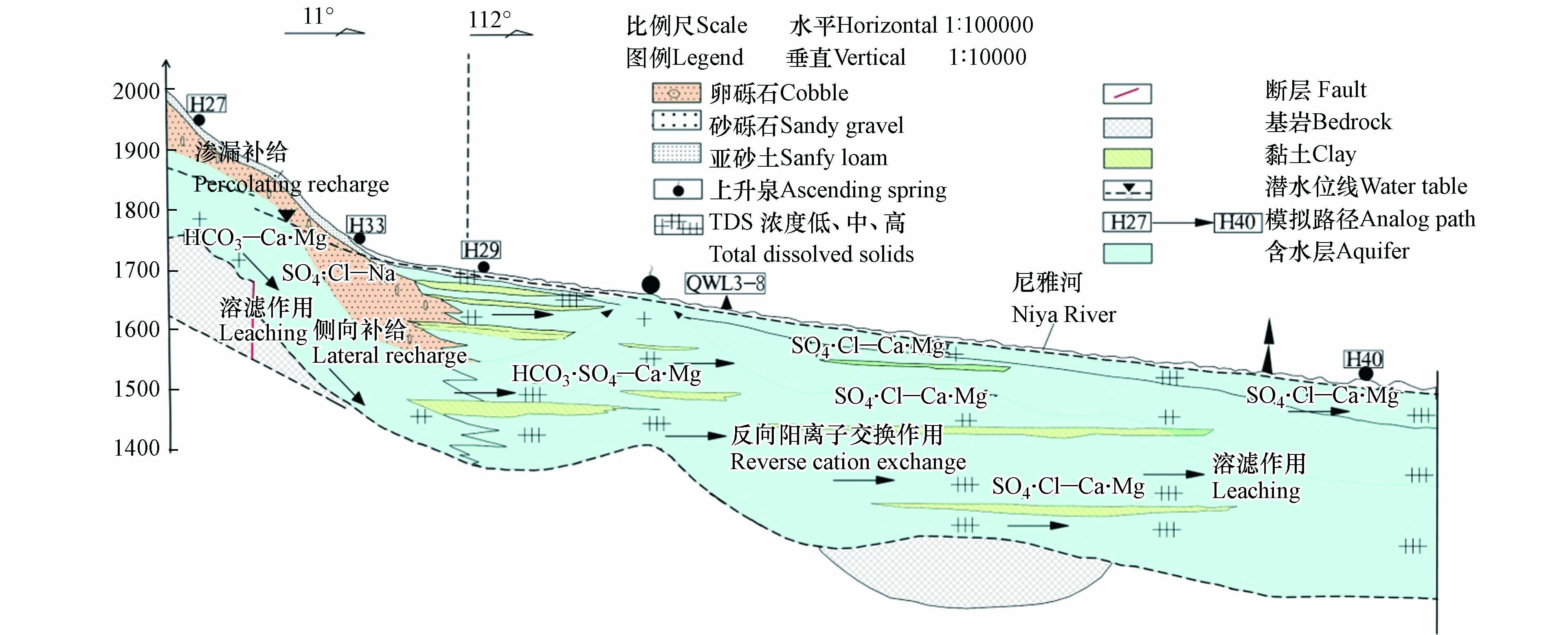
-
在我国西北干旱半干旱地区,地下水是农业灌溉、工业和生活用水的重要水资源[1]。新疆维吾尔自治区(以下简称“新疆”)和田地区地下水水质较差,具体表现在总硬度、氟化物、硫酸盐、氯化物和氨氮严重超标[2-4]。研究地下水化学特征演化规律对帮助了解地下水水质、地下水资源的保护和支持地下水的可持续性利用等具有重要意义[5]。地下水水化学提供了地下水组成的化学指示,揭示了地下水的潜在补给源、循环路径和水文地球化学演化规律[6]。
学者们通过数理统计与地统计法、同位素示踪法、离子比例系数和水文地球化学模拟等方法对地下水水化学特征及演化规律进行研究。Wen等[7]运用离子比例系数、数理统计与地统计等方法对启东市海岸带地下水水化学演化规律进行研究,得出海水入侵和水岩作用是地下水水化学演化规律的主要控制因素;Xiong等[8]通过同位素法和水文地球化学模拟相结合对大沽河含水层水化学演化进行分析,得出海水入侵和人类活动是地下水水化学演化的主要控制因素;李华等[9]利用氢氧同位素、水文地球化学模拟方法对贵阳市三桥地区岩溶地下水水化学演化进行研究,得出岩石溶滤和阳离子交替吸附作用为控制地下水水化学演化的主要因素;Li等[10]利用水文地球化学法和多同位素法相结合对珠江三角洲地下水水化学演化规律进行研究,得出岩石风化是地下水水化学演化的主导机制。Wen等[7]研究结论仅基于零碎的水化学数据,而且深度不够,因为在快速城市化的受污染的地下水环境中,会导致复杂的反应过程发生(例如阳离子交换作用和反硝化作用),从而显著地改变地下水的化学性质;Xiong等[8]和李华等[9]利用同位素和水文地球化学模拟方法,探索溶解成分来源,更加定量化和系统化地分析整个地下水水化学演化过程,提升了研究深度。
近年来,许多学者对和田地区地下水开展了多方面的研究工作:如地下水水资源分布研究[11-12]、地下水水化学特征及成因研究[13-14]和地下水水质评价研究[2-4]等,但对于区域性地下水化学特征及演化规律的定量研究较少。本文以新疆和田地区东部平原区为研究区,运用水文地球化学、因子分析和水文地球化学反向模拟等方法,探讨地下水化学特征及演化规律,以期为该地区地下水合理开发利用与有效保护提供科学依据。
-
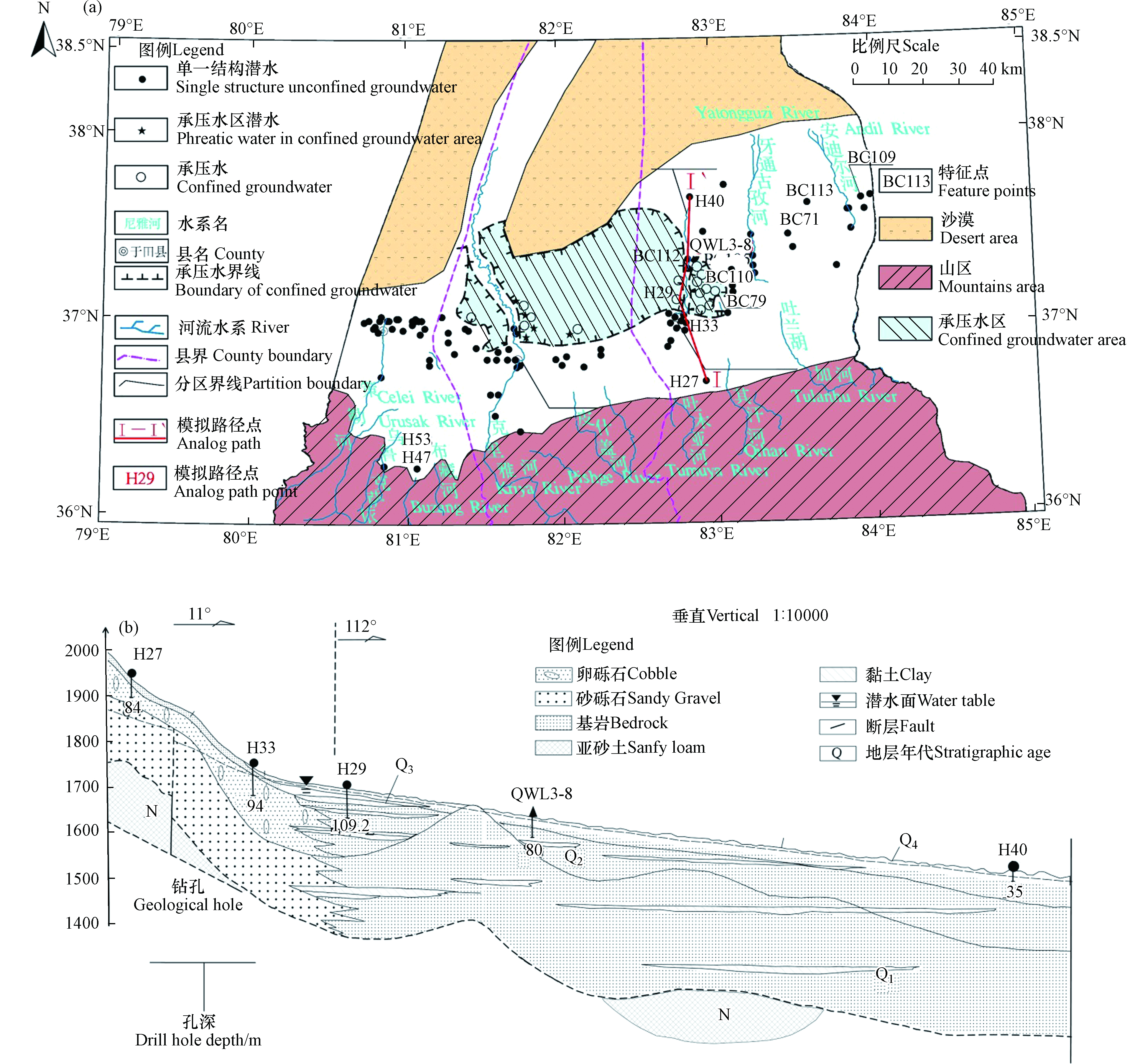
和田地区东部位于新疆塔里木盆地南缘,昆仑山北麓,南部多山区,北部为塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地,地势北低南高,并由西向东缓倾。地理坐标为75°00′— 85°00′E,36°00′— 38°30′N,该地区包括策勒县、于田县和民丰县。该区属暖温带大陆干燥沙漠气候,四季分明,光热资源丰富,年日照时数高达2896 h,降水稀少,年平均降水量为35.6 mm,地表蒸发强烈,实测年蒸发能力高达3137 mm[11]。
研究区地表覆盖了巨厚的第四系松散堆积物,其地层岩性为全新统(Q4)、上更新统(Q3)、中更新统(Q2)和下更新统(Q1)(图1(b)),赋存第四系松散岩类孔隙地下水。含水层岩性沉积规律自南部的单一卵砾石向北部逐步演替为砂砾石、中粗砂、粉细砂、亚砂土和亚黏土,颗粒逐渐变细,层次逐渐增多的多层含水层结构[12]。研究区克里亚河诸小河流域水系各出山口河流从南汇入平原区,形成自南向北贯穿的地下水循环系统。研究区主要以单一结构潜水区为主(地下水埋深大于5 m),仅于田县至民丰县以北少部分区域为上层潜水—下层承压水的双层或多层结构含水层(地下水埋深5—150 m)(图1(a))。
山前倾斜平原为研究区地下水补给区,主要来自河流渗漏补给、渠系及田间灌溉水的入渗补给,其次有少量山区基岩裂隙水的侧向补给;地下水流向与地形坡降一致,径流方向总体由南向北,含水介质较粗,以卵砾石、砂砾石为主,透水性较好,水力坡度较大,约为1‰—4‰(图2)。中下游冲洪积平原与沙漠毗邻,含水层介质变细,以砂、亚砂土和亚粘土为主,地势变缓,水力坡度小于1‰,为地下水主要排泄区[13-14]。排泄方式主要为人工开采、泉水溢出、强烈的地面蒸发、植物蒸腾及向下游的侧向流出等[15]。
-
采样时间为2018年9—10月,根据《地下水环境监测技术规范(HJ/T164—2004)》共采集地下水水样116组(井深5—150 m);其中,单一结构潜水96组、承压水区潜水5组、承压水15组。采集时,聚乙烯水样瓶用所取水样润洗3次;采集后,在现场用0.45 μm的醋酸纤维滤膜过滤,分析的阳离子水样加入硝酸酸化至pH<2,测试前在4 ℃下密封保存。现场测定pH和水温等指标,测定精度分别为0.01℃和1.0 ℃。
各水化学指标(K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、总硬度(以CaCO3计,TH)、Cl−、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ 、${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ 、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和总溶解性固体(TDS)等)由新疆地勘局第二水文地质工程地质大队化验室严格按照《生活饮用水卫生标准(GB5749—2006)》检测完成。其中,K+和Na+测定为火焰原子吸收分光光度法,Ca2+、Mg2+和TH测试为EDTA-2Na滴定法,Cl−测定为硝酸银容量法,${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ 和$ {\rm{CO}}_3^{2-}$ 测定为酸碱滴定法,$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{2-}$ 测定为硫酸钡比浊法,TDS测定为重量法测定。各离子检测下限除TH、${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ 和TDS为0.1 mg·L−1,其余离子均为0.01 mg·L−1。研究区地下水检测数据采用阴阳离子电荷平衡方法进行可靠性检验,计算结果得出误差<5%,说明数据可靠。 -
2018年116组研究区地下水水样的水化学指标统计见表1。研究区地下水总体呈中性或偏碱性,潜水pH值范围为7.11—9.63,均值为8.05;承压水pH值范围为7.12—8.40,均值为8.05。地下水中K++Na+、Cl−、
$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 、TH和TDS浓度变化范围较大,分别为19.37—8848.90、56.36—13462.92、36.62—3954.03、82.05—8913.20、108.60—6549.30 、198.5—41282.7 mg·L−1(表1)。根据《地下水质量标准(GB/T14848—2017)》,高硬度地下水(TH>450 mg·L−1)水样占比58.4%,高咸水地下水(TDS>1000 mg·L−1)水样占比69.6%;说明研究区地下水为高硬度高咸水。研究区地下水各离子均值关系为Na++K+>Mg2+>Ca2+,Cl−>
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ >${\rm{HSO}}_4^{ - } $ (表1),说明地下水中阳离子以Na++K+和Mg2+为主,阴离子以Cl−和SO42−为主;研究区地下水中TH、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 、Cl−含量和TDS的均值具有单一结构潜水>承压水区潜水>承压水的特点。鉴于承压水区潜水富水性较差, 取样点较少(只有5个),样本容量少代表性不明显,且前人研究表明,其水质较差(表1)[2-3]。因此,本文以下地下水化学类型、地下水化学组分来源、地下水水化学控制因素和典型剖面反向模拟部分,仅讨论单一结构潜水和承压水的水化学类型及空间演化规律。 -
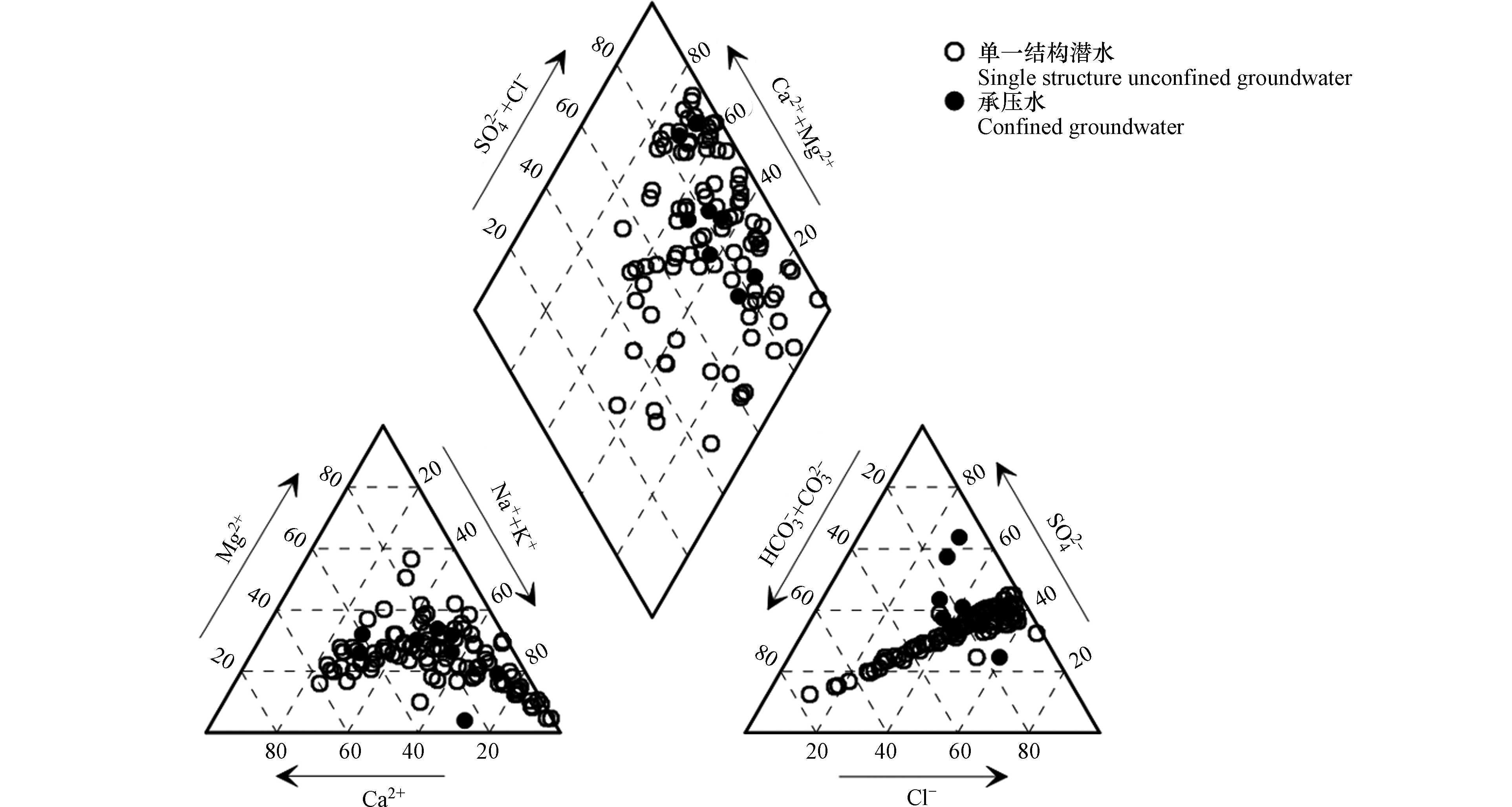
Piper三线图(图3)可以不受人为因素影响,直观地反应研究区地下水水化学总体特征及类型[16]。根据图3可以看出,水样点位于阳离子三角形中、右下部,Na+、Mg2+含量最多,Ca2+次之;阴离子三角形中右部分布的水样点最多,Cl−含量最多,SO42−和HCO3−次之。单一结构潜水水化学类型主要以Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na·Mg·Ca型水(72.9%)和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水(15.6%)为主;承压水水化学类型主要以SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型水(68.8%)和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水(25.0%)为主。
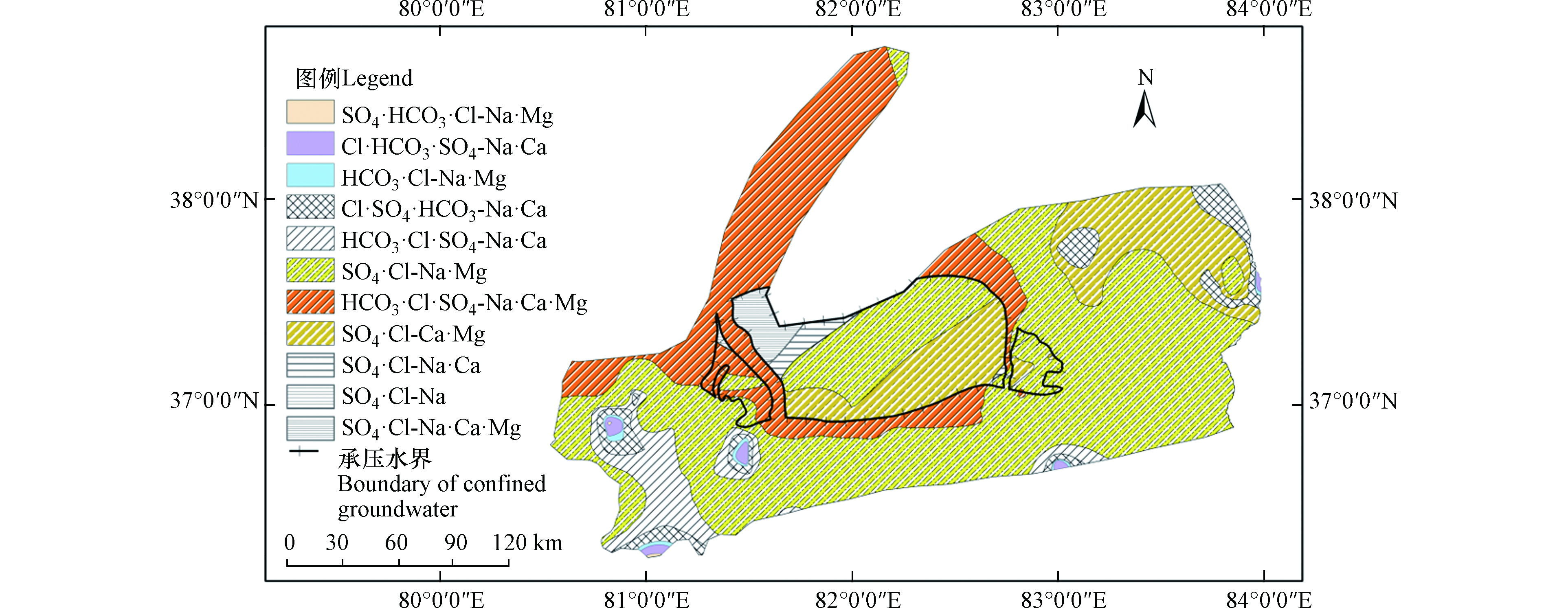
由研究区地下水水化学类型分区图(图4)可知,空间分布上,研究区单一结构潜水水化学类型从西部平原以HCO3·Cl·SO4-Na·Ca型、HCO3·Cl·SO4-Na·Ca·Ma型和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型为主,逐渐过渡到中部平原以HCO3·Cl·SO4-Na·Ca·Ma型和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型为主,最终演化为东部平原的SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型和SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型为主;承压水水化学类型由南向北则由SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型过渡到SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型。
-
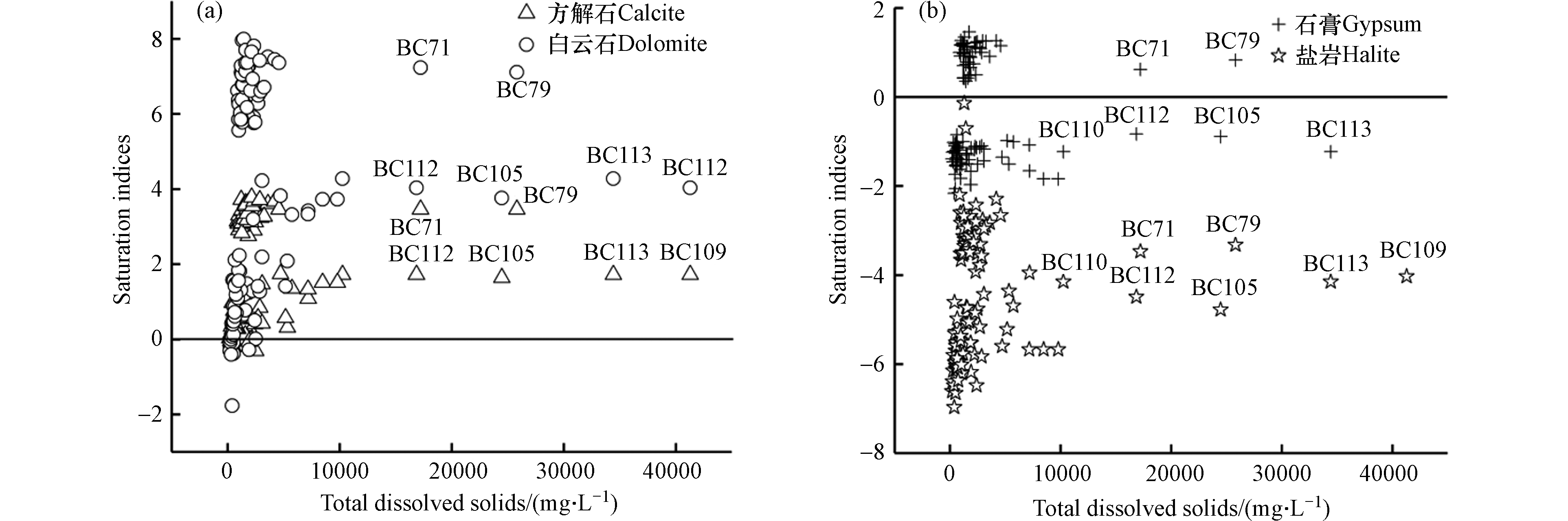
水化学组分变化的主要影响因素首先是离子来源,其次是水文地球化学反应过程,分析不同离子之间的比值关系可揭示其水化学组分来源[17]。从γNa+ /γCa2+、γNa+/γMg2+与γNa+/γHCO3−摩尔浓度比值端元图(图5)可以看出,研究区地下水样点分布于硅酸盐岩端元和蒸发盐岩端元,远离碳酸盐岩端元;说明地下水化学组分主要由硅酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩(石膏、岩盐)所溶解导致,与研究区含水层介质中碳酸盐岩很少相符[18-19]。矿物饱和指数(SI)对于揭示地下水中离子来源具有引导性,SI值大于0,表明矿物处于饱和状态,趋于沉淀;反之,处于溶解状态,趋于溶解[20-21]。图6中89.42%地下水样的方解石、白云石饱和指数(SIDolomit、SICalcite)均大于0,55.80%的地下水样的石膏饱和指数(SIGypsum)小于0,所有水样的岩盐饱和指数(SIHalite)均小于0;说明研究区方解石、白云石处于过饱和状态,石膏和岩盐处于溶解状态,且岩盐一直属于溶解状态,这也是研究区地下水TH和TDS超标的重要因素。
综上,研究区地下水中Ca2+和
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 、Cl−和Na+组分主要受蒸发盐岩(石膏、岩盐)和硅酸盐岩的溶解控制。对比分析图5和图6,在局部地区可能由于蒸发盐岩(石膏)和硅酸盐风化溶解过程中过量输入Ca2+和Mg2+导致碳酸盐岩达到过饱和状态,白云石和方解石等碳酸盐矿物趋于沉淀。 -
因子分析法可以在损失较少信息基础上对地下水水化学各指标内在联系和水化学特征形成规律进行分析,从而提取出地下水水化学特征的成因及演化规律[22]。因子分析前,对研究区单一结构潜水和承压水的111组地下水样的11项水化学指标进行检验,其Bartlett球形检验显著性水平小于0.01,单一结构潜水和承压水的KMO(kaiser-meyer-olkin)检验值分别为0.690和0.525,表明水样数据可用因子分析法分析[23]。利用最大方差法对各因子旋转计算得到旋转因子载荷矩阵,公因子与指标间相关性,按载荷值的绝对值表现,按公因子特征值大于1标准提取3个公因子可知,考虑因子载荷大于0.7的指标可知[24]:
(1)因子F1在单一结构潜水和承压水中分别占比44.0%和41.7%,单一结构潜水中K++Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 、TDS及TH为主要载荷,TDS载荷最高(0.98,表3),且相互之间相关性较好(表2),反映蒸发浓缩与岩石溶滤双重作用导致的蒸发盐岩(石膏、岩盐)矿物溶解对水化学组分影响。这主要是沿地下水流向,单一结构潜水埋深变浅,蒸发浓缩作用加强,易溶盐分冲洗进入地下水中;同时,由图6知石膏和岩盐处于溶解状态,且岩盐一直属于溶解状态,即石膏和岩盐矿物溶解造成对水化学组分的影响。承压水中K++Na+、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 -} $ 、${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 和TDS为主要载荷,且K++Na+、${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 和TDS三者之间相关性较强,即代表岩盐溶解导致水中Cl−和K++Na+浓度增大;从而影响了地下水碳酸盐矿物和石膏的溶解。因此,该因子代表单一结构潜水中蒸发浓缩与岩石溶滤双重作用导致的蒸发岩(石膏、岩盐)矿物溶解,承压水中岩盐等矿物溶滤对地下水水化学组分的影响。
(2)因子F2,在单一结构潜水和承压水中分别占比27.0%和33.8%(表3)。单一结构潜水中
${\rm{NO}}_3^- $ 、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 和pH为主要载荷,说明农业、生活及工业等人类活动对地下水化学组分的控制。这主要是研究区内大量施用农肥[2-4],农肥中的氮肥($ {\rm{NO}}_3^- $ )经过包气带淋滤进入含水层;中下游潜水埋深浅甚至出露,地下水系统处于开放状态,同时,离村镇较近,大量Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 输入。承压水中Ca2+、Mg2+、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 及TH为主要载荷,且${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 与Mg2+、TH无明显相关性,仅与Ca2+相关(表2);说明地下水水化学组分可能来自上层潜水的越流补给和石膏的溶解的影响。因此,该因子代表石膏溶解和人类活动对地下水化学组分的影响。(3)因子F3贡献率,在单一结构潜水和承压水中均占比13.31%(表3);单一结构潜水中HCO3−和pH为主要载荷,且
$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 和TH呈现强相关性;说明水环境酸碱性对地下水化学组分的影响。这主要是潜水含水层受降水和河流补给后,含水层中CO2分压升高,CO2浓度升高后与含水介质中的碳酸盐(白云石)发生化学反应,导致水中Ca2+、Mg2+和${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ >浓度增大,从而导致TH和TDS升高[25]。承压水载荷值中pH最大,且与因子F3表现出强烈的负相关,说明水环境酸碱性对地下水化学组分影响。因此,该因子代表水环境酸碱性对地下水水化学组分的影响。 -
绘制主因子得分图(图7),根据主因子得分在图中分布情况,可以反映地下水化学特征及其演化规律[26-27]。图7(a)中位于左上角地下水样点最多,因子F1得分高,代表地下水化学组分主要受因子F1控制。图7(b)中位于左下角地下水样点最多,位于左上角地下水样点占一定比例,说明地下水化学组分受因子F2一定影响,因子F3则相对较小。
综上,研究区地下水化学组分主要受因子F1控制,其次为F2影响,说明水化学组分受蒸发浓缩与岩石溶滤双重作用导致的蒸发盐岩(岩盐、石膏)溶解所控制,同时人类活动输入有一定的影响;而承压水则受石膏溶解和阳离子交换作用影响。
-
Gibbs图(图8)可以定性地将水化学组分的起源机制及演化过程判断为大气降水、岩石溶滤和蒸发浓缩作用所控制[28]。
单一结构潜水和承压水的TDS变化范围分别为198.50—41282.73 mg·L−1、522.57—10429.74 mg·L−1,其阴阳离子浓度比值范围分别为0.25—1.00、0.40—0.90和0.30—0.90、0.35—0.90,均分布在Gibbs图中上部;表明其水化学起源、组成及演化机制主要受岩石溶滤和蒸发浓缩共同作用控制。Gibbs图中无水样点位于图形下部,说明研究区地下水水化学组分基本不受大气降水作用控制。另有部分地下水样点落在Gibbs图外,说明研究区单一结构潜水可能受到一定程度的人类活动影响,而承压水则可能受阳离子交换作用影响[29]。
-
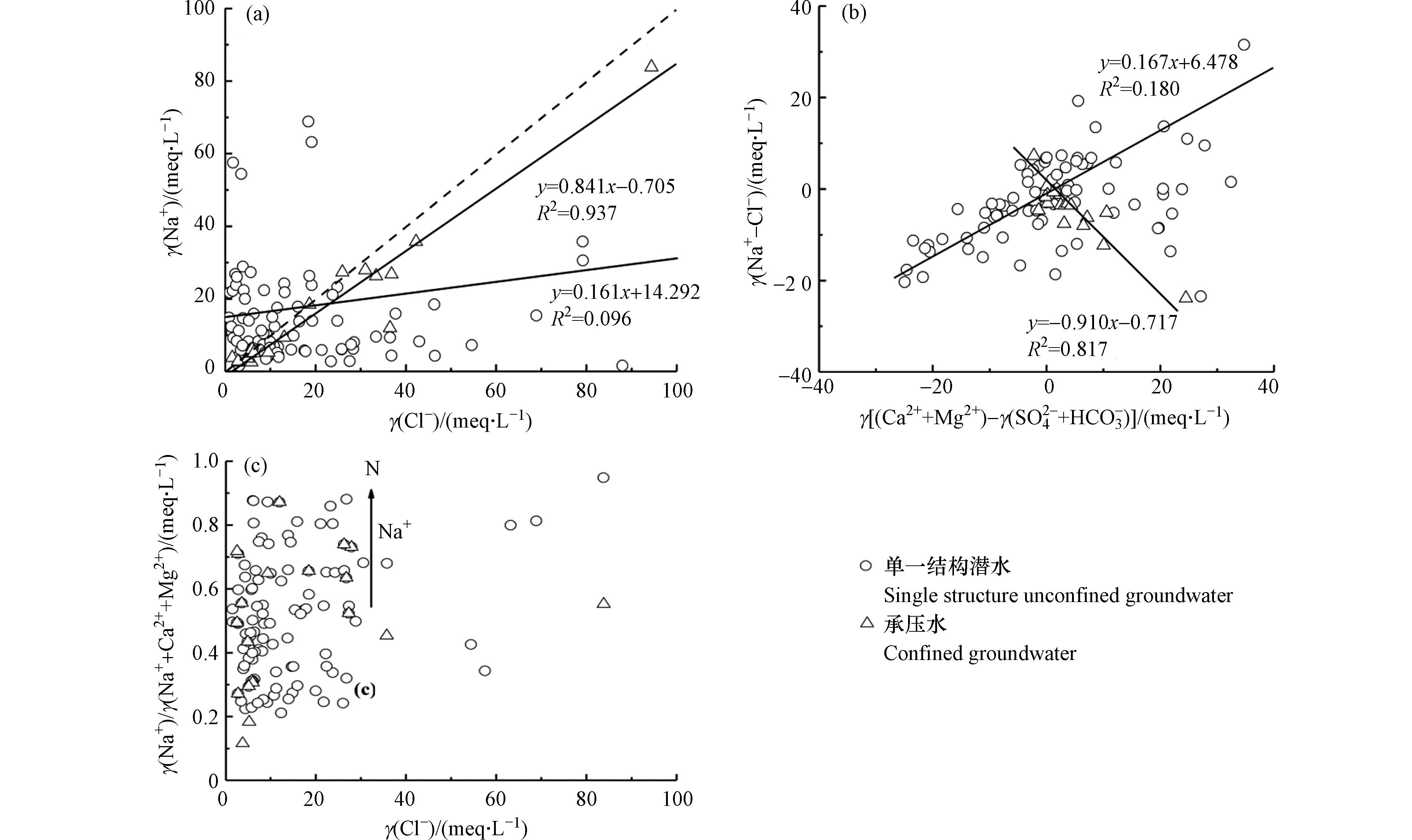
地下水γ(Na++K+)/γ(Cl−)比值图(图9(a))中,57.79%的单一潜水水样点和85.00%的承压水水样点位于1∶1线上方,其余水样点分布于1∶1线下方,且单一结构潜水中Na+与Cl−呈强相关性(R2=0.937),说明单一结构潜水中Na+、Cl−主要来源于岩盐溶解,承压水中还存在阳离子交换反应的影响,使得Na+浓度大于Cl−浓度[30]。引入γ(Mg2++Ca2+-
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 } $ -$ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ )与γ(Na+-Cl−)的比值关系判断承压水是否发生阳离子交换作用,若两者比值在−1左右,则发生反向阳离子交换作用[31]。图9(b)显示,研究区承压水γ(Mg2++Ca2+-${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ -${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ )与γ(Na+-Cl−)呈显著负相关(R2=0.817),且比值在−1左右,说明承压水发生反向阳离子交换反应。另从γ(Na+)/γ(Na++Ca2++Mg2+)与γ(Cl−)关系图可知(图9(c)),沿地下水流向由南向北流动,为多层承压水含水层结构,地下水径流条件差,在含水层中滞留时间长,水岩作用充足,且沉积物颗粒细比表面积大,使得水中Ca2+、Mg2+与含水介质中Na+发生阳离子交换作用,导致承压水中的Na+浓度高于Cl−[32]。 -
利用PHREEQC软件可定量反向模拟各种水文地球化学过程和人为活动影响下的水岩相互作用[33]。沿地下水流向选定Ⅰ—Ⅰ'典型剖面为模拟路径:H27→H33→H29→QWL3-8→H40,其中H27→H33、QWL3-8→H40为潜水路径,H33→H29、H29→QWL3-8为承压水路径(图9)。该模型中根据研究区第四系含水层中主要矿物和111组实测水质数据进行可能矿物相的分析,将岩盐、方解石、白云石及石膏选取为“可能矿物相”[34]。潜水埋藏浅处于开放状态,故将CO2作为潜水路径中“可能矿物相”;而承压水埋藏深处于封闭状态,CO2几乎不参与水文地球化学过程;同时,因承压水含水介质颗粒细其比表面积大,阳离子交换作用强,将CaX2和NaX作为承压水路径中“可能矿物相”[35]。
由模拟结果可知(表4),潜水路径经历了岩盐、方解石、白云石和石膏的溶解作用;随石膏的溶解(−3.19→24.81 mmol·L−1),潜水中Ca2+含量增加,方解石发生沉淀作用(4.01×10−4→−9.8×10−3 mmol·L−1),且随石膏的溶解量增大,方解石的沉淀量随之增大,这与水化学组分来源分析相一致。研究区中下游河流冲积平原,潜水埋藏变浅,受蒸发浓缩作用影响,水中各组分含量增高(对比路径H27→H33与QWL3-8→H40摩尔转移量可知),受降水补给CO2迁入水中(−1.73×10−4→3.34×10−3 mmol·L−1);潜水—承压水路径中岩盐、白云石和石膏一直处于溶解状态。且沿地下水流向,承压水中反向阳离子交换作用强烈,使得水中Ca2+含量降低、Na+含量升高,对比潜水—承压水路径H33→H29→QWL3-8中CaX2和NaX的摩尔转移量(−2.55×10−4→−3.47×10−3、5.11×10−4→6.93×10−3 mmol·L−1),水中Ca2+和Mg2+浓度变化分别为220.66→81.18→21.72 mg·L−1、41.15→71.00→1057.59 mg·L−1,与模拟结果相一致。
-
研究区典型剖面水文地球化学演化过程见图10。山前倾斜平原单一结构潜水受河流渗漏补给,水力坡度较大,从南向北径流与河流流向一致;径流过程中主要发生溶滤作用,为HCO3-Ca·Mg型低TDS水。
中下游河流冲积平原潜水主要受上游潜水侧向径流补给,径流过程中受溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩作用,为SO4·Cl-Na型中TDS水;沿径流路径,水中离子总量累积,同时在地下水埋深较浅区域,受到蒸发浓缩作用强烈,为SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型高TDS水。潜水与承压水水力联系较密切,两者水化学类型相似;因承压水含水介质较细,发生强烈的反向阳离子交换作用,使得承压水中的Ca2+浓度降低,Na+浓度升高;水化学类型由SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型演变为SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型(图10)。
-
(1)研究区地下水中Na+和Mg2+为主要阳离子,Cl−和
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 为主要阴离子,单一结构潜水水化学类型以Cl·SO4·HCO3-Na·Mg·Ca型水(72.9%)和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水(15.6%)为主,承压水水化学类型主要以SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型水(68.8%)和SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型水(25.0%)为主。pH呈中性或偏碱性,高咸水水样占比64.0%,高硬度水样占比58.4%,总体为高硬度高咸水。地下水中TH、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ 、Cl−含量和TDS的均值具有单一结构潜水>承压水区潜水>浅层承压水的特点。(2)研究区地下水水化学组分主要受渗漏补给、溶滤作用、反向阳离子交换作用和蒸发浓缩作用影响。因子分析表明单一结构潜水水化学组分受蒸发浓缩作用与溶滤双重作用导致的蒸发岩(岩盐、石膏)及碳酸盐岩(白云石、方解石)溶解所影响,同时人为活动输出有一定的影响;而承压水水化学组分则受反向阳离子交换作用影响。水中离子主要来源于蒸发岩(岩盐、石膏)的溶解,其次为硅酸盐和碳酸盐的溶解。
(3)典型剖面地下水反向模拟表明:沿地下水流向,水中离子总量累积;岩盐、白云石和石膏均呈溶解趋势,方解石呈沉淀趋势;潜水中发生溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩作用,承压水中发生反向阳离子交换作用。
新疆和田东部平原区地下水化学特征及演化规律
Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the eastern plain of Hotian Prefecture, Xinjiang
-
摘要: 以2018年新疆和田东部平原区116组地下水水质检测数据为基础,综合运用因子分析、Piper三线图、Gibbs模型、离子比值法和水文地球化学模拟等方法对其水化学特征及演化规律进行分析。结果表明:研究区地下水中Na+和Mg2+为主要阳离子,Cl−和
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 为主要阴离子,地下水类型为SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg型高硬度高咸水;因子分析表明该区地下水水化学组分受岩石溶滤作用和蒸发浓缩作用控制;水中离子主要来源于蒸发盐岩的溶解,其次为碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩的溶解。单一结构潜水主要受蒸发浓缩作用、岩石溶滤作用和人类活动等因素影响,承压水受阳离子交换作用影响。水文地球化学模拟结果表明:沿地下水流向,水中离子总量累积,岩盐、白云石和石膏发生溶解,方解石发生沉淀。Abstract: Based on the groundwater quality test data of 116 groups in the eastern plains area of Hotian Prefecture, Xinjiang in 2018, the chemical characteristics and evolution law of groundwater were comprehensively analyzed by means of factor analysis, Piper trigraph, Gibbs model, ion ratio and hydrogeochemical simulation. The results showed that: Na+ and Mg2+ were the main cations the groundwater. Cl− and${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ were the main anions in the groundwater, and the groundwater hydrochemistry type was SO4·Cl—Ca·Mg type high hardness and salt water. Factor analysis showed that the chemical composition of groundwater was controlled by dissolution of rocks and evaporation concentration. The groundwater ions were mainly derived from the dissolution of evaporates rocks, followed by the dissolution of evaporates and carbonates. Single structure unconfined groundwater was mainly affected by evaporation and concentration, dissolution of rocks and human activities while the confined groundwater was affected by cation exchange. Along the groundwater flow direction, the hydrogeochemical simulation results indicate that the total amount of ions in the groundwater accumulated. Halite, dolomite, and gypsum were dissolved, and calcite was precipitated. -

-
表 1 研究区地下水水化学描述性统计
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of hydrochemistry in groundwater in the study area(N=116)
含水层类型
Aquifer type统计量 pH K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $ TH TDS Statistics 单一结构潜水
Single structure unconfined groundwater
(N=96)最小值 Minimum 7.10 26.10 12.00 6.60 14.40 19.00 36.60 0.10 111.60 198.50 最大值 Maximum 9.60 14160.40 702.10 1308.00 14348.60 9889.70 3954.00 46.90 6549.30 41282.70 均值 Mean 8.10 915.90 114.20 135.90 1113.50 920.80 406.20 9.30 844.80 3433.20 标准差 Standard deviation 0.41 2152.37 103.92 209.29 2293.81 1445.66 499.63 10.88 1064.45 6626.08 变异系数 Coefficient of variation 0.05 2.35 0.91 1.54 2.06 1.57 1.23 1.17 1.26 1.93 承压水区潜水
Unconfined groundwater in confined area
(N=5)最小值Minimum 7.40 445.40 33.30 44.50 182.80 389.10 158.70 0.80 266.20 1260.90 最大值 Maximum 8.40 996.60 99.60 195.00 951.30 850.40 963.30 15.90 1052.00 3597.00 均值 Mean 8.00 781.50 78.30 105.20 629.70 581.70 597.80 5.10 628.70 2369.40 标准差 Standard deviation 0.32 359.49 23.49 54.70 295.96 162.88 448.35 5.76 264.05 781.90 变异系数 Coefficient of variation 0.04 0.46 0.30 0.52 0.47 0.28 0.75 1.13 0.42 0.33 承压水
Confined groundwater
(N=15)最小值Minimum 7.12 134.70 15.90 11.80 91.50 183.40 96.50 0.20 113.60 506.30 最大值 Maximum 8.40 2363.80 396.20 690.70 2976.00 3607.60 390.60 3.90 3786.30 10249.70 均值 Mean 8.00 484.20 112.50 137.10 552.90 736.50 351.00 5.30 824.70 2212.20 标准差 Standard deviation 0.40 658.51 106.88 175.49 785.12 898.53 266.76 7.95 973.15 2632.52 变异系数 Coefficient of variation 0.05 1.36 0.95 1.28 1.42 1.22 0.76 1.50 1.18 1.19 注:N为样品数;pH为无量纲,其余指标单位均为mg·L−1。
Note: N is groundwater sample number; pH is dimensionless; units of other parameter are mg·L−1.表 2 地下水水化学指标的旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 2. Rotation factor loading matrix of groundwater
指标
Parameters单一结构潜水
Single structure unconfined groundwater承压水
Confined groundwaterF1 F2 F3 F1 F2 F3 K++Na+ 0.86 0.23 0.36 0.73 0.44 −0.31 Ca2+ 1.86 −0.34 −0.34 0.06 0.89 0.12 Mg2+ 2.86 −0.01 0.03 0.37 0.75 −0.18 Cl− 3.86 0.92 0.03 0.81 0.43 0.15 $ {\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 4.86 0.95 0.01 0.62 0.77 0.01 $ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 5.86 0.32 0.70 0.84 −0.12 −0.19 $ {\rm{NO}}_3^{ - }$ 6.86 0.70 0.57 −0.15 −0.28 0−0.43 TDS 7.86 0.26 0.41 0.98 0.43 0.03 TH 8.86 −0.09 −0 .05 0.46 0.87 −0.1 pH 9.86 −0.83 −0.97 −0.08 −0.04 −0.93 贡献率/%
Contribution rate44.00 27.02 13.31 41.66 33.77 13.31 累计贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate44.00 71.02 84.33 41.66 75.43 88.74 表 3 地下水中各水化学组分Pearson相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficients among chemical constituents in groundwater
K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{ - } $ TDS TH pH K++Na+ 1 Ca2+ 0.258** 1 Mg2+ 0.810** 0.700** 1 Cl− 0.301** −0.178 0.054 1 $ {\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ 0.296** −0.212* 0.042 0.978** 1 $ {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $ 0.864** 0.051 0.623** 0.321** 0.304** 1 $ {\rm{NO}}_3^{2 - }$ 0.034 0.114 0.044 −0.082 −0.101 0.088 1 TDS 0.988** 0.382** 0.829** 0.250* 0.239* 0.817** 0.045 1 TH 0.665** 0.814** 0.985** 0.001 −0.018 0.437** 0.063 0.768** 1 pH 0.259** -0.259** 0.047 0.634** 0.705** 0.163 −0.165 0.218* 0.028 1 注:*显著性水平为0.05(显著);**显著性水平为0.01(极显著)。
Note: *Means the significance level is 0.05(significant); **Means the significance level is 0.01 (extremely significant).表 4 潜水、承压水路径反向模拟结果
Table 4. Reverse simulation results of unconfined groundwater and confined groundwater routes
矿物相
Mineral phase化学式
Chemical formulation潜水路径
Unconfined groundwater route潜水—承压水路径
Confined groundwater routeH27→H33 QWL3-8→H40 H33→H29 H29→QWL3-8 岩盐Halite NaCl 2.05×10−4 3.99×10−3 1.45×10−3 2.61×10−2 方解石Calcite CaCO3 4.01×10−4 −9.80×10−3 −1.25×10−3 −3.84×10−3 白云石Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 1.09×10−4 6.27×10−3 5.24×10−4 2.59×10−3 石膏Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O −3.19 24.87 6.02 −1.05×102 CO2 CO2 −1.73×10−4 3.34×10−3 — — 阳离子交换
Cation exchangeCaX2 — — −2.55×10−4 −3.47×10−3 NaX — — 5.11×10−4 6.93×10−3 注:上述数值为摩尔转移量,正值代表溶解,负值代表沉淀;“—”代表矿物未参与反应。
Note: The above value is the molar transfer. Positive value means solution. Negative value means precipitate. “—” Means mineral nonparticipation in the reaction. -
[1] LIN J, MA R, HU Y L, et al. Groundwater sustainability and groundwater/surface-water interaction in arid Dunhuang Basin, northwest China [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26(11): 1559-1572. [2] 曾妍妍, 吴津蓉, 周金龙, 等. 新疆和田地区地下水质量与污染现状评价 [J]. 人民黄河, 2015, 37(7): 79-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2015.07.020 ZENG Y Y, WU J R, ZHOU J L, et al. Assessment of groundwater quality and pollution in Hotan Region of Xinjiang [J]. Yellow River, 2015, 37(7): 79-81(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2015.07.020
[3] FAN W, ZHOU J L, ZHOU Y Z, et al. Water quality and health risk assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern margin of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang, P. R. China [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment:An International Journal, 2020(5): 1-21. [4] 李玲, 周金龙, 齐万秋, 等. 和田河流域绿洲区地下水“三氮”污染状况及影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(2): 395-403. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018040601 LI L, ZHOU J L, QI W Q, et al. Pollution status and influencing factors of “Three-Nitrogen” in groundwater of oasis area in Hotan River Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(2): 395-403(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018040601
[5] 刘江涛, 蔡五田, 曹月婷, 等. 沁河冲洪积扇地下水水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(12): 5428-5439. LIU J T, CAI W T, CAO Y T, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and the origin in Alluvial proluvial Fan of Qinhe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(12): 5428-5439(in Chinese).
[6] CHRISTOS C, BRUGGEMAN A, KUELLS C, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in gabbro of the Troodos Fractured Aquifer. A comprehensive approach [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 114: 104524-104543. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104524 [7] WEN Y, QIU J H, CHENG S, et al. Hydrochemical evolution mechanisms of shallow groundwater and its quality assessment in the estuarine coastal zone: A case study of Qidong, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020, 17(10): 3382-3407. [8] XIONG G Y, AN Q X, FU T F, et al. Evolution analysis and environmental management of intruded aquifers of the Dagu River Basin of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719(1): 137260-137274. [9] 李华, 文章, 谢先军, 等. 贵阳市三桥地区岩溶地下水水化学特征及其演化规律 [J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 804-812. LI H, WEN Z, XIE X J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of Karst groundwater in Sanqiao District of Guiyang City [J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 804-812(in Chinese).
[10] LI X, TANG C Y, CAO Y J, et al. A multiple isotope (H, O, N, C and S) approach to elucidate the hydrochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in a rapidly urbanized area of the Pearl River Delta, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 724: 137930-137943. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137930 [11] 刘敏. 和田绿洲地下水时空分布规律及其生态环境效应研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2007. LIU M. Study on groundwater spatiotemporal distribution Law and its environmental effects in Hotan oasis[D]. Xi`an: Xi`an University of Technology, 2007(in Chinese).
[12] 马金珠. 新疆和田地区地下水资源及其可持续开发利用 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2002, 22(3): 41-47. MA J Z. Groundwater resources and its sustainable development in Hotan Region, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2002, 22(3): 41-47(in Chinese).
[13] 张艳丽. 和田县(市)地下水水化学基本特征 [J]. 新疆地质, 2008, 26(2): 184-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2008.02.015 ZHANG Y L. Basic hydro-chemical features of groundwater in Hetian County [J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2008, 26(2): 184-188(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2008.02.015
[14] 李玲, 周金龙, 齐万秋, 等. 新疆和田河流域绿洲区浅层地下水水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(3): 14-20. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.03.03 LI L, ZHOU J L, QI W Q, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation reasons of shallow groundwater in oasis area of Hotian River Basin, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(3): 14-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.03.03
[15] 代述勇, 雷加强, 赵景峰, 等. 塔里木盆地南缘策勒绿洲区地下水TDS空间变异及水化学特征分析 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(3): 722-729. DAI S Y, LEI J Q, ZHAO J F, et al. TDS-spatial variability and chemical characteristics of groundwater in cele oasis of the Sounthern Tarim Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(3): 722-729(in Chinese).
[16] PIPER A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses [J]. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 1944, 24: 914-923. [17] 寇永朝, 华琨, 李洲, 等. 泾河支流地表水地下水的水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7): 3142-3149. KOU Y C, HUA K, LI ZHOU, et al. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the surface water and groundwater of the Jinghe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(7): 3142-3149(in Chinese).
[18] 范薇, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 塔里木沙漠公路沿线浅层地下水化学特征 [J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2019, 17(2): 157-165. FAN W, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater along the Tarim Desert highway [J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2019, 17(2): 157-165(in Chinese).
[19] 李玲, 周金龙, 齐万秋, 等. 和田河流域绿洲区地下水中氟的分布特征及形成过程 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(1): 112-118. LI L, ZHOU J L, QI W Q, et al. Distribution and formation process of fluorine in groundwater in oasis area of Hotan River basin [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(1): 112-118(in Chinese).
[20] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水SO42−化学特征及来源 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3550-3558. WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Chemical characteristics and sources if groundwater sulfate in the Kashgar Delta, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8): 3550-3558(in Chinese).
[21] 林韵, 高磊, 李绍恒, 等. 广东江门地热水水文地球化学特征及来源分析[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(2): 512-523. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and source identification of geothermal waters in Jiangmen, Guangdong Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(2): 512-513(in Chinese).
[22] KAZAKIS N, MATTAS C, PAVLOU A, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis for the assessment of groundwater quality under different hydrogeological regimes [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(9): 1-13. [23] MANOJ K, RAMANATHAN A L, RITU T,et al. R, RITU T, et al. A study of trace element contamination using multivariate statistical techniques and health risk assessment in groundwater of Chhaprola Industrial Area, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Uttar Pradesh, India [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 166: 135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.086 [24] CAO Y J, TANG C Y, SONG X F, et al. Identifying the hydrochemical characteristics of rivers and groundwater by multivariate statistical analysis in the Sanjiang Plain, China [J]. Applied Water Science, 2016, 6(2): 169-178. doi: 10.1007/s13201-014-0215-5 [25] 秦正峰. 河北省典型区地下水硬度空间分布特征及其成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. QIN Z F. Spatial distribution characteristics and genetic analysis of groundwater hardness in typical areas of Hebei Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017(in Chinese).
[26] BOAMPONSEM L K, DE FREITAS C R, Williams, D. Source apportionment of air pollutants in the Greater Auckland Region of New Zealand using receptor models and elemental levels in the lichen, Parmotrema reticulatum [J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2017, 8(1): 101-113. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2016.07.012 [27] PANT R R, ZHAN F, REHMAN F, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal[J]. Science of the Total Environment. 2018, 622: 770-782. [28] CIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [29] 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什噶尔河流域地下水形成的水文地球化学过程[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(3): 541-550. Hydrogeochemical processes of groundwater formation in the Kashgar River Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(3): 541-550(in Chinese).
[30] 张杰, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆叶尔羌河流域平原区浅层地下水咸化空间分布及成因 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(23): 126-134. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.23.016 ZHANG J, ZHOU J L, NAI Y H, et al. Spatial distribution and cause of salinization of shallow groundwater in plain terrain of the Yarkant River Basin, Xinjiang [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(23): 126-134(in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.23.016
[31] 柳凤霞, 史紫薇, 钱会, 等. 银川地区地下水水化学特征演化规律及水质评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(9): 2055-2066. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019043003 LIU F X, SHI Z W, QIAN H, et al. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation in Yinchuan area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(9): 2055-2066(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019043003
[32] 赵江涛, 周金龙, 梁川, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水演化的主要水文地球化学过程分析[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1397-1406. ZHAO J T, ZHOU J L, LIANG C, et al. Hydrogeochemical process of evolution of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi, Xinjiang[J]. Environment Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1397-1406(in Chinese).
[33] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051. WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar Delta Area in Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051(in Chinese).
[34] 新疆维吾尔自治区国土资源厅. 新疆维吾尔自治区矿产开发简明图集[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆维吾尔自治区国土资源厅, 2004, 81. Resources department in Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region. Concise atlas of mineral development in Xinjiang Uighur[M]. Xin-jiang: Resources Department in Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region, 2004, 81(in Chinese).
[35] 赵江涛, 周金龙, 梁川, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水反向水文地球化学模拟[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(10): 65-70. ZHAO J T, ZHOU J L, LIANG C, et al. Reverse hydrogeochemical simulation of groundwater in the plain area of Yanqi Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 31(10): 65-70(in Chinese).
-





 下载:
下载: