-
抗生素与人们的生活息息相关,其被广泛用于防治疾病和发展养殖业[1-2]等。相对于美国每年2.3万吨的使用量和欧盟5万吨的使用量而言[3-4],我国以每年超15万吨的使用量成为全球最大的抗生素消费大国[5]。据报道,有将近60%的抗生素使用后被排放到水体环境中[6],这就使得水体受到了污染,无论是水源水[7-8]还是非水源水[9-10]都能检测到浓度为ng·L−1水平的抗生素,一些水体的检出浓度甚至达到mg·L−1水平[11]。目前,污水处理厂对水体中抗生素的处理效果并不是很理想[12-14],这些残留的抗生素会通过食物链放大作用对人体产生蓄积毒性[1, 15-16]。在众多的抗生素中,氨基糖苷类抗生素以其抗菌谱广、低成本、治疗效果好等优点而被大量使用[17-19],值得注意的是,此类抗生素的溶解性较高,导致环境受到其污染的几率大大加大。因此,非常有必要对氨基糖苷类抗生素进行毒性分析,从而为环境风险评估提供一定的数据参考。硫酸阿米卡星(Amikacin sulfate, AMI)是常用的氨基糖苷类抗生素一种,其被广泛用于临床上治疗由细菌感染的革兰氏阴性的患者。有研究表明,AMI造成肾毒性和长期耳毒性的概率为7%—62%[20]。在各类水体、牛奶、土壤和动物组织中检测到较高的残留[21],对环境的潜在危害较大,因此有必要对AMI进行毒理学研究。
除抗生素外,作为污染物之一的重金属对环境也有较大的危害[22]。采矿、冶炼和制造等人类活动都会加剧环境中重金属的污染[23],此外,重金属具有不易降解性、持久性和生物富集等特点,这使得被重金属污染的水体对整个生态系统会产生不可逆转的损害[24]。我国约有2.8×109 m2的农业土壤被镉污染,环境中大于90%的镉污染是由于人类活动造成的[25],镉污染对人类健康存在很大的危害。生产锰的过程中约有55%的锰会排放到废水和废渣中,造成水体氨氮等指标严重超标[26],国内锰污染事件常被报道,“锰三角”也引起了较大的关注[27]。我国近20年来锌的产量是所有重金属中最多的[28],锌的点位超标率达到了0.9%[29],一些环境中锌的含量竟然能达到背景值的5倍多[28]。总之,在众多的重金属污染中,镉、锰和锌对环境造成的污染较为严重,因此有必要对这3种重金属进行毒理学研究。越来越多的研究表明,环境中的污染物都是以混合物形式存在的[30-31]。其中,在众多混合物的毒性研究中,重金属与抗生素的毒性研究较少。重金属离子会改变抗生素的生态危害,并最终影响环境污染的治理和防护,此外,人类活动又极大增加了重金属与抗生素对环境产生复合污染的机会,且硫酸阿米卡星、镉、锰和锌对环境又存在极大的危害,因此有必要探讨其混合毒性规律。
随着混合物体系越来越复杂,使得混合污染物的毒理学评估变得越来越极具挑战性。越来越多的模型被用于评估混合物的毒性,其中最经典的两种模型是浓度加和(concentration addition, CA) 和独立作用(independent action,IA)模型[30, 32]。为了比较两种模型评估结果的差异,采用效应残差比(effect residual ratio, ERR)[33-36]来量化参考模型与实验数据的偏差,即可以定量评估混合物毒性相互作用。李孟涵等[37]采用半数效应 (E50)时的ERR值来表征拟合曲线与实测的偏离程度。Wang等[33]和Qin等[34]认为毒性作用评估需要综合考虑多个效应水平,因此,应用ERR对整个效应曲线上的毒性相互作用表征更有实际意义。
因此,本研究以蛋白核小球藻(Chlorella pyrenoidosa, C.pyrenoidosa)为受试生物,以3种重金属(五水合氯化镉(CdCl2·2.5H2O,Cd)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O,Mn)和七水合硫酸锌(ZnSO4·7H2O, Zn))和AMI为研究对象。采用均匀设计射线法(UD-Ray)[38]设计三组二元混合体系(Cd-AMI、Mn-AMI和Zn-AMI),以此研究3种重金属(Cd、Mn和Zn)与AMI的联合毒性。此外,以CA和IA模型进行毒性相互作用评估,采用ERR来比较两种模型评估结果的差异和动态表征毒性相互作用,以期为客观、准确地评估污染物的环境风险提供的方法和数据参考。
-
试剂:硫酸阿米卡星(amikacin sulfate, AMI)购自上海原叶生物科技有限公司;五水合氯化镉(CdCl2·2.5H2O, Cd)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O, Mn)和七水合硫酸锌(ZnSO4·7H2O, Zn)均购自国药,均为分析纯。抗生素与重金属的理化性质均列于表1,实验所用的储备液(表1)用超纯水配制,并装于棕色瓶,保存于4 ℃的冰箱中备用。
主要仪器:Synery-2酶标仪(美国伯腾仪器有限公司)、MGC-250光照培养箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司)、ESJ182-4万分之一电子天平(沈阳龙腾电子有限公司)、Genex系列移液器(宝予德有限公司)、721分光光度计(上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司)等。
-
蛋白核小球藻(Chlorella pyrenoidosa, C.pyrenoidosa)购自中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会淡水藻种库(FACHB),编号为FACHB-5,培养基、培养条件和培养方法见文献[39]。
-
在自然环境中,污染物常以混合物的形式存在[31],研究混合物的联合毒性可以更准确地对其环境风险进行评估。采用均匀设计射线法(UD-Ray)[38]设计抗生素与重金属的二元混合物体系(B1、B2和B3),每个体系设计均包括5条射线(R1、R2、R3、R4、R5),其设计结果见表2。
-
应用时间毒性微板分析法(t-MTA)[40]测定污染物对C.pyrenoidosa的毒性效应数据。以96孔透明微板作为实验载体,在其四周(36个微孔)加入200 μL的超纯水,以避免边缘效应。以第6、7列的12个微孔作为实验空白对照,加入100 μL的超纯水。在余下48个微孔中依次加入按预实验获得的稀释因子稀释的12个不同浓度的污染物溶液100 μL,详细过程参照文献[41]。最后在空白孔和样品处理孔中均加入100 μL事先培养至对数期的藻液(0.2<OD683<0.3),使得96个微孔内液体总体积为200 μL。以上过程重复3板。加盖,置于(25±1) ℃条件下的光照培养箱中进行培养,分别在24、48、72、96 h时,取出,用酶标仪测定OD683[42-43]。污染物对蛋白核小球藻产生的毒性效应表示为抑制率(E),计算表达式如(1)所示:
-
为了计算任一浓度的单一物质或混合物的效应E,采用两参数模型Logit函数和Weibull函数对1.4节中获得的实验观测浓度-效应数据进行拟合[31]。通过相关系数(R)和均方根误差(RMSE)来判断函数的拟合优度[44-46],确定本实验拟合的最佳函数为Logit函数,计算公式如(2)所示。此外,数据处理均由APtox软件[40]实现。
式中,α为位置参数,β为形状参数或斜率参数,c为污染物的浓度,E表示效应(0≤E≤1)。
-
常采用浓度加和模型(Concentration addition, CA)和独立作用模型(Independent action, IA)[31]对混合物毒性相互作用进行分析。通过比较95%观测置信区间(OCIs)与CA、IA预测线位置来判断混合物毒性相互作用是加和作用、拮抗作用还是协同作用[22, 44, 47]。CA与IA公式如下所示:
式中,m是混合物中组的个数;ci是混合物体系表现出效应x时所对应的第i个组分的浓度;ECx,i是第i个组分的等效应浓度,E(Cmix)是混合物的总效应。
有研究表明,效应残差比(Effect residual ratio, ERR)可被用来量化参考模型与实验数据的偏差[33-35],其公式如下所示:
式中,EOBS为观测效应,EPRD为预测效应,x为参考模型对应的指定效应。当ERR值处于95%OCI区间内、95%OCI以上和95%OCI以下时,毒性相互作用分别为加和作用、拮抗作用和协同作用。
-
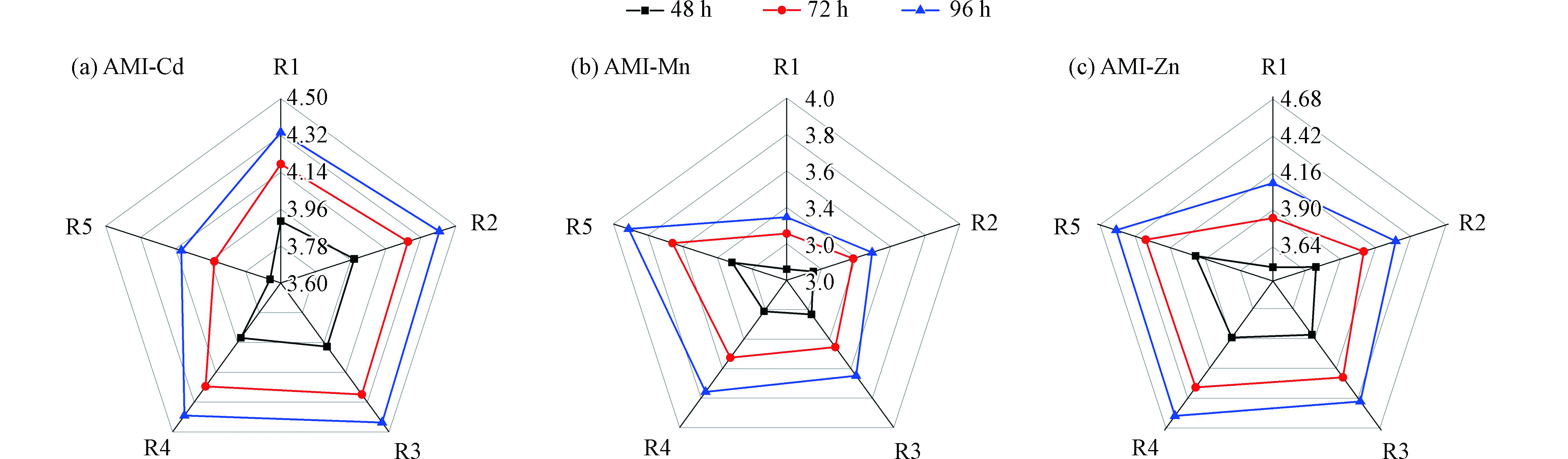
AMI、Cd、Mn和Zn对蛋白核小球藻的单一毒性效应数据参见文献[48]。基于R和RMSE的数值大小[44-46],最终选用拟合效果较好的两参数非线性函数(Logit)对3种重金属(Cd、Mn和Zn)与AMI的二元混合毒性数据进行拟合。常以EC50的负对数(pEC50)为毒性大小的数值[49],图1是三组二元混合体系中射线的pEC50值在不同时间 (48、72、96 h)的雷达图。
由图1可知,三组二元混合体系共15条射线的毒性大小均随时间的延长而变大,呈现明显的时间依赖性,且随暴露时间的延长,毒性在逐渐增大。丁婷婷等[42]发现,3种氨基糖苷类抗生素对青海弧菌和蛋白核小球藻的毒性均随时间而增大。不同混合物体系,其射线的毒性大小顺序不同,如在96 h时,AMI-Cd的5条射线的毒性大小排序为:R5>R1>R4>R2>R3;AMI-Mn的5条射线的毒性大小排序为:R1>R2>R3>R4>R5;AMI-Zn的5条射线的毒性大小排序为:R1>R2>R3>R5>R4。说明混合物组分不同及其构成比例对毒性大小有影响。刘芳等[38]在研究离子液体混合物对发光菌的毒性规律时也发现不同组分和不同组分比例对毒性均有影响。
-
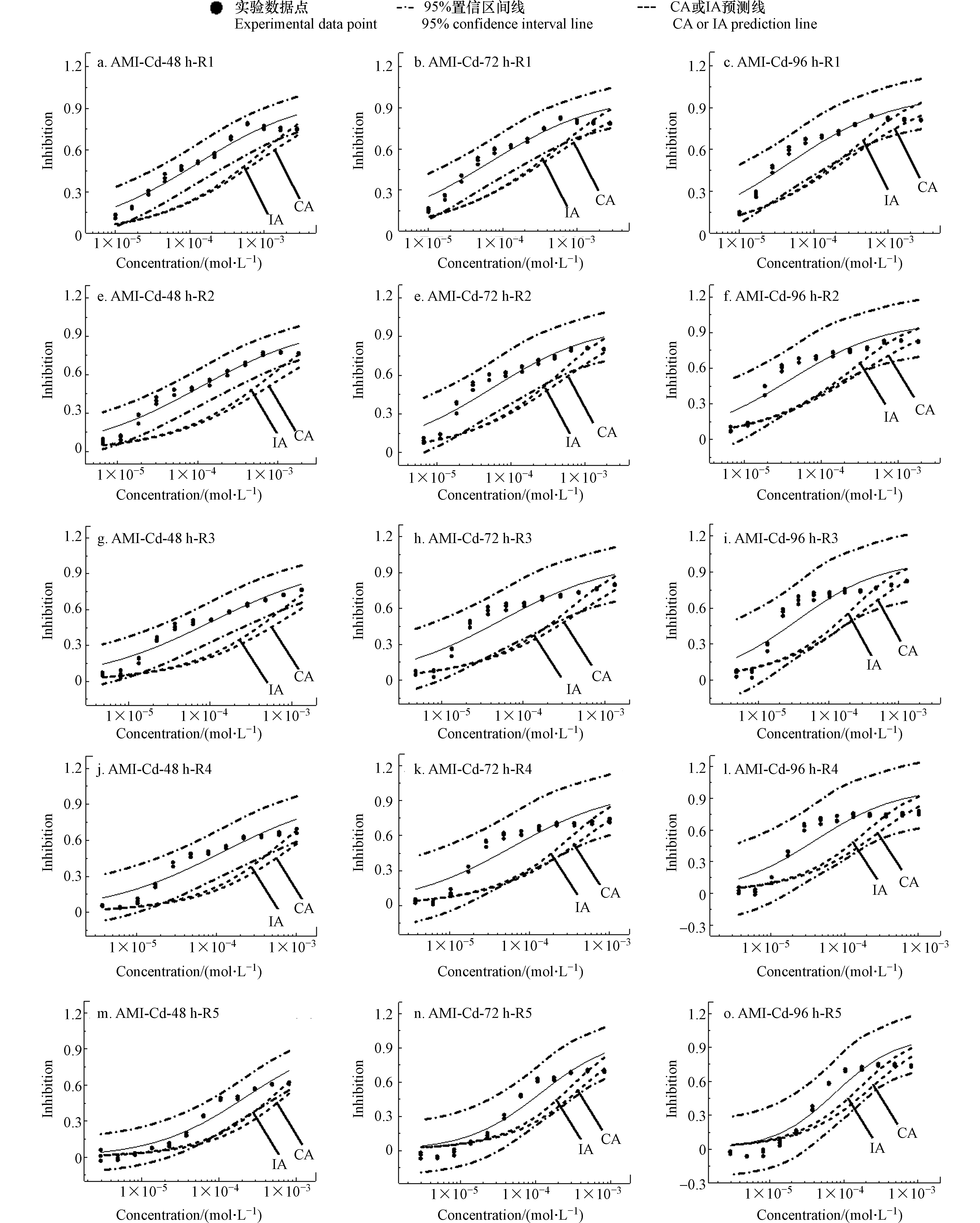
应用CA和IA模型进行混合毒性相互作用分析,结果见图2、图3和图4,其中包括实验数据点、95% OCI、浓度效应曲线(Concentration-effect curves, CRCs)和模型(CA和IA)预测线,由于在24 h时,三组混合物体系基本是加和作用没有给出。
由图2、图3和图4可知,在三组二元混合体系中,CA和IA预测线的位置几乎都在CRCs以下。CA和IA对三组混合物体系中射线的毒性预测线除在较高浓度区域(浓度大于1E-4 mol·L−1时)略有分开外基本上是重合的,也就是说,CA和IA对三个混合物体系的毒性相互作用评估结果基本上是一致的。依据CA和IA,三组混合物体系均呈现出协同作用,且随暴露时间延长逐渐增加或减弱。如在48 h时,AMI-Cd混合物体系中5条射线的中浓度区都呈现强度不同的协同作用,在72 h时,CA和IA预测线与实验观测值偏离程度减小,呈现加和作用或弱协同作用,到了96 h,5条射线均为加和作用;在48 h时,AMI-Zn体系的5条射线在高浓度区均是协同作用,而随着时间的延长,部分射线(R2、R3、R4和R5)的高浓度区变为了加和作用,此外,每条射线在中低浓度区的加和作用在减弱而协同作用在加强,而AMI-Mn体系中R1和R2呈加和作用,R3—R5呈协同作用,且随时间的变化不明显。
在同一个混合体系中,不同射线在不同浓度区域观察到毒性相互作用也有所差异[36, 44]。在R1到R5的过程中,AMI-Cd在中浓度区的协同作用逐渐变为加和作用;在AMI-Mn中,R1和R2的CA和IA预测线几乎都在95% OCI之内,表现为加和作用,但R3、R4和R5在中浓度区有较强的协同作用,但随暴露时间的延长变化不明显。由于R1—R5是组分浓度比不同的5条射线,毒性相互作用的不同,说明组分的浓度比影响混合物的毒性相互作用变化规律,在R1到R5的过程中,AMI-Zn中五条射线的协同作用随时间的延长逐渐趋于明显。可见,不同重金属与AMI构成的混合体系的毒性相互作用也有所不同。
-
效应残差比(Effect residual ratio, ERR)可以用于检验不同效应下预测模型和CRCs的偏差[33],即可定量表征混合物的毒性相互作用。图5、图6和图7分别是AMI-Cd、AMI-Mn和AMI-Zn中各条射线的ERR图。
从图5、图6和图7可看出,分别基于CA和IA的ERR值(毒性相互作用强度)随暴露时间的延长的变化趋势线基本上是重合的,但在不同的混合物体系中,毒性相互作用强度(ERR值)不同。在AMI-Cd体系中,ERR曲线随暴露时间延长逐渐靠近置信曲线下限,R5位于置信区间内,即混合物射线呈现弱协同作用且逐渐减弱。在AMI-Zn体系中,不同射线的ERR曲线随暴露时间延长ERR逐渐偏离置信区间下限,即协同作用逐渐增强。在AMI-Mn体系中,ERR曲线的曲线变化同CA和IA曲线的变化规律。与CA和IA模型相比,ERR可以在效应水平上进行毒性相互作用的定量表征[34-36]。
在AMI-Cd中,除了R1和R2在中效应区出现弱协同作用外,R3、R4和R5在整个效应下都是加和作用;在AMI-Mn中,R1在整个效应区间都表现为加和作用,而其余4条射线在中效应区间为协同作用,在低效应和高效应区间则为加和作用;在AMI-Zn中,除R1在整个效应区间内都为协同作用外,其余射线都呈现出低效应加和而中高效应协同作用的规律。这些都和CA与IA模型(图2、图3和图4)具有很好的一致性,但ERR法能定量评估毒性相互作用动态变化规律。
进一步分析96 h的50%效应的毒性与组分的关系[50],发现AMI-Mn中50%效应时CA和IA对应的ERR值与组分Mn和AMI的浓度比有明显的相关关系(公式6—9);在AMI-Zn中,50%效应时CA和IA对应的ERR值与Zn的比例有正线性关系(公式10—11),而与AMI比例的正线性关系不明显(R2=0.5161);在AMI-Cd中,50%效应时CA和IA对应的ERR值与AMI和Cd组分之间均没有明显的线性关系(R2=0.0437和R2=0.3058)。
-
(1)AMI和3种重金属(Cd、Mn和Zn)构成的二元混合体体系的毒性呈明显的时间依赖性和浓度依赖性。
(2) CA和IA对3个二元混合物体系的预测基本一致,即3个二元混合物体系均呈现出协同作用,且协同作用有一定的时间依赖性,但AMI-Mn体系的协同作用随时间变化没有AMI-Cd和AMI-Zn的毒性相互作用变化的明显。
(3)基于CA和IA的ERR对3个混合物体系的毒性相互作用表征结果也基本一致,但ERR可以定量的表征混合物毒性相互作用强度,且在AMI-Mn和AMI-Zn中,ERR值和组分之间存在一定的线性关系,而在AMI-Cd中ERR值与组分之间没有明显的线性关系。
抗生素与重金属对蛋白核小球藻时间依赖协同作用的动态定量表征
Dynamic and quantitative characterization of time-dependent synergism between antibiotics and heavy metals on Chlorella pyrenoidosa
-
摘要: 以硫酸阿米卡星(Amikacin sulfate, AMI)、五水合氯化镉(CdCl2·2.5H2O, Cd)、四水合氯化锰(MnCl2·4H2O, Mn)和七水合硫酸锌(ZnSO4·7H2O, Zn)为研究对象,以蛋白核小球藻(Chlorella pyrenoidosa, C. pyrenoidosa)为指示生物,采用均匀设计射线法设计3组二元混合体系(AMI-Cd、AMI-Mn和AMI-Zn),并应用时间毒性微板分析法测定其对C. pyrenoidosa的毒性数据,以浓度加和模型(Concentration addition, CA)和独立作用模型(Independent action, IA)为标准加和模型进行毒性相互作用分析,并运用效应残差比(Effect residual ratio, ERR)进行定量动态表征毒性相互作用。结果表明,3组二元混合体系共十五条射线的混合毒性呈明显的时间依赖性和浓度依赖性;依据ERR,CA和IA对三组二元混合体系的毒性评估结果基本一致,但3个混合物体系的毒性相互作用具有不同的时间变化规律,即随暴露时间延长,AMI-Cd中五条射线的中浓度区由协同作用逐渐变为加和作用,AMI-Zn中5条射线在高浓度区的协同作用逐渐变为加和作用,而中低浓度区的协同作用在加强;AMI-Mn的毒性相互作用随时间变化不是很明显;与CA和IA相比,ERR定量地表征了混合物体系的毒性相互作用强度,这为客观和准确地评估污染物的环境风险提供了方法和数据参考。Abstract: Amikacin sulfate (AMI), cadmium chloride pentahydrate (CdCl2·2.5H2O, Cd), manganese chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O, Mn) and zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O, Zn) were selected as the research objects to investigate their combined toxicity towards a freshwater algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa (C. pyrenoidosa) by the time-dependent toxicity microplate analysis. Three binary mixture systems (AMI-Cd, AMI-Mn and AMI-Zn) were designed by uniform design ray method. Concentration addition (CA) and independent action (IA) models were used to analyze toxicity interaction, and the effect residual ratio (ERR) was used to dynamically and quantitatively characterize toxic interaction. The results show that the combined toxicity of 15 rays in three binary systems is of obvious time-dependency and concentration-dependency. The toxicity interaction analyzed by CA and IA for the three binary mixture systems are similar, but different mixture systems have different time regularities. With the prolonging of exposure time, the medium concentration region of the five rays in AMI-Cd gradually changes from synergism to additive effect. The high concentration region of the five rays in AMI-Zn gradually changes from synergism to additive effect, and synergism is strengthening in the middle and low concentration regions. The changing of toxicity interaction within AMI-Mn mixture system with time is not obvious. In addition, compared with CA and IA, ERR quantitatively characterized the toxic interaction intensity of the mixture system, which provides a method and data reference for the objective and accurate assessment of the environmental risk of pollutants.
-

-
表 1 抗生素与重金属理化性质和储备液浓度
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of antibiotic and heavy metals and concentration of stocks
化合物
Name简称
Abbreviation分子式
Molecular formulaCAS-RN 分子量
Formula weight纯度/%
Purity储备液浓度/(mol·L−1)
Stock solution硫酸阿米卡星 AMI C22H43N5O13·2H2SO4 39831-55-5 781.76 ≥67.4 1.33×10−3 五水合氯化镉 Cd CdCl2·2.5H2O 7790-78-5 228.35 ≥99.0 1.08×10−2 四水合氯化锰 Mn MnCl2·4H2O 13446-34-9 197.90 ≥99.0 1.58×10−3 七水合硫酸锌 Zn ZnSO4·7H2O 7446-20-0 287.56 ≥99.0 6.68×10−2 表 2 混合体系组分构成及浓度比(pi)
Table 2. Composition and concentration ratio (pi) of the mixture systems
B1 PCd PAMI B2 PMn PAMI B3 PZn PAMI R1 8.673×10−1 1.327×10−1 R1 9.183×10−1 8.170×10−2 R1 9.500×10−1 5.000×10−2 R2 7.233×10−1 2.767×10−1 R2 8.181×10−1 1.819×10−1 R2 8.837×10−1 1.163×10−1 R3 5.666×10−1 4.334×10−1 R3 6.922×10−1 3.078×10−1 R3 7.916×10−1 2.084×10−1 R4 3.953×10−1 6.047×10−1 R4 5.292×10−1 4.708×10−1 R4 6.551×10−1 3.449×10−1 R5 2.073×10−1 7.927×10−1 R5 3.102×10−1 6.898×10−1 R5 4.318×10−1 5.682×10−1 -
[1] GUO H H, XUE S H, NASIR M, et al. Impacts of cadmium addition on the alteration of microbial community and transport of antibiotic resistance genes in oxytetracycline contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 99(1): 51-58. [2] AGNIESZKA C, JOANNA L, KAUR B S, et al. Influence of metal speciation in wastewater sludge on antibiotic distribution [J]. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 2021, 25(2): 04020078. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000592 [3] PRUDEN A, PEI R T, STORTEBOOM H, et al. Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23): 7445-7450. [4] KUMMERER K. Significance of antibiotics in the environment [J]. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2003, 52(1): 5-7. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg293 [5] WANG Z, DU Y, YANG C, et al. Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1423-1432. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.009 [6] ZHANG Q Q, YING G G, PAN C G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 6772-6782. [7] 李楠, 赵新华. 华北T市某自来水厂抗生素的分布及去除 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(21): 48-52. LI N, ZHAO X H. Distribution and removal of antibiotics in a waterworks in North China [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2017, 33(21): 48-52(in Chinese).
[8] 张君, 程艳茹, 杨海蓉, 等. 重庆地区典型水库表层水体抗生素分布特征研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2018, 43(11): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.11.007 ZHANG J, CHENG Y R, YANG H R, et al. Concentrations and pollution characteristics of typical antibiotics in typical reservoir in Chongqing [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2018, 43(11): 26-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.11.007
[9] 刘晓晖, 卢少勇. 大通湖表层水体中抗生素赋存特征与风险 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(1): 320-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.01.036 LIU X H, LU S Y. Occurrence and ecological risk of typical antibiotics in surface water of the Datong Lake, China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(1): 320-329(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.01.036
[10] 王嘉玮, 魏红, 杨小雨, 等. 渭河西安段磺胺类抗生素的分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2574-2583. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017032402 WANG J W, WEI H, YANG X Y, et al. Occurrence and ecological risk of sulfonamide antibiotics in the surface water of the Weihe Xi'an section [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2574-2583(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017032402
[11] JIANG Y, LI M, GUO C, et al. Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent–receiving river (Wangyang River) in North China [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 112: 267-274. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.075 [12] 徐维海, 张干, 邹世春, 等. 典型抗生素类药物在城市污水处理厂中的含量水平及其行为特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(8): 1779-1783. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.08.023 XU W H, ZHANG G, ZOU S C, et al. Occurrence, distribution and fate of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants [J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(8): 1779-1783(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.08.023
[13] BROWN K D, KULIS J, THOMSON B, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy effluent, municipal wastewater, and the Rio Grande in New Mexico [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 366(2): 772-783. [14] KARTHIKEYAN K G, MEYER M T. Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 361(1-3): 196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.06.030 [15] 徐永刚, 宇万太, 马强, 等. 环境中抗生素及其生态毒性效应研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(3): 11-27. XU Y G, YU W T, MA Q, et al. The antibiotic in environment and its ecotoxicity: A review [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(3): 11-27(in Chinese).
[16] 刘鹏霄, 王旭, 冯玲. 自然水环境中抗生素的污染现状、来源及危害研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(5): 36-42. LIU P X, WANG X, FENG L. Occurrences, resources and risk of antibiotics in aquatic environment: A review [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(5): 36-42(in Chinese).
[17] 吴佳慧, 刘鹏宇. 氨基糖苷类抗生素的发展历程 [J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2019, 44(11): 1275-1282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2019.11.008 WU J H, LIU P Y. The past and present of aminoglycoside antibiotics [J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2019, 44(11): 1275-1282(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2019.11.008
[18] ZHOU J W, HOU B, LIU G Y, et al. Attenuation of pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by hordenine: a combinatorial study with aminoglycoside antibiotics [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(22): 9745-9758. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9315-8 [19] 张红, 程寒飞. 水环境中氨基糖苷类抗性基因污染及研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(10): 121-130. ZHANG H, CHENG H F. Aquatic environmental pollution of aminoglycoside resistance genes: A review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(10): 121-130(in Chinese).
[20] SIEBINGA H, ROBB F, THOMSON A H. Population pharmacokinetic evaluation and optimization of amikacin dosage regimens for the management of mycobacterial infections [J]. J Antimicrob Chemoth, 2020, 75(10): 2933-2940. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa277 [21] 付启明, 欧晓明, 刘红玉. 农产品中氨基糖苷类抗生素的残留检测方法研究进展 [J]. 农药, 2009, 48(11): 784-789, 792. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2009.11.002 FU Q M, OU X M, LIU H Y. Current development of residue detection and analysis of aminoglycoside antibiotics in agricultural products [J]. Agrochemicals, 2009, 48(11): 784-789, 792(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2009.11.002
[22] 宋崇崇, 陶梦婷, 张瑾, 等. 3种重金属对蛋白核小球藻的联合毒性及机理 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(2): 88-95. SONG C C, TAO M T, ZHANG J, et al. Combined toxicity and the mechanisms of three heavy metals to Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(2): 88-95(in Chinese).
[23] KUMAR B, AGRAWAL K, VERMA P. Microbial electrochemical system: A sustainable approach for mitigation of toxic dyes and heavy metals from wastewater [J]. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 2021, 25(2): 04020082. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000590 [24] EOM H, PARK M, JANG A, et al. A simple and rapid algal assay kit to assess toxicity of heavy metal-contaminated water [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 269: 116135. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116135 [25] 綦峥, 齐越, 杨红, 等. 土壤重金属镉污染现状、危害及治理措施 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2020, 11(7): 2286-2294. QI Z, QI Y, YANG H, et al. Status, harm and treatment measures of heavy metal cadmium pollution in soil [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2020, 11(7): 2286-2294(in Chinese).
[26] 金修齐, 黄代宽, 赵书晗, 等. 松桃河流域氨氮和锰污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(1): 385-395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.044 JIN X Q, HUANG D K, ZHAO S H, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of ammonia nitrogen and manganese in Songtao River Basin of Guizhou Province, China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(1): 385-395(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.044
[27] 巴家文, 邢玉花, 安远锋, 等. “锰三角”区域松桃河大口鲇和斑鳜重金属富集及风险评价研究 [J]. 淡水渔业, 2019, 49(4): 108-112. BA J W, XING Y H, AN Y F, et al. Study on heavy metal enrichment and risk assessment of Silurus meridoualis and Siniperca scherzeri in Songtao river of the ‘manganese triangle’ area [J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2019, 49(4): 108-112(in Chinese).
[28] 符志友, 冯承莲, 赵晓丽, 等. 我国流域水环境中铜、锌的生态风险及管理对策 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(11): 70-74. FU Z Y, FENG C L, ZHAO X L, et al. Ecollogical risks and management countermeasures of copper and zinc in water environment of China [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(11): 70-74(in Chinese).
[29] 马其雪, 孙向阳, 李素艳, 等. 园林绿化废弃物堆肥对铅、锌污染土壤上小白菜生理特性的影响 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(11): 2027-2034. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2020.11.13 MA Q X, SUN X Y, LI S Y, et al. Effects of applying green waste compost on physiological characteristics of pakchoi in Pb, Zn contaminated soil [J]. Acta Agriculture Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32(11): 2027-2034(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2020.11.13
[30] MO L Y, LIU S S, ZHU Y N, et al. Combined toxicity of the mixtures of phenol and aniline derivatives to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. -Q67 [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2011, 87(4): 473-479. doi: 10.1007/s00128-011-0374-0 [31] ZHANG Y H, LIU S S, SONG X Q, et al. Prediction for the mixture toxicity of six organophosphorus pesticides to the luminescent bacterium Q67 [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2008, 71(3): 880-888. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.01.014 [32] HUANG W Y, LIU F, LIU S S, et al. Predicting mixture toxicity of seven phenolic compounds with similar and dissimilar action mechanisms to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. nov. Q67 [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011, 74(6): 1600-1606. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.01.007 [33] WANG L J, LIU S S, ZHANG J, et al. A new effect residual ratio (ERR) method for the validation of the concentration addition and independent action models [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2010, 17(5): 1080-1089. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0265-7 [34] QIN L T, LIU S S, ZHANG J, et al. A novel model integrated concentration addition with independent action for the prediction of toxicity of multi-component mixture [J]. Toxicology, 2011, 280(3): 164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.12.007 [35] QU R, LIU S S, CHEN F, et al. Complex toxicological interaction between ionic liquids and pesticides to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. -Q67 [J]. Rsc Advances, 2016, 6(25): 21012-21018. doi: 10.1039/C5RA27096K [36] DOU R N, LIU S S, MO L Y, et al. A novel direct equipartition ray design (EquRay) procedure for toxicity interaction between ionic liquid and dichlorvos [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2011, 18(5): 734-742. doi: 10.1007/s11356-010-0419-7 [37] 李孟涵, 贺子琪, 苗家赫, 等. 重金属Pb与抗生素对发光菌的联合毒性研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(9): 1925-1936. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0103 LI M H, HE Z Q, MIAO J H, et al. Joint toxicity of heavy metal Pb and antibiotics to photobacterium [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(9): 1925-1936(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0103
[38] 刘芳, 刘树深, 刘海玲. 部分离子液体及其混合物对发光菌的毒性作用 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2007, 2(2): 164-171. LIU F, LIU S S, LIU H L. Toxicities of selected ionic liquids and their mixtures to photobacteria (Vibrio-qinghaiensis sp. -Q67) [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2007, 2(2): 164-171(in Chinese).
[39] WANG L J, LIU S S, YUAN J, et al. Remarkable hormesis induced by 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate on Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. -Q67 [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(10): 1440-1445. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.049 [40] 刘树深, 张瑾, 张亚辉, 等. APTox: 化学混合物毒性评估与预测 [J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(14): 1511-1517. doi: 10.6023/A12050175 LIU S S, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y H, et al. APTox: assessment and prediction on toxicity of chemical mixtures [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(14): 1511-1517(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A12050175
[41] 陈琼, 张瑾, 李小猛, 等. 几种抗生素对蛋白核小球藻的时间毒性微板分析法 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 190-197. CHEN Q, ZHANG J, LI X M, et al. Time-dependent microplate toxicity analysis(T-MTA) of several antibiotics to Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 190-197(in Chinese).
[42] 丁婷婷, 董欣琪, 张瑾, 等. 3种氨基糖苷类抗生素对水生生物的时间依赖联合毒性作用比较 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2018, 13(1): 126-137. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170528001 DING T T, DONG X Q, ZHANG J, et al. Comparison of time-dependent joint toxicity interaction of three aminoglycosides antibiotics between two aquatic organisms [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2018, 13(1): 126-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170528001
[43] 王滔, 张瑾, 卞志强, 等. 2种经典模型对抗生素与重金属锌的蛋白核小球藻时间依赖联合毒性作用的评估比较 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(4): 130-139. WANG T, ZHANG J, BIAN Z Q, et al. Comparative evaluation on the time-dependent joint toxicity of antibiotics and heavy metal zinc towards Chlorella pyrenoidosa between two classical models [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(4): 130-139(in Chinese).
[44] ZHANG J, LIU S S, DOU R N, et al. Evaluation on the toxicity of ionic liquid mixture with antagonism and synergism to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. -Q67 [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(7): 1024-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.063 [45] 刘树深. 化学混合物毒性评估与预测方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 25-26. LIU S S. Assessment and prediction of toxicity of chemical mixtures[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 25-26(in Chinese).
[46] 莫凌云, 刘海玲, 刘树深, 等. 5种取代酚化合物对淡水发光菌的联合毒性 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2006, 1(3): 259-264. MO L Y, LIU H L, LIU S S, et al. Joint toxicity of 5 substituted phenols to freshwater photobacteria [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2006, 1(3): 259-264(in Chinese).
[47] LIU L, LIU S S, YU M, et al. Application of the combination index integrated with confidence intervals to study the toxicological interactions of antibiotics and pesticides in Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. -Q67 [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2015, 39(1): 447-456. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.12.013 [48] 陈敏, 张瑾, 董欣琪, 等. 多元抗生素与重金属混合物对蛋白核小球藻的时间依赖性协同与拮抗作用 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 850-859. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1159 CHEN M, ZHANG J, DONG X Q, et al. Time-dependent synergism and antagonism within multi-component mixtures of heavy metals and antibiotics towards Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 850-859(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1159
[49] 宋晓青, 刘树深, 刘海玲, 等. 部分除草剂与重金属混合物对发光菌的毒性 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2008, 3(3): 237-243. SONG X Q, LIU S S, LIU H L, et al. Mixture toxicity of herbicides and heavy metal compounds to photobacteria (Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. —Q67) [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2008, 3(3): 237-243(in Chinese).
[50] 卞志强, 张瑾, 王滔, 等. 氨基甲酸酯类农药对蛋白核小球藻联合毒性作用特点及机制 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(4): 150-162. BIAN Z Q, ZHANG JIN, WANG T, et al. Time-dependent joint toxicity characteristics and mechanisms of five carbamate pesticides towards chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(4): 150-162(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: