-
随着生活水平的提高,居民对于生活质量提出了越来越高的要求。环境质量作为生活质量的重要部分受到了广泛关注。近年来臭气问题在环境问题中显得尤为突出,污水处理厂[1-2]、畜禽养殖场[3-5]、垃圾填埋场[6-7]及石化厂[8]等均会产生并排放大量臭气,不仅使得居民的感官产生不适、影响日常生活[9],甚至会影响到人体的健康[10-12],长期处于恶臭环境中可能会引起血液疾病或癌症等[13]。
基于恶臭对环境及人类的负面影响,我国制定了《恶臭污染物排放标准》(GB14554—1993)[14]用于限制恶臭气体的排放,该标准对8种恶臭气体的排放浓度进行了规定,并使用臭气浓度这一指标用于限制复合恶臭物质的气味浓度[14]。尽管我国已规定了恶臭气体排放限值,但企业或恶臭排放源管理者尚缺乏对恶臭排放进行严格的管控,恶臭问题仍较为严峻[15],这很大程度上是由于恶臭排放的有效数据难以及时准确地进行获取。由于臭气的成分多样[16-17],依靠对臭气成分浓度的测定来控制臭气的排放存在成本高昂、效率低下的问题。因此,建立基于嗅觉感知强度的臭气浓度指标具有现实意义。臭气浓度利用人的嗅觉评价综合气味能直观地反映恶臭对于人嗅觉感官的影响,已成为各国监督气体排放的指标,我国也制定了测定臭气浓度的标准方法(三点比较式臭袋法)[18]。
采用切实高效的臭气浓度测定方法,获得即时准确的臭气浓度数据,能为管理者的决策及环境执法提供可靠的依据,亦可以作为选择适宜的臭气处理方法的参考,以降低处理成本。本文主要针对国内外现有的臭气浓度嗅觉评价方法,比较各嗅觉评价方法的异同点,通过各评价方法的实际应用场景,讨论各嗅觉评价方法的优势与不足之处,为获得切实可行且高效的臭气浓度测定方法提供依据。表1为3种嗅辨方法的对比。
-
国内外的标准方法均采用嗅觉测定法获取臭气浓度,即依赖人的嗅觉感官来量化臭气气味,直观地了解气味对人的影响。嗅觉测定法主要包括4个步骤:采样、稀释、嗅辨、数据储存与处理,即对目标区域内的气体进行采样,利用无臭空气对臭气样品进行一定比例的稀释,稀释后的样品由合格的嗅辨员进行嗅辨,根据嗅辨仪设置的臭气判定模式对样品进行判定,对判定结果进行处理,计算获得臭气浓度。
根据采样和稀释的方法不同,嗅觉测定法可分为动态嗅觉测定法、静态嗅觉测定法以及现场嗅觉测定法。
-
动态嗅觉测定法是指使用样品容器采样,利用动态嗅觉仪的稀释系统对臭气样品按照设定的比例利用无味空气进行稀释,稀释倍数由高到低变化,在符合标准的嗅辨室内由一组嗅辨员对样品进行嗅辨和判定,直到嗅辨员嗅到臭味后停止,对一组嗅辨员的数据处理后得到臭气浓度。目前采用此方法并制定标准化文件的国家主要有欧盟国家(EN 13725∶2003)[19]、美国(ASTM E679-04)[20]和德国(VDI 3881)[21]等。
由于气味单位是很难定义的单位,为便于臭气浓度的表述,欧洲规定了气体浓度单位为OUE·m−3,将臭气样品稀释至50%的人无法嗅出气味,此时的臭气浓度规定为1 OUE·m−3,达到该浓度时的稀释倍数为X,则气体样品的臭气浓度为X OUE·m−3。
-
Hansen等[22]利用取样袋收集气体,利用动态嗅辨仪稀释才采集的气体,使用动态嗅觉法测定样品的臭气浓度,评估生物空气净化器对于育肥猪舍排放臭气的去除效果,并利用PTR-MS在现场测定10种挥发性化合物(VOCs)的浓度。研究表明猪舍空气通过生物空气净化器后,各臭味气体浓度出现不同程度的下降,其中5种挥发性化合物(三甲胺、丁酸、吲哚、对甲苯酚、甲基吲哚)低于检测限,硫化氢浓度从868
$ {\text{μ}}\mathrm{g}\cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-3} $ 降低至94$ {\text{μ}}\mathrm{g}\cdot {\mathrm{m}}^{-3} $ ,臭气浓度从628降低至97。 Capelli等[23-24]使用动态嗅觉法测定了意大利钢铁工业区、化工区和其他工业区的臭气浓度和气体排放速率,将臭气浓度、地形、气象数据导入CALPUFF大气扩散模型模拟气味排放的扩散获得了一定区域范围内每小时的气味浓度值。作者将嗅觉分析和排放扩散模拟的结果相结合,量化了气味源的排放量,确定了3个工业区中钢铁工业区为最重要的臭气源。Romain等[25]通过动态嗅觉法测定了猪舍中猪的整个生长周期的臭气排放,评估了猪的体重与臭气浓度之间的关联性,并利用这些测得的臭气浓度数据校准电子鼻的气味排放因子,以实现对猪舍臭气浓度的连续监测。除此以外,动态嗅觉法还用于检测气味源臭气浓度[26-27]、气味溯源、评估除臭技术的效率[22, 28-29]和获取臭气时空分布信息[30]等。动态嗅觉法的优势在于可在短时间内完成样品稀释,动态嗅辨仪自动记录并处理数据,自动化程度高,嗅辨完成后即可获得臭气浓度值。尽管动态嗅觉法已经在欧美国家得到了广泛的应用,但其作为一种不连续的测定方法缺陷也十分明显。首先在采样时,需使用采样袋在目标区域内进行约三十分钟的采样,测定的结果为采样时间内臭气浓度的均值,无法获得短时间可能产生的高臭气浓度值[31]。其次,样品从采集到嗅辨之间往往间隔几个小时甚至达到三十个小时,存在臭气在采样袋中的气体损失或污染问题,往往使实验室的测定结果与实际臭气浓度存在较大偏差[32]。
-
静态嗅觉测定法由配气员在专门的配气室按照稀释梯度向无臭袋中手动注射一定量的臭气样品。中国(GB/T14675-93)[18]、日本(恶臭防止法)[33]及韩国使用三点比较式臭袋法,即稀释倍数由低到高变化,某一稀释浓度下提供3个嗅辨袋,其中一个嗅辨袋注射有臭气样品,另外两个嗅辨袋内为无臭空气,在嗅辨室内嗅辨员进行嗅辨,合格嗅辨员的数量不少于6名,并要求嗅辨员指出其中有臭气样品的嗅辨袋,逐级递加稀释倍数,直至嗅辨员无法判定出臭气样品时停止实验。
在开始嗅辨前,配气员优先进行嗅辨尝试,从中选择一个既能明显嗅出气味又不强烈刺激的样品,以此稀释倍数作为初始稀释倍数。
-
静态嗅觉法的优势在于设备和技术简单,完成整个嗅辨过程需要的工具为注射器和无臭袋,适用范围广。常用于测定气味阈值[34]、检测臭气排放源的臭气浓度、确定气味源释放恶臭的主要气体成分[35]、臭气溯源等。例如,Lu等[36]选择一天中5个时间点,利用三点比较式臭袋法测定垃圾填埋场距地面1.5 m高度区域的臭气浓度,探究垃圾填埋场臭气排放的时间规律,并使用GC-MS测定各臭气成分浓度,确定提高臭气浓度的主要气体成分。结果表明在春季和秋季的臭气浓度最高可达到3304和3954,普遍高于夏季和冬季,在春季的主要产生含硫化合物、醛、酮等气味阈值较低的化合物。肖洋等[37]使用三点比较式臭袋法在居民投诉异味频发区域以及化工厂厂界测定臭气浓度,发现在化工企业故障设备采样点臭气浓度值为100,超过国标中所规定的70,对臭气浓度较高的点使用便捷式GC-MS确定引起异味的有机化合物种类并测定浓度,根据风向,对照企业污染物名单实现对超标气体污染物快速溯源。Cui等[38]使用三点法测定了北京五家火葬场烟囱出口、焚化炉烟囱出口以及火化车间的臭气浓度以确定火葬场的气味排放水平,其中有工人长期作业的火化车间臭气浓度范围为97—732(平均504),此状态下工人能明显嗅到异味不利于健康,作者结合现场环境指出臭气浓度超标的原因,即火化设备密封性差,火化过程产生的异味泄露到车间,且车间通风条件差,异味无法及时排出。
此方法全程使用人工进行测试[39],操作简单但耗时耗力,且需要保证大量数据的准确性并进行复杂的计算,样品测试效率低[40-41]。同时,完成每个样品的测定需要几十甚至上百个嗅辨袋,资源浪费严重。此外,由于静态嗅觉法是一种不连续的测定方法,故也存在无法获得即时的臭气浓度,并存在样品在采样和运输过程中的损失和污染问题。
-
现场嗅觉测定法包括两种方式,一种是建立移动嗅辨室[42],利用拖车将嗅辨室设立在采样点附近,采样后在移动实验室内完成嗅辨工作,由于移动嗅辨室的条件要求较高,且拖车费用高昂,应用中一般采用第二种方式。第二种方式具体是指在需要测定臭气浓度的场所,由一名嗅辨员开启现场嗅辨仪,并用嗅辨仪自带的面罩覆盖嗅觉器官。嗅辨仪可吸入环境气体并将其与无味空气按一定比例混合后输送到面罩,环境气体的稀释倍数一般由低到高设置。嗅辨员判断面罩内的气体样品是否有臭味,在无法嗅到臭味时停止并记录此时嗅辨仪对应的稀释倍数,换算后得到臭气浓度。本节主要根据第二种方式展开介绍和讨论。
-
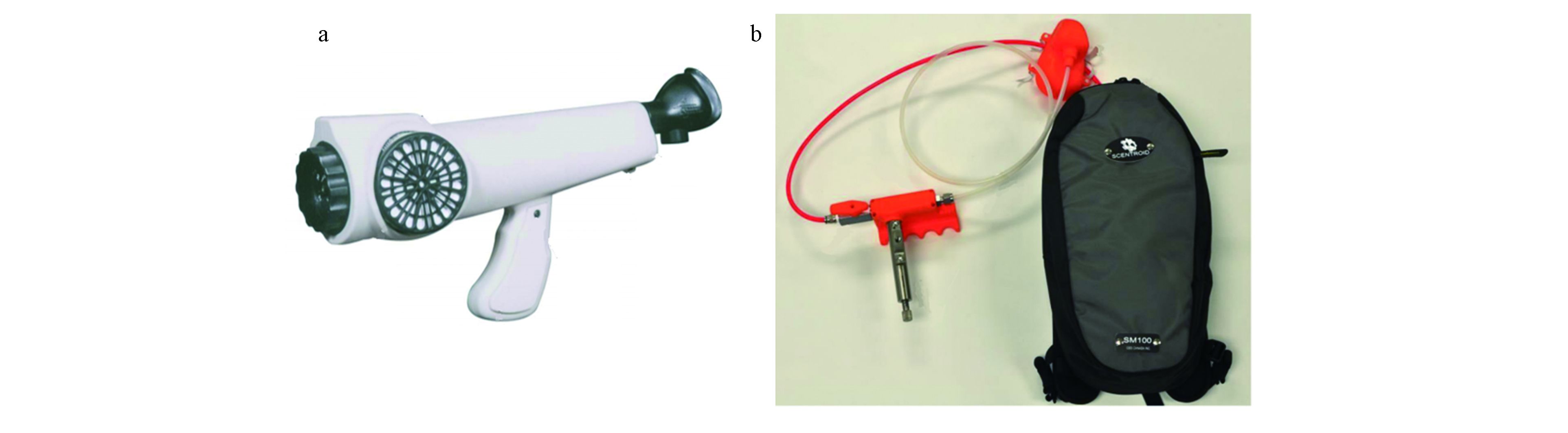
由于现场嗅觉测定法需要在现场进行嗅辨,从成本和方便性考虑,嗅辨仪需要具有便携性,因此体积和质量应尽量小。目前常用的现场嗅辨仪有Nasal Ranger Field Olfactometer[43](以下简称NR)和 Scentroid SM100系列[44]两种。
NR由美国的St. Croix Sensory设计,如图1(a)所示,主要由稀释拨盘、气味过滤器、带止回阀的面罩组成。利用嗅辨员自身的呼吸吸入环境空气,一部分环境空气通过活性炭过滤,形成无味空气。另一部分环境空气与无味空气混合,通过调整稀释拨片控制环境空气的稀释倍数。
Scentroid SM100为IDES Canada Inc.设计的便携式嗅辨仪,如图1(b)所示,主要由便携式压缩空气罐、文丘里泵、滑动阀、面罩等组成。自带的气罐内储存压缩的无味空气,在嗅辨时以20 L·min−1的流量释放无味空气,流速较快的无味空气通过文丘里泵产生真空压强,环境空气在压差的作用下通过限流板进入文丘里泵,混合后得到稀释的气体样品。限流板上钻有15个直径不同的小孔,嗅辨员利用可调节的滑阀,选择实际通过环境空气的小孔,从而改变稀释倍数。
目前还没有标准化文件对于进行现场嗅辨前所需要做的准备工作进行描述,也没有对进行现场嗅辨时的条件进行限制和规定。嗅辨员在进行现场嗅辨时主要是按照嗅辨仪生产公司所规定的流程进行,而不同的公司之间对其产品的使用规定并不相同。
-
现场嗅辨是对臭气浓度的实时测定,更贴近居民闻到臭气的情境,易察觉某时刻由于气象条件等的变化造成即时性的恶臭[45]。且嗅辨过程完成后即可获得臭气浓度的数据,减少了监管者的时间成本。现场嗅辨是实地的测定,无需进行样品的采集、运输和保存,因此该方法无气体损失的问题[46]。对比动态嗅觉法和静态嗅觉法,现场嗅辨法更可能获得真实的臭气浓度值。虽然现场嗅辨法并未作为一个标准化方法,但已经运用于许多的工作中并提供可用的数据,如用于寻找气味源[47];监测气味源的臭气浓度[26];获取臭气空间分布信息并确定气味排放的影响范围[48-50];作为扩散模型的输入数据,在局部空间规划过程中提供有用的信息[51];评估除臭技术的效率等[22, 52- 53]。Byliński等[47]利用Nasal Ranger 现场嗅辨仪对炼油厂附近五个采样点进行臭气浓度测定,30 min完成了臭气浓度数据的获取,在第二采样点得到最高的臭气浓度值(9.3 D/T),有两个采样点的臭气浓度明显高于其余采样点,发现两采样点均靠近污水处理厂,从而快速锁定了气味源。
现场嗅辨的劣势在于目前已有的现场嗅辨仪价格高昂且同时只支持一名嗅辨员进行嗅辨,无法忽略嗅觉差异对测定结果的影响。此外,由于受到仪器的设计缺陷和实时变化的气象情况的双重影响,嗅辨仪的实际稀释倍数与设定值之间一般存在着差异。
-
动态嗅觉测定法使用采样袋采集目标区域内的环境空气,在EN 13725-2003中推荐了FEP(聚乙烯丙烯共聚物)、PVF(聚氟乙烯/Tedlar )和PET(聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯/ Nalophan )的3种材料采样袋。在我国国标GB/T14675-93中,只说明了采用聚酯采样袋,未说明采样袋的具体材料。
由EN 13725-2003推荐的材料制成的采样袋常存在背景气味。未使用过的Tedlar采样袋中的背景气味浓度可达100[54],经冲洗后,背景气味浓度在20—60范围内; 而未使用过的Nalophan采样袋相较于Tedlar采样袋背景气味浓度较低,一般在36—43范围内[55],但由于批次不同,部分Nalophan采样袋的背景气味可高达136—456[56]。在样品臭气浓度较低时,采样袋的背景气味对臭气浓度测定的影响无法忽略,并且臭气浓度不能进行简单的加减,导致测定的臭气浓度大于实际浓度,为进一步对臭气的管理造成了困难。因此,需要采取进一步的措施,以消除或减弱采样袋的背景气味。
Nalophan采样袋因其价钱低廉[57],使用广泛,在无异味的环境中存放一段时间,可降低其背景气味的浓度[54]。Tedlar采样袋加热24 h,加热后立即冲洗并在取样前再次冲洗,背景气味浓度可下降至12[55],但其价格大大高于Nalophan采样袋。对于FEP和PTFE(聚四氟乙烯)采样袋,普遍认为其无背景气味,其中PTFE采样袋的价格最高。
-
在使用动态嗅觉法和三点比较式臭袋法测定臭气时,均需将气体样品采集后运输到标准的嗅辨室内对臭气浓度进行测定。气体样品在长时间的运输过程中无法保持其原有的浓度或性质,主要有三个方面导致气体样品的变化,采样袋以及相关配件对气体的吸附[58-59];气体透过采样袋逸散到空气中[60];采样袋内气体的不稳定[61]。
尽管在相关的标准化文件中已列出推荐的惰性采样袋材料,但采样袋对于气体样品的吸附以及逸散造成的气体样品的损失仍然无法忽视。采样24 h后易损失的臭气成分,如羧酸类、苯酚类、吲哚等,在Tedlar和Nalophan袋中浓度降低50%—>90%。较稳定的含硫化合物,如硫化氢,在Nalophan袋中浓度降低约30%,而在Tedlar袋中浓度降低<5%[62-63]。
为减少气体样品的损失,Kasper等[64]提出在对样品进行分析前对采样袋加热,使采样袋释放吸附在上的样品,对于PTFE袋,分析前加热至57 ℃,在采样48 h后,气味的浓度保持在71.6%—98.8%之间;Man等[63]提出减小采样袋面积与气体体积的比值(S/V),使气体样品填满整个采样袋,可减少气体样品与采样袋内表面的接触面积,从而减少气体的逸散以及采样袋对气体的吸附,使用10 L的FEP袋,当S/V从101减小到30,24 h后的样品回收率从79.6%升至91.8%;Kong等[65]提出减少采样袋填充时间,会减少填充过程中气体的损失。
虽然已有多种方法显示可以减少气体的损失,但随着采样与测定之间时间间隔的增加,气体样品的损失随之增加,为此需尽量缩短时间间隔。使用移动嗅辨室或者使用现场嗅辨仪进行嗅辨,成为获得实际的臭气浓度的较可行方法。
-
在测定臭气浓度时,主要依靠设备的稀释倍数来获取数据,因此实际的稀释倍数与设定值之间若存在偏差将会直接影响测定结果的准确度[66]。
对于动态嗅觉法,其稀释倍数的调节依靠嗅辨仪的稀释系统。有研究表明此系统可能会改变化合物的气味电荷,硫化氢、甲硫醇和二甲硫醚等还原性硫化物在流经嗅辨仪的稀释系统时会受到不同的影响,造成不同程度的流失[67]。对于静态嗅觉法,其稀释倍数的调节主要依靠人工使用注射器抽取一定量的气体样品注入充满无臭空气的气袋中。此方法产生误差的原因主要是注射器的气密性不足以及人工操作的误差。对比以上两种方法,前者稀释倍数的准确度要低于后者[27]。在臭气浓度较低时,静态嗅觉法表现出更高的重复性[68]。在气味浓度大于100时,以上两种方法的测定结果没有显著差异。
对于现场嗅辨法,目前主流的现场嗅辨仪仅依靠改变限流孔的孔径控制稀释倍数,此种控制方法的稳定性仍然存疑,并且在现场测定时,环境的变化十分复杂,风向、气压、风速和温度等都可能会造成稀释倍数的不准确。
Walgraeve等[69]在嗅辨室内使用五种化合物(丁醇、乙酸、丙酸、二甲基硫醚、二甲基二硫化物)对NR和SM100的稀释速率进行测定,SM100实际稀释速率与设定值对应良好,但对于化合物的实际稀释倍数总是大于设定值,相差最大时前者为后者的两倍,NR对于化合物的稀释表现良好,但在稀释倍数≥60时,实际值也会与设定值出现差异,后者总大于前者;Maurer等[66]比较了标准实验室动态嗅觉仪AC'SCENT 嗅觉仪与Scentroid SM100i的稀释倍数的误差,后者的平均误差较前者的高8.87%,SM100i的测定结果高于实际的臭气浓度。以上的研究均在实验室内完成,实验室内的环境条件稳定,现场嗅辨仪的实际稀释倍数与设定值的差异明显,可知在室外条件下差异将进一步扩大。
在实验室条件下的差异主要由嗅辨仪内材料对气味化合物的吸附造成,可在嗅辨仪内部结构进行硅烷化处理以减少气体的吸附。在室外条件下的差异可通过加装传感器获取环境条件数据,在嗅辨结束后根据环境条件数据设置环境因子系数处理臭气浓度数据,使最终的测定结果更接近真实值。
-
各国对嗅辨员的标准进行了规定,EN 13735使用十种参考气体对测评者的嗅觉阈值进行评价,嗅辨员的阈值在可接受参考值的0.5—2倍之间,即嗅辨员之间的阈值最高可相差4倍;GB/T14675-93 使用五种标准臭液筛选嗅辨员,嗅辨员能分辨出沾有标准臭液的纸条即可,未对嗅辨员的嗅觉阈值上限进行限制。以上两种方法都需要至少四名以上的嗅辨员对臭气样品进行评价以减少嗅辨员之间嗅觉的差异造成的误差。
生物嗅觉的可变性不仅存在于嗅辨员之间,同一嗅辨员在嗅辨的地点、时长发生改变时,尤其是在嗅辨员在进行长时间的嗅辨工作后产生嗅觉疲劳,嗅辨结果也会产生差异[70]。在现场嗅觉测定时,嗅辨员直接暴露在室外环境中,环境中的噪音、温度及气味等都会使嗅辨员无法专注于臭气浓度的测定,从而做出不准确的判断。
对于嗅觉差异,目前并没有理想的解决方法,但可通过指定标准对嗅辨员的嗅觉阈值进行限值,在一定周期内多次评估嗅辨员的嗅觉阈值,并在合理的范围内增加嗅辨员并对结果进行处理,使最终的测定结果更接近真实值或更具重复性。
-
本文主要讨论了三种测定臭气浓度的方法,即动态嗅觉测定法、静态嗅觉测定法及现场嗅觉测定法。对比了各方法的适用国家、测定要求、实际应用场景以及存在的缺陷。研究相关文献并结合标准文件,分析发现主要是采样袋的背景气味、气体样品的损失或污染、稀释倍数的准确度以及嗅辨员的嗅觉差异造成了测定结果准确度低。整理得到选择背景气味低的FEP袋或对其他类型的采样袋进行冲洗并在高温下进行预处理可降低背景气味的影响;缩短采样与嗅觉测定的时间间隔可最大程度的减少样品的损失和污染;在现有的现场嗅辨仪内部增加一层不易吸附气体的材料,在测定时记录现场气象条件并引入影响因子可提高现场嗅辨结果的准确度;进一步限制嗅辨员的阈值范围,并对嗅辨员资格进行周期性的复检可增加测定结果的可靠性和可重复性。
基于嗅觉的臭气浓度测定方法综述
A Review on olfactory methods for odor concentration determination
-
摘要: 畜禽养殖、垃圾填埋、化工、市政等活动产生的大量臭气,不仅会影响居民的日常生活,甚至可能会影响人体的健康。世界上很多国家制定了臭气的排放标准,将臭气浓度作为评价臭气的重要指标,并制定了臭气浓度测定的标准化方法,但现行的方法存在耗时长、测定结果不准确等问题,使得臭气排放难以获得有效监管。本文介绍了基于嗅觉的臭气浓度测定方法,分析了各方法的适用范围及优劣势,指出了测定方法中存在的问题并提出可能的解决途径,为进一步完善测定方法提供了参考。Abstract: A large amount of odor produced by livestock, landfill, chemical industry and other industrial activities will not only affect the daily life of local residents, but may also potentially affect human health. Many countries have formulated various standards for odor emission, taking the odor concentration as an important index to evaluate the odor. Meanwhile, standardized methods have also been formulated for the determination of odor concentration. However, current methods typically have issues such as time-consuming and inaccurate measurement results, causing difficulty for obtaining effective monitoring, management and control of odor emission by the authorities. This review study firstly introduced the olfactory determination methods of odor concentration, the application ranges of these methods were discussed. Afterwards, the advantages and disadvantages of each method were analyzed, and the problems existing in the determination methods were discussed, while possible solutions for improvement were proposed. Overall, this study was to provide a reference for the further improvement of the determination for odor concentration.
-
Key words:
- odor concentration /
- olfactometer /
- field olfactometry
-

-
表 1 三种嗅辨方法的对比
Table 1. Comparison of three olfactory discrimination methods
嗅辨
方法
Olfactometry适用
国家
Applicable
country标准文件
Standard采样和运输
Sampling and
transportation嗅辨室
Odor room嗅辨仪器
Olfactometer嗅辨员
Panel优劣势
Advantages and disadvantages动态嗅觉法 美国、
英国、
欧盟、
德国、
加拿大ASTM E690-04、
EN 13725-2003、VDI 3880通过采样袋(FEP\PVF\PET)采样;采样到测定不超过6—30 h;温度保持在25 ℃;避免阳光直射 保持良好的通风;CO2体积分数小于0.15 %;避免阳光直射;无影响测定的噪声和光 动态嗅
辨仪如:Odournet TO8、AC’SCENT
嗅觉仪合格的嗅辨员需满足以下两点:1)从各个阈值(十个参考气体的阈值)估计值的对数(lg10)计算出的标准偏差的对数,应小于2.3
2)单个阈值估算值的几何平均值,以参考气体的质量浓度单位表示,必须落在该参考材料可接受参考值的0.5—2倍之间优势:
快速稀释样品;
自动记录并处理
数据
劣势:
运输耗时久,样品发生泄漏或成分变化;
采样时间长,最终数据结果为采样时间段内均值静态嗅觉法 中国、
日本GB14675-93、
恶臭防止法通过采样袋/瓶采样;采样到测定不超过24 h;温度接近常温;避免阳光直射 远离散发恶臭的场所;室内能通风换气;温度保持在17—25 ℃;可容纳6—7名嗅辨员同时工作;单独开设配
气室注射器、聚酯无臭袋、无臭空气净化装置 年龄18—45岁,不吸烟、嗅觉器官无疾病,男女均可;
能正确嗅辨出五种标准臭液的测试者可作为合格的嗅辨员;
测试合格后可连续三年承担嗅辨员工作优势:
所需设备及技术简单,适用范围广
劣势:
嗅辨数据量大,处理数据慢;
采样时间长,最终数据结果为采样时间段内均值;
运输耗时久,样品发生泄漏或成分变化;现场嗅辨法 美国、
英国、
欧盟、
德国、
加拿大直接采样后测定 1)使用现场嗅辨仪直接在现场嗅辨,无嗅辨室
2)使用拖车建立移动实验室,满足动态嗅觉法的要求现场嗅
辨仪如:Nasal Ranger、Scentroid SM100一般满足动态嗅觉法的规定即可 优势:
采样时间短;
测定结果为即时的臭气浓度;
劣势:
现场嗅辨仪稀释倍数不够精确;
实地环境易对嗅辨员感官产生影响 -
[1] LIU Z Y. Urban sewage treatment odor gas release characteristics and regional differences [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 21: 101190. [2] 王鑫, 池皓, 张鑫倩, 等. 炼化企业污水处理厂恶臭治理设施排放特征及污染控制策略 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2333-2343. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202102027 WANG X, CHI H, ZHANG X Q, et al. Emission characteristics and control strategy of odor treatment processes in refinery wastewater treatment plants [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(7): 2333-2343(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202102027
[3] KECK M, MAGER K, WEBER K, et al. Odour impact from farms with animal husbandry and biogas facilities [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645: 1432-1443. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.182 [4] ZILIO M, ORZI V, CHIODINI M, et al. Evaluation of ammonia and odour emissions from animal slurry and digestate storage in the Po Valley (Italy) [J]. Waste Management, 2020, 103: 296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.12.038 [5] 李永双, 孙波, 陈菊红, 等. 纳米膜覆盖对畜禽粪便好氧堆肥进程及恶臭气体排放的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5554-5562. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103109 LI Y S, SUN B, CHEN J H, et al. Effects of nano-membrane on aerobic composting process and odor emission of livestock manure [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5554-5562(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103109
[6] CAPELLI L, SIRONI S, del ROSSO R, et al. A comparative and critical evaluation of odour assessment methods on a landfill site [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(30): 7050-7058. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.06.009 [7] 周巧丽, 宋玉梅, 周漪波, 等. 广州市某生活垃圾填埋场空气及地下水污染状况分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 760-769. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018061302 ZHOU Q L, SONG Y M, ZHOU Y B, et al. Analysis of air and groundwater pollution in a municipal solid waste landfill site in Guangzhou [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 760-769(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018061302
[8] JIA H H, GAO S, DUAN Y S, et al. Investigation of health risk assessment and odor pollution of volatile organic compounds from industrial activities in the Yangtze River Delta region, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111474. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111474 [9] 陈凌霄, 修光利, 黄银芝. 聚氨酯和聚碳酸酯制造过程的恶臭排放特征和指纹谱 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 755-764. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202005008 CHEN L X, XIU G L, HUANG Y Z. Characteristics and fingerprint spectra of odor pollutants emitted from typical production process of polyurethane and polycarbonate [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(2): 755-764(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202005008
[10] BRANCHER M, GRIFFITHS K D, FRANCO D, et al. A review of odour impact criteria in selected countries around the world [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 1531-1570. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.160 [11] SUCKER K, BOTH R, WINNEKE G. Review of adverse health effects of odours in field studies [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 59(7): 1281-1289. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.113 [12] WU C D, LIU J M, LIU S H, et al. Assessment of the health risks and odor concentration of volatile compounds from a municipal solid waste landfill in China [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 202: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.068 [13] LIU Y J, LIU Y T, LI H, et al. Health risk impacts analysis of fugitive aromatic compounds emissions from the working face of a municipal solid waste landfill in China [J]. Environment International, 2016, 97: 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.10.010 [14] 国家环境保护局, 国家技术监督局. 恶臭污染物排放标准: GB14554—1993[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1994. State Bureau of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China, State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. Emission STANDARDs for odor pollutants: GB14554—1993[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1994(in Chinese).
[15] 章轲. 恶臭居环保举报榜首, 治理市场混乱、技术低效是主要症结 [N]. 第一财经, 2020-11-11. ZHANG K. Odor ranks first in environmental protection reports, the main crux of the problem is the management of market chaos and technical inefficiency[N]. YICAI, 2020-11-11.
[16] WANG Y C, HAN M F, JIA T P, et al. Emissions, measurement, and control of odor in livestock farms: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 776: 145735. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145735 [17] MELSE R W, HOL J M G. Biofiltration of exhaust air from animal houses: Evaluation of removal efficiencies and practical experiences with biobeds at three field sites [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2017, 159: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2017.04.007 [18] 国家技术监督局. 空气质量 恶臭的测定 三点比较式臭袋法: GB/T14675—1993[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. Air quality-Determination of odor-Triangle odor bag method: GB/T14675—1993[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1993(in Chinese).
[19] EN 13725∶2003, Air quality—Determination of odour concentration by dynamic olfactometry[S]. [20] ASTM E679‐04 , Standard Practice for Determination of Odor and Taste Thresholds By a Forced‐Choice Ascending Concentration Series Method of Limits[S]. [21] VDI 3881/Part 2, Olfactometry—odour threshold determination—sampling[S]. [22] HANSEN M, JONASSEN K E N, FEILBERG A. Evaluation of abatement technologies for pig houses by dynamic olfactometry and on-site mass spectrometry [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2014, 40: 253-258. [23] CAPELLI L, SIRONI S, DEL ROSSO R, et al. Olfactory and toxic impact of industrial odour emissions [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 66(7): 1399-1406. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.352 [24] CAPELLI L, SIRONI S, del ROSSO R, et al. Olfactometric approach for the evaluation of citizens' exposure to industrial emissions in the city of Terni, Italy [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(3): 595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.10.054 [25] ROMAIN A C, NICOLAS J, COBUT P, et al. Continuous odour measurement from fattening pig units [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 77: 935-942. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.06.030 [26] NEWBY B D, MCGINLEY M A. Ambient odour testing of concentrated animal feeding operations using field and laboratory olfactometers [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(4): 109-114. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0235 [27] BLAZY V, de GUARDIA A, BENOIST J C, et al. Correlation of chemical composition and odor concentration for emissions from pig slaughterhouse sludge composting and storage [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 276: 398-409. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.031 [28] FRIEDRICH M, KOSMIDER J. Precision of odour abatement efficiency determination in changing conditions [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions , 2012, 30: 265-270. [29] GUTIÉRREZ M C, MARTÍN M A, PAGANS E, et al. Dynamic olfactometry and GC-TOFMS to monitor the efficiency of an industrial biofilter [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512/513: 572-581. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.074 [30] PARKER D B, RHOADES M B, SCHUSTER G L, et al. Odor characterization at open-lot beef cattle feedyards using triangular forced-choice olfactometry [J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 2005, 48(4): 1527-1535. doi: 10.13031/2013.19184 [31] CAPELLI L, SIRONI S, del ROSSO R. Odor sampling: Techniques and strategies for the estimation of odor emission rates from different source types [J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2013, 13(1): 938-955. doi: 10.3390/s130100938 [32] JONASSEN K, PEDERSEN P, RIIS A, et al. Does the choice of olfactometric laboratory affect the efficiency of odour abatement technologies? [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions , 2012, 30: 43-270. [33] 恶臭防治法[S]. Offensive Odor Control Law[S] (in Chinese).
[34] NAGATA Y, TAKEUCHI N. Measurement of odor threshold by triangle odor bag method [J]. Odor measurement review, 2003, 118: 118-127. [35] HANAJIMA D, KURODA K, MORISHITA K, et al. Key odor components responsible for the impact on olfactory sense during swine feces composting [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2306-2310. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.026 [36] LU W J, DUAN Z H, LI D, et al. Characterization of odor emission on the working face of landfill and establishing of odorous compounds index [J]. Waste Management, 2015, 42: 74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.04.030 [37] 肖洋, 王新娟, 韩伟. 工业城市有机化工异味应急监测快速溯源 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(2): 126-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.025 XIAO Y, WANG X J, HAN W. Study of rapid tracing of organic chemical odor emergency monitoring for industrial city [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(2): 126-129(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.02.025
[38] CUI Y Y, ZHAI X M, WANG B C, et al. Characteristics and control measures of odor emissions from crematoriums in Beijing, China [J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2021, 3(8): 1-9. [39] 张旭东. 恶臭动态稀释法在三点比较式臭袋法中的应用探讨 [J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2016, 41(4): 80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2016.04.024 ZHANG X D. Discussion on the application of odor dynamic dilution method in the three point comparison method [J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2016, 41(4): 80-82(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-288X.2016.04.024
[40] 安慧, 赵东风, 张庆冬, 等. 恶臭嗅觉测定研究性实验教学设计 [J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2019, 38(7): 196-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2019.07.047 AN H, ZHAO D F, ZHANG Q D, et al. Experimental teaching design for odor olfactory detection [J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2019, 38(7): 196-199(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2019.07.047
[41] 戎梅. 浅谈三点比较式臭袋法在恶臭监测中的应用// 国家环境保护恶臭污染控制重点实验室. 恶臭污染防治研究进展——第四届全国恶臭污染测试与控制技术研讨会论文集[C]; 2012: 3. Rong M. Discussion on the application of triangle odor bag method in malodor monitoring//National Key Laboratory of Odor Pollution Control for Environmental Protection. Progress in Research on Odor Pollution Prevention-Proceedings of the Fourth National Symposium on Odor Pollution Testing and Control Technology[C]; 2012: 3(in Chinese).
[42] HANSEN M J, JONASSEN K E N, LØKKE M M, et al. Multivariate prediction of odor from pig production based on in situ measurement of odorants [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 135: 50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.03.060 [43] 王媛媛, 王琪, 李贝, 等. 恶臭国标测定方法和便携式恶臭测定仪测定结果的比对分析 [J]. 环境监控与预警, 2017, 9(5): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2017.05.006 WANG Y Y, WANG Q, LI B, et al. Comparative analysis of odor determination by national standard method and portable odor tester [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2017, 9(5): 20-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2017.05.006
[44] IDES Canada Inc. SM100 portable olfactometer[EB/OL]. [45] WIŚNIEWSKA M. Methods of assessing odour emissions from biogas plants processing municipal waste [J]. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 2020, 21(1): 140-147. doi: 10.12911/22998993/113039 [46] HAWKO C, VERRIELE M, HUCHER N, et al. A review of environmental odor quantification and qualification methods: The question of objectivity in sensory analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 795: 148862. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148862 [47] BYLIŃSKI H, LEWKOWSKA P, GĘBICKI J, et al. Identification of aromatic compounds in odours mixture by gas chromatography and field olfactometry techniques [J]. Proceedings of the 12th Modern Analytical Chemistry, 2016: 108-112. [48] BARCZAK R, KULIG A. Odour monitoring of a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Poland by field olfactometry [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2016, 54: 331-336. [49] DALTON P, CARAWAY E A, GIBB H, et al. A multi-year field olfactometry study near a concentrated animal feeding operation [J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2011, 61(12): 1398-1408. [50] BAKHTARI A, MEDINA S. Enhancing VDI3940 grid method via in-field olfactometry to obtain complete odour impact assessment [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2016, 54: 283-288. [51] BADACH J, KOLASIŃSKA P, PACIOREK M, et al. A case study of odour nuisance evaluation in the context of integrated urban planning [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 213: 417-424. [52] HOVE N C Y, DEMEYER P, van der HEYDEN C, et al. Improving the repeatability of dynamic olfactometry according to EN 13725: A case study for pig odour [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2017, 161: 70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2017.06.004 [53] KULIG A, SZYŁAK-SZYDŁOWSKI M. Assessment of the effects of wastewater treatment plant modernization by means of the field olfactometry method [J]. Water, 2019, 11(11): 2367. doi: 10.3390/w11112367 [54] MILLER R M, MCGINLEY M A. Evaluation of background odour in tedlar and nalophan sample bags [J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2008, 2008(4): 590-604. doi: 10.2175/193864708788808032 [55] PARKER D B, RHOADES M B, KOZIEL J, et al. Background odors in tedlar® bags used for CAFO odor sampling[C]//2003, Las Vegas, NV July 27-30, 2003. St. Joseph, MI: American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2003. [56] LAOR Y, RAVID U, HANAN A, et al. Uncertainty of olfactometry measurements caused by sampling issues [J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2012, 2012(3): 1-12. doi: 10.2175/193864712811700444 [57] PAPURELLO D. Direct injection mass spectrometry technique for the odorant losses at ppb(v) level from nalophan™ sampling bags [J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2019, 436: 137-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2018.12.008 [58] MCGARVEY L J, SHORTEN C V. The effects of adsorption on the reusability of tedlar® air sampling bags [J]. AIHAJ - American Industrial Hygiene Association, 2000, 61(3): 375-380. doi: 10.1080/15298660008984546 [59] VAN HARREVELD A. Update on the revised EN 13725: 2021 [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2021, 85: 115. [60] TOLEDO M, GUILLOT J M, SILES J A, et al. Permeability and adsorption effects for volatile sulphur compounds in Nalophan sampling bags: Stability influenced by storage time [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 188: 217-228. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.10.023 [61] LI Q, FU X A, XU K Y, et al. A stability study of carbonyl compounds in Tedlar bags by a fabricated MEMS microreactor approach [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2021, 160: 105611. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2020.105611 [62] HANSEN M J, ADAMSEN A P S, FEILBERG A, et al. Stability of odorants from pig production in sampling bags for olfactometry [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2011, 40(4): 1096-1102. doi: 10.2134/jeq2010.0497 [63] MAN Z, DAI X R, RONG L, et al. Evaluation of storage bags for odour sampling from intensive pig production measured by proton-transfer-reaction mass-spectrometry [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 189: 48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.11.007 [64] KASPER P L, OXBØL A, HANSEN M J, et al. Mechanisms of loss of agricultural odorous compounds in sample bags of nalophan, tedlar, and PTFE [J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2018, 47(2): 246-253. doi: 10.2134/jeq2017.07.0289 [65] KONG X K, WANG L P, XIN Y C, et al. Evaluation of pre-Flushing for the recovery of odorants from intensive pig production in sampling bags measured by PTR-MS[C]//2018 Detroit, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2018: 1. [66] MAURER D L, BRAGDON A M, SHORT B C, et al. Improving environmental odor measurements: Comparison of lab-based standard method and portable odor measurement technology [J]. Archives of Environmental Protection, 2018, 44(2): 100-107. [67] HANSEN M J, ADAMSEN A P S, FEILBERG A. Recovery of odorants from an olfactometer measured by proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry [J]. Sensors , 2013, 13(6): 7860-7871. doi: 10.3390/s130607860 [68] NADDEO V, ZARRA T, OLIVA G, et al. Odour measurement in wastewater treatment plant by a new prototype of e. Nose: Correlation and comparison study with reference to both European and Japanese approaches [J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2016, 54: 85-90. [69] WALGRAEVE C, van HUFFEL K, BRUNEEL J, et al. Evaluation of the performance of field olfactometers by selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2015, 137: 84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2015.07.007 [70] HOVE N C Y, van LANGENHOVE H, van WEYENBERG S, et al. Comparative odour measurements according to EN 13725 using pig house odour and n-butanol reference gas [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2016, 143: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2016.01.002 -



 下载:
下载:



