-
河流的水化学组分记录了流域岩性、气候特征、土壤类型、植被覆盖以及人类活动等信息,这有助于揭示流域的环境质量状况、岩石风化及生物地球化学特征[1-2]。一般认为,大气圈中CO2与地球矿物的交互作用为天然水体中
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+、Mg2+的主要来源,而Na+、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、NO3−来源复杂,主要受控于岩石圈、生物圈、大气圈和智慧圈的影响[3-4]。水体中的主要离子被视为天然的“示踪剂”,通过对水体离子化学组分的研究有助于识别影响离子浓度的主要因素,这能够在一定程度上增加对流域自然环境和人类活动特征的了解。国内外学者针对河流水化学开展了大量研究,Gibbs[5]通过对全球多种水体(降水、海水、湖水、河水)水化学组分的分析,认为岩石风化、大气降水输入和蒸发-结晶作用为全球地表水化学组分的三大控制因素。Kattan[6]对叙利亚幼发拉底河水化学特征的分析表明,河流中的水化学组分受到蒸发、岩石的风化溶解和水温的影响。孙平安等[7]报道了大溶江、灵渠流域地表水中碳酸盐岩的风化溶解为${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+、Mg2+的主要来源,大气降水和人类活动为Na+、K+、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 主要控制因素。Pant等[3]研究发现,蒸发结晶和碳酸盐岩溶解作用是尼泊尔甘达基河离子的主要控制因素。Xiao等[8]基于化学质量平衡法定量分析了我国极端干旱区塔里木河流域地表水溶质来源占阳离子总量的递减顺序为蒸发盐岩溶蚀作用(58.3%)、碳酸盐岩风化(25.7%)、大气输入(8.7%)、硅酸盐岩风化(8.2%)。余冲等[9]针对我国东南沿海受人类扰动较大的韩江流域水化学组分的定量分析结果显示,硅酸盐岩、碳酸盐岩、大气降水和人类活动依次占韩江流域阳离子总量的37.69%、33.04%、21.98%和7.29%。国内学者对黄河、珠江、长江及其重要支流水化学的研究,认为岩石风化和大气降水是影响我国东部湿润地区河流水化学的主要控制因素[10-14],此外针对我国西北干旱和半干旱地区的疏勒河[15]、格尔木河[16]、艾比湖流域[17]、榆树沟流域[18]、额尔齐斯河[19-20]、乌鲁木齐河[21]、吉木乃诸河[22]、塔里木河[8,23]及阿克苏河[24]流域地表水化学特征的研究认为,岩石风化、蒸发-结晶和人类活动为我国西北干旱半干旱地区地表水化学组分构成的主控因素。综上可知,由于不同流域地表水补给类型、下垫面性质、太阳辐射、人类活动等自然和人文要素的空间差异较大,致使不同流域地表水的化学组分具有明显的地域差异性。近年来学者针对我国典型西风区内陆河流域开展的有关地表水方面的研究工作相对较少,尤其是针对新疆伊犁喀什河流域的研究工作,主要集中于地下水系统的划分[25]、水电站工程区构造稳定性研究[26]、引水枢纽工程运行研究[27]等方面,但有关喀什河流域地表水化学方面的研究鲜见报道。
鉴于此,本文以喀什河流域地表水为研究对象,采用数理统计、Piper三线图、离子比值法、Gibbs模型等方法揭示了研究区地表水化学特征,并探讨了影响其水化学组分的控制因素。这在一定程度上丰富了我国典型西风区内陆河流水文学的研究,并为喀什河流域水资源系统决策与管理提供参考。
-
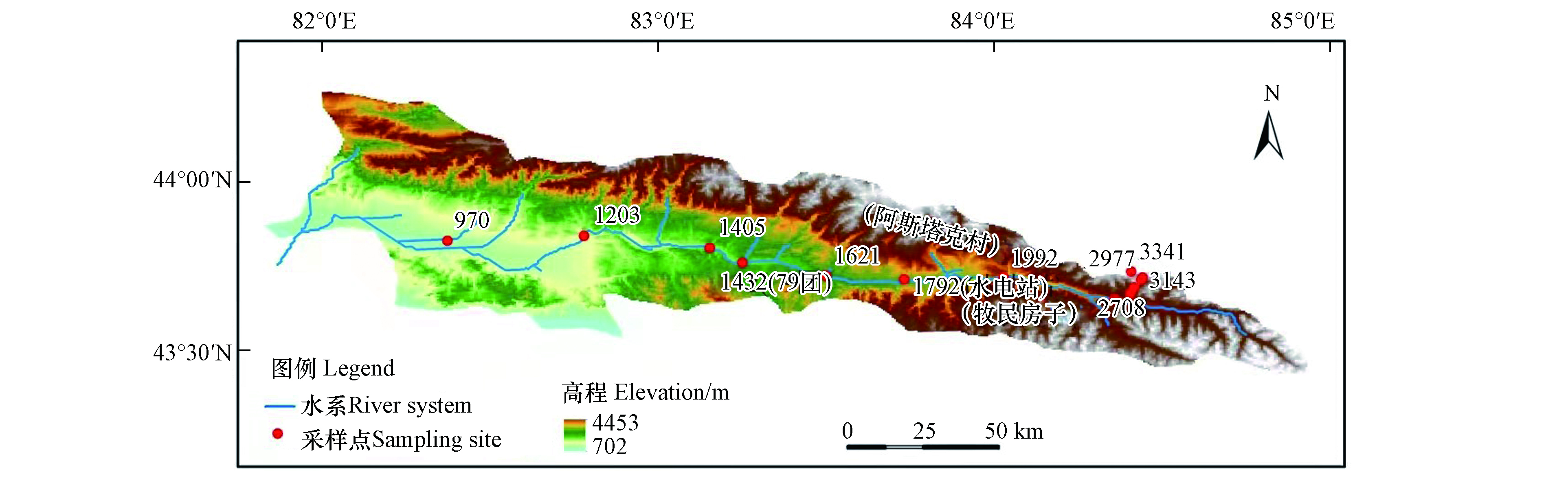
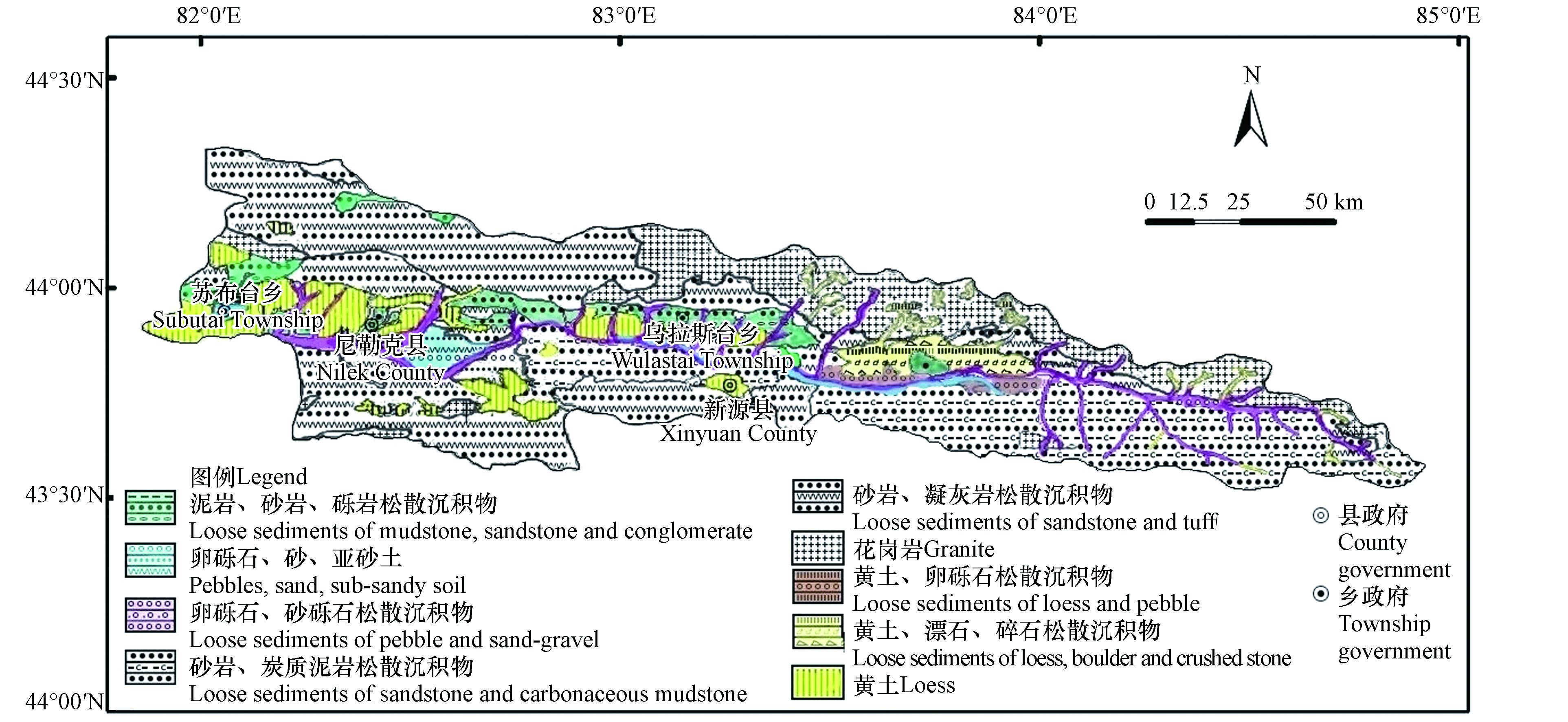
伊犁喀什河是伊犁河的一条重要支流,属融雪型河流,发源于依连哈比尔尕山,流向从东向西,在托海村转向南,最终在雅玛渡汇入伊犁河,喀什河全长316 km,流域面积9541 km2,支流多在右岸,流域内高程800—5500 m,平均含沙量0.47 kg·m−3,河床平均比降为6.8%,多年平均流速(温泉水电站)127.9 m3·s−1,多年平均径流量(托海水文站)38.70×108 m3。喀什河流域地质背景主要有坚硬的结晶岩,主要以片麻岩、石英片岩、大理岩为主的变质岩和花岗岩等,坚硬的层状碎屑岩以砂岩、凝灰岩为主,坚硬-软弱相间的碎屑岩以侏罗系地层为主,为炭质泥岩夹煤层、砂岩,多层结构的砾质土体主要有第三系较软泥岩、砂岩、砾岩互层强风化岩组,其中泥岩含有较多的石膏和其它易溶盐类,志留系岩性由粉砂岩、砂砾岩、灰岩和砂岩组成(图1)[28]。喀什河位于北东南三面环山的喇叭形伊犁河谷地带,其大气降水主要来自西风环流所携带的水汽,其水源补给以冰雪融水为主,降水补给次之,地下水补给为辅的混合型补给类型[29]。
-
2019年1月至7月在喀什河干流采集56个地表水样(图2)。在河水水面10 cm以下进行采集,取样前润洗聚乙烯塑料瓶3次,0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜过滤,存放在聚乙烯样品瓶内,贴好标签密封保存。
地表水水化学指标测试由中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所中心实验室完成。采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(美国安捷伦735 ICP-OES)进行阳离子Ca2+、K+、Mg2+、Na+的测定,采用离子色谱仪(美国戴安ICS-5000)进行阴离子Cl−、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的测定,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ 采用梅特勒G20型电位滴定仪测定,上述各阴阳离子的测试精度均为0.01 mg·L−1,水样的电导率数据采用DDS-307电导仪测定,测试精度为0.01 µS·cm−1;矿化度的测定方法为残渣烘干-重量法,测试精度为0.01 mg·L−1;pH值采用电位测定法,pH测试计选用pHS-2C,测试精度为0.01个pH单位。 -
采用Excel对测试数据进行统计分析,使用阴阳离子平衡法对样品测试数据的可靠性进行检验。所有水样的阴阳离子平衡误差均在±5%范围内,数据精度满足分析要求。采用离子比值法、Gibbs图等方法研究了地表水化学的主要影响因素,运用Origin绘制Piper三线图,分析流域水化学类型。
-
喀什河流域地表水各化学指标的统计分析结果见表1。研究区地表水中Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 离子浓度的均值依次为3.44、1.29、46.70、4.97、1.40、20.70、105.06 mg·L−1,其中阳离子是以Ca2+和Mg2+为主,其阳离子当量浓度呈现Ca2+>Mg2+>Na+>K+的关系,各水样中Ca2+当量浓度占阳离子总量的81%—98.7%,均值为82.8%,平均浓度为46.70 mg·L−1,其中Ca2+浓度高于干旱区河流平均浓度[21];Mg2+当量浓度占阳离子总量的1.2%—6.9%,均值为8.8%,Ca2+和Mg2+的平均浓度占阳离子总量的91.6%。阴离子以${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 为主,离子当量浓度呈现${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ >${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ >Cl−的关系,Cl−含量很低,介于0—10.55 mg·L−1,均值为1.40 mg·L−1;各水样中${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 当量浓度占阴离子总量的81.6%—83%,均值为82.6%,${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 当量浓度占阴离子总量的15.4%—16.9%,均值为16.2%,两者累计占阴离子总量的99.3%;地表水TDS介于184.8—588.12 mg·L−1之间,EC范围为6.3—438 µS·cm−1,均值为174.90 µS·cm−1。西北干旱区地表水中的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ,主要来源于石膏的溶解,其次为硫化物和天然硫的氧化,此外,动植物的枯萎以及含硫植物的分解和氧化也会使得水中的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的含量增加[21]。为了进一步探析喀什河干流中主要离子浓度所处的水平,将该地区河水中的主要离子浓度与全球河流和我国典型干旱区的内陆河流中主要离子浓度的对比分析结果见表2。喀什河干流中Mg2+、Ca2+、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 平均离子浓度为全球河流相应离子浓度均值的1.5—5.8倍不等,但这些离子浓度明显低于塔里木河中的离子浓度。喀什河干流中Mg2+、Cl−和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 离子浓度均低于黑河和乌鲁木齐河,而Ca2+、${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 的浓度低于黑河而高于乌鲁木齐河。喀什河和乌鲁木齐河离子化学特征较为接近,主要原因是研究区和乌鲁木齐河同属干旱西风区的内陆河,水汽来源大体相同,且在水文地质环境和气候等方面两者相似度高。喀什河干流中Na++K+、Mg2+、Cl−和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度较乌鲁木齐河低,这可能主要与喀什河流域地处北东南三面环山的喇叭形伊犁河谷地带有关,这样的地貌特征有利于西风环流所携带水汽的进入,进而在喀什河流域迎风坡形成地形雨,这在一定程度上增加了喀什河流域的降水量,加大了降水作用对喀什河地表水中离子的稀释程度,此外乌鲁木齐河地处天山北坡,相较于喀什河,乌鲁木齐河深居内陆,干旱程度更为严重,降水对离子浓度的稀释程度较喀什河小[29]。黑河干流中主离子浓度高于喀什河对应离子浓度均值的0.23—6.14倍不等,主要原因是黑河处于非季风区,富含水汽的夏季风难以到达河西走廊,水源补给主要是来自于祁连山的冰雪融水,补给来源少,喀什河地处大西洋季风环流区迎风坡,因受西风环流的影响,降水补给量较黑河高[15]。Piper图主要以阳离子(Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+)和阴离子(Cl−、
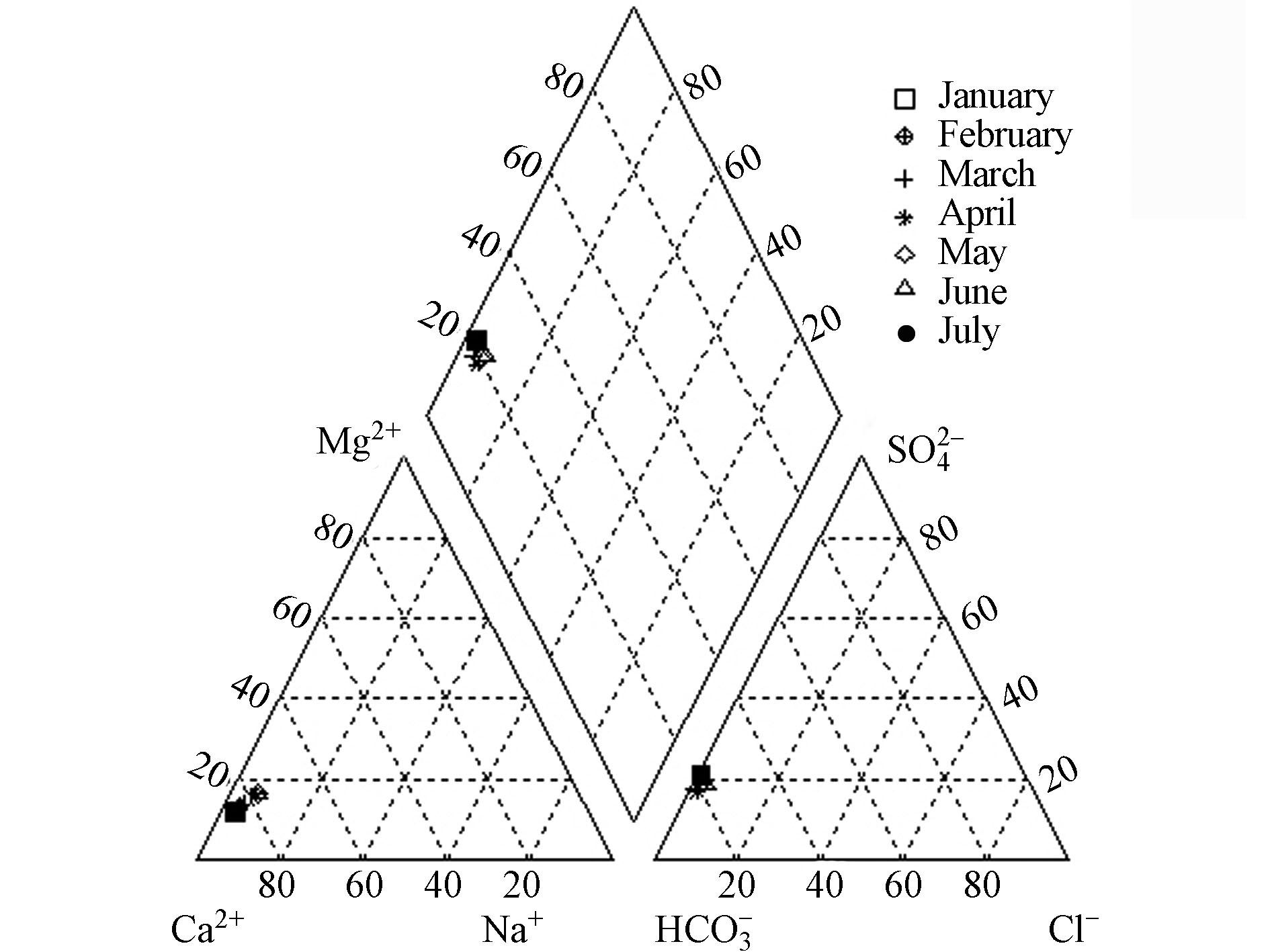
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 、${\rm{CO}}_3^{2-} $ 、${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )的毫克当量百分数来表示,常用于显示不同水体的化学组成特征[30]。由图3可知,喀什河流域地表水的阳离子大部分位于阳离子图的左下角,表明Ca2+在地表水中占优势,其次是Mg2+;在阴离子图中所有水样点均偏向左下角${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 轴线,说明${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 离子占主要优势。综上,HCO3-Ca·Mg和HCO3-Ca型为喀什河流域主要的水化学类型。 -
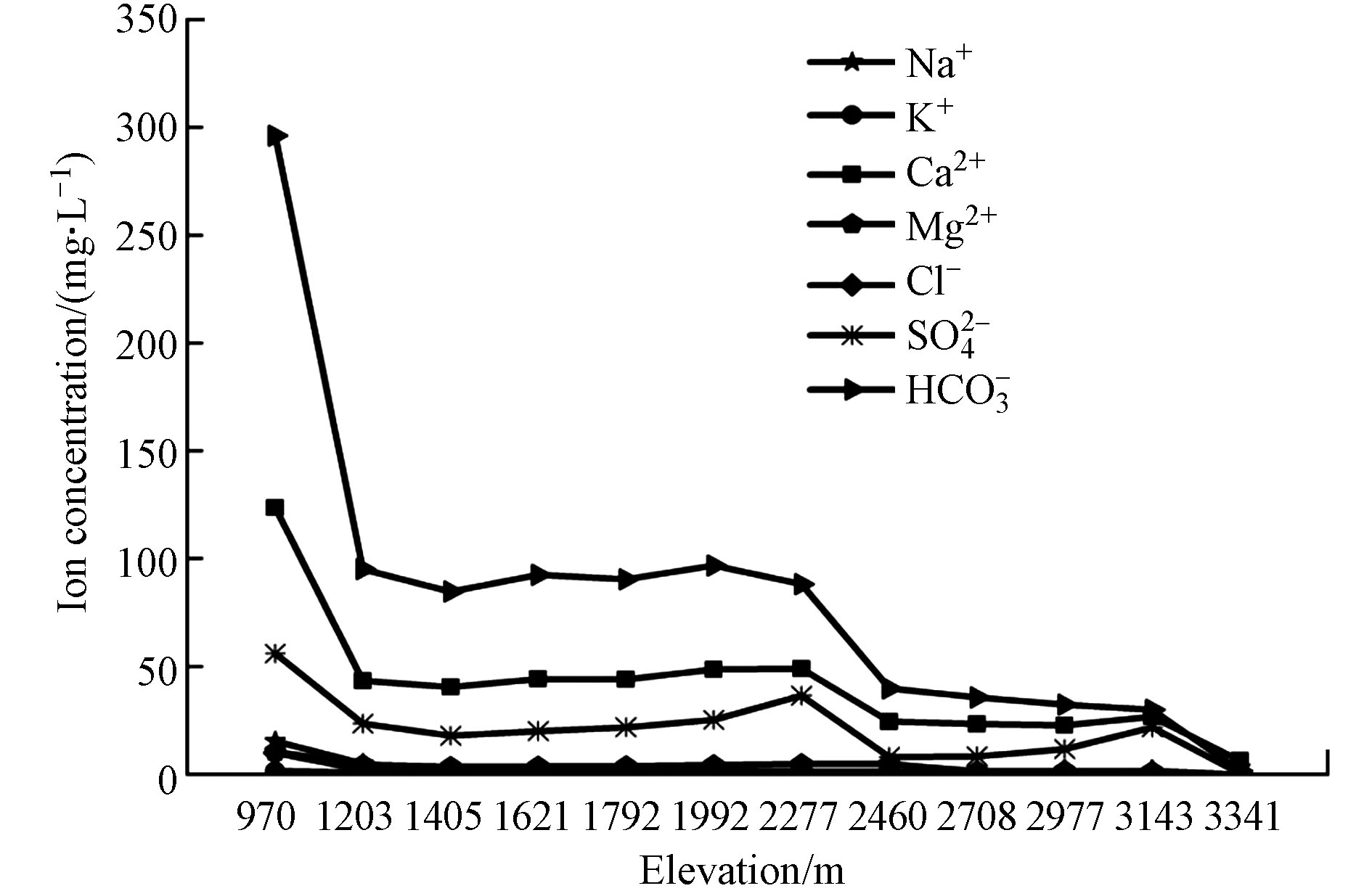
图4为喀什河流域地表水主要离子沿海拔高程的空间变化趋势图,由图4可见,喀什河在海拔970 m至1203 m段,地表水中
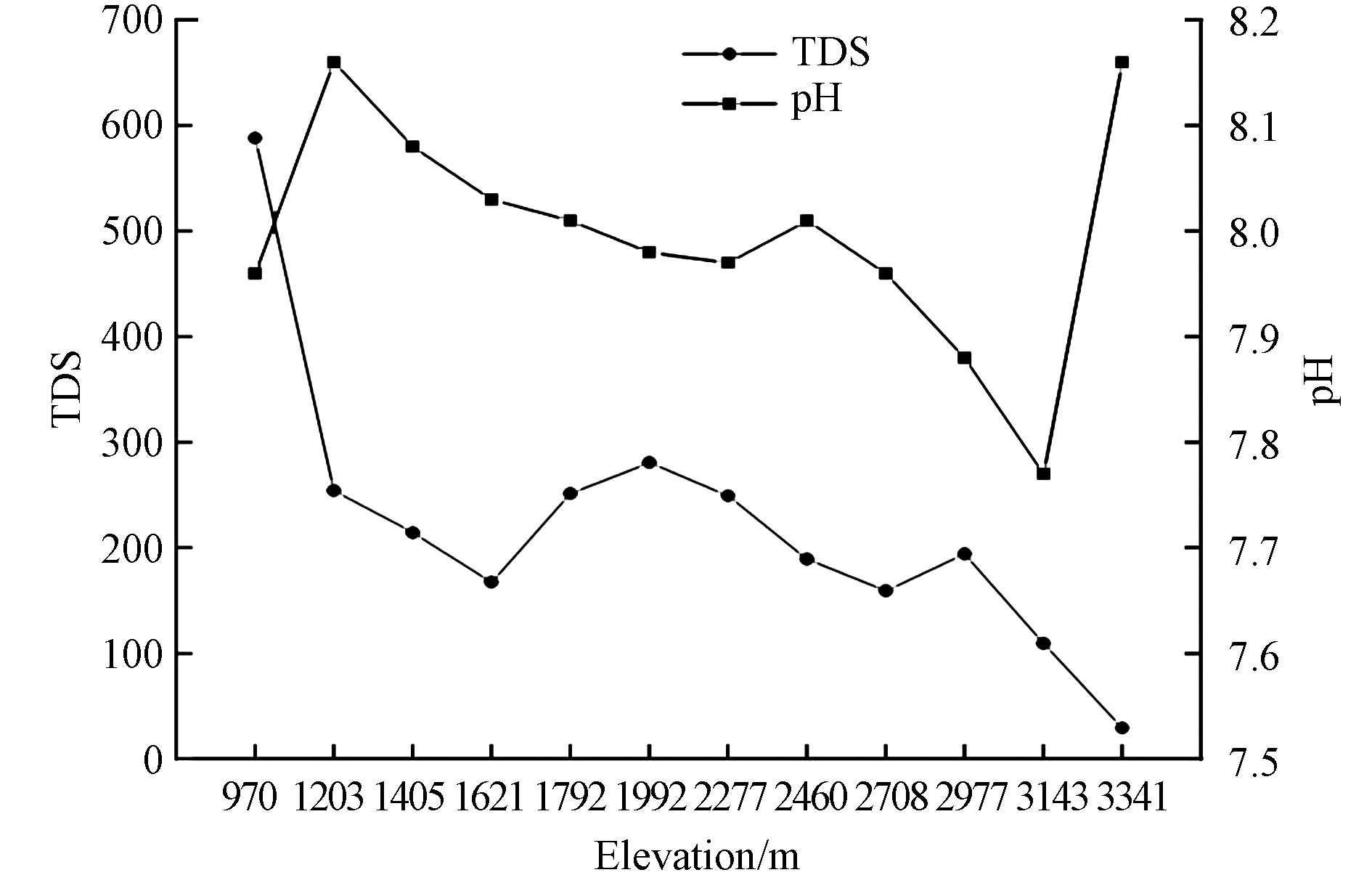
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 呈现急剧降低态势,其余离子降低程度总体较小,其中${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+和SO42-平均浓度在海拔1203 m处分别为95.2、43.38、23.58 mg·L−1,与970 m处相比分别减少了201.03、80.17、32.51 mg·L−1。海拔1203 m至2460 m段主要离子浓度呈先微弱增加后降低的态势。在海拔2460 m至3341 m段主要离子浓度先呈缓慢增加后降低的态势。喀什河流域地表水中主要离子浓度总体随海拔升高而降低,这主要受控于高海拔地区河流冰雪融水占比高,冰雪融水离子浓度低,低海拔地区水岩交互作用较高海拔地区更为强烈、人类活动更为频繁,其释放到水中的主要离子相对较多。结合研究区地质图(图1)和实地勘察可知,在海拔1203 m处有较高山体,970 m处为砂砾石山区河谷,存在地下水补给地表水,970 m至1203 m段地下水相对较浅,当蒸发量大于降水量时,富含盐分的地下水通过毛管力作用向上蒸腾,其所携带的盐分遗留于地表,通过地表径流而汇入喀什河。综上分析,在海拔1203 m至970 m段,离子浓度升高与地下水受到蒸发浓缩、离子交换和岩石风化等作用的共同影响[31],高海拔地区其地下水相对较深,即使当蒸发量大于降水量时其地下水也难以到达地表,这可能是低海拔地区河水中离子浓度大于高海拔的重要原因[32]。河水中的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度在海拔1992 m至海拔2277 m段上升明显,这可能主要与该河段中分布有石膏夹层,释放了大量的氯酸和硫酸有关。在海拔1621—2277 m处河水离子浓度增加,主要原因是此处为研究区中山带(1500—2400 m),该区域降水量大,为森林带,风化水岩交互作用、地下水补给、坡面径流、壤中流等作用较强,导致河水离子浓度主要受到矿物溶解的影响[33]。喀什河干流地表水TDS随着海拔的升高,整体呈下降态势(图5),pH值为7.77—8.16,呈弱碱性,该结果与张杰等[34]在新疆叶尔羌河流域pH值(7.40—8.33)的研究结果相近。TDS值为29.4—588.12 mg·L−1,平均值为243.48 mg·L−1,该平均值低于世界半干旱地区的地表水矿化度的均值(370 mg·L−1)和干旱地区的地表水矿化度平均值(440 mg·L−1)[21],但高于世界河流的平均值(115 mg·L−1)[34]。整体来看,海拔越高TDS浓度越低。这主要与高海拔地区多以冰雪覆盖,水源补给以冰雪融水和降水为主;此外,高海拔地区土壤年轻、可溶性盐少,且高寒区土壤的冻结使盐分难以在表层积聚,坡面径流、壤中流作用相对较弱,人类活动影响微弱[21,35]。
-
表3为喀什河地表水主离子与TDS以及离子间的Pearson相关系数[36]。相关性分析通常用于判断水化学演化过程中的各离子间的关系及主要来源[37]。从表3可知,TDS与Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+、K+、Cl−、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 都有着较强的相关关系,这说明Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+、K+、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 均是喀什河流域地表水TDS的主要贡献者,其中TDS与${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+相关性显著(P<0.01),且相关系数依次高达0.766和0.768,这说明TDS主要来源于河水中的${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和Ca2+。${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 与Mg2+、Ca2+都有着显著的相关关系,三者共同来源于白云岩等碳酸岩盐的风化溶解;${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 与Mg2+、Ca2+也有着较强相关关系,三者共同来源于方解石和白云岩等碳酸岩盐矿物的风化溶解及硫化物的溶解,Na+与K+有显著的相关关系,二者共同来源于长石类硅酸盐岩的风化溶解[38]。 -
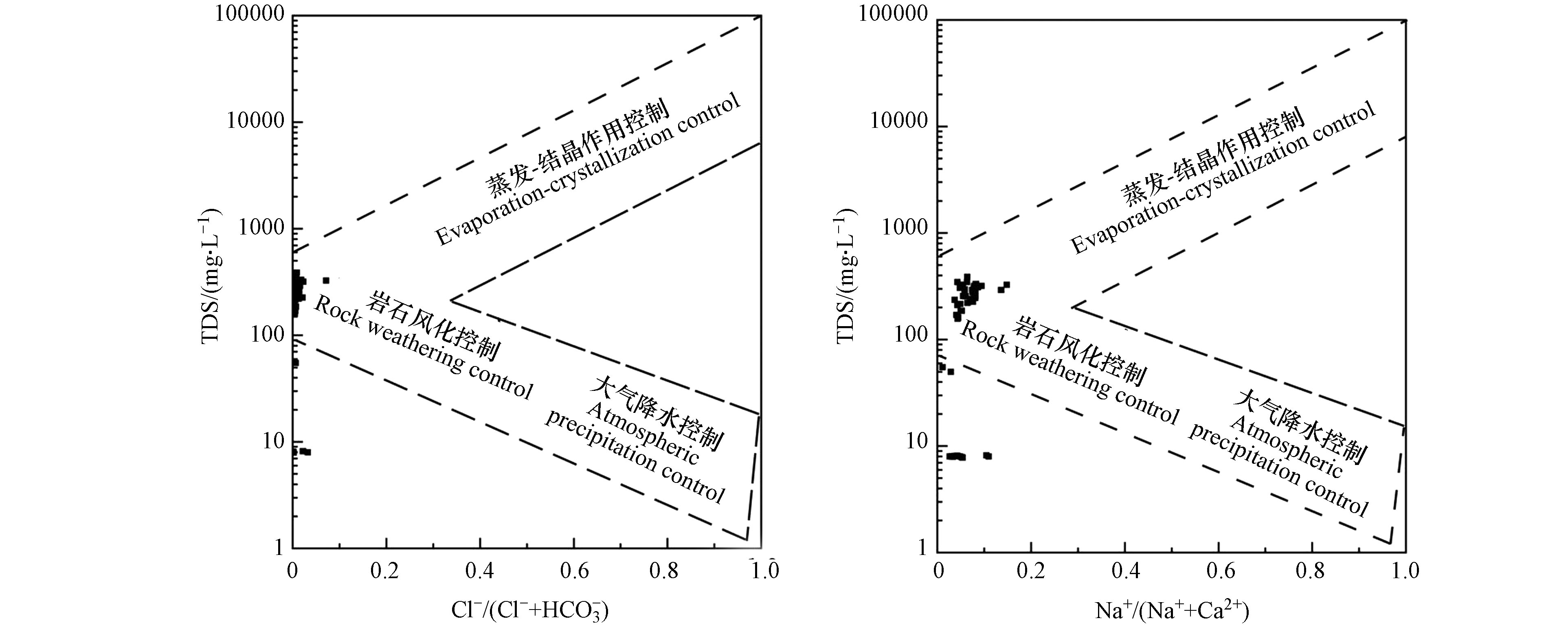
Gibbs图可以定性识别出大气降水、岩石风化和蒸发-结晶等因素控制下的水化学演变特征[5]。由图6可知,喀什河河水样品的数据点大部分落在岩石风化作用控制区,说明喀什河流域地表水主要离子是由岩石风化作用控制。地表水Cl−/Na+平均值为0.41,远低于世界平均降水比值(Cl−/Na+=1.15),这表明大气环流所携带的海盐对喀什河流域地表水离子组分的贡献较小,这是喀什河流域水样中的Na+和Cl−含量略低的重要原因[39]。基于Gibbs模型原理,水样落在图中虚线内,表明水化学受到大气降水、岩石风化、蒸发-结晶作用影响;落在虚线外,表明受到人为因素和阳离子交换作用的影响[40]。图6存在部分水样位于虚线之外,表明人类活动和阳离子交换作用对喀什河地表水化学有一定影响。
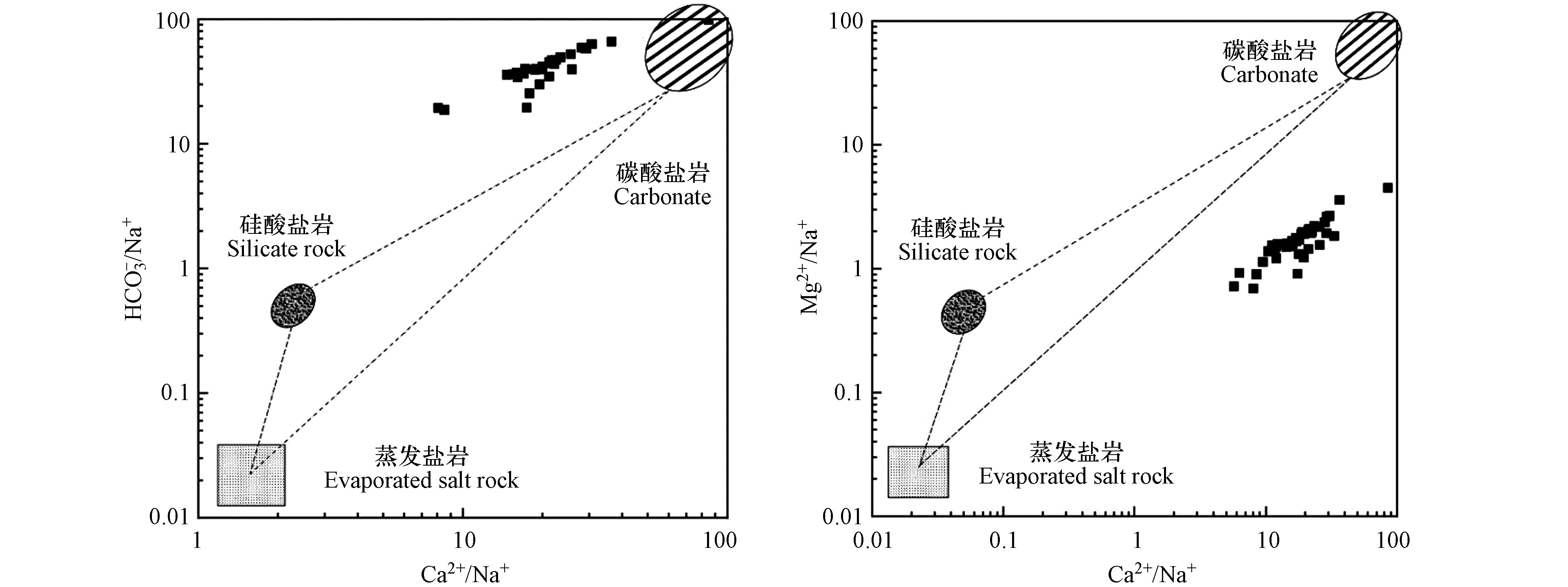
地表水水化学成分主要来源于矿物的风化溶解,K+、Na+主要来源于蒸发岩和硅酸盐岩的溶解,Mg2+、Ca2+主要来源于硅酸盐岩、碳酸盐岩和蒸发岩的溶解,
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和Cl−主要来源于蒸发盐的溶解,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 主要来源于硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩的溶解,通常使用混合图揭示在河流流域中,化学风化作用产生的离子来源[38,41]。根据喀什河地质背景[28],研究区主要分布以大理岩(方解石、白云石)石灰岩(方解石)为主的碳酸盐岩,以花岗岩(钾长石、石英、斜长石)和砂岩(石英、长石)为主的硅酸盐岩,以石膏为主的硫酸盐岩。由于Mg2+/Na+、Ca2+/Na+、${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ /Na+不受蒸发、流速、稀释作用的影响[42-43],Ca2+/Na+与${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ /Na+、Ca2+/Na+与Mg2+/Na+的比值,有助于揭示水化学的起源及矿物溶解的主要来源。由图7可知,喀什河水样中上述离子浓度的比值介于碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩之间,表明其水化学主要受到硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩风化等水岩相互作用的影响,其中以碳酸盐岩风化为主。 -
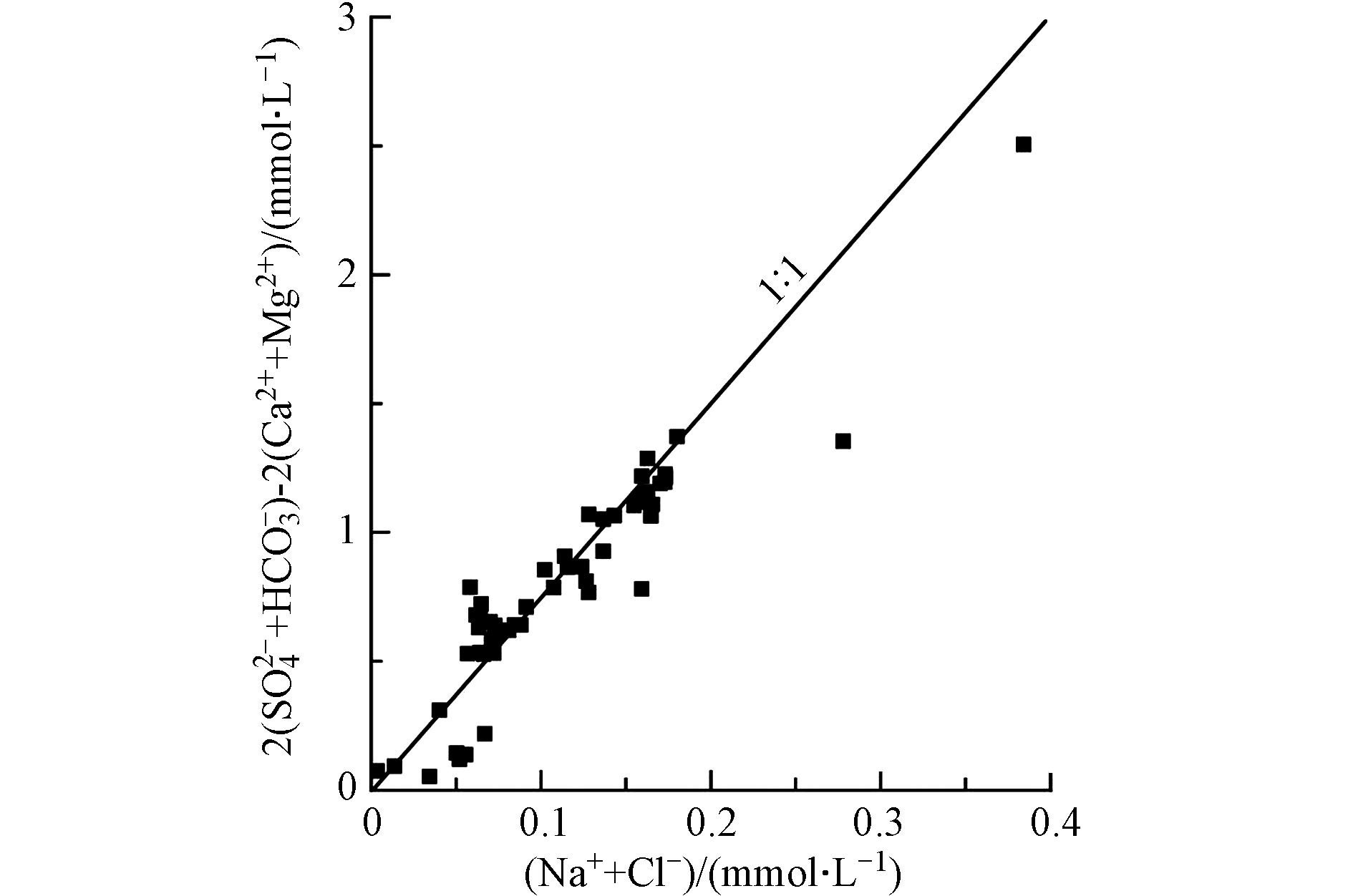
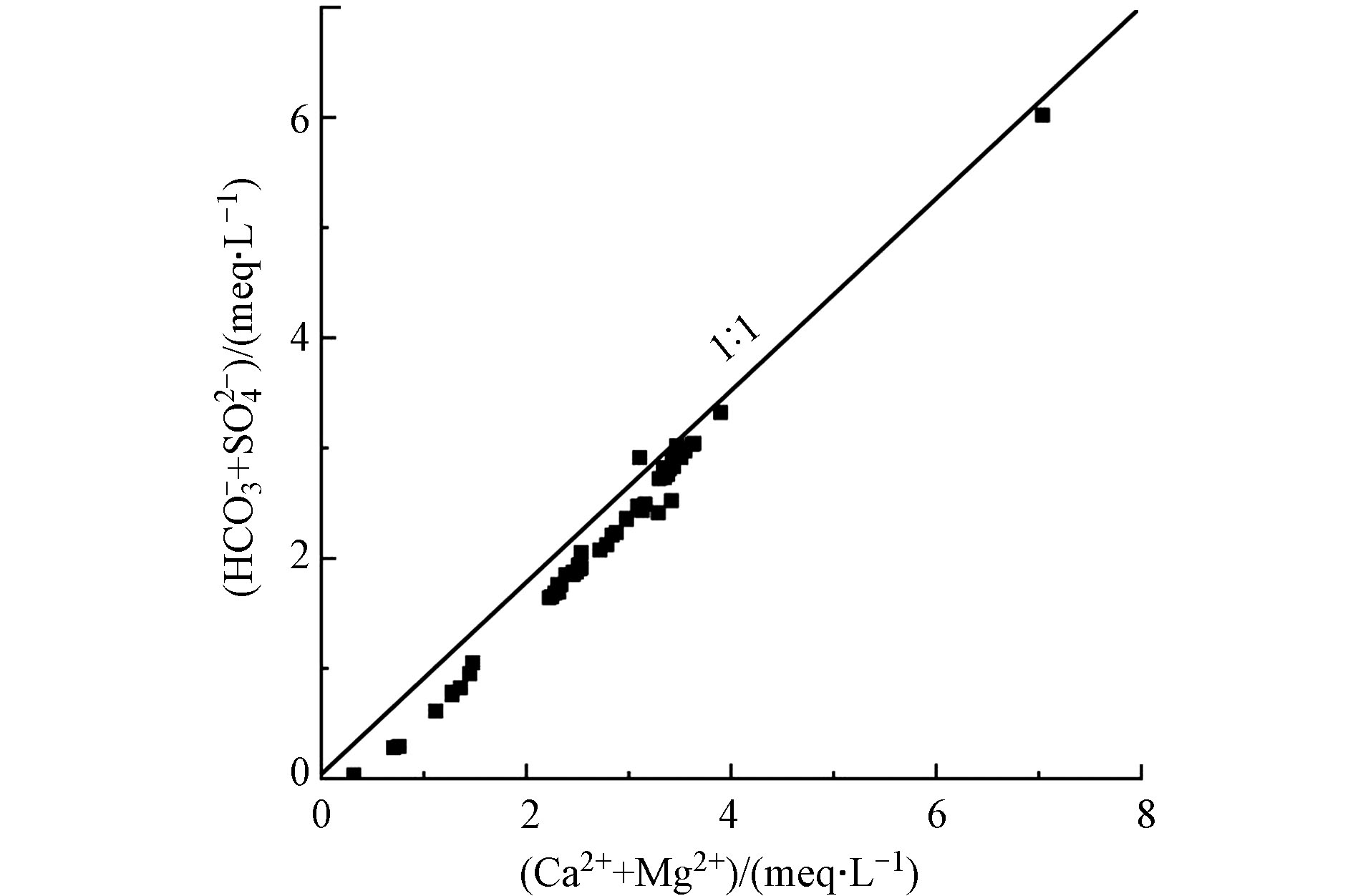
喀什河水样中(Na+-Cl−)/[(2
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )-2(Ca2++Mg2+)]的浓度比值分布在1:1等值线附近(图8),在某些条件下,阳离子会发生交替吸附作用,颗粒会吸收水中的某些阳离子,并将最初吸附在水中的某些阳离子转化为地表水中的组分[44]。(2${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )-2(Ca2++Mg2+)与(Na+-Cl−)的比值可以判断是否发生(Na+-Cl−)的交换作用[45],若水文地球化学过程是以阳离子交换为主,则(Na+-Cl−)/[(2${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )-2(Ca2++Mg2+)]的比值应该分布在1∶1等值线附近。研究区部分水样中(Na+-Cl−)/[(2${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )-2(Ca2++Mg2+)]的浓度比值分布在1∶1等值线的右侧,认为Ca2+、Mg2+和Na+发生离子交换反应,对水样中Na+起到贡献作用。河水从高海拔向低海拔汇流过程中,其流速由快变缓,低海拔(970 m)沉积物颗粒较细,水中的Mg2+和Ca2+与黏土介质表面的Na+间的交替吸附作用明显。综上阳离子交换作用在喀什河流域水文地球化学过程中的作用显著。 -
在图5中可以看出,海拔1621 m和1792 m处TDS分别为167.4 mg·L−1和251.4 mg·L−1,海拔1621 m处的TDS低于1792 m,与1792 m处相比降低了84 mg·L−1,主要原因是海拔1792 m处修建了萨里克特水电站,增大了蒸发面积,加剧了水体的蒸发浓缩,因此使得河水离子浓度升高,表明喀什河流域地表水受到人类活动的影响。强烈的人类活动对水化学发展的影响相对明显,废物,废水和废气的运输导致地表水的Cl−、Na+、
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 等离子化学成分增加[38]。为防御流域自然灾害和保障居民用电安全,而在喀什河山区修建了水电设施,在一定程度上改变了喀什河流域地表水的化学组分。海拔1992 m和2277 m处分别为阿斯塔克村和牧民房子采样点,由图4可知,1992 m、2277 m处Cl−浓度(0.27、0.14 mg·L−1),与2460 m处Cl−浓度(0)相比分别升高了0.27、0.14 mg·L−1;Na+(1.66、1.34 mg·L−1),与2460 m处Na+(1.16 mg·L−1)相比分别升高了0.5、0.18 mg·L−1;${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ (25.38、36.51 mg·L−1),与2460 m处${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ (8.1 mg·L−1)相比分别升高了17.28、28.41 mg·L−1,人们生活区周围的水体有家禽粪尿和生活污水的输入,常含有营养盐NaCl,地表水体中的Cl−可以指示人类活动对水体的影响,水中${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 来源受到农业活动的化学肥料淋滤与石膏物质溶解的影响[46]。1792 m处TDS,1992 m、2277 m处Cl−、Na+、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度较2460 m处,呈上升趋势,但各离子浓度总体变化较小,人类活动对离子组分的影响较弱。 -
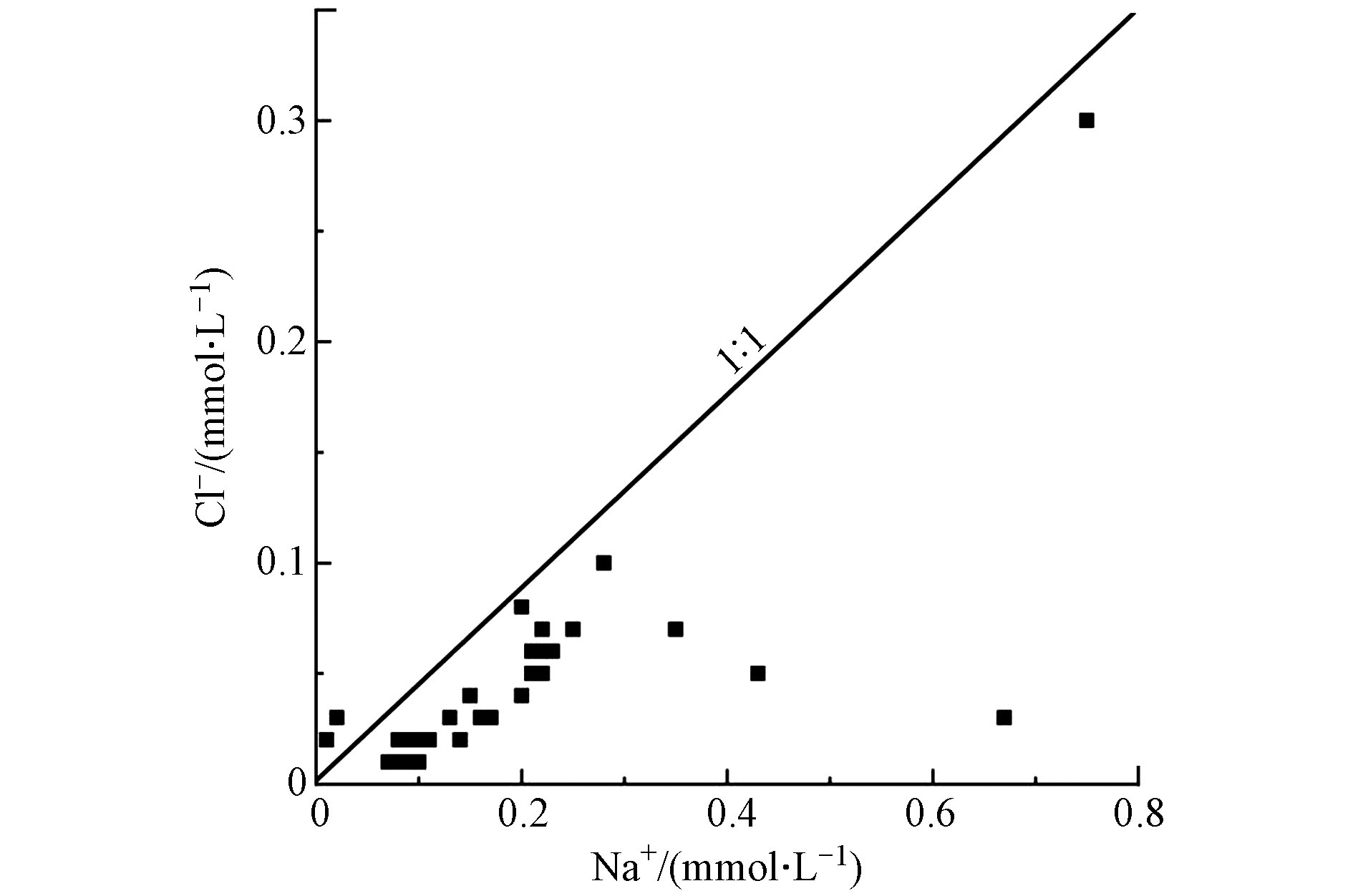
Na+主要来源于硅酸岩和盐岩的风化溶解,而盐岩的溶解会释放等浓度的Cl−和Na+[47],然而喀什河水样中的Cl−和Na+浓度比值偏离1∶1等值线,主要位于靠近Na+一侧(图9),表明钠离子浓度高于氯离子浓度,仍需其它的阴离子来平衡多出来的Na+,表明Na+还有其它来源;Na+/Cl−的浓度比值在6.7—14.5之间,表明该区水样中Na+主要来源不是盐岩,硅酸岩的溶解为其主要来源,研究区地层以砂岩(石英、长石)和花岗岩(钾长石、石英、斜长石)为主的硅酸盐岩与河流之间的溶滤作用,是Na+的主要来源,主要风化溶解如下:
2NaAlSi3O8(钠长石)+2CO2+11H2O→Al2Si2O5(OH)4+2Na++4H4SiO4+2
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 2KAlSi3O8(钾长石)+2CO2+11H2O→Al2Si2O5(OH)4+2K++4H4SiO4+2
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ (
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ +${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )与(Ca2++Mg2+)的比值通常用于研究流域的水文地球化学过程,且可以评估研究区流域的水化学是否源于石膏和碳酸岩的溶解[48-49]。当(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ +${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/(Ca2++Mg2+)的当量浓度比值为1:1,说明受石膏或碳酸岩的风化溶解控制。喀什河水样中(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ +${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/(Ca2++Mg2+)的当量浓度比值均在1:1等值线的线右下方,(Ca2++Mg2+)的当量浓度大于(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ +${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ) (图10),表明应还有其它阴离子来平衡过量的阳离子,即喀什河水样中还有其它Ca2+的来源,部分原因是硅酸岩的溶解。${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 是喀什河地表水中最大的阴离子,来源是碳酸盐岩在水中受到CO2的作用下发生溶解。喀什河水体中Ca2+的来源为岩石中的石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)和石灰石(CaCO3)的溶解。虽然CaCO3在喀什河水中的溶解度小,但CO2的存在易溶解生成溶解性较大的Ca(HCO3)2[22],反应过程如下:CaCO3+CO2+H2O→Ca2++2
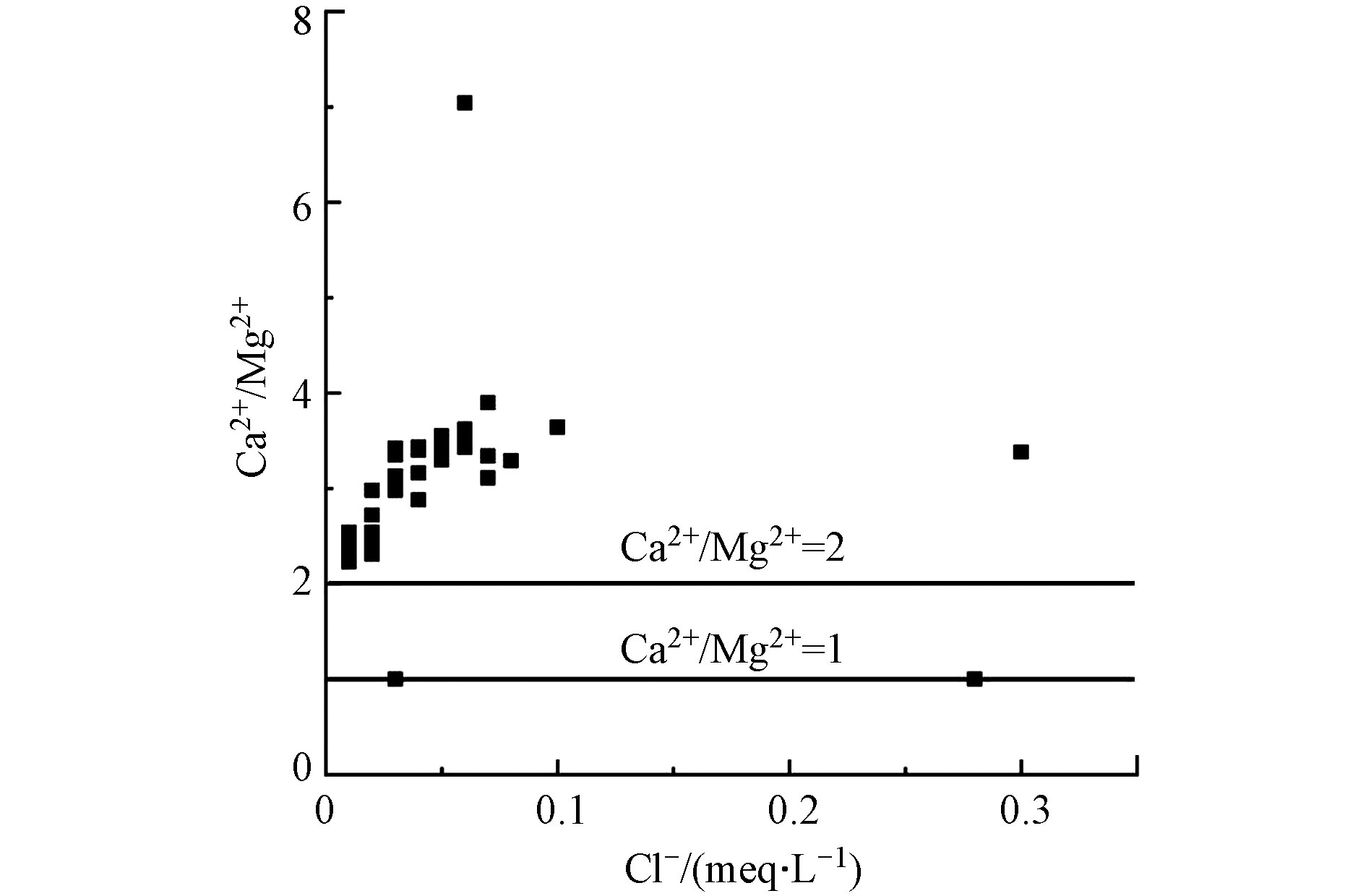
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ Ca2+/Mg2+的比值常用来揭示Mg2+和Ca2+的来源,如果Ca2+/Mg2+=1,说明来源于白云石的溶解[50],若1<Ca2+/Mg2+<2,则说明有更多的方解石溶解,当Ca2+/Mg2+>2时,则说明有石膏或硅酸岩的风化溶解来提供Ca2+。在喀什河流域地表水样中只有2个水样的Ca2+/Mg2+=1,其它水样中的Ca2+/Mg2+均大于2(图11),说明该研究区有碳酸盐岩、石膏或硅酸盐岩的溶解。反应过程如下:
CaCO3+CO2+H2O→Ca2++2
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ CaMg(CO3)2+2CO2+2H2O→Ca2++Mg2++4
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ Na+与Mg2+、Ca2+都有较强的相关关系,说明Na+与Mg2+、Ca2+有着共同的来源,表明有部分来源于硅酸盐岩的溶解。
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 与Mg2+、Ca2+有显著的相关关系(表3),相关系数分别为0.975(P<0.01)和0.977(P<0.01),这表明${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 与Mg2+、Ca2+有共同的来源,根据喀什河地质背景[28],说明碳酸盐岩的风化溶解作用对${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 与Ca2+有贡献。 -
(1)喀什河流域地表水呈弱碱性(7.77≤pH≤8.16),其主要离子浓度总体随海拔升高而降低,主要原因是高海拔流域冰雪融水占比高,河水离子浓度降低,其中阳离子以Ca2+为主,Ca2+当量浓度约占阳离子总量的81%—98.7%,阴离子以
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 为主,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 约占阴离子总量的81.6%—83%;地表水EC均值为174.90 µS·cm−1,其中TDS均值为243.48 mg·L−1,低于世界半干旱区地表水矿化度平均值(370 mg·L−1),同时低于干旱区地表水矿化度平均值(440 mg·L−1),但高于世界河流的平均值(115 mg·L−1)。(2)喀什河流域地表水水化学类型是以HCO3-Ca·Mg和HCO3-Ca型为主,岩石风化和阳离子交换作用为其主要控制因素。
(3)地表水的主要水化学离子主要来自碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩的风化和溶解,
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Mg2+、Ca2+与${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 主要来自白云岩等碳酸岩盐的风化溶解,Na+与K+主要来自长石类硅酸盐岩的风化溶解,1792 m处TDS,1992 m、2277 m处Cl−、Na+、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度较2460 m处,呈上升趋势,但各离子浓度变化小,人类活动对离子组成的影响较弱。
新疆伊犁喀什河流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素
Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in Kashi River Basin, Ili, Xinjiang
-
摘要: 利用2019年1月至7月伊犁喀什河流域的水化学测试数据,采用Piper三线图、相关性分析、Gibbs模型等方法,分析喀什河流域的地表水水化学特征及其控制因素,并对其物质来源进行探讨。结果表明,喀什河流域地表水呈弱碱性(7.77≤pH≤8.16),TDS介于184.8—588.12 mg·L−1之间,其浓度均值(243.48 mg·L−1)低于世界半干旱区地表水TDS的均值(370 mg·L−1),同时低于干旱区地表水TDS的均值(440 mg·L−1),但高于世界河流的均值(115 mg·L−1);阳离子以Ca2+为主,
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 为其主要阴离子,两者分别占其相应离子总量的82.8%和82.6%;研究区主要离子浓度总体随海拔升高而降低,主要原因是高海拔流域冰雪融水占比高;水化学类型以HCO3-Ca·Mg和HCO3-Ca型为主;地表水主要离子受岩石风化作用和阳离子交换作用的影响,主要离子来源于碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩的风化溶解,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Mg2+、Ca2+与${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 主要来自白云岩等碳酸岩盐的风化溶解,Na+与K+主要来自长石类硅酸盐岩的风化溶解,人类活动对离子组分的影响较弱。Abstract: Based on the hydrochemical data of Kashi River Basin from January to July in 2019, this study analyzed the hydrochemical characteristics, the control factors of surface water in Kashi River Basin by using Piper diagrams, correlation analysis and Gibbs model. We also discussed the material source on hydrochemical of surface water. The results as follows: the surface water was weakly alkaline, value of pH was from 7.77 to 8.16, in Kashi River Basin. Average concentration of TDS was 243.48 mg·L−1(the variation range of TDS was 184.8—588.12 mg·L−1),which was lower than that in world semi-arid area (370 mg·L−1) and arid area (440 mg·L−1), but higher than that in world rivers (115 mg·L−1); Ca2+ and${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ were the main ions which respectively account for 82.8% and 82.6% of their corresponding total ions, The concentration of main ions generally decreased with increasing altitude in study area, which was mainly due to the high proportion of melt water from ice and snow in high altitude basin; The hydrochemical types are mainly${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ Ca·Mg and HCO3-Ca; The main ions of surface water are affected by rock weathering and cation exchange. The main ions come from weathering and dissolution of carbonate and silicate rocks.${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ , Mg2+, Ca2+ and${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ mainly come from weathering and dissolution of carbonate rock salt such as dolomite. Na+ and K+ mainly come from weathering and dissolution of feldspar silicate rocks. Human activities have a weak influence on ion components.-
Key words:
- hydrochemical characteristics /
- surface water /
- ion sources /
- chemical genesis /
- Kashi River Basin
-

-
表 1 喀什河流域地表水水化学统计(n=56)
Table 1. Statistical of hydrochemistry composition of surface water in the Kashi River Basin(n=56)
项目
Items均值
Average中值
Median标准差
Standard deviation最小值
Minimum最大值
MaximumpH 7.97 7.96 0.20 7.53 8.39 TDS/(mg·L−1) 243.48 184.8 87.86 29.4 588.12 EC/(µS·cm−1) 174.90 168.1 72.11 6.3 438 Na+/(mg·L−1) 3.44 2.99 2.56 0 15.31 K+/(mg·L−1) 1.29 1.16 0.57 0 2.69 Ca2+/(mg·L−1) 46.70 48.98 16.96 6.30 123.55 Mg2+/(mg·L−1) 4.97 4.80 2.29 0.08 10.61 Cl-/(mg·L−1) 1.40 1.0 1.93 0 10.55 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 20.70 20.09 8.32 0.32 56.09 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 105.06 105.78 48.89 1.57 296.23 表 2 喀什河干流主要离子浓度与其他河流主离子浓度对比分析(mg·L−1)
Table 2. Comparision of major ion concentrations in the Kashi River with other rivers(mg·L−1)
表 3 各常规指标之间相关关系(n=56)
Table 3. Correlation coefficients between major ions in the water(n=56)
离子Ions Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ TDS Na+ 1.00 K+ 0.528** 1.00 Ca2+ 0.768** 0.577** 1.00 Mg2+ 0.867** 0.557** 0.934** 1.00 Cl− 0.806** 0.206 0.415** 0.482** 1.00 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 0.795** 0.461** 0.867** 0.925** 0.448** 1.00 $ {\rm{HCO}}_3^{-}$ 0.827** 0.608** 0.977** 0.975** 0.434** 0.876** 1.00 TDS 0.630** 0.427** 0.768** 0.715** 0.369* 0.631** 0.766** 1.00 注:**P<0.01,*P<0.05. -
[1] 李晓强, 韩贵琳, 董爱国, 等. 九龙江丰水期水化学组成特征及其控制因素 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(3): 697-706. LI X Q, HAN G L, DONG A G, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and controlling factors in Jiulong River(Fujian Province) during the flood season [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(3): 697-706(in Chinese).
[2] XU Z F, LIU C Q. Water geochemistry of the Xijiang basin rivers, South China: Chemical weathering and CO2 consumption [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(10): 1603-1614. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.08.012 [3] PANT R R, ZHANG F, REHMAN F U, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrogeochemistry and its controlling factors in the Gandaki River Basin, Central Himalaya Nepal [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622/623: 770-782. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.063 [4] 曹晏风, 张明军, 瞿德业, 等. 祁连山东端地表及地下水水化学时空变化特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1667-1676. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.034 CAO Y F, ZHANG M J, QU D Y, et al. Temporal-spatial variation of surface and undergroundwater chemistry in the eastern part of Qilian Mountains [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1667-1676(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.034
[5] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [6] KATTAN Z. Chemical and isotopic characteristics of the Euphrates River water, Syria: Factors controlling its geochemistry [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(8): 4763-4778. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3762-z [7] 孙平安, 于奭, 莫付珍, 等. 不同地质背景下河流水化学特征及影响因素研究: 以广西大溶江、灵渠流域为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 123-131. SUN P A, YU S, MO F Z, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors in different geological background: A case study in darongjiang and Lingqu basin, Guangxi, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 123-131(in Chinese).
[8] XIAO J, JIN Z D, DING H, et al. Geochemistry and solute sources of surface waters of the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54/55: 162-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.009 [9] 余冲, 徐志方, 刘文景, 等. 韩江流域河水地球化学特征与硅酸盐岩风化: 风化过程硫酸作用 [J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(4): 390-398. YU C, XU Z F, LIU W J, et al. River water geochemistry of Hanjiang river, implications for silicate weathering and sulfuric acid participation [J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(4): 390-398(in Chinese).
[10] 何姜毅, 张东, 赵志琦. 黄河流域河水水化学组成的时间和空间变化特征 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 1390-1401. HE J Y, ZHANG D, ZHAO Z Q. Spatial and temporal variations in hydrochemical composition of river water in Yellow River Basin, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(5): 1390-1401(in Chinese).
[11] 陈静生, 王飞越, 夏星辉. 长江水质地球化学 [J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(1): 74-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.01.010 CHEN J S, WANG F Y, XIA X H. Geochemistry of water quality of the Yangtze River basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(1): 74-85(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.01.010
[12] 张旺, 王殿武, 雷坤, 等. 黄河中下游丰水期水化学特征及影响因素 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(1): 380-386,393. ZHANG W, WANG D W, LEI K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and impact factors in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River in the wet season [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(1): 380-386,393(in Chinese).
[13] 刘松韬, 张东, 李玉红, 等. 伊洛河流域河水来源及水化学组成控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1184-1196. LIU S T, ZHANG D, LI Y H, et al. Water sources and factors controlling hydro-chemical compositions in the yiluo river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1184-1196(in Chinese).
[14] 禤映雪, 唐常源, 曹英杰, 等. 北江流域水化学时空变化及化学风化特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(6): 1078-1087. XUAN Y X, TANG C Y, CAO Y J, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of hydro-chemistry and chemical weathering characteristics in the Beijiang river basin [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(6): 1078-1087(in Chinese).
[15] 周嘉欣, 丁永建, 曾国雄, 等. 疏勒河上游地表水水化学主离子特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(9): 3315-3324. ZHOU J X, DING Y J, ZENG G X, et al. Major ion chemistry of surface water in the upper reach of Shule river basin and the possible controls [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(9): 3315-3324(in Chinese).
[16] 汪生斌, 祁泽学, 王万平, 等. 格尔木河水化学特征及成因 [J]. 水资源保护, 2020, 36(5): 93-98. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2020.05.014 WANG S B, QI Z X, WANG W P, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of formation of the Golmud River [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2020, 36(5): 93-98(in Chinese). doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2020.05.014
[17] 朱世丹, 张飞, 张海威, 等. 新疆艾比湖主要入湖河流同位素及水化学特征的季节变化 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(6): 1707-1721. doi: 10.18307/2018.0622 ZHU S D, ZHANG F, ZHANG H W, et al. Seasonal variation of the isotope and hydrochemical characteristics of the main lake rivers in Lake Ebinur, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(6): 1707-1721(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2018.0622
[18] 王晓艳, 李忠勤, 蒋缠文, 等. 天山哈密榆树沟流域夏季洪水期河水水化学特征及其成因 [J]. 冰川冻土, 2016, 38(5): 1385-1393. WANG X Y, LI Z Q, JIANG C W, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of the summer river water in Yushugou basin, Eastern Tianshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2016, 38(5): 1385-1393(in Chinese).
[19] 韦虹, 吴锦奎, 沈永平, 等. 额尔齐斯河源区融雪期积雪与河流的水化学特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(4): 1345-1352. WEI H, WU J K, SHEN Y P, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of snow meltwater and river water during snow-melting period in the headwaters of the Ertis River, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(4): 1345-1352(in Chinese).
[20] 刘峰, 李忠勤, 郝嘉楠, 等. 额尔齐斯河源春季水化学及稳定同位素特征研究 [J]. 冰川冻土, 2020, 42(1): 234-242. LIU F, LI Z Q, HAO J N, et al. Study on the hydrochemical and stable isotope characteristics at the headwaters of the Irtysh River in spring [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2020, 42(1): 234-242(in Chinese).
[21] 吴丽娜, 孙从建, 贺强, 等. 中天山典型内陆河流域水化学时空特征分析 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(5): 149-156. WU L N, SUN C J, HE Q, et al. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation of hydrochemical characteristics of the typical inland river in the middle of Tianshan mountains [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 24(5): 149-156(in Chinese).
[22] 宋梦媛, 李忠勤, 王飞腾, 等. 新疆吉木乃诸河水体氢氧同位素和水化学特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(7): 1809-1820. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019050402 SONG M Y, LI Z Q, WANG F T, et al. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and hydrochemical parameters of water samples from the Jimunai River Basin, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(7): 1809-1820(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019050402
[23] 王建, 韩海东, 赵求东, 等. 塔里木河流域水化学组成分布特征 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2013, 30(1): 10-15. WANG J, HAN H D, ZHAO Q D, et al. Study on hydrochemical components of river water in the Tarim river basin, Xinjiang, China [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2013, 30(1): 10-15(in Chinese).
[24] SUN C J, CHEN Y N, LI X G, et al. Analysis on the streamflow components of the typical inland river, Northwest China [J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2016, 61(5): 970-981. [25] 蒋显忠, 夏平. 伊犁盆地地下水系统划分研究 [J]. 地下水, 2020, 42(4): 44-45. JIANG X Z, XIA P. Study on groundwater system division in Yili basin [J]. Ground Water, 2020, 42(4): 44-45(in Chinese).
[26] 王成虎, 张彦山, 熊玉珍, 等. 喀什河水电站工程区构造稳定性研究 [J]. 地质力学学报, 2008, 14(2): 135-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.004 WANG C H, ZHANG Y S, XIONG Y Z, et al. Tectonic stability analysis of the kax river hydroelectric project area [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(2): 135-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.004
[27] 李金环, 涂新富. 伊犁州喀什河下游灌区费尔干式引水枢纽工程运行浅谈[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2005, 28(增刊2): 67-68. LI J H, TU X F. A brief discussion on operation of Fergan type water diversion project in the lower irrigation area of Kashi River in Yili Prefecture[J]. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 28(Sup 2): 67-68 (in Chinese).
[28] 王小丽. RS与GIS支持下的伊犁谷地地质灾害风险评价 : 以尼勒克县滑坡为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013. WANG X L. Geological hazard risk assessment on Ili valley based on RS and GIS —A case study of landslide in nilka County[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2013(in Chinese).
[29] 高瑞, 穆振侠, 彭亮, 等. 水量平衡与能量平衡模式下的VIC模型在喀什河流域的应用研究 [J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2018, 37(1): 106-112. GAO R, MU Z X, PENG L, et al. Application research of VIC model with the mode of water balance and energy balance in Kashi river basin [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2018, 37(1): 106-112(in Chinese).
[30] 张艳, 吴勇, 杨军, 等. 阆中市思依镇水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(9): 3230-3237. ZHANG Y, WU Y, YANG J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristic and reasoning analysis in siyi town, Langzhong city [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(9): 3230-3237(in Chinese).
[31] 贾思达. 三江平原松花江—挠力河流域地下水与地表水转化关系研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. JIA S D. Groundwater-surface water interaction in Songhuajiang-naoli river basin of Sanjiang plain[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019(in Chinese).
[32] 朱艺文. 西安黑河流域汇水区不同水体稳定同位素和水化学特征研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2017. ZHU Y W. Stable isotope and hydrochemical characteristics of different water bodies in the catchment area of Heihe, Xi 'an[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2017.
[33] 梁云, 吕斌, 钟庆. 乌鲁木齐南山中山带气候特征分析 [J]. 新疆气象, 2002(3): 20-21. LIANG Y, LU B, ZHONG Q. Research on the climatology features of middle zone of Nanshan mountain in Urumqi [J]. Bimonthly of Xinjiang Meteorology, 2002(3): 20-21(in Chinese).
[34] 张杰, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 新疆叶尔羌河流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1706-1713. ZHANG J, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristic and their controlling factors in the Yarkant river basin of Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 1706-1713(in Chinese).
[35] 杨玲. 石羊河流域多水体可溶离子水化学特征及控制因素[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2017. YANG L. Chemical characteristics and control factors of multi-type water resource in Shiyang river basin[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2017(in Chinese).
[36] 尹恒, 姜丽丽, 裴尼松, 等. 基于水化学和多元统计的煤矿采空积水识别 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(27): 11051-11058. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.27.011 YIN H, JIANG L L, PEI N S, et al. Identification of coalmine goaf groundwater based on hydrogeochemistry and multivariate statistics [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(27): 11051-11058(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.27.011
[37] 董维红, 孟莹, 王雨山, 等. 三江平原富锦地区浅层地下水水化学特征及其形成作用 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(2): 542-553. DONG W H, MENG Y, WANG Y S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation of the shallow groundwater in Fujin, Sanjiang plain [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(2): 542-553(in Chinese).
[38] 张涛, 王明国, 张智印, 等. 然乌湖流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010. ZHANG T, WANG M G, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in ranwu lake basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010(in Chinese).
[39] 刘佳驹, 赵雨顺, 黄香, 等. 雅鲁藏布江流域水化学时空变化及其控制因素 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(11): 4289-4297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.039 LIU J J, ZHAO Y S, HUANG X, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of hydrochemistry and its controlling factors in the Yarlung Tsangpo River [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(11): 4289-4297(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.11.039
[40] 朱世丹, 张飞, 张海威. 艾比湖流域河流水化学季节特征及空间格局研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(3): 892-899. ZHU S D, ZHANG F, ZHANG H W. The seasonal and spatial variations of water chemistry of rivers in Ebinur Lake Basin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(3): 892-899(in Chinese).
[41] 孙瑞, 张雪芹, 吴艳红. 藏南羊卓雍错流域水化学主离子特征及其控制因素 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2012, 24(4): 600-608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.04.014 SUN R, ZHANG X Q, WU Y H. Major ion chemistry of water and its controlling factors in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2012, 24(4): 600-608(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.04.014
[42] JIANG L G, YAO Z J, LIU Z F, et al. Hydrochemistry and its controlling factors of rivers in the source region of the Yangtze River on the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 155: 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.04.009 [43] THOMAS J, JOSEPH S, THRIVIKRAMJI K P. Hydrochemical variations of a tropical mountain river system in a rain shadow region of the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 63: 456-471. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.03.018 [44] 王晓曦, 王文科, 王周锋, 等. 滦河下游河水及沿岸地下水水化学特征及其形成作用 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1): 25-33,73. WANG X X, WANG W K, WANG Z F, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of river water and groundwater along the downstream Luanhe River, northeastern China [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1): 25-33,73(in Chinese).
[45] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159: 252-261. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.018 [46] 周迅, 朱春芳. 福建省晋江市浅层地下水硝酸盐含量特征及其水化学指示意义 [J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(2): 177-182. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.02.08 ZHOU X, ZHU C F. The nitrate content characteristics of shallow groundwater in Jinjiang city, Fujian Province, and their hydrochemical indication significance [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(2): 177-182(in Chinese). doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.02.08
[47] FU C C, LI X Q, MA J F, et al. A hydrochemistry and multi-isotopic study of groundwater origin and hydrochemical evolution in the middle reaches of the Kuye River basin [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 98: 82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.08.030 [48] MAURYA P, KUMARI R, MUKHERJEE S. Hydrochemistry in integration with stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to assess seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Kachchh district, Gujarat, India [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 196: 42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.09.013 [49] AYADI Y, MOKADEM N, BESSER H, et al. Hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (δ18O and δ2H) tools applied to the study of Karst aquifers in southern Mediterranean basin (Teboursouk area, NW Tunisia) [J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2018, 137: 208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.10.018 [50] XIAO J, JIN Z D, ZHANG F, et al. Major ion geochemistry of shallow groundwater in the Qinghai Lake catchment, NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 67(5): 1331-1344. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1576-4 -










 下载:
下载: