-
随着我国工业化和城市化的迅速发展,能源消耗日益增长,城市人口迅速膨胀,机动车保有量激增,导致NOx、一氧化碳(CO)和VOCs等臭氧(O3)前体物排放量不断增加[1-4],O3逐渐成为我国城市环境空气的主要污染物,严重威胁了人类健康和植物生长[5],也引起了众多学者的广泛关注. 近年来,大量研究围绕光化学烟雾和臭氧污染展开,结果表明,在短期内排放源大致不变的情况下,气象条件是影响臭氧污染最重要的因素,臭氧污染典型气象条件表现为太阳辐射强、气温高、相对湿度适宜、地面小风速及特定的风向[6-9].
宁夏回族自治区地处中国西北部内陆,气候干燥、太阳辐射强,日照时间长[10],为臭氧前体物的转化提供了有利的气象条件,加之近年来,受城市化及宁东能源化工基地(简称“宁东基地”)污染排放影响,造成宁夏臭氧污染天气频发. 特别是2017年银川市日最大8小时浓度(O3−8 h)值超出二级标准,达到轻度及以上污染达48 d,臭氧污染引起了自治区政府及相关部门高度重视. 近年来,学者们对银川市臭氧污染及气象条件特征等方面开展了分析研究[11-14],结果表明,银川市臭氧浓度日变化呈单峰性,午后易出现臭氧超标,臭氧浓度与紫外辐射强度和气温呈正相关、与相对湿度呈负相关. 目前,对宁夏其它地市的臭氧污染的气象条件特征研究较少,宁夏臭氧污染预报预警技术支撑薄弱. 按中国气象局要求,从2018年起,每年5—9月全国各省市开展臭氧污染气象条件等级预报业务,但由于缺乏技术支撑,目前宁夏臭氧污染气象条件等级预报业务也仅是以经验为主,随意性大,精细化程度不够,预报服务效果不理性.
本文针对宁夏臭氧污染现状及臭氧污染等级客观精细化预报服务业务需求,利用环境和气象数据,采用相关性分析和概率统计方法,从臭氧污染高影响气象因子着手,在分析各地市臭氧污染气象条件特征基础上,综合考虑各气象因子对臭氧生成的贡献大小,建立宁夏臭氧污染气象条件评价指标体系;基于评分及预报效果检验评估结果,参照《全国臭氧气象预报业务规范》,建立臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型和等级预报标准. 研究结果将为宁夏臭氧污染气象条件客观化精细化预报提供技术支撑,实现臭氧污染气象条件定量化精细化监测,为宁夏各地市臭氧污染预报预警及科学应对臭氧污染提供技术支撑和决策参考.
-
环境空气质量数据来源于宁夏回族自治区生态环境监测站提供的2017—2020年宁夏五地市(银川市、石嘴山市、吴忠市、中卫市、固原市)18个环境空气质量国控监测点及宁东基地5个区控监测点O3质量浓度逐小时数据和城市O3−8 h数据. 同期气象数据来源于宁夏气象信息中心,为距离环境监测点最近的自动气象站逐小时气温、相对湿度、风速、风向、总云量、降水等,其中,2017—2019年总云量资料为银川市、中卫市和固原市气象站保留3次人工观测的中午14时总云量数据,用于臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型建立;另外,还使用了风云4号卫星反演的2020年五地市及宁东地区总云量资料,用于指数预报模型预报效果检验评估. 宁夏行政区划及环境空气监测站点和气象观测站点位置见图1.
-
臭氧超标率(E)定义:根据《环境空气质量指数(AQI)技术规定》(HJ 633—2012)臭氧二级标准为1 h平均浓度大于200 μg·m−3.
式(1)中,t1是某个时间段内臭氧浓度超出200 μg·m−3的时次,t是总时次,E为臭氧超标率.
太阳辐射强度是影响臭氧浓度变化的重要原因之一,太阳辐射强弱又与温度有关[15],因此分析温度对臭氧污染的影响非常重要. 本文参考相关文献[16],统计不同度区间的臭氧平均浓度和超标率,分别将气温与其他气象因子联立,统计联立后的臭氧平均浓度和超标率,即以气温为参照,研究其他气象因子对臭氧平均浓度和超标率的影响,从而确定所有气象因子的影响权重,最后得出指数预报模型及等级预报分级标准.
-
研究表明,臭氧是二次污染物,主要来源于挥发性有机物(VOCs)和氮氧化物(NOx)的光化学反应[17-18]。本文选取了白天的臭氧浓度和气象要素进行相关性分析,结果表明,各地臭氧浓度与气温均呈明显正相关,相关系数为0.64—0.72;与相对湿度均呈较明显负相关,相关系数−0.36—−0.55;与风速呈弱正相关,相关系数0.11—0.32. 由于风向用0—360数值表示,如:北风用0标记,东风用90标记;总云量用0—10的整数数据标记,如晴天无云标记为0,满天云系标记为10成云;宁夏全年降水过程较少,无降水或微量降水自动气象观测均标记为0,而臭氧浓度数值变化范围较大,因此,臭氧浓度与风向、总云量和降水量的相关性不明显(见表1).
-
为进一步探讨气象要素变化对臭氧浓度的影响,通过对2017—2019年宁夏5个地市及宁东基地臭氧浓度和超标率进行分类统计发现,气温、相对湿度、风速、云量、降水等气象要素对臭氧浓度和超标率都有影响. 各地臭氧浓度和超标率均随气温升高而升高,气温超过30℃时,各地平均臭氧浓度和超标率分别为130.3—184.0 μg·m−3、0.1 %—19.2%. 各地臭氧浓度和超标率均随湿度增大而减小,较干燥的环境(相对湿度≤55%)臭氧浓度和超标率相对较高,各地分别为95.1—134.7 μg·m−3、0.1%—6.0%,相对湿度在55%以上时臭氧浓度和超标率较低. 风速小于1 m·s−1时,各地臭氧浓度和超标率均较低,风速在2—3 m·s−1之间时,臭氧浓度和超标率相对较高,各地分别为96.2—124.2 μg·m−3、0.2%—4.9%,风速在5 m·s−1及以上时,臭氧浓度也较高,但不易出现超标. 不同风向下各地臭氧浓度和超标率无明显变化. 云量对臭氧影响表现为:云量在0—3成的晴天各地臭氧平均浓度和超标率均较高,分别为112.4—149.0 μg·m−3、0.9%—7.9%,云量在4—10成的多云或阴天较低. 降水对臭氧浓度和超标率也有一定影响,无雨时臭氧浓度和超标率分别为102.8—135.8 μg·m−3、0.5%—3.0%,小时雨量大于1 mm,臭氧浓度明显降低,除银川超标率为1.6 %外,其它地市未出现臭氧浓度超标.
-
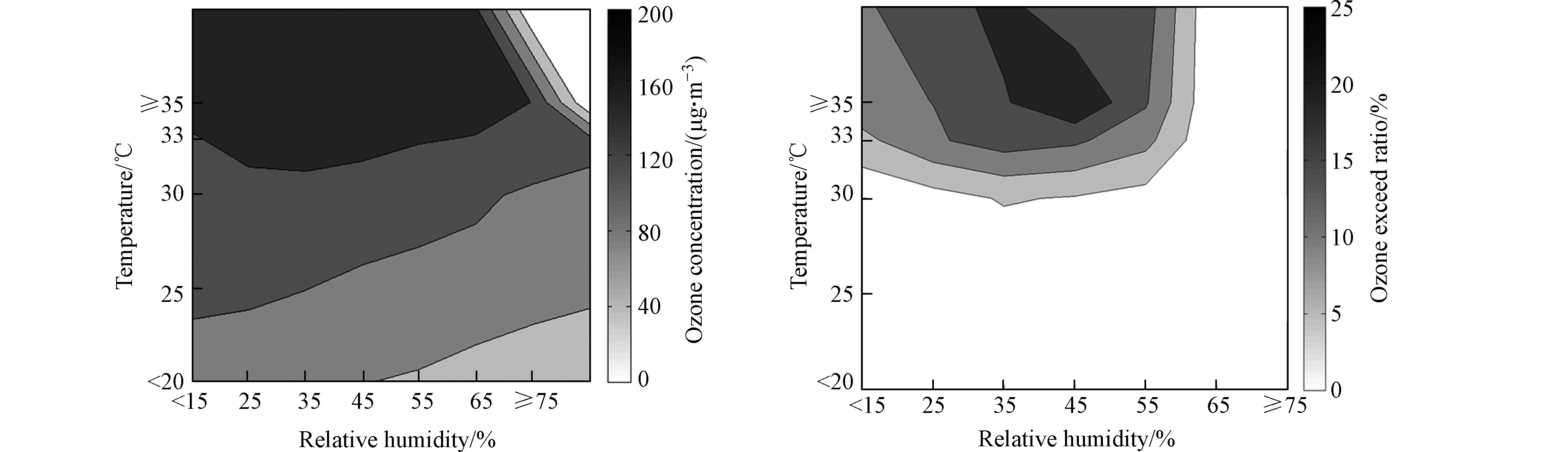
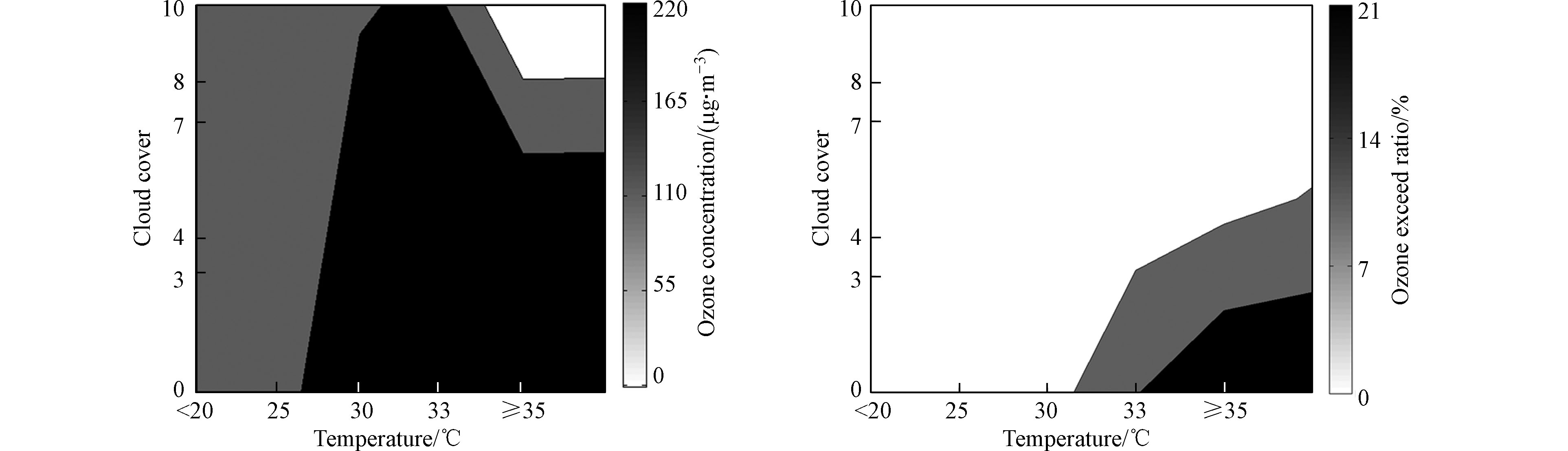
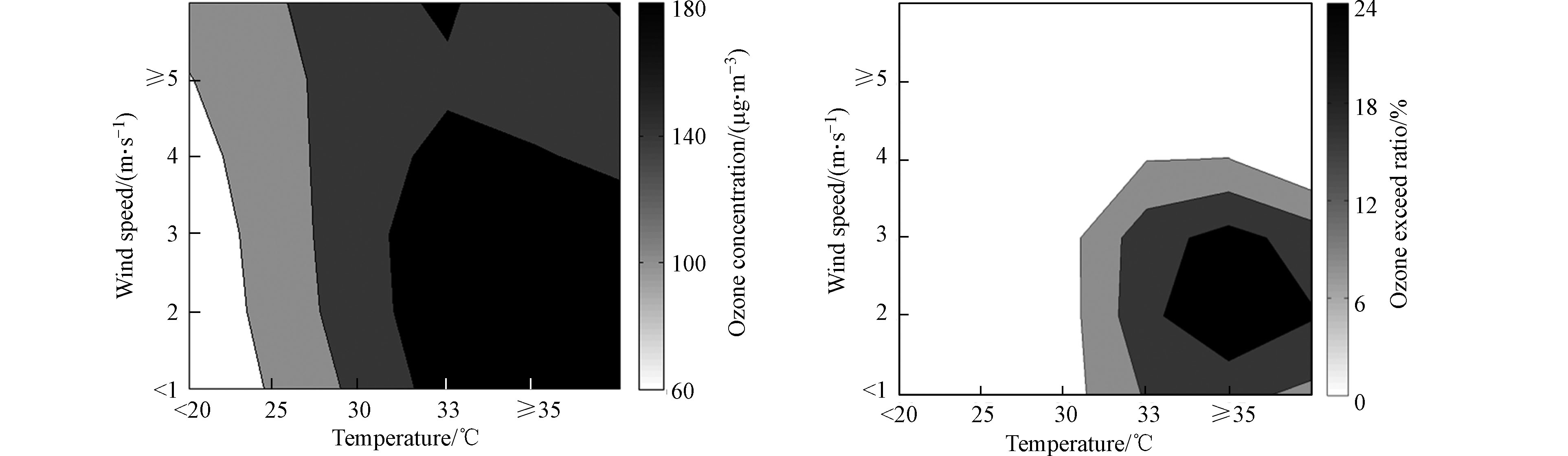
为了突出温度对臭氧浓度的影响并兼顾考虑其它气象因子的影响,以银川市为例,对气象因子联合对臭氧浓度的影响进行分析. 结果表明,当气温在30℃以上,相对湿度在15%—55%之间,臭氧浓度和超标率均较高,分别在149.7—189.2 μg·m−3、8.2%—23.9%之间;湿度大于55%,臭氧浓度和超标率相对较低(见图2). 云量对于臭氧浓度和超标率的影响也与温度密切相关,阴天臭氧浓度和超标率均较低;当气温在30℃以上,云量在0—3成的晴好天气,臭氧浓度和超标率均增大,分别在202.1—218.9 μg·m−3、12.5%—19.2%之间(见图3). 风速对于臭氧浓度的影响,在不同的温度区间下表现也不一样,温度在25℃以下,臭氧浓度相对较低,不会引起臭氧超标,当温度大于30℃,风速在2—3 m·s−1之间时,臭氧浓度和超标率均明显增大,分别在157.0—171.0 μg·m−3、10.8%—23.1%之间,风速在5 m·s−1及以上时,臭氧浓度也较高,但不易出现超标(见图4). 风向对臭氧超标率的影响也与温度密切相关,温度在25℃以下,不同风向下的臭氧超标率都很小,当气温在30℃以上,不同风向下的臭氧浓度和超标率都较大,分别在152.1—179.8 μg·m−3、9.4%—29.5%之间(图略),进一步说明温度是影响臭氧浓度的最主要因子,风向对臭氧浓度影响较小.
分析结果表明,气温超过30℃时,当相对湿度在15%—55%之间、云量小于3成、风速在2—3 m·s−1之间时,臭氧浓度和超标率均较高.
-
从以上分析看,温度是臭氧污染的高敏感的气象因子[19],臭氧浓度和超标率随着气温升高而明显升高,相对湿度、云量、风速对臭氧浓度的影响也较为明显,降水也有一定影响,但宁夏属于干旱少雨地区,全年各地降水次数少,同时降雨时气温也相对较低,湿度也较大,这两个气象要素也可间接代表降水对臭氧浓度影响,风向对臭氧浓度和超标率的影响不明显.
基于上述分析结果,选取气温、相对湿度、云量、风速做为臭氧污染气象条件评价气象因子,将温度作为臭氧污染的高敏感的气象因子,综合考虑五地市及宁东地区不同温度区间的臭氧浓度和超标率大小进行气温基础(Ts)评分,平均浓度越大、超标率越高,评分愈大. 评分规则为:臭氧平均浓度在80 μg·m−3以下得0分,80—100 μg·m−3得1分,100—120 μg·m−3得2分,以此类推,浓度每增加20 μg·m−3增加1分;超标率为0时得0分,0—2%得1分,2%—4%得2分,以此类推,超标率每增加2%增加1分,各地市气温基础分为臭氧浓度和超标率得分的平均值(见表2). 从表2可看出,银川市、石嘴山市、吴忠市、中卫市、固原市、宁东气温基础分最高值分别为8分、8分、5分、4分、3分、5分,南北差异较大,由于银川市和石嘴山市是宁夏臭氧污染最严重的区域,臭氧浓度高,易出现臭氧超标[13],气温基础分较高;而固原市臭氧浓度为全区最低,且不易出现臭氧超标,气温基础分最低,评分结果符合宁夏臭氧污染实际状况.
以银川市为例,基于上述分析并结合相关研究成果[13-14],气温与相对湿度联合评分结果(见表3),表明了在同样的气温条件下,不同湿度对臭氧形成贡献不一样,例如温度在33—35℃之间时,相对湿度在15%—55%之间,评分为8分,大于气温基础分6分,说明该等级下相对湿度在15%—55%之间对臭氧的生成有促进作用;温度在33—35℃之间时,相对湿度≥65%,评分为5分,小于气温基础分6分,说明该等级下湿度≥65%对臭氧浓度有削弱作用. 参考相关文献[16],各气象因子单独评分为气温与其它气象因子联合评分减去气温基础分.
银川市相对湿度单独评分:将气温与相对湿度联合评分减去气温基础分得到相对湿度单独评分(见表4). 从表4可看出,湿度对臭氧浓度的作用,正值表示对臭氧生成有促进作用,负值表示对臭氧的生成有减弱作用. 气温超过30℃时,相对湿度在15%—55%之间,最有利臭氧生成,相对湿度超过65%以上时,不利于臭氧的生成.
银川市云量单独评分:将气温与云量联合评分减去气温基础分得到云量单独评分(见表4). 从表4可看出云量对臭氧浓度的作用,正值表示对臭氧生成有促进作用,负值表示对臭氧的生成有减弱作用. 气温超过30℃时,云量小于3成,最有利臭氧生成,云量超过8成,不利于臭氧的生成.
银川市风速单独评分:将气温与风速联合评分减去气温基础分得到风速单独评分(见表4). 从表4可看出风速对臭氧浓度的作用,正值表示对臭氧生成有促进作用,负值表示对臭氧的生成有减弱作用. 当气温超过30℃时,风速1—3 m·s−1最有利于臭氧生成,风速大于4 m·s−1不利于臭氧的生成.
由于气象因子对各地市臭氧浓度的影响较一致,气温基础分差异较大,气温与其它气象因子联合评分也会有明显差异,但两者的差值一致,所以各地市除气温外的其它气象因子单独评分均采用表4评分结果.
另外,由于宁夏属于高海拔、高辐射地区,五地市及宁东代表站海拔高度在1110.9—1753 m之间,海拔高度最低为银川市,海拔高度最高为固原市,地势南高北低,南北差异明显. 研究也表明,随着海拔高度增加,近地面紫外辐射强度也增加[20],而太阳紫外线辐射强度与臭氧浓度呈正比[13-14]. 从表2也可看出,宁夏自北向南臭氧超标率明显降低,但臭氧浓度降低不明显,由于无紫外线辐射强度客观预报模式产品,为使臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型算法实现业务化,且突出紫外线辐射对臭氧浓度影响,将海拔高度引入评分体系(Hbs). 综合考虑宁夏各地下垫面特征、污染排放特征等,评分规则为:海拔高度在1500 m以下,评分为0分,超过1500 m评分为1分.
-
综合各气象因子并考虑太阳辐射对臭氧污染的影响,将海拔高度引入预报评价模型,给出的宁夏臭氧污染气象条件指数(OPMCI)预报模型为:
式(2)中,Ts为各地市气温基础评分,Rhs为相对湿度单独评分,Cls为总云量单独评分,WSs为风速单独评分,Hbs为海拔高度评分.
根据宁夏臭氧污染气象条件指数OPMCI总评分,参照《全国臭氧气象预报业务规范》,将OPMCI从小到大分为1—6级,从不易臭氧污染到极易臭氧污染,建立了臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型和等级预报标准. 从2017—2020年宁夏各地市臭氧污染状况看,污染级别为轻度及以下,出现4级中度臭氧污染的天数也较少,未出现5级及以上重度臭氧污染. 为建立与宁夏臭氧污染实际情况相适应且对臭氧污染预报有指导意义的气象条件等级预报标准,等级预报分级标准评分区间的划分预留了5级评分,排除了6级预报结果(见表5).
-
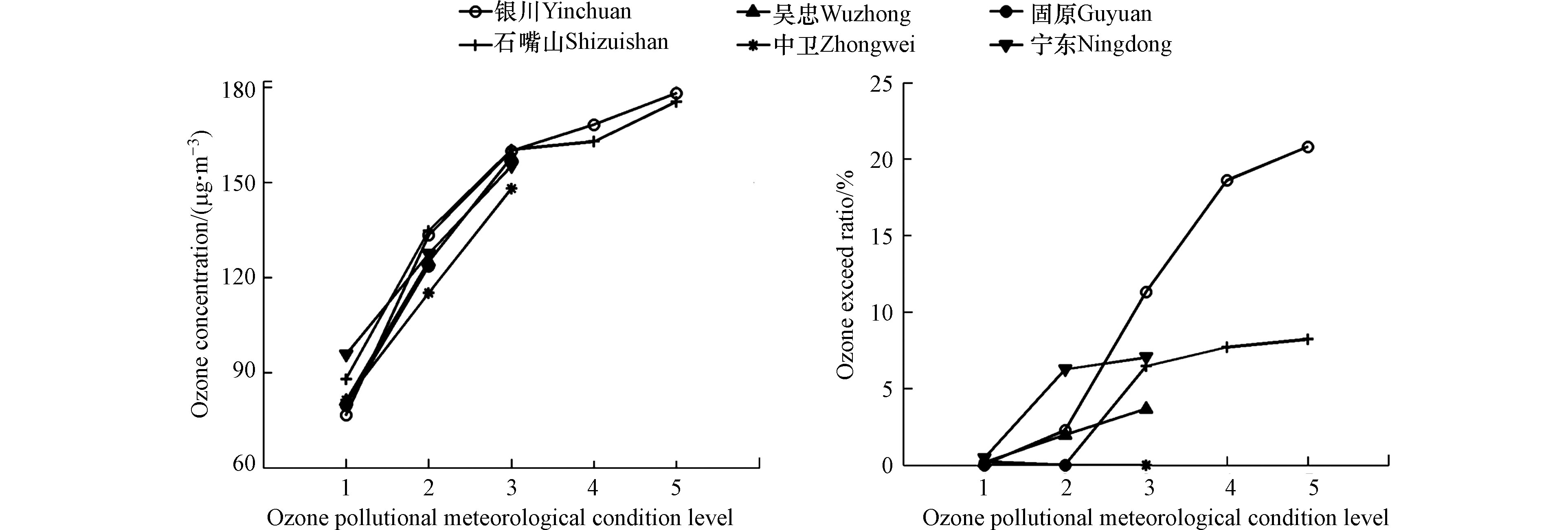
基于臭氧污染气象条件评分标准、指数预报模型及等级预报分级标准,对2020年5—9月宁夏五地市及宁东基地进行逐时臭氧污染气象条件等级预报,统计了不同等级下的臭氧浓度和超标率. 并依据《环境空气质量指数(AQI)技术规定》(HJ 633—2012),对2020年5—9月宁夏五地市及宁东基地臭氧浓度进行了分级. 结果表明,银川市、石嘴山市臭氧污染气象条件等级预报为1—5级,吴忠市、中卫市、宁东基地为1—3级,固原市为1—2级,且气象条件等级越高,各地臭氧浓度和超标率也越大(见图5). 臭氧污染气象条件等级预报与臭氧污染等级相一致的准确率银川市为77.4%、石嘴山市为87.9%、吴忠市为89.5%、中卫市为93.4%、固原市为99.9%、宁东基地为92.1% ,各地臭氧污染气象条件等级预报与臭氧浓度实际等级较为一致,其中,银川市等级预报准确率最低,固原市最高,也说明了银川市作为宁夏首府城市,随着城市人口增多,汽车保有量增大,本地及其周边污染企业臭氧前体物的排放和输送,加之有利于臭氧浓度升高的气象条件对臭氧污染的影响较大,而固原市为宁夏经济最不发达地区,人口和污染企业少、海拔高、辐射强,气象条件对臭氧污染的影响较大. 检验评估结果符合宁夏臭氧污染实际情况,指数预报模型算法及等级预报分级标准可为宁夏臭氧污染气象条件客观精细化预报业务提供技术支撑,对臭氧污染预报有指导意义.
-
(1)宁夏各地市臭氧浓度与气温均呈明显正相关,相关系数为0.64—0.72,臭氧浓度和超标率随着气温升高而明显升高;与相对湿度呈较明显负相关,相关系数−0.36—−0.55,相对湿度≤55%的较干燥的环境臭氧浓度和超标率相对较高;与风速呈弱正相关,相关系数0.11—0.32,风速在2—3 m·s−1之间时,臭氧浓度和超标率较高;与风向的相关性不明显,不同风向下的臭氧浓度和超标率变化不明显;与总云量相关性也不明显,但总云量在3成及以下时,臭氧浓度和超标率较大.
(2)选取气温、相对湿度、总云量、风速作为臭氧污染气象条件预报的评价因子,并将海拔高度引入预报评价模型,间接表征了太阳辐射对臭氧浓度的影响,建立了宁夏臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型;考虑宁夏臭氧污染的实际状况,建立了宁夏臭氧污染气象条件预报分级标准.
(3)预报效果检验评估结果表明,各地臭氧污染气象条件等级预报与臭氧浓度实际等级较为一致,且气象条件等级越高,各地臭氧浓度和超标率也越大. 指数预报模型算法及等级预报分级标准可为宁夏臭氧污染气象条件客观精细化预报业务提供技术支撑,对臭氧污染预报有指导意义.
宁夏臭氧污染气象条件特征及等级预报标准体系研究
Study on the characteristics of meteorological conditions and grade forecast standard system of ozone pollution in Ningxia
-
摘要: 利用2017—2019年期间每年的5—9月宁夏各地臭氧逐小时质量浓度数据和气象要素数据,基于相关性分析和概率统计方法,在分析臭氧敏感气象要素特征基础上,综合各气象因子对臭氧生成贡献大小,并考虑各地海拔高低、污染状况等,建立了宁夏臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型及等级预报标准. 结果表明,宁夏各地臭氧浓度与气温均呈明显正相关,相关系数为0.64—0.72,臭氧浓度和超标率随着气温升高而明显升高;与相对湿度呈较明显负相关,相关系数为−0.36—−0.55,相对湿度≤55%的较干燥环境臭氧浓度和超标率相对较高;与风速呈弱正相关,相关系数为0.11—0.32,风速在2—3 m·s−1之间时,臭氧浓度和超标率较高;总云量在3成及以下时,臭氧浓度和超标率较大. 宁夏臭氧污染气象条件指数预报模型主要由气温、相对湿度、总云量、风速评分构成,并将海拔高度引入评分体系,间接代表了太阳辐射对臭氧浓度的影响. 预报效果检验评估显示,各地臭氧污染气象条件等级预报与臭氧浓度实际等级较为一致,且气象条件等级越高,各地臭氧浓度和超标率也越大,指数预报模型算法及等级预报分级标准可为宁夏臭氧污染气象条件客观精细化预报业务提供技术支撑,对臭氧污染预报有指导意义.Abstract: Using hourly ozone mass concentration and meteorological data from May to September in Ningxia, 2017—2019, based on correlation analysis and probability statistics methods, and on the basis of analyzing the characteristics of ozone sensitive meteorological elements, considering the contribution of various meteorological factors to ozone generation comprehensively, the Ningxia ozone pollution meteorological condition index forecast model and grade forecast standard were established. The results show that the ozone concentration and temperature in over Ningxia are obviously positively correlated, the correlation coefficient is from 0.64 to 0.72, the ozone concentration and the ozone exceed ratio increase significantly as the temperature rises; Significantly negatively correlated with relative humidity, the correlation coefficient is from −0.36—−0.55, relatively high ozone concentration and over standard rate in a relatively dry environment with a relative humidity of 45% or less; Weak positive correlation with wind speed, the correlation coefficient is from 0.11 to 0.32, when the wind speed is between 2—3 m·s−1, the ozone concentration and exceed ratio are high; When the total cloud cover is 30% or less, the ozone concentration and exceed ratio are relatively high. The Ningxia ozone pollution meteorological condition index forecast model is composed of temperature, relative humidity, total cloud cover, and wind speed score. And introducing altitude into the scoring system, indirectly represents the effect of solar radiation on ozone concentration. The forecast effect evaluation shows that the forecast level of meteorological conditions of ozone pollution is consistent with the actual level of ozone concentration. The higher the level of meteorological conditions, the greater the ozone concentration and the exceed ratio. The algorithm of index forecast model and the classification standard of grade forecast can provide technical support for objective and fine forecast of meteorological conditions of ozone pollution in Ningxia, and is instructive to ozone pollution forecast.
-
Key words:
- ozone pollution /
- meteorological conditions /
- index forecast /
- grade standard /
- Ningxia
-

-
表 1 宁夏五地市及宁东基地气象要素与臭氧浓度相关系数
Table 1. Correlation coefficients of meteorological elements and ozone concentration in five cities of Ningxia and Ningdong base
站点
Station气温
Temperature湿度
Humidity风速
Wind speed风向
Wind direction云量
Cloud cover降水量
Precipitation银川 0.67 −0.36 0.18 0.013 −0.022 −0.039 石嘴山 0.71 −0.49 0.24 −0.018 −0.021 0.041 吴忠 0.69 −0.42 0.23 0.015 −0.101 −0.059 中卫 0.71 −0.49 0.24 −0.102 −0.026 0.026 固原 0.64 −0.55 0.32 −0.032 0.025 −0.132 宁东 0.72 −0.42 0.11 0.011 −0.011 −0.021 全区平均 0.69 −0.46 0.22 −0.019 −0.026 −0.031 表 2 气温基础分(Ts)
Table 2. Basic temperature score (Ts)
站点
Station气温/℃ Temperature T< 20 20≤T<25 25≤T<30 30≤T<33 33≤T<35 T≥ 35 银川 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 70.8 99.7 133.4 159.4 165.5 184.0 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.3 4.2 10.8 12.8 19.2 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 3 5 6 8 石嘴山 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 76.4 104.9 132.9 157.1 167.0 181.1 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.0 1.5 10.3 12.1 18.6 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 2 5 6 8 吴忠 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 67.5 91.9 121.8 141.3 143.5 150.4 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.1 0.7 2.8 6.5 10.8 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 2 3 4 5 中卫 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 71.4 101.8 122.9 138.2 143.0 144.5 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.0 0.2 0.7 3.1 6.5 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 2 2 3 4 固原 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 69.6 101.9 118.8 130.3 144.7 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.1 2.1 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 1 2 3 宁东 平均浓度/(μg·m−3) 74.4 99.4 121.1 141.2 144.4 165.8 超标率(E)/% 0.0 0.1 0.4 2.2 6.2 8.1 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 2 3 4 5 表 3 气温与相对湿度联合评分
Table 3. Combined scores of temperature and relative humidity
相对湿度(Rhs)/%
Relative humidity气温/℃
TemperatureT<20 20≤T<25 25≤T<30 30≤T<33 33≤T<35 T≥35 Rh<15 0 1 3 6 7 9 15≤Rh<25 0 1 3 7 8 10 25≤Rh<35 0 1 3 7 8 10 35≤Rh<45 0 1 3 7 8 10 45≤Rh<55 0 1 3 5 6 8 55≤Rh<65 0 1 3 5 6 8 65≤Rh<75 0 1 3 4 5 7 Rh≥75 0 1 3 4 5 7 气温基础分(Ts) 0 1 3 5 6 8 表 4 单独评分(联合评分−气温基础分)
Table 4. Individual scores (joint score-basic temperature score)
气象要素
Meteorological element气温/℃ Temperature T<20 20≤T<25 25≤T<30 30≤T<33 33≤T<35 T≥35 相对湿度/% Rh<15 0 0 0 1 1 1 15≤Rh<25 0 0 0 2 2 2 25≤Rh<35 0 0 0 2 2 2 35≤Rh<45 0 0 0 2 2 2 45≤Rh<55 0 0 0 0 0 0 55≤Rh<65 0 0 0 0 0 0 65≤Rh<75 0 0 0 −1 −1 −1 Rh≥75 0 0 0 −1 −1 −1 总云量/成 0—3 0 0 0 1 1 1 4—7 0 0 0 0 0 0 8—10 0 0 0 −1 −1 −1 风速/(m·s−1) V<1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1≤V<2 0 0 0 1 1 1 2≤V<3 0 0 0 1 1 1 3≤V<4 0 0 0 0 0 0 4≤V<5 0 0 0 −1 −1 −1 V≥5 0 0 0 −1 −1 −1 表 5 臭氧污染气象条件预报分级标准及等级描述
Table 5. Classification standards and descriptions of meteorological conditions for ozone pollution
臭氧污染气象条件指数OPMCI总评分
Classification standards and descriptions of meteorological等级
Grade描述
Description≤2分 1级 很不利于臭氧生成 3—5分 2级 不利于臭氧生成 6—8分 3级 较利于臭氧生成 9—10分 4级 有利于臭氧生成 11—12分 5级 非常有利于臭氧生成 >12分 6级 极有利于臭氧生成 -
[1] LIPPMANN M. Health effects of tropospheric ozone: Review of recent research findings and their implications to ambient air quality standards [J]. Journal of Exposure Analysis and Environmental Epidemiology, 1993, 3(1): 103-129. [2] NISHANTH T, PRASEED K M, KUMAR M K S, et al. Observational study of surface O3, NOx, CH4 and total NMHCs at kannur, India [J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2014, 14(3): 1074-1088. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2012.11.0323 [3] 段玉森, 张懿华, 王东方, 等. 我国部分城市臭氧污染时空分布特征分析[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2011, 23(增刊1): 34-39. DUAN Y S, ZHANG Y H, WANG D F, et al. Spatial-temporal patterns analysis of ozone pollution in several cities of China[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2011, 23(Sup 1): 34-39(in Chinese).
[4] 程麟钧, 王帅, 宫正宇, 等. 京津冀区域臭氧污染趋势及时空分布特征 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2017, 33(1): 14-21. CHENG L J, WANG S, GONG Z Y, et al. Pollution trends of ozone and its characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(1): 14-21(in Chinese).
[5] RAJAB J M, MATJAFRI M Z, LIM H S, et al. Daily distribution map of ozone (O3) from AIRS over Southeast Asia [J]. Energy Research Journal, 2010, 1(2): 158-164. doi: 10.3844/erjsp.2010.158.164 [6] 马志强, 王跃思, 张小玲, 等. 北京城区与下游地区臭氧对比研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4): 924-929. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.04.016 MA Z Q, WANG Y S, ZHANG X L, et al. Comparison of ozone between Beijing and downstream area [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(4): 924-929(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.04.016
[7] 徐少才, 薛莲, 薛传文, 等. 青岛市大气臭氧的生成敏感性及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2016, 28(2): 19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2016.02.005 XU S C, XUE L, XUE C W, et al. Analysis of formation sensitivity and influencing factors of ambient O3 in Qingdao [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2016, 28(2): 19-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2016.02.005
[8] 包艳英, 徐洁, 张明明, 等. 大连市臭氧污染特征及典型污染日成因 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2017, 33(4): 167-178. doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2017.04.21 BAO Y Y, XU J, ZHANG M M, et al. The characteristics of ozone pollution and causes of A typical ozone pollution episode in Dalian [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(4): 167-178(in Chinese). doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2017.04.21
[9] 卢秀娟, 巨天珍, 谢顺涛, 等. 兰州地区大气臭氧时空变化及影响因素研究 [J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(4): 355-363. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.111 LU X J, JU T Z, XIE S T, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of atmospheric ozone in Lanzhou and its influencing factors [J]. Earth and Environment, 2018, 46(4): 355-363(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2018.46.111
[10] 桑建人, 刘玉兰, 林莉. 宁夏太阳辐射特征及太阳能利用潜力综合评价 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(1): 122-125. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.01.022 SANG J R, LIU Y L, LIN L. Characteristic of solar radiation in ningxia and integrated evaluation on utilization potential of solar energy [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2006, 26(1): 122-125(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.01.022
[11] 杨丽蓉, 郭英茹, 张俊生, 等. 银川市臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2016, 42(2): 55-59. YANG L R, GUO Y R, ZHANG J S, et al. Analysis of the pollution characteristics and influencing factors of the ozone in Yinchuan city [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2016, 42(2): 55-59(in Chinese).
[12] 王伟, 白娟, 杨丽蓉, 等. 银川市臭氧质量浓度时空分布特征及相关因子分析 [J]. 宁夏工程技术, 2016, 15(4): 304-307,312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2016.04.004 WANG W, BAI J, YANG L R, et al. Analysis of the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of ozone concentration and correlation factors in Yinchuan [J]. Ningxia Engineering Technology, 2016, 15(4): 304-307,312(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2016.04.004
[13] 王建英, 崔洋, 杨亚丽, 等. 银川市臭氧污染特征及其气象条件诊断分析 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2020, 32(4): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2020.04.006 WANG J Y, CUI Y, YANG Y L, et al. Ozone pollution characteristic and its meteorological condition diagnosis in Yinchuan [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2020, 32(4): 24-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2020.04.006
[14] 史霖, 王建英, 杨军, 等. 银川市臭氧浓度与气象要素的相关性及其预测方法研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2020, 45(4): 125-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2020.04.026 SHI L, WANG J Y, YANG J, et al. Correlation between ozone concentration and meteorological elements over Yinchuan and prediction method [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2020, 45(4): 125-128(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2020.04.026
[15] 闫雨龙, 温彦平, 冯新宇, 等. 太原市城区臭氧变化特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2261-2268. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016043001 YAN Y L, WEN Y P, FENG X Y, et al. Variation and the influence factors of ozone in urban area in Taiyuan [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2261-2268(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016043001
[16] 张丽, 梁碧玲, 李磊. 深圳市臭氧污染气象条件指数研究及业务应用 [J]. 气象科技进展, 2019, 9(3): 160-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1973.2019.03.023 ZHANG L, LIANG B L, LI L. Ozone pollution meteorological condition index in Shenzhen and its operational application [J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology, 2019, 9(3): 160-165(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1973.2019.03.023
[17] 王冰, 李光明, 马红磊, 等. 濮阳市VOCs污染特征及其臭氧生成潜势分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2020, 36(3): 59-65. WANG B, LI G M, MA H L, et al. Analysis of VOCs pollution characteristics and ozone generation potential in Puyang [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2020, 36(3): 59-65(in Chinese).
[18] 杜桂敏, 张良, 王晓利, 等. 衡水夏季典型时段VOCs污染特征及O3污染过程分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2020, 36(6): 72-79. DU G M, ZHANG L, WANG X L, et al. Analysis of VOCs pollution characteristics and O3 pollution process in the typical summer period of Hengshui [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2020, 36(6): 72-79(in Chinese).
[19] 严仁嫦, 叶辉, 林旭, 等. 杭州市臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(3): 1128-1136. YAN R C, YE H, LIN X, et al. Characteristics and influence factors of ozone pollution in Hangzhou [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(3): 1128-1136(in Chinese).
[20] 余志康, 孙根年, 冯庆, 等. 青藏高原旅游气候舒适性与气候风险的时空动态分析 [J]. 资源科学, 2014, 36(11): 2327-2336. YU Z K, SUN G N, FENG Q, et al. Tourism climate comfort and risk for the Qinghai-Tibet plateau [J]. Resources Science, 2014, 36(11): 2327-2336(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: