-
石河子市是位于新疆乌昌石区域中部的工业城市,近几年随着经济的快速发展,其大气污染较为严重,冬季以细颗粒物(PM2.5)为首要污染物的污染天时有发生[1-4]. 无机元素作为细颗粒物的主要成分之一,大部分具有容易富集和难以降解的特点,尤其是重金属元素在人体中的富集会危害人体器官健康,造成不可逆的功能性障碍[5-7]. 近年来北京市[8]、上海市[9]、沈阳市[10]、广州市[11]、成都市[12]、乌鲁木齐市[13]、珠三角区域[14]等对PM2.5中无机元素的研究主要针对重金属元素。王琼等[15]研究认为,北京冬季大气PM2.5中元素的致癌风险高于夏季,污染日大气PM2.5中元素的致癌风险高于清洁日,PM2.5中元素的健康风险具有较为明显的季节性变化特征,冬季有针对性地控制大气PM2.5污染,对人体健康意义深远. 任慧清等[16]通过研究石河子市冬季5种重金属元素(Ni、Cu、Zn、Pb、Fe),并选取重金属元素Zn进行大鼠肺部损伤实验发现,供暖季石河子市PM2.5浓度为(109.9±58.8) μg·m−3, PM2.5和Zn浓度的升高能够显著抑制超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,引起对大鼠肺部的损伤.李瑶等[17]通过对石河子市进行PM2.5高精度遥感反演发现,石河子市PM2.5的空间分布呈现北低南高,西低东高的特点. 丁俊男等[18]通过富集因子法研究河南省典型城市采暖季PM2.5中无机元素的来源,发现郑州市、洛阳市和平顶山市的Se、Cd、Br、Pb、Zn、Cu、Co、Sc、Cr、Ni、As、Mn、Ba等元素的富集因子大于10,主要来源于人为源,这13种元素质量浓度在22种元素中占比为18.9%—26.3%,主要来源于燃煤、机动车、扬尘和建筑尘等,Ni、Co、Sr、Ba 还有来自其他排放源的贡献. 张晶晶等[19]通过研究昌吉市采暖季PM2.5的污染特征发现,采暖季PM2.5的浓度高于非采暖季5.6倍,采暖季首要污染物为PM2.5,比例最高占66.3%.
石河子市工业区主要集中在城区北部,紧邻城区. 石河子市冬季以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天频发,PM2.5中富集的重金属元素会损害人体器官,研究PM2.5中无机元素的变化特征和来源对于评价城市环境质量,制定环境治理对策具有重要意义[20-21]. 本研究在石河子市城区和工业区进行冬季PM2.5样品采集,分析2个功能区无机元素的浓度水平和变化特征,并通过富集因子法(EF)对冬季PM2.5污染来源进行解析[22-23].
-
石河子市工业区主要集中在城区北部,在城区和工业区内共设置2个采样点,采样点信息如表1所示,城区采样点位于环境监测站楼顶,其正东方向1.6 km处为阳光学校国控站点,正南方向1.2 km处为艾青诗歌馆国控站,工业区采样点位于大全新能源股份有限公司(大全)办公楼楼顶,工业区排放源主要以化工、电力、电解铝、硅冶炼、水泥等大型重工业高架点源为主. 2个采样点同时开展为期2个月的全天候PM2.5采样,采样点距地垂直高度均不低于10.0 m,周围无明显污染源,因此能够代表周围区域大气环境特征.
-
在石河子市城区和工业区的2个采样点均使用武汉天虹TH-16A型四通道采样器进行采样(另外两通道平行采样备用),各通道采样流量均为16.7 L·min−1. 采样日期为2020年12月1日—2021年1月31日,共采集62 d,采样时间为每天10:00—翌日09:00,累积采样时长23 h. 每日采样滤膜为一张直径47 mm的石英纤维滤膜(Q膜,Pall,Sweden)和一张直径47 mm的聚丙烯滤膜(P膜,Whatman,Sweden),具体方法按照《环境空气颗粒物(PM2.5)手工监测方法(重量法)技术规范》[24]要求. 利用电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS,Agilent 7800,America)对滤膜进行元素分析,取1/4面积滤膜,放置于聚四氟乙烯消解罐中,加入5.0 mL MOS级硝酸,放置2 h后再加入2.0 mL MOS级盐酸,2.0 mL优级纯H2O2,加盖密封后,用微波消解萃取仪消解(在10 min内升温到190 ℃后至少保持30 min). 待消解罐冷却至室温,再利用赶酸器在140 ℃将消解液浓缩至约0.5 mL(约4—5 h),用超纯水转移定容为25.0 mL,然后进行仪器分析. 包括Be、Na、Mg、Al、K、Ca、V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Se、Mo、Ag、Cd、Ba、Tl、Pb、Th、U,共24种.
-
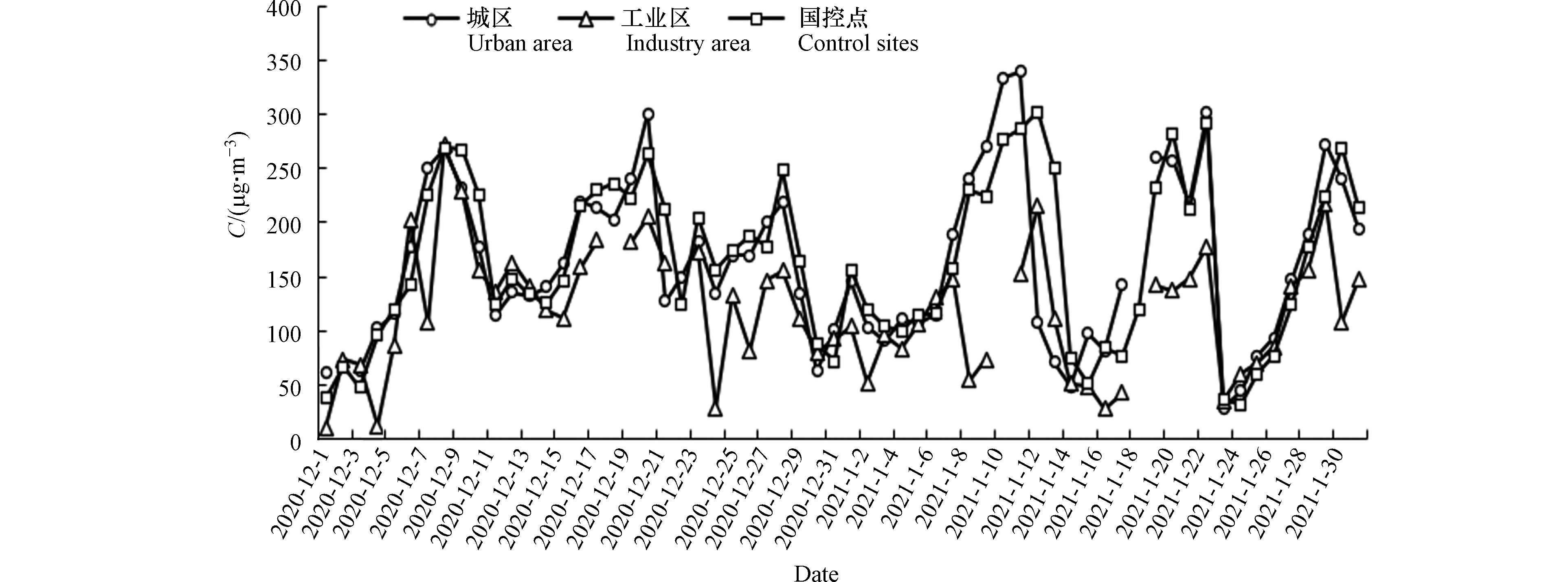
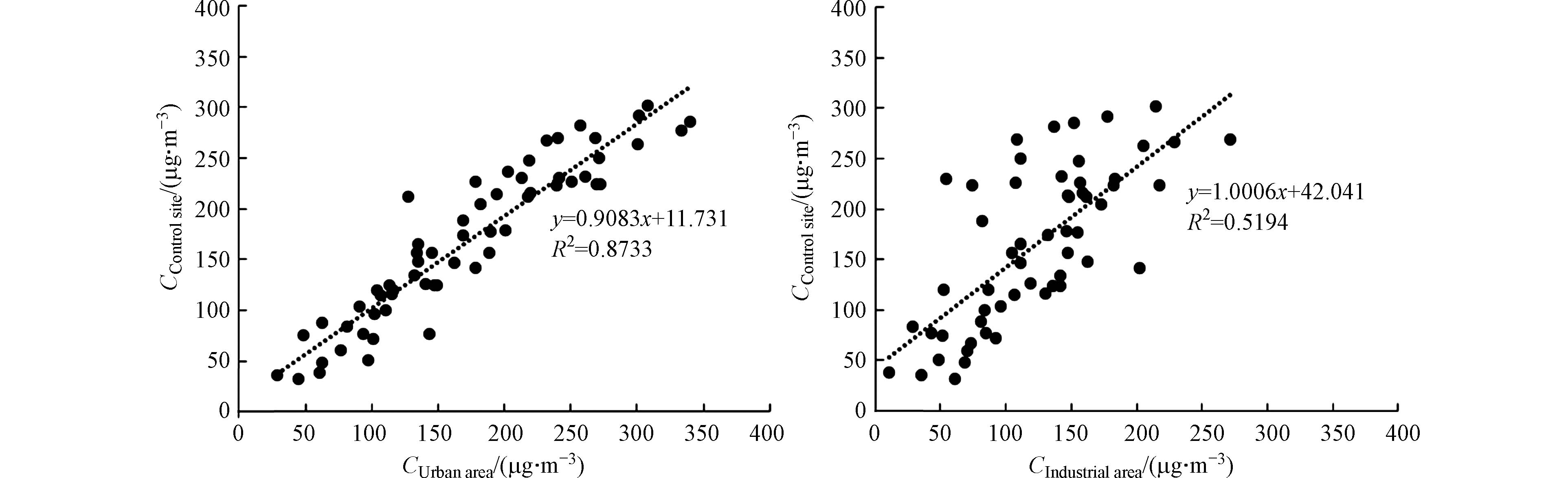
对P膜进行样品称重,根据采集样品量和采样体积计算PM2.5浓度[24],并与石河子市国控站PM2.5值进行对比,如图1所示. 一般认为PM2.5的相关性在80%—120%之间是合理的[25],城区和工业区手工采样PM2.5值与国控站进行比较,可判断手工采样PM2.5的代表性和各点位PM2.5的差异,城区采样点的PM2.5浓度值与国控站的PM2.5浓度值相关系数R2为0.87,线性关系较好,而工业区采样点的PM2.5浓度值与国控站的PM2.5浓度值相关系数R2为0.52,说明工业区PM2.5污染浓度特征与城区有所不同.
-
2020年12月1日—2021年1月31日在石河子市共采样62 d,以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天占比较高,如表2所示,采样期石河子市空气质量为优的天数为0,重度污染天最多,占整个采样期的38.7%,严重污染天数占整个采样期的14.5%,以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天数占整个采样期的98.4%,
如图2所示,采样期内共发生6次污染过程,其中2020年12月发生3次,2021年1月发生3次,污染过程时间最长的持续8 d,最大PM2.5日均值发生在2021年1月12日,国控站测得日均值为302.0 μg·m−3. 整个采样期国控站PM2.5的日均值为165.0 μg·m−3,以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天PM2.5日均值为167.2 μg·m−3,两者数据很接近,与《环境空气质量标准》( GB 3095—2012) [26]中规定的PM2.5日均浓度二级标准限值( 75 μg·m−3 )相比,超过75 μg·m−3的天数为54 d,占整个采样期的87.1%,说明石河子市冬季以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天形势非常严峻. 整个采样期城区手工采样的PM2.5质量浓度日均值为164.7 μg·m−3,工业区手工采样的PM2.5质量浓度日均值为113.6 μg·m−3,表明城区PM2.5污染程度高于工业区. 两采样点直线距离约12.0 km,城区采样点距离国控点较近,由图2可知,城区手工PM2.5与国控点PM2.5的变化趋势较一致,采样期两者PM2.5平均差值为6.7 μg·m−3,说明两者相关性好,误差较小. 工业区主要以化工、火电、电解铝、硅冶炼、水泥等重工业高架点源排放为主,冬季石河子北部区域地面风场以弱偏北风为主,城区位于工业区的下风向,有研究表明一定条件下工业区高架点源对10.0—12.0 km范围区域影响明显[27-28],石河子城区PM2.5浓度高的原因可能与工业区企业高架点源排放和远距离传输到城区有关.
-
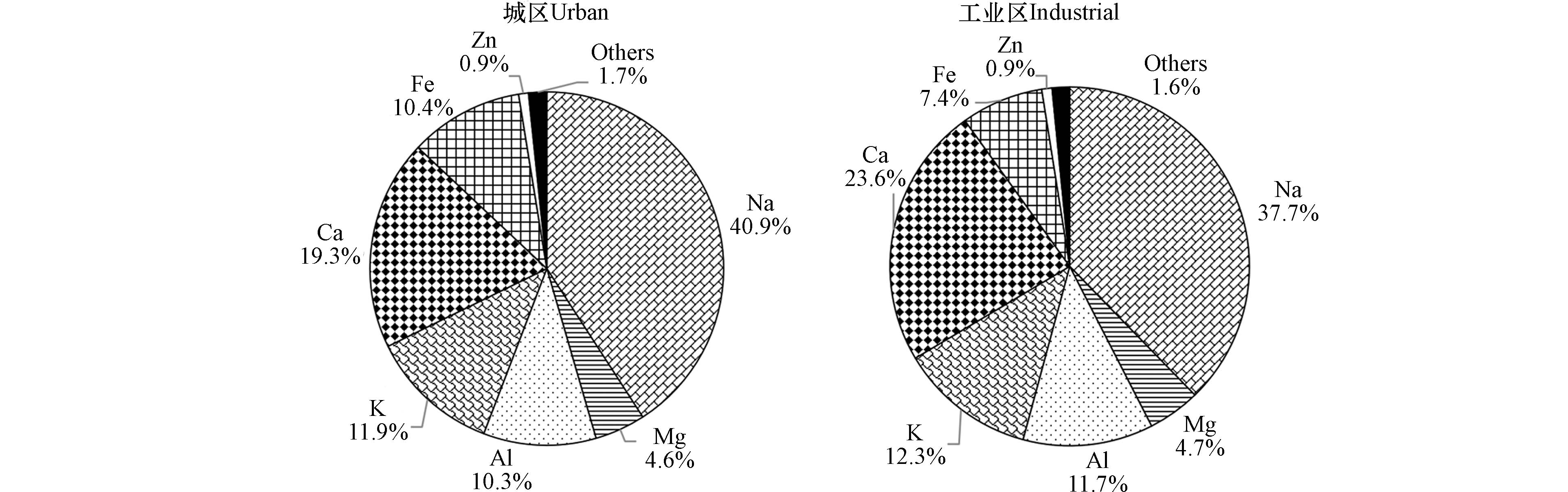
石河子市城区和工业区环境PM2.5中元素浓度如表3所示,城区PM2.5中元素浓度由高到低依次为:Na>Ca>K>Fe>Al>Mg>Zn>Pb>Mn>Cu>Ba>As>Cr>V>Ni>Cd>Mo>Co>Se>Tl>Be>U>Ag>Th, 工业区PM2.5中元素浓度由高到低依次为:Na>Ca>K>Al>Fe>Mg>Zn>Pb>Mn>Cr>V>Ba>As>Cu>Ni>Mo>Cd>Co>Tl>Be>U>Se>Th>Ag. 采样期城区PM2.5中元素浓度和为4353.0 ng·m−3,工业区PM2.5中元素浓度和为3556.6 ng·m−3,城区和工业区元素K、Ca、Na、Mg、Al、Fe质量浓度较大,均超过了100.0 ng·m−3,6种元素在城区元素总浓度的占比为97.4%,在工业区元素总浓度的占比为97.5%,说明这6种元素为石河子市无机元素的主要组成部分. 从采样期元素浓度均值来看,工业区的元素浓度值低于城区,说明无机元素在城区PM2.5颗粒物上的富集程度高于工业区. 昌吉市与石河子市同为乌昌石区域城市,赵强等[29]研究发现昌吉市因春、夏、秋季多风,易导致扬尘发生,冬季冰雪覆盖裸土,施工较少,冬季燃煤量大,污染物积累导致元素浓度与PM2.5质量浓度规律不符,元素浓度表现为秋季>夏季>春季>冬季,即冬季元素浓度水平最低,同时与国内南部城市广州市[30]、中部城市南昌市[31]以及北部城市天津市[32]冬季PM2.5中无机元素浓度对比发现,石河子市和昌吉市等区域PM2.5中无机元素浓度水平低于其他城市,原因可能为石河子市冬季大雪覆盖裸土,扬尘较少所致.
从石河子市城区和工业区元素在无机元素中的占比来看(图3),占比最大的为Na元素,城区Na元素占比40.9%,工业区占比37.7%,其次为Ca元素,城区占比19.3%,低于工业区的23.6%,城区Fe元素占比为10.4%,工业区为7.4%,表明城区的Na、Fe元素相对占比较高,而工业区的Ca元素占比较高,从浓度水平来看,两者元素浓度较为接近.
-
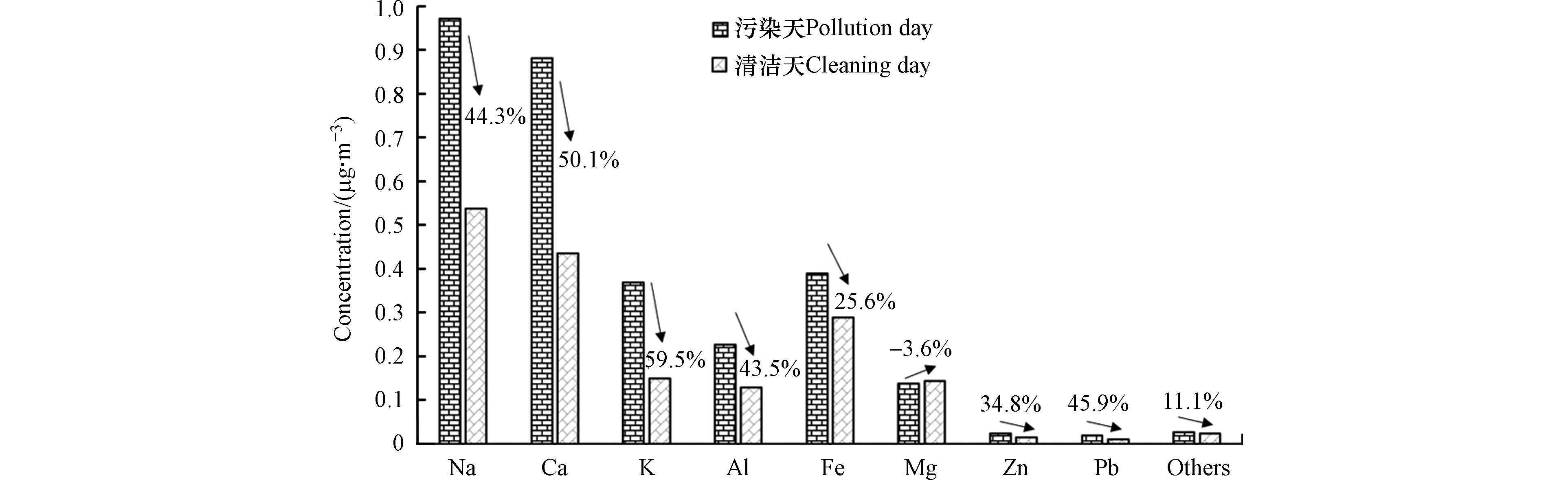
不同的PM2.5污染条件下,元素浓度特征不同,选取非沙尘天的典型污染天2021年1月12日(PM2.5日均值为302.0 μg·m−3)和清洁天2021年1月24日(PM2.5日均值为32.0 μg·m−3)的元素浓度进行对比,如图4所示,与污染天相比,清洁天Na和Ca元素的浓度下降水平较大,下降水平均超过0.4 μg·m−3,其次为K、Al和Fe元素,表明污染天Na和Ca元素的浓度累积量最大. 从下降百分比来看,主要元素浓度下降百分比由高到低依次为:K>Ca>Pb>Na>Al>Zn>Fe,K和Ca元素的浓度百分比下降均超过50%,其中K元素的浓度百分比下降最大,为59.5%,Ca元素为50.1%,表明污染天K和Ca元素的累计速率较快.
-
富集因子法(EF)采用双重归一化的数据处理方法研究人为源和天然源对PM2.5中元素的贡献程度,通过无机元素浓度的富集因子(EF) 来研究大气颗粒物中元素的富集程度,分析PM2.5中污染物的来源,在各类研究中应用较为广泛[33,34]. 元素的富集程度越高,环境PM2.5中相应元素的浓度较地壳物质中相应元素的浓度越高,说明人为因素对环境PM2.5的贡献越大[35].富集因子的计算公式为:
式中:Ci表示为第i种元素的浓度,μg·m−3,Cr表示为选定的表征背景的参比元素的浓度,μg·m−3. 根据富集因子(EF)分级法则,当EFi>100时,表明第i种元素明显受到人为源的影响,当100≥EFi>10时,表明第i种元素受人为扰动,当EFi≤1时,表明第i种元素在环境PM2.5中没有富集. 石河子市土壤主要为灰漠土、潮土和草甸土,本研究中各元素的土壤背景值取自于《中国土壤元素背景值》[36]中以上3种土壤的均值,并选则Al元素作为参比元素[37].
石河子市2020年冬季PM2.5中24种元素的富集因子(EF)如表4所示,由于城市周围土壤不同,石河子市与郴州市[38]、温州市[39]等地级市元素EF值有所不同,城区和工业区的K、Ca、Na、Mg、Fe元素的富集因子均大于1000,表明PM2.5颗粒物中这5种元素主要来自人为源,受周围自然源的影响较小,是典型的人为排放的污染元素,通常Na、K元素多来自生物质燃烧和餐饮油烟,Fe元素多来自于地壳物质或燃煤,Ca元素主要来源是石灰和水泥[40,41],石河子市PM2.5中Ca元素主要来自建筑扬尘以及电石厂原料氧化钙、碳酸钙等,张靳杰[42]研究认为机动车尾气颗粒物中无机元素排放因子最高的是K、Ca、Na、Mg,说明石河子市冬季PM2.5受工业区排放、机动车和地壳物质以及餐饮油烟等的影响,城区Se、Cd、Pb 元素富集因子大于10,工业区Se、Cd、Pb、Ag 元素富集因子大于10,通常Se是燃煤标识物,Cd来自工业粉尘,Pb是机动车排放的标识性元素[43,44],说明环境PM2.5中这些元素受燃煤、工业粉尘和机动车等人为扰动影响. Cu、Zn、As、Cr、Mn、Ba等元素富集因子值较低,受人为扰动影响较小,主要来自天然源.
-
(1) 2020年冬季在石河子市进行为期61d的PM2.5样品采集中,重度及以上污染天数占整个采样期的53.2%,以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天数占整个采样期的98.4%,采样期城区PM2.5的日均值为164.7 μg·m−3,工业区PM2.5的日均值为113.6 μg·m−3,PM2.5污染较为严重;
(2) 采样期城区PM2.5中元素浓度为4.4 μg·m−3,工业区为3.6 μg·m−3,城区和工业区PM2.5中无机元素的主要成分均为Na、Mg、K、Ca、Al、Fe,6种元素在城区元素中的占比为97.4%,在工业区元素中的占比为97.5%,表明2个功能区PM2.5中元素浓度差异性较小. 污染天K和Ca元素的累积速度最快,Na和Ca元素的累积量最大;
(3) 石河子市2020年冬季PM2.5中主要富集元素为K、Ca、Na、Mg、Fe,富集元素主要来源于工业区、机动车、地壳物质以及餐饮油烟等,城区的元素富集程度和污染程度略高于工业区.
2020年冬季石河子市城区和工业区PM2.5中无机元素污染特征及来源
Characteristics and sources of the inorganic elements of PM2.5 in Shihezi urban and industrial areas in winter, 2020
-
摘要: 石河子市是位于新疆乌昌石区域中部的工业城市,2020年12月和2021年1月在石河子市城区和工业区共布设2个采样点,全天候采集细颗粒物(PM2.5)样品61 d,利用电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)对24种元素含量进行分析,并通过富集因子法(EF)解析PM2.5中无机元素的污染特征及来源. 结果表明,冬季采样期间,石河子市重度及以上污染天数占整个采样期的53.2%,以PM2.5为首要污染物的污染天数占整个采样期的98.4%,采样期城区和工业区的PM2.5日均值分别为164.7 μg·m−3和113.6 μg·m−3,表明石河子市冬季PM2.5污染严重;采样期城区和工业区PM2.5中无机元素浓度分别为4.4 μg·m−3和3.6 μg·m−3,主要成分均为K、Ca、Na、Mg、Al、Fe,6种元素之和在城区和工业区元素中的占比分别为97.4%和97.5%,表明这6种元素为城区和工业区元素的主要组分,城区和工业区主要元素组成差异性较小,污染天K和Ca元素的累积速度最快,Na和Ca元素的累积量最大;石河子市2020年冬季PM2.5中主要富集元素为K、Ca、Na、Mg、Fe,富集元素主要来源于工业区、机动车、地壳物质以及餐饮油烟等,城区元素富集程度和污染程度略高于工业区.Abstract: Shihezi is an industrial city located in the middle of Wu-Chang-Shi region in Xinjiang. 2 sampling sites were set up in Shihezi urban and industrial areas in December 2020 and January 2021, The fine particles (PM2.5) were collected for 61 days in total. 24 kinds of elements were analyzed by ICP-MS, and the characteristics and sources of the inorganic elements of PM2.5 were investigated by using enrichment factor method (EF). The results showed that: During the sampling period in winter, the number of the severe pollution days accounted for 53.2% of the whole sampling days, and the pollution days with PM2.5 as the primary pollutant accounted for 98.4% of the whole sampling period. The daily mean values of PM2.5 in urban and industrial areas were 164.7 μg·m−3 and 113.6 μg·m−3, respectively, demonstrating the heavy air pollution in winter in Shihezi city; The concentrations of the inorganic elements of PM2.5 in urban and industrial areas were 4.4 μg·m−3 and 3.6 μg·m−3, respectively, in the sampling period. The main components of the inorganic elements of PM2.5 in urban and industrial areas were K, Ca, Na, Mg, Al and Fe. These 6 kinds of elements were the primary components of the inorganic elements, and accounted for 97.4% and 97.5% of the whole elements amount in total in urban and industrial areas. The composition structure showed little difference for the inorganic elements of PM2.5 between the urban and industrial areas; The main enriched elements in PM2.5 of Shihezi city in winter were K, Ca, Na, Mg and Fe, and mainly come from industries, motor vehicles, crustal substances and cooking fume, etc. The enrichment and pollution degree of elements in urban areas were slightly higher than those in industrial areas.
-

-
表 1 采样点信息
Table 1. Sample sites information
采样点
Sample sites环境监测站
Environmental monitoring station大全
Daquan经度 86.0576 E 86.0957 E 纬度 44.3133 N 44.4220 N 高度/m 14.0 13.0 功能区 城区 工业区 有效样品/个 60 61 与国控站距离 阳光学校西1.6 km 阳光学校北12.0 km 表 2 采样期污染天数
Table 2. The number of pollution days in sampling period
优
Excellent良
Good轻度
Light中度
Medium重度
Heavy严重
Severe污染天数/d 0 9 8 12 24 9 PM2.5为首要污染物天数/d 0 8 8 12 24 9 表 3 采样点元素浓度
Table 3. Elements concentration of 2 sample sites
元素
Elements城区/(ng·mc3)
Urban工业区/(ng·m−3)
Industrial比值
Ratio广州市[30]/ (ng·m−3)
Guangzhou天津市[31]/ (ng·m−3)
Tianjin南昌市[32]/ (ng·m−3)
NanchangBe 0.2 0.3 0.6 — — — Na 1779.0 1342.0 1.3 1210.0 1925.0 — Mg 201.7 168.4 1.2 390.0 1188.0 537.0 Al 448.4 416.7 1.1 1190.0 1377.0 740.0 K 520.1 436.2 1.2 2480.0 4081.0 734.0 Ca 838.4 840.9 1.0 1390.0 5278.0 1207.0 V 1.9 4.9 0.4 — 4.9 9.0 Cr 4.3 5.6 0.8 13.5 176.7 20.0 Mn 13.9 7.6 1.8 83.4 190.9 43.0 Fe 453.9 263.4 1.7 1220.0 4357.0 571.0 Co 0.3 0.4 0.8 — 1.2 4.0 Ni 1.3 1.8 0.7 8.6 87.9 150 Cu 10.0 4.3 2.4 112.0 239.1 19.0 Zn 39.3 32.9 1.2 670.0 945.1 279.0 As 5.5 4.3 1.3 35.1 43.4 10.0 Se 0.3 0.3 1.1 — — — Mo 0.4 0.6 0.7 — — — Ag 0.1 0.1 0.4 — — — Cd 0.5 0.5 1.0 6.1 10.2 5.0 Ba 6.1 4.7 1.3 — 51.2 325.0 Tl 0.2 0.3 0.7 — — — Pb 27.2 19.9 1.4 190.0 541.1 106.0 Th 0.1 0.2 0.3 — — — U 0.1 0.3 0.3 — — — 总和 4353.0 3557.0 24.5 8999.0 20498.0 4759.0 备注:“—”表示未检测出. 表 4 石河子市PM2.5中24种元素EF值
Table 4. Enrichment factors of 24 elements in PM2.5 of Shihezi city
序号
Serial number元素
ElementsPM2.5富集因子
Enrichment factors of PM2.5A层土元素
Element of layer A soil郴州市[38]EF值
Enrichment
factors of
Chenzhou City温州市[39]EF值
Enrichment
factors of
Wenzhou City城区
Urban工业区
Industrial质量分数(×106)/(g·g−1)
Mass percentage1 Be 1.1 2.1 187.7 — — 2 Na 14765.3 11986.5 151.0 — 22.2 3 Mg 2840.9 2551.4 89.0 — 3.0 4 Al 1.0 1.0 562.0 0.02 — 5 K 3325.4 3001.5 196.0 — 11.6 6 Ca 3704.0 3998.0 283.7 — 20.1 7 V 0.3 0.9 7293.3 45.7 0.4 8 Cr 1.0 1.4 5510.0 106.8 112.5 9 Mn 0.3 0.2 63266.7 14.0 7.7 10 Fe 2078.6 1297.9 273.7 0.6 3.7 11 Co 0.3 0.4 1250.0 — 5.0 12 Ni 0.6 1.0 2496.7 66.8 38.7 13 Cu 5.9 2.7 2136.7 370.0 227.5 14 Zn 7.3 6.6 6753.3 155.8 509.7 15 As 7.6 6.4 910.0 521.1 301.0 16 Se 17.5 16.8 20.0 — — 17 Mo 2.4 3.8 206.7 — — 18 Ag 5.5 15.6 11.7 1599.2 — 19 Cd 61.5 64.7 9.5 10880.9 1691.0 20 Ba 0.2 0.1 50133.3 3.3 — 21 Tl 5.4 8.0 54.7 — — 22 Pb 15.9 12.6 2136.7 262.4 176.8 23 Th 0.1 0.3 1030.7 — — 24 U 0.3 1.3 261.7 — — 备注:“—”表示未检测出. -
[1] 元雪婷, 杨静. 乌昌石区域耗煤行业排放特征及对空气质量的影响 [J]. 工业安全与环保, 2020, 46(9): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2020.09.016 YUAN X T, YANG J. Emission characteristics of the coal-consumption industries in Wuchangshi area and its impact on air quality [J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 46(9): 60-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2020.09.016
[2] 闵月. 天山北坡乌昌石地区污染天气过程的气象特征研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. MIN Y. The Meteorological characteristics of air pollution in northern slope of Tianshan Mountains[D]. Lanzhou, Lanzhou University, 2020(in Chinese).
[3] 王晴, 王宝庆, 蔡宁宁, 等. 乌昌石区域化石燃料固定燃烧点源大气污染物排放清单及时空分布 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(6): 712-716. WANG Q, WANG B Q, CAI N N, et al. Emission inventory of atmospheric pollutants from fossil fuel fixed combustion point source and its temporal and spatial distribution in Wuchangshi area [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(6): 712-716(in Chinese).
[4] 张斌, 吕宝磊, 王馨陆, 等. 利用集合深度学习方法订正空气质量数值预报结果: 以新疆乌昌石城市群为例 [J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(5): 931-938. ZHANG B, LÜ B L, WANG X L, et al. Improving air quality forecast accuracy in Urumqi-Changji-Shihezi region using an ensemble deep learning approach [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2020, 56(5): 931-938(in Chinese).
[5] HAN X, LIU Y Q, GAO H, et al. Forecasting PM2.5 induced male lung cancer morbidity in China using satellite retrieved PM2.5 and spatial analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 607/608: 1009-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.061 [6] BENMERAD M, SLAMA R, BOTTURI K, et al. Chronic effects of air pollution on lung function after lung transplantation in the Systems prediction of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (SysCLAD) study [J]. European Respiratory Journal, 2017, 49(1): 1600206. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00206-2016 [7] ZHAI Y B, LIU X T, CHEN H M, et al. Source identification and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 from Changsha [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 493: 109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.106 [8] 王淑兰, 柴发合, 杨天行. 北京市不同尺度大气颗粒物元素组成的特征分析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2002, 15(4): 10-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.04.004 WANG S L, CHAI F H, YANG T X. Characteristics analysis of elements contained in air suspended particles with different sizes in Beijing [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 15(4): 10-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2002.04.004
[9] 胡鸣, 张懿华, 赵倩彪. 上海市冬季PM2.5无机元素污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(7): 1993-1999. HU M, ZHANG Y H, ZHAO Q B. Characteristics and sources of inorganic elements in PM2.5 during wintertime in Shanghai [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(7): 1993-1999(in Chinese).
[10] 田莎莎, 张显, 卞思思, 等. 沈阳市PM2.5污染组分特征及其来源解析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(2): 487-496. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.02.006 TIAN S S, ZHANG X, BIAN S S, et al. Characteristics of PM2.5 pollution components and their sources in Shenyang [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(2): 487-496(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.02.006
[11] 赵金平, 谭吉华, 毕新慧, 等. 广州市灰霾期间大气颗粒物中无机元素的质量浓度 [J]. 环境化学, 2008, 27(3): 322-326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.03.010 ZHAO J P, TAN J H, BI X H, et al. The mass concentrations of inorganic elements in atmospheric particles during haze period in Guangzhou [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 27(3): 322-326(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.03.010
[12] 李友平, 刘慧芳, 周洪, 等. 成都市PM2.5中有毒重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7): 2225-2232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.052 LI Y P, LIU H F, ZHOU H, et al. Contamination characteristics and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 in Chengdu [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(7): 2225-2232(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.052
[13] 纪元, 康宏, 李刚. 乌鲁木齐市冬季重污染天气下PM2.5中重金属污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 干旱环境监测, 2016, 30(3): 127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1504.2016.03.007 JI Y, KANG H, LI G. The heavy metal pollution characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 under the heavy pollution of Urumqi winter weather [J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 2016, 30(3): 127-131(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1504.2016.03.007
[14] 张洛红, 范芳, 蒋炜炜, 等. 珠三角地区大气PM2.5中重金属污染水平及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(1): 370-380. ZHANG L H, FAN F, JIANG W W, et al. Concentrations and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta Region [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(1): 370-380(in Chinese).
[15] 王琼, 董小艳, 杨璐璐, 等. 基于北京市大气PM2.5中9种元素的环境健康风险评价 [J]. 环境卫生学杂志, 2018, 8(3): 197-203. WANG Q, DONG X Y, YANG L L, et al. Environment health risk assessment on 9 elements in PM2.5 in Beijing [J]. Journal of Environmental Hygiene, 2018, 8(3): 197-203(in Chinese).
[16] 任慧清, 鲁建江, 宁建英, 等. 石河子市PM2.5中重金属污染及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(6): 1716-1725. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019041004 REN H Q, LU J J, NING J Y, et al. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 of Shihezi City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(6): 1716-1725(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019041004
[17] 李瑶, 刘琳, 胡潭高, 等. 石河子市PM2.5浓度的遥感反演研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2018, 43(1): 138-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.01.031 LI Y, LIU L, HU T G, et al. Remote sensing estimation model of PM2.5 mass concentration in Shihezi city [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2018, 43(1): 138-142(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.01.031
[18] 丁俊男, 王帅, 王瑞斌, 等. 河南省典型城市PM2.5无机元素污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2017, 33(6): 25-32. DING J N, WANG S, WANG R B, et al. Characteristics and sources analysis of inorganic elements in PM2.5 in typical cities of Henan Province [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(6): 25-32(in Chinese).
[19] 张晶晶, 张清花. 昌吉市采暖期和非采暖期PM2.5和PM10污染特征分析 [J]. 干旱环境监测, 2018, 32(1): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1504.2018.01.005 ZHANG J J, ZHANG Q H. Pollution characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in heating and non-heating season in Changji city [J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 2018, 32(1): 24-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1504.2018.01.005
[20] TAIWO A M, HARRISON R M, SHI Z B. A review of receptor modelling of industrially emitted particulate matter [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 97: 109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.07.051 [21] XU L L, YU Y K, YU J S, et al. Spatial distribution and sources identification of elements in PM2.5 among the coastal city group in the Western Taiwan Strait region, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 442: 77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.045 [22] 乔宝文, 刘子锐, 胡波, 等. 北京冬季PM2.5中金属元素浓度特征和来源分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(3): 876-883. QIAO B W, LIU Z R, HU B, et al. Concentration characteristics and sources of trace metals in PM2.5 during wintertime in Beijing [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(3): 876-883(in Chinese).
[23] KYLLÖNEN K, KARLSSON V, RUOHO-AIROLA T. Trace element deposition and trends during a ten year period in Finland [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(7): 2260-2269. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.045 [24] 环境保护部. 中华人民共和国环保行业标准: 环境空气颗粒物(PM2.5)手工监测方法 HJ 656—2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2013. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Environmental Protection Standard of the People's Republic of China: Technical Specifications for gravimetric measurement methods for PM2.5 in ambient air. HJ 656—2013[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2013(in Chinese).
[25] 杨佳美, 戴启立, 刘保双, 等. 关中地区背景点位环境空气PM2.5来源解析与多模型结果对比 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(2): 184-192. YANG J M, DAI Q L, LIU B S, et al. Source apportionment of ambient PM2.5 at background sites in Guanzhong area, China: Comparison of results obtained by multiple models [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(2): 184-192(in Chinese).
[26] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 环境空气质量标准 GB 3095—2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2016. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. National Standard (Mandatory) of the People's Republic of China: Ambient air quality standard. GB 3095—2012[S]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 2016(in Chinese).
[27] 王伟平, 苏高利, 杨海鹏. 城北高架点源对西湖风景区影响的研究 [J]. 气象, 2002, 28(1): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2002.01.003 WANG W P, SU G L, YANG H P. A study on influence of high elevation point source of northern Hangzhou on the scenic zone of west lake [J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2002, 28(1): 13-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0526.2002.01.003
[28] 陈瑞. 城市高架点源对空气质量的影响分析 [J]. 浙江树人大学学报, 2003, 3(5): 77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2714.2003.05.022 CHEN R. Effects of high chimney emission on air quality in the urban area [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Shuren University, 2003, 3(5): 77-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2714.2003.05.022
[29] 赵强. 昌吉市大气颗粒物污染特征及来源解析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2018. ZHAO Q. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter in Changji City[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2018(in Chinese).
[30] 符小晴, 彭晓武, 王钰钰, 等. 广州市大气PM2.5中元素特征及重金属健康风险评价 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2018, 35(2): 154-158. FU X Q, PENG X W, WANG Y Y, et al. Characteristic of elements in PM2.5 and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Guangzhou [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2018, 35(2): 154-158(in Chinese).
[31] 董海燕, 古金霞, 姜伟, 等. 天津市颗粒物中元素化学特征及来源 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2012, 24(1): 25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2012.01.007 DONG H Y, GU J X, JIANG W, et al. Character and source analysis of chemical element in particulate matters in Tianjin [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2012, 24(1): 25-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2012.01.007
[32] 樊孝俊, 徐义邦, 赵阳. 南昌市秋季大气PM2.5中金属元素污染及生态风险评价 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2016, 32(2): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2016.02.004 FAN X J, XU Y B, ZHAO Y. The pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in PM2.5 in autumn in Nanchang [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(2): 26-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2016.02.004
[33] 王永慧, 刘芃岩, 于泊蕖, 等. 保定市日间、夜间大气PM2.5中无机组分的特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(9): 1941-1948. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016122201 WANG Y H, LIU P Y, YU B Q, et al. Characteristics and source analysis of inorganic components in PM2.5 samples collected during daytime and night in Baoding City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(9): 1941-1948(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016122201
[34] 滕彦国, 庹先国, 倪师军, 等. 攀枝花工矿区土壤重金属人为污染的富集因子分析 [J]. 土壤与环境, 2002, 11(1): 13-16. TENG Y G, TUO X G, NI S J, et al. Application of an enrichment factor in determining anthropogenical pollution ofheavy metal in topsoil [J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2002, 11(1): 13-16(in Chinese).
[35] 姬亚芹, 朱坦, 冯银厂, 等. 用富集因子法评价我国城市土壤风沙尘元素的污染 [J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 39(2): 94-99. JI Y Q, ZHU T, FENG Y C, et al. Application of the enrichment factor to analyze the pollution of elements in soil dust in China [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 2006, 39(2): 94-99(in Chinese).
[36] 中国土壤环境背景值研究[Z]. 北京市, 中国环境监测总站, 2001.01. 01. Research on the environmental background of soil in China[Z]. Beijing, Environmental Monitoring of China, 2001.01. 01(in Chinese).
[37] 赵晓亮, 岳阳霞, 许端平, 等. 阜新市秋冬季节PM2.5中无机元素污染特征及来源 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10): 4247-4258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.007 ZHAO X L, YUE Y X, XU D P, et al. The pollution characteristics and source analysis of inorganic elements in PM2.5 during autumn and winter in Fuxin [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10): 4247-4258(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.10.007
[38] 杨麒, 傅致严, 刘湛, 等. 郴州市大气PM2.5中无机元素污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(6): 133-140. YANG Q, FU Z Y, LIU Z, et al. Characteristics and sources of inorganic elements in atmospheric PM2.5 at Chenzhou city [J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 46(6): 133-140(in Chinese).
[39] 郑元铸, 葛琳琳, 郑旭军, 等. 温州市区PM2.5无机元素污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(1): 84-91. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.01.2016051802 ZHENG Y Z, GE L L, ZHENG X J, et al. Characteristics and source apportionment of inorganic elements in PM2.5 in Wenzhou, Zhejiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(1): 84-91(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.01.2016051802
[40] TIAN H Z, WANG Y, XUE Z G, et al. Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007 [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(23): 11905-11919. doi: 10.5194/acp-10-11905-2010 [41] ZHANG W J, SUN Y L, ZHUANG G S, et al. Characteristics and seasonal variations of PM2.5, PM10, and TSP aerosol in Beijing [J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(6): 461-468. [42] 张靳杰. 武汉市机动车尾气VOCs和颗粒物排放特征研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019. ZHANG J J. Study on the characteristics of volatile organic compounds and particulate matter from on-use vehicles in Wuhan[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[43] 郭海全, 郝俊杰, 李天刚, 等. 河北平原土壤重金属人为污染的富集因子分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(4): 786-791. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.04.007 GUO H Q, HAO J J, LI T G, et al. Application of an enrichment factor in determining anthropogenic pollution of heavy metal in topsoil in Hebei plain [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(4): 786-791(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.04.007
[44] 陈翠华, 倪师军, 何彬彬, 等. 江西德兴矿区土壤重金属污染的富集因子分析 [J]. 金属矿山, 2005(12): 57-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2005.12.017 CHEN C H, NI S J, HE B B, et al. Enrichment factor analysis of soil pollution by heavy metals in Dexing mining area, Jiangxi Province [J]. Metal Mine, 2005(12): 57-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2005.12.017
-



 下载:
下载: