-
天然有机质(natural organic matter, NOM)是一类由植物降解和微生物代谢产生的有机化合物[1],包括小分子的有机酸、糖类、胺类和醇类等;大分子的富里酸、胡敏酸、胡敏素以及胞外分泌物(EPS)等。鉴于NOM的种类多样性和生态环境系统复杂性,NOM在实际土壤和水环境中是由一系列繁简不一、大小不均、性质各异、功能多样的有机物和无机物构成的混合体。
土壤中的NOM组分经过了一系列的演变,按照存在形态可分为颗粒态、胶体态和溶解态有机碳;按照水溶解度可分为疏水性、亲水性和两亲性有机碳;按照酸碱度可分为疏水/亲水酸性、中性和碱性有机碳[2];按照生化性质可分为腐殖质、土壤微生物量碳、可溶性有机碳和易氧化有机碳。
土壤有机质(soil organic matter, SOM)中约80%的组分为腐殖质。腐殖质是一种混合物,由不同分子量和含氧官能团的大分子化合物组成[3],其主要由胡敏酸(humic acid, HA)、胡敏素(humin, HM)和富里酸(fulvic acid, FA)组成,分子量分布在几百到几百万之间,呈疏松的“海绵体”状,因而呈酸性,具有亲水性、阳离子交换性能、络合能力、胶体特性和生物活性等特性[4]。
NOM的稳定性会受到气候、土壤(土层深度)、植被、海拔等因素的影响[5]。Jiménez-González等的研究结果表明,NOM的组成随环境因子的变化而变化,影响较大的几个环境因子为气候、植被和地质基质[6]。在生态环境系统中,溶解性有机质(dissolved organic matter, DOM)被认为是SOM中最活跃、最重要的组分。DOM不仅可影响矿物表面的性质,而且可一定程度上决定营养物质、重金属元素和有机化合物的环境行为,包括生物有效性、迁移和转化[7]。因此,阐明NOM的结构与性质,深度理解它们与有机污染物、重金属、土壤矿物的相互作用,明确有机碳库固定和稳定等对描述NOM的环境行为有着重大的意义,同时这些方面依然是土壤学领域的研究热点和重点[8-9]。
-
NOM由于自身的物化性质以及与土壤中其他组分的强相互作用,如有机物、重金属、无机矿物等,大部分在土壤中呈不溶态。NOM的提取,就是利用各种方法将它们从无机矿物和非NOM成分中分离提取,这也是研究NOM的前提条件之一。NOM的提取方法多种多样,Stevenson认为理想的提取方法应满足:①组分性质不变,②针对与黏土或无机离子结合的有机组分,③具有代表性,④适用于各种类型的土壤这4点要求[10]。
目前关于NOM的提取尚没有统一的标准方法,主要是影响提取的因子众多,比如:提取剂的种类、提取方法、土壤类型、提取的物料比或土水质量比温度、pH等[11]。本综述简单概述了不同提取方法和提取剂的作用机制与适用范围,具体情况如表1所示。
水提法和盐提法能够有效提取DOM,但存在一定的缺陷。水提法在提取DOM的同时容易将其他易溶于水的成分浸提出来,复杂化后续分离过程,并且容易导致土壤黏性粒分散而难获得可供分析的清澈溶液[12];盐提法由于引入了外来离子使得杂质的含量升高,不利于后续DOM的表征及各种试验的开展[23]。使用酸提法可以提取溶于酸的部分NOM,使用该方法与碱提法结合可得到3种腐殖质的粗产物。其中,代表性的HF主要是用于去除粗产物中的硅杂质,从而降低NOM粗产物中的灰分,减小杂质对实验的干扰。NaOH稀溶液是最常用的碱性提取剂,NaOH中的Na+可以取代吸附于NOM上的金属阳离子,高pH环境还可以改变有机质的溶解状态,因此能有效地提取腐殖质。但是,过量NaOH溶液会加速NOM的水解和氧化,从而降低NOM的提取效率。因此,在使用NaOH溶液提取NOM的过程中通入N2以有效地抑制上述反应,这已成为国际腐殖质协会推荐的提取胡敏酸的标准方法之一。此外,在使用NaOH提取NOM时可以适当加入KOH,因为K+可以促使溶液中的无机胶体絮凝,但是KOH来源少,成本高,离子半径大,渗透能力较低,因此在实验中也较为少用。酸提法、碱提法主要也是提取DOM,然而近期的研究表明酸、碱的介入,也会使DOM溶液发生絮凝、荧光淬灭等物理化学性质变化[24-25],进而影响后续研究。络合提取剂中用Na4P2O7溶液提取NOM也是常采用的方法,但Na4P2O7溶液的萃取效率比NaOH法低大约30%[19],该方法的不足之处在于它可能改变NOM的组成,提取出的NOM灰分含量也相对较高。对上述6种提取方法而言,均存在他们的各自的优势和不足之处,目前文献中酸提法、碱提法、络合剂提取法是最为常用的几种实验方法。酸提法与碱提法中,HCl和NaOH作为提取剂对NOM的结构和性质影响相对较小,可提取的组分主要包括溶于酸或碱的DOM,在NOM中含量比例较高的难溶HM等,相对于其他方法而言比较满足Stevenson所提出的理想提取方法。络合剂提取法适用于提取与金属络合的腐殖质,提取效率较低,灰分较高,所提取组分结构复杂,常与碱提法配合使用,极少单独使用。
通过提取剂提取的腐殖质粗产物依然含有许多的杂质,灰分较高,因此要经过一系列的提纯以降低杂质含量,降低对后续研究的干扰。国际腐殖质协会(IHSS)推荐了纯化腐殖质的方法[17],此方法已广泛运用于实际研究中。针对HA的纯化,使用稀HF-HCl溶液去除HA中的矿物成分。Krosshavn等研究了用NaOH溶液提取粗HA,并使用稀HF-HCl溶液纯化粗HA的方法,结果表明,尽管对HA的提取效率较低,但其对结构组成影响较小[18]。随后经透析除去小分子杂质,最后得到纯度相对较高的HA。针对FA的纯化,一些盐分和小分子的有机物可通过离子交换柱(XAD-8)去除,黏粒物质和硅杂质等则可通过HF-HCl混合溶液去除,再使用饱和H+阳离子交换树脂将FA溶液中的盐分脱离出来,最后得到纯度相对较高的FA[26-27]。
针对HM的提取与纯化,HM与土壤组分之间的结合主要通过氢键和共价键,因此提取的关键之处在于如何高效破坏它们之间的结合方式。在使用酸碱将土壤中的HA与FA提取后,剩下的土样就是HM的粗产物,还需要进一步的纯化处理,目前主要通过HF-HCl混合液或偶极非质子传递溶剂两类破坏HM与土壤组分间的氢键。常见的偶极非质子传递溶剂有:甲基异丁基甲酮(MIBK)、二甲基亚砜(DMSO)、二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)和丙酮等。
-
NOM的物化性质决定了它们的环境行为,认识它们的结构组成和性质,比如极性、芳香性、疏水性、官能团、微观形态特性、分子量、氧化还原性等是理解NOM与地球化学元素、与污染物间的相互作用的关键[28-30]。针对上述性质指标的描述,目前对NOM的表征主要是通过元素分析、傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)、紫外可见吸收光谱、X-射线光电子能谱(XPS)、三维荧光光谱和固态核磁共振碳谱(13C NMR)、电子顺磁共振波谱(EPR)等光谱学分析方法[31],并与数学模型、计量化学联合分析,形成多技术串联以明确NOM的物化结构和性质。
元素分析法是表征NOM最为简单而重要的方法之一,该方法通过测定NOM中C、H、O、N等元素的组成来反映其芳香性和极性的大小。H/C,C/N,O/C值可以反映NOM的组成和来源,其中H/C值反映了烃类物质的不饱和程度,该值越低,则不饱和程度越大,间接表明芳香烃类物质含量较高[32];C/N值可以反映NOM的来源;O/C值可判断NOM中含氧官能团的含量。(N+O)/C比值通常被用来表示极性指数,(N+O)/C比值越大,极性指数越高。
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)是近年来广泛使用的分析手段之一,通过测定分子振动过程中的能级跃迁来推断和验证有机化合物结构。红外测定在NOM研究中常用的是KBr压片法,可用于表征有机官能团的组成,并且可用于判断提取出的NOM中是否含有重金属离子和黏土矿物等无机杂质。
核磁共振技术是目前研究NOM碳基结构特征最有效的方法之一。13C NMR波谱可直接对固体样品进行检测,不会破坏待测样品的结构,能对NOM中有机碳结构进行半定量分析。
紫外-可见光谱分析可用于测定简单有机物的官能团结构。通过样品紫外-可见光区的吸收峰信号强弱可以用来测定NOM的浓度,也可以通过E2/E3,E3/E5和E4/E6等一些紫外-可见特征值来预估NOM的腐殖化程度,还能一定程度上研究金属离子与腐殖质之间的相互作用[33-34]。
X-射线光电子能谱(XPS)可用于检测NOM表面化学元素含量和各元素的存在形态,可检测样品中H和He以外所有元素,但受到XPS技术方面的影响,该检测手段只用于NOM的表面元素含量和形态分析。鉴于NOM在环境中与其它物质相互作用方式主要集中在界面,该方法所测得的结果相对于其他界面性质和结构的表征结果来说不具有代表性。
透射电镜(TEM)和原子力显微镜(AFM)是观察NOM微观形貌的直接手段。由于透射电镜的精度对样品要求较高,其应用一定程度上受到了限制。可将NOM均匀分散于光滑的云母片上,通过显微镜的轻敲模式来获取NOM的表面形貌图像。
反相高压液相色谱(RP-HPLC)能够测定NOM的极性分布[35],极性较强的组分在C18反相色谱柱上的保留时间较短,极性弱的组分则保留时间较长。通过确定标准物质Kow与色谱出峰时间的对应关系,将NOM的出峰时间转换为Kow的分布情况,从而得到NOM的极性分布。该方法近年来也被广泛应用于NOM的研究中。
电子顺磁共振波谱(EPR)可用来检测NOM表面的持久性自由基(PFR)的信号强度,PFR作为NOM的重要理化性质之一,可由此来判断NOM在土壤中腐殖化的程度;还可以用来研究不同的种植模式和降雨对NOM的影响;评估NOM的反应活性[36];通过与元素分析法相结合还可判断NOM在实验过程中芳香性的变化[37]。
除了上述提到的方法外,根据NOM研究需求的不同,还可以增加一些其他的方法对NOM进行表征,例如热重分析、质谱、滴定、CO2气体吸附法等可以表征NOM的热稳定性、比表面积、孔径大小、官能团定量分析、分子结构、物质组成解析能力较强而备受关注。此外,还有许多新的表征技术应用于NOM的性质分析,例如三维荧光-平行因子法、傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱(FT-ICR-MS)或凝胶色谱与二维相关分析方法的联合应用、FT-ICR-MS与核磁共振技术串联分析,这些都有助于对NOM组分结构和物化性质深度理解[38-42]。
-
土壤生态系统组成极其复杂,主要为矿物、有机成分和微生物。然而,这些成分不是独立存在的,它们在土壤中互相关联。在众多交叉关联中,NOM与土壤矿物间的相互作用由于两者的强化学活性,被视作是影响NOM环境行为最为重要的一种相互作用。NOM和矿物之间的相互作用是控制环境中有机碳稳定性的关键因子,两者可以形成有机-无机复合体而稳定存在于土壤环境中。本综述主要是从环境因素对NOM稳定性的影响,土壤矿物与NOM的吸附与解吸,以及矿物-NOM复合体对土壤中污染物的影响三方面来阐述NOM在土壤中的环境行为。
-
NOM的组成、分子量大小、含量等性质会受到海拔、气候、土层厚度、NOM所处环境、土地利用变化、光照等因素的影响。有研究表明随着温度的升高会加速NOM的分解并提高NOM的周转量[43]。随着海拔的增高,NOM的含量也逐渐增加,但NOM的稳定性却逐渐降低。SOM在土壤的微孔区域内可被有效保护以免受微生物侵害,但土壤耕作可以暴露以前在土壤微孔区域内受到有效保护的SOM,从而加速了微生物对SOM的分解[44-45]。随着土层深度的增加,NOM的含量也会随之减少。在NOM中,DOM吸收太阳光可生成多种光致活性物种(RPS),如激发三线态DOM(3DOM*)、单线态氧(1O2)和羟基自由基(·OH)等,这些RPS在有机污染物的光降解过程中起着重要的辅助作用[46],同时金属离子的存在能够加快DOM的光化学降解过程[47]。
-
首先,土壤矿物与NOM间的主要相互作用方式为吸附,两者相互作用后土壤矿物和NOM的性质均顺势改变[48]。Kleber等发现土壤矿物对NOM的吸附提高了NOM的热稳定性和化学稳定性[49],而且通过吸附解吸实验证明了NOM与土壤矿物结合后的复合体具有高度稳定性[50]。刘治清等的研究结果显示,土壤矿物可以通过配体交换、阳离子桥(包括水桥)、阴/阳离子交换、范德华力和疏水键合这6种吸附方式吸附NOM[51],其中NOM的分子量越大、酸性越强、芳香度越高,越容易被土壤矿物吸附[52]。针对矿物与NOM间吸附的作用机制,王磊等对矿物与NOM分子的相互作用强度进行了总结,将两者间的作用力分为化学吸附、物理吸附、电子供受体作用,其中化学吸附与电子供受体两类作用力较强,静电作用与范德华力作用较弱[53],如表2所示。
土壤矿物对吸附后NOM的解吸主要取决于土壤矿物吸附NOM的相互作用机制。Mikutta等认为通过配体交换作用吸附在矿物表面的NOM较难解吸;而范德华力存在于黏土矿物的疏水表面与NOM的非极性基团之间,阳离子桥是多价离子连接的矿物表面负电中心与带负电的NOM官能团,这两种相互作用方式结合力较弱,通过这2种方式被吸附的NOM较易发生解吸行为[54]。
-
土壤中大部分NOM可以与金属离子、金属氧化物、金属氢氧化物以及粘土矿物通过各种方式形成稳定的金属-有机物复合物,对NOM的环境行为也能起到决定性作用。究其原因,是由于NOM中含有相当数量的功能性官能团,它们可以与金属元素形成新的络合化学键。在土壤和沉积物中,NOM极易与弱晶形的Fe/Al氧化物以矿物-NOM共沉淀的方式形成复合体,进而改变矿物理化性质,并改变NOM的迁移活性、与污染物相互作用能力等。
-
土壤中的重金属具有迁移能力强、滞留时间长、不易降解等特性,易被作物吸收累积,最终通过食物链作用进入人体,进而威胁人体健康。NOM对重金属的环境行为具有重要影响,其可与金属离子形成生化稳定的络合物,从而影响重金属的生物有效性、存在形态和迁移活性。
-
NOM作为天然吸附剂或络合剂,可直接与土壤溶液中的重金属离子相互作用[55],潜在的相互作用机制有:离子交换、表面吸附、络合、静电吸附、凝胶作用和胶溶作用等。鉴于NOM的特殊物理化学结构,NOM对重金属的吸附会受到pH、重金属类别、分子量、离子强度、NOM所含官能团、NOM结构、NOM浓度等的影响。单瑞娟等通过腐殖酸吸附重金属Cd的淋溶实验证明了pH对吸附和解吸的影响[4];杨毅等则确定了pH与NOM的分子量对吸附过程的影响[56]。此外,NOM的类别,即NOM的物理化学性质在重金属吸附-解吸中也扮演着重要的角色。王俊比较了HA和FA对紫土中Pb、As吸附-解吸行为的影响,结果显示HA对土壤吸附Pb、As起促进作用,FA则对土壤吸附Pb、As起抑制作用[57].
近年来,随着光谱表征技术的进步,也有研究表明官能团是影响NOM对金属离子吸附-解吸的主要因素之一[58-59],不同类型的土壤中提取出的NOM官能团结构差异明显,从而导致它们与重金属之间的相互作用存在差异。NOM中的大量含氧、氮、硫官能团可为重金属的吸附提供吸附位点。张佳等研究了HA对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附特征并通过二维光谱分析技术分析发现HA中官能团参与Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附顺序为:羧基>酚羟基>醇羟基>甲基。其中,羧基主要参与同Cr(Ⅵ)的络合反应;酚羟基、醇羟基和甲基则是Cr(Ⅵ)还原的主要电子供体[60-61]。
DOM对重金属的吸附会使得重金属更容易发生迁移至水体和沉积物-水界面中,对水生动植物、水体环境造成威胁。然而,由于各重金属的活性不同,其吸附-解吸的程度也存在一定程度的差异,有研究发现在众多重金属中,Cd和As的活性较大,被吸附后容易解吸而被动植物吸收,经食物链传递至人体,对人类及其他动物健康造成危害[62]。
-
NOM能与重金属元素形成高稳定性的络合物,影响重金属的形态转化[63],进而影响它们的生物有效性。土壤中重金属赋存形态可分成可交换态、弱酸溶解态、可还原态(铁锰氧化物结合态)、可氧化态(有机质结合态)和残渣态5种,其中以可交换态、弱酸溶解态、可还原态和可氧化态存在的重金属通常被认为是具有迁移活性的;而残渣态重金属是环境惰性的,其对植物几乎无毒害作用[64-65]。
NOM对重金属形态转化与生物有效性同样受到pH、NOM含量等多种因素的影响。刘利军研究了不同pH条件下腐植酸对土壤中As形态转化的影响。腐殖酸浓度较低时,水溶态、可交换态和碳酸盐结合态、铁-锰氧化物结合态的As主要向残渣态转化;腐殖酸含量较高时As主要向有机态及硫化物结合态转化;随着pH的升高,土壤中As向较稳定形态转化[66]。王浩等研究发现,土壤的酸化和SOM的积累都会影响重金属在土壤中的形态,随着土壤pH的降低,交换态重金属含量增加,而碳酸盐结合态则下降;SOM的积累导致结合态重金属的比例显著上升,而氧化物结合态和残渣态重金属的比例下降[67]。
重金属形态主要以残渣态为主,还有少量的铁-锰氧化物结合态和有机物结合态,最少的是可交换态[68]。在NOM的影响下,一部分转化为迁移性和活性较差的残渣态,该形态重金属性质稳定,在自然条件下不易释放,能长期稳定在沉积物中,不易被植物所吸收;另有一部分重金属因为环境因素和NOM的影响转化为迁移性和活性较强的交换态,该形态重金属容易被植物吸收,对环境、生态和食物链的影响最大。当重金属转化为弱酸溶解态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机质结合态时相对稳定,但对土壤环境较敏感,土壤环境一旦发生改变,这三种形态的重金属就容易释放到环境中,对环境造成危害。
-
有机污染物由于其强毒性、持久性、生物蓄积性、强迁移活性,对野生动植物和人类的健康构成巨大威胁而备受关注[69]。残留在土壤中的污染物本就极其难以根除,与土壤中的NOM发生各种物理化学相互作用后,其迁移行为会受到影响,并增加了完全去除的难度,因此对于NOM与有机污染物间相互作用的研究是十分必要的。
-
鉴于NOM复杂的分子结构和丰富的表面官能团,以及在土壤中的高含量,NOM对土壤中有机污染物的环境行为起着决定性的作用。NOM与有机污染物的相互作用方式有:离子交换、配位交换、共价结合、鳌合、疏水分配、氢键结合和π-π相互作用等[70-72]。
当土壤和沉积物中NOM的总有机碳含量大于0.1%时,其对疏水性有机污染物(HOCs)的吸附作用占各种相互作用的主导[73]。NOM对有机污染物之间的吸附解吸与NOM和有机污染物的官能团、极性、结构、环境pH等因素密切相关。Kile等应用13C NMR和XPS计算了NOM中各官能团含量,发现含氧官能团的相对含量与有机污染物的吸附容量呈良好的负相关关系[74]。其原因在于NOM中含氧官能团的氧含量越高,其极性越强,则对非离子性化合物的亲和能力就越弱。
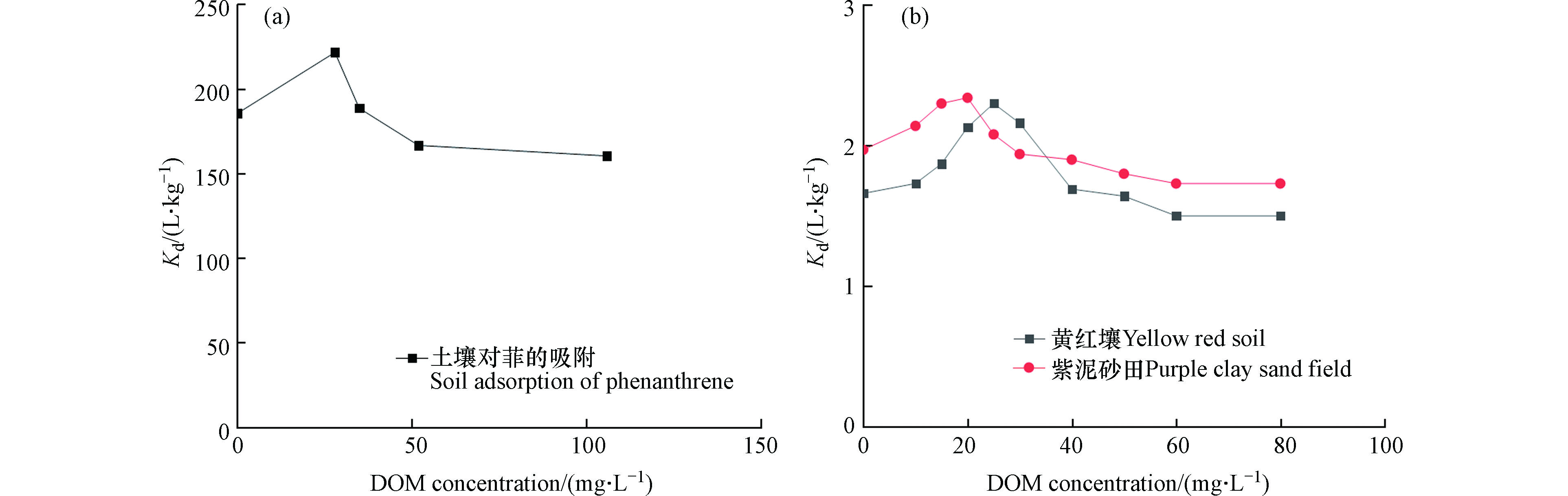
从NOM的结构来看,烷基碳有利于菲的吸附,主要是因为NOM的烷基碳结构由结晶和无定形两种吸附域组成,其中无定形亚甲基碳是HOCs吸附的主要推动力之一[75]。Xing和 Pignatello的研究结果显示,在吸附的最初阶段,吸附的有机污染物主要是进入较为疏松的NOM中,这时吸附以分配为主;随着时间的推移一部分便扩散并吸附到NOM内部致密的玻璃相(glassy regions)表面并可能伴随发生了孔填充(pore filling)效应从而导致等温线的非线性增强[76-77],这种非线性吸附可能会导致有机污染物解吸滞后,以及吸附老化锁定的现象发生,从而使得有机污染物固定在土壤中难以去除。Ling和Gao等研究了土壤DOM浓度对菲的吸附情况如图1(a)所示[78-79],凌婉婷研究了不同土壤中DOM浓度与“莠去津”的吸附情况如图1(b)所示[80],随着DOM浓度的增大,有机物的吸附分配系数增加,有利于其对有机污染物的吸附。但是,DOM浓度增加到一定值后,继续增大,则其吸附有机污染物的分配系数减小,抑制其对有机污染物的吸附。
在土壤和沉积物-水界面中,NOM是有机污染物的良好载体,对NOM的定位及稳定性起着决定性的作用,直接影响到污染物的迁移转化。一方面亲水性DOM增加了有机污染物在土壤中的溶解度,提高其迁移能力;另一方面疏水性的DOM与有机污染物在土壤表面共同作用,提高了土壤对低极性和非极性有机污染物的结合能力,抑制了其迁移[81]。由于DOM和有机污染物性质的不同,以及其所处环境的不同,有机污染物的生物有效性也会因此发生改变。有机污染物与DOM的结合一方面可能降低其生物有效性。Haitzer等研究结果表明,随着DOM浓度的升高,苯并[a]芘在“秀丽隐杆线虫”中的生物富集因数(BCF48)呈曲线下降趋势[82]。另一方面,又可能提高其生物有效性和对动物的急性毒性。Song等发现污泥DOM能加剧除草剂“绿麦隆”对小麦种子发芽率、根伸长的毒害[83];Bejarano等研究发现DOM显著减低了“百菌清”、“毒死蜱”对雌雄动物的急性毒性,但却提高了“氟虫腈”对雄性动物的急性毒性[84]。除此以外,有机污染物的迁移提升从而加速其在动植物上富集,进而影响有机污染物的环境风险。
-
土壤中NOM的存在不仅影响着有机污染物的吸附、解吸和迁移转化,还影响着有机污染物的降解。一方面,DOM可作为光敏化剂,在光照作用下,能够产生一系列RPS(如三重态有机物3DOM*,羟基自由基·OH,单态氧1O2等);另一方面,DOM又能作为光屏蔽剂或活性物种的淬灭剂,抑制有机污染物的光降解。李恭臣等发现富里酸对多环芳烃的光降解有着很大的影响[85]。在低浓度时,因为富里酸分子吸收光子较多而产生的大量的羟基自由基对于荧菎和芘的分解起到促进作用[86]。在光辐射的过程中,1O2的量子产率较高,含氧量高,羧基成分相对较高的组分。含氧基团吸收光能以后可以产生更多的1O2和·OH,对菲的光降解有明显促进作用[87]。钟明洁等研究则发现HA具有光屏蔽作用,从而抑制“嗪草酮”的光降解[88]。
-
本文综述了NOM的性质、提取方法、表征技术,在土壤中的环境行为以及它们与外源污染物的相互作用。NOM成分较复杂,主要组分为腐殖质,且容易受到自然环境中各种因素的影响。提取方法较多,以酸性提取剂和碱性提取剂为主。其物化结构分析方法以元素分析、红外光谱、核磁共振技术为主要手段。其中NOM在土壤中的环境行为主要涉及到土壤矿物对土壤有机质的吸附与解吸。矿物与NOM通过配体交换,阳离子桥(包括水桥),阴离子交换,阳离子交换,范德华相互作用和疏水键合六种机制相互结合,有机质—矿物复合体的物理化学性质与结构都会发生改变。NOM与重金属之间会通过离子交换、表面吸附、络合作用等反应进行吸附,其中pH、有机质官能团、有机质含量、分子量大小等条件都会影响有机质对重金属的吸附与解吸,同时也影响着土壤环境中重金属的形态转化。有机污染物主要通过氢键结合、配位交换、疏水分配、共价结合、鳌合、离子交换和π-π相互作用、电子转移等方式与NOM发生相互作用,会促进吸附或者抑制吸附,还会对有机污染物的降解产生影响。
尽管目前关于NOM的研究取得了一定的进展,但是关于NOM的研究还是不够深入,在今后的研究中,以下几个方面值得关注:
(1)在NOM提取方面,提取方法的不同,NOM会因为各种物质的介入、受到不同程度的影响,因此还需要继续探究最合适的提取方法。
(2)有机质、土壤矿物、有机污染物、重金属、微生物这五者之间存在的相互作用相关研究虽然已有报道,但因这些组分比较复杂,作用机制说法不统一,还需要更加深入的研究。
(3)在NOM与外源污染物相互作用方面,关于吸附、解吸、降解、生物有效性、物质形态转化方面已经做了许多的研究,但污染物种类、气候、环境pH、含水率、温度等条件的不同,两者间的相互作用也会存在较大差异。除此以外随着经济的发展产生的新型外源污染物,例如抗生素、农药等,因为其物理化学性质不同,结构复杂,与NOM之间的相互作用,结合机制也不尽相同,因此也还需要进行更加深入的研究。
综上所述,有机质在土壤环境中的各种作用机制研究还存在许多不足之处,特别是在有机质、有机质-矿物复合体与重金属、有机污染物方面。有机质的深入研究可以为将来对土壤污染修复、土壤水分及肥力保持、碳循环的控制提供巨大的参考价值。
天然有机质的性质分析及其与土壤矿物和外源污染物相互作用研究进展
Research progress on analysis of the properties of natural organic matter and its interaction with soil minerals and exogenous pollutants
-
摘要: 天然有机质(natural organic matter, NOM)在土壤环境中扮演着重要的角色,其对土壤水分的保持、植物的生长,污染物的迁移转化、土壤矿物颗粒的团聚和碳循环均有着重要影响。因此,明确NOM的环境行为以及它们与污染物的相互作用有着重要的生态环境意义。本文综述了各种不同性质NOM的提取及纯化方法,并分析了它们的优缺点;介绍了NOM常用的光谱学表征技术;并通过综述NOM与土壤矿物间的相互作用,描述了NOM的环境行为;论述了NOM与外源重金属和有机污染物之间的相互作用方式、机制以及影响因素,并描述了NOM和污染物在土壤环境中的迁移转化和它们潜在的环境风险。基于对NOM性质、环境行为等的全方位深度解剖,可更加深入认识NOM在土壤环境中的重要作用,为将来的土壤污染修复、肥力保持、碳循环等的研究提供理论基础。Abstract: Natural organic matter (NOM) plays an important role in the soil environment. It has an important impact on the soil moisture retention, plant growth, migration of pollutants, agglomeration of soil mineral particles and carbon cycle. Therefore, there is an urgent need to clarify the environmental behavior of NOM and its interaction with pollutants. Firstly, this review summarized the extraction and purification methods of NOM with different properties, and analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of each method. Secondly, it introduced the commonly used spectroscopic characterization techniques of NOM, and described the environmental behavior of NOM. Moreover, the interaction mode, mechanism and influencing factors between NOM and exogenous heavy metal and organic pollutants were introduced in detail, as well as the migration of NOM and pollutants in soil environment and their potential environmental risks. The purpose of this review is to provide a systematic understanding of NOM. On this basis, it is hoped that this review can provide comprehensive information about the nature of NOM itself, its environmental behavior, and its interactions with pollutants. Based on the comprehensive and in-depth anatomy of the natural and environmental behavior of NOM, we can have a deeper understanding of the important role of NOM in the soil environment. Subsequently, this review may provide a theoretical basis for future research on soil pollution remediation, fertility maintenance, and carbon cycling.
-

-
图 1 (a)土壤中DOM浓度与菲的吸附分配系数关系 [79],(b)不同土壤中DOM浓度与“莠去津”的吸附分配系数关系[80]
Figure 1. (a) The relationship between DOM concentration in soil and phenanthrene adsorption distribution coefficient [79], (b) The relationship between DOM concentration in different soils and atrazine adsorption distribution coefficient[80]
表 1 不同提取方法和提取剂的作用机制与适用范围概述
Table 1. Overview of the mechanism and scope of application of different extraction methods and extractants
提取方法
Extraction method常用提取剂
Common extractants作用机制与适用范围
Mechanism and scope of application参考文献
References水提法 H2O 适用于DOM的提取,提取的DOM含量低、组分简单、疏水性小、芳香性高。 [12] 盐提法 K2SO4、KCl、CaCl2 通过添加外源离子增强土壤中DOM与溶液中电解质的配体交换作用,减少DOM与土壤矿物吸附作用力而使DOM解离出来。KCl可提取微生物源 DOM;CaCl2难以浸提出高缩合的DOM组分;K2SO4提取的DOM含量更高、组分更复杂、疏水性更大、芳香性更低。其中K+可以促使溶液中的无机胶体絮凝。 [12-13] 酸提法 HCl、HF FA溶于酸碱,HCl可用于提取FA,HF可与硅杂质反应,主要用于降低粗产物中的灰分。 [14-18] 碱提法 NaOH、KOH Na+可以取代吸附于NOM上的金属阳离子,高pH环境还可以改变NOM的溶解状态。HA溶碱不溶酸,NaOH可用于提取HA。 络合剂提取法 Na4P2O7、EDTA 利用Na4P2O7和EDTA等破坏土壤中金属-有机质络合物,用于提取与金属络合的DOM、HM。 [19-20] 有机提取法 CH3COCH、二甲亚砜
(DMSO)、Sulpholane等使用有机提取剂(乙醚、丙酮、甲醇等)在索氏提取器中进行提取,依次去除非腐殖物质,二甲亚砜(DMSO)可用于破坏HM与土壤组分间的氢键。 [21-22] -
[1] MATILAINEN A, GJESSING E T, LAHTINEN T, et al. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83(11): 1431-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.018 [2] LEENHEER J A, CROUé J-P. Aquatic organic matter: Understanding the unknown structures is key to better treatment of drinking water [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2003, 37: 18-26. doi: 10.1021/es032333c [3] 马连刚, 肖保华. 土壤腐殖质提取和分组综述 [J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(4): 465-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.04.015 MA L G, XIAO B H. Review on extraction and fractionation of humic substances from soils [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(4): 465-471(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2011.04.015
[4] 单瑞娟, 黄占斌, 柯超, 等. 腐植酸对土壤重金属镉的淋溶效果及吸附解吸机制研究 [J]. 腐植酸, 2015(1): 12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9212.2015.01.005 SHAN R J, HUANG Z B, KE C, et al. Study on humic acid for leaching effect of cadmium in soil and its adsorption-desorption mechanism [J]. Humic Acid, 2015(1): 12-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9212.2015.01.005
[5] HOU Y, HE K, CHEN Y, et al. Changes of soil organic matter stability along altitudinal gradients in Tibetan alpine grassland [J]. Plant and Soil, 2019, 444: 1-20. doi: 10.1007/s11104-019-04232-5 [6] JIMéNEZ-GONZáLEZ M A, ÁLVAREZ A M, CARRAL P, et al. Influence of soil forming factors on the molecular structure of soil organic matter and carbon levels [J]. Catena, 2020, 189: 104501. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104501 [7] MARSCHNER B, KALBITZ K. Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils [J]. Geoderma, 2003, 113(3/4): 211-235. [8] STOCKMANN U, ADAMS M A, CRAWFORD J W, et al. The knowns, known unknowns and unknowns of sequestration of soil organic carbon [J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2013, 164: 80-99. [9] 潘根兴, 丁元君, 陈硕桐, 等. 从土壤腐殖质分组到分子有机质组学认识土壤有机质本质 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(5): 451-470. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.05.0451 PAN G X, DING Y J, CHEN S T, et al. Exploring the nature of soil organic matter from humic substances isolation to SOMics of molecular assemblage [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(5): 451-470(in Chinese). doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.05.0451
[10] STEVENSON F J. Humus chemistry: genesis, composition, reactions[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1994. [11] 李忠佩, 焦坤, 吴大付. 不同提取条件下红壤水稻土溶解有机碳的含量变化 [J]. 土壤, 2005, 37(5): 512-516. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2005.05.008 LI Z P, JIAO K, WU D F. Soluble organic C content of paddy soils in subtropical China in relation to extraction conditions [J]. Soils, 2005, 37(5): 512-516(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2005.05.008
[12] 王贵胤, 张世熔, 周玲, 等. 不同试剂提取紫色土溶解性有机碳含量研究 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2012, 25(6): 2184-2189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2012.06.046 WANG G Y, ZHANG S R, ZHOU L, et al. Study on concentration of dissolved organic carbon by different extractants in purple soil [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 25(6): 2184-2189(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2012.06.046
[13] ZHENG X C, LIANG Y H, WU Y S. Influence of extractants and filter materials in the extraction of dissolved organic matter (DOM) from subtropical agricultural soil [J]. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 2018, 30(3): 165-172. [14] SCHNITZER M, KHAN S U. Soil organic matter[M]. New York: Elsevier, 1975. [15] MENG F, YUAN G, WEI J, et al. Humic substances as a washing agent for Cd-contaminated soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 100(181): 461-467. [16] ROSA A, ROCHA J, FURLAN M. Humic substances of peat: study of the parameters that influence on the process of alkaline extraction [J]. Quimica Nova, 2000, 23(4): 472-476. doi: 10.1590/S0100-40422000000400008 [17] VELTHORST E, NAKKEN-BRAMEIJER N, MULDER J. Fractionation of soil organic matter [J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 73(3): 237-251. doi: 10.1080/03067319908032666 [18] KROSSHAVN M, KÖGEL‐KNABNER I, SOUTHON T, et al. The influence of humus fractionation on the chemical composition of soil organic matter studied by solid‐state 13C NMR [J]. Journal of Soil Science, 1992, 43(3): 473-483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1992.tb00153.x [19] HORI S, OKUDA A. Purification of humic acid by the use of ion exchange resin [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1961, 7(1): 4. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1961.10430948 [20] KHAN S. Humic acid fraction of a gray wooded soil as influenced by cropping systems and fertilizers [J]. Geoderma, 1970, 3(3): 247-254. doi: 10.1016/0016-7061(70)90025-X [21] 宋凡浩, 吴丰昌, 郭飞, 等. XAD树脂吸附技术提取和分级土壤富里酸研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(11): 173-177. SONG F H, WU F C, GUO F, et al. Review on extraction and fractionation of soil fulvic acid by XAD resin adsorption technique [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(11): 173-177(in Chinese).
[22] TSUTSUKI K, KUWATSUKA S. Characterization of humin-metal complexes in a buried volcanic ash soil profile and a peat soil [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1992, 38(2): 297-306. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1992.10416493 [23] 吴东明, 邓晓, 李怡, 等. 土壤溶解性有机质的提取与特性分析研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(3): 6-11. WU D M, DENG X, LI Y, et al. Progress in extraction and characteristic analysis of dissolved organic matter in soil [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(3): 6-11(in Chinese).
[24] MCADAMS B C, AIKEN G R, MCKNIGHT D M, et al. High pressure size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) determination of dissolved organic matter molecular weight revisited: Accounting for changes in stationary phases, analytical standards, and isolation methods [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(2): 722-730. [25] POULIN B A, RYAN J N, AIKEN G R. Effects of iron on optical properties of dissolved organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(17): 10098-10106. [26] HAYES T, HAYES M, SKJEMSTAD J, et al. Isolation of humic substances from soil using aqueous extractants of different pH and XAD resins, and their characterisation by 13C-NMR, in humic substances and organic matter in soil and water environment: Characterization, Transformations and interactions, international humic substances society[C]. Inc, St Paul, MN55108, USA, 1996: 13-24. [27] DAIGNAULT S, NOOT D, WILLIAMS D, et al. A review of the use of XAD resins to concentrate organic compounds in water [J]. Water Research, 1988, 22(7): 803-813. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(88)90017-6 [28] 凌婉婷, 徐建民, 高彦征, 等. 溶解性有机质对土壤中有机污染物环境行为的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(2): 326-330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2004.02.033 LING W T, XU J M, GAO Y Z, et al. Influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on environmental behaviors of organic pollutants in soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(2): 326-330(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2004.02.033
[29] LI Q, GUO X, CHEN L, et al. Investigating the spectral characteristic and humification degree of dissolved organic matter in saline-alkali soil using spectroscopic techniques [J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2017, 11(1): 76-84. doi: 10.1007/s11707-016-0568-1 [30] 许伟. 水溶性有机物的电子转移能力及其对微生物异化铁还原影响的研究[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学, 2009. XU W. Electron transfer capability of dissolved organic matter and its effects on microbial dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University, 2009.
[31] BOGUTA P, SOKOŁOWSKA Z. Interactions of Zn (II) ions with humic acids isolated from various type of soils. Effect of pH, Zn concentrations and humic acids chemical properties [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0153626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153626 [32] THURMAN E M. Organic geochemistry of natural waters[M]. Washington: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [33] MCDONALD S, BISHOP A G, PRENZLER P D, et al. Analytical chemistry of freshwater humic substances [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2004, 527(2): 105-124. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2004.10.011 [34] FUENTES M, GONZáLEZ-GAITANO G, GARCíA-MINA J M. The usefulness of UV–visible and fluorescence spectroscopies to study the chemical nature of humic substances from soils and composts [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(12): 1949-1959. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.07.024 [35] NAMJESNIK-DEJANOVIC K, CABANISS S E. Reverse-phase HPLC method for measuring polarity distributions of natural organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(4): 1108-1114. [36] NOVOTNY E H, MARTINNETO L. Effects of humidity and metal ions on the free radicals analysis of peat humus [J]. Geoderma, 2002, 106(3): 305-317. [37] POSPíŠILOVá L, HORáKOVá E, FIŠERA M, et al. Effect of selected organic materials on soil humic acids chemical properties [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 187: 109663. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109663 [38] MINOR E C, SWENSON M M, MATTSON B M, et al. Structural characterization of dissolved organic matter: A review of current techniques for isolation and analysis [J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(9): 2064-2079. [39] 何伟, 白泽琳, 李一龙, 等. 溶解性有机质特性分析与来源解析的研究进展 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 359-372. HE W, BAI Z L, LI Y L, et al. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 359-372(in Chinese).
[40] CAO X, AIKEN G R, BUTLER K D, et al. Comparison of the chemical composition of dissolved organic matter in three lakes in minnesota [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 1747-1755. [41] YU M, HE X, LIU J, et al. Characterization of isolated fractions of dissolved organic matter derived from municipal solid waste compost [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 635: 275-283. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.140 [42] WENMING X, ZHANG S, LIN R, et al. Evaluating soil dissolved organic matter extraction using three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy [J]. Pedosphere, 2017, 27(5): 968-973. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60466-1 [43] DAVIDSON E A, JANSSENS I A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change [J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7081): 165-173. doi: 10.1038/nature04514 [44] JASSO-FLORES I, GALICIA L, CHáVEZ-VERGARA B, et al. Soil organic matter dynamics and microbial metabolism along an altitudinal gradient in Highland tropical forests [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140143. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140143 [45] 杨光辉. 大兴安岭地区土壤有机质空间分布特征规律研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2019. YANG G H. Study on spatial distribution characteristics of Soil Organic Matter in the Daxinganling region[D]. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2019 .
[46] 马哲, 王杰琼, 陈景文, 等. pH对不同来源溶解性有机质光致生成活性物种量子产率的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(9): 1889-1895. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017012301 MA Z, WANG J Q, CHEN J W, et al. Effect of pH on the quantum yield of reactive photo-induced species generated in different sources of DOM [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(9): 1889-1895(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017012301
[47] GAO H, ZEPP R G. Factors influencing photoreactions of dissolved organic matter in a Coastal River of the Southeastern United States [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1998, 32(19): 2940-2946. [48] SMERNIK R J, KOOKANA R S. The effects of organic matter–mineral interactions and organic matter chemistry on diuron sorption across a diverse range of soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 99-104. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.066 [49] KLEBER M, SOLLINS P, SUTTON R. A conceptual model of organo-mineral interactions in soils: self-assembly of organic molecular fragments into zonal structures on mineral surfaces [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(1): 9-24. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9103-5 [50] KAHLE M, KLEBER M, JAHN R. Retention of dissolved organic matter by phyllosilicate and soil clay fractions in relation to mineral properties [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(3): 269-276. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.11.008 [51] 刘治清, 宋晶, 李学, 等. 饱和细粒土固结过程中矿物组分与有机质的三维表征 [J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(5): 1299-1306. LIU Y Q, SONG J, LI X, et al. Three-dimensional characterization of mineral and organic compositions in process of consolidation of saturated fine-grained soil [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(5): 1299-1306(in Chinese).
[52] TOMBáCZ E, LIBOR Z, ILLES E, et al. The role of reactive surface sites and complexation by humic acids in the interaction of clay mineral and iron oxide particles [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(3): 257-267. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.11.002 [53] 王磊, 应蓉蓉, 石佳奇, 等. 土壤矿物对有机质的吸附与固定机制研究进展 [J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(4): 805-818. WANG L, YING R R, SHI J Q, et al. Advancement in study on adsorption of organic matter on soil minerals and its mechanism [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(4): 805-818(in Chinese).
[54] MIKUTTA R, MIKUTTA C, KALBITZ K, et al. Biodegradation of forest floor organic matter bound to minerals via different binding mechanisms [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(10): 2569-2590. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.002 [55] MATILAINEN A, VEPSäLäINEN M, SILLANPää M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 159(2): 189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2010.06.007 [56] 杨毅, 兰亚琼, 金鹏康, 等. 腐殖酸与Cd2+的结合特性及其影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1198-1203. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090804 YANG Y, LAN Y Q, JIN P K, et al. Characteristic and influential factors of humic acid complexed with Cd2+ [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1198-1203(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090804
[57] 王俊. 腐殖酸对砷在土壤中的形态转化和生物有效性的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2017. WANG J. Electron transfer capability of dissolved organic matter and its effects on microbial dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017.
[58] LEE H H, WENG Y H, LI K C. Electro-ultrafiltration study on Aldrich humic substances with different molecular weights [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 63(1): 23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2008.03.030 [59] MARSAC R, BANIK N L, LüTZENKIRCHEN J, et al. Modeling metal ion-humic substances complexation in highly saline conditions [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 100(79): 52-64. [60] ZHANG J, CHEN L, YIN H, et al. Mechanism study of humic acid functional groups for Cr (VI) retention: two-dimensional FTIR and 13C CP/MAS NMR correlation spectroscopic analysis [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 100(225): 86-92. [61] ZHANG J, YIN H, CHEN L, et al. The role of different functional groups in a novel adsorption-complexation-reduction multi-step kinetic model for hexavalent chromium retention by undissolved humic acid [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237: 740-746. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.120 [62] 余国营, 吴燕玉. 土壤环境中重金属元素的相互作用及其对吸持特性的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 1997, 16(1): 30-36. YU G Y, WU Y Y. Effects of heavy metals joint action on their characteristic of sorption and desorption in brown soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1997, 16(1): 30-36(in Chinese).
[63] 吕殿青, 王宏, 潘云, 等. 容重变化对土壤溶质运移特征的影响 [J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2010, 33(1): 75-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2537.2010.01.017 LV D Q, WANG H, PAN Y, et al. Effect of bulk density changes on soil solute transport characteristics [J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2010, 33(1): 75-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2537.2010.01.017
[64] 孙花, 谭长银, 黄道友, 等. 土壤有机质对土壤重金属积累、有效性及形态的影响 [J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2011, 34(4): 82-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2537.2011.04.018 SUN H, TAN C Y, HUANG D Y, et al. Effects of soil organic matter on the accumulation, availability and chemical speciation of heavy metal [J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2011, 34(4): 82-87(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2537.2011.04.018
[65] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [66] 刘利军, 洪坚平, 闫双堆, 等. 不同pH条件下腐植酸对土壤中砷形态转化的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(1): 134-141. LIU L J, HONG J P, NI S D, et al. Effects of humic acid on transformation of soil As in different pH conditions [J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(1): 134-141(in Chinese).
[67] 王浩, 章明奎. 有机质积累和酸化对污染土壤重金属释放潜力的影响 [J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(3): 538-541. WANG H, ZHANG M K. Effects of organic matter accumulation and acidification on release potential of heavy metals from polluted soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2009, 40(3): 538-541(in Chinese).
[68] 马丽, 宋雁辉, 徐政雄. 浅析土壤重金属形态转化与土壤污染治理 [J]. 环境影响评价, 2019, 41(5): 18-21. MA L, SONG Y H, XU Z X. Review of conversion of heavy metals speciation in soil and soil pollution control [J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2019, 41(5): 18-21(in Chinese).
[69] KILUNGA P I, SIVALINGAM P, LAFFITE A, et al. Accumulation of toxic metals and organic micro-pollutants in sediments from tropical urban rivers, Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 179: 37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.081 [70] 占新华, 周立祥, 杨红, 等. 水溶性有机物与多环芳烃结合特征的红外光谱学研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 47-53. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.01.008 ZHAN X H, ZHOU L X, YANG H, et al. Infrared spectroscopy of DOM-PAHs complexes [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 47-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.01.008
[71] TRUBETSKAYA O E, TRUBETSKOJ O A, VOYARD G, et al. Determination of hydrophobicity and optical properties of soil humic acids isolated by different methods [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 132: 84-89. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.004 [72] RODRíGUEZ F J, SCHLENGER P, GARCíA-VALVERDE M. A comprehensive structural evaluation of humic substances using several fluorescence techniques before and after ozonation. Part I: Structural characterization of humic substances [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 476: 718-730. [73] SCHWARZENBACH R P, WESTALL J. Transport of nonpolar organic compounds from surface water to groundwater. Laboratory sorption studies [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1981, 15(11): 1360-1367. [74] KILE D E, WERSHAW R L, CHIOU C T. Correlation of soil and sediment organic matter polarity to aqueous sorption of nonionic compounds [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(12): 2053-2056. [75] RAN Y, SUN K, YANG Y, et al. Strong sorption of phenanthrene by condensed organic matter in soils and sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(11): 3952-3958. [76] XING B, PIGNATELLO J J. Time‐dependent isotherm shape of organic compounds in soil organic matter: Implications for sorption mechanism [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 1996, 15(8): 1282-1288. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620150805 [77] XING B, PIGNATELLO J J. Dual-mode sorption of low-polarity compounds in glassy poly (vinyl chloride) and soil organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(3): 792-799. [78] LING W, WANG H, XU J, et al. Sorption of dissolved organic matter and its effects on the atrazine sorption on soils [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2005, 17(3): 478-482. [79] GAO Y, XIONG W, LING W, et al. Impact of exotic and inherent dissolved organic matter on sorption of phenanthrene by soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 140(1): 138-144. [80] 凌婉婷. 溶解性有机质对莠去津在土壤/矿物-水界面行为的影响及其机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005. LING W T. The influence of Dissolved organic matter on atrazine sorption and desorption by soils and minerals[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2005 .
[81] 付高阳, 谯华, 彭伟, 等. 溶解性有机质对土壤中有机污染物迁移转化的影响因素 [J]. 当代化工, 2016, 45(9): 2221-2223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.09.054 FU G Y, QIAO H, PENG W, et al. Influence of dissolved organic matter on migration and transformation of organic pollutants in soil [J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(9): 2221-2223(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2016.09.054
[82] HAITZER M, HöSS S, TRAUNSPURGER W, et al. Relationship between concentration of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and the effect of DOM on the bioconcentration of benzo[a]pyrene [J]. Aquatic Toxicol, 1999, 45(2): 147-158. [83] SONG N, YANG Z, ZHOU L, et al. Effect of dissolved organic matter on the toxicity of chlorotoluron to Triticum aestivum [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18(1): 101-108. [84] BEJARANO A C, CHANDLER G T, DECHO A W. Influence of natural dissolved organic matter (DOM) on acute and chronic toxicity of the pesticides chlorothalonil, chlorpyrifos and fipronil on the meiobenthic estuarine copepod Amphiascus tenuiremis [J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology & Ecology, 2005, 321(1): 43-57. [85] 李恭臣, 夏星辉, 周追, 等. 富里酸在水体多环芳烃光化学降解中的作用 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(8): 1604-1611. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.08.017 LI G C, XIA X H, ZHOU Z, et al. Effects of fulvic acid on photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous solution [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(8): 1604-1611(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.08.017
[86] 张思杰, 孙孝龙. 土壤中大分子有机质相关研究进展及应用 [J]. 环境与发展, 2019, 31(4): 117, 119. ZHANG S J, SUN X L. Research progress and application of macromolecular organic matter in soil [J]. Environment and Development, 2019, 31(4): 117, 119(in Chinese).
[87] MADDIGAPU P R, MINELLA M, VIONE D, et al. Modeling phototransformation reactions in surface water bodies: 2, 4-Dichloro -6-nitrophenol as a case study [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(1): 209-214. [88] 钟明洁, 陈勇, 胡春. 水溶液中嗪草酮的光化学行为研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(7): 1470-1474. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.07.020 ZHONG M J, CHEN R, HU C. Photochemical fate of metribuzin in aqueous solution under simulated sunlight irradiation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(7): 1470-1474(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.07.020
-



 下载:
下载:

