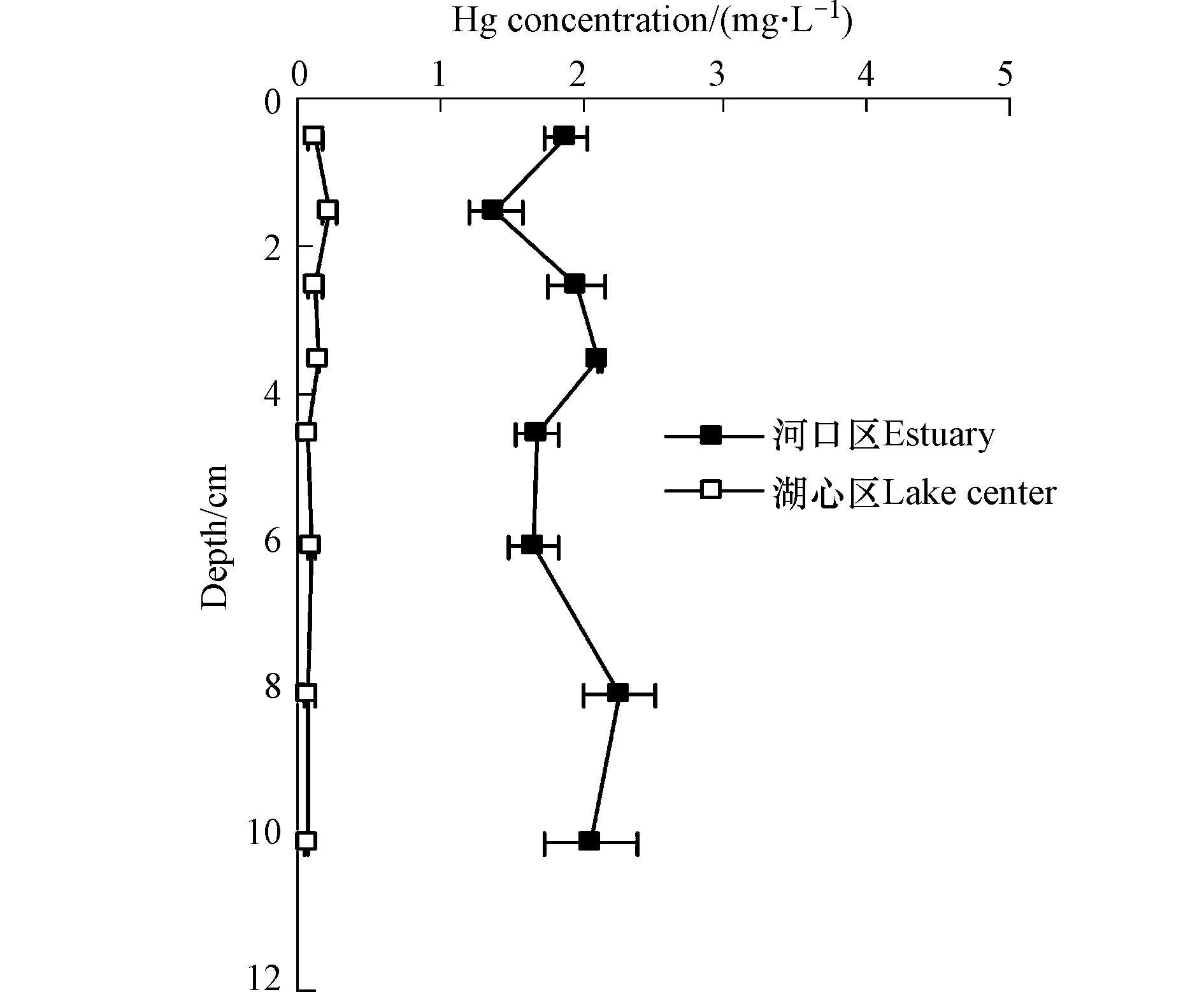
南四湖南阳湖区河口与湖心底泥间隙水Hg浓度的分布见图3,河口与湖心间隙水Hg浓度差异极大,河口区表层11 cm内底泥间隙水Hg浓度维持在1.5—2.3 mg·L−1之间,垂向上波动较大,随深度增加未表现出明显规律,湖心区Hg浓度维持在0.05—0.6 mg·L−1之间,垂向上表现出随深度增加先增大后降低规律,浓度最大值出现在2 cm深度处,为0.6 mg·L−1。南阳湖河口区间隙水Hg浓度较湖心区高5—10倍,南阳湖位于南四湖最北段,靠近济宁市区,城区生活污水和工业废水经泗河入南阳湖,泗河应是南阳湖区重金属Hg污染的最主要来源之一[7]。另外,河口区表层底泥粒度较大,多以中粉砂为主,湖心区颗粒粒径较小,多维持在极细粉砂至中粉砂水平[9],好氧型的砂质底泥受生物活动等影响相对于有机质底泥更剧烈,这些扰动使得底泥中的酸可挥发性硫化物(AVS)氧化,使原本与AVS结合的重金属Hg等被释放出来[16],进一步增加了河口区间隙水中Hg的浓度。底泥间隙水中Hg浓度与其在底泥-水界面的动态交换有着非常密切的关系,湖泊底泥中的有机碎屑与颗粒物质的降解要高于水土界面或湖水中,底泥有机物的降解导致有机物结合态或可交换态重金属通过孔隙水不断析出,从而向上覆水中释放[17]。在风浪等动力扰动下,更深层底泥的有机物降解或矿化速率会增强,不断通过孔隙水向上释放Hg,从而导致上覆水中Hg负荷的增加。
-
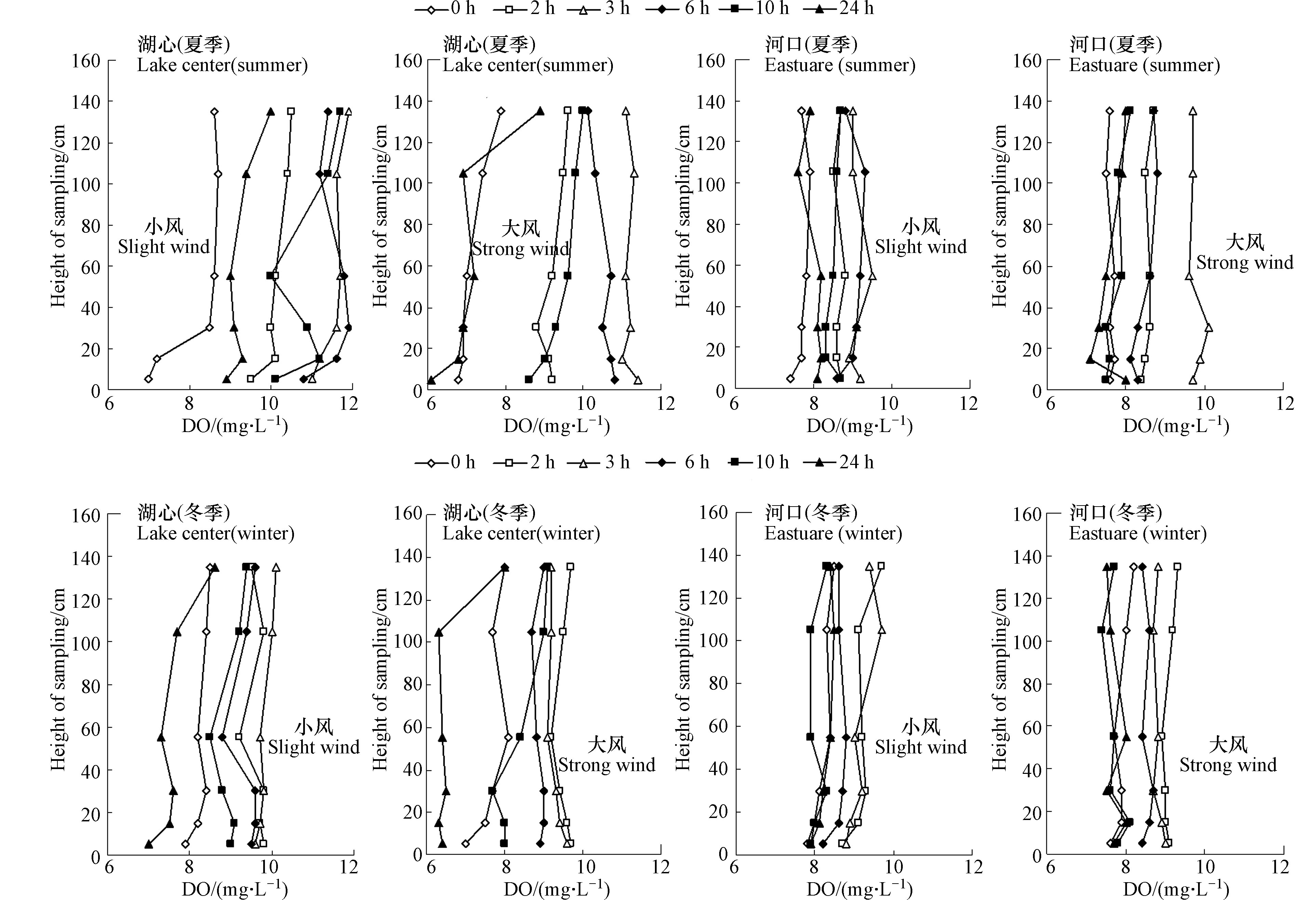
风浪过程中水体不同深度DO动态分布见图4。由图4可见,在风浪开始前,夏季河口与湖心水体DO均有随深度增加而明显减小的趋势,河口与湖心DO分别由表层的7.8 mg·L−1和8.6 mg·L−1逐步降低到底层的7.0 mg·L−1和7.3 mg·L−1,冬季DO随水深增加变化幅度较小。在风浪过程中,DO垂向分布差异被均匀化,从表层水体至底泥表面DO含量相对均匀,水动力条件改变了DO在水体的原有分布特征,改善了下层水体甚至底泥-水界面的氧化条件。图4显示,大风扰动下水中DO浓度同小风扰动DO浓度几乎没有差异,但正常情况下,大风扰动作用导致溶解氧的融入量必定高于小风,这说明扰动作用下融入的溶解氧被悬浮物中的中小分子量有机物所消耗,中小分子量有机物被氧化,导致悬浮物的结构组成以矿物构架为主的铁、硅等无机大分子胶体为主,更有利于水中溶解性重金属的吸附[18]。进入沉降状态后,水体DO含量开始逐步降低,但河口与湖心差异明显,不论冬季还是夏季,湖心区DO降低幅度更大,研究表明,南阳湖湖心区表层底泥有机质含量在15%左右,河口区仅为3%左右[9],悬浮颗粒有机质的巨大差异应是导致DO降幅差异的最主要原因。
Hg等重金属与硫离子或有机质活性基团结合生成难溶于水的物质,在风浪等动力扰动下,水体中含氧条件大大增强,使得硫化物含量减少,Hg等重金属与有机物及硫化物的结合能力下降,从而促进Hg的释放[19]。另外,风浪扰动增加了水体的溶解氧,水体的耗氧有机物随风浪的增大其含量减少,降低了水体的还原条件,使得Hg等重金属与Fe-Mn氧化物的结合更加稳固,减小了Fe-Mn氧化物结合态释放到水溶液中的可能性[20]。
-
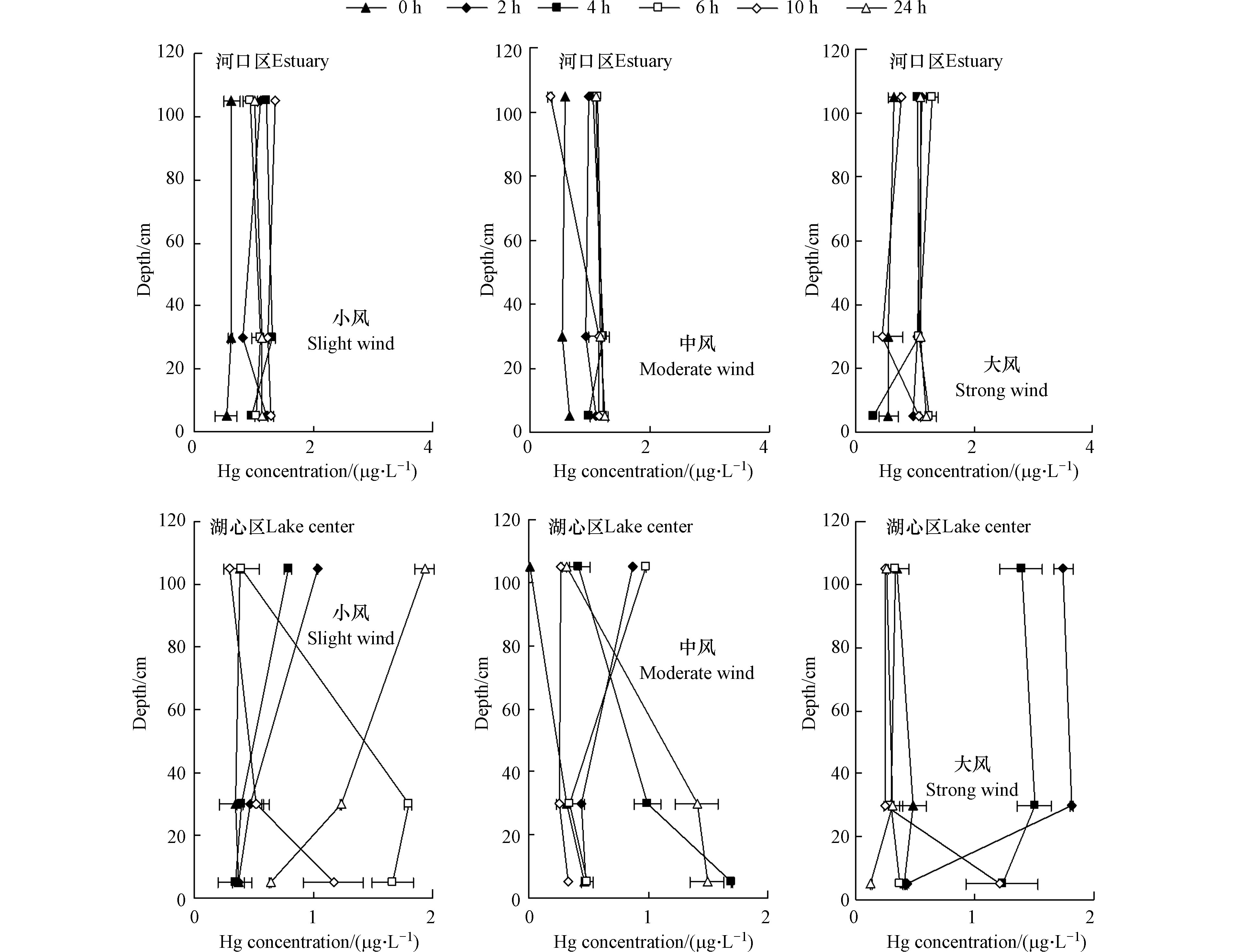
图5可见,南阳湖河口与湖心夏季在不同风浪条件下水体Hg浓度差异显著,河口区水柱中Hg浓度维持在1.5—2.5 μg·L−1之间,湖心区维持在0.1—0.2 μg·L−1之间,对比《地表水环境质量标准GB3838—2002》,南阳湖河口区Hg污染较为严重,夏季水体Hg浓度属于劣Ⅴ类标准,动力扰动下间隙水高浓度Hg向上覆水释放为其主要原因。河口区在小风、中风和大风扰动下,水柱中Hg浓度均呈现出随扰动时间增加而增加的趋势,但其增量同风浪强度没有明显依赖关系,各风速扰动下Hg浓度之间的差异并不明显,小风、中风和大风扰动4 h后,水柱中Hg的平均浓度分别由初始的1.36、1.86、1.90 μg·L−1增大到2.55、2.55、2.08 μg·L−1,而湖心区在小风、中风和大风扰动4 h后,水柱中Hg平均浓度分别由初始0.12、0.15、0.09 μg·L−1变为0.15、0.09、0.1 μg·L−1,风浪扰动下Hg浓度未有明显变化。湖心区,小风、中风和大风扰动4 h后,水柱中悬浮物平均浓度分别由初始12、19.5、19.8 mg·L−1增大到164.7、373.3、2209.3 mg·L−1,大风扰动下悬浮物平均浓度是中风扰动下的5.9倍,是小风扰动下的13.5倍;河口区,小风、中风和大风扰动4 h后,水柱中悬浮物平均浓度分别由初始16.1、16.5、29.4 mg·L−1增大到127.1、294.3、1170.8 mg·L−1,大风扰动下悬浮物平均浓度是中风扰动下的3.9倍,是小风扰动下的9.2倍。由此可见,风浪扰动下水柱中颗粒物浓度的快速增加并没有导致水体中Hg浓度的显著增高,水体中溶解性Hg浓度同水体中悬浮颗粒物含量未呈现正相关。重金属在水环境中的迁移、赋存主要以颗粒态的形式进行,其动态释放现象与不同扰动强度支配着不同形态颗粒物的参与有关,是由物理、化学和生物过程共同作用的结果[4,21]。路永正等[22]也研究表明,生物扰动下,水柱中溶解态的重金属含量较低,释放到溶液中Pb和Cd等主要吸附在悬浮颗粒上。南阳湖底泥中的Hg以碳酸盐结合态和残渣晶格态为主[9],占比在60%以上,碳酸盐结合态对pH值最敏感,酸性条件下容易释放, 而南阳湖湖水呈弱碱性,且风浪扰动增加了水体的溶解氧,提高了水体的氧化条件[20],进一步提高了颗粒物对水体中Hg的吸附能力。大风扰动下,较多颗粒物对Hg的吸附共沉淀起到关键作用,使得大风下水体Hg浓度反而较小风扰动时低。
图6为风浪扰动下冬季南阳湖底泥再悬浮和沉降过程水柱中Hg浓度的动态变化。冬季,河口区在小风、中风和大风扰动下,水柱中Hg平均浓度亦呈现增加趋势,分别由初始的0.59、0.59、0.58 μg·L−1增大到1.06、1.08、0.80 μg·L−1,中风扰动下Hg平均浓度同小风扰动下较为接近,大风扰动下Hg平均浓度反而较小风和中风时低。冬季湖心区小风、中风和大风扰动4 h后,水柱中Hg平均浓度分别由初始的0.36、0.26、0.41 μg·L−1变为0.52、1.06、1.22 μg·L−1,风浪扰动后,水柱中Hg浓度增大显著,个别时段浓度会超过1 μg·L−1。冬季,在风浪扰动下,河口区和湖心区水中Hg浓度均会出现1 μg·L−1以上的情况,超过劣Ⅴ类水质标准,存在较大风险。现场调查发现,南阳湖湖面在冬季被大量菹草覆盖,由于植被的影响,相同的水动力条件下冬季的底泥再悬浮量明显低于夏季,湖心区和河口区在冬季大风下最大悬浮物增量分别为1290 g·m−2和998 g·m−2,而夏季大风下最大悬浮物增量分别高达3203 g·m−2和1290 g·m−2,大风作用下夏季比冬季的最大悬浮物增量分别高62.2%和22.6%。微量重金属含量在水柱中的分布主要受水中颗粒物吸附或共沉淀过程的制约[23],风浪扰动下冬季南阳湖悬浮颗粒物偏低,颗粒物吸附共沉淀作用降低,从而增大了水柱中重金属Hg浓度的风险。另外,冬季温度偏低,有机质的矿化过程较慢,在风浪扰动下,加速了有机质在底泥-水界面处的迁移和转化过程,从而增加了底泥Hg向上覆水的释放风险[3,24]。
风浪扰动停止后,河口区和湖心区水柱中Hg浓度总体均呈下降趋势,但有波动,尤其是冬季湖心区,在小风和中风扰动后的沉降阶段,Hg浓度波动非常大,同悬浮物的沉降相比,存在明显滞后效应,20 h的沉降时间很难将Hg浓度降低到初始标准。
-
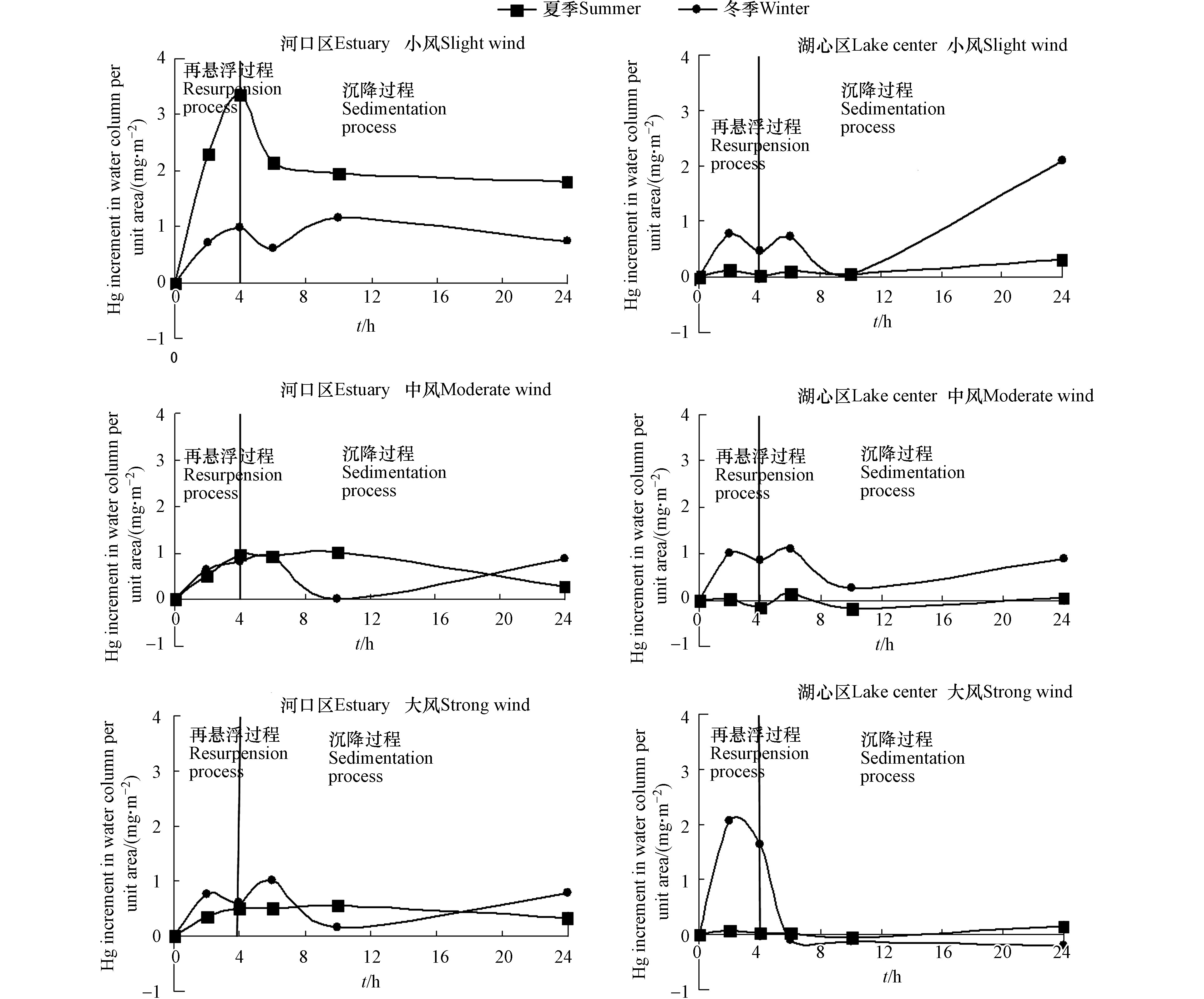
南阳湖夏季和冬季河口与湖心单位面积水体Hg增量(FHg)对风浪强度的响应过程见图7。主要表现为:在风速过程(0—4 h)中,水体FHg除夏季湖心区外普遍有上升变化,在沉降过程(4—24 h)中,水体FHg总体呈现为波动性下降趋势,尤其是冬季湖心区在小风和中风停止扰动后,FHg波动最为剧烈。在风浪扰动的风速过程阶段,河口区FHg随时间变化最为明显,夏季和冬季Hg的释放增量在小风、中风和大风扰动下分别为3.36、0.95、0.50 mg·m−2和0.97、0.81、0.61 mg·m−2,小风过程Hg增量相对较大,大风过程Hg增量相对较小。湖心区,冬季时3 种风速扰动下,均表现为Hg的释放,夏季在小风和大风时表现为Hg的较小释放,中风时波动明显。风浪停止后的沉降过程(4—20 h)阶段,除冬季湖心区外,其它湖区FHg表现出波动性降低趋势,冬季湖心区在小风过后的沉降阶段FHg滞后效应明显,从4 h的0.46 mg·m−2上升到24 h的2.1 mg·m−2。这种差异与河口和湖心表层底泥颗粒尺寸的较大差异有关,河口区表层底泥粒度较大,多以中粉砂为主,湖心区颗粒粒径较小,多维持在极细粉砂至中粉砂水平,较小颗粒物的沉降相对于风速变化存在明显滞后效应,具有一个凝聚增大的过程[14],从而导致了湖心区沉降阶段FHg的无规则波动。
由图7可见,FHg变化量对风浪强度的响应关系随季节的不同而有所变化,但未表现一定规律。冬季湖心区在3种风浪扰动下,FHg有不同程度的增大趋势,夏季则表现为降低或基本不变,河口区在小风和中风下FHg增量表现为夏季大于冬季,大风下,则表现为冬季大于夏季。南阳湖区冬季水面长有大量菹草,风浪扰动下水体悬浮物浓度较夏季大大降低,但重金属Hg含量并未表现出降低规律,菹草的生长对扰动下底泥Hg的释放并不能起到较好控制效果。菹草利用通气组织向根际输送O2进而氧化根部附近底泥中的金属Hg硫化物[25],使吸附或结合相Hg金属离子重新释放出来,促进底泥Hg离子的释放,同时菹草生长能为间隙水提供氧气等氧化剂,降低二价硫离子的生成,进而减少甲基汞的形成风险[26]。
-
(1)风浪扰动下,南阳湖河口与湖心水柱中Hg浓度均呈增加趋势,河口区,冬季和夏季水柱中Hg浓度分别由0.5 μg·L−1和1.5 μg·L−1左右增加到1.0 μg·L−1和2.5 μg·L−1左右,湖心区,小风、中风和大风扰动下,冬季水柱中Hg浓度分别由0.36、0.26、0.41 μg·L−1增加到0.52、1.06、1.22 μg·L−1,夏季Hg浓度相对较低,风浪扰动增加了南阳湖Hg的生态风险,使该区域水体Hg浓度达到劣Ⅴ类水质标准。南阳湖河口区间隙水Hg浓度较湖心区高5—10倍,维持在1.5—2.3 mg·L−1之间,风浪等动力扰动使得Hg不断通过孔隙水向上覆水释放为其主要原因。风浪扰动停止后,水柱中Hg浓度总体呈波动性下降,但沉降20 h很难将其浓度降低到初始标准。
(2)风浪扰动下,南阳湖河口与湖心水柱中Hg浓度增量同风浪强度没有明显依赖关系,河口区夏季和冬季Hg的释放增量在小风、中风和大风扰动下分别为3.36、0.95、0.50 mg·m−2和0.97、0.81、0.61 mg·m−2,小风过程Hg增量较大,大风过程Hg增量反而较小。风浪扰动增加了水体的溶解氧,提高了水体的氧化条件,进一步提高了颗粒物对水体中Hg的吸附能力。大风扰动下,较多颗粒物对Hg的吸附共沉淀起到关键作用,使得水体Hg浓度反而较小风扰动时低。
(3)风浪扰动下,南阳湖河口与湖心水柱中Hg浓度增量对风浪强度的响应关系随季节的不同而有所变化,但未表现出一定规律。南阳湖冬季水面长有大量菹草,风浪扰动下水柱中重金属Hg含量并未表现出降低规律,菹草的生长对扰动下底泥Hg的释放并不能起到明显控制效果。
致谢:中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所为本实验提供Y型底泥再悬浮装置和实验场所,在此表示感谢!
风浪扰动下南四湖南阳湖区底泥Hg的动态迁移规律模拟
Simulation of dynamic migration rules of Hg under different winds and waves in sediments of Nanyang Lake area, Nansi Lake, China
-
摘要: 风浪等动力扰动下底泥重金属的释放研究主要集中在含量变化上,而对其动态迁移过程,尤其是悬浮后的沉降过程则少有涉及。本文以重金属Hg污染较为严重的山东南四湖南阳湖区为研究对象,借助Y型旋浆式底泥再悬浮发生装置,通过常见风情条件下底泥原柱样再悬浮和沉降过程模拟,对不同风浪条件下典型重金属Hg在底泥-水界面的动态迁移过程进行了研究。结果表明,风浪扰动下,南阳湖水柱中Hg浓度呈增加趋势,夏季和冬季河口区Hg浓度分别由1.5 μg·L−1和0.5 μg·L−1左右增加到2.5 μg·L−1和1.0 μg·L−1左右,湖心区分别由0.1 μg·L−1和0.3 μg·L−1左右增加到0.12 μg·L−1和1.0 μg·L−1左右,风浪扰动增加了底泥Hg的释放风险,间隙水高浓度Hg向上覆水释放为其主要原因;风浪扰动停止后,水柱中Hg浓度总体呈波动性下降,但20 h很难降低到初始浓度;水柱中Hg浓度增量同风浪强度没有明显依赖关系,夏季和冬季河口区Hg的释放增量在小风(1.75 m·s−1)、中风(3.63 m·s−1)和大风(6.02 m·s−1)扰动下分别为3.36、0.95、0.50 mg·m−2和0.97、0.81、0.61 mg·m−2,大风过程Hg增量反而较小,大风扰动导致更多悬浮颗粒物对Hg的吸附共沉淀起到关键作用;水柱中Hg浓度增量在季节上未显示一定规律,南阳湖冬季水面大量菹草覆盖,菹草的生长对扰动下底泥Hg的释放没有起到明显控制效果。Abstract: Researches on sediment heavy metals releasing were mainly focus on content changing under the disturbance of winds and waves, etc, and the dynamic migration processes, especially the settlement processes after suspension, were rarely studied. In this article, taking Nanyang area of Nansi Lake, highly polluted by Hg, as research object, with the help of Y-shape sediment resuspension simulation apparatus, simulating the resuspension and sedimentation of intact sediment cores in common wind conditions, the dynamic transfer process of Hg at sediment-water interface was studied under different winds and waves. Results showed that the Hg concentration in water column of Nanyang Lake had the increasing trend under winds and waves disturbance, and the Hg concentration increased from about 1.5, 0.5 μg·L−1 to about 2.5, 1.0 μg·L−1 and from about 0.1, 0.3 μg·L−1 to about 0.12, 1.0 μg·L−1 at estuary and center of Nanyang Lake in summer and winter, respectively. The releasing risk of Hg increased under disturbance of winds and waves, and the upward releasing to overlying water from higher Hg concentration in interstitial water was the main reason. After stopping winds and waves disturbance, the Hg concentration in water column generally decreased with fluctuation, and it was difficult to reduce to the initial concentration in 20 hours. There was no significant dependence between Hg concentration increment and disturbance intensity of winds and waves, under slight (1.75 m·s−1), moderate (3.63 m·s−1) and strong winds (6.02 m·s−1) disturbance, the Hg releasing increments were 3.36, 0.95, 0.50 mg·m−2 and 0.97, 0.81, 0.61 mg·m−2 at estuary in summer and winter, respectively. The Hg concentration increments under strong winds were relatively small, and the more suspended particles caused by strong winds disturbance played a key role in adsorption and co-precipitation of Hg. The Hg concentration increments did not show rules regularly with season, and the growth of Potamogeton crispus L, covering all the Nanyang Lake area in winter, did not play an obvious control effect on the sediment Hg releasing under disturbance.
-
Key words:
- winds and waves disturbance /
- Hg /
- dynamic transfer process /
- release increment /
- Nansi Lake
-

-
表 1 南四湖南阳湖区全年(2012年10月—2013年9月)各频率段风速累计加权均值统计
Table 1. Cumulative weighted mean statistics of wind speeds in each frequency band (October 2012—September 2013) of Nanyang Lake area, Nansi Lake
项目 Item 背景风速
Background wind speed小风速
Slight wind speed中风速
Moderate wind peed大风速
Strong wind speed风速累计频率段 <31.67% 31.67%—63.33% 63.33%—95% >95% 平均风速/(m·s−1) 0.42 1.75 3.63 6.02 平均历时 难于统计 难于统计 ≈150 min ≈120 min -
[1] KAZANCL N, LEROY S A G, ÖNCLEL S, et al. Wind control on the accumulation of heavy metals in sediment of Lake Ulubat, Anatolia, Turkey [J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2009, 43(1): 89-110. [2] 尤本胜, 王同成, 范成新, 等. 风浪作用下太湖草型湖区水体N、P动态负荷模拟 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2008, 28(1): 33-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.01.008 YOU B S, WANG T C, FAN C X et al. The simulation of ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus loading variations under the influence of wind-wave in aquatic macrophytes areas of Lake Taihu [J]. China Environment Science, 2008, 28(1): 33-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.01.008
[3] QIAN J, ZHENG S S, WANG P F, et al. Experimental study on sediment resuspension in Taihu lake under different hydrodynamic disturbance [J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics Ser. B, 2011, 23(6): 826-833. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(10)60182-5 [4] ZHU G W, CHI Q Q, QIN B Q. Heavy-metal contents in suspended solids of Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu and its environmental significances [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2005, 17(4): 676-680. [5] 毕春娟, 陈振楼, 李猛, 等. 再悬浮作用下长江口近岸沉积物中Cd、Pb和Cr的迁移与释放 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(9): 2512-2521. BI C J, CHEN Z L, LI M, et al. Transport and release of Cd, Pb and Cr from the Yangtze estuarine sediments during sediment resuspension event [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(9): 2512-2521(in Chinese).
[6] 池悄悄, 朱广伟, 张占平, 等. 风浪扰动对太湖水体悬浮物重金属含量的影响 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2006, 18(5): 495-498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2006.05.009 CHI Q Q, ZHU G W, ZHANG Z P, et al. Effects of wind-wave disturbance on heavy metal contents in suspended solids of Lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2006, 18(5): 495-498(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2006.05.009
[7] 沈吉, 张祖陆, 杨丽原, 等. 南四湖-环境与资源研究[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2008, 141-159. SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, YANG L Y, et al. Nansi Lake-environmental and resource studies[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2008: 141-159 (in Chinese).
[8] 杨丽原, 沈吉, 张祖陆, 等. 南四湖表层底泥重金属污染及其风险性评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2003, 15(3): 252-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009 YANG L Y, SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in superficial sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2003, 15(3): 252-256(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009
[9] 张智慧, 李宝, 梁仁君. 南四湖南阳湖区河口与湖心沉积物重金属形态对比研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(5): 1408-1416. ZHANG Z H, LI B, LIANG R J. Comparison of sediment heavy metal fractions at estuary and center of Nanyang Zone from Nansi Lake, China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(5): 1408-1416(in Chinese).
[10] 尤本胜, 王同成, 范成新, 等. 太湖沉积物再悬浮模拟方法 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(5): 611-617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.018 YOU B S, WANG T C, FAN C X, et al. Quantitative simulative method of sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(5): 611-617(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.05.018
[11] 朱广伟, 秦伯强, 张路, 等. 太湖底泥悬浮中营养盐释放的波浪水槽实验 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2005, 17(1): 61-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2005.01.010 ZHU G W, QIN B Q, ZHANG L, et al. Wave effects on nutrient release of sediments from Lake Taihu by flume experiments [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2005, 17(1): 61-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2005.01.010
[12] 张运林, 秦伯强, 陈伟民, 等. 太湖水体中悬浮物研究 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2004, 13(3): 266-271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2004.03.014 ZHANG Y L, QIN B Q, CHEN W M, et al. A study on total suspended matter in Lake Taihu [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Bain, 2004, 13(3): 266-271(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2004.03.014
[13] 范成新. 一种室内模拟水下沉积物再悬浮状态的方法及装置[P]. 中国专利: ZL200420025427.9, 2005-01-12. FAN C X. Y-type sediment resuspension apparatus[P]. Chinese Patent: CN ZL200420025427.9, 2005-01-12(in Chinese).
[14] 尤本胜. 太湖沉积物再悬浮和沉降过程中物质的动态迁移及其定量化[D]. 南京: 中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所, 2007: 11-22. YOU B S. Dynamic transfer of nutrients and their quantification in sediment resuspension and sedimentation processes in Lake Taihu[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007: 11-22 (in Chinese).
[15] 刘新, 王秀, 赵珍, 等. 风浪扰动对底泥内源磷钝化效果的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(8): 3064-3071. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.08.031 LIU X, WANG X, ZHAO Z, et al. Effect of wind and wave disturbance on passivation of internal phosphorus in sediment [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(8): 3064-3071(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.08.031
[16] 贾艳霞, 尹洪斌, 唐婉莹. 河蚬扰动对不同质地沉积物中重金属生物有效性与毒性的影响 [J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(2): 67-73. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.02.011 JIA Y X, YIN H B, TANG W Y. Effects of Corbicula fluminea disturbance on bioavailability and toxicity of heavy metals in sediments with different qualities [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2019, 35(2): 67-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2019.02.011
[17] 覃雪波, 孙红文, 彭士涛, 等. 生物扰动对沉积物中污染物环境行为的影响研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(1): 59-69. QIN X B, SUN H W, PENG S T, et al. Review of the impacts of bioturbation on the environmental behavior of contaminant in sediment [J]. Acta Ecologic Sinica, 2014, 34(1): 59-69(in Chinese).
[18] 李大鹏, 黄勇, 李勇, 等. 沉积物扰动持续时间对悬浮物中磷形态数量分布的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 379-384. LI D P, HUANG Y, LI Y, et al. Impacts of sediment disturbance time on the distribution of phosphorus forms in suspended solids [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 379-384(in Chinese).
[19] JOZSEF H, KLARA P. Investigation on the pollution source of bottom sediments in the lake balaton [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2002, 73: 65-78. doi: 10.1016/S0026-265X(02)00053-X [20] 池悄悄, 朱广伟, 张占平, 等. 风浪扰动对太湖水体重金属形态的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2007, 26(2): 228-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.02.025 CHI Q Q, ZHU G W, ZHANG Z P, et al. Effects of wind-wave disturbance on heavy metals speciations in the water of Lake Taihu [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2007, 26(2): 228-231(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.02.025
[21] FONES G R, DAVISON W, HOLBY O, et al. High-resolution metal gradients measured by in situ DGT/DET deployment in Black Sea sediments using an autonomous benthic lander [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2001, 46: 982-988. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.4.0982 [22] 路永正, 阎百兴. 颤蚓扰动作用对铅镉在沉积物-水相中迁移的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(2): 251-255. LU Y Z, YAN B X. Effect of bioturbation by worms on the transport of Pb and Cd between sediments and waters [J]. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(2): 251-255(in Chinese).
[23] LOPEZ D L, GIERLOWSKI-KORDESCH E, HOLLENKAMP C. Geochemical mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals in a lake affected by acid mine drainage: Lake Hope, Vinton County, Ohio [J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 2010, 213(1-4): 27-45. [24] 汪福顺, 刘丛强, 灌瑾, 等. 贵州阿哈水库沉积物中重金属二次污染的趋势分析 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2009, 18(4): 379-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2009.04.014 WANG F S, LIU C Q, GUAN J, et al. Trend analysis of the recycling of heavy metals in sediments of Aha Lake, Guizhou Province [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtza Basin, 2009, 18(4): 379-383(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2009.04.014
[25] 张弛, 王树功, 郑耀辉, 等. 生物扰动对红树林沉积物中AVS和重金属迁移转化的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(11): 3037-3045. ZHANG C, WANG S G, ZHENG Y H, et al. The effects of roots and crabs’ bioturbation on AVS, migration and transformation of heavy metals in mangrove sediments [J]. Acta Ecologic Sinica, 2010, 30(11): 3037-3045(in Chinese).
[26] BENOIT J M, SHULL D H, ROBINSON P, et al. Infaunal burrow densities and sediment monomethyl mercury distributions in Boston Harbor, Massachusetts [J]. Marime Chemistry, 2006, 102(1): l24-l33. -



 下载:
下载: