-
持久性有机污染物(POPs)是指难以在环境中降解,易通过食物链富集,能经大气的远距离传输从而影响到区域乃至全球环境的半挥发、高毒性污染物[1-2]。与其他环境介质中的污染物相比,大气POPs具有存续时间长、分布面积广、治理难度大的特点。不同的大气POPs在不同浓度水平下的污染性具有较大差异,且污染物会通过大气的水平运动和不同程度的扰动等传输方式在全球环境中迁移、转化,从而造成世界性的大气污染问题。与此同时,长时间暴露于大气污染物中可能会对各类生物体产生慢性毒性影响,造成不可逆的健康问题。因此,监测及评估大气POPs浓度水平对于研究污染物的分布、转化以及污染防治具有极为重要的意义。
目前大气POPs的监测技术主要包括主动大气采样(active air sampling,AAS)和被动大气采样(passive air sampling,PAS)两种技术方法。主动采样是指利用吸附材料对颗粒相及气相中的污染物进行采样,并对其总量进行计量的一种方法,采样材料通常为聚氨酯泡沫(PUF)、半透膜(SPM)、玻璃纤维滤膜(GFF)和石英纤维滤膜(QFF)等[3]。主动采样技术的优点是能够在短时间内采集数百立方米的大气样品,并获得准确的采样体积,从而实现对短时间内污染物浓度变化的监测[2]。然而该技术也存在缺点,比如污染物穿过吸附材料未被吸附、挥发性污染物从滤膜收集的颗粒物上挥发,采样装置成本较高,依赖于电力的支持与人员的长期监护等等,因此主动采样难以应用于对大气有机污染物的大范围多点采样工作。
相对于主动采样而言,被动采样技术是一种以污染物在不同环境介质之间的逸度差为动力,利用分子扩散或渗透原理对污染物进行吸附的平衡采样技术[4]。从目前主流的采样器类型来看,被动采样器具有成本较低、结构简单、操作方便、无需电力支持与人员长期监护等优点,从而能实现对大范围内多点位的大气污染物的同步监测,在一定程度上弥补大气主动采样技术的不足[5]。但是,被动采样技术也存在一定的缺点,例如:无法测定采样空气的体积、采样周期较长等等。通常来说,被动采样技术因其廉价、高效的特性而在多种研究场合被广泛使用。
本文将对大气被动采样原理及几种常见的大气被动采样装置的结构组成、采样原理、特点及应用状况进行介绍。本文提及的几种被动采样器具有不同的优缺点及适用情况,能够依据环境中不同的采样污染情况、污染物类型选择合适的采样器从而实现对污染物的有效监测采样,可为后续大气持久性有机污染物样品的采样方法研究提供参考。
-
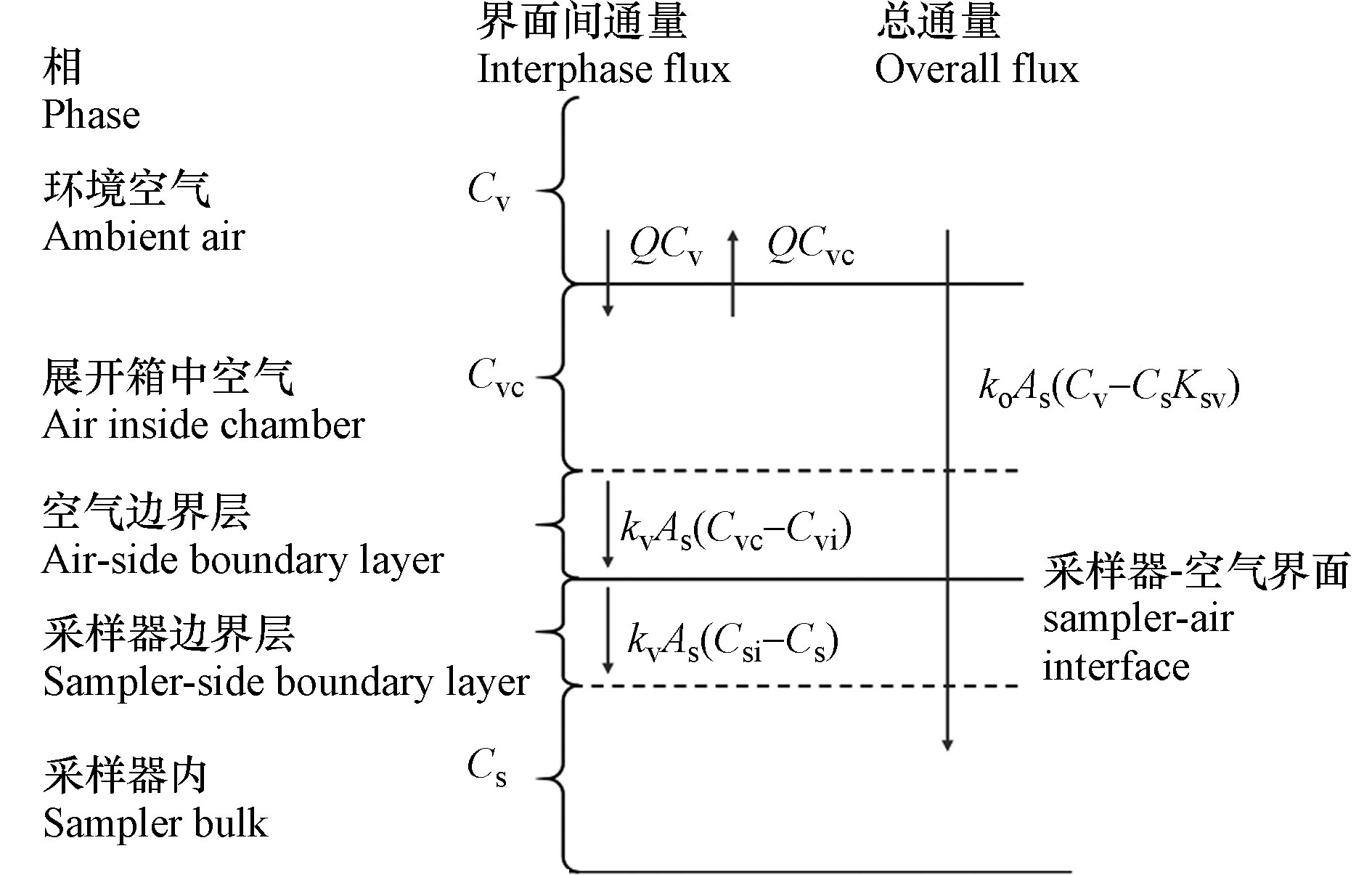
PAS技术基于分子扩散或渗透原理,利用具有较强吸附能力的材料来采集空气中的有机污染物。Whitman双膜阻尼理论能够清晰地解释气相污染物在被动采样器与空气之间交换的原理,其概念模型如图1所示[6]。
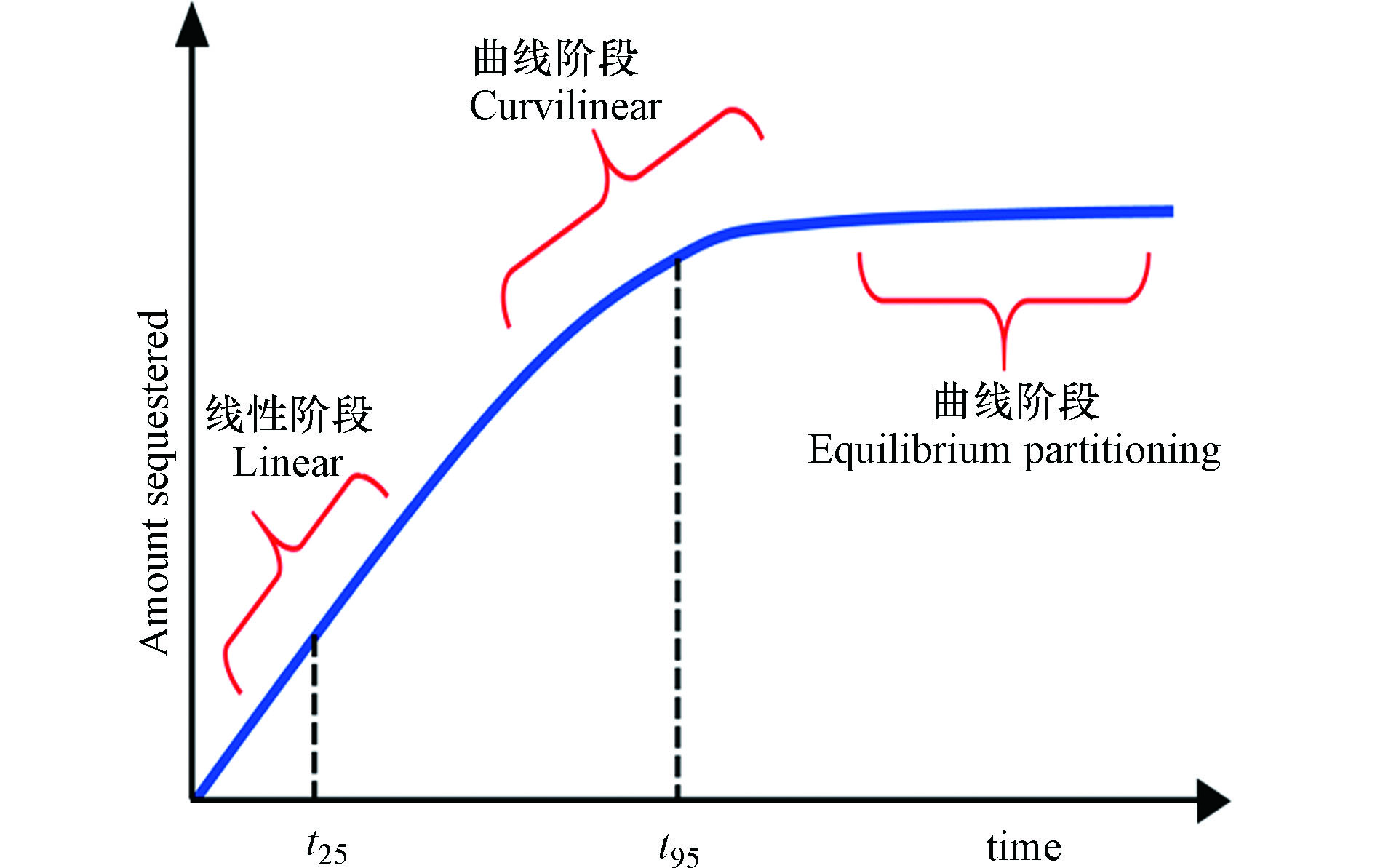
采样器对污染物的采样是污染物富集与逸失共同作用的结果,随着气相污染物在吸附材料上不断富集,污染物的逸失速率也会逐渐增加,当富集速率与逸失速率相等时,采样达到动态平衡。因此理论上[7-8]被动采样过程可分为如图2所示的3个阶段:动力学控制的线性阶段(kinetically controlled linear phase),曲线阶段(curvilinear phase)和平衡阶段(equilibrium phase)。
-
大气被动采样装置的区分标准主要是吸附材料。目前已有文献报道的大气被动采样装置主要包含如下几种:半透膜被动采样装置(SPMD-PAS)、聚氨酯泡沫塑料被动采样装置(PUF-PAS)、聚合物涂层玻璃被动采样装置(POG-PAS)、高分子树脂聚合物被动采样装置(XAD-PAS)等。下面将对上述几种大气被动采样装置的原理、特点及应用情况等方面进行介绍。
-
SPMD是由Huckins等[9-10]于1990年设计的一种半透膜采样器,采用填充着三油酸甘油酯的低密度聚乙烯(low density polyethylene,LDPE)膜管作为采样材料,模拟了有机物在水相中经生物膜进入生物有机相的平衡分配过程。Petty等[11]于1993年首先利用SPMD-PAS采集气相中的POPs,侧面反映了该采样器是一种高效的大气被动采样装置。
-
假设利用SPMD-PAS采集大气中污染物的过程为动力学控制的线性阶段,则污染物在大气中的浓度CA(ng·m−3)可以利用式子(1)[12]估算:
式中,mSPMD(ng)为SPMD-PAS对污染物的吸附量;RS(m3·d−1)为大气污染物的采样速率;t(d)为SPMD-PAS的采样时间。
-
SPMD-PAS最早被设计提出时,常运用于监测水相中的有机污染物,随着科学技术的不断发展,其也实现了改良。目前SPMD-PAS已具有完备的理论支持以及商业产品体系。该装置的采样周期长(几周—几年),适用于对大气污染物的长期监测。与同类装置相比,该装置具有容量大、耐饱和性强的优点[9, 13],但操作过程较为繁琐[14],运输与安装时样品容易被装置中的油脂污染,造成监测的失败。此外,采样时必须将装置放入未经化学处理的木质或不锈钢Stevenson箱中来减少温度、风、雨等环境要素的影响[15],且样品的净化分析过程较为复杂,需利用凝胶渗透色谱(GPC)去除甘油酯。
-
Zhu等[16-19]研究了SPMD-PAS采集多氯联苯(PCBs),PAHs,有机氯农药(OCPs)[20]的采样速率R与其量化、物化性质间的定量结构-性质关系(QSPR),建立了多参数QSPR模型。模型表明POPs的SPMD采样率可以通过其相关分子的量子化学性质、总能量、范德华面积和分子的总偶极矩来预测,模型还从分子水平解释了影响SPMD-PAS采样速率的主要因素为上述POPs与采样器中三油酸甘油酯分子之间的相互作用和在三油酸甘油酯中形成空穴容纳POPs所需的能量。
近年来,国内外有一些关于SPMD-PAS应用的研究,如刘国卿等[21]利用SPMD对珠三角地区大气中的多环芳烃(PAHs)进行了为期一年的监测,证实了SPMD被动式采样技术监测大气污染物的有效性。研究结果表明,SPMD主要采集的是大气中的气态PAHs;该地区不同季节大气中PAHs的浓度分别为:138.63 ng·m−3(1—3月),286.0 ng·m−3(4—6月),322.0 ng·m−3(7—9月)和392.55 ng·m−3(10—12月)。由此可见,温度也是影响大气中气态PAHs浓度水平的一个外在因素,高温季节大气中气态PAHs的浓度水平明显低于低温季节;而在地域上,气态PAHs含量呈现中间高、南北低的特点,气态PAHs含量较高区域多集中于中部机动车尾气排放严重的广州及其周边城市,该区域气态PAHs年平均浓度可达74.4 ng·d−1。
-
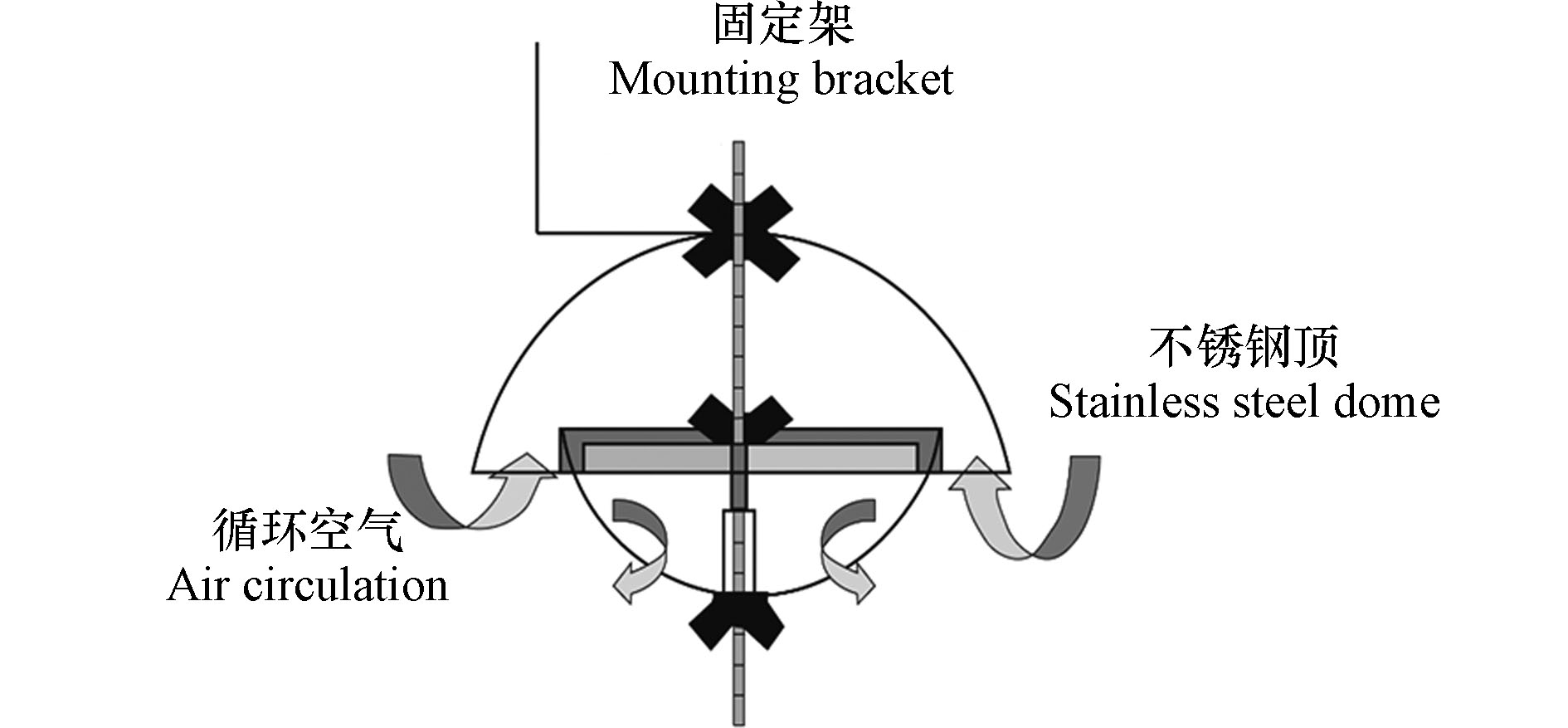
PUF-PAS是Shoeib等[7]于2002年设计提出的,吸附材料是聚氨酯泡沫塑料(PUF)。如图3所示,PUF采样器的主体由两个大小不同的不锈钢盖和1根固定主轴的螺旋杆组成,采样时PUF碟固定于主轴上,形成一个不完全封闭的空间,该装置能够极大地减少风、雨水和光照等因素对采样结果的影响。
-
PUF-PAS对于大气污染物的采样过程主要处于线性吸附阶段,其采样速率的主要影响因素是空气侧边界层传质的制约,主要表现为特定化合物分子扩散系数和边界层厚度的影响。除此以外,较高的温度、较高的风速等环境因素在一定程度上能提高采样速率。
Shoeib等[7]推导了使用PUF对空气中气态有机污染物进行采样时的浓度关系式:
采样的有效体积VA(cm3)可以表示为:
其中,CPUF和CA分别表示污染物在PUF和大气中的浓度(ng·cm−3),VPUF(cm3)为PUF的体积,APUF(cm2)为PUF的表面积,kA为污染物大气传输系数,KPUF-A为污染物PUF-大气平衡分配系数,t(d)为采样时间。
-
PUF-PAS凭借其原理可靠、运输成本低、便于携带、操作简便、样品分析流程简单等优点而被广泛应用[16],且该技术的采样周期短(几周—几月,一般为3个月),无需专业人员操作。与此同时,该技术有采样量小、易饱和的缺点[2];对样品进行处理时,难以将颗粒物与气相样品分离;部分POPs达不到该采样器的采样标准,无法监测[15]等。
-
近年来,国内有许多关于PUF-PAS应用的研究,如刘俊文等[23]介绍了利用PUF-PAS采集的POPs浓度估算大气中POPs浓度水平的3种计算方法,分别为主动采样校正法、等效体积法、添加回收率指示物法。主动采样校正法适用于线性采样阶段,等效体积法适用于高挥发性大气有机污染物,而添加回收率指示物法则通过使用效能参考化合物(PRCs/DC)来提高从PUF-PAS采样材料上污染物浓度推算出环境介质中污染物实际浓度的能力。对于PAS,该研究团队提出了以下3点展望:(1)进一步完善不同条件下污染物物化属性及采样数据的数据库;(2)根据不同气象和地理条件设计出具备不同功能的理想被动采样器;(3)修订PAS样品采集、样品分析的统一指导手册。
蒋昊余[24]建立了PUF-PAS对生物质燃烧标志物的采样方法,在中南半岛、巴基斯坦、中国西南地区和珠江三角洲地区等研究区域对左旋葡聚糖、甘露聚糖和半乳聚糖进行了采样分析,并探究了生物质燃烧与POPs形成之间的关系。其中生物质燃烧标志物主要包括CO、CO2、NO、NO2、颗粒物、PAHs等直接污染物及土壤释放的POPs等伴生污染物。实验结果显示,PUF-PAS能够有效采集生物质燃烧标志物,填补了被动采样技术采集生物质燃烧标志物空间尺度上的研究空白。该学者还指出后续研究可围绕生物燃烧标志物的季节性差异、生物质燃烧污染物大气迁移及区域健康等方向展开。
刘攀亮[25-26]利用PUF-PAS对兰州境内18个采样点进行了冬夏季大气样品的采集和硝基多环芳烃(NPAHs)的监测,研究了大气中NPAHs的浓度水平、空间分布以及季节变化情况,并判断了NPAHs一次排放和二次排放的形成源。实验结果表明,夏季NPAHs的平均浓度为(15±11) ng·m−3,冬季为(8.6±8.1) ng·m−3,夏季NPAHs的平均浓度明显高于冬季。铝厂、钢厂、电厂等工业企业的废气排放是NPAHs一次形成的主要原因,而二次形成的主要原因是兰州地区夏季较强的光化学反应;族谱特征分析结果显示,冬夏季大气NPAHs污染物中占比最高的均为1N-NAP和2N-NAP;NPAHs/PAHs比值表明,夏季高温促进了PAHs的降解和NPAHs的二次形成。该研究的不足之处在于未能对NPAHs的形成过程、浓度水平影响因素及四季变化进行研究分析。
-
POG-PAS是由Harner等[8]设计的另一种大气被动采样器,该采样器的采样介质为玻璃圆柱体上均匀涂敷的1 μm厚的高分子聚合物乙烯-醋酸乙烯酯树脂(ethylene vinyl acetate,EVA)。该采样器的外部构造与PUF大气被动采样器相同,在内部构造中略有不同。
-
污染物从大气进入被动采样器的效率取决于化合物在聚合物固定相中的吸收效率。在吸附材料为EVA的条件下,这种吸收是由装置在大气中污染物浓度与EVA中污染物浓度之间不断重新建立平衡的能力驱动的。
假设POG大气被动采样器初始采样速率是恒定的,吸附在EVA中目标样品的浓度CEVA随着时间线性增加,即采样过程处于线性吸附阶段,则在该阶段吸附在EVA中目标样品的质量M为:
其中,t是采样时间(d),b是通过绘制M与时间关系图确定的采样率,即b = KAAEVACA,kA是污染物在大气中的传质系数(cm·d−1),AEVA是采样介质暴露部分的平面区域面积(cm2),CA是污染物在空气中的浓度。一旦确定了采样器的传质系数kA,就可以通过等式4来计算CA。
随着采样介质中污染物浓度的增加,采样量将呈曲线变化,当采样过程处于平衡状态时,净摄取(dCEVA/dt)将接近于零。污染物在空气中的浓度(CA)与在采样介质中的浓度具有以下关系:
如果已知目标污染物的EVA-空气平衡分配系数(KEVA-A),则只要测得EVA上污染物的浓度,再利用式(5)就可计算出空气中污染物的浓度。
-
POG作为一种薄膜,其容纳POPs的能力较低,但空气浓度/暴露时间的变化反应迅速。相较于早前研究中的窗户有机薄膜[27]与植物叶片表面薄蜡膜[28-29],POG的潜在优势是聚合物涂层的厚度可以在取样器之间保持标准化和均匀化,并且暴露时间可以保持一致。与本文介绍的其他3种大气被动采样器相比,该采样器时间分辨率高,采样速率较快[13]。此外,POG-PAS可以做到高表面体积比,从而可以快速(小时或天)平衡目标分析物,所需采样时间通常在一周以内[8, 30-31]。但该PAS装置的缺点是采样介质EVA在实验室制备与采样器运输过程中易受污染,导致实验较难控制空白对照。
-
目前,国内对于POG-PAS的相关研究相对较少,而国外已有许多应用研究,如Harner等[8]利用POG-PAS装置对高浓度气相PCB进行了室内实验,研究了EVA厚度与风速对于PCB采样结果的影响。实验结果显示,用厚度不同的EVA进行PCB采样时,PCB的累积量会随着EVA厚度的增加而增加,这表明EVA吸收PCB是通过将PCB吸收到整个聚合物基质中来实现的;4 m·s−1的风场导致EVA对PCB的吸收率较风速为零时增加了大约6倍,在大风条件下,达到平衡所需的时间相比于100 h减少了5—20 h,但如果将POG装在由倒置的不锈钢碗组成的展开室内时,这种风速效应便会减弱。其主要原因是较高的风速降低了POG表面上方微边界层的厚度,阻碍了空气侧质量的传递,这表明被动采样器空气侧PCB受到的阻力对PCB向POG传递的阻力起主要作用。
Farrar等[30]将POG-PAS采样器暴露于环境中18 d,评估了其化合物吸收率和达到平衡的时间。实验结果显示,对于PCB-18和PCB-138,采样达到平衡的时间分别在几小时到20 d之间变化;在不同的3 d周期内反复部署采样器,可检测到从2—10 m3空气中分离出的PCB同系物。该课题组[29]还将POG-PAS采样器部署在19个欧洲国家的38个站点,通过实验数据的反向轨迹分析来研究POPs短期内的空间变化性和影响POPs空间分布的因素。实验结果显示,与偏远地区(65 pg/采样器)相比,多溴二苯醚(PBDEs)在城市中的浓度高达1000 pg/采样器,表明了PBDEs的浓度水平与人口密度有着密切关系;POPs的短期空间变化受气团来源的强烈影响,相较于内陆地区,在受海洋气团影响的大多数地点的实验水平均较低。该研究团队对未来POG采样和处理程序的改进提出了几点建议:(1)建立一种能更好地将EVA聚合物涂敷在玻璃表面的方法;(2)采用不同的几何形状来设计POG-PAS。
-
XAD-PAS采样器是由Wania等[32]设计的,采样介质为苯乙烯-二乙烯基苯共聚物XAD-2粉末。如图4所示,该采样器的内部是填充着XAD-2树脂粉末的网状不锈钢圆筒,外壳则由不锈钢顶盖和底端开口的金属套筒组成,对内部结构起着保护作用,并减少了风、雨等外界因素对采样结果的影响。空气通过底部开口与顶部小孔进行交换,气态污染物通过内部不锈钢网孔进入,被XAD吸附。
-
目前POG-PAS对POPs等大气污染物的采样过程一般处于线性吸收阶段。POPs在大气与采样介质XAD-2之间的传质可用Fick第一定律描述[32]:
其中,dm(pg)是采样介质在时间间隔dt(d)内收集POPs的质量,CAir(pg·m−3)是POPs的大气浓度,CSurface(pg·m−3)是采样介质表面POPs的浓度,k(m·d−1)是传质系数,A(m2)是采样介质与大气接触的面积。
在线性吸收阶段,相对于吸收速率,解吸速率非常慢,因此,可认为CSurface的有效值为0。在这种情况下,POPs在采样器中的浓度CPAS(pg·m−3)与在大气中浓度CAir(pg·m−3)和暴露时间t(d)有下列关系:
其中,R(m·d−1)是采样器对污染物的采样速率,它结合了式子6中的k与A。目前已有大量研究证明[32-34],采样速率R与环境温度、压力、风速、采样器构型等因素有关。
-
XAD-PAS具有吸附容量大、吸附化合物种类多的优点,适用于挥发性较强的POPs的采样,同时适合在偏远地区对POPs的长期监测或空气中POPs年平均浓度的监测。其缺点是结构复杂、制作与运输成本高、操作繁琐,采样器的采样周期较长[35],一般为几周至几年,因此也限制了其进一步的应用与发展。
-
近年来,国内多位学者对该采样器均有一些研究,如Shen等[36]利用XAD-PAS在大洲范围内评估了2000/2001年大气中PCBs和PBDEs的空间浓度变化性,测定了它们的年综合空气浓度。采样点包括加拿大、美国、墨西哥、伯利兹和哥斯达黎加共40个站点。
Hayward等[37]利用部署在安大略省南部农村的两个主动空气采样器(AAS、大容量和小容量泵)和两个被动空气采样器(PAS、PUF-PAS和XAD-PAS),比较了上述4种采样器测定9种农药的数据差异性。研究表明,不同采样技术测得的农药空气浓度在统计学上并无显著差异,且它们一致性随着部署周期的延长而提高;XAD-PAS可以最经济有效地收集空气样本从而实现评估长期空气中典型农药的浓度变化趋势;ASS则适用于采样时间短于1个月的短时采样。
张静星[38]使用分别填充XAD-2、XAD-4、XAD-16 3种树脂的XAD-PAS采样器对大气中几种POPs进行了采样,填补了目前不同型号XAD-PAS对大气POPs采样研究的空白。研究表明,3种树脂应用的XAD-PAS对POPs的采样阶段均处于线性吸附阶段,并且采集富集特征相似;XAD-16所组成的采样器的采样性能优于XAD-2和XAD-4,具有应用于低浓度水平POPs区域的潜在可能。该学者还尝试利用3D打印技术对传统AAS进行改进,并证明其有效性,为今后研究POPs提供了新方法。
-
大气被动采样技术的发展,对空气中痕量污染物的监测有着重要意义。目前,该技术已经日渐成熟,采样器种类丰富,相关应用研究也得到了广泛应用[39-40]。被动采样装置种类较多,本文仅提及了常见的4种装置,这些大气被动采样装置各具特色,SPMD-PAS具有完备的理论支持以及商业产品体系,适用于对大气污染物的长期监测;PUF-PAS成本低廉、便于携带、操作简单,应用最为广泛;POG-PAS具有高表面积体积比,并可以通过改变聚合物的表面积及厚度从而改变采样时间及采样灵敏度,适用于大气污染物的短期采样及同种污染物的采样比较研究;XAD-PAS吸附容量大、吸附化学物种类多,适用于在偏远地区对POPs的长期监测或空气中POPs年平均浓度的监测。总之,被动采样技术在采样过程中具有较高的灵活性和代表性,能及时应对环境中的各种污染情况。
大气被动采样在国内外已经有很多研究报道,相关技术日渐成熟。未来该领域的研究方向为:(1)外界环境因素(如风速、温度、湿度、光照等)变化对PAS采样结果的影响研究;(2)新型大气被动采样器与新型吸附材料的研发;(3)针对同一种污染物进行不同大气采样器之间的对比研究。一旦上述研究方向能取得相应进展,在运用大气被动采样技术的过程中就能够依据污染物特性的不同选择不同的装置与吸附材料,从而取得较高的经济与环境优势,并凭借其廉价、简便的优点对大气持久性有机污染物进行长期多点的监测,获得高准确性的数据,这对于研究污染物的整体污染情况及迁移、转化与污染评价都具有深远的意义。
大气持久性有机污染物被动采样技术研究进展
Research progress on the passive sampling techniques ofpersistent organic pollutants in the atmosphere
-
摘要: 持久性有机污染物(POPs)通常种类繁多,结构复杂,以痕量或超痕量的方式存在于环境介质与生物体中,具有较高的生物毒性和环境危害性。近年来,被动采样技术在环境监测领域及POPs污染水平评价方面应用广泛,发展迅速,根据不同的吸附材料可将被动采样器划分不同的装置类型。本文综述了大气持久性有机污染物被动采样技术(passive atmospheric sampling, PAS)的基本原理,总结了半透膜被动采样器(SPMD-PAS)、聚氨酯泡沫塑料被动采样器(PUF-PAS)、聚合物涂层玻璃被动采样器(POG-PAS)、高分子树脂聚合物被动采样器(XAD-PAS)这几种常见的大气被动采样器的组成结构、采样原理、特点及应用情况,分析了大气被动采样技术研究领域的动态,提出了被动采样技术目前亟需要关注的问题和存在的主要困难,并展望了该领域的研究前景。Abstract: Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) have a great variety with complex structures. Usually, in the environment medium and organism, POPs are present at trace or ultra-trace concentrations, which poses the high biological toxicity and environmental harmfulness. In recent years, passive sampling technology has been widely used and developed rapidly in the field of environmental monitoring and POPs pollution level assessment. The different types of passive samplers can be divided by various adsorption materials. This paper gives an overview of the basic principle of passive sampling techniques (PAS) for POPs in the atmosphere, and summarizes the structure, sampling principle, characteristics and application of several passive samplers, including semi-permeable membrane device passive sampler (SPMD-PAS), polyurethane foam passive sampler (PUF-PAS), polymer-coated glass passive sampler (POG-PAS) and resin-based passive sampler (XAD-PAS). The development research of PAS is analyzed, and the problems and difficulties of passive sampling technology is also pointed out. Finally, this study prospected the research direction and prospect in this field.
-

-
-
[1] RUBIO E, VALVERDE M, ROJAS E. Effects of atmospheric pollutants on the Nrf2 survival pathway [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2010, 17(2): 369-82. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0140-6 [2] 王晓燕. 大气持久性有机污染物检测方法探究 [J]. 环境与发展, 2019, 31(11): 112, 118. WANG X Y. Study on the detection method of persistent organic pollutants in atmosphere [J]. Environmental and Development, 2019, 31(11): 112, 118(in Chinese).
[3] 朱青青, 刘国瑞, 张宪, 等. 大气中持久性有机污染物的采样技术进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(2): 50-60. ZHU Q Q, LIU G R, ZHANG X, et al. Progress on the sampling techniques of persistent organic pollutants in atmosphere [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016, 11(2): 50-60(in Chinese).
[4] TADEUSZ GÓRECKI, JACEKNAMIEŚNIK. Passive sampling [J]. Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 21(4): 276-291. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(02)00407-7 [5] 张颖, 吕天峰, 梁宵, 等. 主动采样技术在中国大气POPs监测中的应用 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2009, 25(1): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2009.01.005 ZHANG Y, LV T F, LIANG X, et al. Application of active air sampling in monitoring of persistent organic pollutions in atmosphere of China [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2009, 25(1): 14-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2009.01.005
[6] BARTKOW M, BOOIJ K, KENNEDY K, et al. Passive air sampling theory for semivolatile organic compounds [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 60(2): 170-176. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.033 [7] SHOEIB M, HARNER T. Characterization and comparison of three passive air samplers for persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(19): 4142-4151. [8] HARNER T, FARRAR N J, SHOEIB M, et al. Characterization of polymer-coated glass as a passive air sampler for persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37: 2486-2493. [9] HUCKINS J N, TUBERGEN M W, MANUWEERA G K. Semipermeable membrane devices containing model lipid: A new approach to monitoring the bioavaiiability of lipophilic contaminants and estimating their bioconcentration potential [J]. Chemosphere, 1990, 20(5): 533-552. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(90)90110-F [10] 汪盼盼, 王静, 刘铮铮, 等. 几种常见被动采样技术在水环境中研究进展 [J]. 环境监控与预警, 2016, 8(4): 31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2016.04.009 WANG P P, WANG J, LIU Z Z, CHEN J Y. Research progress in several common passive sampling techniques in water environment [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2016, 8(4): 31-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2016.04.009
[11] PETTY J D, HUCKINS J N, ZAJICEK J L. Application of semipermeable membrane devices(SPMDs) as passive air samplers [J]. Chemosphere, 1993, 27(9): 1609-1624. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(93)90143-S [12] LOHMANN R, CORRIGAN BP, HOWSAM M, et al. Further developments in the use of semipermeable membrane devices(SPMDs) as passive air samplers for persistent organic pollutants: field application in a spatial survey of PCDD/Fs and PAHs [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(12): 2576-2582. [13] HUCKINS J N, MANUWEERA G K, PETTY J D, et al. Lipid-containing semipermeable membrane devices for monitoring organic contaminants in water [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1993, 27: 2489-2496. [14] 张干, 刘向. 大气持久性有机污染物(POPs)被动采样 [J]. 化学进展, 2009, 21(2): 297-306. ZHANG G, LIU X. Passive atmospheric sampling of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2009, 21(2): 297-306(in Chinese).
[15] 朱秀华, 王鹏远, 施泰安, 等. 持久性有机污染物的环境大气被动采样技术 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(10): 1956-1969. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.10.020 ZHU X H, WANG P Y, SHI T A, et al. Environmental atmospheric passive sampling technology for persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(10): 1956-1969(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.10.020
[16] ZHU X H, ZHOU C Z, HENKELMANN B, et al. Monitoring of PAHs profiles in the urban air of Dalian, China with active high-volume sampler and semipermeable membrane devices [J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 2013, 33(3): 265-288. doi: 10.1080/10406638.2013.777672 [17] ZHU X H, DING G H, LEVY W, et al. Quantitative relationship for air sampling rates of polychlorinated biphenyls by semipermeable membrane devices with their structures and properties [J]. Computer and Applied Chemistry, 2011, 28(1): 6-10. [18] ZHU X H, DING G H, LEVY W, et al. QSPR study about sampling rates of semipermeable membrane devices for monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in Alps air [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56: 1884-1889. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4511-2 [19] WANG W, QIN S T, SONG Y, et al. Pollution level and distribution of PCDD/PCDF congeners between vapor phase and particulate phase in winter air of Dalian, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(Supplement): S36-S39. [20] 王俊, 张干, 李向东, 等. 珠江三角洲地区大气中有机氯农药的被动采样观测 [J]. 环境化学, 2007, 26(3): 395-398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.03.028 WANG J, ZHANG G, LI X D, et al. Passive sampling and observation of organchlorine pesticides in the atmosphere of the Pearl River Delta region [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2007, 26(3): 395-398(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.03.028
[21] 刘国卿, 张干, 李军, 等. 利用SPMD技术监测珠江三角洲大气中多环芳烃 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(3): 340-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.020 LIU G Q, ZHANG G, LI J, et al. Studies on monitoring atmospheric PAHs utilizing SPMD technique in the Pearl River Delta. [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(3): 340-344(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.020
[22] 高丹. 被动采样持久性有机污染物检测技术及其应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2014. GAO D. Application research of persistent organic pollutants test techniques by passive sampling technology[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[23] 刘俊文, 李琦路, 李军, 等. PUF大气被动采样技术对POPs的采样计算 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(3): 107-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.03.026 LIU J W, LI Q L, LI J, et al. Theory and concentration calculations of PUF atmospheric passive sampling technique for persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(3): 107-112(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.03.026
[24] 蒋昊余. 利用被动采样技术研究区域生物质燃烧及其对大气持久性有机污染物的贡献[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2018. JIANG H Y. Using polyurethane foam-based passive air sampling technique to investigate regional biomass burning and the contribution to atmospheric persistant organic pollutants[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018(in Chinese).
[25] 刘攀亮. 中国西部兰州盆地大气硝基多环芳烃污染特征及呼吸暴露风险[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. LIU P L. Contamination characteristics and inhalation exposure risk of atmospheric nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Lanzhou Valley, Western China[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019(in Chinese).
[26] 王俊, 张干, 李向东, 等. 珠江三角洲地区大气中多环芳烃的被动采样观测 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2007, 20(1): 42-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2007.01.008 WANG J, ZHANG G, LI X D, et al. Monitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere of the Pearl River Delta using PUF-passive air sampler [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 20(1): 42-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2007.01.008
[27] BUTT C M, DIAMOND M L, TRUONG J, et al. Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in southern ontario as measured in indoor and outdoor window organic films [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38: 724-731. [28] BARBER J L, THOMAS G O, KERSTIENS G, et al. Air-side and plant-side resistances influence the uptake of airborne PCBs by evergreen plants [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36: 3224-3229. [29] CALAMARI D, TREMOLADA P. DI GUARDO A. et al Chlorinated hydrocarbons in pine needles in Europe: Fingerprint for the past and recent use [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1994, 28: 429-434. [30] FARRAR N J, HARNER T J, SWEETMAN A J, et al. Field calibration of rapidly equilibrating thin-film passive air samplers and their potential application for low-volume air sampling studies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39: 261-267. [31] FARRAR N, PREVEDOUROS K, HARNER T, et al. Continental scale passive air sampling of persistent organic pollutants using rapidly equilibrating thin films (POGs) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 144(2): 423-433. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.057 [32] WANIA F, SHEN L, LEI Y D, et al. Development and calibration of a resin-based passive sampling system for monitoring persistent organic pollutants in the atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(7): 1352-1359. [33] WANG X P, GONG P, YAO T D, et al. Passive air sampling of organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers across the tibetan plateau [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(8): 2988-2993. [34] ZHANG X, WONG C, LEI Y D, et al. Influence of sampler configuration on the uptake kinetics of a passive air sampler. [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(1): 397. [35] GIOIA R, JONES K C, HARNER T. The use of different designs of passive samplers for air monitoring of persistent organic pollutants[J].Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 48: 33-56. [36] SHEN L, WANIA F, LEI Y D, et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the North American atmosphere [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 144(2): 434-444. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.054 [37] HAYWARD S J, GOUIN T, WANIA F. Comparison of four active and passive sampling techniques for pesticides in air [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(9): 3410-3416. [38] 张静星. 大气典型卤代持久性有机污染物XAD树脂采样研究[D]. 武汉: 江汉大学, 2018. ZHANG J X. Sampling study on persistent organic pollutants by several types of XAD[D]. Wuhan: Jianghan University, 2018(in Chinese).
[39] SEETHAPATHY S, TADEUSZ GÓRECKI, et al. Passive sampling in environmental analysis [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2008, 1184(1/2): 234-253. [40] KOT-WASIK A, ZABIEGA A B, URBANOWICZ M, et al. Advances in passive sampling in environmental studies [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2007, 602(2): 141-163. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.09.013 -



 下载:
下载: