-
有机磷酸酯类物质(OPEs)是一类人造化学物质,根据化学结构中取代基团不同可分为烷基类OPEs、卤代烷基类OPEs和芳香基类OPEs [1]. 由于OPEs具有阻燃性、延展性、耐强酸碱、耐强氧化性等优良特性,逐渐成为多溴联苯醚的替代品[2-3],被广泛用于纤维织物、工程塑料、合成树脂、建筑材料、合成橡胶和电子产品的生产加工[4]. 然而,大部分OPEs具有半挥发性,环境中不易分解,并可以通过长距离传输迁移,在生物体内产生积蓄作用等[5-6],长期暴露会对生物体产生神经毒性、内分泌干扰毒性、生殖毒性和致癌性[7],这对生态环境和人类健康构成较大的潜在风险. 因此,近几年来OPEs一直是环境[8] 、食品[1] 、水生态[9]、人体健康[10]等领域的研究热点之一.
目前,水中OPEs的检测主要采用气相色谱质谱联用法和液相色谱串联质谱法,前处理一般采用固相萃取法(SPE)[8,11]. 由于OPEs的广泛应用[12],分析过程常用的耗材都可能成为检测过程中的污染来源,如试剂、样品瓶、移液枪吸头、SPE小柱及上样管路、离心管、滤膜等. LIANG等[13]对空白水样进行过滤和固相萃取后测得OPEs的总浓度在0.006—0.064 μg·L−1.
我国部分河流湖泊中几种常见OPEs的浓度在4.20×10−3 — 1.75 μg·L-1[14-16],与国外一些主要河流OPEs浓度差异不大[17];国外一些受地表水污染影响的地下水部分OPEs的浓度超过0.10 μg·L-1 [18];国内部分饮用水中常见OPEs的浓度在0.055 — 0.82 μg·L−1 [19]. 有研究显示,部分OPEs在浓度大于0.01 μg·L−1时可能产生生态风险[20]. 综合水环境中OPEs浓度水平、生态风险判定方法及现阶段的仪器灵敏度,利用直接进样法检测OPEs可满足需求. 直接进样法较SPE法过程简单、效率高, 可有效减少污染来源. 尽管如此,检测过程中仍然存在一定的背景污染,如庞龙等[21]研究城市污水处理工艺对OPEs的去除效果时,空白样品中检出了较高浓度的TCEP, TPhP和TCPP(1.5—7.5 μg·L−1);梁钪等[22]检测污水中OPEs时发现常用的滤膜会带来不同程度的污染;秦威振等[7]检测室内灰尘中OPEs时发现LC流动相及管路存在背景污染.
本文通过将检测过程分为仪器检测和前处理两部分,将每部分的各环节进行分解实验,探究检测过程污染来源,并提出相应的降低或消除污染措施对方法进行优化,为提高OPEs检测的准确性和灵敏度提供有效途径;利用优化后的方法检测污水实际样品及加标样品,对方法的准确度和精密度检验,以验证方法的实用性.
-
Waters Xevo TQ-XS高效液相色谱-串联质谱仪(美国 Waters 公司)、电喷雾离子源;甲醇和甲酸均为质谱级,购自上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司.
标准品:磷酸三甲酯(TMP)、磷酸三乙酯(TEP)、磷酸三丙酯(TPrP)、磷酸三异丁酯(TiBP)、磷酸三正丁酯(TnBP)、三(2-氯乙基)磷酸酯(TCEP)、三(2-氯丙基)磷酸酯(TCPP)、三(1,3-二氯异丙基)磷酸酯(TDCP)、磷酸三丁氧乙酯(TBEP)、磷酸三(2-乙基己基)酯(TEHP)、磷酸三苯酯(TPhP)、磷酸三甲苯酯(TCrP)、磷酸甲苯二苯酯(CDP)、2-乙基己基二苯基磷酸酯(EHDPP)、磷酸三(2, 3-二溴丙基)酯(TDBPP)、磷酸三(三溴新戊基)酯(TTBNP)16种化合物的标准液(100 μg·mL−1)购自Accustandard公司,TnBP-D27,TCPP-D18,TPhP-D15 3种内标的标准物质购自TRC公司.
-
ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18色谱柱(100 mm×2.1 mm×1.7 µm);柱温:40 °C;流动相流速:0.3 mL·min−1;A相0.02%甲酸水溶液,B相甲醇. 洗脱梯度:0—3.0 min,40%—75%B;3.0—8.0 min,75%—100%B;8.0—12.0 min,100%B;12.1—14.0 min,40%B. 进样体积:10 µL.
离子源:电喷雾正离子模式(ESI+),检测方式:多反应监测模式(MRM);去溶剂气温度:500 ℃,流速:900 L·h−1;毛细管电压:1.5 kV;定性定量离子对、锥孔电压、碰撞能等见表1.
-
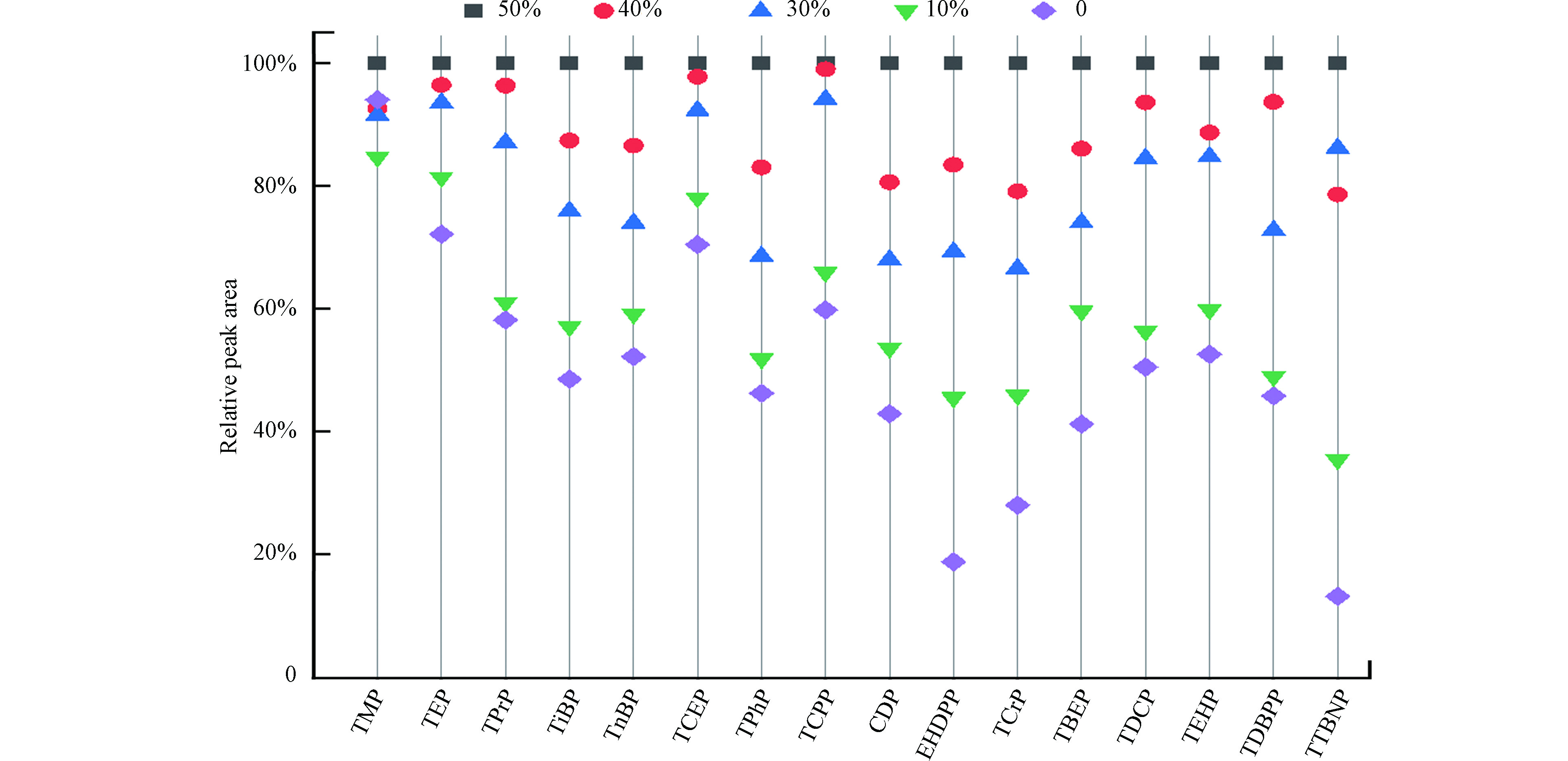
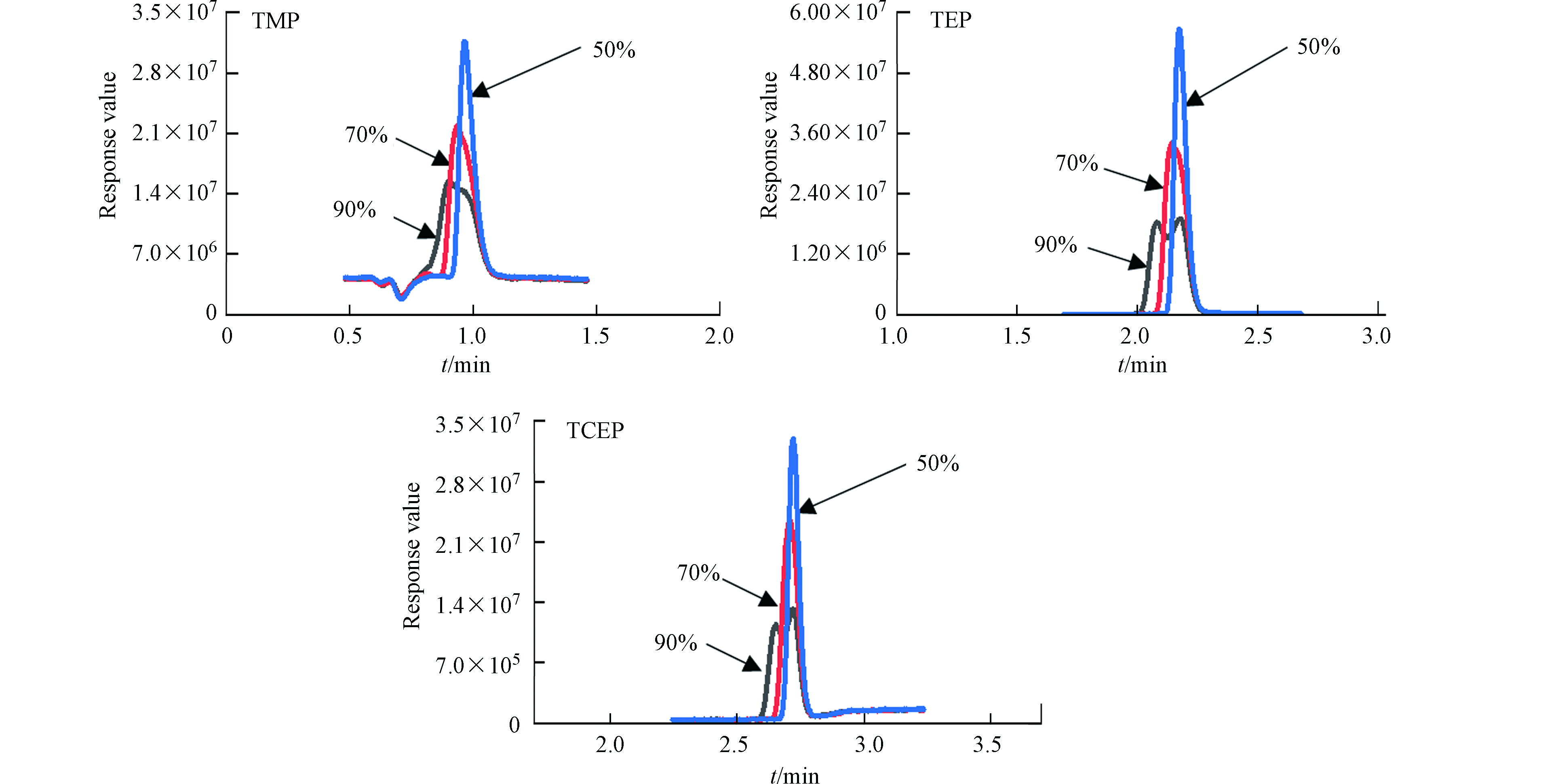
配置8份16种OPEs浓度均为1.00 μg·L−1的溶液,样品溶剂中甲醇含量分别为100%、90%、70%、50%、40%、30%、10%、0%,对样品分别测定.TMP、TEP和TCEP在100%、90%、70%甲醇水溶剂中,会因为溶剂效应产生峰展宽和裂分(如图1所示),当样品溶剂甲醇含量降低至50%时,溶剂效应消失. 当样品溶剂中甲醇含量从50%降至0%,不同目标物的峰面积变化情况见图2,目标物的峰面积随样品溶剂中甲醇含量下降而变小. 结合目标物的溶解性数据(见表2)发现,当溶剂中甲醇含量降低时, 目标物的峰面积降低程度与其水溶性成正相关,如TCEP、TCPP和TDCP在水中的溶解度分别为6.99×10−3、1.20×10−3、6.98×10−3 g·L−1,3种目标物在0%的甲醇水溶液中时测得峰面积分别为50%甲醇水溶液测得峰面积的70.5%、59.8%和50.5%. 水溶解性更小的TCrP和TTBNP在0%的甲醇水溶液中时测得峰面积分别为50%甲醇水溶液测得峰面积的28.1%和13.2%. 因此,综合考虑溶剂效应和化合物溶解性的影响,最终选择50%甲醇水溶液作为样品溶剂.
-
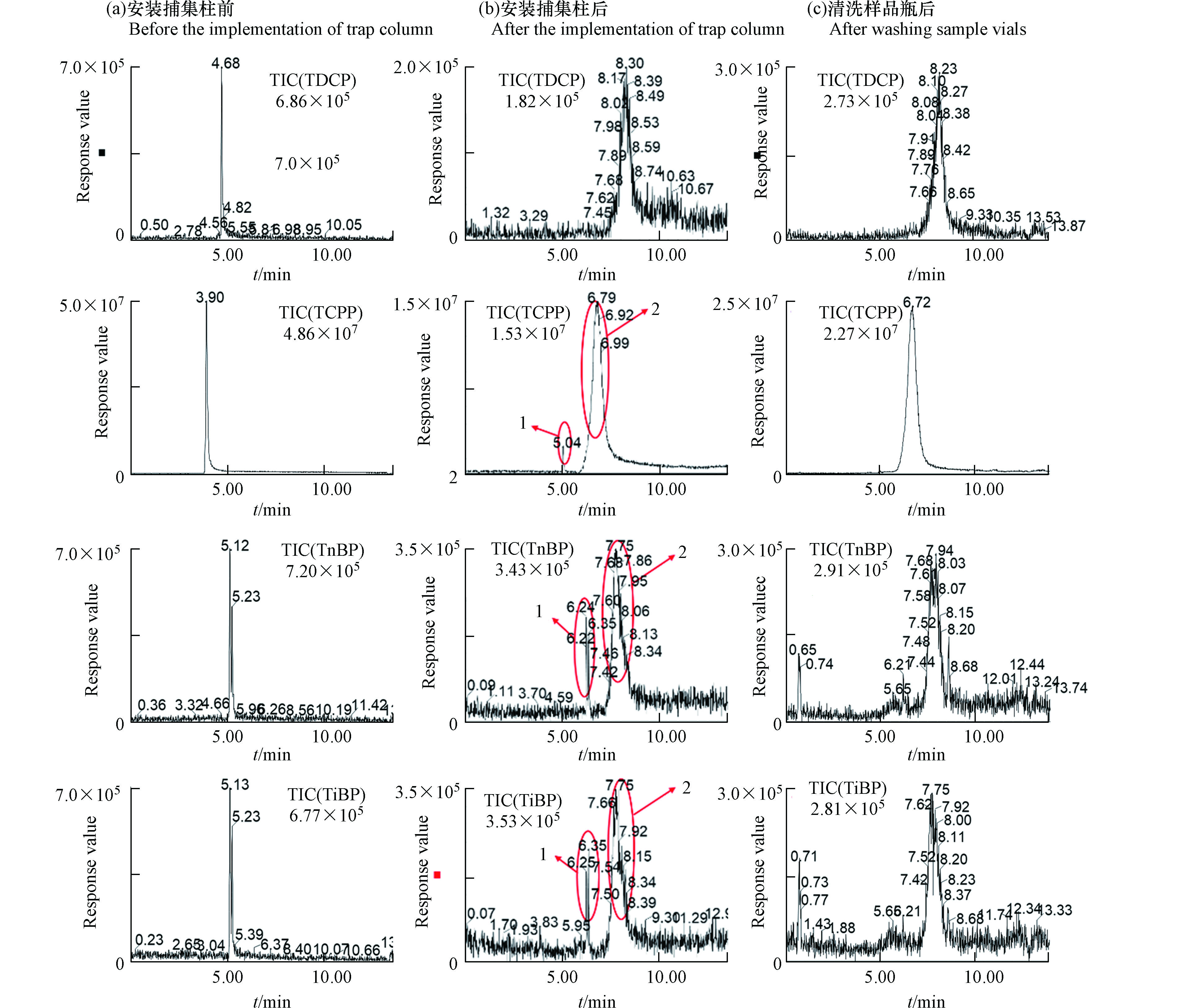
空白样品的配制:用玻璃量筒依次量取5 mL的纯水和5 mL的甲醇于玻璃离心管中,涡旋振荡混匀. 用玻璃滴管移取约1 mL于玻璃进样瓶中,对空白样品进行分析. 分析结果显示,TCPP、TiBP、TnBP和TDCP均有检出(如图3(a)所示),采用标准加入法对检出的目标物进行半定量,得到TCPP、TiBP、TnBP和TDCP的浓度分别为0.78、0.88、0.033、0.019 μg·L−1,其来源可能有两个:一是空白样品中含有待测物质污染,二是色谱前端流动相或流动相管路中有待测物溶出,流动相流经色谱柱后被色谱柱截留,随着流动相洗脱强度增加逐渐被洗脱. 秦威振[10]对室内灰尘中5种OPEs进行检测时,以ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(100 mm×2.1 mm, 1.7 μm)为捕集柱,将流动相和仪器管路中的目标物与待测液中目标物分开,去除了仪器本底干扰. 捕集柱安装在进样系统前,可将流动相或管路溶出的待测物预先捕集,随流动相梯度变化依次洗脱,其保留时间滞后于样品中待测物,样品中目标物与管路及流动相中的干扰物分离,从而消除其对样品分析的影响. 为验证本研究中待测物质检出原因,在进样系统前加装了捕集柱(Isolator Column, 50 mm×2.1 mm),加装捕集柱前后对空白样品测定结果如图3(a,b)所示. 图中可以看出,安装捕集柱后,每种化合物的色谱峰被分离成1和2,1为样品中目标物的色谱峰,2为捕集柱捕获的进样器前端污染物的色谱峰. 安装捕集柱后,TDCP的背景污染已经消失,但TCPP、TiBP和TnBP仍有检出,这表明空白样品的背景污染除色谱前端外,还有部分来自样品,而空白样品配置过程未接触过可能含有OPEs的材料,因此样品瓶引入污染的可能性较大. 用甲醇清洗样品瓶3次后重新对空白样品进行测试,结果如图3(c)所示,从图中可以看出TCPP、TnBP和TiBP均未检出,这表明样品瓶引入的背景污染不容忽视,需要对不同来源和材质的样品瓶的进行背景污染研究.
-
空白样品的配制见2.2节,将空白样品分别置于4个不同品牌的2 ml样品瓶(瓶身材质均为硼硅酸玻璃,盖垫均为聚四氟乙烯硅胶复合垫片)中,进样分析. 结果显示,TEP、TiBP、TnBP、TCEP、TCPP、TDCP有不同程度检出,具体数据如表3所示.表3可看出,4个样品中TiBP、TCPP和TDCP的检出率最高,检出浓度在7.40×10−3—0.203 μg·L−1.TEP、TnBP、TCEP也有较高频率的检出,检出浓度在5.50×10−3—0.185 μg·L−1.用甲醇清洗样品瓶2—3次后,重新进样分析,待测物均未检出,这表明不同品牌的样品瓶的背景污染均可以通过甲醇清洗消除.
-
本研究采用直接进样法对水中目标物进行分析,样品预处理过程包括水样的定量移取、添加内标、过滤和混匀等操作. 使用PP材质移液枪吸头定量移取空白样品,添加内标,不过滤膜,混匀后测定. 结果显示,TCEP、TCPP、TCrP、TBEP和TEHP有检出,它们的浓度在9.85×10−2—0.925 μg·L−1. 用玻璃针筒替代移液枪重复上述操作,结果显示目标物均未检出,这表明PP材质移液枪吸头会引入背景污染,在样品定量移取过程避免使用PP材质的移液枪吸头,用玻璃针筒予以替代.
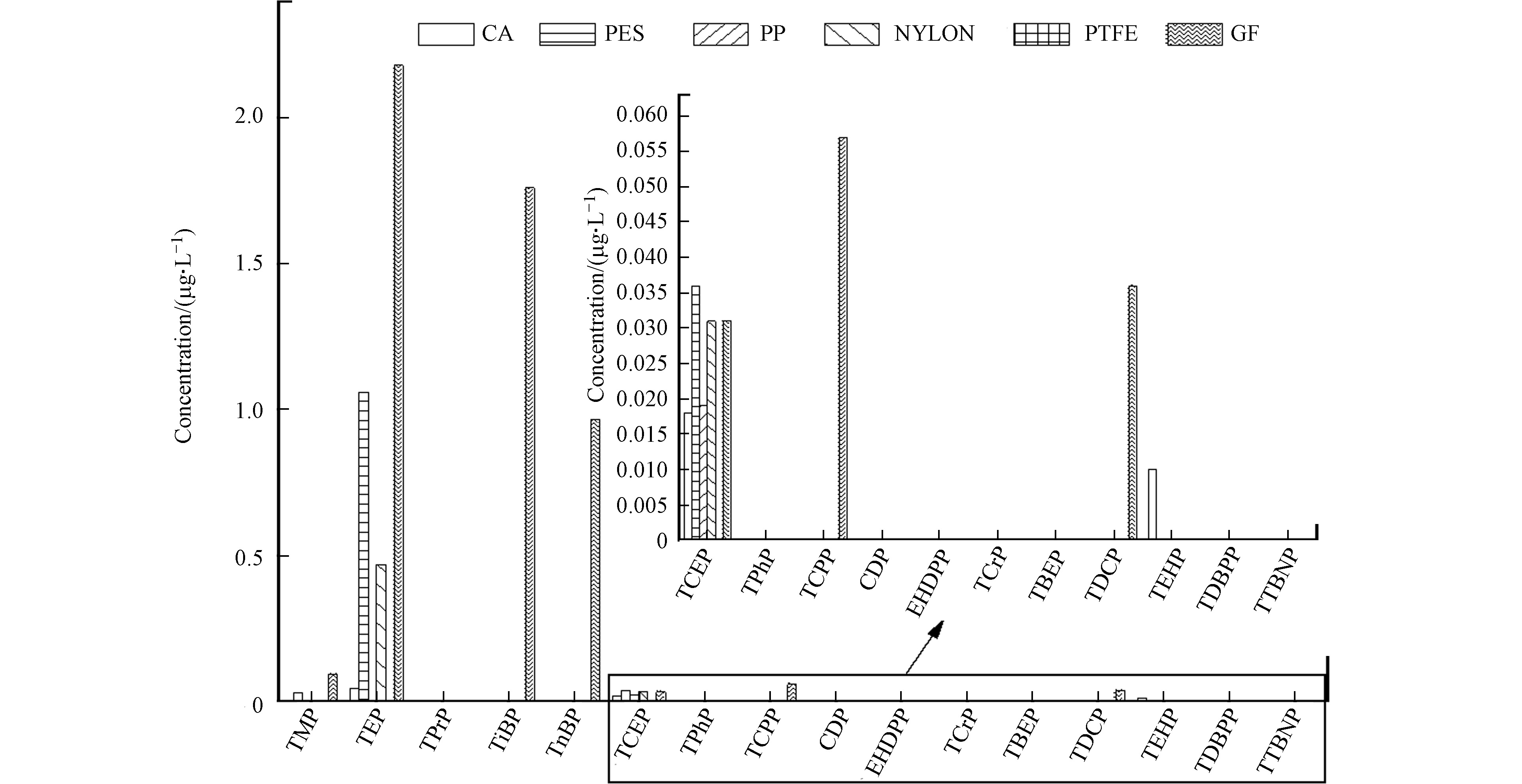
配置6个空白样品,加入内标,涡旋振荡混匀,分别用醋酸纤维素(CA)滤膜、聚醚砜(PES)滤膜、尼龙(NYLON)滤膜、聚丙烯(PP)滤膜、亲水聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)滤膜和玻璃纤维滤膜(GF)过滤,上机分析后得到不同材质滤膜的背景污染情况,结果见图4. 图4可以看出,GF、PES、NYLON和CA材质的滤膜有高浓度TEP检出,这与LIANG 等的研究结果一致[13],其中,样品过GF滤膜后TEP浓度可高达2.0 μg·L−1以上,另外,GF、PES、NYLON、PP和CA等5种材质滤膜均有TCEP的检出,只有亲水PTFE材质滤膜对16种OPEs全部未检出,因此选择PTFE滤膜作为样品预处理过滤使用.
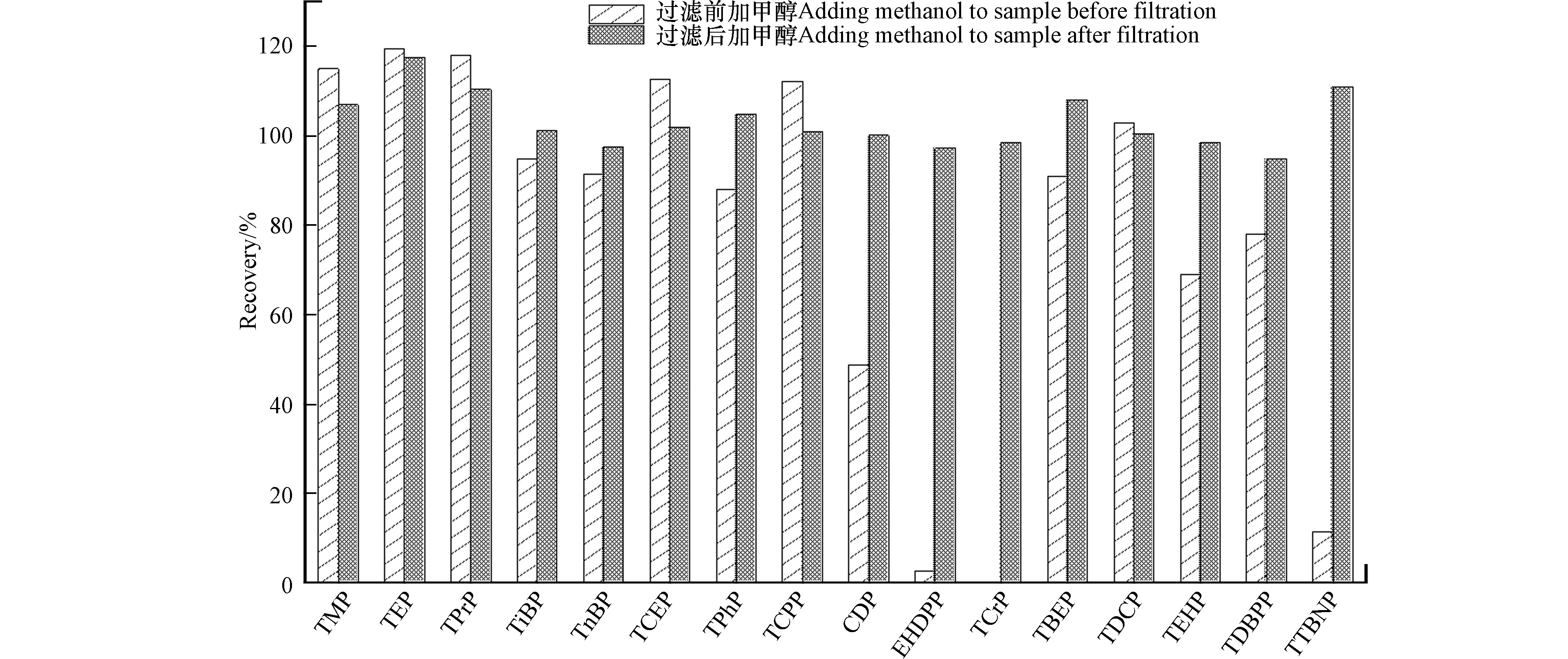
另外,本文研究了PTFE滤膜对16种OPEs的吸附作用,配置两份16种OPEs浓度均为1.00 μg·L−1的样品溶液,一份样品经PTFE滤膜过滤后加入1倍体积的甲醇,在另一份样品中先加入1倍体积的甲醇,再经PTFE滤膜过滤. 两份样品过滤后均加入内标,混匀,上机分析,结果如图5所示. CDP、TCrP、EHDPP、TTBNP在纯水中过滤后,回收率小于50%,其中过滤导致TCrP完全损失;而加入甲醇后再过滤,样品回收率均在80%以上. 这可能是由于这几种化合物脂溶性强,在纯水中溶解度小,容易吸附在样品瓶壁和滤膜上造成损失,而过膜前加入甲醇,增加了样品的溶解度使吸附作用减弱. 因此,加入1倍体积甲醇后再过滤样品可以最大程度减少脂溶性较强OPEs因吸附作用造成的损失.
-
方法优化前后分别绘制了标准曲线,优化前不同浓度范围下16种OPEs的标准曲线相关系数见表4. 当R2大于0.995时,认为曲线具有较好的线性相关性,在该条件下,TBEP、TTBNP的线性范围为0.10—10.0 μg·L−1,TiBP、TCEP、TPhP的线性范围为0.50—50.0 μg·L−1,TCPP和TDCP的线性范围为5.0—50.0 μg·L−1,其他化合物的线性范围均为0.050—10.0 μg·L−1. 方法优化后各目标物标准曲线结果见表5,除TTBNP的线性范围为0.10—10.0 μg·L−1外,其他目标物的线性范围为0.020—10.0 μg·L−1和0.050—10.0 μg·L−1,在2个数量级的浓度范围内16种目标物的标准曲线R2均大于0.995.以满足线性相关系数大于0.995时,各目标物线性范围下限作为最低空白添加浓度(见表5),再以各目标物最低空白添加浓度溶液的响应外推至信噪比为3时对应的浓度,得到水中16种OPEs方法检出限范围在1.40×10−3—3.99×10−2 μg·L−1. 以上实验数据表明,通过方法优化,提高了目标物低浓度范围内的线性相关性,同时提高了直接进样法测定OPEs的灵敏度.
-
在优化好的方法条件下,配置低(0.10 μg·L−1)、中(2.0 μg·L−1)、高(20.0 μg·L−1)3个浓度水平的空白加标样品,每个浓度设置6个平行样,过滤后上机分析,得到16种OPEs在3个浓度水平下的加标回收率和相对标准偏差(RSD),结果见表6. 水样中16种OPEs的加标回收率在70.4%—110%之间,相对标准偏差在1.8%—15.4%之间,结果表明该方法的准确度和精密度良好.
-
在优化好的分析条件下,测定了3个污水处理厂出水水样中16种OPEs的本底浓度(BC,μg·L−1),并对每个样品进行了6次基体加标实验,加标量均为100 pg,水样加标浓度为0.10 μg·L−1,通过计算得到加标回收率(R, %)和相对标准偏差(结果见表7). 表7可以看出,3个实际水样16种OPEs的单体浓度在ND—0.24 μg·L−1,加标回收率在70.5%—119%之间,6次平行测定的相对标准偏差分别为2.6%—18.7%、3.1%—20.2%和3.1%—25.8%,表明该方法的准确度和精密度良好.
-
本文研究了直接进样-高效液相色谱质谱联用法测定水中16种OPEs的背景污染情况,通过在液相色谱进样器前端流路安装捕集柱,消除了流动相和管路引入的TCPP、TiBP、TnBP和TDCP的背景污染;样品瓶会产生TEP、TiBP、TnBP、TCEP、TCPP和TDCP的背景污染,使用前用甲醇清洗2—3次可以消除. 在样品预处理时,选用玻璃注射器代替PP材质的移液枪吸头对样品进行定量移取,可避免PP材质吸头中OPEs的溶出影响;CA、PES、Nylon、PP、GF等5种材质的滤膜均有TCEP的背景污染,亲水PTFE滤膜无背景污染,但对脂溶性强的OPEs具有较强的截留作用,通过过滤前向水样加入等体积的甲醇,再进行过滤可以将目标物的回收率提高至80%以上. 方法优化后,各物质标准曲线R2均大于0.995,检出限在1.40×10−3—0.04 μg·L−1;空白加标实验结果表明,16种OPEs在0.10、2.0和20.0 μg·L−1加标水平下,回收率和相对标准偏差(n=6)分别在70.4%—110%和1.8%—15.4%,表明方法的精密度和准确度良好;利用污水水样和加标样品对优化的方法进行了验证,加标回收率在70.5%—119%之间,相对标准偏差在2.6%—25.8%之间. 本文对OPEs检测中产生背景污染的过程进行了分析,并提出了相应的消除措施,解决了OPEs检测本底高的难题,为该类化合物快速而准确的测定提供了有效途径.
直接进样- LC-MS/MS测定水中16种有机磷酸酯类化合物
Simultaneous determination of 16 organophosphates in waters by direct injection LC-MS/MS
-
摘要: 本文通过对空白污染消除和样品前处理方法优化,建立了直接进样-高效液相色谱串联质谱测定水中有机磷酸酯类化合物(OPEs)的检测方法. 通过液相色谱流路中安装捕集柱、清洗进样瓶、以玻璃注射器代替移液枪、过滤用PTFE滤膜可以消除相应空白污染;通过水样过滤前加入1倍体积甲醇可以减少滤膜对高脂溶性OPEs的截留,物质回收率提高至80%以上. 方法优化后,16种OPEs标准曲线R2均大于0.995,检出限在1.40×10−3—0.04 μg·L−1. 实验室空白水样低、中、高浓度的物质加标回收率和相对标准偏差(n=6)分别在70.4%—110%和1.8%—15.4%;污水处理厂出水水样的物质加标回收率和相对标准偏差(n=6)分别为70.5%—119%和2.6%—25.8%. 因此,优化的方法具有较高的精密度和准确度,可以满足直接进样法检测OPEs的需求.
-
关键词:
- 有机磷酸酯类物质(OPEs) /
- 直接进样 /
- 高效液相色谱串联质谱法 /
- 背景污染消除.
Abstract: A method was developed for simultaneous determination of 16 organophosphates (OPEs) in waters by liquid chromatography tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry with direct injection. Sources and solution of whole process blank pollution and the optimization of pretreatment method were studied. Pollutions can be eliminated by installing catcher column, washing sample vials, replacing pipette tip with glass syringe, and using PTFE membrane during the filtration process. In order to decrease the retention of OPEs with high fat solubility on membrane, the same volume of methanol was added to samples before filtering. The results showed that recoveries of OPEs were improved to over 80% using the optimizing method. And the R2 of calibration curve was greater than 0.995, the detection limits of OPEs in water ranged from 1.40×10−3 μg·L−1 to 0.04 μg·L−1. The recoveries and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) (n=6) for low, medium and high levels spiking blanks ranged from 70.4% to 110% and from 1.8% to 15.4%, respectively. The recoveries of spiking waste water ranged from 70.5% to 119% with RSDs (n=6)of 2.6%—25.8%. All the results above showed that the method is sensitive, accurate and reliable, and it can meet the requirements for the determination of OPEs in water by direct injection.-
Key words:
- organic phosphates(OPEs) /
- direct injection /
- LC-MS/MS /
- eliminating of blank pollution.
-

-
表 1 16种有机磷酸酯类阻燃剂MRM检测条件
Table 1. Optimized mass-spectrometric conditions for determining of 16 OPEs
化合物
Compounds母离子
Parent ion(m/z)子离子
Product ion(m/z)锥孔电压/V
Cone voltage碰撞电压/ eV
Collision voltage对应内标
Internal standardsTMP 141 108.9* 36 14 TnBP-D27 78.9 36 20 TEP 183 98.9* 2 16 155 2 8 TPrP 225.1 98.9* 2 16 140.9 2 10 TiBP 267.2 99* 10 17 155 10 9 TnBP 267.2 99* 25 15 155 25 9 EHDPP 363.1 77* 18 42 251 18 18 TBEP 399.1 199* 2 14 299.1 2 12 TEHP 435.3 98.9* 38 30 323.2 38 6 TCEP 286.9 98.9* 30 25 TCPP-D18 160.9 30 16 TCPP 327 99* 30 24 175 30 11 TDCP 430.8 99* 16 26 209 16 15 TDBPP 698.7 99* 30 24 298.8 30 17 TTBNP 1018.5 65.1* 58 51 145 58 37 TPhP 327 152* 28 36 TPhP-D15 77 28 36 TCrP 369 165* 30 45 91 30 35 CDP 341 152* 30 37 91 30 37 TnBP-D27 294.3 101.9* 16 18 166.1 16 12 TCPP-D18 347.1 101.9* 10 20 183.1 10 12 TPhP-D15 342.2 81.8* 40 42 159.8 40 38 表 2 16种有机磷酸酯类化合物的水溶解性数据
Table 2. Water Solubility of 16 OPEs
化合物
CompoundsCAS 分子量
Molecular weight水溶解度/(g·L−1)
Water solubility水溶解度/(mol·L−1)a
Water solubilityTMP 512-56-1 140.1 500 3.57 TEP 78-40-0 182.2 496 2.72 TPrP 513-08-6 224.2 6.46 2.88×10−2 TiBP 126-71-6 266.3 1.62×10−2 6.09×10−5 TnBP 126-73-8 266.3 0.28 1.05×10−3 EHDPP 1241-94-7 362.4 1.90×10−3 5.25×10−6 TBEP 78-51-3 398.5 1.10 2.76×10−3 TEHP 78-42-2 434.6 2.06×10−3 4.75×10−6 TCEP 115-96-8 285.5 6.99 2.45×10−2 TCPP 13674-84-5 327.6 1.20 3.65×10−3 TDCP 13674-87-8 430.9 6.98×10−3 1.62×10−5 TDBPP 126-72-7 697.6 8.02×10−3 1.15×10−5 TTBNP 19186-97-1 1018.5 4.50×10−4 4.42×10−7 TPhP 115-86-6 326.3 1.91×10−3 5.86×10−6 TCrP 1330-78-5 368.4 2.17×10−4 5.88×10−7 CDP 26444-49-5 340.3 1.15×10−3 3.38×10−6 a 数据来自US EPA. 表 3 不同品牌空白样品瓶检测结果
Table 3. Test results of different brand of blank sample vials
化合物
Compounds浓度/(μg·L−1)
Concentrations样品瓶A
Sample vial A样品瓶B
Sample vial B样品瓶C
Sample vial C样品瓶D
Sample vial DTEP 1.74×10−2 — — 1.10×10−2 TiBP 5.65×10−2 0.106 8.00×10−3 1.23×10−2 TnBP 1.33×10−2 0.108 5.50×10−3 — TCEP 3.94×10−2 0.185 2.22×10−2 1.75×10−2 TCPP 0.118 9.93×10−2 7.40×10−3 2.01×10−2 TDCP 1.85×10−2 0.203 1.22×10−2 4.00×10−2 表 4 优化前不同浓度范围内标准曲线的相关系数
Table 4. Results of standard curve before optimization
化合物
Compounds0.050—10.0 μg·L−1 0.10—10.0 μg·L−1 0.50—50.0 μg·L−1 1.00—50.0 μg·L−1 5.00—50.0 μg·L−1 TMP 0.998 — — — — TEP 0.999 — — — — TPrP 0.999 — — — — TnBP 0.998 — — — — TCrP 0.999 — — — — TEHP 0.999 — — — — CDP 0.998 — — — — EHDPP 0.999 — — — — TDBPP 0.998 — — — — TTBNP — 0.999 — — — TBEP 0.977 0.996 — — — TiBP 0.959 0.989 0.997 — — TCEP 0.944 0.968 0.998 — — TPhP 0.967 0.994 0.997 — — TCPP 0.379 0.762 0.972 0.982 0.990 TDCP 0.104 0.423 0.920 0.962 0.990 表 5 方法优化后标准曲线结果
Table 5. Results of standard curve after optimization
化合物
Compounds线性范围/(μg·L−1)
Linear range线性方程
Linear equation相关系数
Correlation coefficient
(R2)检出限/(μg·L−1)
Detection limitTMP 0.050—10.0 y=0.314 x + 3.10×10−4 0.999 3.99×10−2 TEP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.448 x + 5.33×10−4 0.999 3.50×10−3 TPrP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.486x + 4.81×10−4 0.999 4.30×10−3 TiBP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.264x + 8.95×10−4 0.999 3.60×10−3 TnBP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.406x + 5.05×10−4 0.999 2.70×10−3 TCEP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.138x + 4.54×10−4 0.997 1.50×10−2 TPhP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.996x + 5.69×10−3 0.999 3.50×10−3 TCPP 0.020—10.0 y= 7.25x + 3.62×10−2 0.999 1.40×10−3 CDP 0.050—10.0 y= 0.239x + 6.69×10−4 0.999 1.59×10−2 EHDPP 0.050—10.0 y= 0.123x − 1.35×10−5 0.998 1.40×10−2 TCrP 0.020—10.0 y= 0.946x + 2.96×10−4 0.999 1.44×10−2 TBEP 0.020—10.0 y= 7.33×10−2x + 5.55×10−5 0.999 4.10×10−3 TDCP 0.050—10.0 y= 9.20×10−2x − 2.14×10−5 0.998 2.81×10−2 TEHP 0.020—10.0 y= 8.65×10−2x + 4.38×10−4 0.999 1.60×10−3 TDBPP 0.050—10.0 y= 4.38×10−2x − 4.70×10−4 0.995 2.94×10−2 TTBNP 0.10—10.0 y= 4.83×10−3x + 7.93×10−6 0.996 3.09×10−2 表 6 水样中16种OPEs的回收率和精密度(n=6)
Table 6. Recoveries and RSD of 16 OPEs in water samples(n=6)
化合物
Compounds低浓度 中浓度 高浓度 回收率/%
RecoveryRSD/% 回收率/%
RecoveryRSD/% 回收率/%
RecoveryRSD/% TMP 90.6 3.8 88.7 3.1 86.7 4.0 TEP 91.5 3.6 84.6 2.6 83.9 3.4 TPrP 94.0 1.9 98.3 2.2 95.3 3.6 TiBP 92.1 2.5 105 2.0 101 3.7 TnBP 92.1 1.8 108 3.7 105 3.4 TCEP 91.5 3.4 86.2 2.6 96.2 3.6 TCPP 91.2 2.1 110 1.9 102 3.2 TPhP 88.5 4.7 104 2.2 100 3.0 TCrP 82.7 5.9 102 3.9 97.1 3.2 TBEP 95.6 4.3 110 2.8 107 2.9 TDCP 110 8.7 85.3 3.6 91.7 3.0 TEHP 85.1 4.8 72.7 2.6 70.4 3.5 CDP 89.5 15.4 110 4.1 102 3.0 EHDPP 84.5 7.2 102 3.8 96.9 3.3 TDBPP 92.1 2.5 72.2 2.6 82.7 2.2 TTBNP 86.3 8.7 83.1 3.7 92.9 5.7 表 7 实际样品及加标样品准确度和精密度
Table 7. Accuracy and precision of water samples and spiked samples
化合物
Compounds样品1
Sample 1样品2
Sample 2样品3
Sample 3本底浓度/
(μg·L−1)加标回收率/% RSD/% 本底浓度/
(μg·L−1)加标回收率/% RSD/% 本底浓度
(μg·L−1)加标回收率/% RSD/% TMP 0.098 85.9 6.0 0.044 99.6 11.6 0.082 98.0 9.8 TEP 0.119 99.4 12.0 0.092 106 12.9 0.068 103 9.0 TPrP ND 118 3.2 ND 118 3.1 ND 119 3.1 TiBP 0.186 91.1 18.7 0.082 103 20.2 0.028 99.8 14.9 TnBP 0.026 89.8 2.6 0.014 107 5.1 0.074 105 3.4 TCEP 0.238 97.4 14.9 0.156 96.1 20.1 0.185 94.8 16.4 TPhP 0.072 75.5 10.7 0.011 100 5.1 0.011 98.5 5.6 TCPP 0.023 86.0 4.3 0.044 108 15.1 0.043 109 6.7 CDP 0.05 101 2.8 0.02 82.3 10.4 ND 90.8 12.4 EHDPP ND 79.0 8.2 0.016 87.0 10.6 0.019 91.2 12.8 TCrP 0.02 79.4 12.0 ND 103 5.0 ND 101 4.5 TBEP 0.026 81.1 9.8 ND 113 4.2 ND 111 4.0 TDCP ND 80.8 4.2 0.059 110 14.5 0.054 104 8.6 TEHP ND 106 5.2 ND 82.5 16.5 ND 70.5 25.8 TDBPP ND 94.0 9.5 ND 91.1 11.3 ND 91.8 6.2 TTBNP ND 95.9 9.2 ND 101 11.1 ND 94.6 15.0 -
[1] 杨吉双, 张庆合, 苏立强. 食品中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂检测技术的研究进展 [J]. 色谱, 2020, 38(12): 1369-1380. YANG J S, ZAHNG Q H, SU L Q. Advances in the development of detection techniques for organophosphate ester flame retardants in food [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2020, 38(12): 1369-1380(in Chinese).
[2] 徐怀洲, 王智志, 张圣虎, 等. 有机磷酸酯类阻燃剂毒性效应研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2018, 13(3): 19-30. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170601001 XU H Z, WANG Z Z, ZHANG S H, et al. Research progress on toxicity effects of organophosphate flame retardants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2018, 13(3): 19-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170601001
[3] 马强, 白桦, 王超, 等. 气相色谱-质谱法测定玩具中的4种阻燃剂 [J]. 分析试验室, 2010, 29(4): 37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2010.04.010 MA Q, BAI H, WANG C, et al. Determination of 4 flame retardants in toys by GC-MS [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2010, 29(4): 37-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2010.04.010
[4] 闫振飞, 廖伟, 冯承莲, 等. 典型有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分析方法研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(1): 94-108. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20190509002 YAN Z F, LIAO W, FENG C L, et al. Research progress on analysis methods of typical organophosphate esters(OPEs) flame retardants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(1): 94-108(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20190509002
[5] 高小中, 许宜平, 王子健. 有机磷酸酯阻燃剂的环境暴露与迁移转化研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 56-68. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150103001 GAO X Z, XU Y P, WANG Z J. Progress in environment exposure, transport and transform of organophosphorus flame retardants [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 56-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150103001
[6] 赖莺, 黄旖珏, 黄宗平, 等. 超高效液相色谱-质谱法测定涂料中四溴双酚A和磷酸三(1, 3-二氯-2-丙基)酯 [J]. 分析试验室, 2017, 36(8): 881-885. LAI Y, HUANG Y J, HUANG Z P, et al. Determination of tetrabromobisphenol A and tris (1, 3-dichloroisopropyl) phosphate in coatings by UPLC-MS [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2017, 36(8): 881-885(in Chinese).
[7] 曹美苑, 兰青, 许凭厘, 等. 城市生活饮用水中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分布特征研究 [J]. 广州化工, 2019, 47(5): 119-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.05.044 CAO M Y, LAN Q, XU P L, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of organic phosphate flame retardant in drinking water in Guangzhou [J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(5): 119-122(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2019.05.044
[8] 胡晓辉, 仇雁翎, 朱志良, 等. 环境中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂分析方法的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(12): 2076-2086. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.013 HU X H, QIU Y L, ZHU Z L, et al. Research progress on analytical methods of organophosphate ester flame retardants in the environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(12): 2076-2086(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.12.013
[9] 王艺璇, 段玉双, 耿存珍. 有机磷酸酯在水环境中的残留及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2015, 32(10): 935-939. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2015.10.027 WANG Y X, DUAN Y S, GENG C Z. Occurrence of organophosphate ester in aquatic environment and ecological risk assessment [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2015, 32(10): 935-939(in Chinese). doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2015.10.027
[10] 秦威振, 毛丽莎, 陈裕华, 等. 人尿中4种有机磷酸酯阻燃剂代谢物的固相萃取-高效液相色谱-串联质谱测定法 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2019, 36(4): 365-368. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2019.04.020 QIN W Z, MAO L S, CHEN Y H, et al. Determination of four metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants in human urine by solidphase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2019, 36(4): 365-368(in Chinese). doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2019.04.020
[11] 刘星, 刘茜, 孙禾琳, 等. 海洋水体中24种有机磷酸酯的测定分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3581-3584. LIU X, LIU X, SUN H L, et al. Determination of 24 kinds of organic phosphate in ocean water [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(12): 3581-3584(in Chinese).
[12] 林殷, 杜凤娟, 王璨, 等. 微波辅助萃取-气相色谱质谱法测定聚合物中9种有机磷酸酯化合物 [J]. 分析试验室, 2017, 36(2): 226-230. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2017.0050 LIN Y, DU F J, WANG C, et al. Determination of 9 organophosphorus esters in polymer by microwave-assisted extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2017, 36(2): 226-230(in Chinese). doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2017.0050
[13] LIANG K, NIU Y M, YIN Y G, et al. Evaluating the blank contamination and recovery of sample pretreatment procedures for analyzing organophosphorus flame retardants in waters [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 34: 57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.01.022 [14] 何丽雄, 曹曙霞, 曾祥英, 等. 固相萃取/气相色谱-质谱联用技术快速测定水中有机磷酸酯阻燃剂与增塑剂 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2013, 32(4): 437-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2013.04.008 HE L X, CAO S X, ZENG X Y, et al. Determination of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in water using solid phase extraction coupled with GC-MS [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2013, 32(4): 437-441(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2013.04.008
[15] 秦宏兵, 范苓, 顾海东. 固相萃取-气相色谱/质谱法测定水中6种有机磷酸酯类阻燃剂和增塑剂 [J]. 分析科学学报, 2014, 30(2): 259-262. doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2014.02.026 QIN H B, FAN L, GU H D. Determination of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in environmental water by solid phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2014, 30(2): 259-262(in Chinese). doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2014.02.026
[16] 张文萍, 张振飞, 郭昌胜, 等. 环太湖河流及湖体中有机磷酸酯的污染特征和风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1801-1810. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008266 ZHANG W P, ZHANG Z F, GUO C S, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in rivers and water body around Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 1801-1810(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008266
[17] BACALONI A, CAVALIERE C, FOGLIA P, et al. Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry determination of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in drinking and surface waters [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2007, 21(7): 1123-1130. doi: 10.1002/rcm.2937 [18] REGNERY J, PÜTTMANN W, MERZ C, et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in anthropogenically affected groundwater [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring:JEM, 2011, 13(2): 347-354. doi: 10.1039/C0EM00419G [19] LI J, YU N Y, ZHANG B B, et al. Occurrence of organophosphate flame retardants in drinking water from China [J]. Water Research, 2014, 54: 53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.031 [20] 李栋, 张圣虎, 张芹, 等. 长江南京段水源水中有机磷酸酯的污染特征与风险评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 205-212. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201907149 LI D, ZHANG S H, ZHANG Q, et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in source water of the Nanjing section of the Yangtze River [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 205-212(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201907149
[21] 庞龙, 张肖静, 庞榕, 等. 城市污水处理工艺对有机磷酸酯类化合物的去除 [J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(3): 98-103. doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2016.03.019 PANG L, ZHANG X J, PANG R, et al. Removal of organophosphate esters in municipal wastewater treatment process [J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(3): 98-103(in Chinese). doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2016.03.019
[22] 梁钪, 牛宇敏, 刘景富. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定污水中14种有机磷酸酯阻燃剂 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(10): 1681-1685. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.011 LIANG K, NIU Y M, LIU J F. Determination of 14 organophosphate ester flame retardants in wastewater by UPLC-MS/MS [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(10): 1681-1685(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.10.011
-



 下载:
下载: