-
我国矿产资源丰富,种类繁多,为经济发展做出了巨大贡献,但是随着社会的快速发展,所需要的矿产资源总量随之增加。选矿作为矿产开采中的重要环节之一,在工艺实施过程中,处理1 t 矿石的耗水量为4—6 t,且需投入药剂数十克,甚至是数千克,而残留在废水中的药剂为65%左右[1]。这些含有大量有害药剂的废水如果不加以处理而被随意排入环境,不仅污染区域内水体,对动植物产生毒害作用,同时经多途径进入食物链,并对人体健康产生威胁。处理选矿废水使其达标排放或循环利用[2],是一个重要的行业问题。
水杨羟肟酸可以与金属矿中的阳离子产生反应形成螯合物[3],提高选矿过程中的选矿效率,目前已被广泛应用于一些氧化矿选矿过程中,但也因被大量滥用使其成为残留于选矿废水中较为典型的选矿药剂。水杨羟肟酸分子中含有苯环,属于难降解有机污染物,具有较强的生物毒性,进入到环境中对区域生态会产生一定的污染,同时会通过各种各样的途径进入到动植物和人体内,毒害器官,扰乱内分泌系统,危及生物的生命安全[4]。
选矿药剂的处理方法主要有自然净化法[5],酸碱中合法[6],混凝沉淀法[7],微生物处理法[8]等。这些方法存在投资成本高,二次污染风险大,适应性不强和操作难度大等缺点。硫酸根自由基(SO4−·)具备较高的氧化还原电位(2.5—3.1 V),其应用在水处理中受到广泛的关注,是一种具有发展潜力的有机污染物高级氧化技术[9—12]。SO4−·主要是通过光照、加热、金属离子等外部因素作用于过硫酸盐而产生,具有稳定,二次污染风险低,适应性强等特点[13],SO4−·氧化技术是环境友好型的新技术[14]。
本论文拟研究微波(MW)活化过硫酸钾(PS)降解典型选矿药剂水杨羟肟酸的效果及反应机制:考察水杨羟肟酸降解效果与PS浓度、微波功率、溶液初始pH等的关系;考察选矿废水中常见阴、阳离子对有机选矿药剂降解的影响;考察降解过程中总有机碳变化;通过乙醇与叔丁醇的捕获实验考察活性自由基类型。最终,经综合分析,确定微波活化过硫酸盐解水杨羟肟酸的机制。该研究将在理论和技术层面上为微波活化过硫酸盐降解水环境中的有机选矿药剂给予支撑。
-
化学试剂:水杨羟肟酸(工业纯),过硫酸钾(爱建德固赛(上海)引发剂有限公司,分析纯),氯化 钾(麦克林试剂(上海)有限公司,优级纯), 碳酸氢钾、氢氧化钾、邻二苯酚、五水合硫酸铜(麦克林试 剂(上海)有限公司,分析纯),乙醇、叔丁醇、硫酸(西陇科学股份有限公司,分析纯),甲醇(西陇科学股份有限公司,HPLC 纯),九水合硅酸钠(国药集团化学试剂有限公司,分析纯),硝酸钾七水合硫酸铁(天津市大茂化学试剂厂,分析纯),水杨酸(天津市致远化学试剂有限公司,分析纯)。实验中所有溶液均使用超纯水配制。
仪器设备:实验室用微波炉(MKX-H1C1A 实验室微波炉,青岛迈可威微波应用设备有限公司), PHSJ-5 型 pH 计(上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司),UV2100 紫外分光光度计(优尼柯仪器有限公司, 上海),TOC 分析仪(德国元素分析系统公司,德国),T6 新世纪紫外可见分光光度计(北京谱析通用 仪器有限责任公司),FL2200 型高效液相色谱仪(浙江福立分析仪器有限公司),电热水浴加热锅 (DK-200- L Ⅲ , 黄骅菲斯福实验仪器有限公司).
-
模拟选矿废水配制水杨羟肟酸溶液,加入过硫酸钾后,放入微波炉中进行降解反应。分别设置微波功率为160—300 W、反应溶液初始pH值为3.0—11.0、阳离子浓度(Fe2+和Cu2+)为0、0.05、0.10、0.25、0.50 mmol·L−1,阴离子浓度(HCO3−、Cl−、NO3−和SiO32−)为0、5、10、25、50 mmol·L−1等不同因素对水杨羟肟酸降解的影响。在反应体系中,分别加入作为自由基捕获剂的叔丁醇和乙醇,以对微波活化过硫酸盐降解水杨羟肟酸的主要机制进行分析。
-
通过紫外分光光度法分析降解过程中水杨羟肟酸的浓度变化,λ=235 nm,0—50 mg·L−1水杨羟肟酸的标准曲线为y=0.0244x−0.0093,R2=0.9996。利用高效液相色谱仪(FL2200型,250 mm×4.0 mm C18反相色谱柱)对水杨羟肟酸进行检测。流动相:甲醇∶水∶磷酸=65∶35∶4(体积比),流速0.6 mL·min−1,柱温为室温;检测波长235 nm,进样体积50 μL。分析水杨酸时,液相色谱紫外检测器波长为300 nm,其他条件同水杨羟肟酸。
-
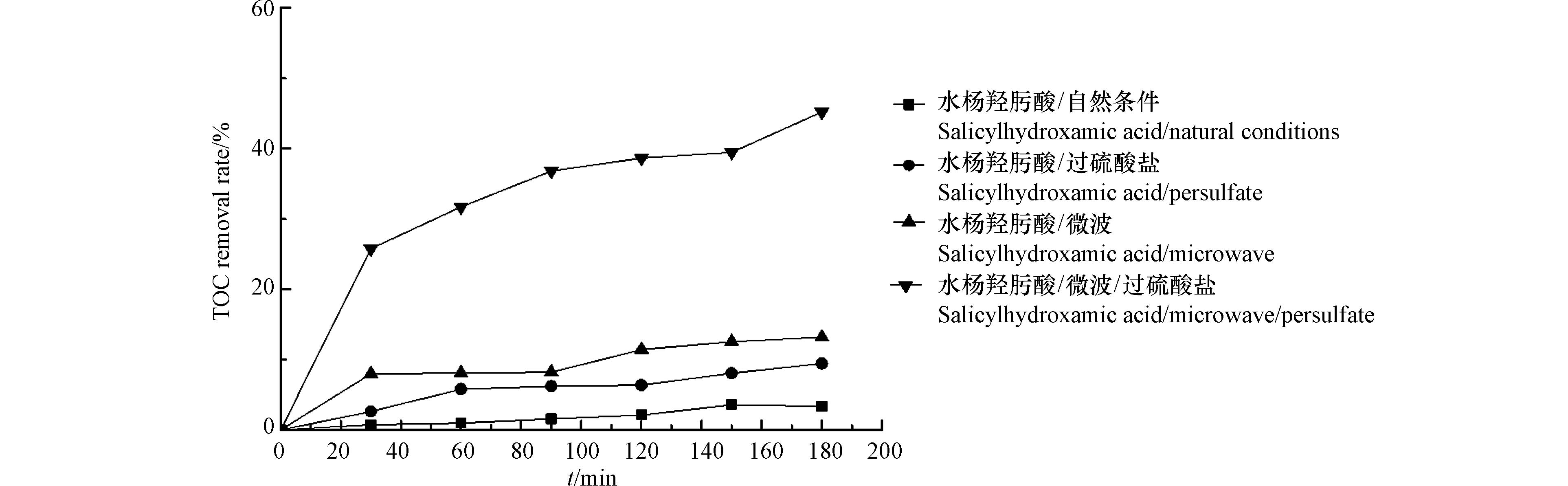
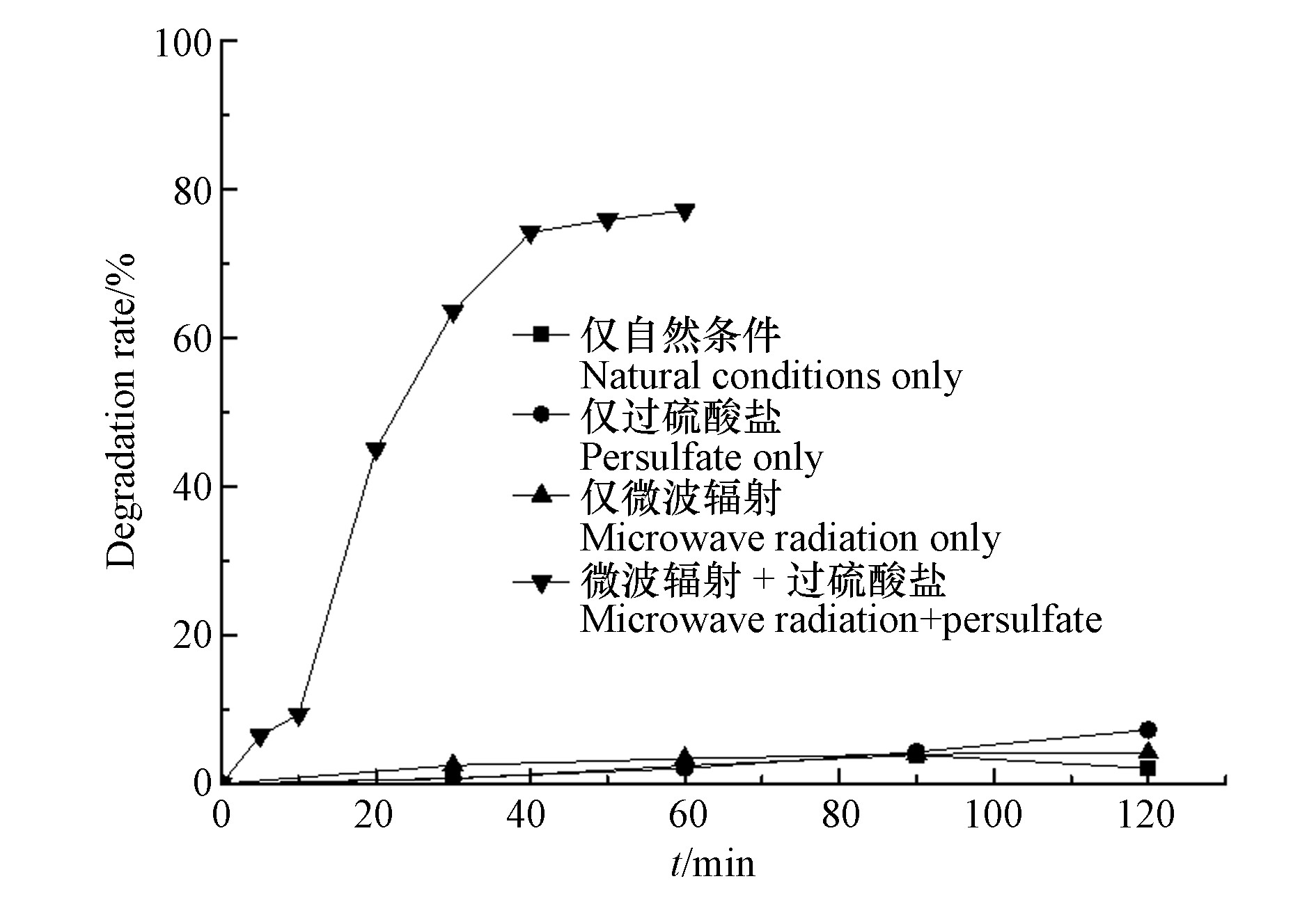
考察微波辐射、过硫酸盐和微波活化过硫酸盐等不同反应条件下,水杨羟肟酸的降解。配制浓度为20 mg·L−1的水杨羟肟酸在仅自然条件下进行自然降解;在浓度为20 mg·L−1的水杨羟肟酸溶液中添加5 mmol·L−1过硫酸盐进行仅添加过硫酸盐条件下的反应;固定水杨羟肟酸浓度为20 mg·L−1,设置微波辐射功率为250 W观察在仅微波条件下水杨羟肟酸的降解效果;设置水杨羟肟酸浓度为20 mg·L−1,微波辐射功率为250 W,过硫酸盐浓度为5 mmol·L−1的MW/PS体系下水杨羟肟酸的降解效果如图1所示。
由图1可以看出,水杨羟肟酸在自然状态下可以发生自然降解,但是降解率极低。在仅过硫酸盐条件下相较于自然降解有一定提升,但幅度较小;仅微波辐射条件下时经过120 min的反应后, 当微波功率为250 W时,降解率仅为4.13 %,说明水杨羟肟酸具有一定的热稳定性。综合以上,可能是由于水杨羟肟酸分子中含有苯环为难降解有机物。而经微波活化过硫酸盐降解60 min后,水杨羟肟酸的降解率相较于单因素条件下有明显提升。
由于水杨羟肟酸是芳香烃有机污染物,具有一定的稳定性,无法实现完全矿化。微波活化过硫酸盐对水杨羟肟酸的去除程度可通过矿化率予以表征。实验中,水杨羟肟酸和过硫酸盐浓度分别为20 mg·L−1和5 mmol·L−1,微波功率为250 W,180 min的反应后,测定TOC的变化,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,在MW/PS体系对TOC具有最高去除率,反应180 min后,去除率达45.22%,而其他条件最高为10%左右,证明微波活化过硫酸盐矿化水杨羟肟酸的有效性。研究结果说明,MW/PS反应体系能够有效活化过硫酸盐氧化降解水杨羟肟酸。
-
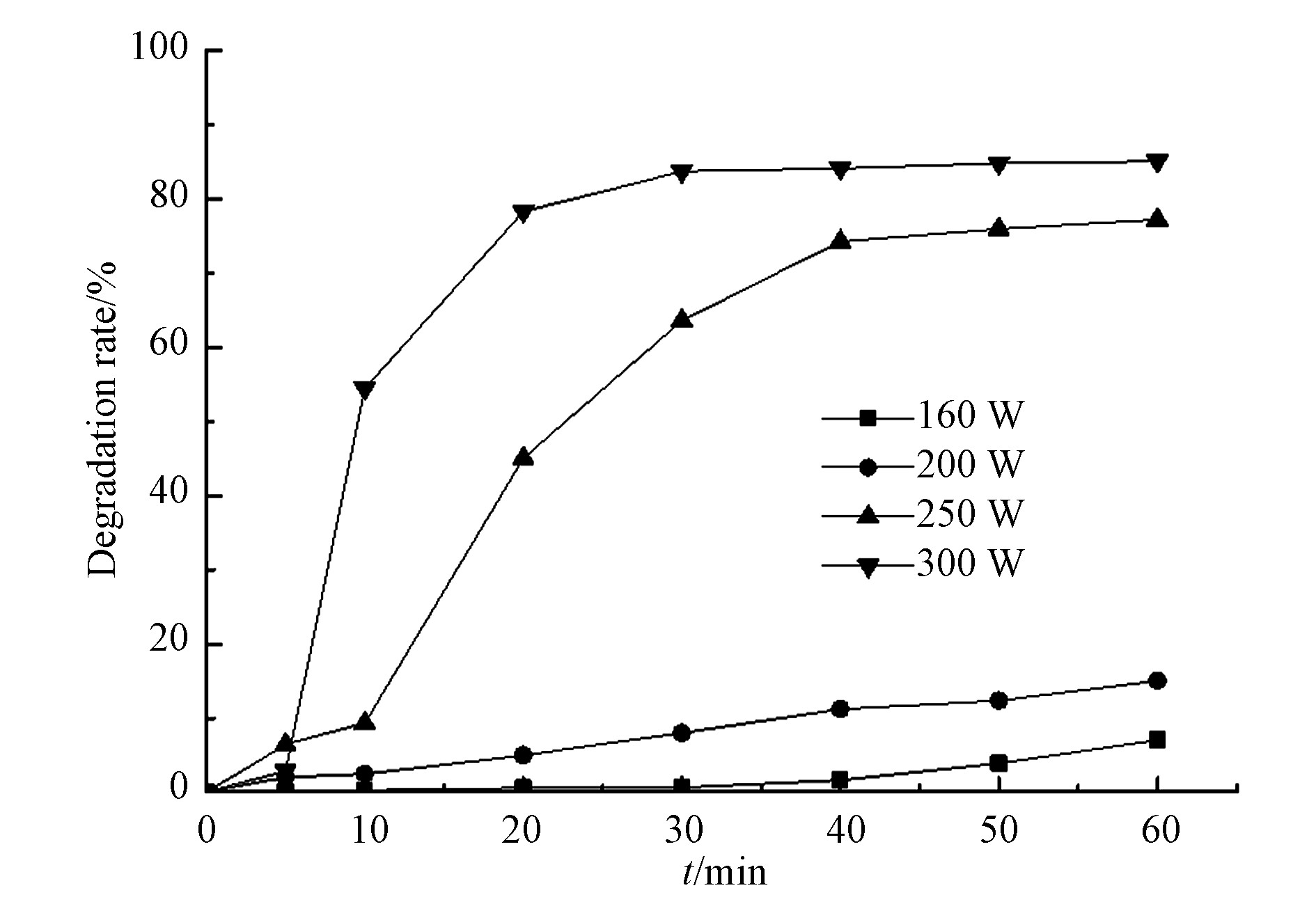
为探索微波/过硫酸盐中微波功率变化对水杨羟肟酸降解效果的影响,实验设定微波功率为160—300 W,过硫酸盐和水杨羟肟酸浓度分别为5 mmol·L−1、20 mg·L−1,实验结果见图3。水杨羟肟酸在160 W和200 W的微波功率下去除率较低,反应60 min后,降解率分别为7.02 %、15.02 %。在微波功率为250 W的条件下,进行40 min的反应后,水杨羟肟酸的降解率为74.28 %,而在微波功率为300W的条件下,仅进行30 min的反应后,水杨羟肟酸降解率便高达83.69%。因此水杨羟肟酸的去除效果随着微波功率的提高而增加。微波对反应溶液能够产生加热效应,且此加热效应随微波功率的升高而显著增加,使反应活化能降低,进而促进水杨羟肟酸的降解,使得过硫酸盐中的O—O键更加容易断裂生成有活性的SO4−(式1)。但是当微波功率达到250 W和300 W后,反应经过40 min后趋于平缓,可能是因为由过硫酸盐分解产生的硫酸根自由基半衰期较短[15],且在降解过程中产生大量中间产物对自由基产生了消耗,导致反应在后期趋于平缓。
-
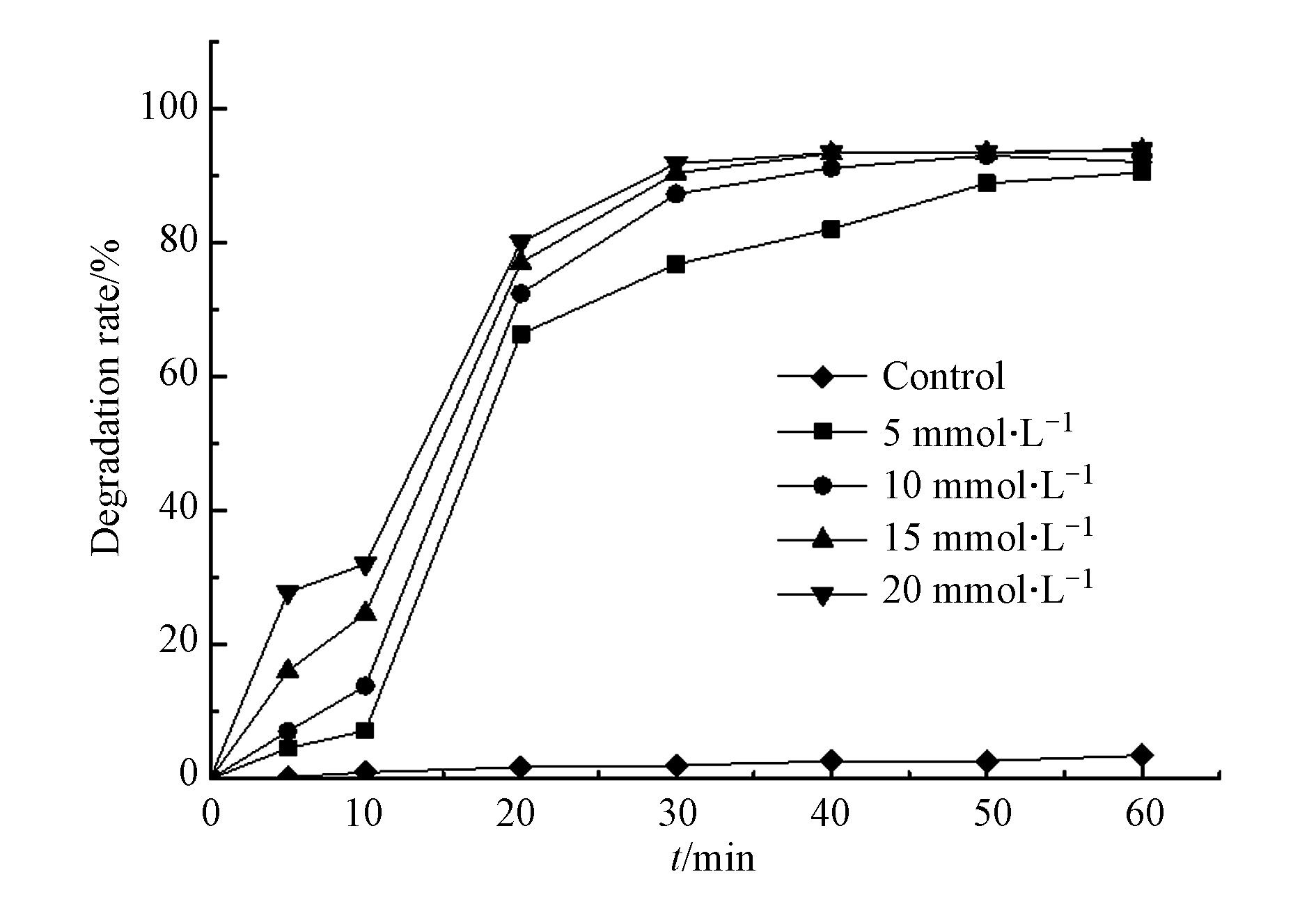
过硫酸盐作为反应体系中的氧化剂,使用量直接影响废水处理效果和成本,过高浓度也有可能造成水体的二次污染。为考察硫酸盐投加量的影响,设定过硫酸盐浓度为0—20 mmol·L−1,微波功率和水杨羟肟酸的浓度分别250 W、20 mg·L−1。由图4可知,水杨羟肟酸经 30 min 反应后,随着过硫酸盐浓度从5 mmol·L−1增加到 20 mmol·L−1,其去除率由76.84 %提高至91.88 %,反应了过硫酸盐浓度在一定范围内对降解水杨羟肟酸的促进效果。
分析水杨羟肟酸的降解率随过硫酸盐浓度增加而增大的原因,可能是因为较高过硫酸盐浓度经微波活化产生更多的SO4−·,进而使反应体系中有着更强的氧化效应,同时加快了与水杨羟肟酸的接触频率,进而促进了反应溶液中水杨羟肟酸的降解。
-
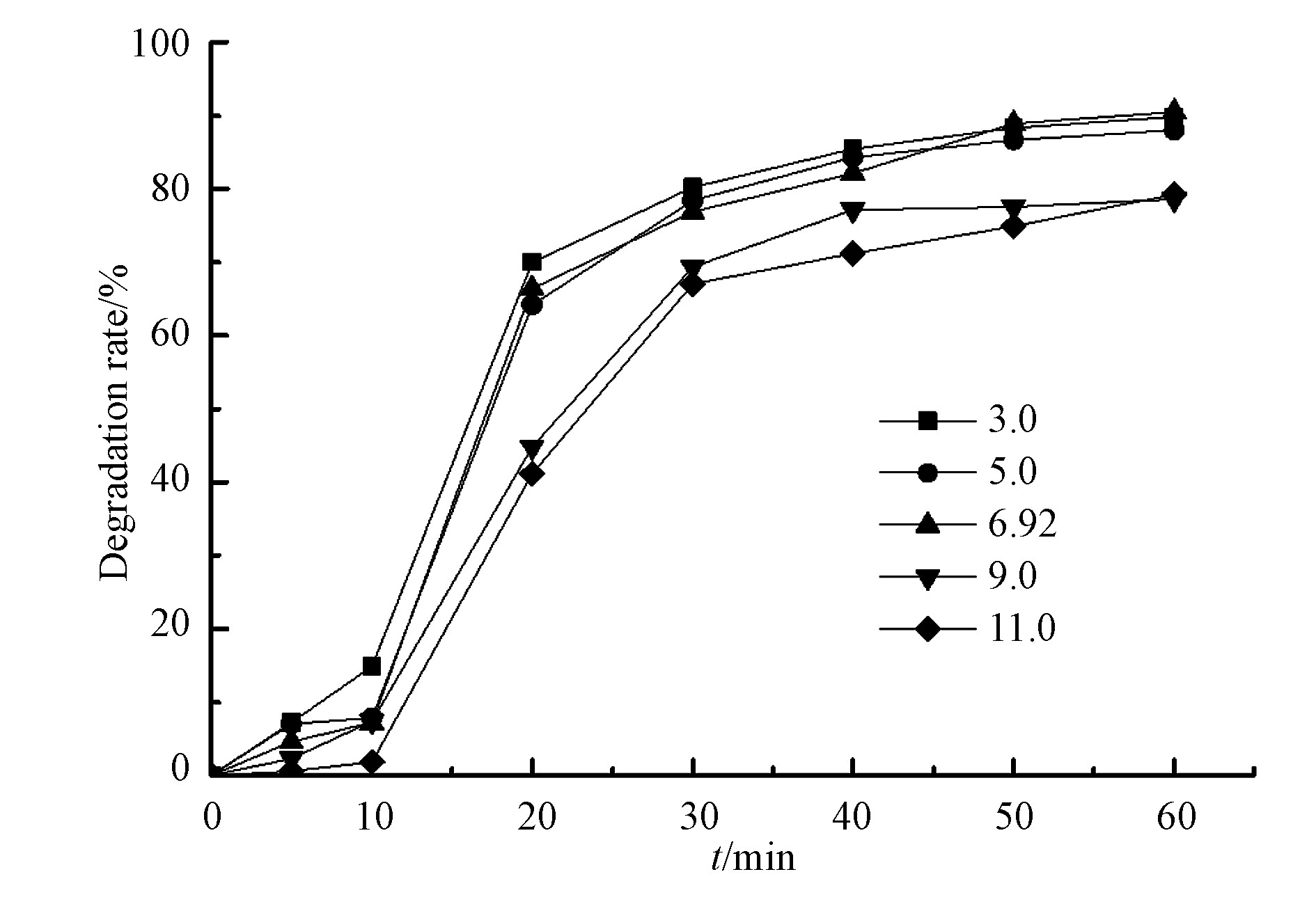
实际选矿废水因多种药剂的添加使其具有酸性或碱性,进而影响水体中化合物的存在形态及反应体系中自由基的种类[16],最终对药剂的去除效果产生影响。设置水杨羟肟酸为20 mg·L−1,过硫酸盐5 mmol·L−1,微波功率250 W,通过KOH、H2SO4对反应溶液pH值进行调节,考察微波活化过硫酸盐降解水杨羟肟酸在pH值为3.0—11.0范围内的变化趋势,结果见图5。如图5所示,溶液pH值发生变化,水杨羟肟酸去除效果发生相应变化。随着溶液初始pH值从3.0 提高至11.0,经微波辐射反应30 min时水杨羟肟酸的降解率由80.18 %降低到69.35 %,且在反应60 min时在碱性条件下水杨羟肟酸的降解率仍低于酸性和中性条件下的降解率。
水杨羟肟酸随pH发生变化的原因是可能是在酸性条件下,有大量的H+存在,而H+能够与S2O82−反应(式(2)和(3)),生成更多的SO4−·。而在碱性条件下,SO4−·易发生式(4)和式(5)的反应,且碱性条件下OH−的氧化还原电位(E0=2.3 V)比SO4−·的氧化还原电位低[17],随初始pH的升高,由式(5)生成的的OH−消耗了部分SO4−·,导致溶液中单位体积的SO4−·浓度降低,因此影响反应体系中SO4−·对水杨羟肟酸的氧化降解,使水杨羟肟酸去除率降低。因此,相比较碱性条件下,水杨羟肟酸在酸性和中性条件下去除率更高。
-
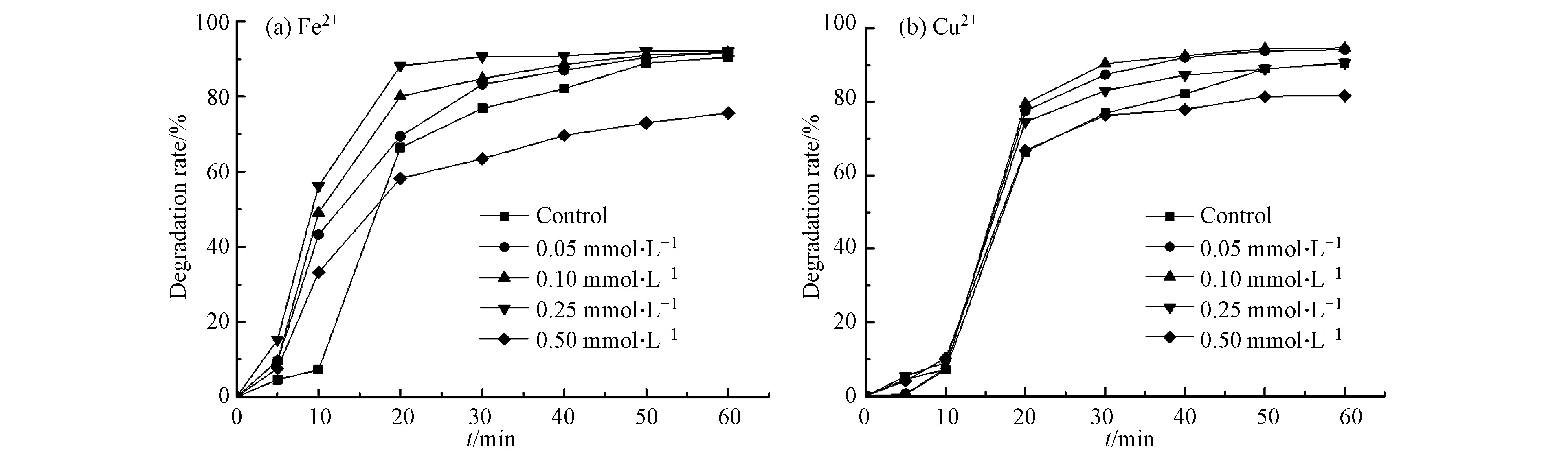
在天然矿石中存在着大量的金属离子,部分金属离子广泛存在于选矿过程中并最终留存于选矿废水中,会对微波活化过硫酸盐反应体系降解水杨羟肟酸的降解效果产生影响。在过渡金属反应体系中,Fe2+和Cu2+可作为活化剂,使微波活化过硫酸盐产生硫酸根自由基的反应活化能降低,利于SO4−·的生成。因而,实验考察Fe2+和Cu2+的存在对水杨羟肟酸降解效果的影响。实验设置微波功率、过硫酸盐、水杨羟肟酸的浓度分别为250 W、5 mmol·L−1、20 mg·L−1,Fe2+和Cu2+的添加浓度为0—0.5 mmol·L−1,观察其对水杨羟肟酸降解的影响,结果如图6所示。
从图6可知,当反应溶液中的Fe2+由0增加到0.25 mmol·L−1,在反应20 min后,水杨羟肟酸降解率达到88.19 %;0.10 mmol·L−1的Cu2+添加,使水杨羟肟酸的去除率在反应40 min后达到92.44 %。在一定的浓度范围内,随着Fe2+和Cu2+浓度的增加,水杨羟肟酸的降解率呈增长趋势。Fe2+可以活化过硫酸盐产生SO4−·(式7)[16],较低浓度的Cu2+也能够发挥协同作用,加速过硫酸盐活化分解(式8)。随着溶液中添加Fe2+和Cu2+浓度的增加,在同一时间内相较于未添加Fe2+和Cu2+的反应溶液,在单位体积内反应生成更多的SO4−·参与到水杨羟肟酸的降解反应,进而促进了水杨羟肟酸的降解。但是当反应体系中的Fe2+增加到0.5 mmol·L−1以及Cu2+浓度由0.10 mmol·L−1增加到0.25 mmol·L−1后,对水杨羟肟酸的降解产生了一定的抑制效果,是因为当反应体系中Fe2+和Cu2+过多时,过量的Fe2+和Cu2+作为催化剂使反应体系产生更多的SO4−·,而过高的SO4−·将引发式(10)和式(11)的猝灭反应,且在反应溶液中存在的Fe2+和Cu2+过量会对过硫酸盐自由基产生一定的消耗(式9)[18],从而对水杨羟肟酸的降解产生抑制[19]。图6表明,加入溶液中Fe2+浓度到0.5 mmol·L−1时出现抑制效果,而加入的Cu2+浓度到0.25 mmol·L−1时就出现了抑制效果。根据相关研究[9],可知在反应过程中对过硫酸盐的活化效果为Cu2+>Fe2+,使得溶液中加入Cu2+后更容易导致SO4−·发生猝灭反应,进而使得加入较低浓度的Cu2+时就对水杨羟肟酸的降解产生抑制效果。在反应前期可能是因为在反应溶液温度较低且Cu2+较为稳定,使得 Cu2+未全部加入到活化反应中,所以实验反应前期水杨羟肟酸的降解率较低。
-
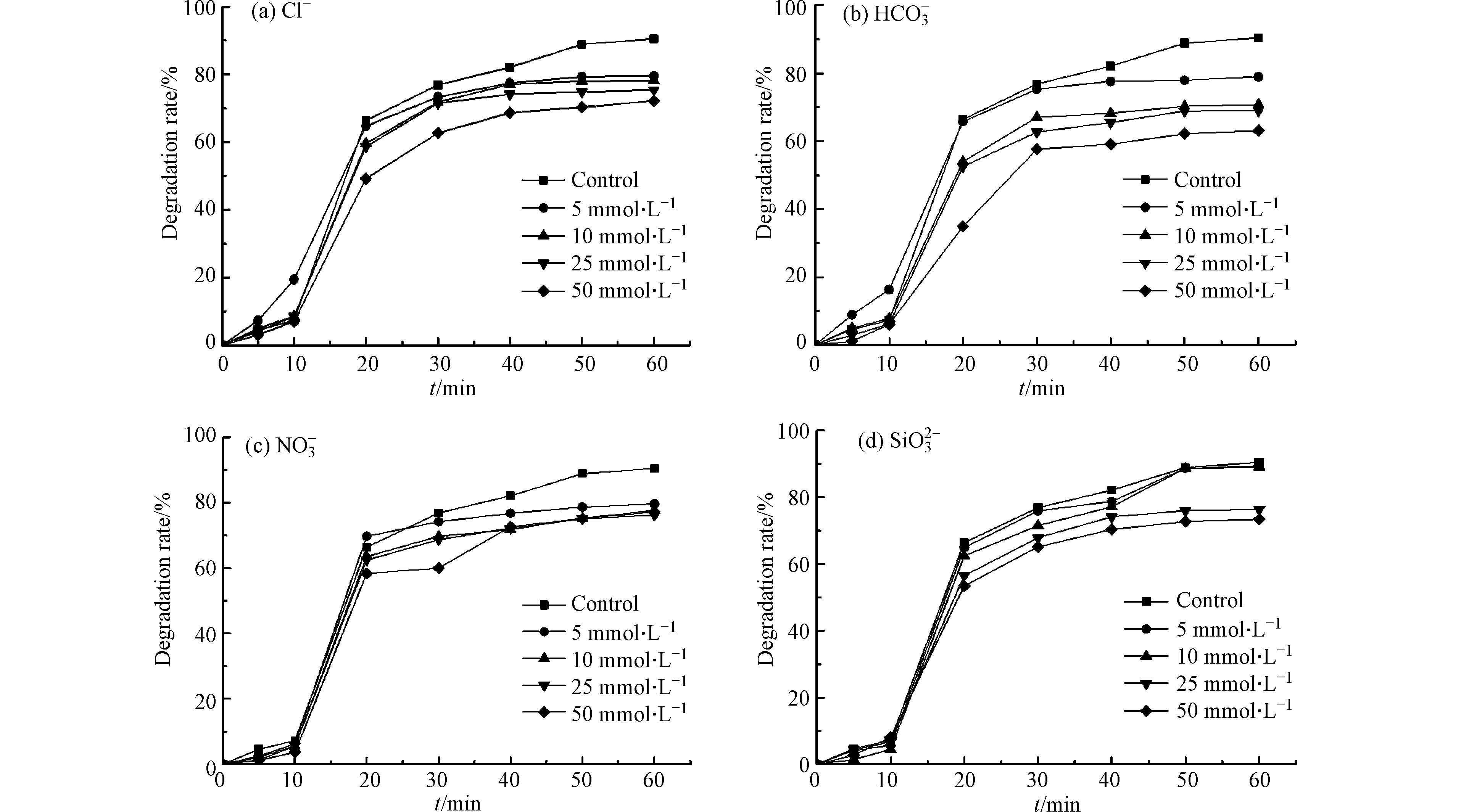
考查选矿废水中广泛存在的硝酸根离子(NO3 − )、氯离子(Cl−)和碳酸氢根离子(HCO3−),以及潜在的硅酸根离子(SiO32−)对微波活化过硫酸盐降解水杨羟肟酸的影响。阴离子浓度为0—50 mmol·L−1,过硫酸盐、水杨羟肟酸的浓度分别为5 mmol·L−1、20 mg·L−1,微波功率250 W,实验结果如图7所示。
由图7可见, 阴离子NO3−、Cl−、SiO32−和HCO3−的存在均对水杨羟肟酸的降解起到抑制作用,抑制效果随着添加量的增加而增强。在50 mmol·L−1的添加量下,反应60 min后,Cl−、HCO3−、NO3−和 SiO32−在MW/PS体系中对水杨羟肟酸的降解率分别降低到72.14 %、63.16 %、77.16 %和73.44 %。究其原因,可能是在各阴离子的竞争下,使得与水杨羟肟酸反应的硫酸根自由基减少,所生成的Cl·(式12)、HCO3·(式13)与·NO3(式14)的氧化能力均低于硫酸根自由基[20],最终导致较低的水杨羟肟酸去除率。
-
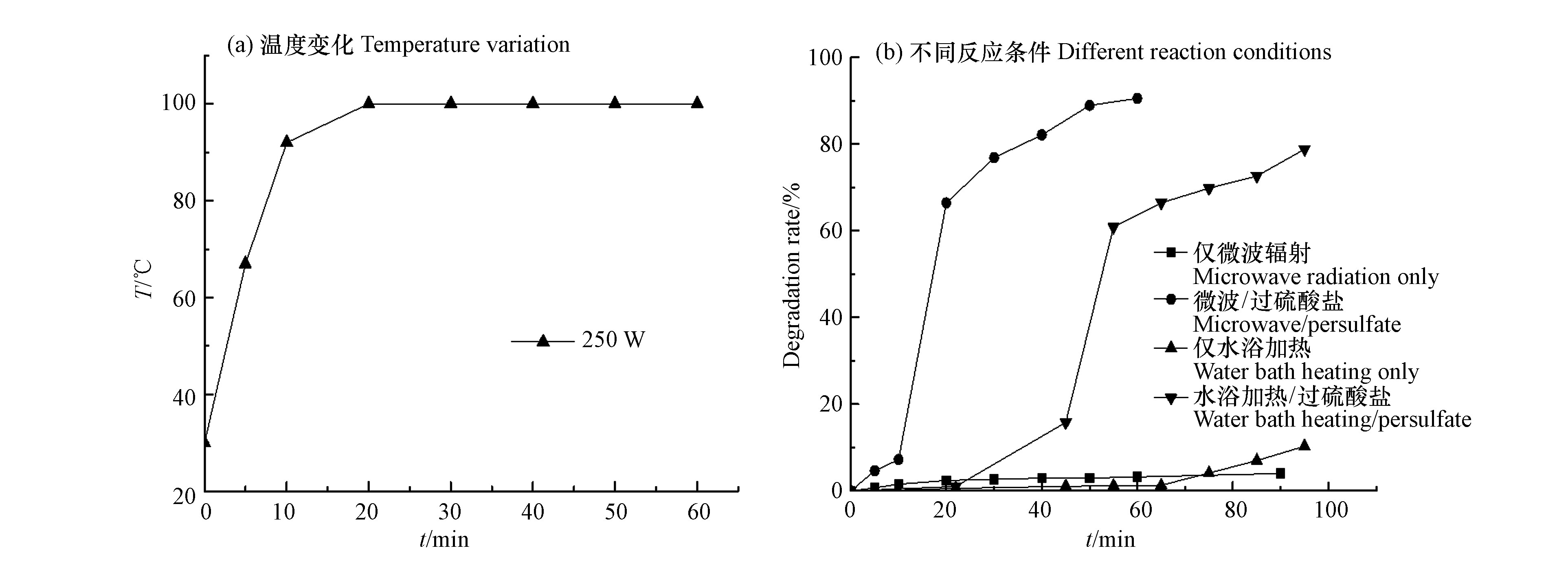
由于微波自身特性的原因,在反应过程中同时存在热效应和非热效应。目前,对于热效应和非热效应的作用仍存有争议[21-22]。对热效应和非热效应在反应过程中发生的作用仍有一定的争议。本研究中,利用水浴加热模拟250 W微波反应时的升温过程,并考察20 mg·L−1水杨羟肟酸的去除效果,以对比分析MW/PS降解水杨羟肟酸的热效应和非热效应。
由图8可以看出,在反应条件为仅微波辐射和仅水浴加热时,水杨羟肟酸几乎不发生降解,经MW/PS反应60 min后,水杨羟肟酸的降解率为90.51 %;而在水浴加热活化过硫酸盐反应体系中,经95 min获得相同的温度梯度后,水杨羟肟酸的降解率为78.8 %。因此,MW/PS降解水杨羟肟酸过程中存在热活化效应和非热效应。非热效应的发生,原因是微波由电场和磁场组成,而电场存在着周期性,使得反应溶液中极性分子的运动表现出往复特征,在吸收微波能量后,反应物质会发生更剧烈的分子运动,分子间的摩擦引起反应溶液温度升高的同时也使得反应体系中自由基和污染物质发生碰撞反应的几率增加,从而加速反应的过程[23]。
-
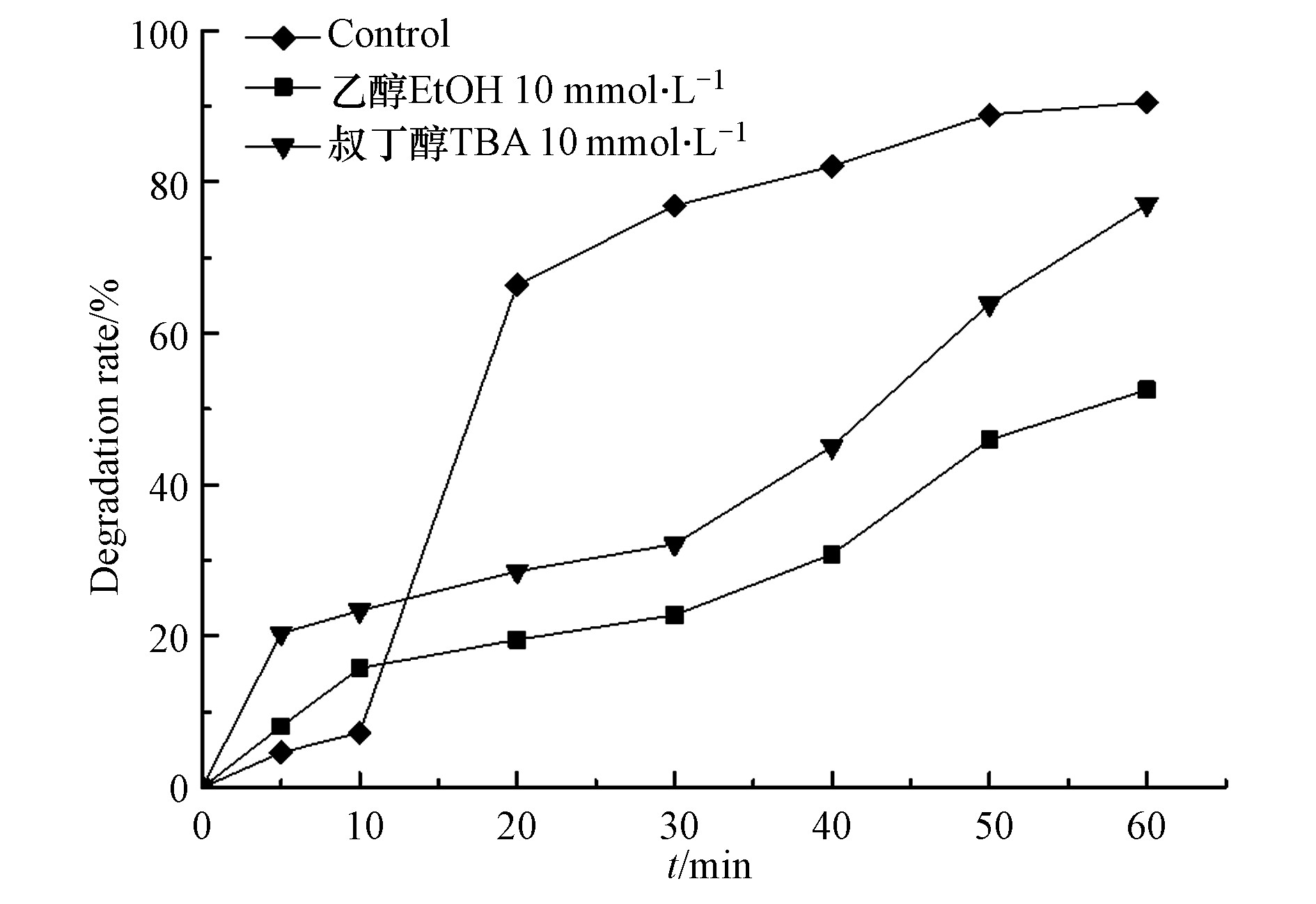
通过乙醇(EtOH)和叔丁醇(TBA)考察微波活化过硫酸盐的过程中SO4−·和·OH的作用。乙醇与SO4−·和·OH均能够以较快速率发生反应,用以同时清除体系中的SO4−·和·OH;而叔丁醇对·OH有着更高的反应速率,可看作其是对·OH的选择性清除[24-26],设定微波功率250 W,过硫酸盐、水杨羟肟酸的浓度分别为5 mmol·L−1、20 mg·L−1,分别投加10 mmol·L−1的EtOH或TBA至反应体系中,然后对水杨羟肟酸降解进行观察,实验结果如图9所示。
由图9可知,在反应前10 min,投加乙醇和叔丁醇至反应体系后,水杨羟肟酸的去除效果有所提升,可能是在微波的非热效应作用下,在反应前期因反应溶液中具有更多的极性分子影响而使得分子间有着更高的碰撞摩擦概率,从而对水杨羟肟酸的降解起到了促进作用[27]。反应10 min后,不管是投加乙醇或叔丁醇后,水杨羟肟酸的降解均显现出明显的抑制,且乙醇的抑制效果更显著,说明在反应体系中同时存在SO4−·和·OH。经计算分析,·OH、SO4−·对降解反应的贡献率分别为13.45 %、24.53 %,证明在MW/PS反应体系中SO4−·对水杨羟肟酸的降解起主要作用,·OH起次要作用。
-
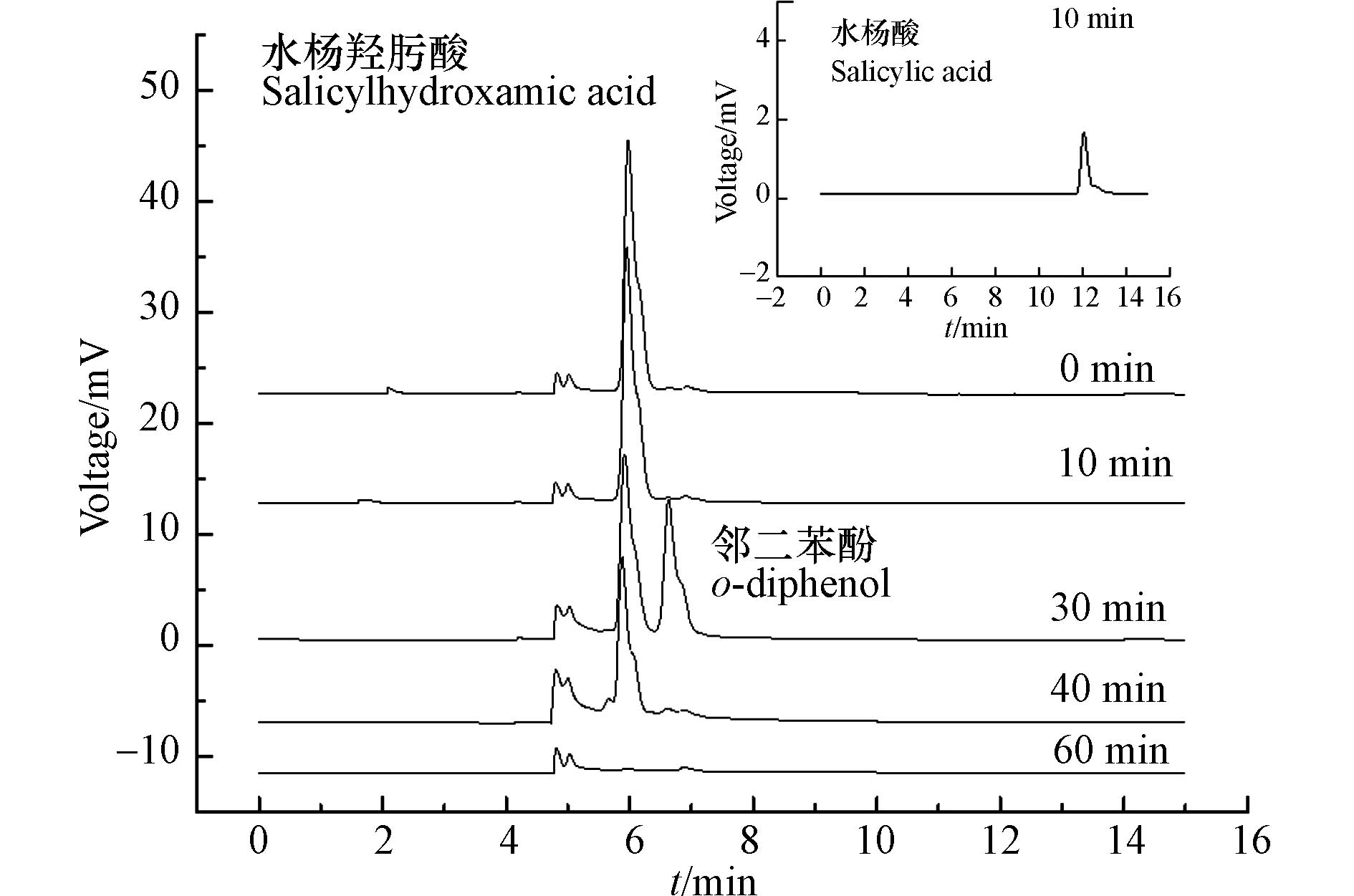
反应溶液经液相色谱分析得到色谱图,如图10所示。经对标分析,水杨羟肟酸的出峰时间为5.95 min,在5.0 min出现稳定色谱峰,推测其可能是杂质物质。反应10 min后,在300 nm的检测波长下,色谱流出曲线在12.02 min的色谱峰与标准物质对比,推断为水杨酸;当反应进行到30 min时,在230 nm波长条件下检测出6.63 min的色谱峰为邻二苯酚,但是在12 min左右处未检测到水杨酸,说明水杨羟肟酸在SO4−·作用下可以较快转化为水杨酸,水杨酸又迅速转化为邻二苯酚;降解至40 min时水杨羟肟酸和生成的邻二苯酚同时被氧化降解,且部分生成的邻二苯酚被氧化降解;降解至60 min时,水杨羟肟酸和邻二苯酚近乎被完全氧化降解。由以上结果结合矿化分析以及参考文献[28]推测,在MW/PS降解体系下,水杨羟肟酸存在以下的降解途径:水杨羟肟酸→水杨酸→邻二苯酚→其它小分子物质+二氧化碳+水。
-
(1)MW/PS体系对水杨羟肟酸具有显著的降解效果。增加过硫酸盐投加量和加大微波功率,水杨羟肟酸的去除率随之增加;对比水浴加热和MW/PS体系对水杨羟肟酸的降解效果,证明热活化效应在微波活化过硫酸盐中起主要作用。
(2)水杨羟肟酸的去除率随着pH值(3.0—11.0)的增大而降低;反应溶液中存在较低浓度金属离子Fe2+(0.05—0.25 mmol·L−1)和Cu2+(0.05—0.10 mmol·L−1)时对MW/PS降解水杨羟肟酸均有促进作用,但随着金属离子投加浓度的增大对水杨羟肟酸的降解反而起到抑制作用;自然水体中常见的Cl−、HCO3−、NO3−和 SiO32−对水杨羟肟酸的降解均有抑制作用.
(3)通过自由基清除剂乙醇和叔丁醇的作用,证明SO4−·在MW/PS体系降解水杨羟肟酸中起主要作用。 MW/PS体系对水杨羟肟酸有较强的矿化效果。通过分析,推测水杨羟肟酸先后被降解为水杨酸和邻苯二酚,然后水杨羟肟酸和其中间产物进一步被氧化降解为小分子物质,甚至被矿化为二氧化碳和水。
微波活化过硫酸盐降解典型选矿药剂水杨羟肟酸
Degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid by microwave activated persulfate
-
摘要: 以水杨羟肟酸为目标污染物,利用微波活化过硫酸盐的高级氧化技术考察微波功率、过硫酸盐投加量、反应溶液初始pH、主要金属离子和常见阴离子等因素对水杨羟肟酸降解影响。结果表明,水杨羟肟酸的降解率随着微波功率和过硫酸盐投加量的增加而提高; 当反应溶液pH=3时,水杨羟肟酸的降解率最高,而提高pH对水杨羟肟酸的降解有抑制作用; Fe2+,Cu2+的添加对水杨羟肟酸的降解表现出低促高抑的效果,最佳添加量分别为0.25 mmol·L−1、0.1 mmol·L−1; 无机阴离子Cl−、HCO3−、NO3−、SiO32−的添加均抑制水杨羟肟酸的降解; 反应180 min后,水杨羟肟酸得到明显矿化,主要中间产物为水杨酸和邻二苯酚。研究证明了热活化效应在微波活化过硫酸盐降解水杨羟肟酸过程中的重要性,以及SO4−·的主导作用。Abstract: An advanced oxidation technology of persulfate activated by microwave was developed with salicylhydroxamic acid as the target pollutant. The effects of microwave power, persulfate dosage, initial pH of reaction solution, main metal ions and common anions on the degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid were investigated.The results showed that the degradation rate of salicylhydroxamic acid increased with the increase of microwave power and the dosage of persulfate.When the pH of the reaction solution was 3, the degradation rate of salicylhydroxamic acid was the highest, and the degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid was gradually inhibited with the increase of the initial pH of the reaction solution.The addition of Fe2+ and Cu2+ in the reaction system had the effect of low promoting and high inhibiting on the degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid, and the optimal supplemental levels were 0.25 mmol·L−1 and 0.1 mmol·L−1.The addition of inorganic anions Cl−, HCO3−, NO3−, SiO32− inhibited the degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid.After reaction for 180 min, salicylhydroxamic acid was mineralized obviously, and the main products were salicylic acid and o-diphenol.The study proved the importance of thermal activation effect in the process of microwave activated persulfate degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid,and the leaded role of SO4−·.
-
Key words:
- microwave /
- persulfate /
- salicylhydroxamic acid /
- beneficiation reagents
-

-
-
[1] 侯春燕. 选矿废水处理研究进展 [J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(6): 226, 271. HOU C Y. Progress in research on treatment of ore dressing wastewater [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2020, 46(6): 226, 271(in Chinese).
[2] 唐明刚, 张红地. 选矿废水处理及回用技术探讨 [J]. 冶金与材料, 2019, 39(6): 100-101. TANG M G, ZHANG H D. Discussion on treatment and reuse technology of mine wastewater [J]. Metallurgy and Materials, 2019, 39(6): 100-101(in Chinese).
[3] 王成行, 邱显扬, 胡真, 等. 水杨羟肟酸对氟碳铈矿的捕收机制研究 [J]. 中国稀土学报, 2014, 32(6): 727-735. WANG C H, QIU X Y, HU Z, et al. Flotation mechanism of bastnaesite by salicylhydroxamic acid [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2014, 32(6): 727-735(in Chinese).
[4] 杨萍, 黄金波, 曾维伟. 浅谈金属矿山选矿尾矿的废水处理 [J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(8): 69-70, 73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.08.023 YANG P, HUANG J B, ZENG W W. Discussion on the wastewater treatment of metal mine beneficiation tailings [J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2018, 36(8): 69-70, 73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.08.023
[5] 赵永红, 成先雄, 谢明辉, 等. 选矿废水中黄药自然降解特性的研究 [J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2006, 33(6): 33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2006.06.013 ZHAO Y H, CHENG X X, XIE M H, et al. Study on natural deterioration of xanthate in flotation wastewater [J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2006, 33(6): 33-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2006.06.013
[6] FENG D, van DEVENTER J S J, ALDRICH C. Removal of pollutants from acid mine wastewater using metallurgical by-product slags [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2004, 40(1): 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2004.01.003 [7] 黄筱迪, 张松. 我国磷矿选矿废水处理工艺综述 [J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(5): 223-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.05.145 HUANG X D, ZHANG S. Review on the treatment technology of phosphate ore dressing wastewater in China [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2020, 46(5): 223-224(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.05.145
[8] 尹业兴, 李青云, 刘幽燕. 产碱杆菌DN25去除金矿废水中的氰 [J]. 化工环保, 2017, 37(1): 49-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2017.01.009 YIN Y X, LI Q Y, LIU Y Y. Removal of cyanide from gold mining wastewater using Alcaligenes sp. DN25 [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2017, 37(1): 49-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2017.01.009
[9] 邓靖, 冯善方, 马晓雁, 等. 均相活化过硫酸氢盐高级氧化技术研究进展 [J]. 水处理技术, 2015, 41(4): 13-19. DENG J, FENG S F, MA X Y, et al. Research development in advanced oxidation processes based on homogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2015, 41(4): 13-19(in Chinese).
[10] 杨世迎, 杨鑫, 王萍, 等. 过硫酸盐高级氧化技术的活化方法研究进展 [J]. 现代化工, 2009, 29(4): 13-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4320.2009.04.004 YANG S Y, YANG X, WANG P, et al. Advances in persulfate oxidation activation methods of persulfate oxidation [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2009, 29(4): 13-19(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4320.2009.04.004
[11] YANG S Y, WANG P, YANG X, et al. Degradation efficiencies of azo dye Acid Orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 179(1/2/3): 552-558. [12] 张磊, 祝思频, 袁熙, 等. 微波活化过硫酸盐降解典型选矿药剂丁基黄药的研究 [J]. 有色金属工程, 2020(11): 93-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.11.014 ZHANG L, ZHU S P, YUAN X, et al. Study on the degradation of butyl xanthate by microwave activated persullfate [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020(11): 93-100(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.11.014
[13] 沈一君, 彭明国, 徐彬焜, 等. 紫外活化过硫酸盐降解二苯甲酮-4的动力学影响及降解机理与风险评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(1): 174-182. SHEN Y J, PENG M G, XU B K, et al. Degradation of BP4 by UV-activated persulfate process: Kinetic, mechanism and risk [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(1): 174-182(in Chinese).
[14] 林天来, 刘秀峰, 黄灿克. 光源强度对UV活化过硫酸盐降解甲基叔丁基醚效果的影响研究 [J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2017, 42(5): 103-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2017.05.032 LIN T L, LIU X F, HUANG C K. Effect of light intensity on UV-assited persulfate degradation of MTBE [J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2017, 42(5): 103-105(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2017.05.032
[15] 杨世迎, 陈友媛, 胥慧真, 等. 过硫酸盐活化高级氧化新技术 [J]. 化学进展, 2008, 20(9): 1433-1438. YANG S Y, CHEN Y Y, XU H Z, et al. A novel advanced oxidation technology based on activated persulfate [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2008, 20(9): 1433-1438(in Chinese).
[16] 王鸿斌, 王群, 刘义青, 等. 亚铁活化过硫酸盐降解水中双氯芬酸钠 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 869-875. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040806 WANG H B, WANG Q, LIU Y Q, et al. Degradation of diclofenac by ferrous activated persulfate [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 869-875(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040806
[17] 郑伟, 杨曦, 张金凤, 等. Fe(Ⅱ)/K2S2O8对水体中As(Ⅲ)的氧化研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2007, 30(11): 41-42, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2007.11.015 ZHENG W, YANG X, ZHANG J F, et al. Oxidation of as (ⅲ) by Fe(ⅱ)/K2S2O8 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 30(11): 41-42, 57(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2007.11.015
[18] 周爱娟, 赵玉珏, 刘芝宏, 等. Fe(Ⅱ)活化过硫酸盐处理喹啉工艺参数优化及生物毒性 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4795-4803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.019 ZHOU A J, ZHAO Y J, LIU Z H, et al. Accelerated quinoline removal by Fe(II)-activated persulfate: Parameters optimization and biological detoxification analysis [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4795-4803(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.019
[19] 王群, 卢晓辉, 白晓峰, 等. Cu2+对热活化过硫酸钾氧化双酚S效果的影响 [J]. 水处理技术, 2018, 44(2): 42-45, 55. WANG Q, LU X H, BAI X F, et al. Effect of cupric ion on bisphenol S degradation by thermal activated potassium persulfate [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2018, 44(2): 42-45, 55(in Chinese).
[20] 郭佑罗, 关小红, 高乃云, 等. 紫外/过硫酸盐工艺降解水中氯贝酸的研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(7): 2014-2019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.07.016 GUO Y L, GUAN X H, GAO N Y, et al. Kinetics of clofibric acid degradation by UV/persulfate system in aqueous solution [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(7): 2014-2019(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.07.016
[21] 王陆瑶, 孟东, 李璐. “热效应”或“非热效应”: 微波加热反应机理探讨 [J]. 化学通报, 2013, 76(8): 698-703. WANG L Y, MENG D, LI L. Thermal or nonthermal microwave effects-the mechanism of microwave heating [J]. Chemistry, 2013, 76(8): 698-703(in Chinese).
[22] 马双忱, 姚娟娟, 金鑫, 等. 微波化学中微波的热与非热效应研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2011, 74(1): 41-46. MA S C, YAO J J, JIN X, et al. Progress for thermal and non-thermal effects of microwave chemistry [J]. Chemistry, 2011, 74(1): 41-46(in Chinese).
[23] 王禹, 孙海涛, 王宝辉, 等. 微波的热效应与非热效应 [J]. 辽宁化工, 2006, 35(3): 167-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2006.03.015 WANG Y, SUN H T, WANG B H, et al. A study on thermal efficiency and non- thermal efficiency of microwave [J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2006, 35(3): 167-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2006.03.015
[24] 马京帅, 吕文英, 刘国光, 等. 热活化过硫酸盐降解水中的普萘洛尔 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(2): 221-228. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016060204 MA J S, LYU W Y, LIU G G, et al. Degradation of propranolol in aqueous solution by heat-activated persulfate [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(2): 221-228(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016060204
[25] LIANG C J, SU H W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(11): 5558-5562. [26] 孙鹏, 柳佳鹏, 王维大, 等. 活性炭强化热活化过硫酸盐降解对硝基苯酚 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4779-4785. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.017 SUN P, LIU J P, WANG W D, et al. Active carbon enhanced thermal activation of persulfate for degradation of p-nitrophenol [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4779-4785(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.017
[27] 孙晓娟, 苏跃增, 金凤明. 微波化学非热效应初探 [J]. 江苏石油化工学院学报, 2000, 12(3): 42-45. SUN X J, SU Y Z, JIN F M. A study on non - thermal efficiency of microwave chemical reaction [J]. Journal of Jiangsu Institute of Petrochemical Technology, 2000, 12(3): 42-45(in Chinese).
[28] 章丽萍, 项俊, 严振宇, 等. O3降解水杨羟肟酸选矿废水机理研究 [J]. 矿业科学学报, 2019, 4(1): 79-85. ZHANG L P, XIANG J, YAN Z Y, et al. Mechanism study on ozonization degradation of salicylhydroxamic acid in flotation wastewater [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2019, 4(1): 79-85(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: