-
随着垃圾渗滤液处理新标准的颁布[1],传统的生化处理工艺无法达标排放,所以必须对生化出水进行深度处理. 截至目前,膜处理已经广泛应用于垃圾渗滤液深度处理,但是垃圾渗滤液经纳滤(NF)、反渗透(RO)等膜过滤处理后截留下的浓缩液,约为垃圾渗滤液总量的20%—30%[2]. 垃圾渗滤液浓缩液呈棕褐色,具有可生化性很差、盐分和难降解有机物含量高等特点[3].目前,垃圾渗滤液浓缩液处理主要通过回灌、蒸发、高级氧化和回喷焚烧等方法[4]. 然而,回灌法会造成有机物和盐分的积累,影响填埋场的稳定性;蒸发法工艺复杂,能耗高;回喷焚烧法存在对于炉膛及相关设备的腐蚀以及结焦结渣问题. 因此,如何有效的对垃圾渗滤液浓缩液进行处理,是垃圾渗滤液处理中的一个新难题.
高级氧化技术(AOPs)是利用光、电、催化剂等方式产生具有强氧化性的自由基(如·OH、SO4−·、·O2−等),将难降解有机污染物氧化降解成为小分子中间产物,甚至直接降解为CO2和H2O[5]. 因其具有高效和易于操作等显著优势,近年来越来越多的被用于垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的处理研究[6-8]. 基于SO4−·高级氧化技术氧化能力更强和半衰期更长,对难降解有机物的去除潜力更大[9]. SO4−·的产生可以通过对过硫酸盐(PS)进行热活化、紫外活化和过渡金属活化等活化方式[10]. 为进一步改良单一活化方式,将电化学引入热活化过硫酸盐不仅能加快反应速率,而且对降低能耗也有很好的效果[11-12]. 此外,垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中盐分含量高,特别是Cl−,经电化学氧化转化为ClO−等强氧化性物质,能够间接氧化、促进难降解有机物的去除[13].
因此,本实验采用电/过硫酸盐催化氧化垃圾渗滤液浓缩液,研究了初始过硫酸盐(PS0)浓度、温度、反应时间和极板间距对氧化效果的影响,并对最佳实验条件下反应前后的垃圾渗滤液浓缩液进行紫外-可见光谱、三维荧光光谱和傅里叶红外光谱分析,以探究其溶解性有机物的降解机理.
-
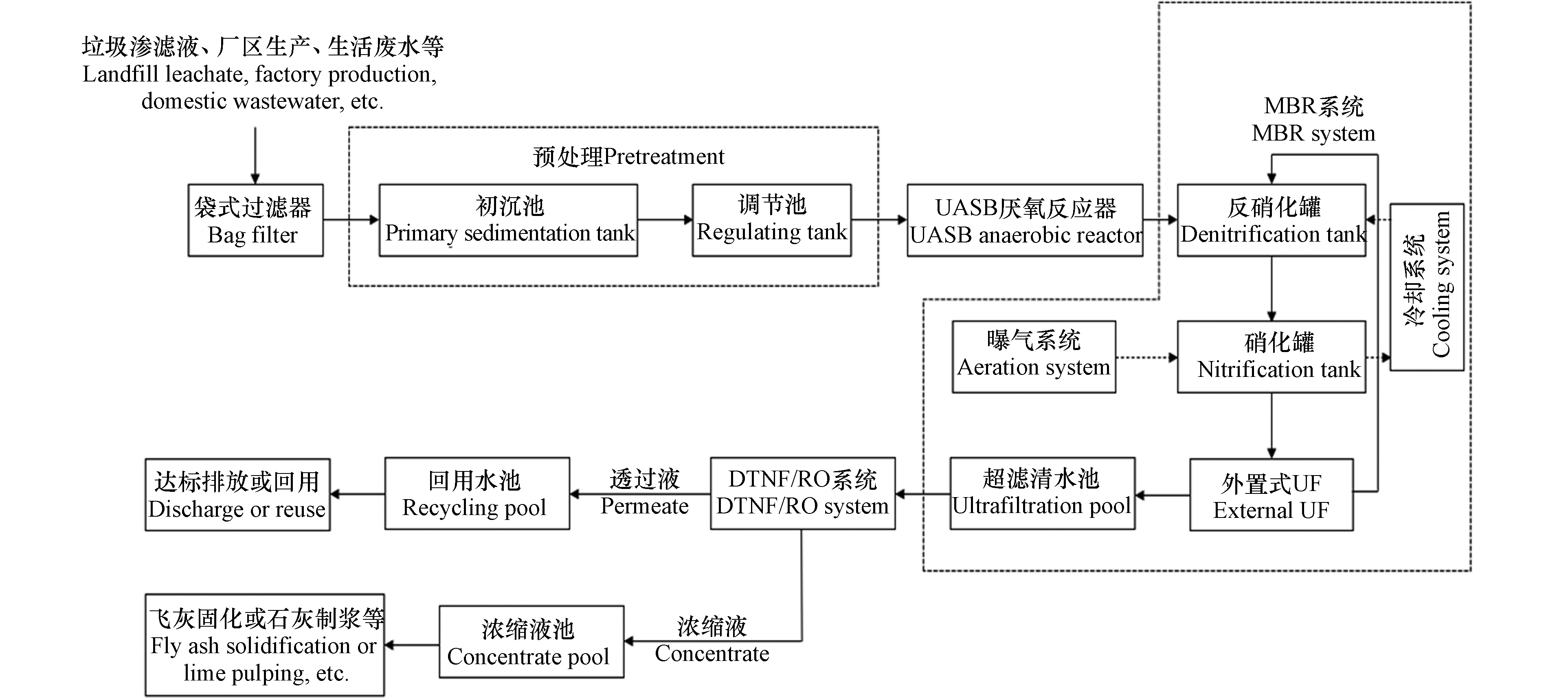
实验所用垃圾渗滤液浓缩液取自江西省南昌市某生活垃圾焚烧发电厂. 在该焚烧厂中,渗滤液经过“预处理+UASB反应器+MBR系统+DTNF/RO系统”组合工艺处理,其中DTNF/RO系统产生的浓缩液进入浓缩液池,然后回用于灰飞固化、石灰制浆等. 工艺流程见图1.
此次实验所用的浓缩液取自浓缩液池,取样之后,水样保存在4℃的冰箱中,以备实验所用.原液颜色呈棕褐色,色度为500—550,pH值为7.0—8.0,COD为2000—2500 mg·L−1,氨氮为30—35 mg·L−1,Cl−浓度为10000—13000 mg·L−1.
-
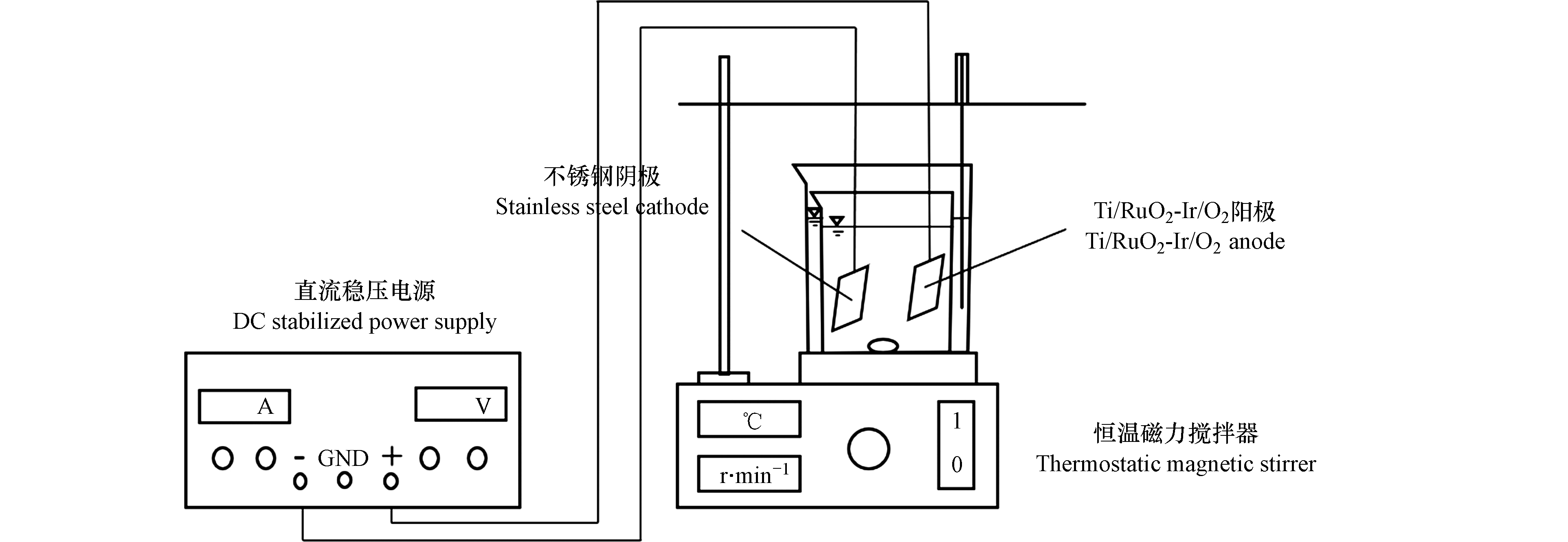
实验装置见图2. 实验装置主要有容积为500 mL、1 L烧杯,MP6010D可调直流稳压电源,85-2A磁力搅拌器,阳极和阴极均为尺寸长×宽=5 cm×5 cm的极板,实际有效面积为15 cm2,阳极材料采用Ti/RuO2-Ir/O2(钛∶钌∶铱=6∶3∶1),不锈钢为阴极.
量取500 mL垃圾渗滤液浓缩液于烧杯中,并使原液液面浸没于盛有液体水的1 L烧杯中,用磁力搅拌器进行搅拌,待温度升高到设定温度时,添加一定剂量的Na2S2O8,然后在之前研究的电流密度为8 A·dm−2的最佳条件下,不调节水样的初始pH值,在一定的实验条件下进行电解反应,反应过程中保持整个体系在设定的温度,处理后的溶液经0.45 μm微孔滤膜抽滤,最后对其相关指标进行分析检测. 在本实验中,选取PS0浓度、温度、反应时间和极板间距为主要影响因素,对色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率的影响,并对最佳实验条件下反应前后的垃圾渗滤液浓缩液进行紫外-可见光谱、三维荧光光谱和傅里叶红外光谱分析,以探究其溶解性有机物的降解机理.
-
色度:稀释倍数法;pH值:SevenCompact pH计S210测定;COD:微波密闭消解快速测定COD;氨氮:纳氏试剂光度法;Cl−浓度:硝酸银滴定法.
-
以超纯水为参比,用待测水样润洗石英比色皿2—3次,再在石英比色皿中加入待测水样进行测定. 采用UV2300Ⅱ双光束紫外可见分光光度计对电解处理前后水样进行紫外-可见全波长扫描,扫描条件:吸光度(Abs),波长范围200—900 nm,扫描速度400 nm·min−1,采样间隔1 nm,狭缝宽1.5 nm,响应速度为快速,样品池为1 cm石英比色皿.
-
用待测水样润洗2—3次石英比色皿,再在石英比色皿中加入待测水样进行测定.利用日立F-7000荧光光谱仪对处理前后水样进行光谱扫描,扫描条件:波长范围Ex=200—500 nm,Em=250—650 nm,激发波长间隔10 nm,响应时间0.002 s,狭缝宽5 nm,扫描速度2400 nm·min−1.
-
待测水样在真空干燥箱中烘干24 h,取少量烘干后产生的固体,在室温下与过量的KBr在玛瑙研钵中充分研磨,并压成待测薄片,维持3—5 min. 采用FTIR对处理前后水样进行傅里叶红外光谱扫描,扫描条件:透射率(T%),光谱范围4000—400 cm−1,扫描间隔1 cm−1, 分辨率4 cm−1.
-
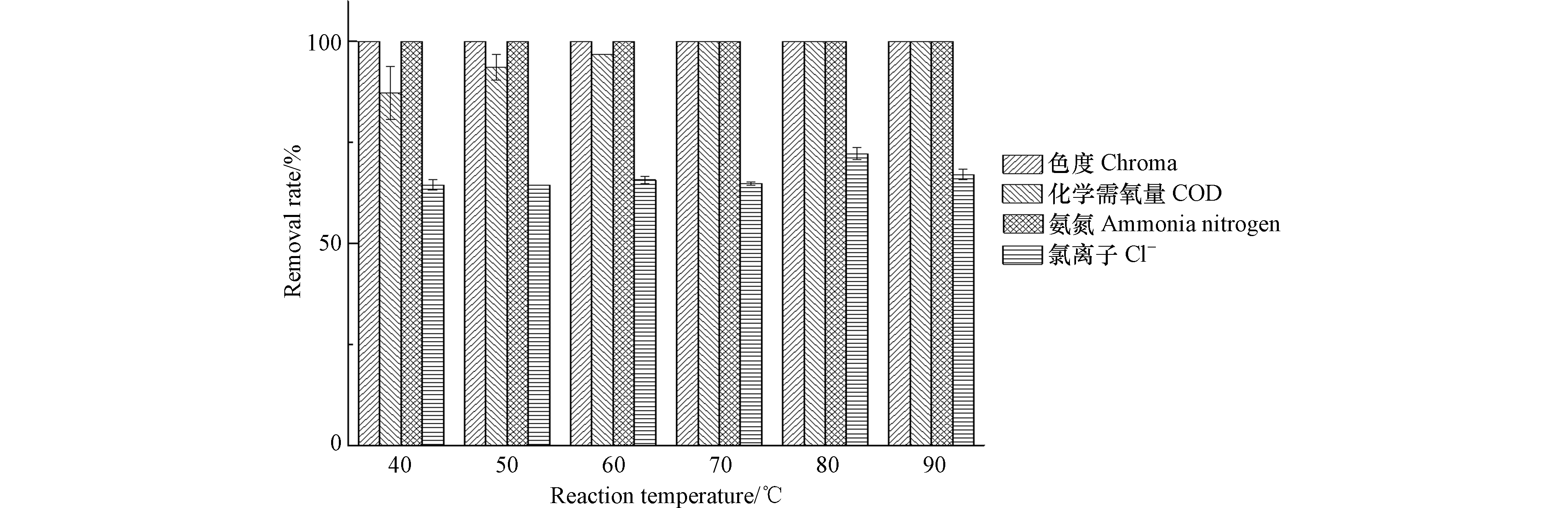
在电流密度为8 A·dm−2,极板间距为1 cm,初始pH值为7.8,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1,温度分别在40、50、60、70、80、90℃,反应4 h的条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率随温度的变化如图3所示.
由图3可知,温度对色度和氨氮的去除率影响不大,在不同温度时,色度和氨氮均被基本完全去除. 这是因为Cl−浓度高,阳极析出Cl2溶于水生成HClO,利用HClO的强氧化性间接氧化并加快去除色度和氨氮[14]. 随着温度的升高,COD去除率先逐渐增大后趋于稳定,当温度达到70℃,COD去除率为100.0%,这是由于过硫酸钠被热活化产生大量的SO4−·,将难降解有机物完全氧化降解[15].Cl−去除率随温度的升高呈逐渐增加的趋势,在70℃时,Cl−去除率为64.9%,当温度达到80℃时,Cl−去除率最大为72.2%,继续升高温度,Cl−去除率反而减小,可能是由于温度升高使Cl−向阴极扩散脱氯的速度加快[16]. 综上比较,考虑能耗和水分的蒸发量,反应体系温度控制在70℃为最佳.
-
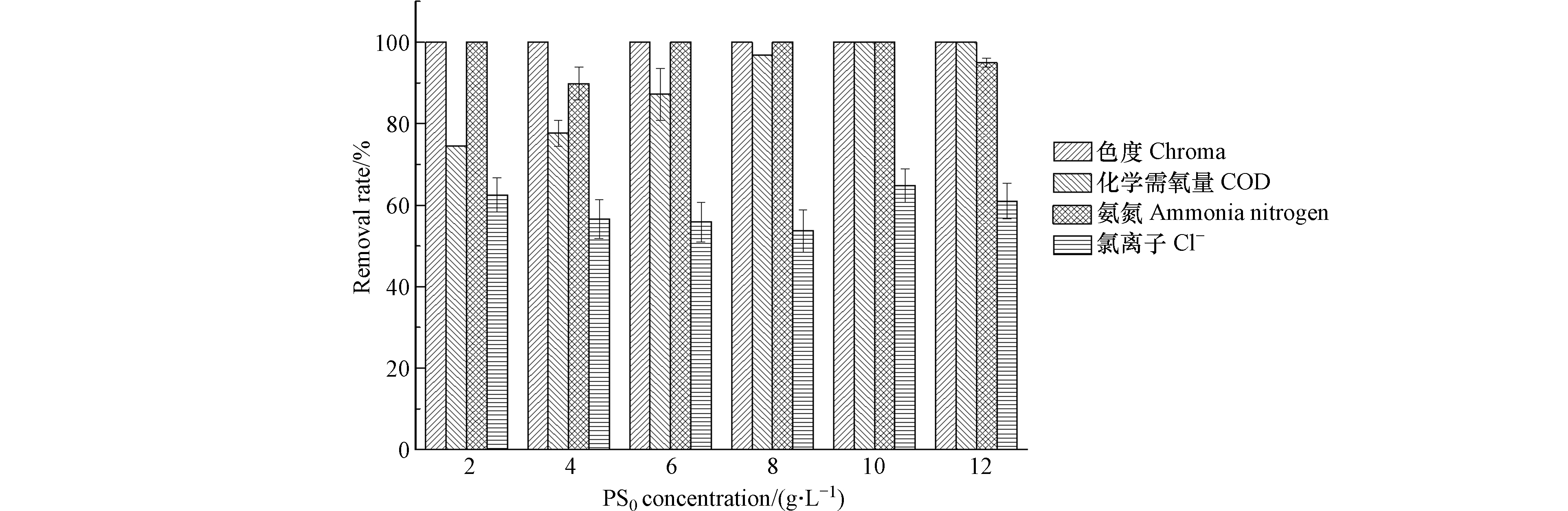
在电流密度为8 A·dm−2、极板间距为1 cm、初始pH值为7.8,整个体系保持在70℃反应4 h,PS0浓度分别为2、4、6、8、10、12 g·L−1的条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率随PS0浓度的变化如图4所示.
由图4可知,PS0浓度对色度的去除率几乎无影响,不同PS0浓度时,色度均基本被完全去除. 随着PS0浓度的增大,COD去除率呈增加趋势,在PS0浓度为10 g·L−1时,COD去除率达到100.0%. 该反应体系对氨氮有较好的去除效果,去除率均在90.0%以上.Cl−去除率随PS0的增大呈先减小后增大趋势,在PS0浓度为10 g·L−1时,Cl−去除率最高. 由于随着PS0浓度的增加,相同时间内会生成更多的SO4−·,但是PS0浓度过高,可能会与生成的SO4−·反应,降低氧化效果.因此,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1时最佳.
-
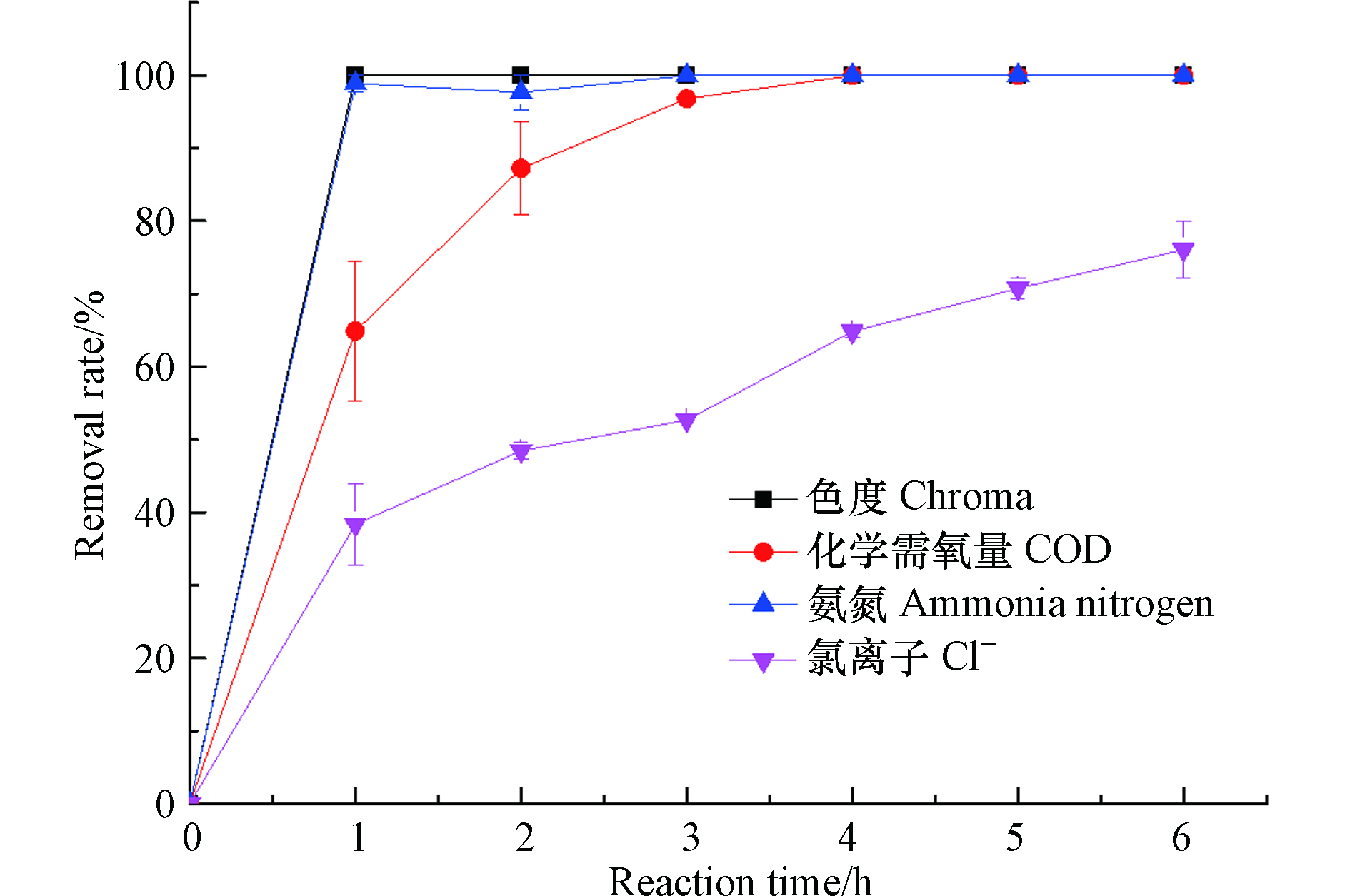
在电流密度为8 A·dm−2、极板间距为1 cm、初始pH值为7.8,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1,温度控制在70℃,反应时间分别为1、2、3、4、5、6 h的条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率随反应时间的变化如图5所示.
由图5可知,随着反应时间的增加,垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率逐渐增大. 色度和氨氮在反应1 h时,均基本被完全去除,继续增加反应时间,色度和氨氮的去除率变化不大. 在反应的前4 h,COD的去除率随着反应时间的增加而增大,在反应4 h时,COD的去除率达到100.0%. Cl−去除率随着反应时间的增加而逐渐增大,在反应4 h时,去除率为64.9%,在反应6 h时,去除率达到76.1%. 可能是由于随着反应时间的增长,阳极间接氧化反应生成Cl2、HClO、ClO−等强氧化性物质的时间增加.
-
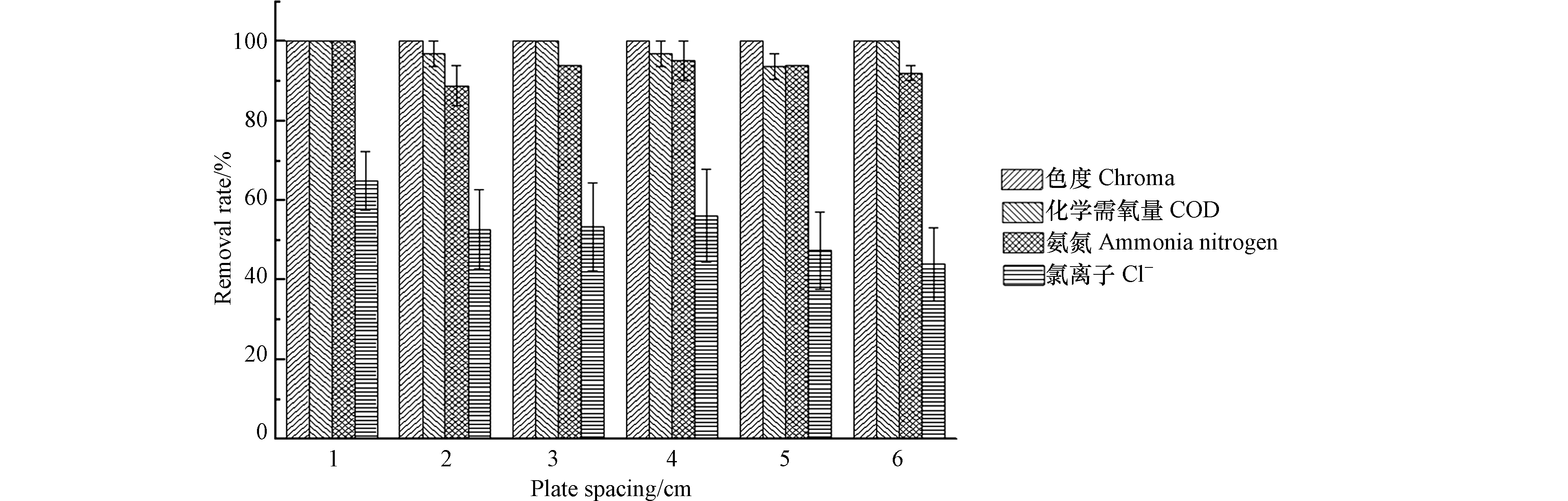
在电流密度为8 A·dm−2,初始pH值为7.8,整个体系保持在70℃反应4 h,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1,控制极板间距分别为1、2、3、4、5、6 cm的条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率随极板间距的变化如图6所示.
由图6可知,反应4 h后,色度、COD和氨氮去除效果明显. 极板间距对色度去除率的影响很小,在反应4 h后去除率均为100.0%. 在极板间距为1 、3 、6 cm时,COD去除率均为100.0%. 在极板间距为1 cm时,氨氮基本被完全去除,之后极板间距增大,氨氮去除率反而略有减小.可能是因为在反应过程中受到传质的影响. 由图6可知,Cl−去除率随着极板间距的增加呈下降趋势,极板间距为1 cm时,Cl−去除率最大,之后随着极板间距的增大,Cl−去除率有所降低. 从电化学角度考虑,极板间距越小,一方面可以降低能耗,增大极板表面发生直接氧化反应的几率;另一方面,在极板表面产生的·OH、SO4−·和ClO−等氧化物质扩散距离减小,有利于氧化物直接/间接氧化难降解有机物,有利于提高氧化效果[17]. 但是,极板间距过小,很容易导致短路,造成氧化效果下降[18]. 因此本实验极板间距以1 cm为宜.
-
以Ti/RuO2-IrO2为阳极,不锈钢为阴极,在初始pH值为7.8,电流密度为8 A·dm−2,极板间距为1 cm,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1,整个体系保持在70℃反应4 h的最佳实验条件下,处理前后垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的紫外-可见全波长扫描如图7所示.
由图7可知,垃圾渗滤液浓缩液处理前有三个明显的特征峰,分别位于200—250 nm、350—380 nm、380—420 nm处,吸光度均较高.电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理后位于200—250 nm的吸光度大于处理前,这是因为过硫酸钠的加入使整个体系的无机阴离子含量增加. 处理后有一个明显的吸收峰,位于280—300 nm处,吸光度小于处理前,曲线变的更加平滑,整体有蓝移趋势,400 nm之后吸光度整体较小.这是由于电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理后水样中有机物被大量的降解,其中含有的共轭双键、羧基、羰基等大分子物质及多环芳香类多聚物结构被破坏,被氧化分解成结构简单的、非共轭的物质,使吸收峰减弱并蓝移[19]。
垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中有机物组成成分非常复杂,在紫外光谱上不表现特征吸收,很难确定有机物各组分子结构的详细信息,一般用特定波长的吸光度或比值表征其性质.SUVA254表征芳香族化合物及其衍生物、含苯环和不饱和C=C的化合物[20].E250/E365表征有机物的腐殖化程度且与比值呈反比[21]. 由图7可知,处理后的SUVA254从处理前的3.0下降到1.9,表明处理后有机物的芳构化程度明显减小,不饱和C=C被氧化降解. E250/E365从1.25增加到26.45,说明处理后有机物的腐殖化程度降低,腐殖质的分子量及聚合度减小.
-
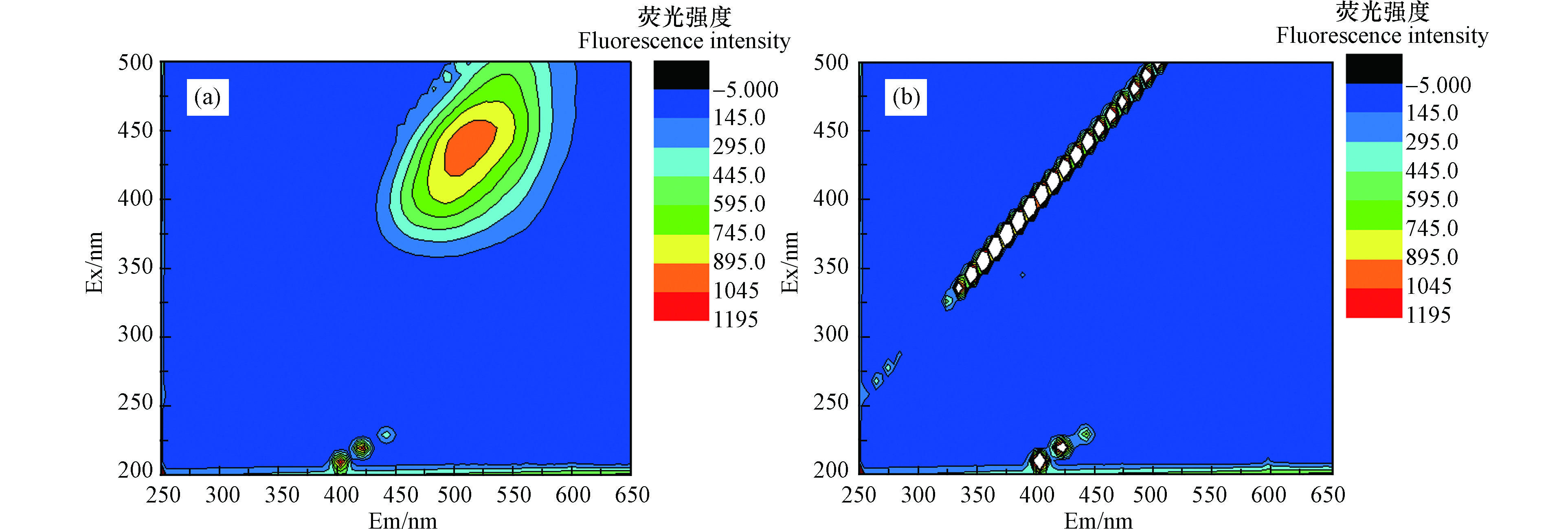
电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理前后垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的三维荧光光谱如图8所示. 由图8可知,电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理前(a)垃圾渗滤液浓缩液有一个特征峰(Ex/Em=440/515)为类胡敏酸物质,荧光强度为996.8. 由于类胡敏酸物质中含有杂环、芳香环和多环化合物,并由碳链或对位键连接成网状结构使其分子结构稳定性很强,解释了传统的生化处理很难将其降解.电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理后(b)垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中类胡敏酸物质的荧光特征峰消失,几乎不存在荧光特性物质.说明该反应体系对DOM有很好的去除效果.
-
傅里叶红外光谱能在不破坏水样分子结构的基础上,对水样中有机物官能团组成进行定性分析.电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理前后垃圾渗滤液浓缩液的傅里叶红外光谱如图9所示.
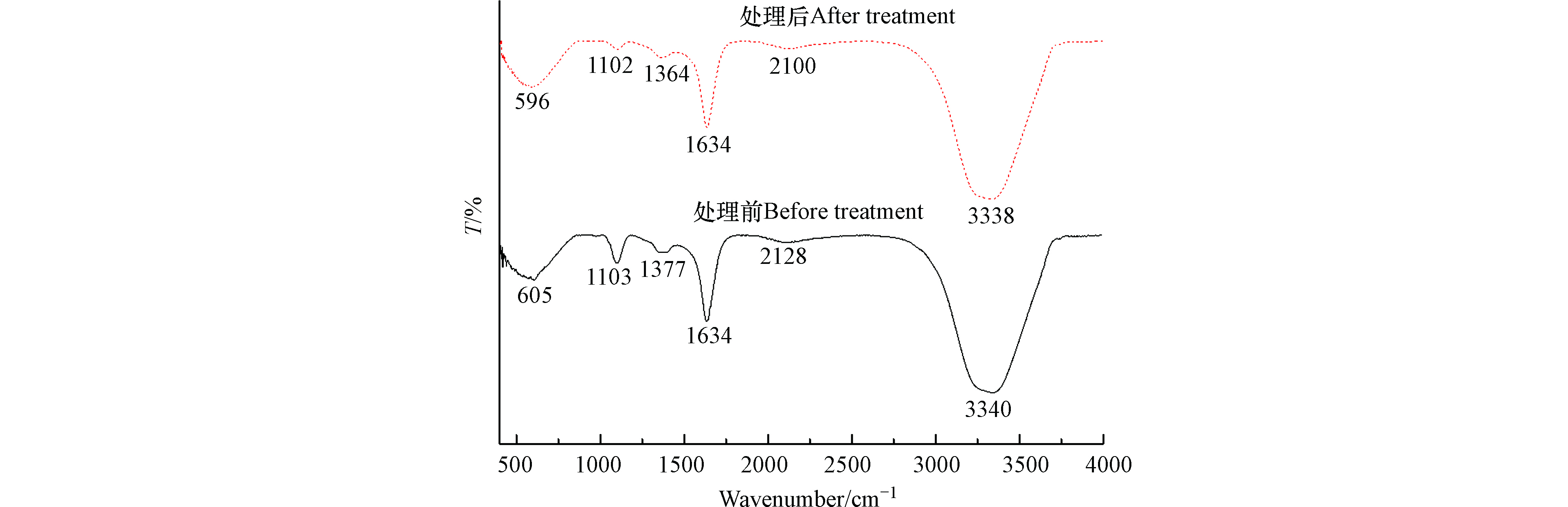
参考相关文献[22-26]及图9可知,在3340 cm−1左右的吸收特征峰,可能与羟基的O—H伸缩振动、氨基的N—H振动有关.在2128 cm−1左右的吸收峰,可能与C≡C或C≡N伸缩振动、C=C=C、C=C=O等不对称伸缩振动有关. 在1634 cm−1处的吸收峰,可能与苯类芳环上C=C骨架振动、酰胺C=O伸缩振动、醌C=O伸缩振动有关. 在1377 cm−1左右的吸收峰,可能与酚羟基的O—H弯曲振动和C—O伸缩振动或COO—基反对称伸缩振动、—OCH3弯曲振动有关. 在1103 cm−1左右的吸收特征峰,可能与碳水化合物、多糖类及酯类的C—O伸缩振动有关. 在605 cm−1左右的吸收特征峰,可能与C—N、N—H及苯和取代苯类芳环上C—H的面外弯曲振动有关. 说明垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中含有众多种类丰富的官能团的有机物.
水样经电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理后,3340 cm−1、2128 cm−1左右处吸收峰降低,说明垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中大分子有机物被氧化降解.1634 cm−1处吸收峰有明显下降,说明有机物内部的共轭双键体系含量下降. 1377 cm−1左右的吸收峰降低,说明部分酚羟基被ClO−、·OH和SO4−·等间接/直接氧化降解. 1103 cm−1左右的吸收特征峰有显著降低,说明有机物被大量氧化. 605 cm−1左右的吸收特征峰有显著降低,说明有机物中蛋白质类物质含量减少. 总之,经电/过硫酸盐催化氧化体系处理后垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中有机物的官能团吸收强度有降低,大部分有机物被降解.
-
(1)电/过硫酸盐催化氧化垃圾渗滤液浓缩液有很好的效果,在初始pH值为7.8,电流密度为8 A·dm−2,极板间距为1 cm,PS0浓度为10 g·L−1,整个体系保持在70℃反应4 h的最佳实验条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl−去除率分别为100.0%、100.0%、100.0%和64.9%.
(2)采用紫外-可见光谱、3D-EEMFS和FTIR对电/过硫酸盐催化氧化处理前后的垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中溶解性有机物降解机理进行分析,结果表明,处理后DOM的芳构化程度降低,腐殖化程度降低,腐殖质的分子量及聚合度减小;类胡敏酸物质基本被完全氧化去除;有机物内部的共轭双键、酚羟基、苯和取代苯类芳环上C—H等官能团吸收强度下降,大部分有机物被氧化降解.
电/过硫酸盐催化氧化垃圾渗滤液浓缩液
Coupled heat-activated persulfate/electrochemistry for catalytic oxidation landfill leachate concentrate
-
摘要: 垃圾渗滤液浓缩液是垃圾渗滤液生化出水经NF/RO膜截留的废液,盐分和溶解性有机物(DOM)含量高,特别是难降解有机物.实验采用电/过硫酸盐催化氧化垃圾渗滤液浓缩液,研究了初始过硫酸盐(PS0)浓度、温度、反应时间和极板间距对氧化效果的影响,结果表明,在初始pH值为7.8,电流密度为8 A·dm-2,极板间距为1 cm,PS0浓度为10 g·L-1,整个体系保持在70℃反应4 h的最佳实验条件下,色度、COD、氨氮和Cl-去除率分别为100.0%、100.0%、100.0%和64.9%.紫外-可见光谱分析表明,处理后垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中DOM的芳构化程度降低,腐殖化程度降低,腐殖质的分子量及聚合度减小.三维荧光光谱分析表明,处理后的垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中类胡敏酸物质基本被完全氧化去除.傅里叶红外光谱分析表明,处理后的垃圾渗滤液浓缩液中有机物的官能团吸收强度下降,大部分有机物被氧化降解.Abstract: The landfill leachate concentrate is the waste liquid intercepted by the NF/RO membrane from the biochemical effluent of the landfill leachate. It has a high content of salt and dissolved organic matter (DOM), especially the refractory organic matter. The experiment used heat-activated persulfate/electrochemistry to catalyze the oxidation of landfill leachate concentrate, and studied the effects of initial persulfate (PS0) concentration, reaction temperature, reaction time and plate spacing on the oxidation effect. The results showed that the initial pH value of 7.8, the current density was 8 A·dm-2, the plate spacing was 1 cm, the PS0 concentration was 10 g·L-1, and the entire system was kept at 70°C for 4 h. Under the best experimental conditions, the removal rates of chroma, COD, ammonia nitrogen and Cl- were 100.0%, 100.0%, 100.0%, and 64.9%, respectively. UV-vis spectra showed that the degree of aromatization, humus, relative molecular mass and polymerization degree decreased of DOM in the landfill leachate concentrate after treatment. 3D-excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectra(3D-EEMFS) showed that the humic acid-like substances were basically completely oxidized and removed from the landfill leachate concentrate after treatment. FTIR showed that the absorption intensity of functional groups of organic matter in the treated landfill leachate concentrate decreased, and most of the organic matter was oxidized and degraded after treatment.
-
Key words:
- landfill leachate concentrate /
- electrochemistry /
- heat activation /
- persulfate
-

-
-
[1] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准GB 16889—2008[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2008. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People′s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. National Standard (Mandatory) of the People's Republic of China: Standard for pollution control on the landfill site of municipal solid waste. GB 16889—2008[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[2] 邓旭亮, 荣丽丽, 张春燕, 等. 膜滤浓缩液处理技术研究进展 [J]. 工业水处理, 2011, 31(6): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2011.06.003 DENG X L, RONG L L, ZHANG C Y, et al. Research progress in the treatment of membrane filtration concentrate [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2011, 31(6): 10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2011.06.003
[3] LI X, ZHU W, WU Y, et al. Recovery of potassium from landfill leachate concentrates using a combination of cation-exchange membrane electrolysis and magnesium potassium phosphate crystallization [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 144: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.01.035 [4] 张皓贞, 张超杰, 张莹, 等. 垃圾渗滤液膜过滤浓缩液处理的研究进展 [J]. 工业水处理, 2015, 35(11): 9-13. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2015.35(11).009 ZHANG H Z, ZHANG C J, ZHANG Y, et al. Research progress in the treatment of concentrated solution produced from landfill leachate treated by membrane filtration [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2015, 35(11): 9-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2015.35(11).009
[5] 李章良, 郭海灵. 高级氧化技术处理垃圾渗滤液的研究现状与进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(5): 30-33. LI Z L, GUO H L. Status and process of advanced oxidation processes on landfill leachate treatment [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(5): 30-33(in Chinese).
[6] CUI Y H, XUE W J, YANG S Q, et al. Electrochemical/peroxydisulfate/Fe3+ treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate after ultrafiltration [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 353: 208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.101 [7] WANG H, WANG Y, LI X, et al. Removal of humic substances from reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) concentrated leachate using continuously ozone generation-reaction treatment equipment [J]. Waste Management, 2016, 56: 271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.07.040 [8] HU Y, LU Y, LIU G, et al. Effect of the structure of stacked electro-Fenton reactor on treating nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachate [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 202: 191-197. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.103 [9] SILVEIRA J E, GARCIA-COSTA A L, CARDOSO T O, et al. Indirect decolorization of azo dye Disperse Blue 3 by electro-activated persulfate [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 258: 927-932. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.143 [10] 朱新良, 童祯恭, 李俊, 等. 高级氧化技术降解垃圾渗滤液研究进展 [J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(5): 24-29. ZHU X L, TONG Z G, LI J, et al. Research progress on degradation of landfill leachate by advanced oxidation technology [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(5): 24-29(in Chinese).
[11] XUE W J, CUI Y H, LIU Z Q, et al. Treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate after ultrafiltration by electrochemically assisted heat activation of peroxydisulfate [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 231: 115928. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115928 [12] SILVEIRA J E, ZAZO J A, CASAS J A. Coupled heat-activated persulfate - Electrolysis for the abatement of organic matter and total nitrogen from landfill leachate [J]. Waste Management, 2019, 97: 47-51. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.07.037 [13] 龚逸, 王云海, 朱南文, 等. 垃圾渗滤液膜滤浓缩液的电化学氧化处理研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2015, 37(5): 11-16. GONG Y, WANG Y H, ZHU N W, et al. Advanced treatment of concentrated leachate from membrane filtration using electrochemical process [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2015, 37(5): 11-16(in Chinese).
[14] TURRO E, GIANNIS A, COSSU R, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of stabilized landfill leachate on DSA electrodes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 190(1-3): 460-465. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.085 [15] 王以茜. 过硫酸盐法去除焚烧厂渗滤液反渗透膜进水富里酸研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. WANG Y Q. Removing fulvic acid from influent of reverse osmosis treated leachate from incineration plant by persulfate[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019(in Chinese).
[16] 郭晓磊. 过硫酸盐高级氧化技术处理垃圾渗滤液纳滤浓缩液的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. GUO X L. Treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate by persulfate advanced oxidation technology[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[17] 陈宇, 张杰, 李彦龙, 等. 电化学氧化法处理垃圾浓缩液影响因素研究 [J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(S1): 737-739,757. CHEN Y, ZHANG J, LI Y L, et al. Effects of electrochemical oxidation on concentrated leachate treatment [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(S1): 737-739,757(in Chinese).
[18] LONG A, ZHANG H. Selective oxidative degradation of toluene for the recovery of surfactant by an electro/Fe2+/persulfate process [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(15): 11606-11616. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4406-x [19] 蔡先明, 秦侠, 张丽, 等. 催化湿式过氧化氢氧化处理垃圾渗滤液及其DOM光谱分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(9): 2930-2935. CAI X M, QIN X, ZHANG L, et al. Hydrogen peroxide catalytic wet oxidation of leachate and the spectroscopic analysis of dissolved organic matters [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(9): 2930-2935(in Chinese).
[20] NISHIJIMA W, GERALD E, SPEITEL J. Fate of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon produced by ozonation on biological activated carbon [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 56(2): 113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.03.009 [21] 黄诗蔚, 吴烈善, 拜俊岑, 等. Gd/Fe-C复合材料对垃圾渗滤液有机质降解的研究 [J]. 工业水处理, 2020, 40(11): 97-101. HUANG S W, WU L S, BAI J C, et al. Degradation organic matter in landfill leachate by Gd/Fe-C composite material [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2020, 40(11): 97-101(in Chinese).
[22] 何小松, 于静, 席北斗, 等. 填埋垃圾渗滤液中水溶性有机物去除规律研究 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(9): 2528-2533. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)09-2528-06 HE X S, YU J, XI B D, et al. The remove characteristics of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate during the treatment process [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(9): 2528-2533(in Chinese). doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)09-2528-06
[23] 胡云琪. Fe-Mn/AC催化臭氧/过硫酸盐处理垃圾渗滤液生化出水实验研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2018. HU Y Q. The study of the ad Vanced treatment of leachate landfill biochemical tail water by Fe-Mn/AC catalytic ozone-persulfate[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2018(in Chinese).
[24] LIU Z P, WU W H, SHI P, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachate during the combined treatment process of air stripping, Fenton, SBR and coagulation [J]. Waste Management, 2015, 41: 111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.03.044 [25] LI T, XU Z, HAN X, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii and its effect on the mobility of zinc [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(5): 570-576. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.031 [26] WANG H W, LI X Y, HAO Z P, et al. Transformation of dissolved organic matter in concentrated leachate from nanofiltration during ozone-based oxidation processes (O3, O3/H2O2 and O3/UV) [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 191: 244-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.01.021 -



 下载:
下载: